Bio 189 Unit 2 Study Guide
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
What is a peptide bond?
A bond that links two amino acids together.
Hydrogen bonds between amine and carboxyl groups form which level of protein structure?
b) Secondary structure
__ proteins aid in correctly folding newly formed proteins.
d) Chaperone
How are glycosidic links made and broken?
A dehydration reaction builds glycosidic links. Hydrolysis breaks them apart.
What type of polysaccharide are each of these?
Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
What type of bond links fatty acids to glycerol?
Ester linkage
What type of fatty acid is each of these?
Saturated, Unsaturated, Polyunsaturated
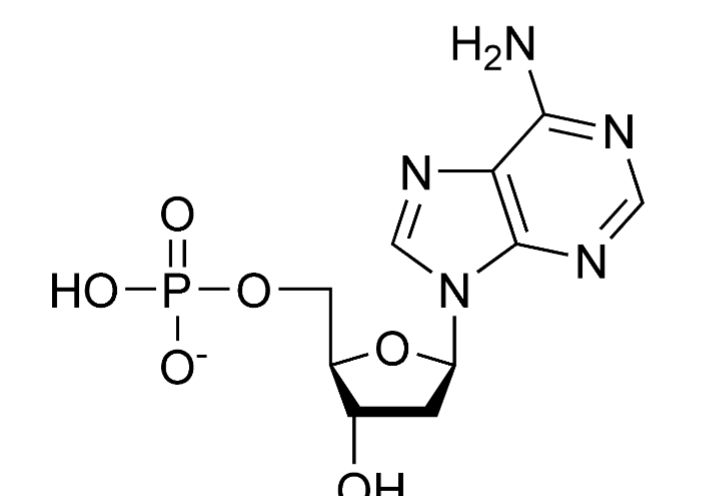
What monomer is this?
Nucleotide. Could be a purine or a pyrimidine. Sections: sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. Forms nucleic acids (DNA or RNA). Linked by phosphodiester bonds. Roles: genetic information, energy transfer. Next monomer joins at the 3' carbon. Adenine complements with Thymine (DNA) or Uracil (RNA).
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA contains deoxyribose, RNA contains ribose. DNA uses thymine, RNA uses uracil. DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded.
What is the complementary DNA sequence of 5’ – ACCGGT – 3’? Where in the cell would DNA be transcribed into RNA? Where in the cell would RNA be translated into a protein?
5' - ACCGGT - 3' -> 3' - TGGCCA - 5'. RNA sequence: 5' - AUG GCA - 3'. DNA is transcribed into RNA in the nucleus. RNA is translated into protein in the ribosomes.
What is the difference between bound and free ribosomes?
Bound ribosomes produce proteins for export or in lysosomes. Free ribosomes produce proteins for use within the cell.
What are three differences between a plant cell and an animal cell?
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and central vacuoles. Animal cells have centrioles and lysosomes.
Which of these is true regarding chromatin?
e) Chromatin is made of nucleic acids and amino acids
What is chromatin?
Combination of DNA and the proteins that bind to it (histones)
What are the main functions of the cytoskeleton?
Supports the cell and maintains shape, controls position and movement of organelles, helps anchor the cell and/or organelles in place
What are the three components of the cytoskeleton?
Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments, Microtubules
What system allows our cells to ensure vesicles make it to where they need to go?
The vesicle transport system. Motor proteins. The centrosome.
What connects collagen to the cell?
Integrins
What holds animal cells together?
Integrins, fibronectin, proteoglycans, collagen
Do all cells respond to all signals? What ensures the signal is reached only by the correct cell type?
Not all cells respond to all signals. Specific receptors ensure the signal is reached only by the correct cell type.
What is the step-by-step process in cells for using signal from their environment?
The cell must have a specific receptor that can detect the signal. If the cell has the receptor, the signal transduction pathway is activated, consisting of a signal, receptor and response.
What type of cell signaling is involved in the nervous system?
The nervous system uses synaptic signaling. Mitosis uses paracrine signaling. Cancer cells also use paracrine signaling. The endocrine system uses hormones.
What are the steps of the signal transduction pathway?
Reception, Transduction, Amplification, Response
What are the different types of receptors a signal can bind to?
G protein-coupled receptors and Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
What can receptor tyrosine kinases do that G-protein coupled receptors can't do?
Receptor tyrosine kinases can phosphorylate tyrosine residues and activate multiple relay proteins simultaneously.
What type of cell death happens when a cell begins swelling and eventually ruptures?
Necrosis
What is programmed cell death?
Apoptosis
What are some end results of a signal transduction pathway?
Alter gene expression, regulate enzymes, growth (mitosis), immune response, nerves
What are the 4 polymers (macromolecules) that all living things require?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
What are the building blocks that make up those polymers?
Monomers
What are the biological roles of carbohydrates?
Energy storage, structural components, cell signaling
Carbohydrates are composed of what 3 atoms mainly?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What is a simple sugar called?
