Protein Methods and Techniques for Purification and Analysis
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Purification of Proteins
Proteins can be purified from a mixture through a series of separations based on physical properties such as size and charge.
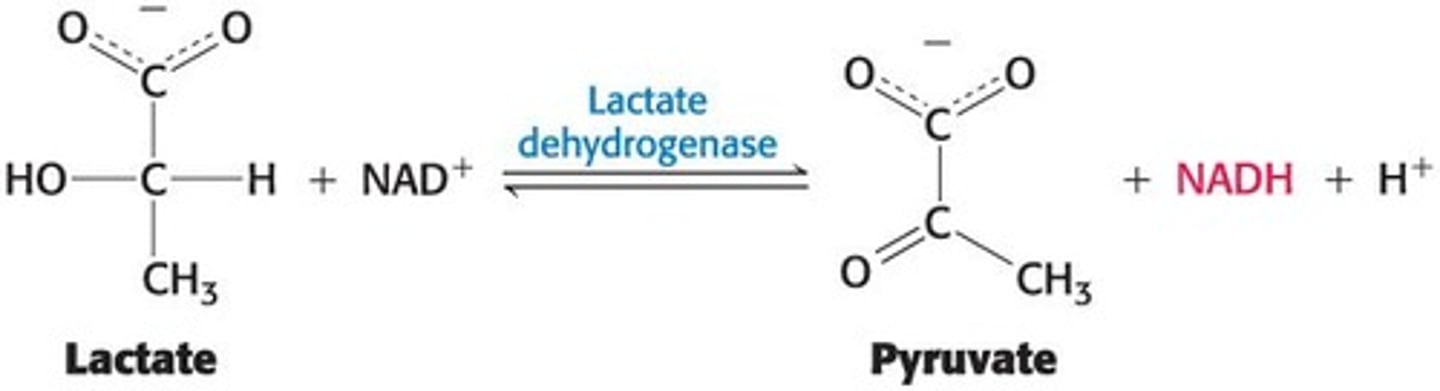
Assay for Lactate Dehydrogenase
