1.1.7 culturing microorganisms
1/4
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
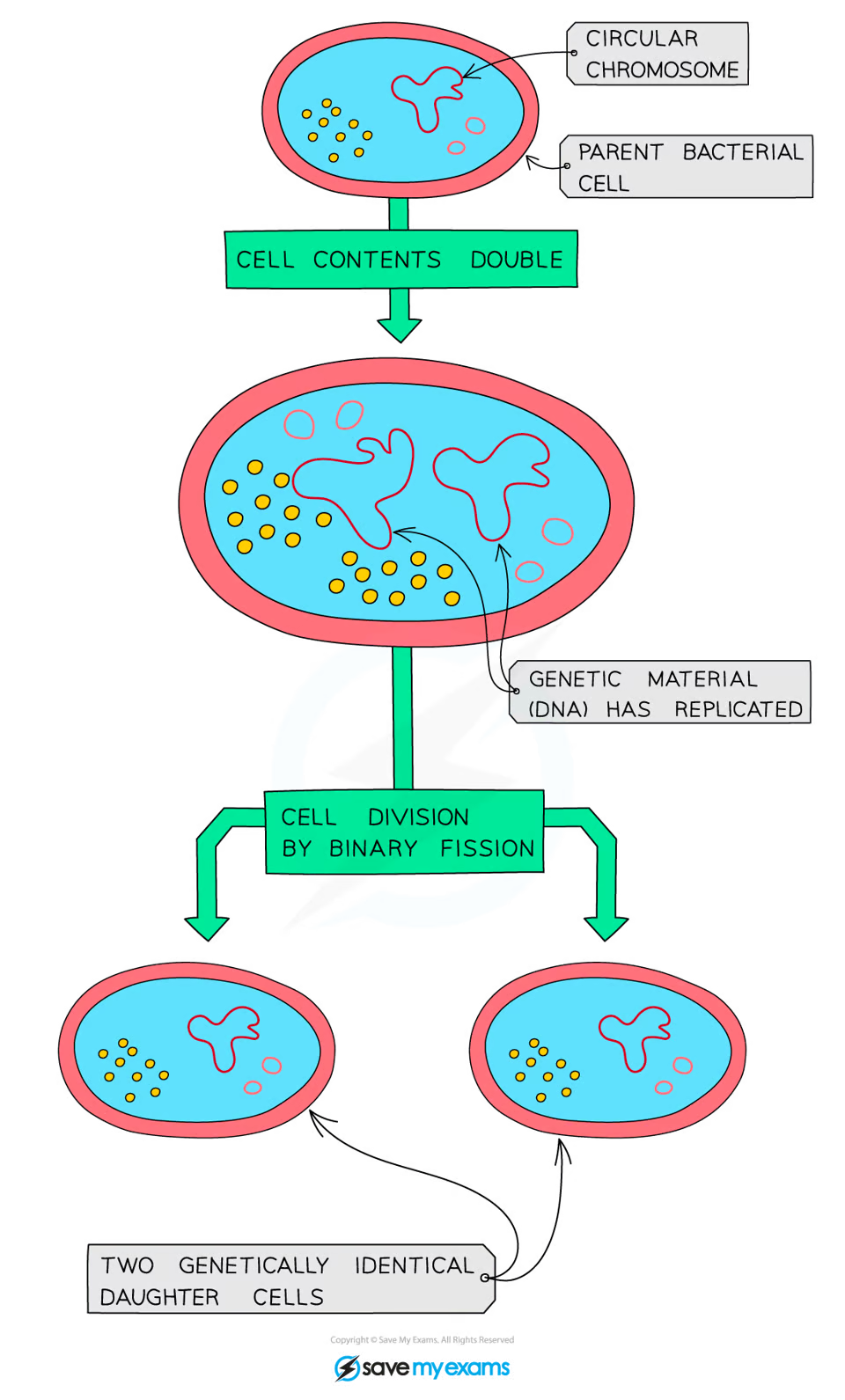
binary fission
each division of one cell produces two cells - no. of cells increases by power of 2 each time binary fission occurs
bacteria multiply by type of simple cell division: binary fission
in right conditions, bacterial cell prapares to divide by replicating genetic material before increasing in size
copies of each piece of circular DNA moves to each end of cell before cytoplasm divides, new cell walls form around each daughter cell
growing bacterial cultures in lab
effects of disinfectants & antibiotics on microorganisms investigated using cultures of bacteria growth in lab
