1 - Levels of organisation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Levels of organisation
Chemical/molecular
Cellular
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Organism
(1) Chemical level
Atoms e.g hydrogen
Molecules e.g water
Chemical level (Larger Molecules)
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
High energy compounds
Cell
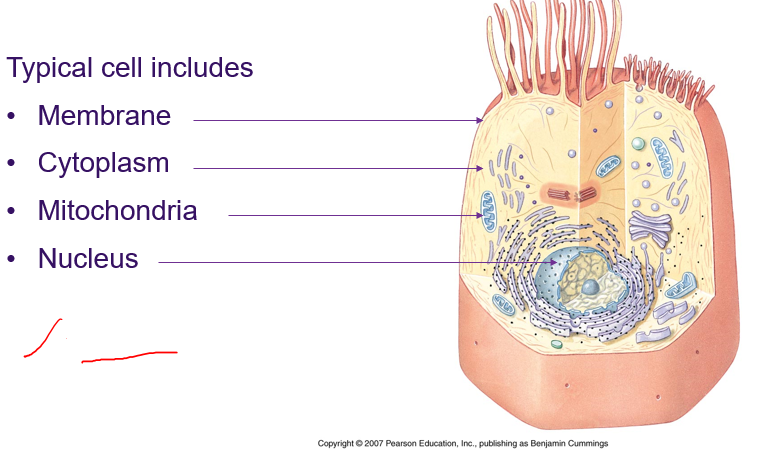
(2) Cellular level
Cells = smallest unit of life e.g. bacteria
Cellular differentiation = higher life forms contain cells specialised for different functions e.g sperm
(3) Tissue level
Cells + extracellular material/fluids
Tissues
Organs
Organ system
Epithelia
Connective
Muscle
Neural
Epithelia
Flat
Cover exposed surfaces
Line internal passageways/chambers
Produce glandular secretion
Connective tissues
3D
Store substances
Structural support
Store energy
Muscle tissues
Contracts to produce active movement
Neural tissue
Conducts electrical impulses
Carries/transmits info
(4) Organ level
a discrete collection of 2 or more tissues cooperatively performing a function
(5) Organ system
Integumentary
Skeletal
Muscular
Nervous
Endocrine
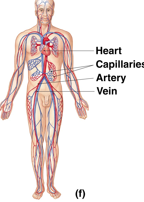
Cardiovascular
Lymphatic
Respiratory
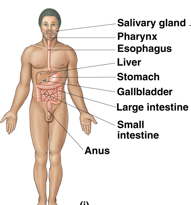
Digestive
Urinary
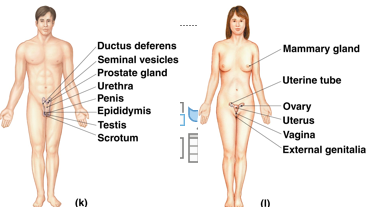
Reproductive
Integumentary
Protection
Thermoregulation
Sensation
Skeletal