An assay for the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase detects NADH spectrophotometrically.
Specific Activity
The ratio of enzyme activity to the amount of protein in the mixture.
Goal of Purification
To maximize the specific activity.
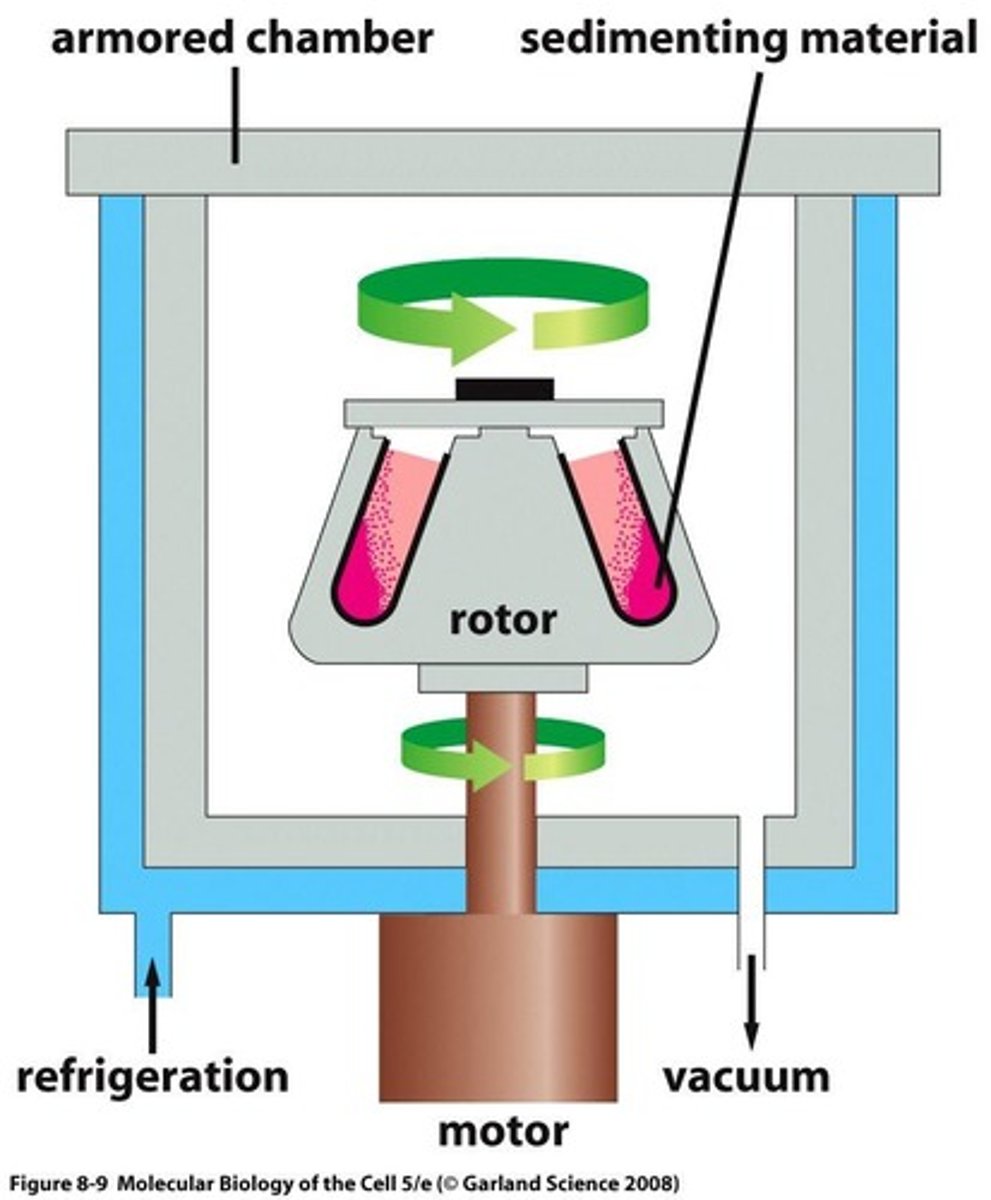
Centrifugation
Separates based on density through sedimentation of objects in a solvent, and is time dependent.
