Chapter 4: Consciousness
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle. When tested under "free running conditions" (meaning there were no light or time cues), it was found that the body's circadian rhythm lasted beyond 24 hours.
jet lag
a disruption of circadian rhythms due to crossing time zones

suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
a pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm. In response to light, the SCN causes the pineal gland to adjust melatonin production, thus modifying our feelings of sleepiness
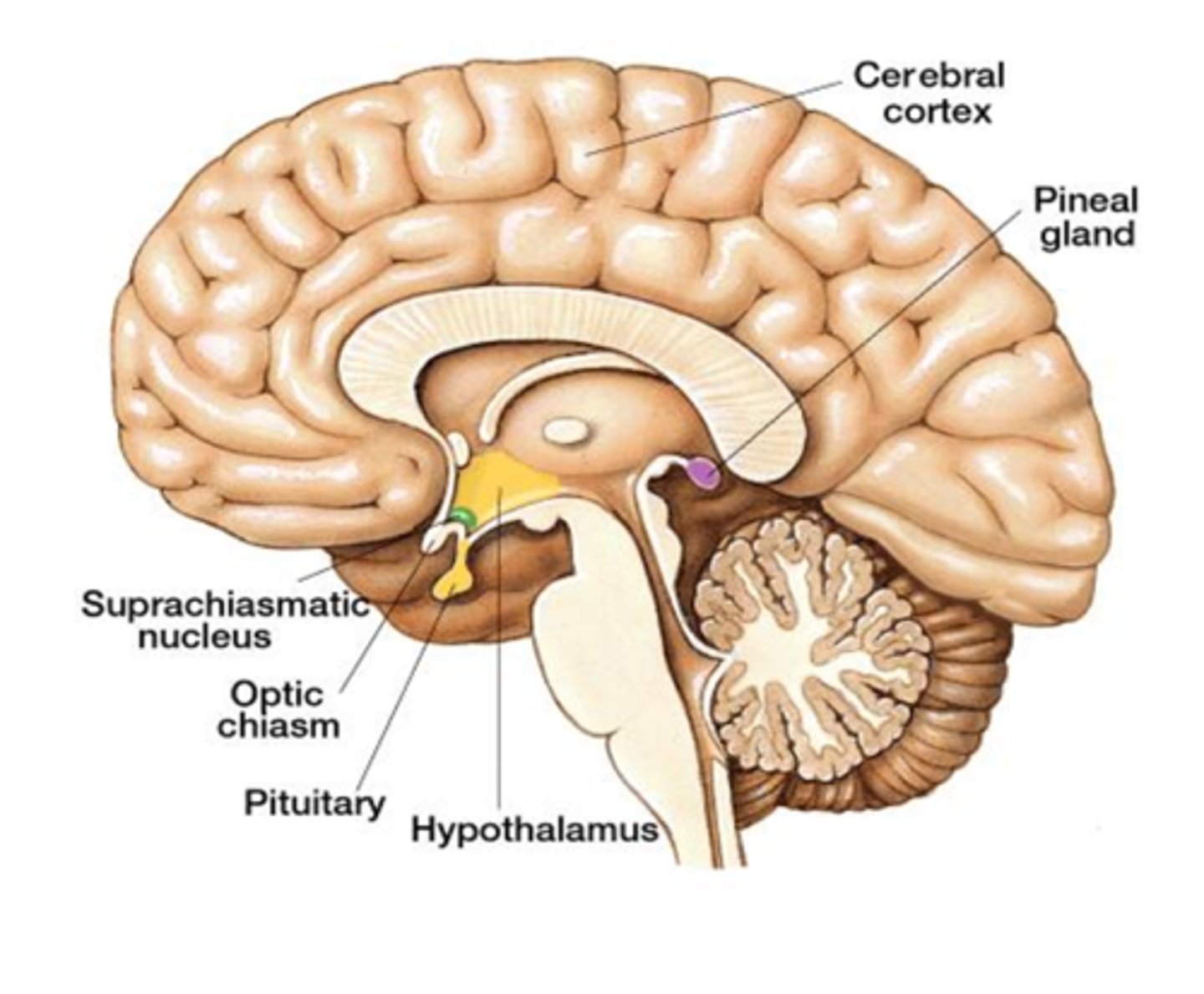
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness. Sunlight decreases melatonin and darkness increases melatonin.
