OCR Computer Science 1.3
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is a network?
A group of computer systems connected to each other allowing for communication.
Name 4 factors that affect network performance
Bandwidth
No. of users
Interference
Distance to travel
Signal strength
Amount of data to transfer
What is bandwidth?
The maximum amount of data that can be sent at a time
What is a LAN?
Over a small geographical area
All infrastructure owned by network owner
What is a WAN?
Over a a large geographical area
Infrastructure owned by third party companies.
How does a client/server network operate?
Client makes a request to the server.
Server manages the request and responds.
What is a server?
a powerful, dedicated computer that provides specific services, resources, or data
What does the server control?
Network security, backups
What are 3 advantages of client-server networks?
Easy to add new clients to the server.
Hardware, software and resources can be shared across the network.
Can be controlled centrally to easily backup data and download software.
What are 3 disadvantages of client-server networks?
Central point of failure.
Large amounts of traffic will slow down the network.
Malware can spread quickly across the network.
How does a peer-to-peer network operate?
Data is shared directly between systems without requiring a central server.
What are 3 advantages of peer-to-peer networks?
Easier to set up as no central server.
Clients are not dependent on server.
Perfect for quickly sharing files
What are 3 disadvantages of peer-to-peer networks?
No central device to manage backups and security - must be done individually.
Computer performance will decrease with more devices connected.
How is data sent across a network?
Broken down into smaller packets.
Redirected by routers.
Reassembled when reaches destination.
Why are packets used?
Allows large files to be transferred quickly.
What is network topology?
The layout of computers in a network
What is a star toplogy?
Each computer connected to a central device, such as a hub or switch.
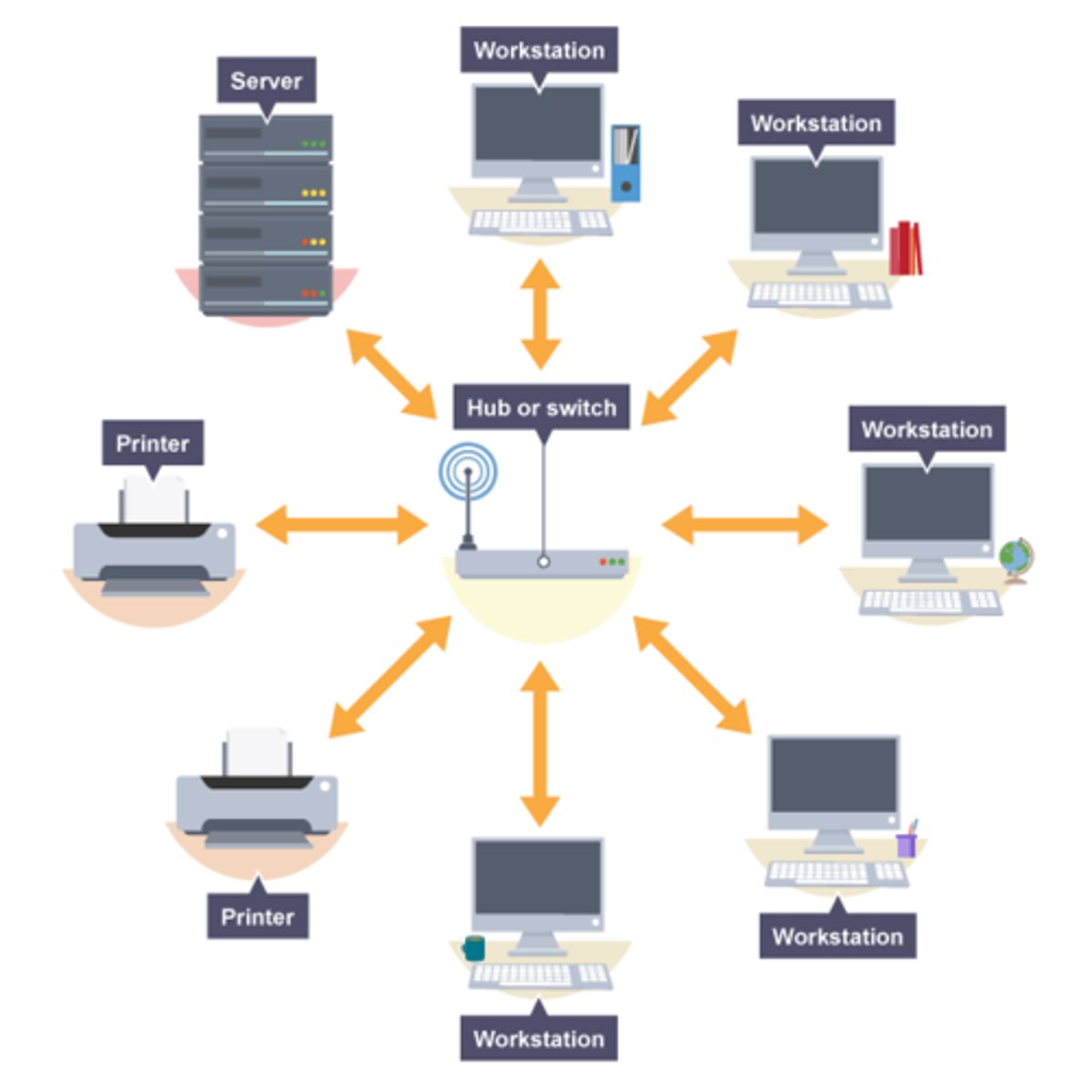
How does a star topology work?