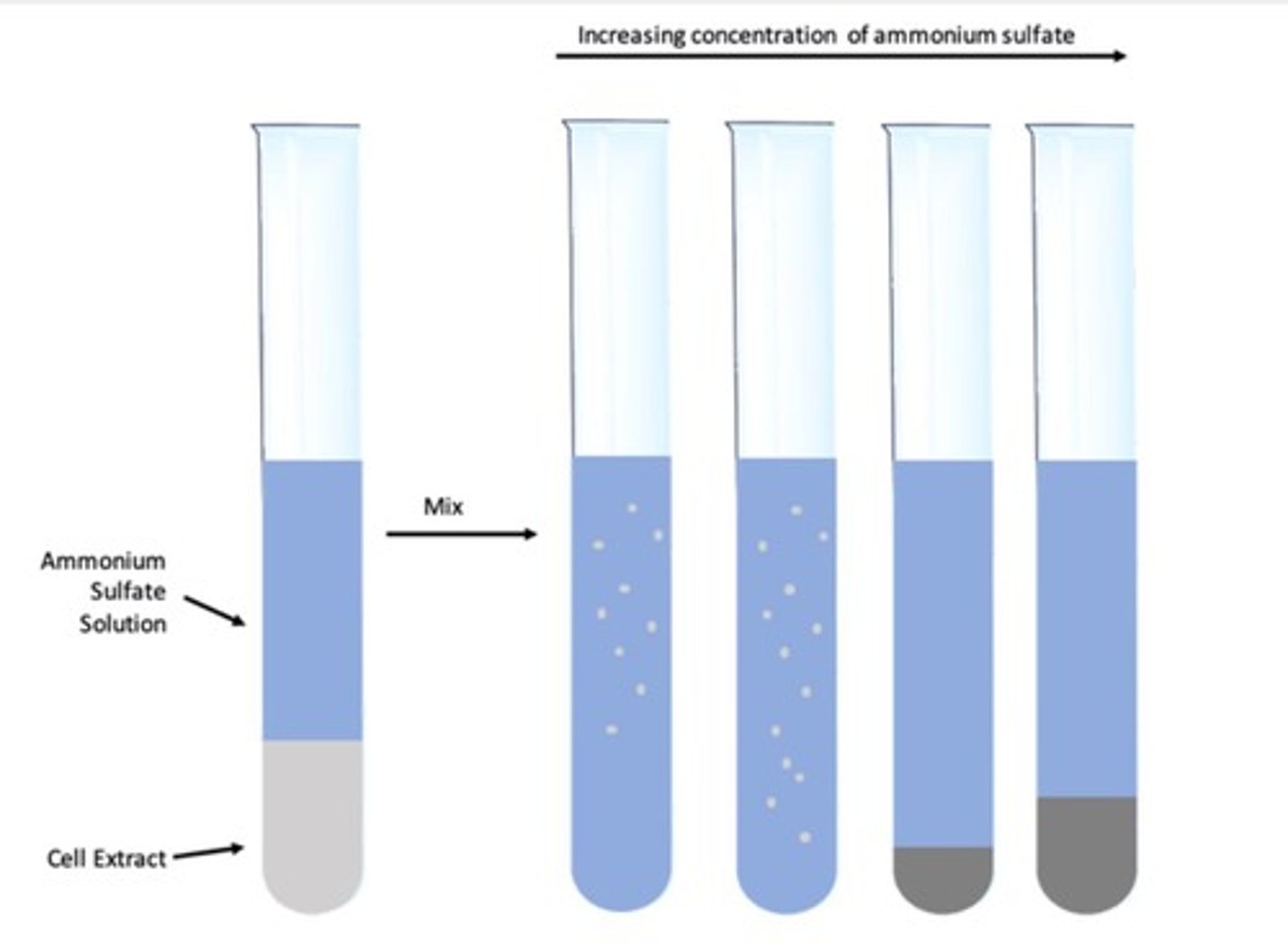
Salting Out
The effect by which most proteins are less soluble at high salt concentrations.
Dialysis
A method to separate proteins from small molecules by using a semipermeable membrane.
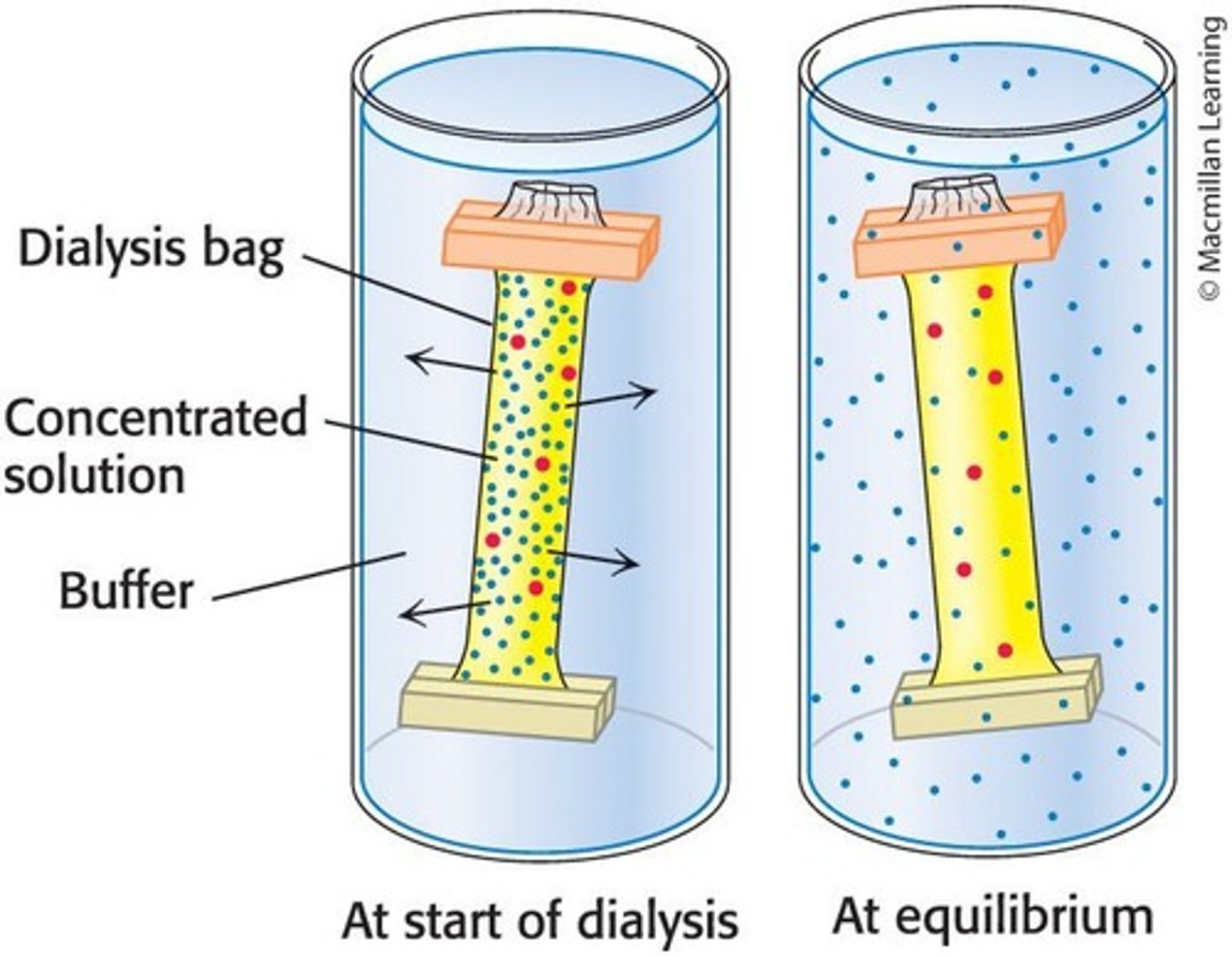
Dialysis Membrane
A cellulose membrane with pores that allows smaller molecules and ions to diffuse while retaining larger molecules.
