6. CT, CBCT, MRI
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
what are the three possible tomographic projections of 3D imaging?
axial
coronal
sagittal
what is the projection image of 3D imaging?
posterior-anterior view of skull
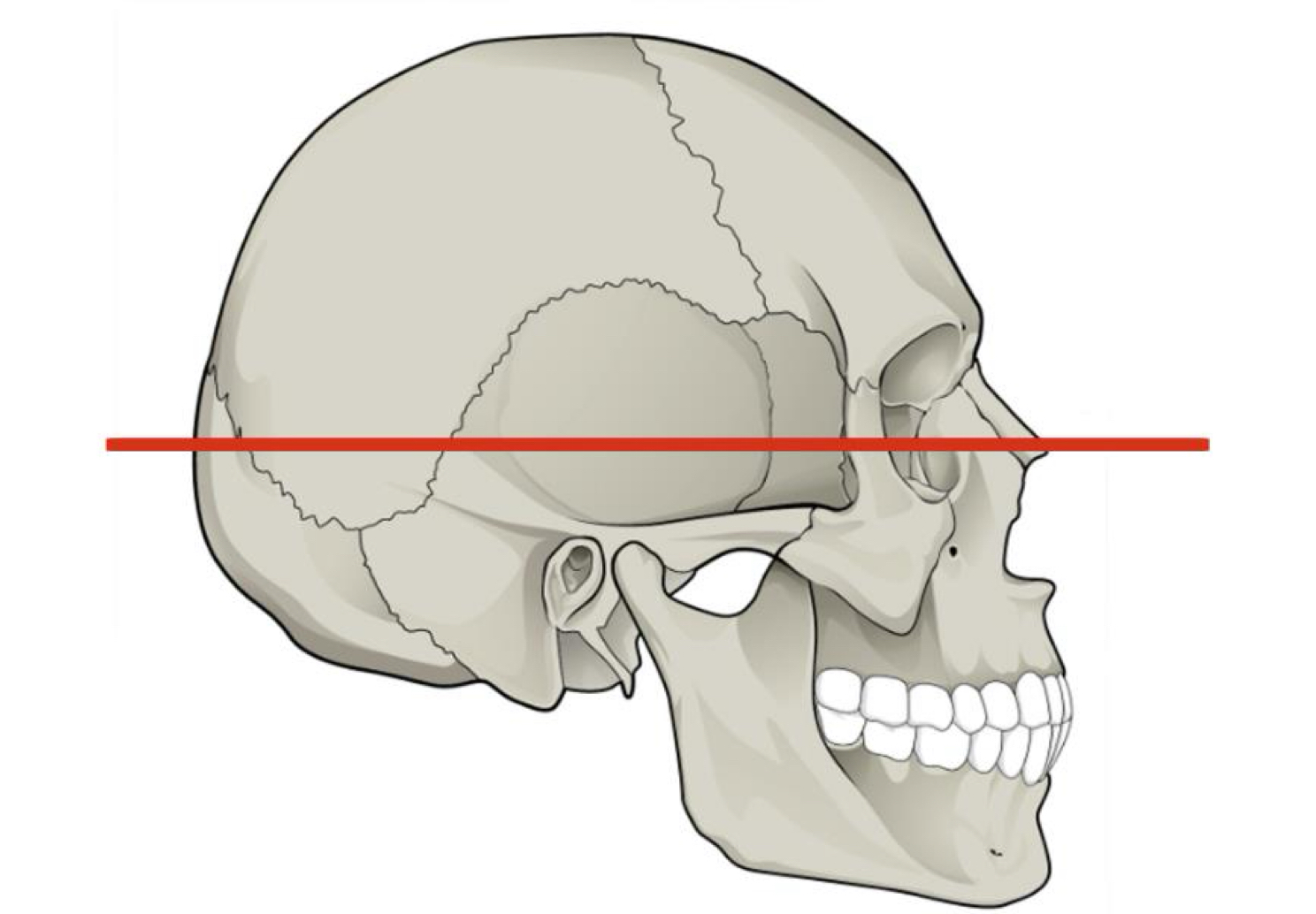
Which view divides the skull into inferior and superior parts?
