Condensation and Conjugate Addition Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is an aldol?
A structure that contains both a hydroxyl group and a double bonded oxygen.
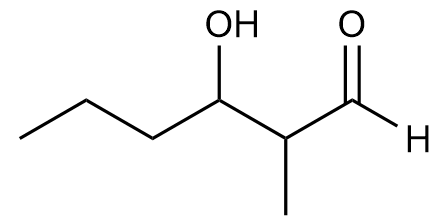
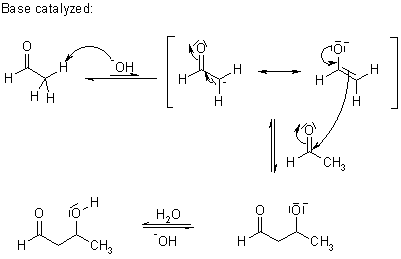
What mechanism is depicted?
An aldol addition reaction.
True or False: Aldol addition reactions are reversible?
True.
An aldol addition reaction can be reversed through a process known as a retro-aldol reaction, in which the OH of an aldol is deprotonated, and the intermediate alkoxide ejects the enolate. Reprotonation results in two molecules of the starting aldehyde or ketone.
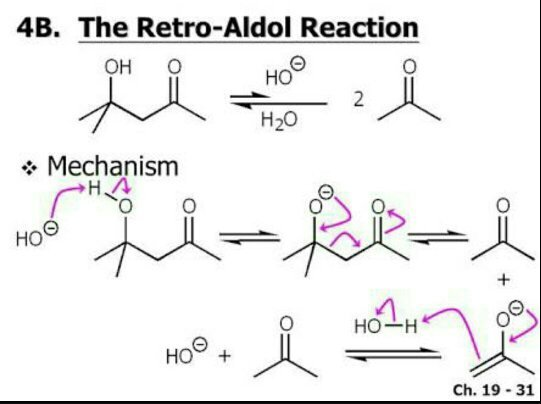
What is an aldol condensation reaction?
When an aldol addition product undergoes more forceful conditions (the addition of heat) to force the formation of an enone (a structure containing a double bonded oxygen near to an alkene double bond).
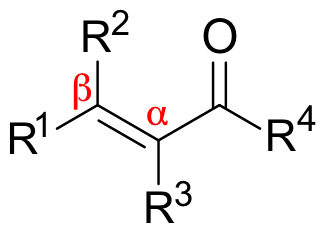
What molecule acts as a leaving group in an aldol condensation reaction? Explain why.
OH-. While it is typically considered a poor leaving group, the formation of a stable conjugated system, as well as the elimination of water, allows the overall reaction to occur.
What reactant(s) can convert an aldehyde to a primary alcohol?
NaBH4 or LiAlH4.
What reactants are necessary for the conversion of an alkene to an alkane?
1.) H2, Pd
True or False: Aldol condensation reactions can only be performed under basic conditions.
False.
An aldol condensation reaction can be performed under acidic or basic conditions. Under acidic conditions, the reaction involves the formation of an enol to act as a nucleophile and a protonated aldehyde or ketone acts as the electrophile, with water being eliminated from the structure.
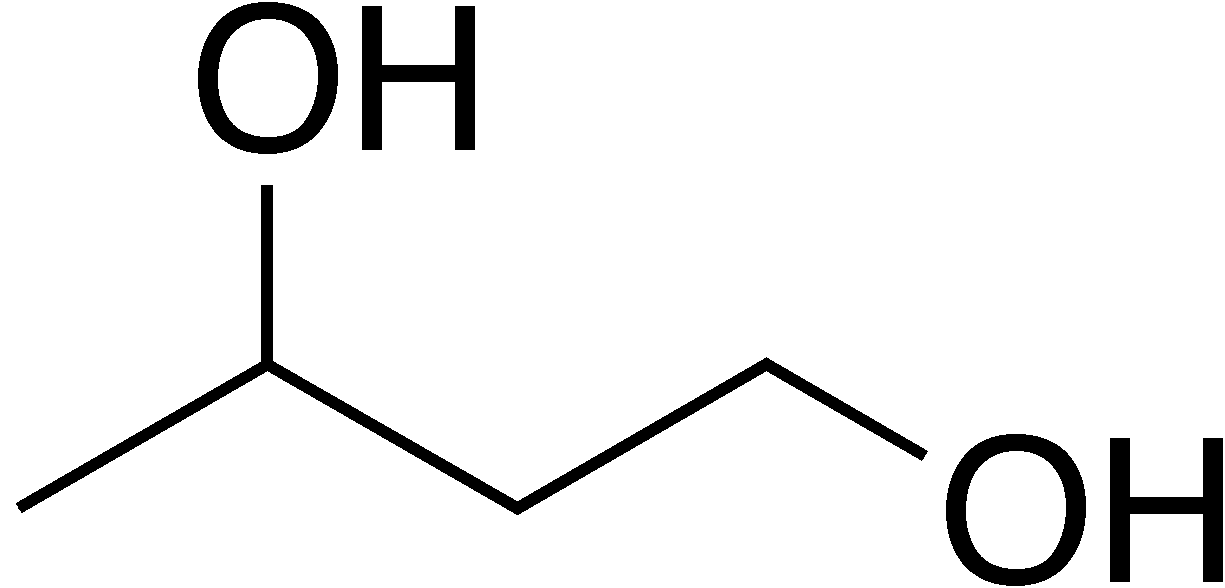
How can this structure be formed from an aldol?