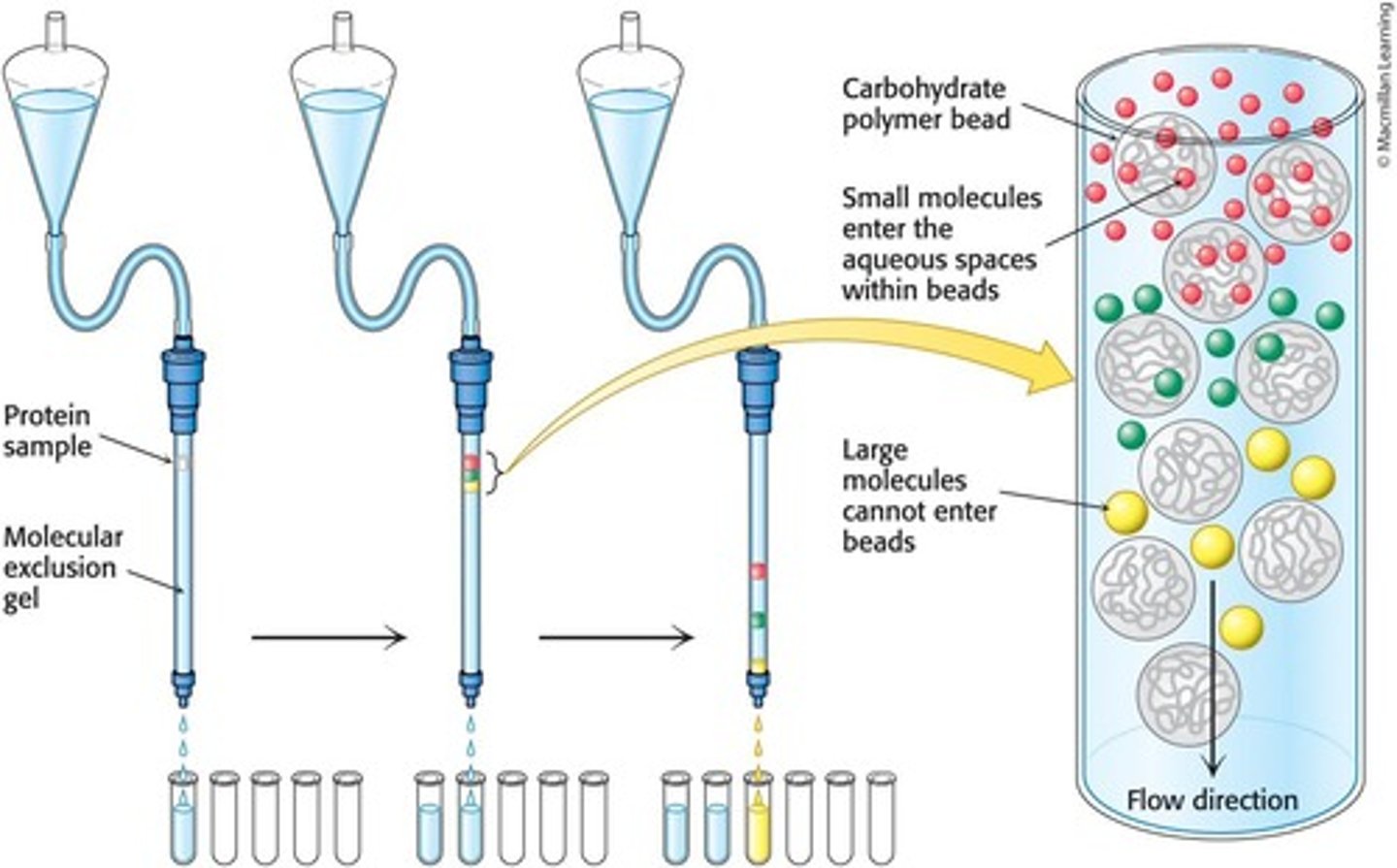
Gel-Filtration Chromatography
Separates proteins on the basis of size using porous beads in a column.