axial
Which view divides the skull into an interior and posterior part
Coronal
Which view divides the school into right and left
Sagittal
Horizontal plane
Axial
Frontal plane
Coronal
Medium plane, parallel to suture of skull
Sagittal
axial
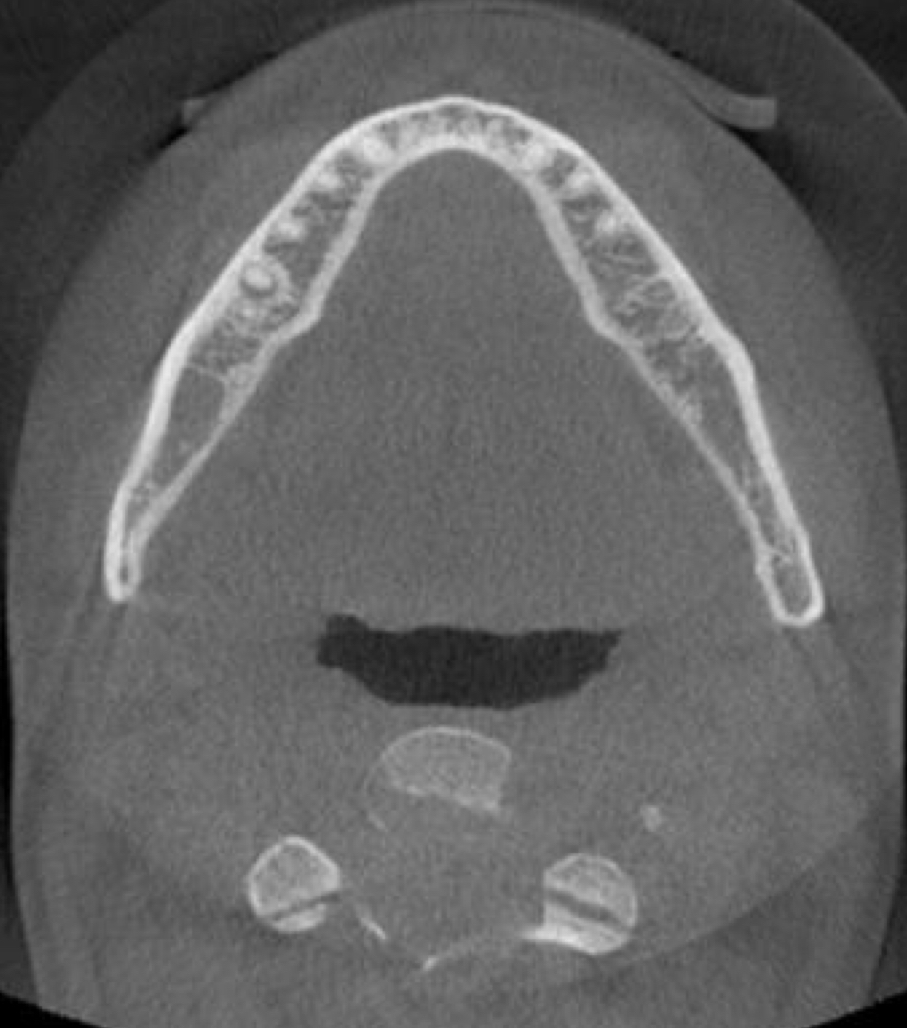
axial
coronal
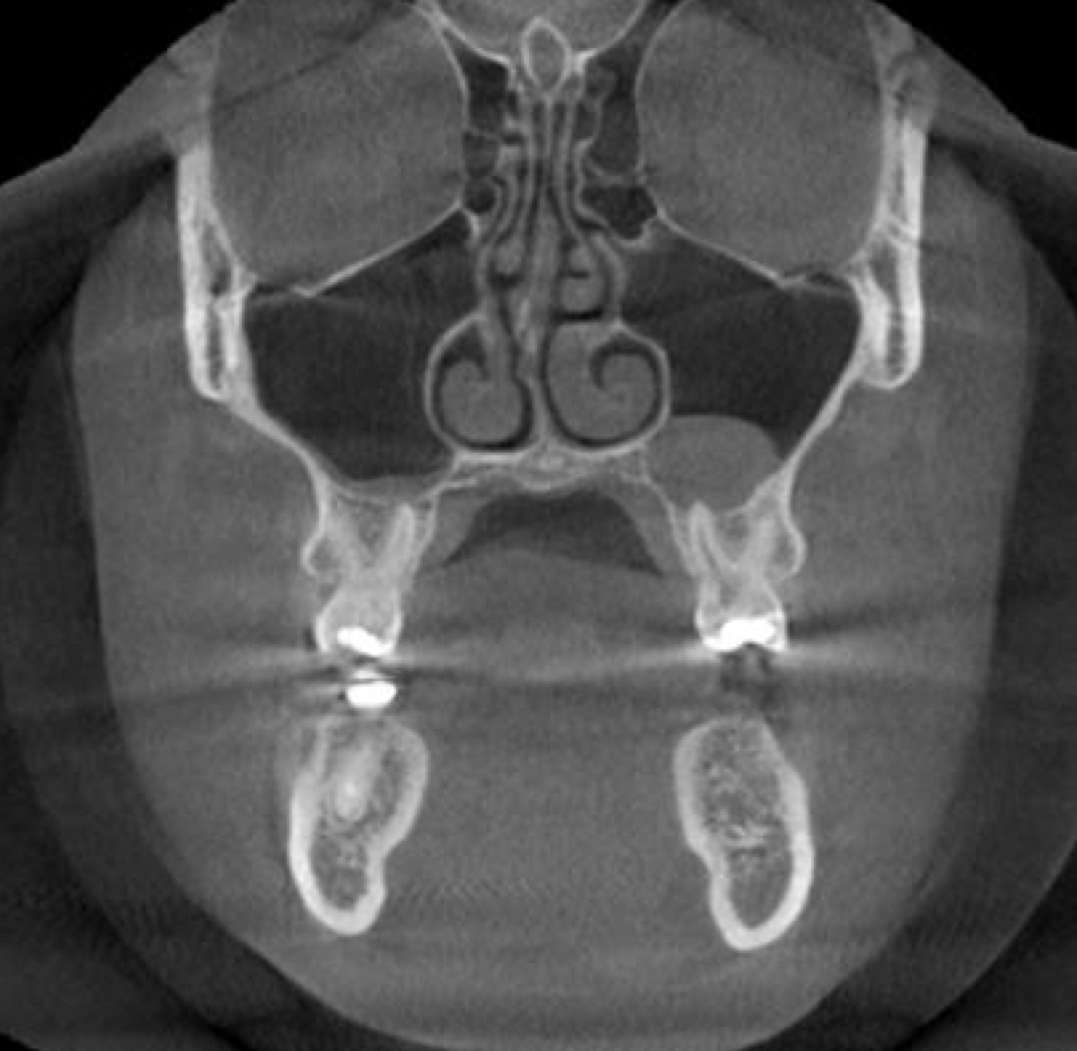
