WGU C949 Data Structures and Algorithms
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
A functions whose cost scales linearly with the size of the input
O(n)
Iterating over a collection of data once often indicates an ______ algorithm. (alphabet for-loop example)
O(n)
A functions whose cost scales logarithmically with the input size
O(log n)
Which type of function works by breaking down large problem into smaller and smaller chunks?
O(log n)
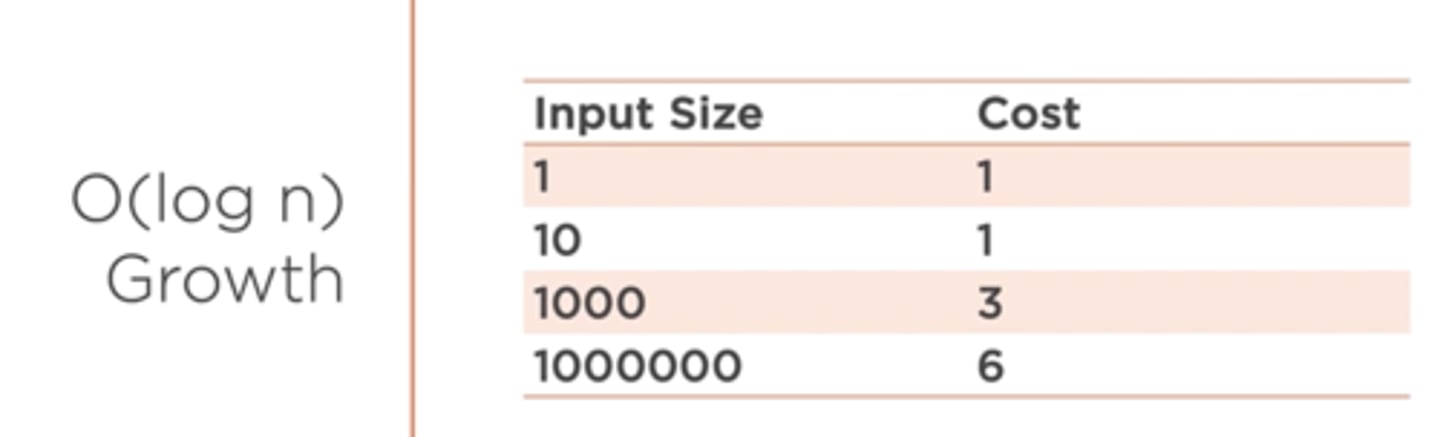
As the size of the input grows the cost of the algorithm does not increase at the same rate. The overall cost of performing an operation on 1,000,000 items is only twice that of performing the operation on 1,000 items.
O(log n)
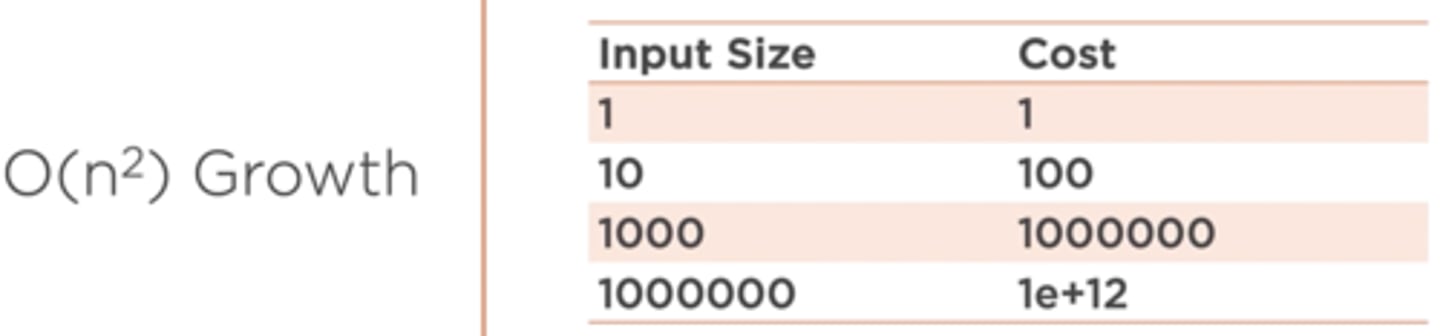
A function that exhibits quadratic growth relative to the input size
O(n^2)
An example of this type of function is doubly nested loop
O(n^2)
Which type of function gets really expensive really quickly?
O(n^2)
A function that has two inputs that contribute to growth
O(nm)
An example of this type of function is when there is a nested loop that iterates of two distinct collections of data
O(nm)
Are Big-O cases used in the best or worst situations?