Ion-Exchange Chromatography
Separates proteins on the basis of charge using charged beads in a column.
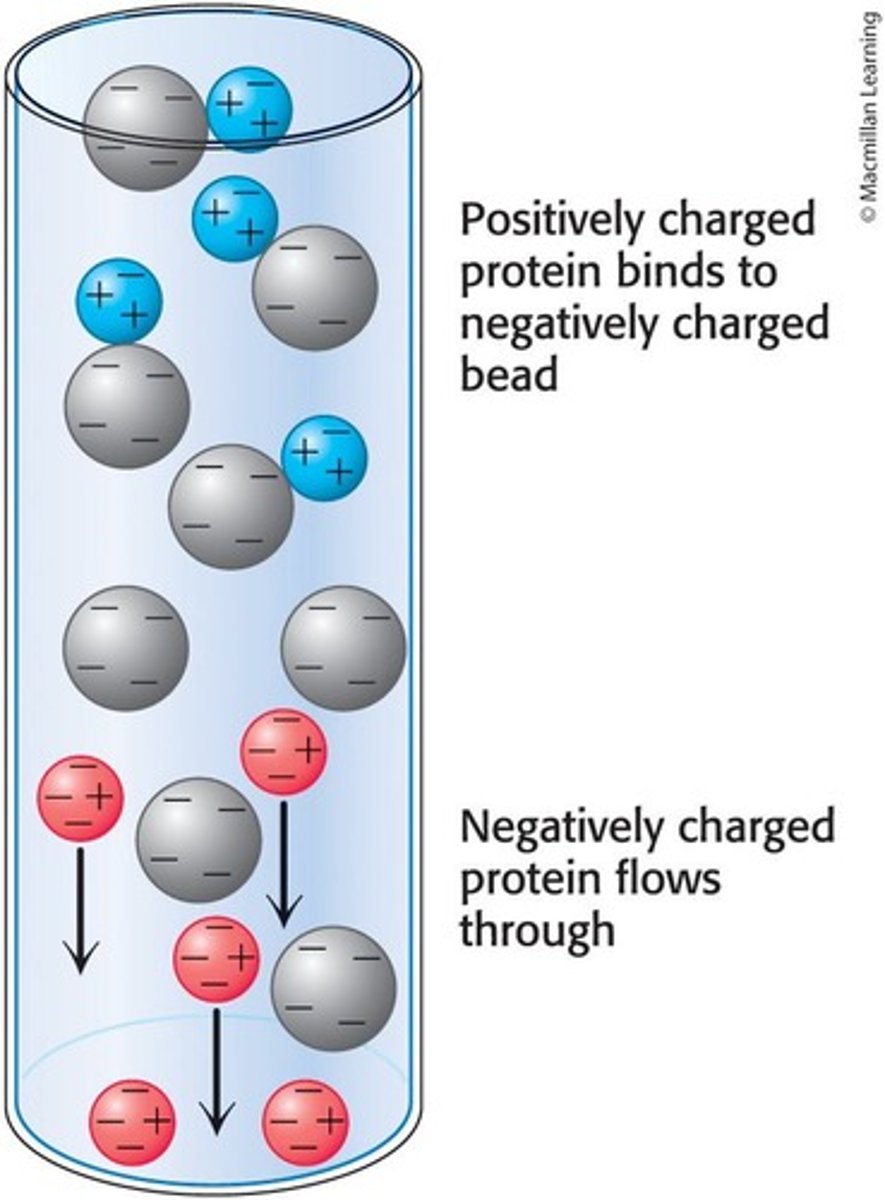
Cation Exchange Chromatography
Uses negatively-charged beads to separate positively charged proteins.