coronal

sagittal
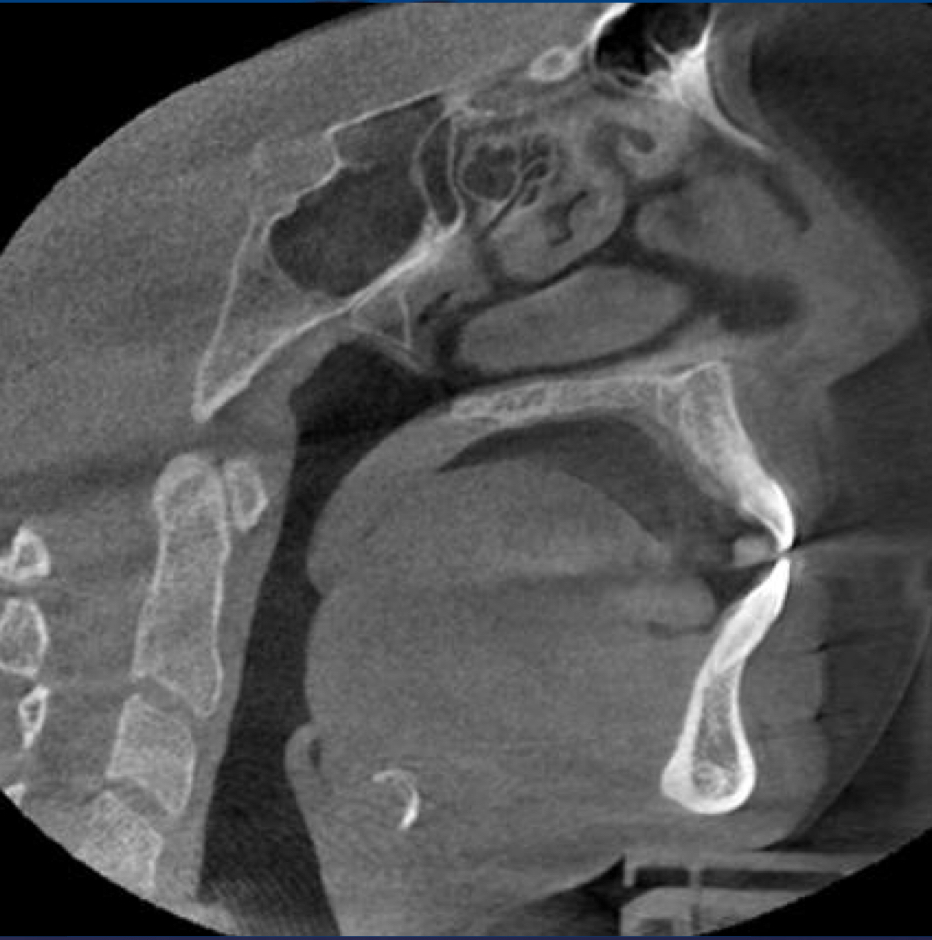
sagittal
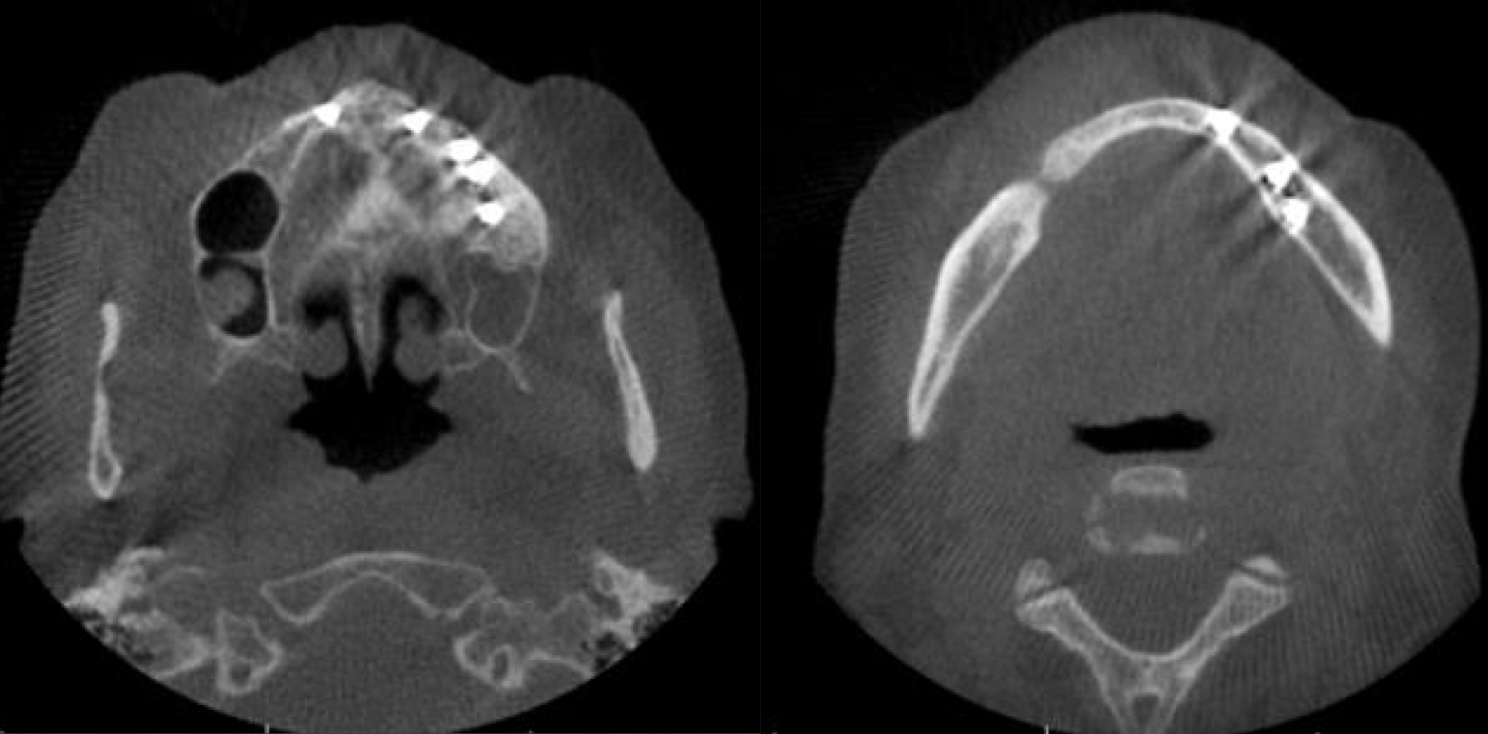
which advanced imaging modality?
