ch5 natural selection
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
natural selection
success of survival and reproduction of individuals within population that results from interactions with environment
natural selection requires:
variation that’s heritable and results in differential reproductive success
fitness
measured by proportionate contribution it makes to future generations (ex: dark green frogs surviving and reproducing more than lighter frogs)
evolution
changes in gene frequency through time resulting from natural selection and producing changes in characteristics of population
adaptation
genetic determine characteristic (behavior, morphological, physiological) that improves an organisms ability to survive and reproduce prevailing environmental conditions
alleles
different versions of same gene. created by mutations that are heritable changes in gene or chromosome. (ex: fur coat coloration)
monophyletic
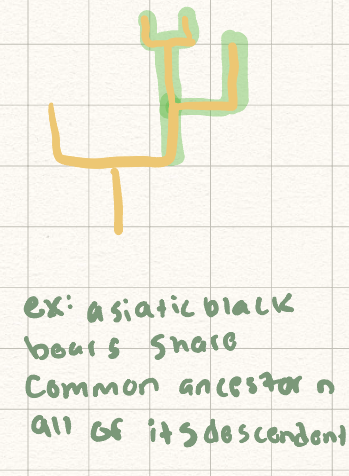
paraphyletic

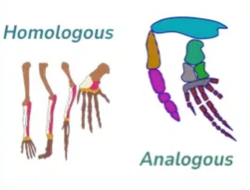
homologous structures
-common ancestor
-similar anatomy
-similar or diff functions
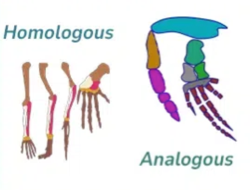
analogous structures
-different ancestry
-dissimilar anatomy
-similar functions
(bird wing and butterfly wing)
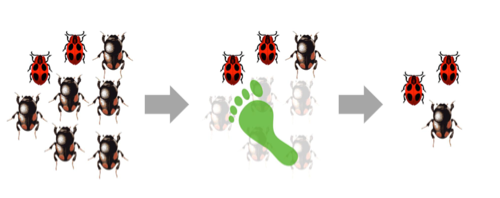
sexual selection
different reproduction owing to variation in ability to obtain mates
inbreeding
mating among relatives
-increase homozyhosity
-expose harmful recessive alleles (inbreeding depression)
gene flow
migration between populations
-introduces new alleles
-increases heterozygosity
how to tell if population is evolving?
hardy weinberg assumptions
1 random mating
2 no mutations
3 no genetic drift (large population)
4 no migration
5 no natural selection
inbred and gene flow effects on pumas?
heart deformities, low/malformed sperm, cryptorchidism
genetic drift
changes in allele freq due to chance (Natural selection tends be stronger in large populations, while drift can be more of a force in small populations.)
allopatric
: reproductive isolation develops between populations in physical
isolation.
sympatric
reproductive isolation develops within the "cruising range" of an existing species, in consequence of special biological propertie
Biological Species Concept (BSC)
group of organisms that can interbreed naturally and produce viable fertile offspring
limitations of Biological Species Concept (BSC)
Doesn’t apply to asexual organisms.
Difficult for fossils.
Hard to test in practice
advantages of Biological Species Concept (BSC)
Ties neatly into speciation mechanisms (e.g. allopatric, sympatric).
Phylogenetic Species Concept (PSC)
The smallest diagnosable cluster of organisms that share a unique evolutionary history and a common ancestor, distinguishing it from other such
clusters
advantages of Phylogenetic Species Concept (PSC)
Applicable to asexual organisms and fossils; Easy to test
limitations of Phylogenetic Species Concept (PSC)
Splits groups into many more species
than BSC would.
Requires lots of genetic or morphological
data