Anion Exchange Chromatography
Uses positively-charged beads to separate negatively charged proteins.
Affinity Chromatography
Takes advantage of the affinity of some proteins for specific molecules called ligands.
Ligands
Specific molecules that some proteins have a high affinity for in affinity chromatography.
Column in Chromatography
A glass or plastic column containing a bead-based matrix used for protein separation.
Molecular Exclusion Chromatography
Another name for gel filtration chromatography, which separates proteins based on size.
Protein Precipitation
The salt concentration at which a protein precipitates differs from one protein to another.
Diffusion in Dialysis
Smaller molecules and ions diffuse down their concentration gradients and emerge in the solution outside the dialysis bag.
Beads in Ion-Exchange Chromatography
Charged beads in the column interact with proteins based on their charge.
Release of Bound Protein
The bound protein in affinity chromatography is released by passing a solution enriched in the ligand.
Suspension in Chromatography
The suspension or liquid is applied at the top of the chromatography column.
Porous Beads
Beads used in gel-filtration chromatography that allow small proteins to enter while excluding large proteins.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Uses very fine beads in columns and pressure to move the liquid through the column, leading to sharper separations between proteins and a more rapid separation.
Resolving Power
Related to the number of potential sites of interaction between the protein and the column beads.
Electrophoretic Techniques
Methods that separate proteins based on their charge and size.
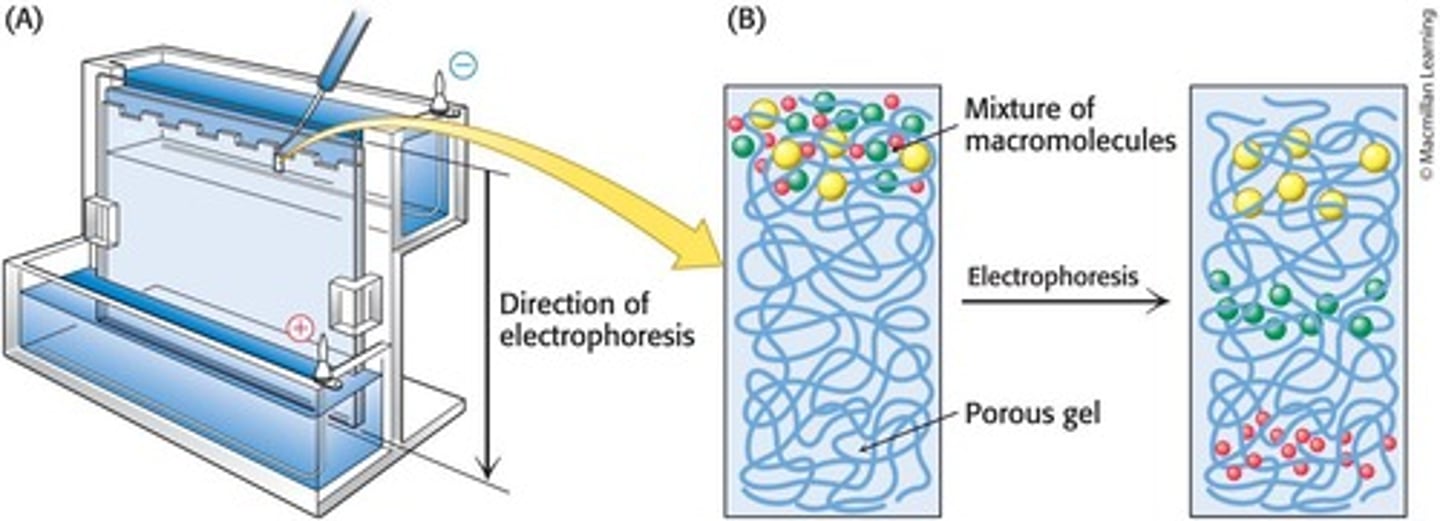
Native Gels
Non-dissociating gels that leave the proteins in their natural conformation, affecting migration rate.
Dissociating Gels
Gels that break down proteins into their individual polypeptides, where shape is not an issue.