Cone beam computed tomography
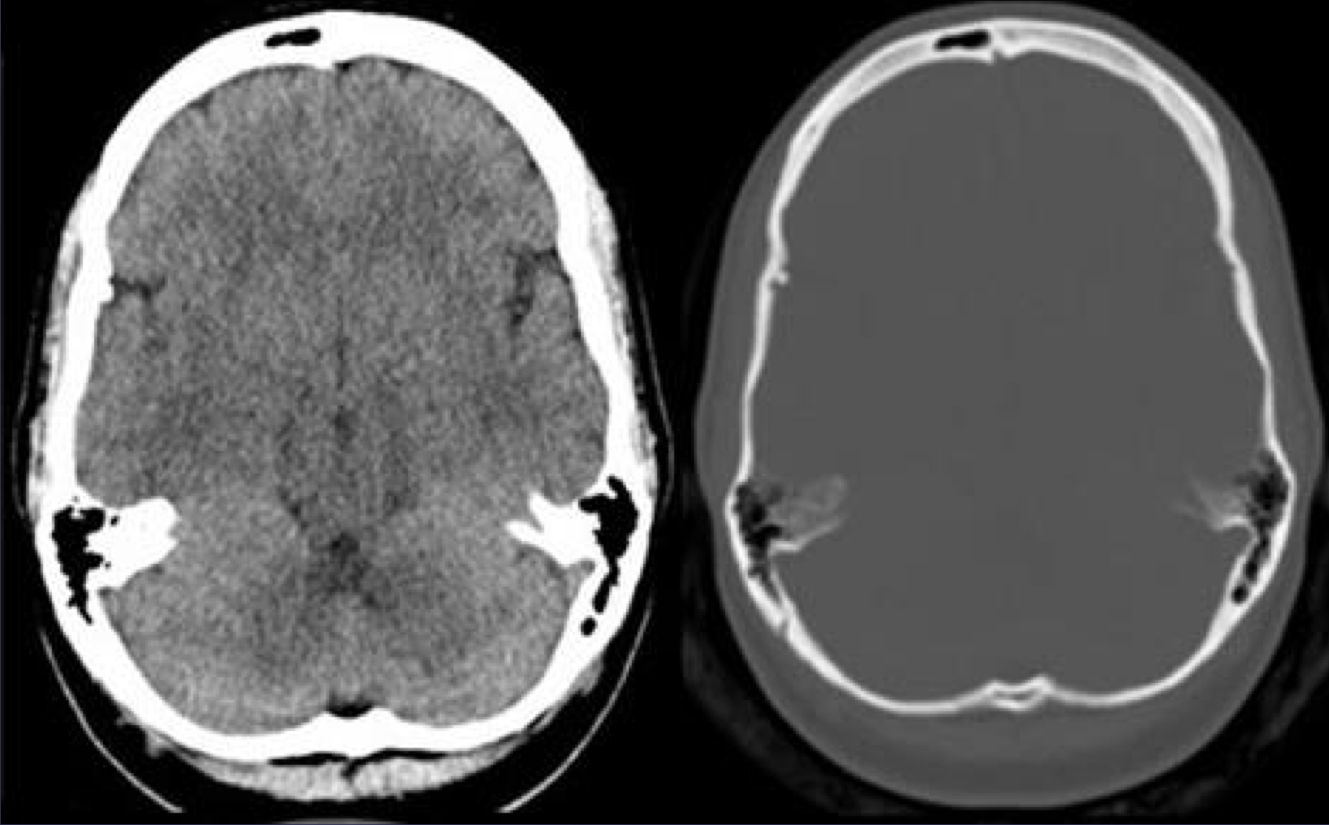
Computed tomography
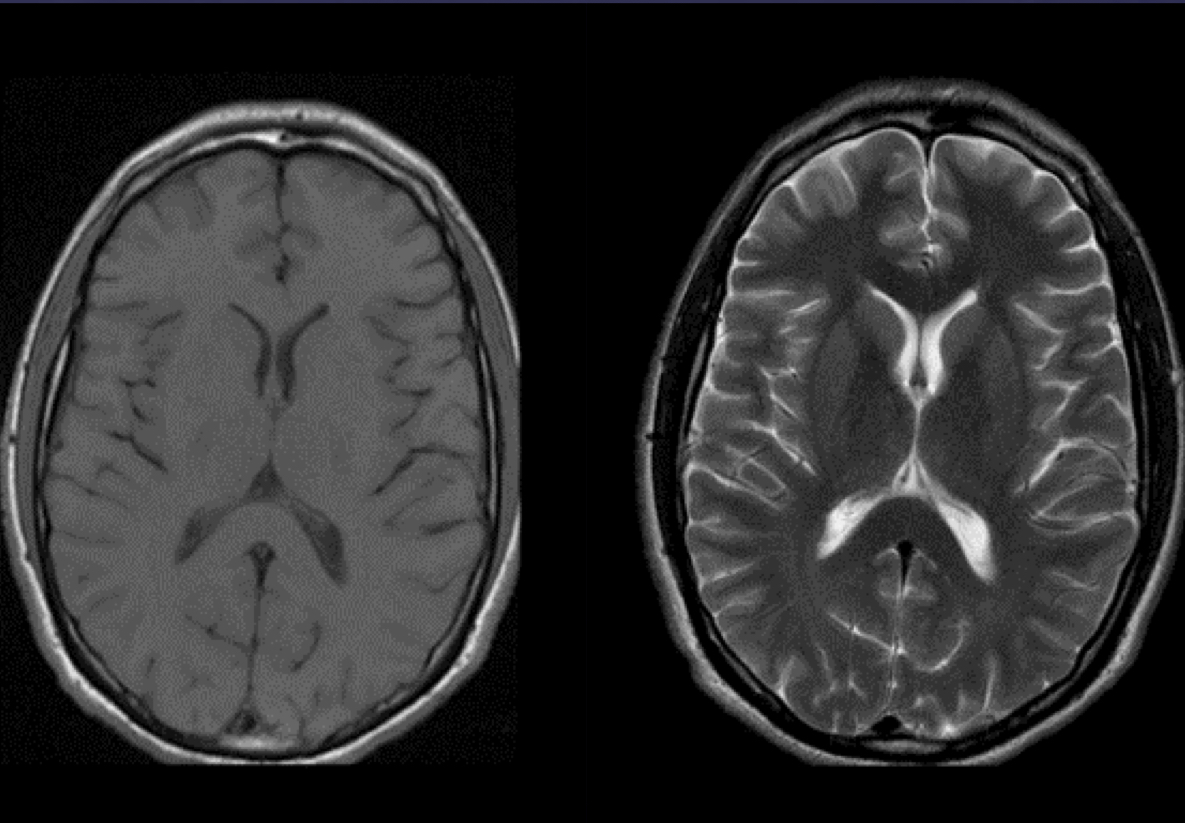
Magnetic resonance imaging
what shape is CT x-ray beam?
fan
which advanced imaging modality is like pre-cut load? which is like loaf uncut?
CT vs CBCT
what is 3D imaging version of the pixel?
voxel, each is only one shade of gray
the CT number is proportional to what?
the degree of attenuation of x-rays caused by the material w/in that voxel
Bone Hounsfield number
+1000
soft tissue Hounsfield number
+40 - +80
water Hounsfield number
0
fat Hounsfield number
-60 to -100
lung Hounsfield number
-400 to -600
air Hounsfield number
-1000
what do Hounsfield numbers/CT numbers depend on?
density of anatomic structure in the image
explain bone window vs soft tissue window
These are two different settings of CT, which is a major part of the scan. For bone window you can see the details of the bone for soft tissue window. You can see the details of soft tissues. This happens because you can change box content and soft tissues, and all Vauxhall within the bone look the same and vice versa The Hounsfield number is the same despite the visual changes.
Which advanced imaging technique has these advantages:
Uniform magnification
Lateral coronal and axial views available
Post acquisition reformatting may provide additional views
CT
Which advanced imaging technique has these disadvantages:
Limited availability
Expensive
Results and relatively high dose of radiation
Radiologist required for acquisition and interpretation/read and evaluate
CT
Which advanced imaging technique has these uses:
Investigation of severe trauma
Evaluation of neoplasia
Assessment of chronic inflammation or infection
used to be standard treatment planning for the edentulous mouth
CT
edentulous
lacking teeth
Definition for which advanced imaging technique: uses x-ray beam that is cone shaped as opposed to fan shaped x-ray be of traditional multi slice CT
CBCT (cone beam computed tomography)
For which advance imaging technique was accessibility addressed in lecture?
CBCT
For which advanced imaging technique is image acquisition:
Rotating platform/gantry is fixed to x-ray source and image detector
Source and detector rotate around a fulcrum fixed within the center of ROI
CBCT
ROI
region of interest
Which advanced imaging technique flow is as follows:
Image acquisition → raw data → image volume
software needed
CBCT
CT or CBCT:
Multiple rotations of the gantry
CT
CT or CBCT:
More dose
CT
CT or CBCT:
Good contrast resolution good soft tissue detail
CT
CT or CBCT:
Little scatter, due to a narrow beam
CT
CT or CBCT:
More expensive
CT
CT or CBCT:
Single rotation of the gantry
CBCT
CT or CBCT:
Less dose
CBCT
CT or CBCT:
Poor contrast resolution, poor soft tissue detail (good bone)
CBCT
CT or CBCT:
More scatter, due to a wide conical beam
CBCT
CT or CBCT:
Less expensive
CBCT
what is spatial resolution dependent on?
primarily voxel size
smaller voxel = higher resolution
what voxel sixes are available for CBCT?
0.076 mm - 0.6 mm
scout view
a low-resolution, preliminary radiographic image taken during a CT or MRI exam to localize the region of interest and guide the acquisition of the detailed, diagnostic images
what are five reconstructed images from CBCT data?
MPR
reconstructed panoramic
cross-sections (PA)
reconstructed lateral ephalometrc radiograph
ray sum
MIP
volume rendering
airway measurement
image fusion
artifacts
metallic beam hardening
pt motion
what are the seven visual techniques that can be used for CBCT?
MPR
linear oblique
cross-sectional
ray sum
volumetric rendering
volume rendering
MIP
Which reconstructed image from CBCT data describes the following:
CBCT produces isotropic voxels directly from the data set
Excellent spatial resolution in all three panels
Are axial, coronal, sagittal
MPR
from which reconstructed image would one create and change focal trough?
reconstructed panoramic
which reconstructed mage would provide info on:
osseous morphology of edentulous site
anatomic quantification
preexisting pathology
bone pattern
cross-sectional images of teeth and periapical areas/edentulous areas
can evaluate quality and size of bone, ideal for implant Tx planning
which reconstruction is ideal for implant Tx planing?
cross-sectional imaging of teeth and periapical areas/edentulous areas
CBCT
reconstructed vs normal lateral cephalometric radiograph
reconstructed: made of ray sum and MIP images
regular: magnification, require ruler in image
ray sum imaging CBCT technique
a post-processing technique where rays are cast through the 3D CT dataset, and the attenuation values along these paths are summed to create a 2D image resembling a digital radiograph
slice of orthogonal/MPR image thickened by increasing the number of adjacent voxels included in the display
MIP CBCT technique
maximum intensity projection
involves projecting the voxel with the highest attenuation value onto every view throughout the volume onto a 2D image
clearer view of dense areas like bone and teeth, making it easier to visualize structures; what’s going on
which visualizing technique:
Achieved by evaluating each voxel value among an imaginary projection ray from observers eyes with a particular volume of interest and representing only the highest value at the display value
voxel intensities that are below an arbitrary threshold our eliminated
MIP
which CBCT reconstruction?
allows visualization of volumetric data by selective display of voxels w/in a data set
volume rendering (remove content = better view)
what are four things you can see through volume rendering CBCT reconstruction?
airway measurement
image fusion
artifacts
pt motion
how many panoramic scans are equal to one CBCT scan?
9.4
large FOV (field of view) avg CBCT effective dose
131
medium FOV (field of view) avg CBCT effective dose
88
small FOV (field of view) avg CBCT effective dose
34
voxel size changes with dose how? low dose mode?
smaller voxel size (better) = higher dose
there is a “low dose mode”
96kV
2.5 mA
4.5
what are the seven relevant CBCT applications?
dental implant planning - cross-sectional imaging
TMJ assessment
evaluation of osseous and dental pathology
endo: root canals
ortho: unerupted tooth position
position of impacted supernumerary teeth - small FOV
locating impacted third molar & proximity to IAN canal (inferior alveolar nerve)
why is buccal lingual thickness important?
dental implants
tooth extraction
endo - max sinus, IAN canal
ortho movement
what are the four anatomic landmarks that need to be avoided/prevent injury of?
Floor of the maxillary sinus
Nasopalatine canal
Inferior alveolar nerve canal
Anterior extension of inferior alveolar canal
accessory neurovascular canals
Mental neurovascular canal and foreman
what are these morphology of?
Knife edge ridges
Submandibular fossa
Developmental variation
Post extraction irregularity
Enlarged marrow spaces
osseous morphology of edentulous spaces
what are some anatomic quentifiaions of CBCT?
Dimensions for implant
Placement: height, width, and edentulous span
Orientation access of viola Ridge height
can site of CBCT have preexisting pathology?
no site should be pathology free
what is the relevant anatomy for area of #13?
L max sinus (floor, buccal cortical plate, crest of ridge)
how does one assess TMJ?
panoramic radiograph and MRI
what are panoramics useful for concerning TMJ?
gross osseous changes of condyles
what are cross-sectional images useful for concernin TMJ?
Allows thorough assessment of TMJs
Articular surface of the condoles
Glenoid fossa
Articular eminence
corticated borders (thinning, missing)
Position of condyles within the fossa
Assess relationship of condo to the Glenoid fossa
measure degen changes
what are MRIs useful for concerning TMJ?
evaluation of soft tissue structures, specifically articular disc which lies between the mandibular condyle and the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
Assessing buccal-lingual expansion caused by the lesion
Association of the lesion and its effect on inferior alveolar canal
osseous eval
what can CBCT detect or endo treatments?
missed canal
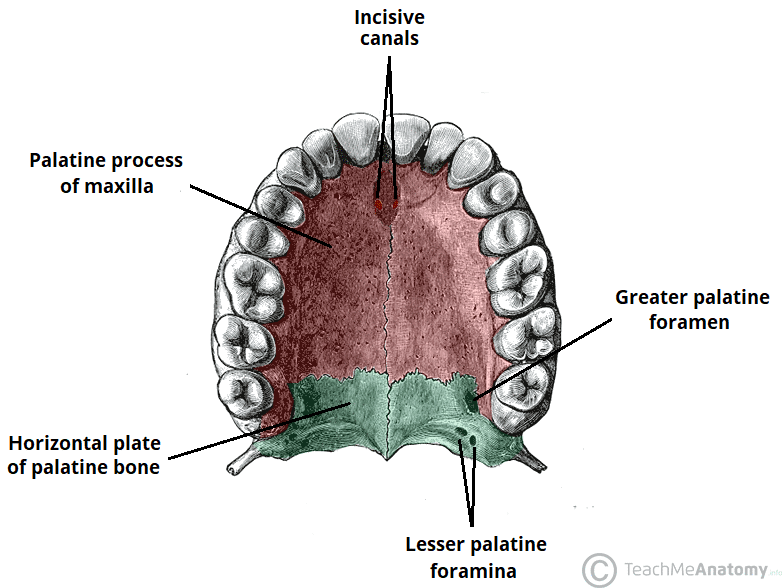
describe location of nasopalatine canal
what is this?
labial undercut
a triangular indentation in the maxilla or tissue in the area of the lip. more common in edentulous (toothless) individuals, can cause problems when a patient receives a complete denture, as it may interfere with the denture's stability, cause tissue trauma, or lead to poor facial aesthetics due to excessive flange thickness.
what are these characteristics of?
These are smooth depressions on the facial surface of the anterior maxilla
Dental implants could perforate through the undercut during placement
labial undercut
what are these characteristics of?
mandibular posterior
dental implants could perforate through the undercut during placement
lingual undercut