in correct conditions, some species of bacteria (such as coli) can multiply once every 20 minutes. this is good, as large cultures of bacteria for study can be grown in short periods of time
to multiply quick, bacteria require adequate supply of nutrients(carbohydrates,proteins,minerals & vitamins) and appropriate temperature(varies depending on species being grown)
warmer temps promote faster growth
school labs maximum temp allowed = 25°C
above 25°C more harmful pathogens are likely to grow
bacteria able to grow in nutrient broth solution or as colonies on agar gel plate
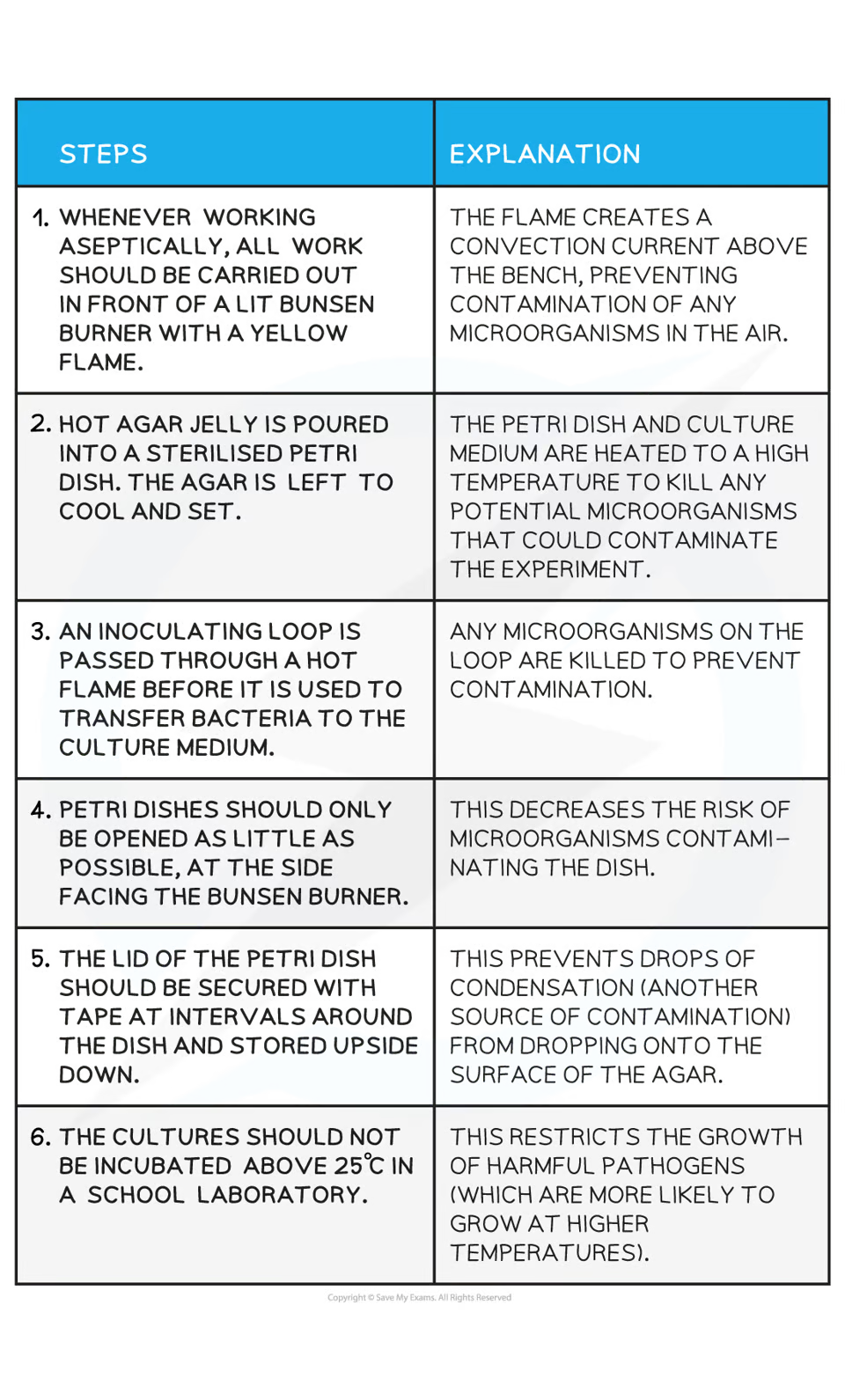
uncontaminated cultures & aseptic techniques
vital that uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms are grown in lab
presence of competing spacies may affect growth of cultures & validity of study performed on them