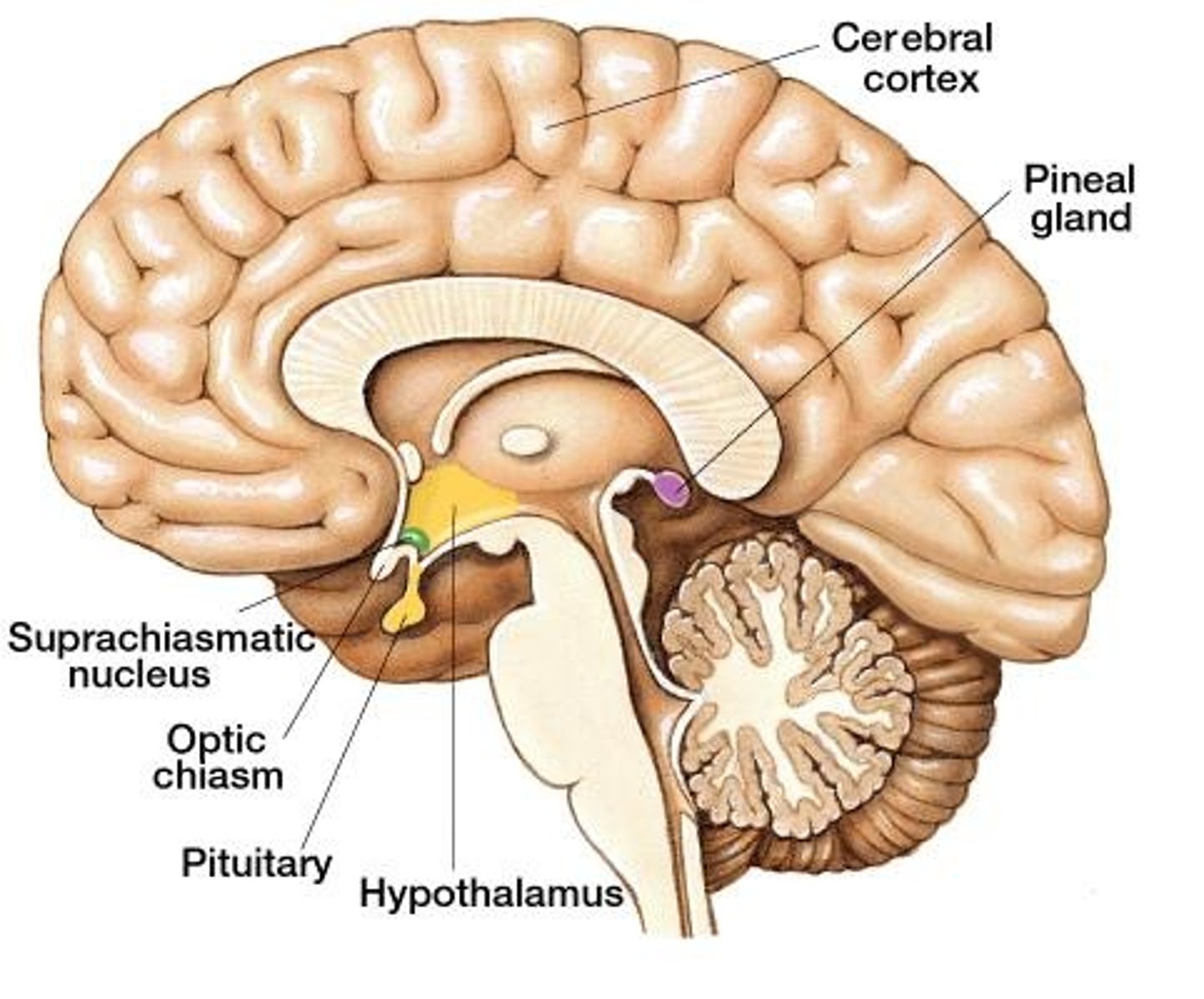
EEG (electroencephalogram)
shows brain's electrical activity by positioning electrodes over the scalp. Invented by Hans Berger. This device is often used in sleep studies.
REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep, a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because although there is a great deal of brain activity, the body is paralyzed during REM. REM sleep is thought to recharge the brain.
NREM sleep
non-rapid eye movement sleep; encompasses all sleep stages except for REM sleep
Stage 1 sleep
Very light sleep where if woken up, a person might not even realize they had been asleep. This stage is characterized by alpha and theta waves. A person might experience a hypnagogic hallucination during this stage.
hypnagogic hallucinations
vivid sensory phenomena that occur during the onset of sleep
myoclonic jerk
an involuntary muscle spasm of the whole body that jolts the person completely awake. This may happen as a result of a hypnagogic hallucination and typically occurs during stage 1.
ex. The feeling of falling in dream and then jolting awake. The dream is the HH and the jolting awake is the myocolonic jerk..
Stage 2 of sleep cycle
Considered light sleep but characterized by more theta waves and a growing number of delta brain waves. In this stage researchers use an EEG to look for K complex and Sleep Spindles, which are characteristic of stage 2 sleep. Later in the night and more towards the morning, people move between stage 2 and REM sleep in the sleep cycle.
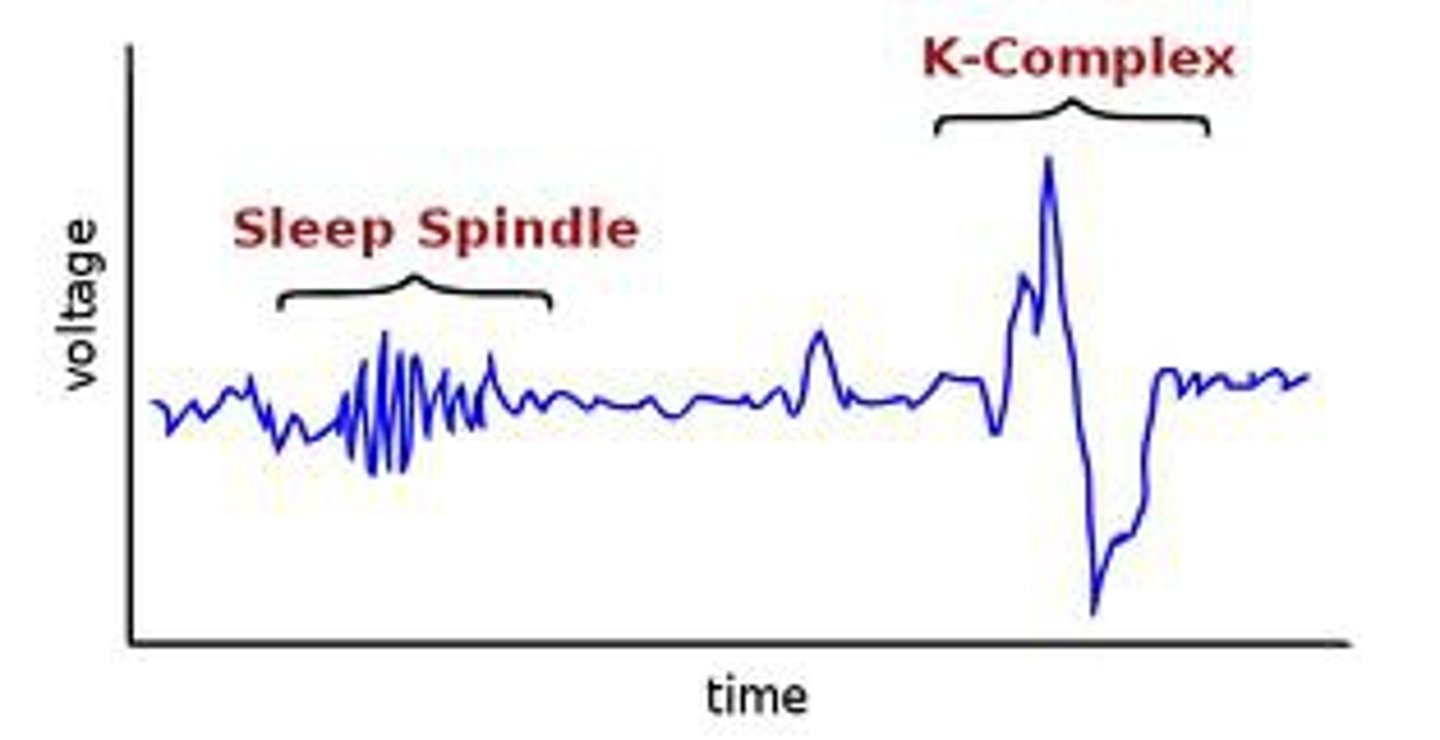
K complexes
single high-voltage spikes of brain activity that occur during stage 2
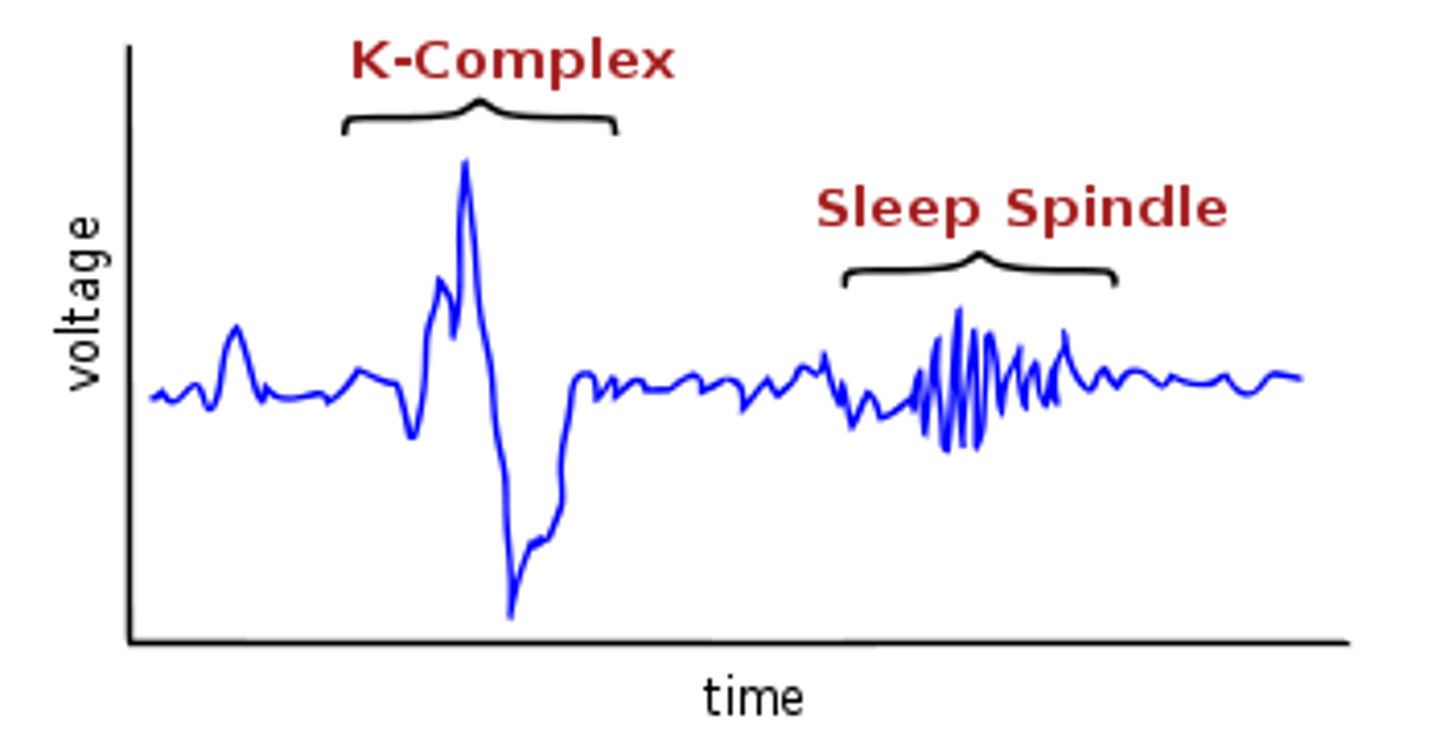
sleep spindles
short bursts of brain waves detected in stage 2 sleep
Stage 3 or stages 3 and 4 of sleep
Some researchers group stages 3 and 4 together as just stage 3 and some do not. The distinction, if there is one to be made is that stage 4 has more delta waves present. Other than that, they are the same and this is considered deep sleep or slow wave sleep. Deep sleep tends to occur very early in the night in the sleep cycle. Deep sleep is also thought to help recharge the body. Most sleep disorders such as parasomnias occur during stages 3 and 4.
Sleep cycle
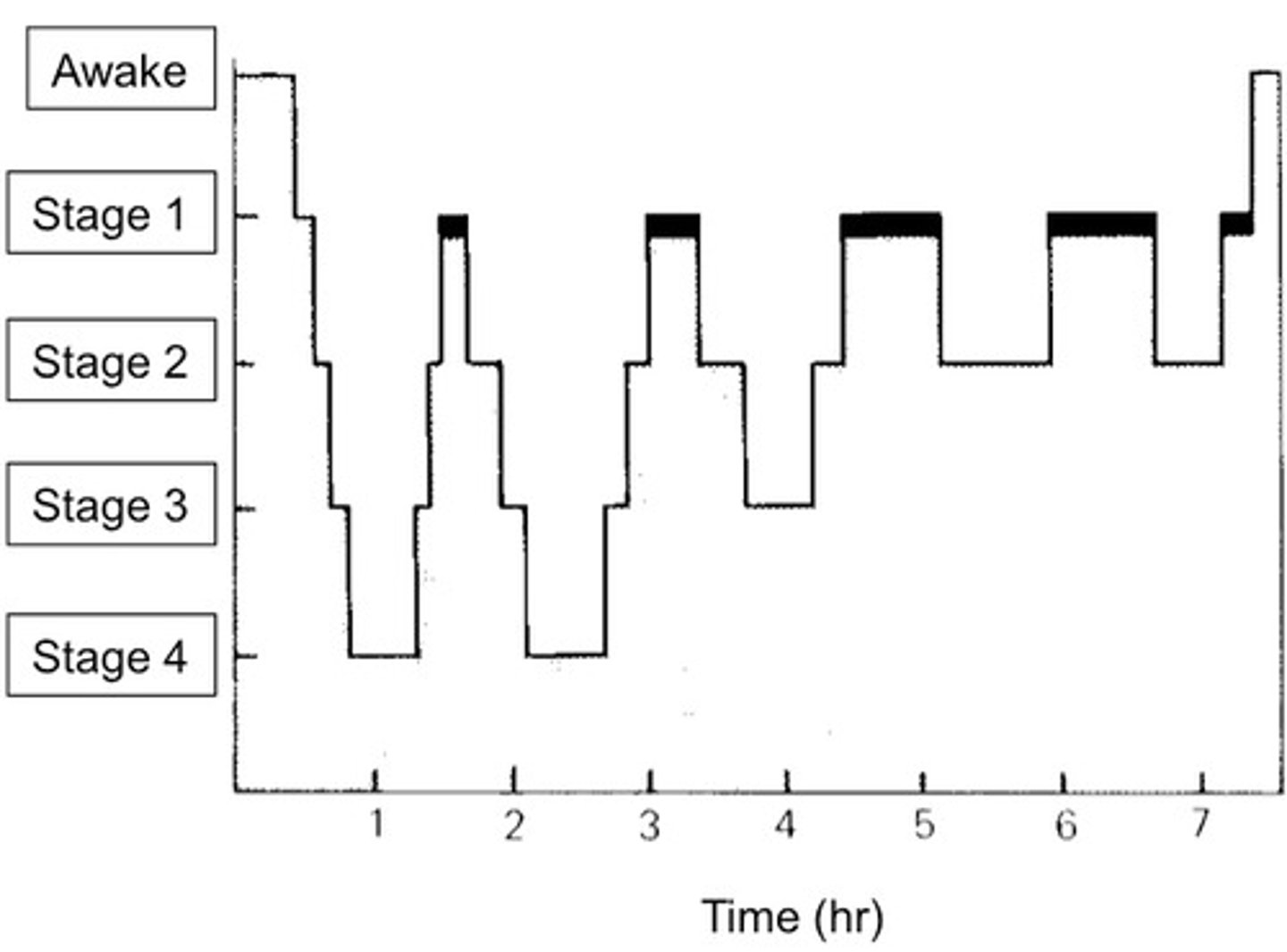
Each cycle lasts 90 minutes and on a typical night we experience 5 cycles. A person cycles down from being awake, to being relaxed, then moving through stages 1-4. In stages 1-4 heart rate, breathing and, brainwaves decrease. The person then cycles back up (meaning heart rate, breathing, and brainwaves increase to enter into REM sleep. People experience deep sleep early in the night and longer episodes of REM towards the morning. This is why most sleep disorders impact people early