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE)
A technique used to separate proteins based on their size.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
Allows accurate determination of mass by denaturing proteins with SDS.
SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate)
An anionic detergent that denatures proteins.
SDS Binding Ratio
For most proteins, 1 molecule of SDS binds for every 2 amino acids.
Electrophoretic Mobility
The mobility of proteins in SDS-polyacrylamide gels is linearly proportional to the logarithm of their mass.
Isoelectric Point (pI)
The pH at which a protein has no net charge.
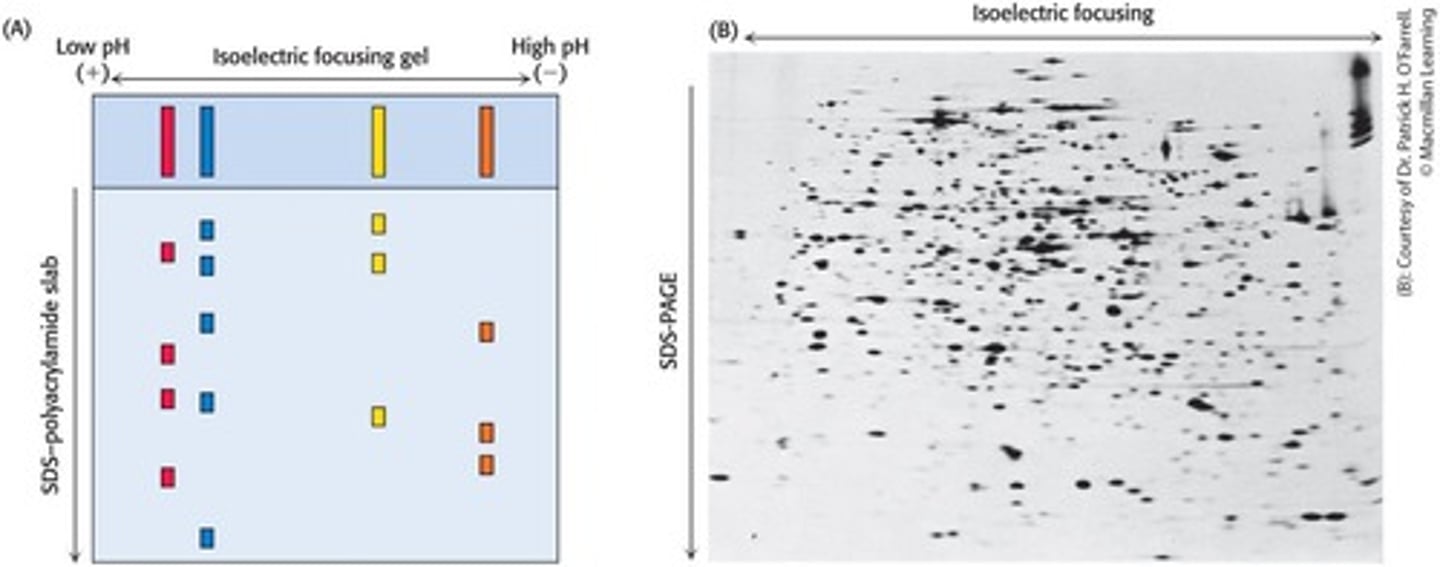
Isoelectric Focusing
A technique that separates proteins in a gel based on their isoelectric point.
Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis
Separates proteins in two directions: isoelectric focusing horizontally and SDS-PAGE vertically.
Sedimentation Coefficients
Quantify the rate of movement of molecules when exposed to a centrifugal force, expressed in Svedberg units (S).
Svedberg Units (S)
A measure where a smaller S value indicates slower movement in a centrifugal field.
Ultracentrifugation
Used to analyze the physical properties of biomolecules, such as mass, density, shape, and interactions.
Protein Visualization
Proteins separated by SDS-PAGE are visualized by staining the gel with dyes such as Coomassie blue.
Mass Determination
Electrophoresis can determine protein mass based on migration in gels.
Protein Expression Detection
Two-dimensional electrophoresis can detect differences in protein expression under different physiological circumstances.
Migration to pI
In isoelectric focusing, each protein migrates to its pI where its electrophoretic mobility is zero.
Mass and Shape Influence on Sedimentation
A more massive particle sediments more rapidly than a less-massive particle; elongated particles sediment more slowly than spherical ones.
S value
A measure of the sedimentation rate of a particle in a centrifuge, expressed in Svedberg units.