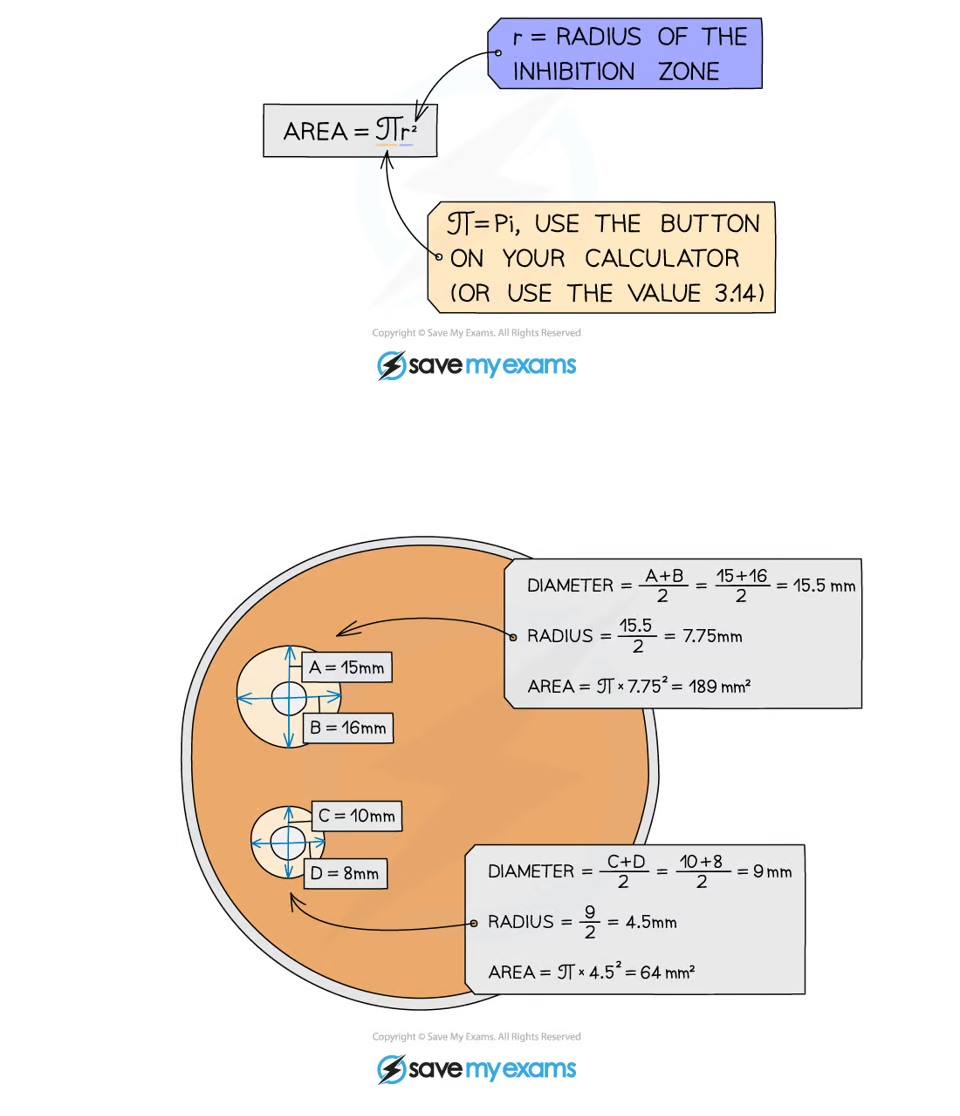
calculating inhibition zone area
calculating area of clear zone = more accurate way of comparing effect of different substances on bacterial growth that judging by sight
inhibition - area where no bacterial growth has occurred, larger zone = more effective substance
effectiveness of different antibiotics, antiseptics or disinfectants can be determined by calculating area of inhibition zone around disc of tested substance
calculation in image
calculating bacteria in a population
average amount of time taken for bacterial cell in population to divide = mean division time
number of times cell divides & how many cells it produces determined if you know mean division time & how long division has been occurring