Worst
Which statement is static?
readonly Contact[] contacts = new Contact[];
readonly Contact contacts = new Contacts[100];
readonly Contact contacts = new Contacts[100];
A container where data is stored in nodes consisting of a single data item and a reference to the next node
Linked List
A ______ is a container where nodes of data are linked together into a list
Linked List
Linking together complex nodes into a single structure
Linked List
Each link in a chain for a linked lists is called a ______
node
What two things do nodes contain?
1. the value
2. reference to next item in the list
Give a coded example on how to create a 3 chained linked list of nodes.
Node head = new Node(1);
head.Next = new Node(2);
head.Next.Next = new Node(3);
A list where we start at the first node and follow the chain of nodes iterating over each until we get to the end
Singly Linked List
A list that builds on the singly linked list by adding reverse iteration.
Doubly Linked List
Give a coded example on how to create a doubly linked list
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(2);
Node node3 = new Node(3);
node1.Next = node2;
node2.Previous = node1;
node2.Next = node3;
node3.Previous = node2;
The first and last nodes of a doubly linked list should have a value of ______
null
Adds a value to the beginning of the list
AddHead
Adds a value at the end of the linked list
AddTail
Finds the first node whose value equals the provided argument
Find
Returns true if the specified value exists in the list, false otherwise
Contains
Removes the first node on the list whose value is equal to the argument
Remove
A doubly linked list where the values are inserted and sorted in order