Each computer transfers data in packets to central hub or switch.
Hub or switch looks at destination address and transfers packets directly to intended computer.
Name 3 advantages of a star topology.
Improved security - central firewall.
If one cable fails, not all other devices are affected.
Fast data transfer, as wires are not shared with other computers.
Name 3 disadvantages of star topology.
Requires additional hardware such as central switch or extra cables.
Central point of failure.
What is a full mesh topology?
All devices are connected to each other
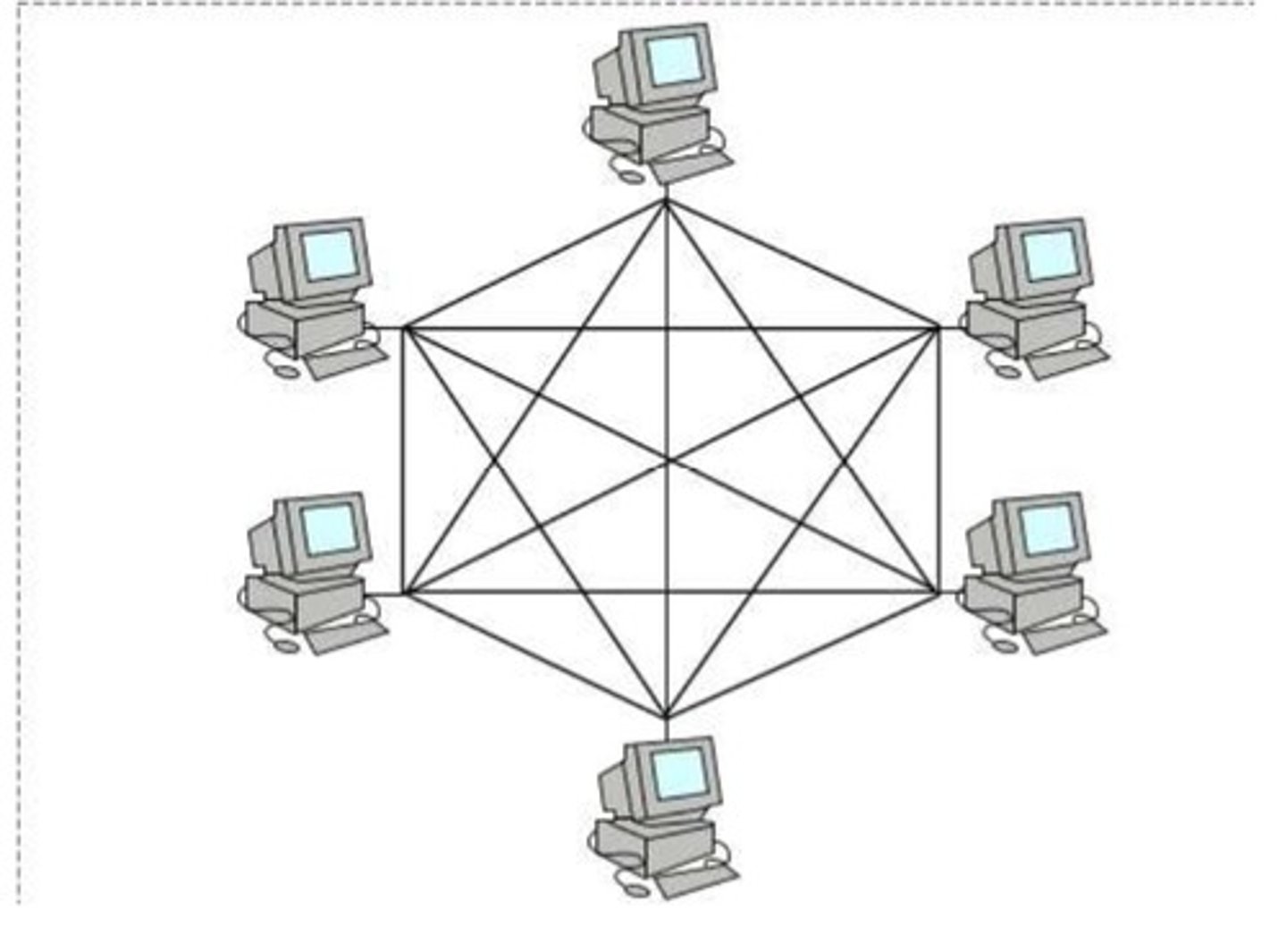
What is a partial mesh topology?
Not all devices are fully connected

How does a mesh topology work?
Data packets are transferred to the destination address along the quickest path
Name 3 advantages of mesh topology
No central point of failure - there are alternative routes the data can take.
Data can be transferred from multiple devices at the same time.
New systems can be added without disrupting the whole network.
Name 3 disadvantages of mesh topology
Very expensive to install if wired.
Backups and security checks not done centrally.
Can involve redundant connections (where some cables are not being used and are unnecessary)
What is a node?
any device on a network
What is a WAP?
Wireless Access Point
Provides a link between wired and wireless networks.
Creates a wireless LAN
What is a router?
Transfers data packets between networks.
How do routers work?
Transferred from router to router.
Receive packets and use the IP address to determine the best route for the data.
What is a switch?
Used to connect devices on a LAN
How does a switch work?
Receives packets from nodes, reads the destination address, and forwards the data to its destination.
Generates a list of MAC addresses of all devices and scan for the matching destination.
What is an NIC?
Network Interface Card
Internal piece of hardware required for devices to connect to a wireless network.
Includes a MAC address.
What are the 3 types of transmission media?
Ethernet cables.
Fibre optic cables.
Copper cables.
What are ethernet cables used for?