in the night. As we get older, we spend less time in deep sleep and REM sleep and end up spending more time in stage 2. Some researchers believe that this change as we age might impact physical and mental aging.
Brain waves during sleep
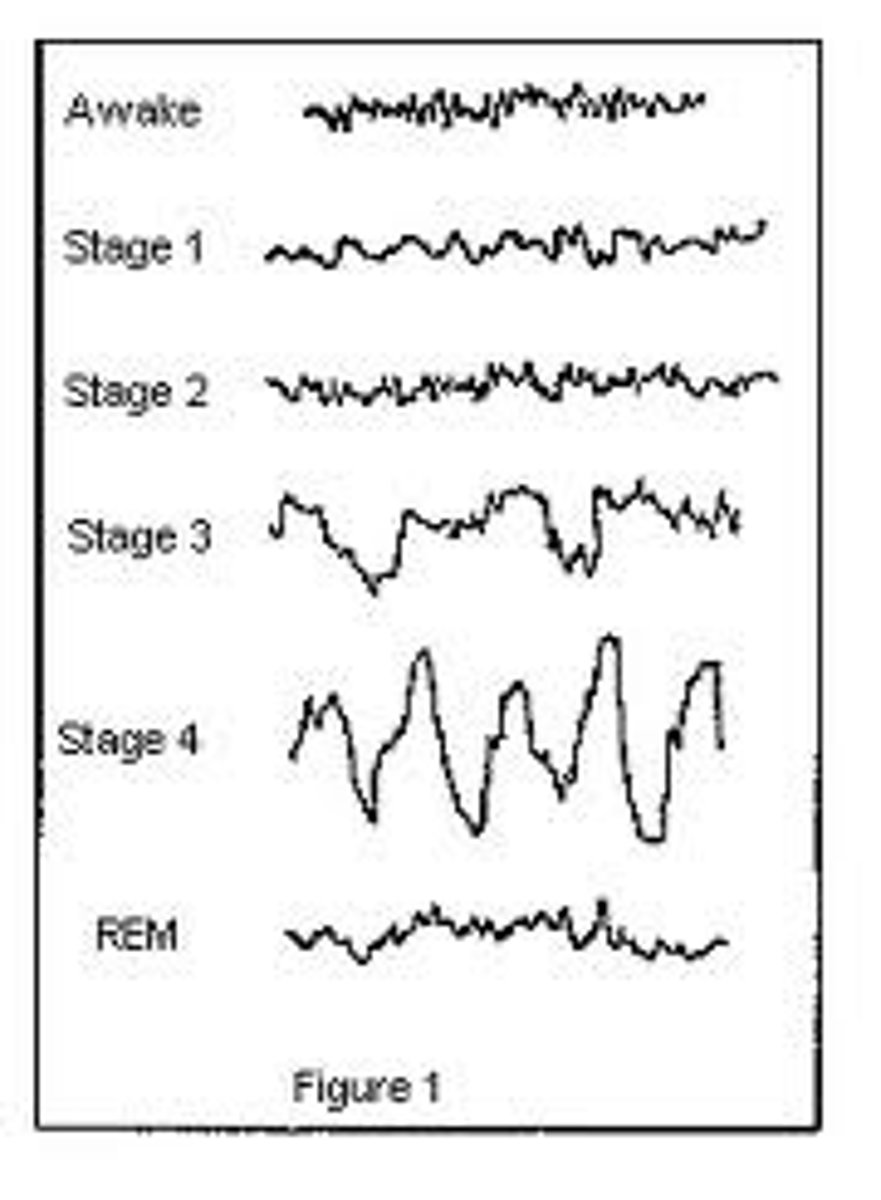
Beta waves- Alert
Alpha waves- relaxed
Theta waves- early sleep stages
Delta waves- associated with deep sleep
Brain waves during REM are very active and more closely resemble the beta waves that occur when we are awake.
REM rebound
the tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation (created by repeated awakenings during REM sleep)
*If you don't get enough REM sleep on a given night, the next time you sleep might have a slightly altered sleep cycle where you jump right into REM to "rebound" from the loss.
NREM rebound
the tendency for NREM sleep to increase following NREM sleep deprivation
*If you don't get enough NREM sleep (deep sleep) on a given night, the next time you sleep might have a slightly altered sleep cycle where you jump right into NREM to "rebound" from the loss.
restorative sleep theory
NREM sleep relaxes the body, REM sleep relaxes the brain. Sleep according to this theory is a time to restore normal body and brain functioning, while also repairing any damage.
adaptive sleep theory