Sorted List
Adds the specified item to the linked list in the sort order of the item type
Add
A way of organizing, storing, and performing operations on data
Data Structure
A data structure that stores subitems, with a name associated with each subitem.
record
A data structure that stores an ordered list of items, with each item is directly accessible by a positional index.
Array
A data structure that stores ordered list of items in nodes, where each node stores data and has a pointer to the next node.
linked list
A data structure in which each node stores data and has up to two children, known as a left child and a right child.
binary tree
A data structure that stores unordered items by mapping (or hashing) each item to a location in an array.
hash table
A tree that maintains the simple property that a node's key is greater than or equal to the node's childrens' keys.
max heap
A tree that maintains the simple property that a node's key is less than or equal to the node's childrens' keys.
min heap
A data structure for representing connections among items, and consists of vertices connected by edges.
graph
This represents an item in a graph.
vertex
This represents a connection between two vertices in a graph.
edge
A Last-in, First-out (LIFO) data container
Stack
When something is retrieved from a stack, does it come from the top or bottom of the stack?
Top
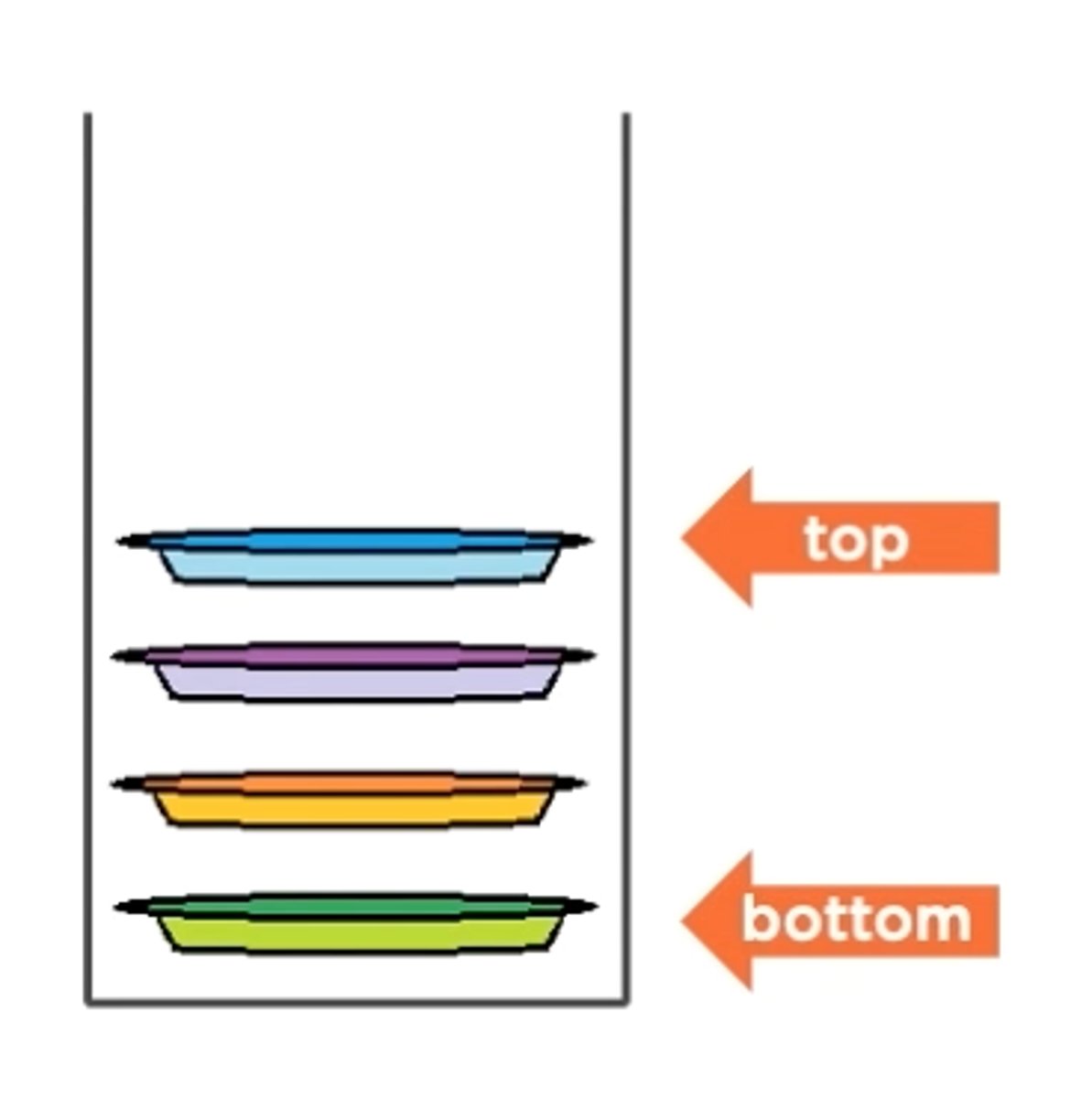
A First-in, First-out (FIFO) container
Queue
When something is removed from a queue, does it come from the head or the tail?
Head
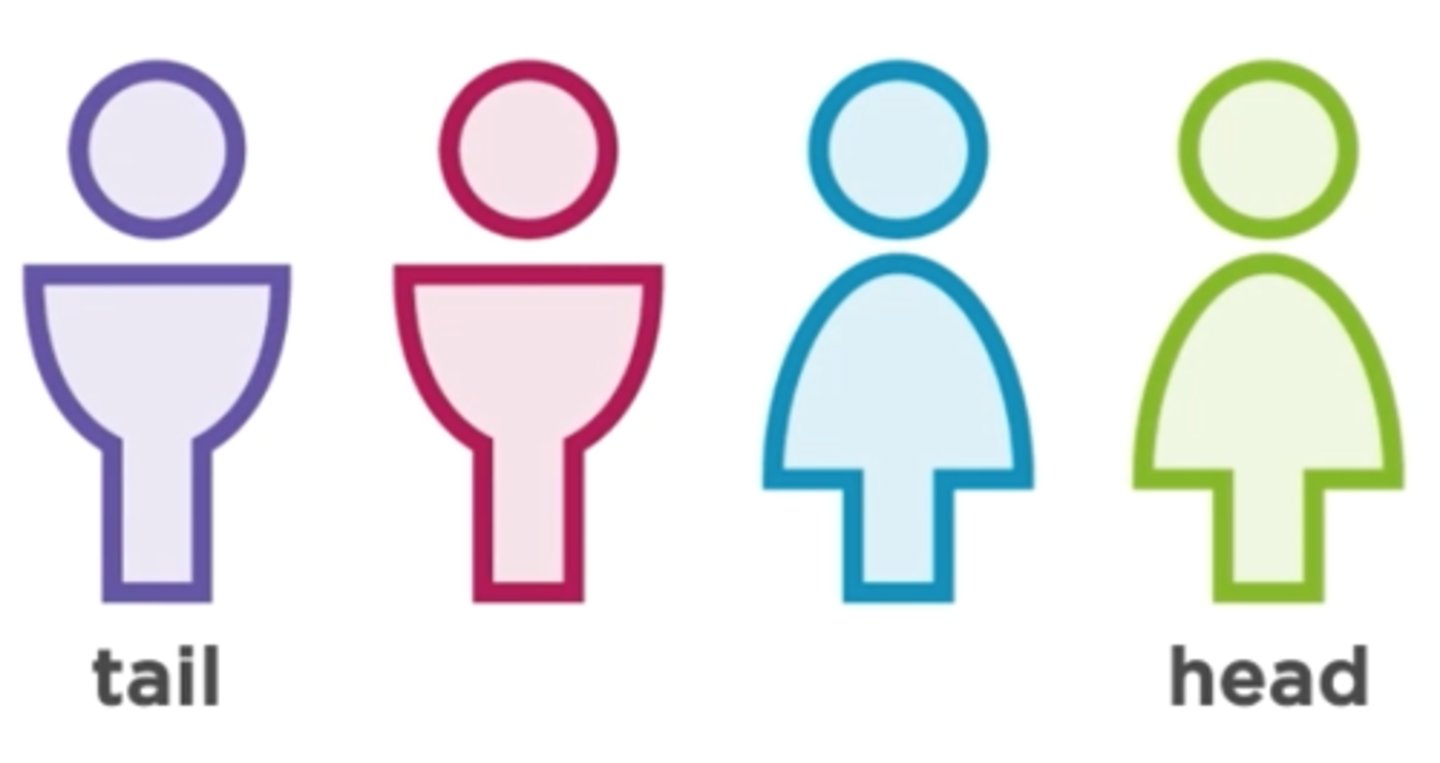

When something is added to a queue, does it get added to the head or the tail?
