Spermatogenesis
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are the 2 outcomes for the division of a spermatogonial stem cell?
self renew
commit to differentiation
What is the spermatogonial stem cell niche?
specialised physical and chemical environment
What causes spermatogonial stem cell self renewal?
paracrine signals from other cells in the niche
What are some examples of paracrine signals that cause a spermatogonial stem cell to self renew (3)?
FGF2
GDNF
CXCL12
What is the essential signal for spermatogonial stem cell self renewal?
GDNF from peritubular myoid cells
What happens if spermatogonial self renewal fails?
run out of stem cells = spermatogenesis fails
What signal is required for spermatogonial differentiation when a spermatogonium divides?
retinoic acid
How does retinoic acid cause a cell to become committed to meiosis in a male (2)?
acts as a ligand for nuclear transcription
upregulates Stra8 = committed to meiosis
What vitamin is required for the formation of retinoic acid?
vitamin A
What type of hormone is retinoic acid?
steroid
What influences whether a spermatogonial stem cell differentiates or self renews?
position relative to niche - affects availability of mitogens
What is the name given to male germ cells undergoing meiosis?
spermatocytes
What are homologous chromosomes (3)?
normal diploid (2n) cell
46 chromosomes in 23 pairs
pairs are homologous - one maternal and one paternal
What phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur in?
interphase
What are sister chromatids (2)?
replicated DNA
each chromosome has 2 identical sister chromatids joined at the centromere
What does meiosis I result in (2)?
homologous chromosome separation (unique to meiosis)
exchange of genetic information (in prophase I)
What does meiosis II result in?
separation of sister chromatids
What stage of spermatogenesis does meiosis I occur in in males?
primary spermatocytes
What stage of spermatogenesis does meiosis II occur in in males?
secondary spermatocytes
In which stage of meiosis does the change in ploidy occur (i.e. 2n → n)
meiosis I
What allows the movement of developing germ cells across the epithelium?
breaking and reforming of germ cell-sertoli cell adherens junctions
What type of junction forms the blood-testis barrier?
tight junctions between sertoli cells
Where do male germ cells move to after meiosis?
move past blood-testis barrier into immunologically privileged site - sertoli tight junctions ‘unzip’ to allow this
Why is the blood-testis barrier important?
helps avoid immune rejection of haploid cells
What happens to spermatogenesis when leydig cells are destroyed experimentally (4)?
reduced testosterone
gradual degeneration of spermatogenesis
NO POST-MEIOTIC GERM CELLS
androgens essential for progression through meiosis
What change occurs in post-meiotic germ cells?
morphological changes
What is spermiogenesis?
germ cell remodelling
What changes occur during spermiogenesis (4)?
cytoplasm condenses
acrosome and tail formation (polarisation)
DNA compaction
cytoplasmic storage of mRNAs required for future translation
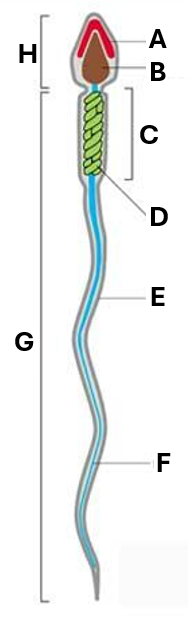
What different parts of the spermatozoa are indicated by A-H (8)?
A. acrosomal vesicle
B. nucleus
C. midpiece
D. mitochondrion
E. plasma membrane
F. flagellum
G. tail
H. head

What does ‘A’ indicate on this diagram of a spermatozoa?
acrosomal vesicle
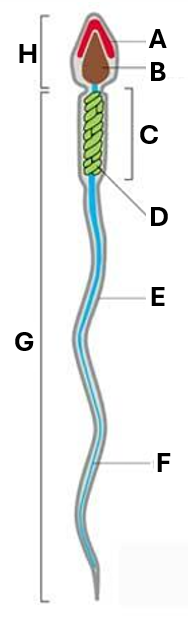
What does ‘B’ indicate on this diagram of a spermatozoa?
nucleus
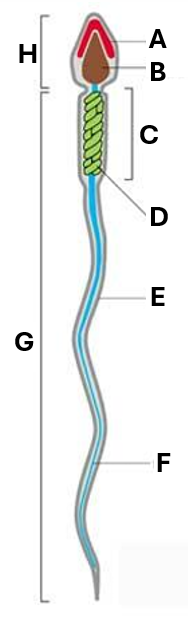
What does ‘D’ indicate on this diagram of a spermatozoa?
mitochondrion
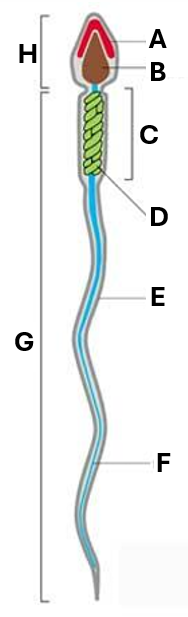
What does ‘F’ indicate on this diagram of a spermatozoa?
flagellum
What are the 4 phases of spermiogenesis?
golgi phase
cap phase
acrosomal phase
maturation phase
What happens during the golgi phase of spermiogenesis (3)?