On a LAN to transfer data between nodes.
What are copper cables?
Older, slower cables.
Used less frequently as can be affected by electromagnetic interference.
What are fibre-optic cables?
Very fast but more expensive and fragile cables that send data as pulses of light.
What are fibre optic cables used for?
To send data quickly across a WAN.
What is the internet?
A global network of interconnected networks
What is the world wide web?
A collection of interconnected web pages and documents accessible by the internet
What does a web server do?
Receives to the web browser (client) request to display web pages - prepares it and returns it so it can be displayed
Where must websites be stored?
On web servers
Give an example of what a domain name looks like
e.g. www.google.com
What does a DNS store?
Domain Name Server
Stores domain names and their corresponding IP addresses where the website is stored.
What is an IP address in terms of domain names?
Unique address which the web page is stored on
Describe the steps taken to display a website
1. Domain name is typed into search bar of browser.
2. Query is sent to DNS for corresponding IP address of domain name
3. DNS server checks if it has an IP address. If it does, it is sent to the web browser
4. The browser then connects to the server and accesses the web site
What is the cloud?
A term to refer to networks of servers on the internet
What are some purposes of the cloud?
Running applications, remote processing, storing data.
Name 3 advantages of cloud storage
Accessible from anywhere.
No need to buy expensive hardware to store data.
Cloud host provides security and back-ups for you.
Huge capacity.
Multiple people can access it at a time.
Name 3 disadvantages of the cloud
If internet connection is lost, it becomes unstable.
Personal data is stored on another company's servers.
Dependent on host for security.
What are characteristics of wired connections?
Faster,
More secure,
Restricted movement,
Requires NIC
What are characteristics of wireless connections?
Slower,
Less secure,
Freedom of movement,
Requires WNIC (wireless NIC)