Unit 0 - Scientific Foundations of Psychology - AP Psychology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Operational Definition
Clear, precise, quantifiable definition of your variables — allows replication and collection of reliable data
Qualitative Data
Descriptive data (eye colors)
Quantitative Data
Numerical data (Ideal for statistics)
Directionality Problem
Which direction does the correlation go? (Depression causes low self-esteem, low self-esteem causes depression)
3rd Variable Problem
Different variable is responsible for relationship (ice cream & murder)
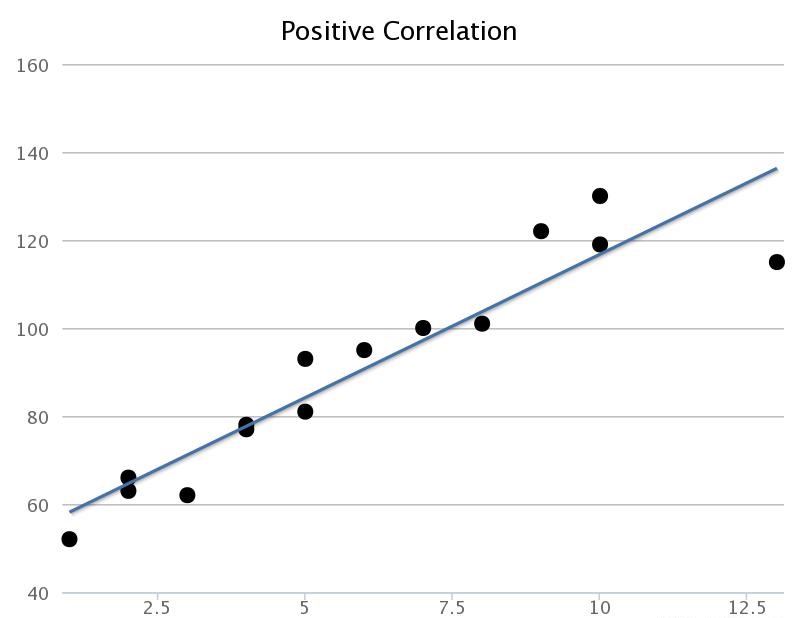
Positive Correlation
Variables increase & decrease together
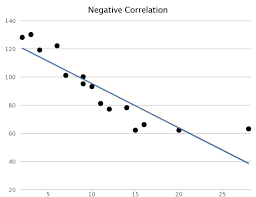
Negative Correlation
One variable increases as the other variable decreases
Independent Variable
Purposefully altered by researcher to look for effect
Experimental Group
Received the treatment
Control Group
Placebo, baseline
Dependent Variable
Measured variable, dependent on independent variable
Placebo Effect
Any observed effect on behavior that is caused by the placebo
Double-Blind Experiment
Experiment where neither the participants nor the experimenter are aware of which condition people are assigned
Single-Blind Experiment
Experiment in which only participants are blind to which condition people are assigned
Confounding Variable
Error/flaw in study that is accidentally introduced
Random Assignment
Assigns participants to either control or experimental group at random - increases chance of equal representation among groups
ALLOWS you to say cause/effect
Naturalistic Observation
Observes people in their natural settings
Adv: Real world validity
Disadv: No cause/effect
Case Study
Studies one person in great detail
Adv: Collects lots of info
Disasv: No cause/effect
Meta-analysis
Combines multiple studies to increase sample size and examine effect sizes
Descriptive Statistics
Shows shape of the data
Mean
Average (use in normal distribution)
Median
Middle # (used in skewed distribution)
Mode
Occurs most often in a data set
Bimodal distribution
Has two modes, usually indicates good/bad scores
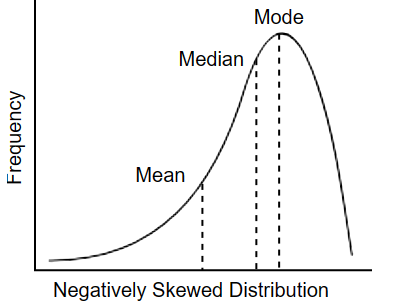
Negatively Skewed Distribution
Mean is to the left, mode is to the right
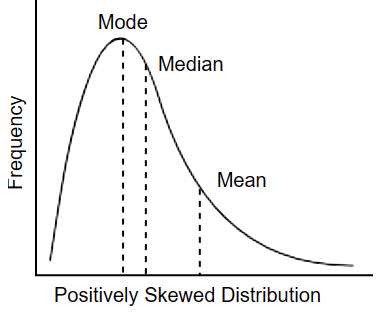
Positively Skewed Distribution
Mean is to the right, mode is to the left
Range
Distance between smallest and biggest #
Standard Deviation
Average amount the scores are spread from the mean (bigger # = more spread)
Inferential Statistics
Establishes significance (meaningfulness)
Statistical Significance
Results not due to chance (smaller # = better)
Effect Size
Data has practical significance (bigger = better)
Confidentiality (ethical guidelines)
Names & info kept secret
Informed Consent (ethical guidelines)
Must agree to be part of study
Informed Assent (ethical guidelines)
Minors AND their parents must agree
Debriefing (ethical guidelines)
Must be told the true purpose of the study (done after for deception)
No harm (ethical guidelines)
No mental nor physical harm
Surveys
Usually turned to correlation, subject to self report bias
Social desirability (Surveys)
People lying to look desirable/good
Wording effects (Surveys)
How you frame the question can impact your answers
Random Sample
Method for choosing participants for your study — everyone has a chance to take part, increases generalizability
Representative Sample
Sample mimics the general population
Convenience Sample
Select participants on availability — less representative & less generalizability
Sampling Bias
Sample isn’t representative, due to convenience sampling
Cultural norms
Behaviors of a particular group can influence research results
Experimenter/participant bias
Experimenter/participant expectations can influence the outcome
Cognitive bias
Bias in thinking/judgement
Confirmation bias (cognitive)
Only searching for info that supports pre-existing beliefs
Hindsight Bias (cognitive)
Thinking you could’ve known the outcome “all along”
Overconfidence (cognitive)
Overestimate our knowledge/abilities
Hawthorne effect (cognitive)
People changing behavior when watched