Humanistic approach
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Humanistic approach
What is universal law?
absolute rules of human behaviour - suggests everyone acts the same
Humanistic approach
What is holism?
looks at the whole (eg: all experiences of the person), rather than the constituent parts
Humanistic approach
What does congruent mean?
when a person’s 'ideal self' is in line with their 'actual self’
Humanistic approach
What does incongruent mean?
when a persons 'ideal self' is not in line with their 'actual self', causing unpleasant feelings
Humanistic approach
What does free will mean?
you can decide what you do yourself (autonomy)
Humanist
What do humanistic psychologists believe?
although external/internal factors influence us, humans beings are self-determining + have freewill
emphasise the importance of subjective experience and each person's capacity for self-determination
so psychology should consider/study subjective experiences → reject scientific models that establish general laws for behaviour
Humanist approach
Why do Maslow and Rogers reject scientific models?
Believe we are all unique so should have a 'person centred approach'
Humanistic approach
What are the ‘idea self’ and ‘real self’?
Ideal: internalised concept of the perfect image of ourselves, often used to compare w/ actual self’s behaviour w/
Real: internalised concept of how the person views themself
Humanistic approach
What are the stages of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
physiological (Eg: food, water)
safety (eg: protection, security)
love/belonging (eg: affection, relationships)
self-esteem needs (eg: achievement, cofidence)
self actualisation (reaching your full potential - all lower levels need to be met to do this)
(developed 1950s)
Humanistic approach
what is a practical use of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
a way for employers to get the best out of their employees by understanding their needs
Humanist approach
What are some examples of self actualisation?
morality
creativity
spontaneity
lack of prejudice
Humanist approach
What is the effect of incongruence on self worth?
to achieve personal growth the need to have congruence
when incongruence exists, self-actualisation is not possible due to low feelings of self worth
Humanist approach
What are ‘conditions of worth’?
when parents place limits of criteria their child must meet to achieve worth
Humanist approach
Carl Rogers:
What did Roger’s say people strive to achieve?
What did Rogers feel about Freud?
Where does Roger’s claim worth issues stem from?
their ideal self as they are motivated by self improvement
that he delt with the ‘sick half’ of psychology (vs the humanistic approach which deals with explanations of healthy growth)
childhood where conditions of worth were applied
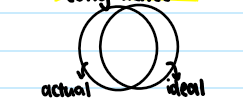
Humanist approach
what does this diagram show?
congruence
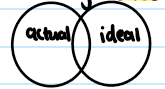
Humanist approach
what does this diagram show?
incongruence
Humanist approach
What creates low/high self worth?
humans have a need to feel nurtured by significant people in their lives (Eg: parents) → if given freely (unconditional positive regard) people develop a healthy sense of self worth
children who get negative regard (eg: criticism, blame) develop low self worth → to avoid, parent’s should blame the behaviour, not the child
Humanist approach
What is a method of measuring the self, congruence, and conditions of worth?
Stevenson (1953)’s Q-sort assessment
was adopted into Client Centred Therapy by Rogers
it’s a measurement of (in)congruence by a series of cards containing personal statements (eg: ‘needs recognition from others’)
the person sorts the cards to describe the real self, and ideal self
Humanist approach
How does Rogers deal with incongruence?
Developed client-centred therapy:
Provides: genuineness, empathy and unconditional positive regard to increase a patient's feelings of self-worth → reduce the level of incongruence
Humanist approach
Evaluation: promotes a positive image of the human condition
humanistic psychology offers a refreshing alternative vs eg: Freud viewed humans as being enslaved by their past → sees people as good, free to work for self-improvement, and in control of their life → Roberts et al (2000) showed that adolescents w/ strong belief in fatalism (their lives = decided by events outside of their control) = more at risk of depression → SO humanistic approach can improve quality of life
Humanist approach
Evaluation: holism
doesn’t isolate key variables, so may have more ecological validity than other theories because it considers meaningful behaviour in it’s real life context BUT could be seen as unscientific bcs if can’t isolate key variables, can’t establish cause/effect
Humanist approach
Evaluation: research to say outside factors can influence our psychological process
eg: acute stress can be explained by the sympathetic adrenal Medullary system (largely out of people’s control) → suggests that humans behaviour isn’t necessarily always ‘free’ like humanistic approach suggests
Humanist approach
Evaluation: relatively little impact on psych as a whole
although Roger’s theory revolutionised counselling, + Maslow’s HON used to explain motivation (esp. in the workplace → increasing productivity + economic benefits), has limited impact on pscyh as a whole → bcs it has v limited evidence + lots of abstract ideas
Humanist approach
Evaluation: cultural bias
freewill, + personal growth = v individualistic, whereas collectivistic cultures (eg: Japan and China) emphasise interdependence → so some cultures don’t identify easily with this theory, so it’s culturally bound + limits application