theory of sleep proposing that animals and humans evolved sleep patterns to avoid predators by sleeping when predators are most active.
ex. humans sleep at night because at one point humans would have been highly vulnerable to predators if they slept in broad daylight.
Sleep Disorders
serious and consistent sleep disturbances that interfere with daytime functioning and cause subjective distress
insomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep

RLS (restless leg syndrome)
A condition where unpleasant sensations (itching, twitching, tingling, crawling) in the lower legs are accompanied by an irresistible urge to move the legs

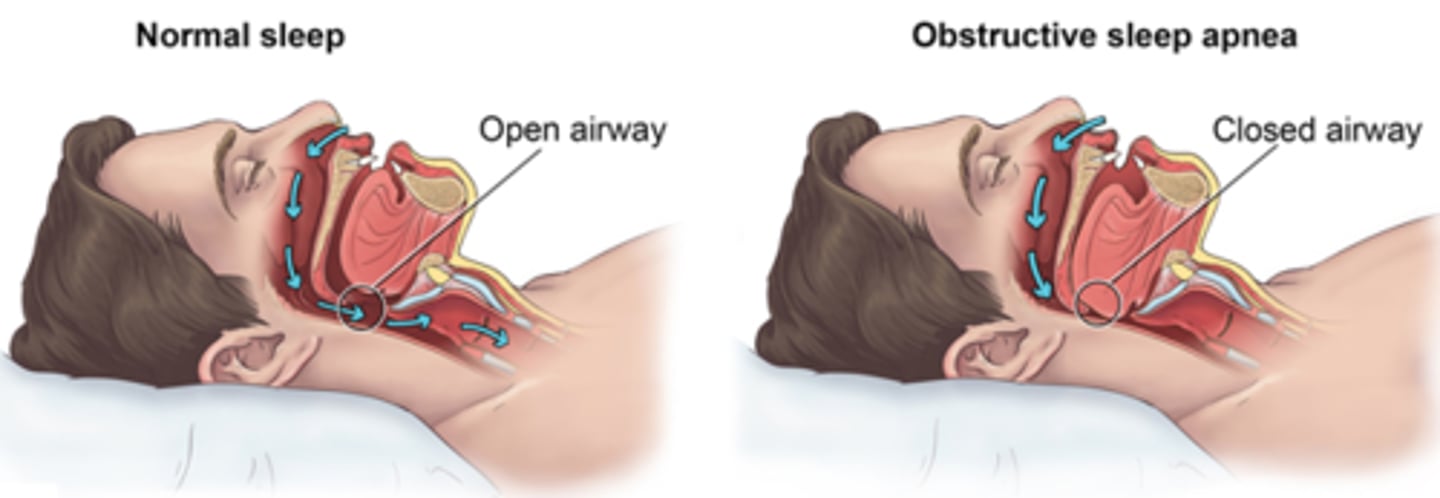
sleep apnea
a disorder in which the person stops breathing for brief periods while asleep. This is typically treated with a CPAP machine that helps the airway to stay open while the person is sleeping.
somnambulism
sleepwalking

night terrors (sleep terrors)
A sleep disturbance characterized by an episode of increased physiological arousal, intense fear and panic, frightening hallucinations, and no recall of the episode the next morning. Occurs during stages 3 and 4.

sleep paralysis
A temporary condition in which a person is unable to move upon awakening in the morning or during the night.
Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times. Cataplexy is a symptom of narcolepsy.
Cataplexy (narcolepsy)
A sudden loss of voluntary muscle strength and control that is usually triggered by an intense emotion.
Parasomnias
A category of sleep disorders characterized by arousal or activation during sleep or sleep transitions; includes things like sleepwalking and sleep terrors.
activation synthesis model of dreams
The theory that brain activity during sleep produces dream images that the brain combines to make into a story. This theory was developed by Allan Hobson and is based on the idea that dreams are random and don't hold any kind of latent meaning.
lucid dream
Dream in which the dreamer is aware of dreaming while it is happening and can control the content
psychoactive drug
A drug that alters consciousness, perception, mood, and behavior.
physical dependence (addiction)
a condition in which a person has physically adapted to a drug so that he or she must take the drug regularly in order to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Tolerance (habituation)
A condition in which increasing amounts of a physically addictive drug are needed to produce the original, desired effect.
withdrawal symptoms
Unpleasant physical reactions, combined with intense drug cravings, that occur when a person abstains from a drug on which he or she is physically dependent.
drug rebound effect
Withdrawal symptoms that are the opposite of a physically addictive drug's action.
ex. withdrawing from caffeine might make a person depressed, fatigued, or lethargic.
depressants
inhibit brain activity and energy levels (ex. alcohol, barbiturates, tranquilizers). GABA is increased and reduces brain activity.
Opiates
(narcotics)- chemically similar to morphine and relieve pain. Mimic the bodies own endorphins. (ex. heroin, oxycontin, demerol).
Stimulants
increase brain activity and energy levels (ex. caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine). Can create stimulant induced psychosis or schizophrenia like hallucinations. Sometimes amphetamines are used to help treat disorders such as narcolepsy.
Psychadelics (hallucinogens)
distort sensory perceptions (ex. mescaline from the peyote cactus, psilocybin from mushrooms, LSD, which is a synthetic drug, and marijuana). LSD influences serotonin levels to create hallucinations.
Club drugs
a fairly new category that is a hybrid stimulant and psychedelic. The most common example of this category is MDMA or ecstasy. Death often results from dehydration and hyperthermia. Blocks serotonin reuptake to influence mood.