round cell becomes polar
golgi → head end
centrioles → tail end
What happens during the cap phase of spermiogenesis (2)?
acrosomal vesicle forms cap over nucleus
primitive flagellum forms
What happens during the acrosomal phase of spermiogenesis?
acrosome begins to spread around nucleus
What happens during the maturation phase of spermiogenesis (2)?
mitochondria gather in midpiece
excess cytoplasm is lost as residual body
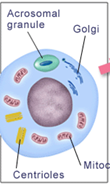
What stage of spermiogenesis is shown in this image?
golgi phase (1st phase)
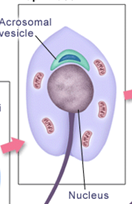
What stage of spermiogenesis is shown in this image?
cap phase (2nd phase)
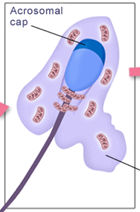
What stage of spermiogenesis is shown in this image?
acrosomal phase (3rd phase)
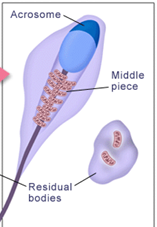
What stage of spermiogenesis is shown in this image?
maturation phase (4th phase)
What happens to residual bodies produced in the maturation phase of spermiogenesis?
phagocytosed by sertoli cells
How is DNA packaged into sperm (3)?
replacement of somatic histones with specialised histones
transcription stops
histones → transition proteins → protamines
What shape is DNA packaged into in somatic cells and why?
solenoid - DNA remains accessible for cellular processes
What shape is DNA packaged into in sperm and why?
annulus - tighter packed than somatic cells as does not need to be accessed
What % of histones are replaced with protamine when DNA is packaged into sperm?
85%
When does transcription stop during spermatogenesis?
early spermatid nucleus
What is spermiation?
spermatozoa release from sertoli cells
What happens during spermiation (3)?
sertoli-germ cell junctions undergo extensive remodelling
sperm released
leave behind residual body that is phagocytosed by sertoli cell
Where are specific germ cell stages found?
grouped together in seminiferous epithelium
How are the different germ cell stages arranged in male rodents in the seminiferous tubule?
segmental arrangement
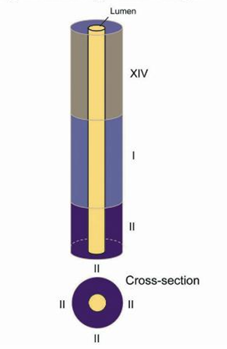
How are the different germ cell stages arranged in male humans in the seminiferous tubule?
helical arrangement
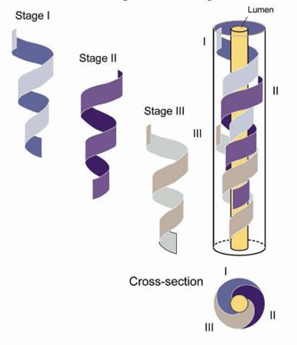
Why are there different stages of germ cell development in the same seminiferous tubule (3)?
allows continual release
not all sections of tubule releasing spermatozoa at same time
prevents periods of infertility
How long does human spermatogenesis take?
64 days
How long does mouse spermatogenesis take?
35 days
Why are different parts of the seminiferous tubule at different stages of germ cell development? What causes this? (3)
spatial availability of retinoic acid
need retinoic acid available to start at stage 1
availability controlled by coordination of other cells in the niche
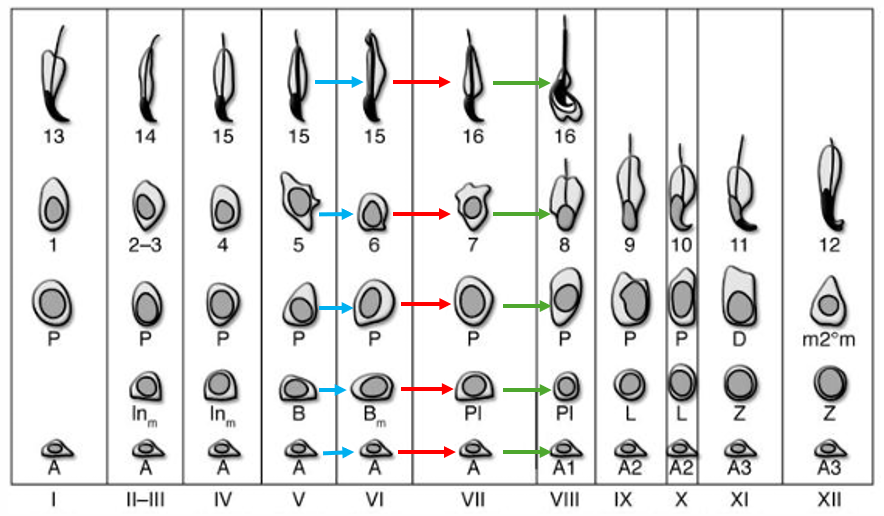
Why are different stages of spermatogenesis grouped together (2)?
different stages in different cells take the same amount of time as each other
e.g. all the blue arrows take the same amount of time as each other, all the red take the same amount of time etc…