Tail
A queue-like container which is both First-in, First-out and Last-in, Last-out
Doubly Ended Queue (deque)
Which type of function allows for items to be added or removed from the beginning or end?
Doubly Ended Queue (deque)
A data structure where nodes have parent-child (1:N) relationship
Tree
Each node in a Tree has at least ______ parent, but the number of children depends on the type of tree
one
Every node in a tree has how many parents?
one
Every part of a tree spawns how many children?
0 or more
Nodes that have no children are called what?
Leaf nodes
How many data items does each node on a tree contain?
one
At most how many children can each node have in a binary tree?
two
The maximum number of children that each node can have
Degree
The maximum amount of edges between that node and a leaf
Height
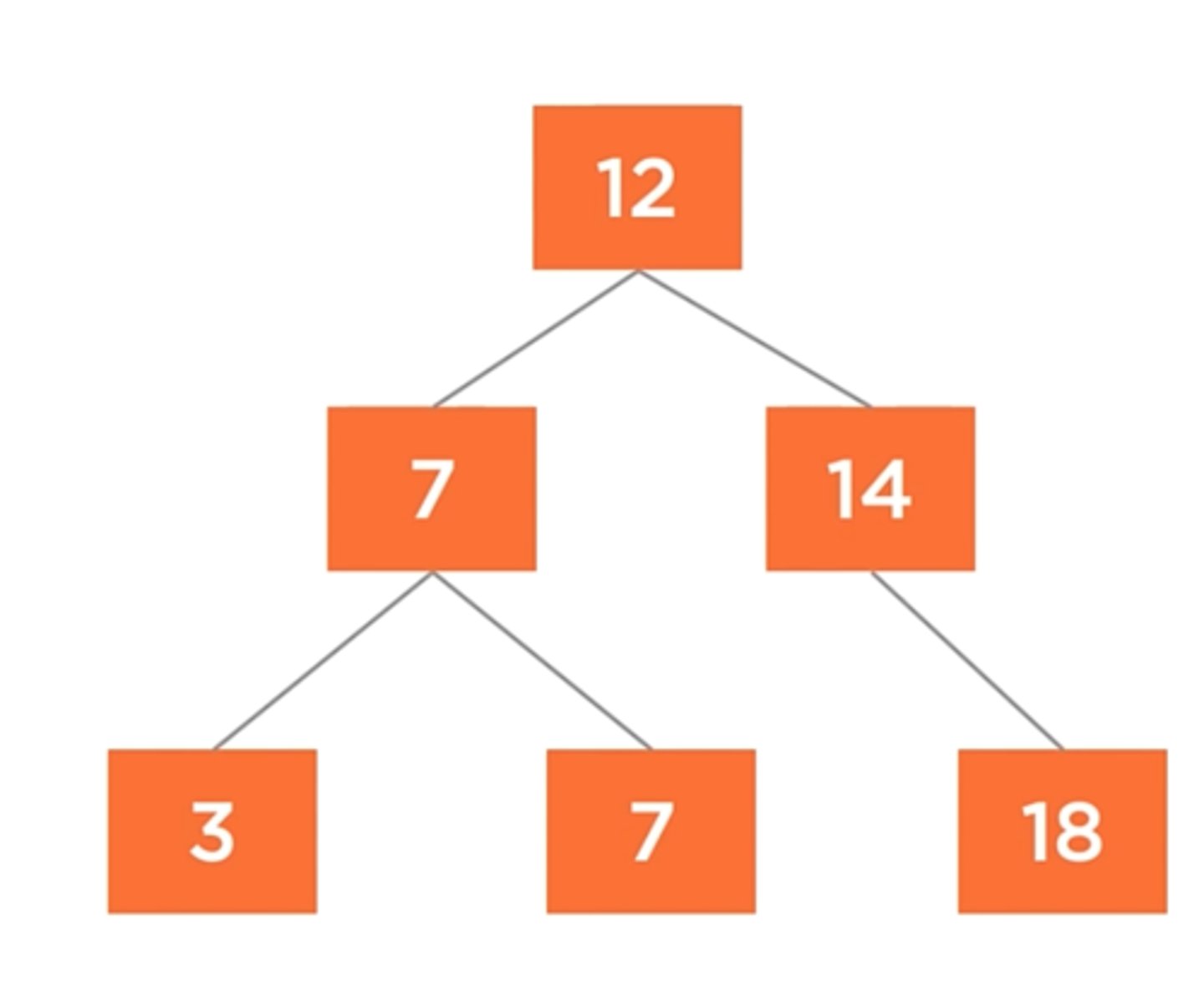
When smaller values are added to this tree smaller values are added to the left
Binary Search Tree
The smallest value in a binary search tree will be on the bottom most ______, while the largest value will be on the bottom most ______
left
right
The insertion complexity on average of a binary search tree
O(log n)
The insertion complexity with the worst case of a binary search tree
O(n)
The node is visited before it's children
Pre-order
The left child is visited before the node, then the right child
In-order
The left and right children are visited before the node
Post-order
An example of why pre-order traversals are useful
To create an identical copy of a tree
What are in-order traversals useful for?
Sorting trees from least to greatest
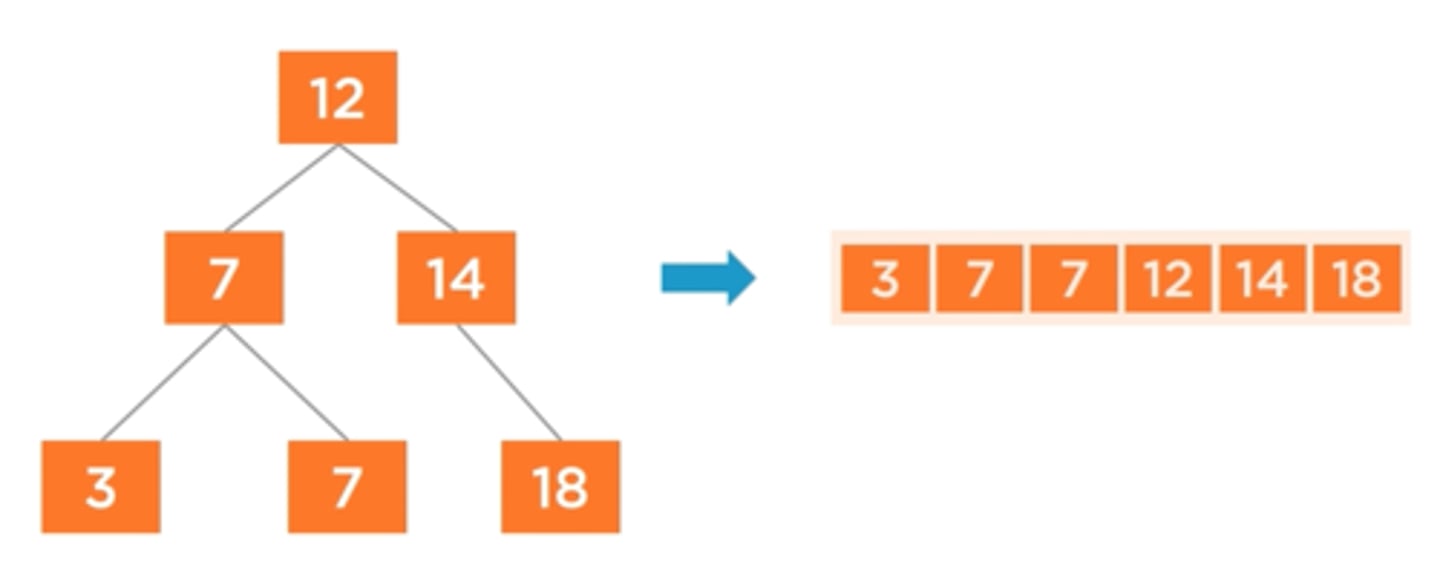
What are post-order traversals useful for?
To delete every node in a tree
The average case, best case and worst case for Traversal Complexity
O(n)
Searching in Binary Search Tree
O(log n)
How can a leaf node be removed from a tree?
Unlinking the node
How can a node with One Child be removed from a tree?
Promote the child
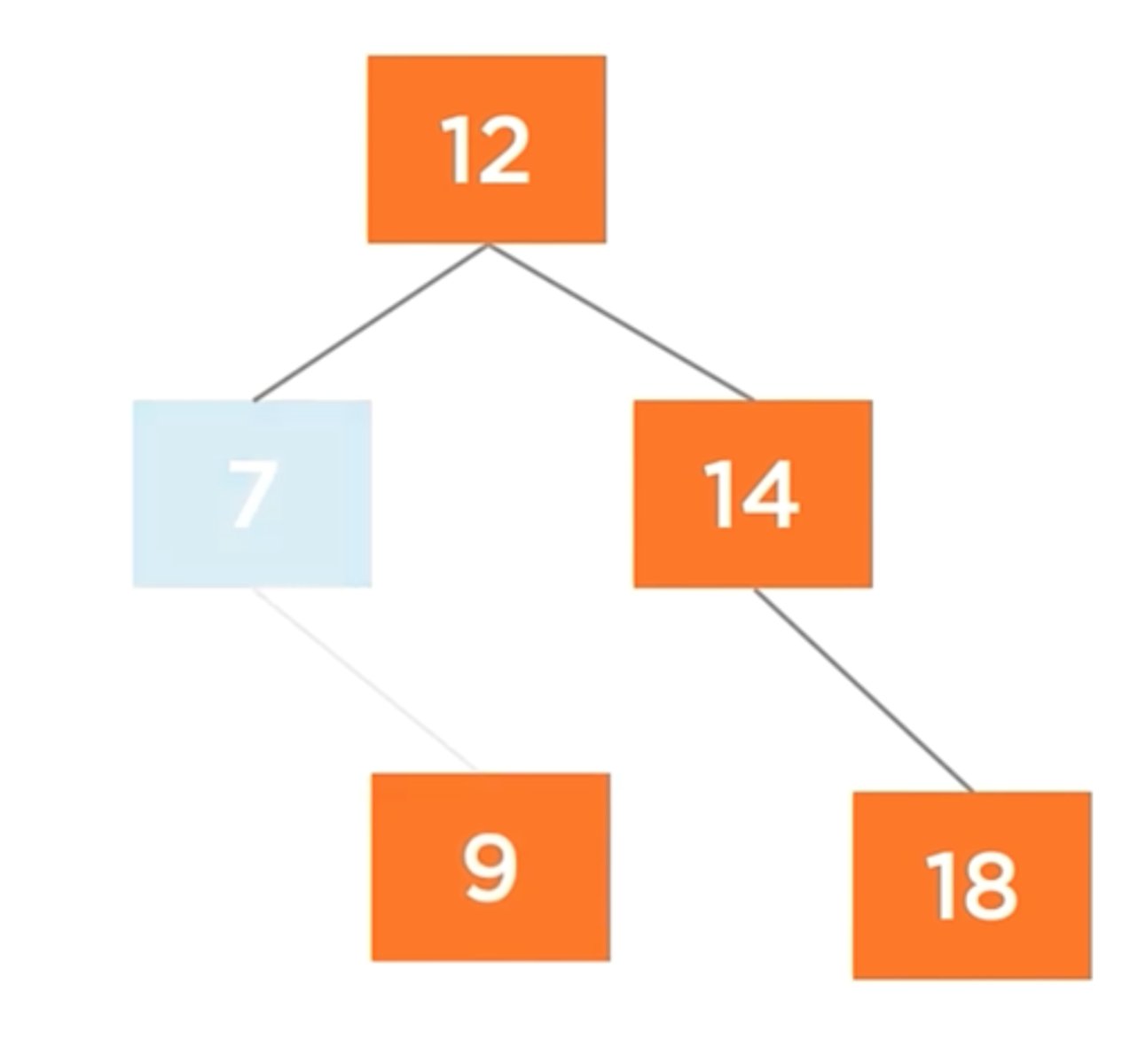
How can a node with Two Children be removed from a tree?
Move the successor's child up to the root node.
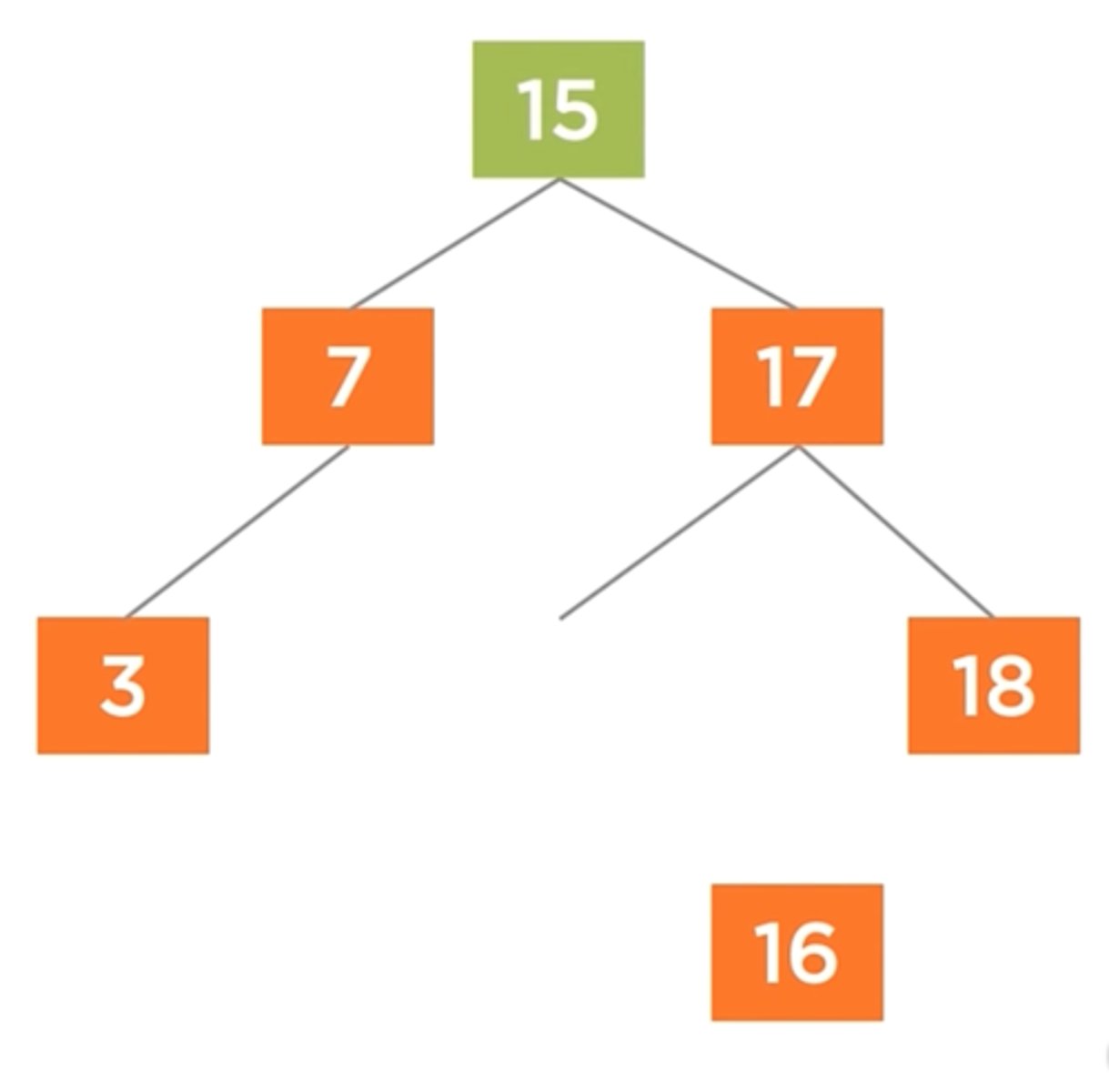
Removal Complexity in a Binary Tree
O(log n)
Containers that contain key-value pairs
Associative Array
A collection of key/value pairs where the key can only exist once in the collection
Associative Array
An associative array container that provides O(1) insert, delete and search operations
Hash Table
A function that maps data of arbitrary size to data of a fixed size
Hash Function
For a function to qualify as a hash function it has to have what three properties
Stability
Uniformity
Security
A hash function always generates the same output given the same input
Stability
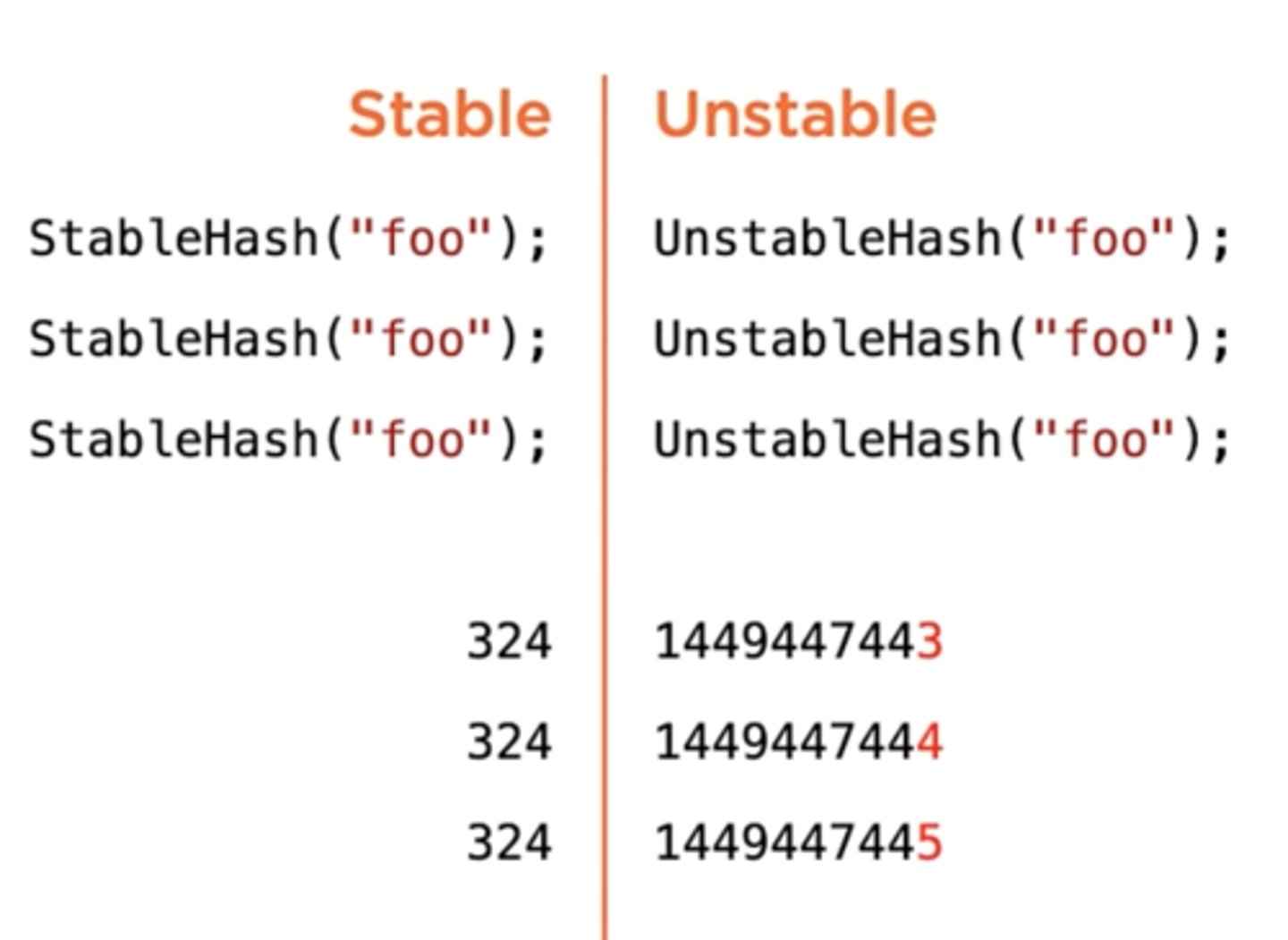
A hash algorithm should distribute its resulting has value uniformly throughout the output space
Uniformity
A secure hashing algorithm cannot be inverted (the input derived from the output hash)
Security
An integer counter that represents how many variables reference an object
Reference Count
Equation for finding the middle value of an array
(high + low)/2
(DO NOT ROUND UP)
If an object is assigned to null (int = null;), will the object be considered for garbage collection?
Yes (it's considered for garbage collection right once it's assigned to null)
These can have any value, but cannot have matching keys
Dictionaries
Dictionary keys must be _____ and ______
unique
immutable
What method removes a value from a dictionary?
remove();
Which method removes a key from a dictionary?
pop();
Which method removes a key-value pair from a dictionary?
popitem();
Which method removes all keys from a dictionary?
keys();
There are 3 items in a stack, the next line of code is "push('item');". How many items are now in the stack?
4
1. Visit node
2. Traverse left
3. Traverse right
Preorder Traversal (Binary Tree)
Cannot handle sets, lists or dictionaries
Hash Function
A modulo hash function is used to map to indices 0 to 9. The hash function should be: key % _____
10
key % 1000 maps to indices 0 to ____.
999
A modulo hash function for a 50 entry hash table is: key % _____
50
A hash function computes a bucket index from an item's _____.
key
A 100 element hash table has 100 _____.
buckets
For a well-designed hash table, searching requires _____ on average.
O(1)
In a Hash Table keys need to be ______.
unique
Given a hash table with 100 buckets and modulo hash function, in which bucket will HashInsert(table, item 334) insert item 334?
34