Molecular weight
The mass of a molecule, typically expressed in Daltons (g/mol).
Pancreatic trypsin inhibitor
Protein with an S value of 1 and a molecular weight of 6520.
Cytochrome c
Protein with an S value of 1.83 and a molecular weight of 12,310.
Ribonuclease A
Protein with an S value of 1.78 and a molecular weight of 13,690.
Myoglobin
Protein with an S value of 1.97 and a molecular weight of 17,800.
Trypsin
Protein with an S value of 2.5 and a molecular weight of 23,200.
Carbonic anhydrase
Protein with an S value of 3.23 and a molecular weight of 28,800.
Concanavalin A
Protein with an S value of 3.8 and a molecular weight of 51,260.
Malate dehydrogenase
Protein with an S value of 5.76 and a molecular weight of 74,900.
Lactate dehydrogenase
Protein with an S value of 7.54 and a molecular weight of 146,200.
Recombinant DNA technology
A method that allows for the production and purification of proteins in large quantities and with modifications.
Affinity tags
Molecular labels attached to proteins that facilitate their purification or visualization.
Antibodies
Proteins synthesized in response to the presence of a foreign substance called an antigen.
Epitope
A specific group or cluster of amino acids on a target molecule that an antibody recognizes.
Polyclonal antibodies
Heterogeneous mixtures of antibodies derived from multiple antibody-producing cell populations.
Monoclonal antibodies
Identical antibodies produced by clones of a single antibody-producing cell.
Hybridoma cells
Hybrid cells generated by fusing normal antibody-producing cells with immortal cells from cancer.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
A method that quantifies the amount of protein present by linking an antibody to an enzyme.
Horseradish peroxidase
An enzyme that reacts with a substrate to produce a colored product in ELISA.
Indirect ELISA
A method used to detect the presence of antibodies in a sample by using a secondary antibody that is linked to a detectable enzyme.
Sandwich ELISA
A type of ELISA that uses two antibodies to capture and detect a specific antigen.
Western Blotting
A technique that allows for the detection of specific proteins in a sample after separation by SDS-PAGE, transfer to a membrane, and staining with antibodies.
Primary antibody
An antibody that is specific for the target protein of interest.
Secondary antibody
An antibody that binds to the primary antibody and is often conjugated to an enzyme or fluorescent tag for detection.
Co-immunoprecipitation
A method used to identify binding partners of a specific protein by using an antibody to pull down the protein and its interacting partners.
Fluorescent Markers
Substances that allow for the visualization of proteins in cells using fluorescence microscopy.
Immunoelectron Microscopy
A technique that uses antibodies conjugated with electron-dense materials to visualize specific antigens at a very fine spatial resolution.
Cryo-Electron Microscopy
A method that determines the structures of large proteins and macromolecular complexes by rapidly freezing samples and using electron microscopy.
SDS-PAGE
A method used to separate proteins based on their size using a polyacrylamide gel.
Agarose beads
Beads used in co-immunoprecipitation that are coated with proteins to capture antibody-bound complexes.
Fluorescence microscopy
A technique that uses fluorescence to visualize the location of proteins within cells.
Gold-conjugated antibodies
Antibodies that are labeled with gold particles for visualization in immunoelectron microscopy.
Transmission electron microscope
A type of electron microscope that uses a beam of electrons to create an image of a sample.
Multimeric Protein
A protein that consists of multiple subunits or polypeptide chains.
Three-dimensional representation
A model created from two-dimensional projections obtained through cryo-electron microscopy.
Protein function
The specific biological activity or role that a protein plays within a cell or organism.
Cellular location of the protein
The specific area within a cell where a protein is found.
Protein sequence determination
The process of identifying the amino acid sequence of a protein.
Homogenization
A process to break down cells to release proteins for purification.
HPLC
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography, uses finer beads and higher pressure for faster separations.
Western blot
A method using antibodies to detect specific proteins in a sample.
ELISA
A technique that uses antibodies and color change to identify a substance.
Electron microscopy
A method to visualize proteins at a much higher resolution than light microscopy.
Genomic techniques
Methods that can be used alongside proteomic techniques to determine amino acid sequences.
Cryoelectron microscopy
A technique used to determine the three-dimensional structure of proteins.
First step in protein purification
Centrifugation is the initial step to separate proteins from a homogenate.