Through the addition of the reducing agent LiAlH4 or NaBH4.
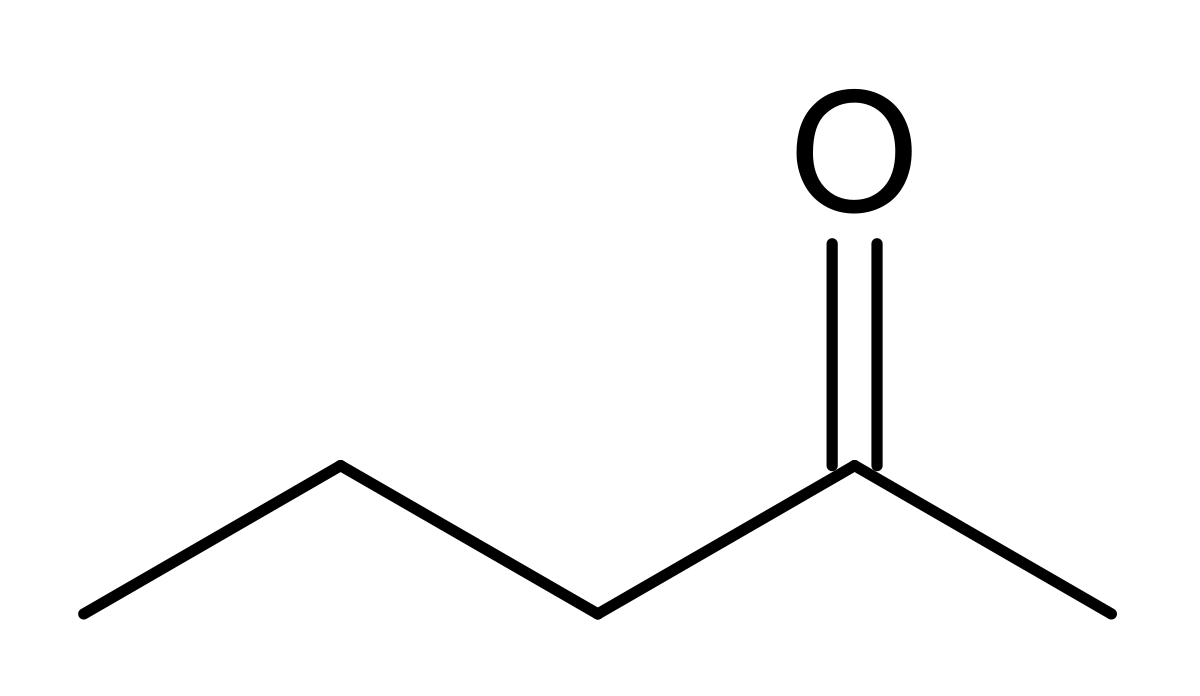
How can this structure be formed from an aldol condensation product?
Through the addition of Pd/C and H2, in order to hydrogenate the double bond present in an aldol condensation product?
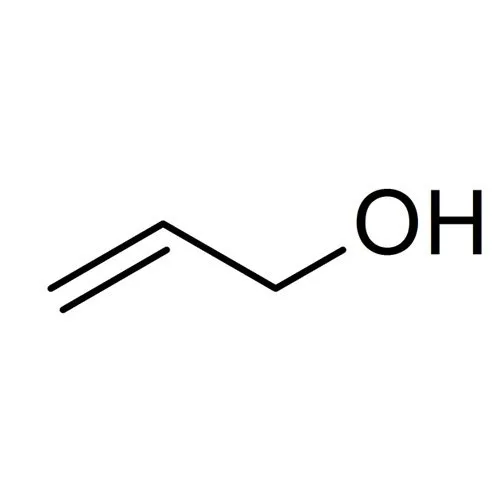
How can this structure be formed from an aldol condensation product?
Through the addition of a reducing agent, such as LiAlH4, to reduce the double bonded oxygen to an alcohol.
What is a crossed aldol reaction?
A reaction in which two different carbonyl compounds react together, with one acting as a nucleophile and the other acting as an electrophile, to form an aldol product.
What are the preferred reactants to use in a crossed aldol reaction?
An aldehyde that is unable to form an enolate, such as formaldehyde, trimethylacetaldehyde, or benzaldehyde.
Why is it difficult to prevent the aldol product of benzaldehyde from continuing on to the aldol condensation product?
Because the product is highly conjugated, and thus favored.
Can a strong base be used to perform a crossed aldol reaction?
Yes. The resulting enolate forms without any equilibration to other enolates.
Why are ketones more commonly used as enolates rather than aldehydes?