Monosaccharide
What are the monomers (building blocks) of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
If a simple sugar contains 2 carbons, what is it called?
Dioses
If a simple sugar contains 3 carbons, what is it called?
Trioses
What is a Golgi Apparatus’ function?
Receive, sorts and packages proteins for transport out of the cell
If a simple sugar contains 4 carbons, what is it called?
Tetroses
If a simple sugar contains 5 carbons, what is it called?
Pentoses
If a simple sugar contains 6 carbons, what is it called?
Hexoses
If a simple sugar contains 7 carbons, what is it called?
Heptoses
What are some examples of simple sugars?
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
If 2 simple sugars link together, what is it called?
Disaccharide
What reaction linked two simple sugars together?
Dehydration reaction or condensation reaction
What is the linkage called when two simple sugars are linked together?
Glycosidic linkage
What is it called when a few simple sugars are linked together?
Oligosaccharide
What is it called when many simple sugars are linked together?
Polysaccharide
Give 3 examples of polysaccharides and where they occur?
Starch in plants, Glycogen in animals, Cellulose in plant cell walls
Can we digest cellulose? Why or why not?
No, because we lack the enzyme to break the Beta-1,4-glycosidic linkage
What is the functional role of Glycogen?
Energy storage in animals
What is the functional role of Starch?
Energy storage in plants
What is the functional role of Cellulose?
Structural component of plant cell walls
What is the functional role of Chitin?
Structural component in exoskeletons and fungi cell walls
What is the functional role of Peptidoglycan?
Structural support in bacterial cell walls
How would you recognize the structure of a carbohydrate?
Presence of C, H, O in a 1:2:1 ratio, ring structure
What are the types of lipids?
Fats, Phospholipids, Steroids
What elements are fats mainly composed of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What are the monomers (building blocks) of triglycerides and phospholipids?
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
Describe the chemical structure of an unsaturated fatty acid.
Contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds
What is an unsaturated fatty acid commonly called?
Oil
Where is an unsaturated fatty acid mainly found?
Plants and fish
Give an example of something you eat that contains unsaturated fatty acids.
Olive oil
Describe the chemical structure of a saturated fatty acid.
Contains no carbon-carbon double bonds
What is a saturated fatty acid commonly called?
Fat
Where is a saturated fatty acid mainly found?
Animals
Give an example of something you eat that contains saturated fatty acids.
Butter, lard
What is a simple fat called?
Triglyceride or Triacylglycerol
What are the molecules that compose a simple fat? How many of each?
One glycerol and three fatty acids
What are the main functions of lipids?
Energy storage, insulation, protection
What bond/interaction links simple fats together?
Ester linkage
What is the biological role of a simple fat?
Energy storage
Define amphipathic
Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Define phospholipids
A lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group
Define bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids arranged tail-to-tail
What are the 4 parts of a phospholipid?
Glycerol, two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a polar head group
Which parts of a phospholipid are hydrophobic? Hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic: Fatty acid tails; Hydrophilic: Phosphate group and polar head
What are the biological roles of phospholipids?
Main component of cell membranes (lipid bilayers)
What are the parts of a steroid?
Four fused carbon rings
Why is a simple fat hydrophobic?
Mostly composed of nonpolar C-H bonds
What are the biological roles of proteins?
Enzymes, structural components, transport, defense, movement, cell signaling
Or enzymes, defensive, hormonal/regulatory, receptors, storage, structure, transport, and movement
What are the monomers (building blocks) of proteins?
Amino acids
What parts of amino acid monomers are the same?
Amino group, carboxyl group, and a central carbon
What part of amino acid monomers is different?
The R group
How many amino acids are needed in the human body?
20
What are the properties of the three groups of amino acids?
Nonpolar, polar and charged (acidic and basic)
How many amino acids are in each group?
Nonpolar (9), Polar (6), Charged (5)
Describe an oligopeptide
A short chain of amino acids
What are the biological roles of steroids?
Cell signaling (hormones)
Describe protein primary structure. Part? Bond? Shape?
Sequence of amino acids; Amino acids; Peptide bond; Linear chain
Describe protein secondary structure. Part? Bond? Shape?
Folding of the backbone; Backbone; Hydrogen bonds; Alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet
Describe protein tertiary structure. Part? Bond? Shape?
3D folding of a single polypeptide chain; R-groups; Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges; 3D shape
Describe protein quaternary structure. Part? Bond? Shape?
Association of two or more polypeptide chains; Polypeptide chains; Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges; Multi-subunit protein
What conditions can affect protein structure?
Temperature, pH, salt concentration
Describe a polypeptide
A long chain of amino acids
Define denaturation
Loss of a protein's native structure
What are the biological roles of nucleic acids?
Information storage and transfer, enzymatic roles
What are the two nucleic acids in the human body?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
What is each nucleic acid's biological role?
Storage of genetic information, transmission of genetic info, and use of genetic info
What are the monomers (building blocks) of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides