Week 1 forces and scientific notation
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
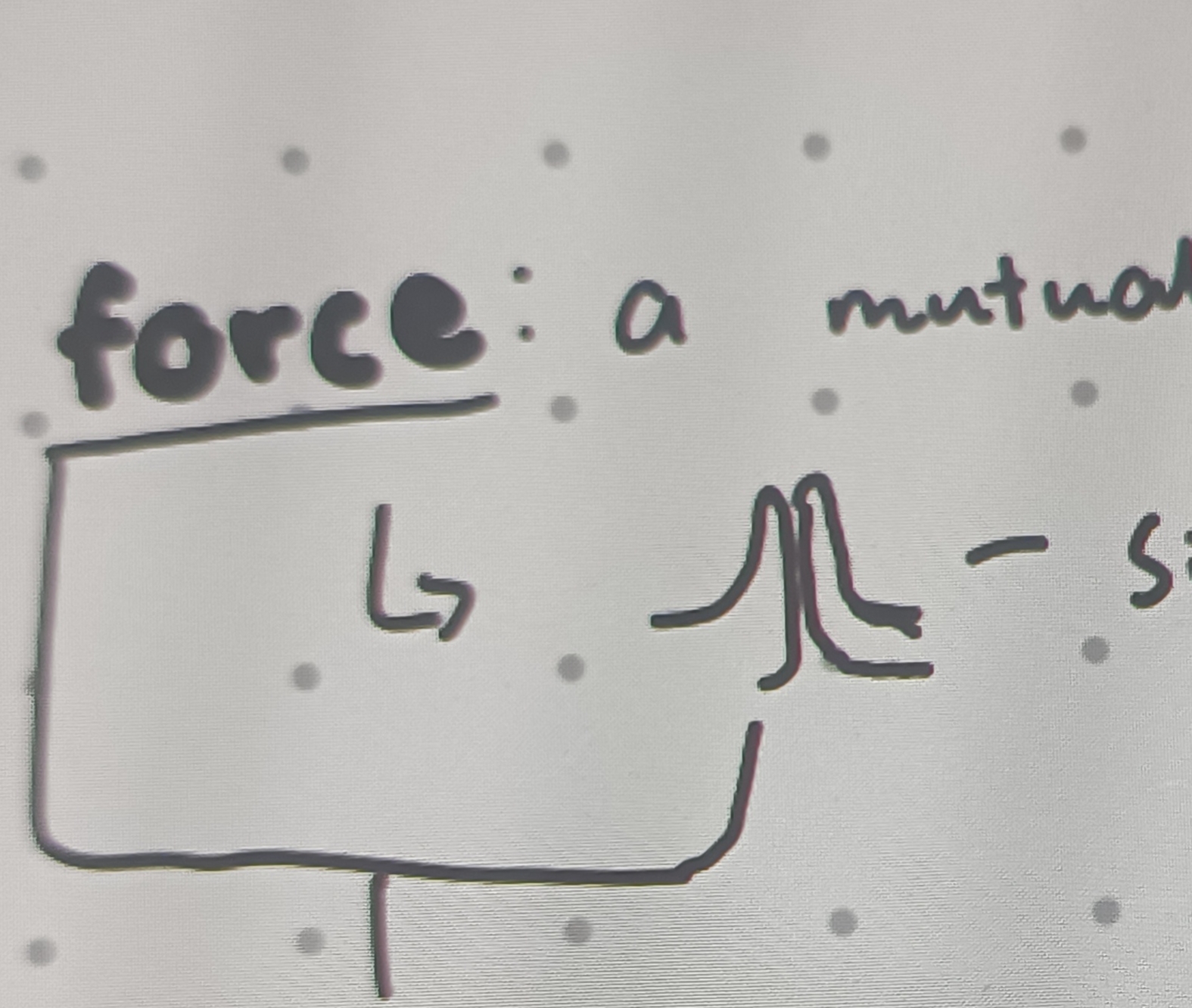
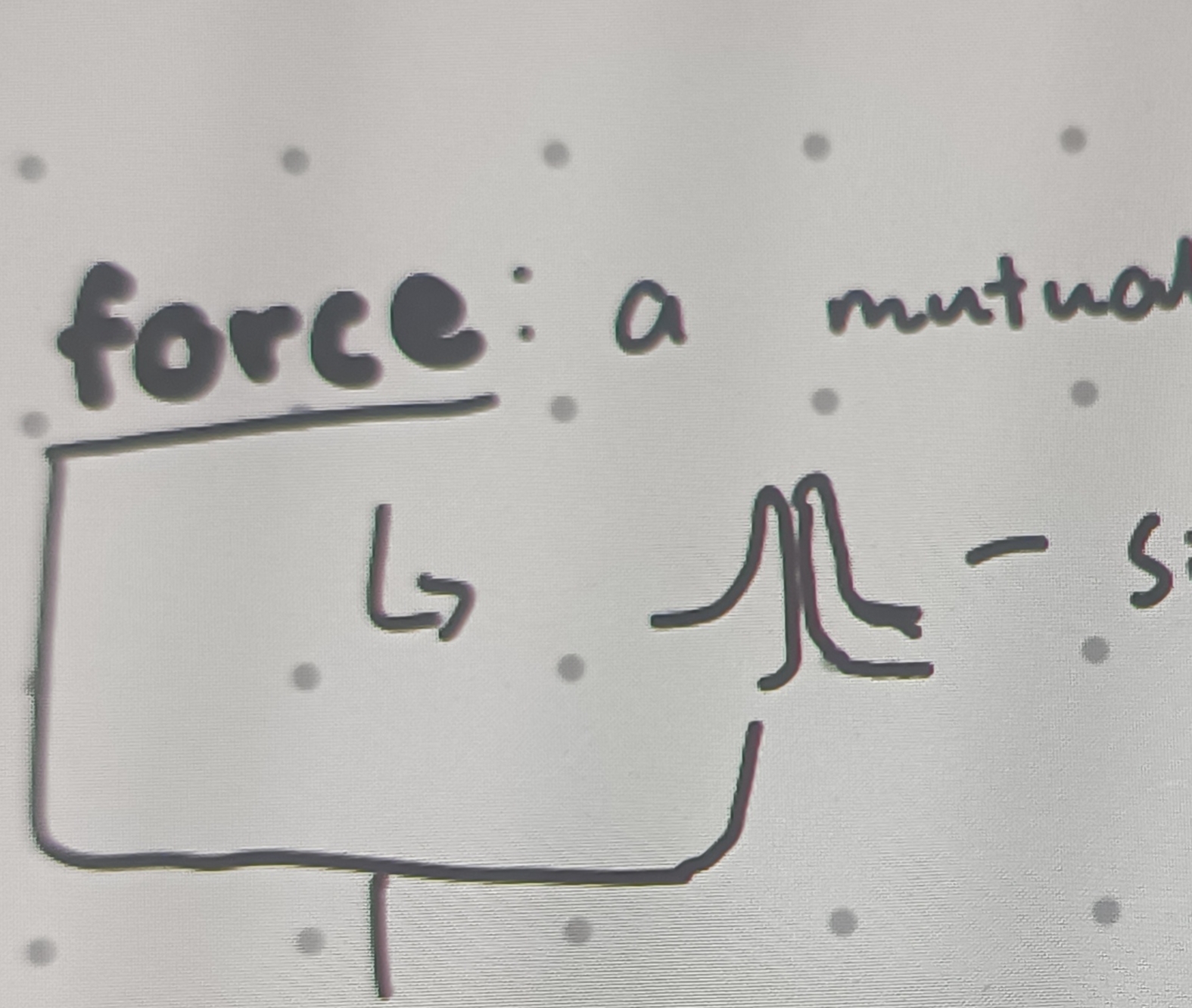
What is a force?
A mutual interaction between two objects
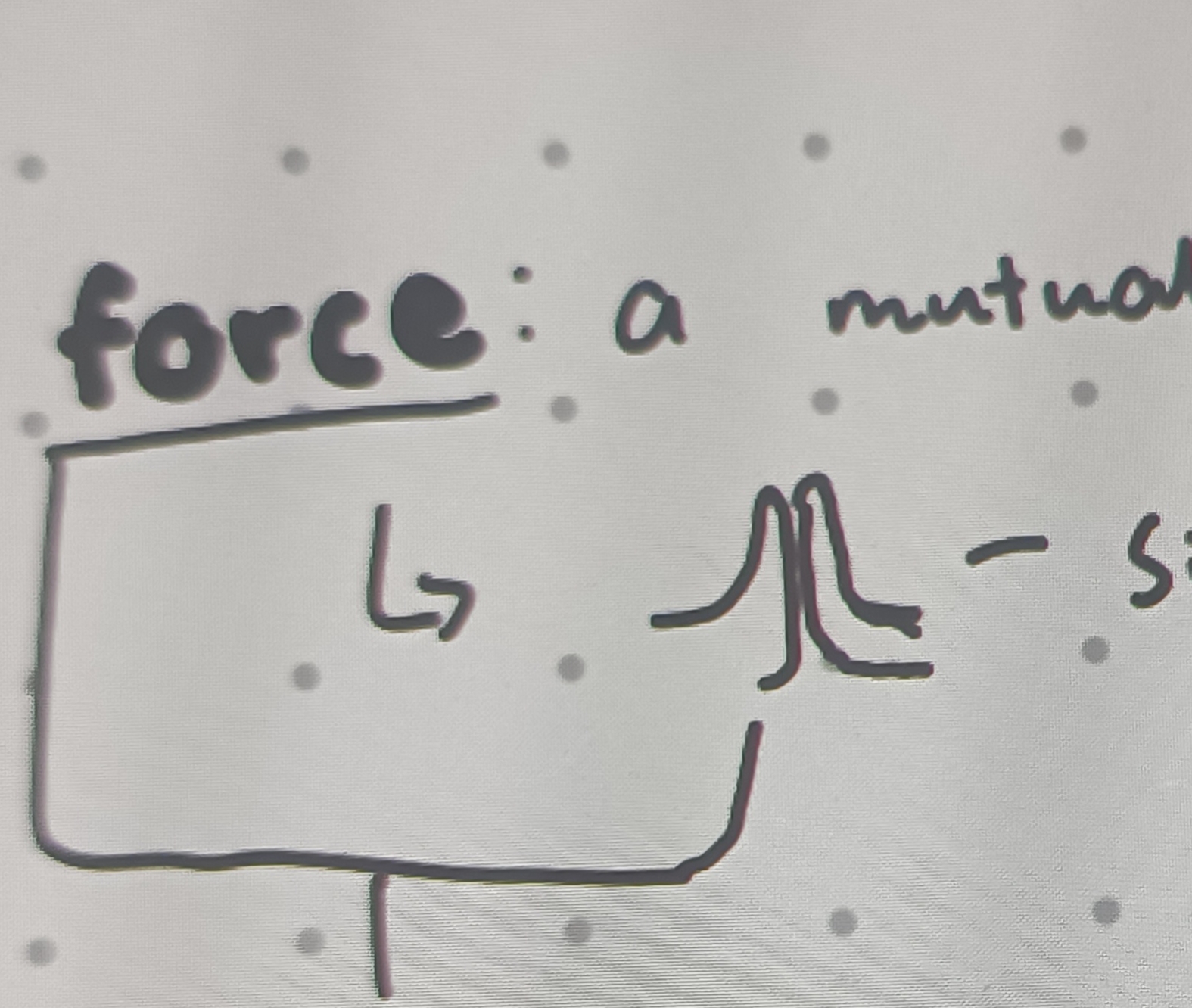
Forces always occur in ?
Pairs (cannot occur in isolation)
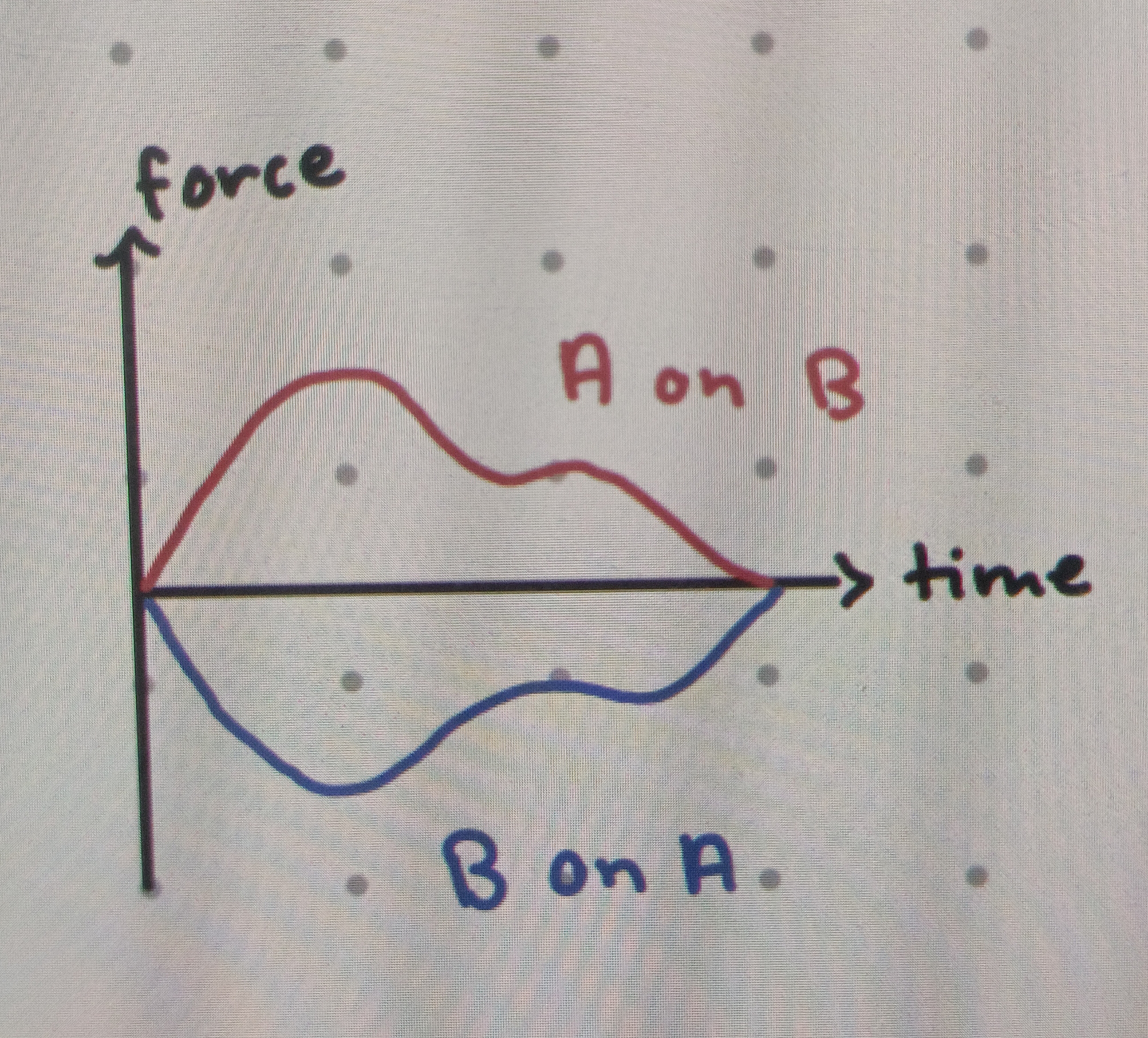
Which direction and magnitude do forces occur in?
OPPOSITE direction, and SAME magnitude
Do forces act simultaneously or at different times to each other?
Simultaneously
Unit for force
Newton (N)

Properties of Forces: type
Forces pairs are of the same type

Properties of Forces: magnitude?
SAME magnitude

Properties of Forces: direction?
OPPOSITE direction

What does it mean when a forces is the same type? Give examples
When both forces are the same type, e.g. pull and pull | push and push | gravitational and gravitational | electrical and electrical
force pair of a push force
Push
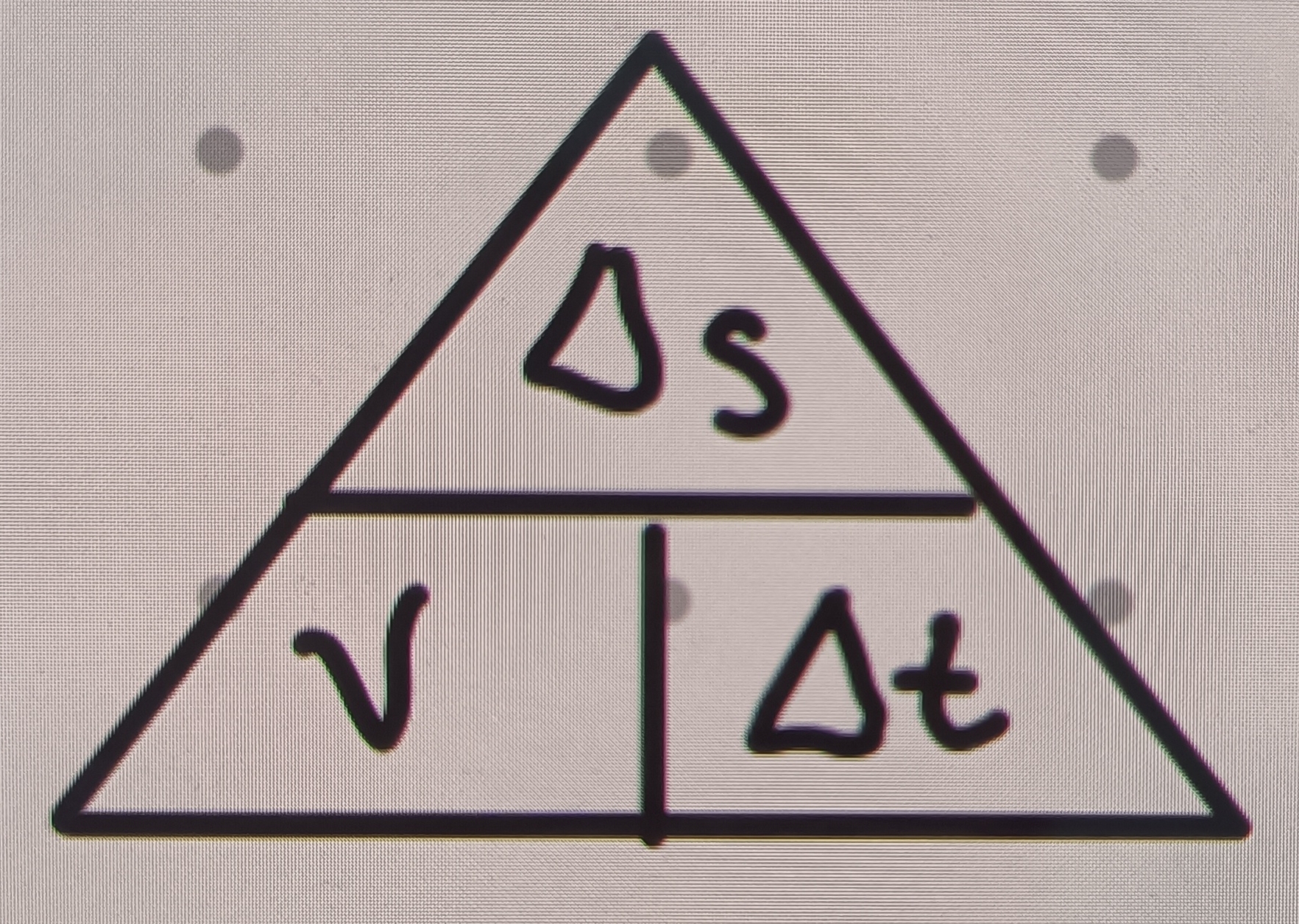
velocity measures
A change in displacement (∆s) over a change in time (∆t)
Velocity equation
∆s÷∆t
Speed measures?
The distance travelled (d) over the change in time (∆t)
Speed equation
d÷∆t

a scaler quantity
A quantity that has a MAGNITUDE ONLY
What are some examples of scaler quantities?
Mass e.g. kg
Volume e.g. L
temperature

a vector quantity?
A quantity that has a Magnitude and a Direction
What are some examples of vector quantities?
Velocity (v), acceleration (a), gravity, Force
How are vectors expressed
arrows
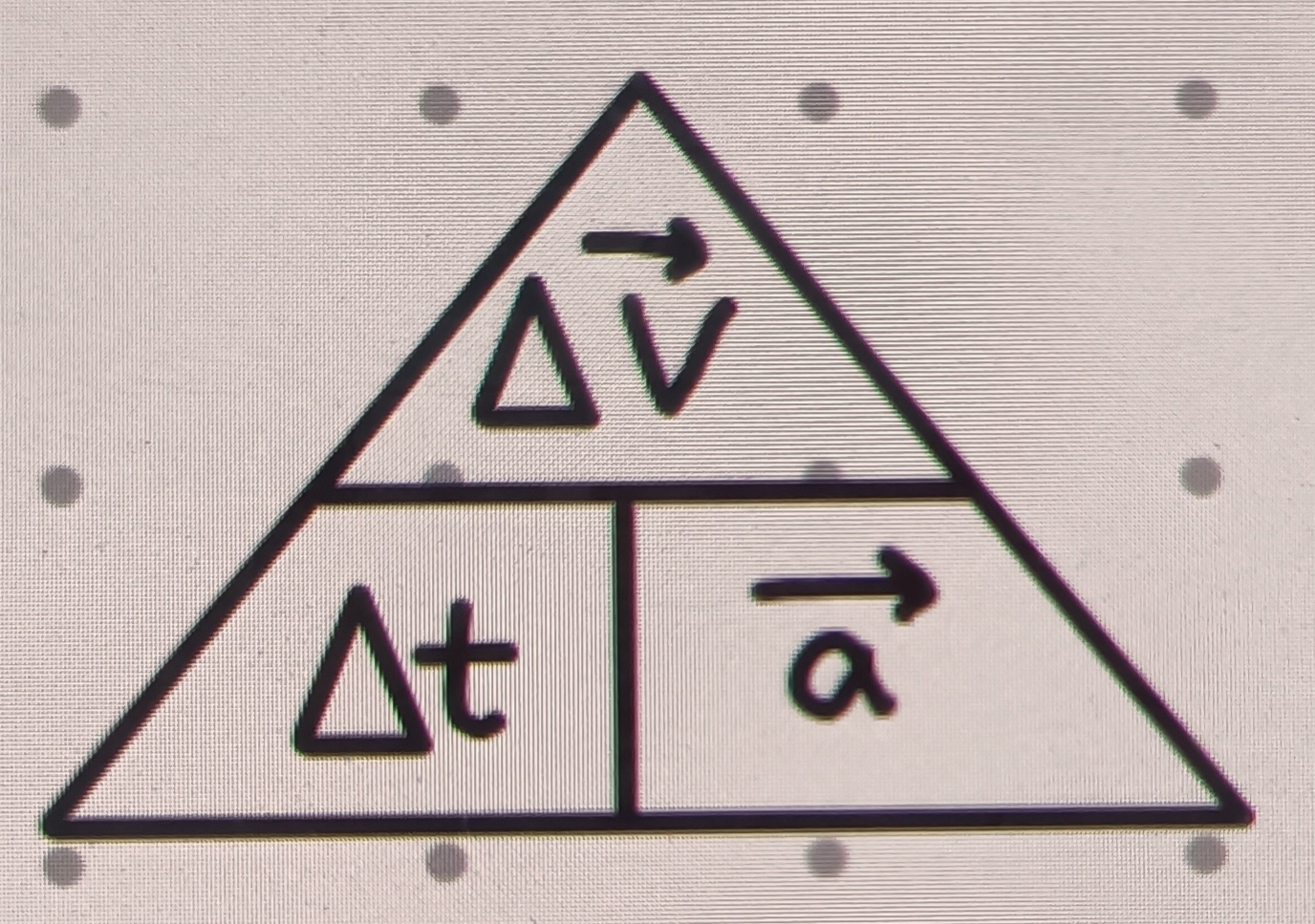
Equation for acceleration (a)
∆v/∆t
Unit for acceleration (a)
m/s/s = m/s² = ms-2
Unit for velocity (v)
m/s = ms-1
Why do objects accelerate (move)
Objects accelerate because of an unbalanced force acting on the object
Inertia?
The reluctance of an object to change its state of motion
Change in state of motion?
Acceleration
Newton's 2nd law definition words
Acceleration depends:
Directly on the unbalanced or net Force
Inversely on the objects mass, M
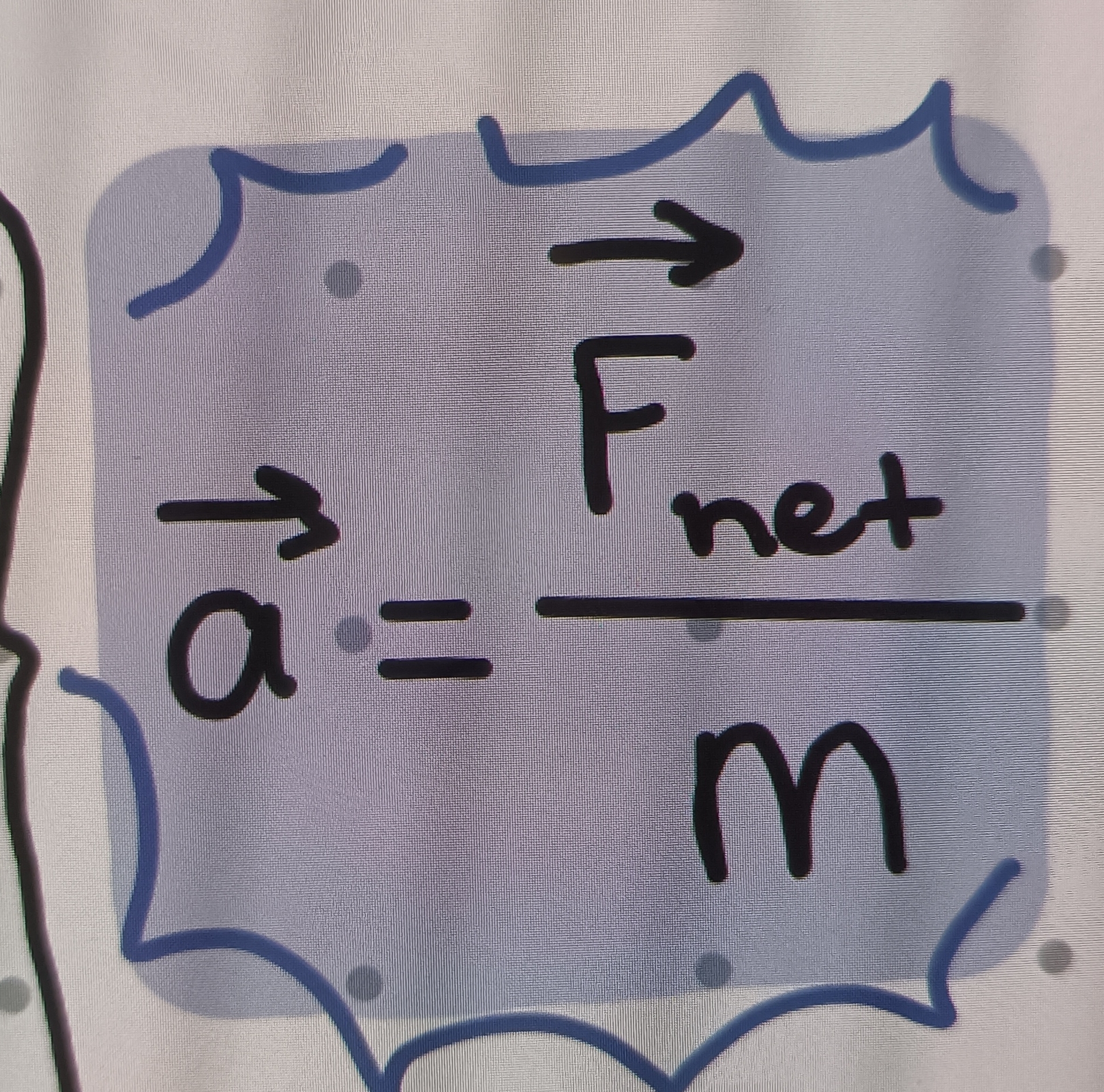
Newton's 2nd Law equation
Ma=Fnet

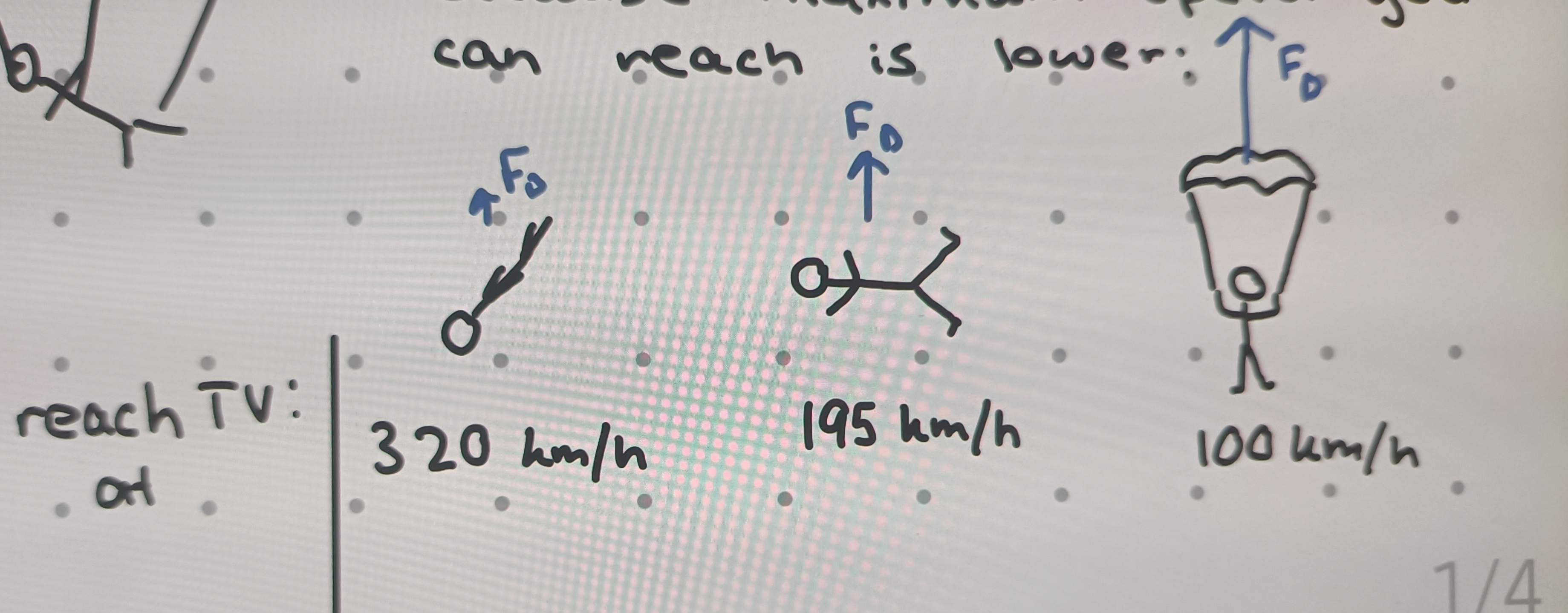
Objects with a larger surface move how
Slower
What affect does a parachute have on drag force and terminal velocity
Increases drag force, therefore, reduces terminal velocity
Explain terminal velocity
When an object is still moving at its same speed, just not getting any faster
Why does more surface area increase drag and reduce terminal velocity
Because the maximum speed object can reach is lower
Free body diagram step 1
Start with force pair diagram
Free body diagram step 2
Isolate object of interest
FBD step 3
Add to the object, only those forces directly affecting the object

FBD step 4
Treating the forces as vectors, find the net Force
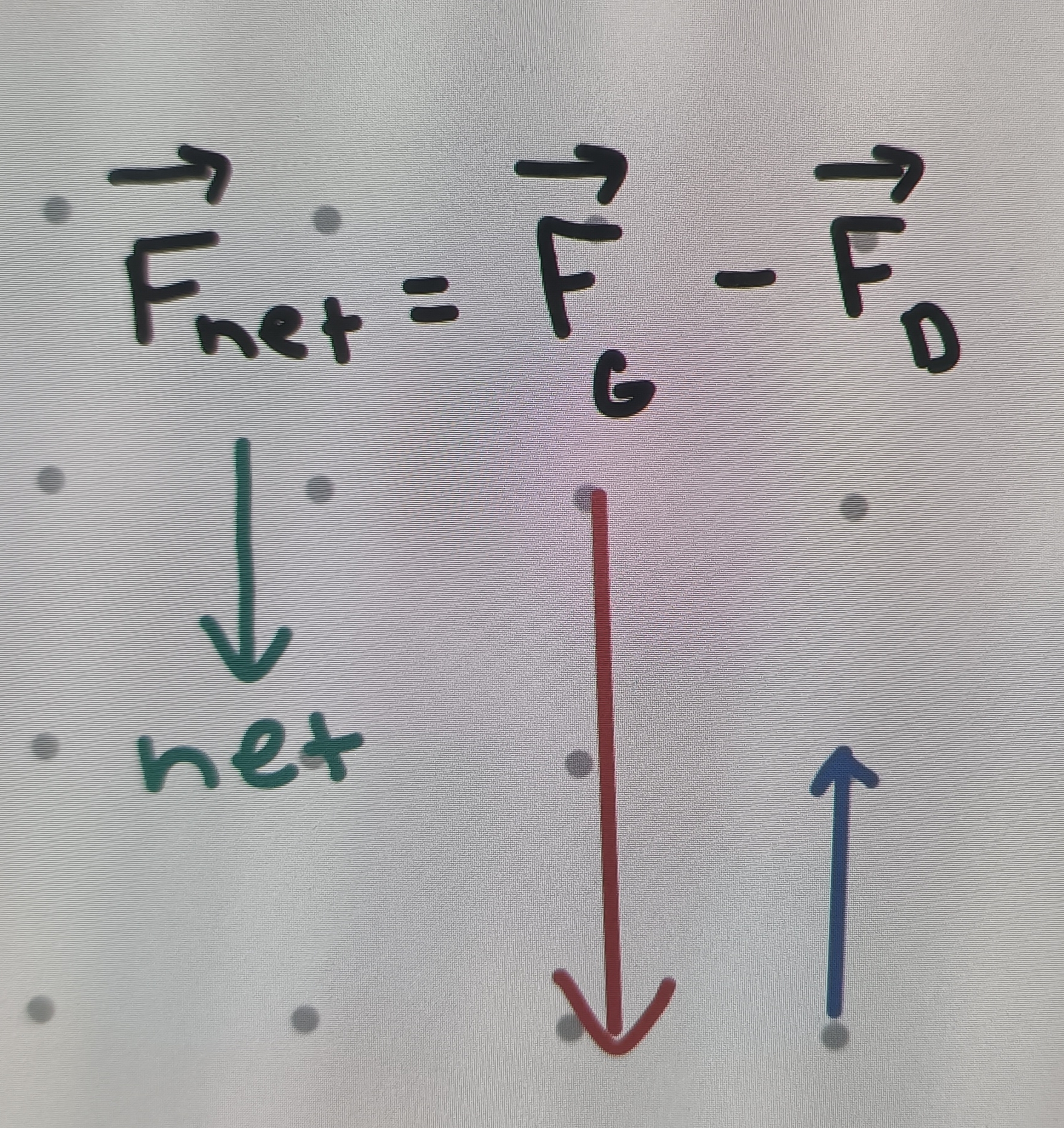
What is the net force of an object during terminal velocity
0 N
What is acceleration at terminal velocity
a = 0km/h²
What is Velocity at terminal velocity
Remains the same speed
What is the inverse relationship between acceleration and Mass
As Mass increase, acceleration decreases
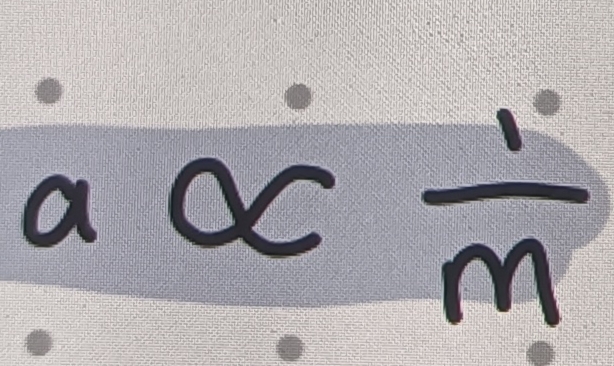
What is the direct relationship between acceleration and Force
As acceleration increases, Force increases
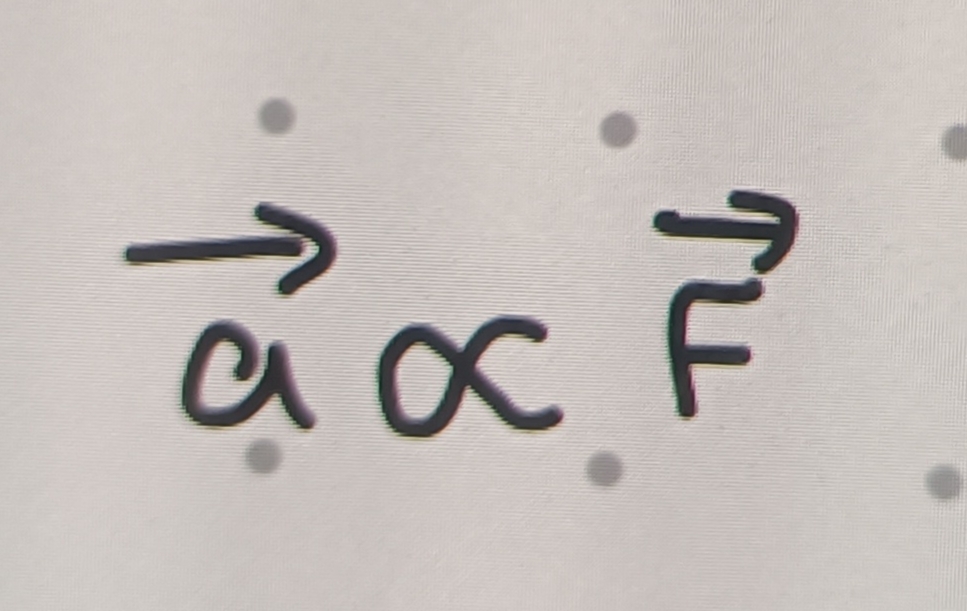
Unit for weight (same as force)
Newton (N)

Formula/equation for weight
mass × gravity=
m×g
What is weight definition
Force exerted on mass by gravity