Because when aldehydes are subject to deprotonation at the alpha carbon, they are likely to attack any aldehyde remaining in solution, leading to a mixture of products.
What is a Claisen Condensation?
A reaction in which two molecules of an ester react to form a beta-keto ester.
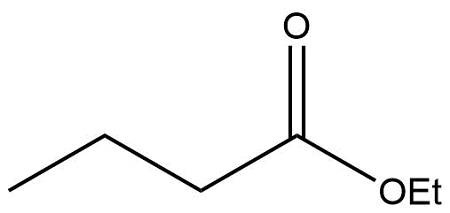
What are the reactants necessary for a Claisen Condensation to take place? Explain the reasoning behind them.
1.) An alkoxide (that must be matched to the ester)
2.) H3O+
The alkoxide deprotonates the alpha carbon to form an enolate, and the H3O+ is applied as a second step to protonate the intermediate product.
What conditions are necessary for a Crossed Claisen reaction to take place?
One of the two reacting esters must not be able to form an enolate (essentially lacking an alpha carbon).
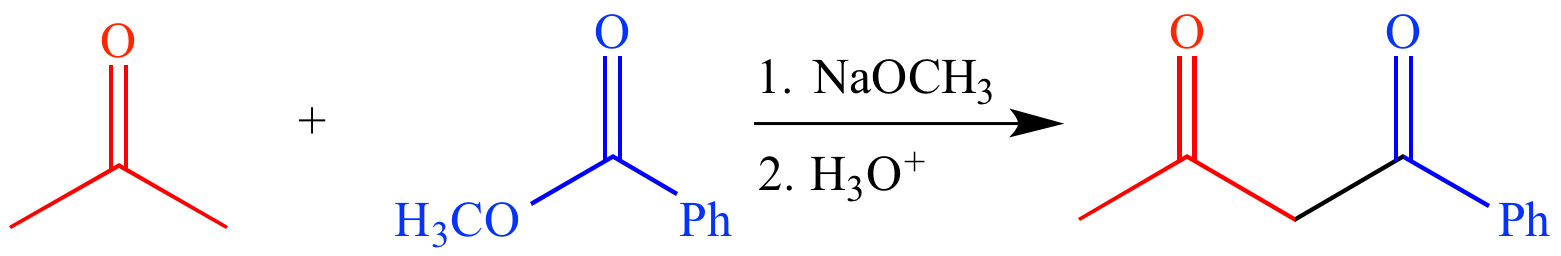
Is this a viable reaction?
Yes. It is a Claisen Condensation reaction. While these reactions typically take place between two esters, it is possible to have a reaction take place between a ketone (which forms an enol) and an ester (which is unable to form an enol).
What is the condensation product in a Claisen Condensation?
It consists of whatever carbon-based group was eliminated from one of the esters, as well as a hydroxide (for example, EtOH).
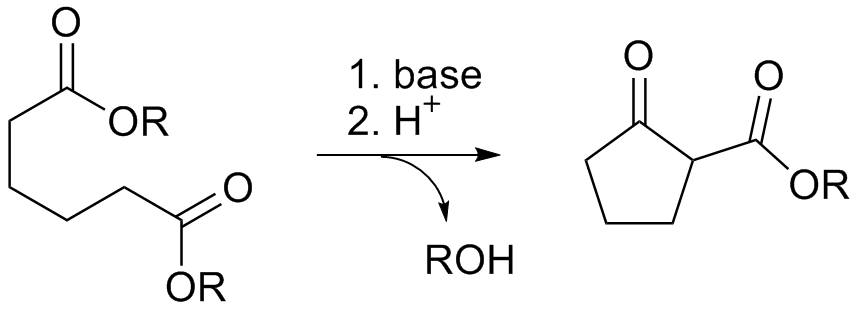
What reaction is depicted?
The Dieckmann Condensation, in which an intramolecular Claisen Condensation takes place.
True or False: Every step in a Claisen or Dieckmann Condensation is reversible.
True.
All steps in a Claisen or Dieckmann Condensation reaction are potentially reversible, with product accumulating in situations where deprotonation to form a stable anion is possible.
Is the beta carbon electrophilic or nucleophilic?
It is electrophilic, due to the positive charge placed on it in one of the resonance structures of a saturated aldehyde or ketone.
What is conjugate addition?
The addition of a nucleophilic group at the beta carbon.
True or False: When reacting with a Grignard reagent, an unsaturated aldehyde or ketone will only produce the carbonyl addition product.
False.
The Grignard reagent will result in a mixture of products, with the majority resulting from carbonyl addition, but a small portion resulting from conjugate addition.
What is a Michael Addition?
A type of conjugate addition in which enolates or enamines are used as the nucleophiles.
What is a Robinson Annulation?
A reaction in which an initial Michael Addition is then followed by an intramolecular aldol conjugation, leading to the formation of a cyclohexanone ring, typically fused to another six-membered ring.
What reactants are necessary for a Mannich Reaction?
A ketone, a secondary amine, and an aldehyde.
What type of products are formed in a Mannich Reaction?
Beta-aminoketones.