support, protection
Muscular
movement
Nervous
communication
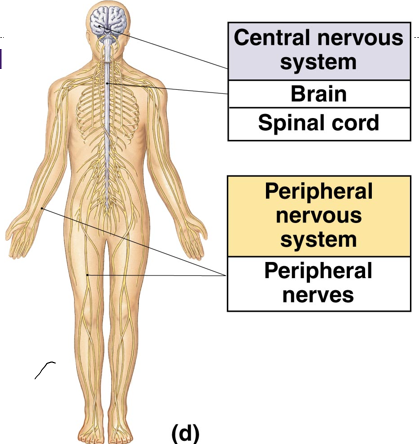
Endocrine
hormones to communicate
Cardiovascular
transportation
Lymphatic
Deal with pathogens
Immune response
Respiratory
ventilation
Digestive
digestion of nutrients
Urinary
excrete waste
Reproductive
Reproduce
Fetus
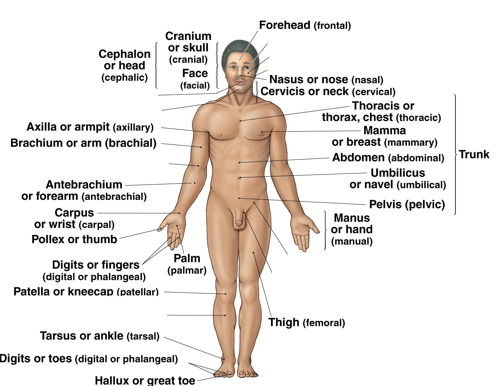
Anatomical landmarks (front)
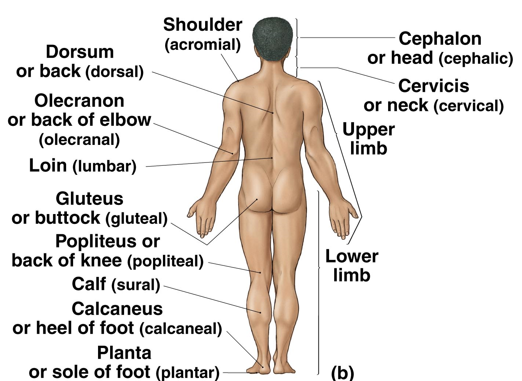
Anatomical landmarks (back)
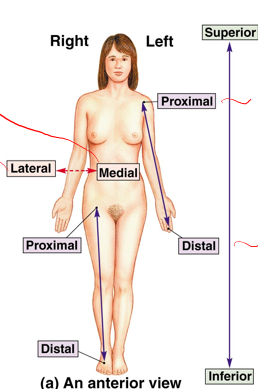
Anatomical position

Directional terms - anterior
Superior - head
Inferior - feet
Lateral - side
Medial - mid line
Proximal - nearest to trunk
Distal - furthest from trunk
Proximal
Distal
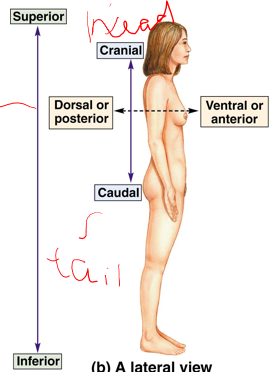
Directional terms (lateral)
cranial - head
caudal - tail
dorsal/posterior - back
ventral/anterior - front
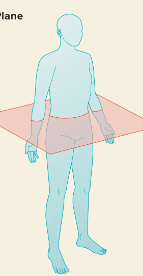
frontal plane
split forward + back

sagittal plane
left + right
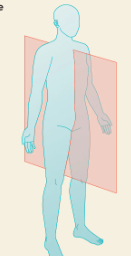
transverse plane
split top + bottom half
dorsal cavity
contains brain and spinal cord
ventral cavity
contains thoracic, abdominal, pelvic organs
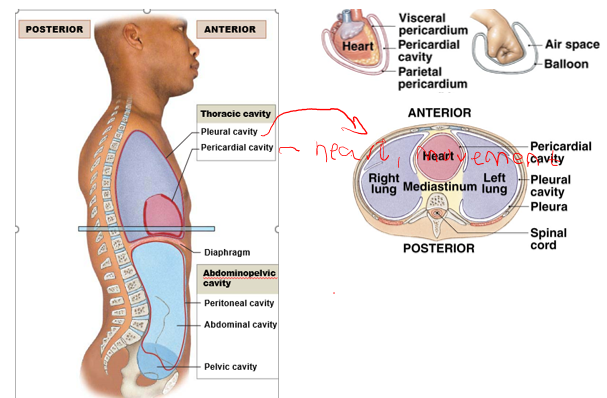
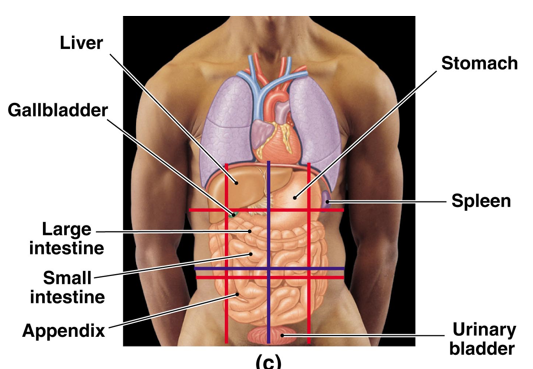
Thoracic + Abdominalpelvic cavity
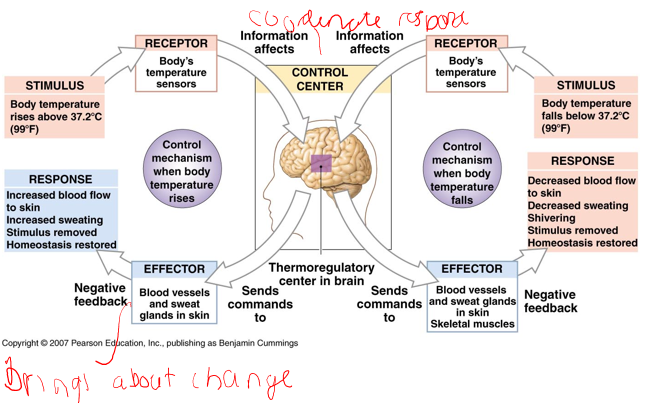
Homeostasis
the maintenance of a constant internal environment
Negative feedback - opposes variation from normal
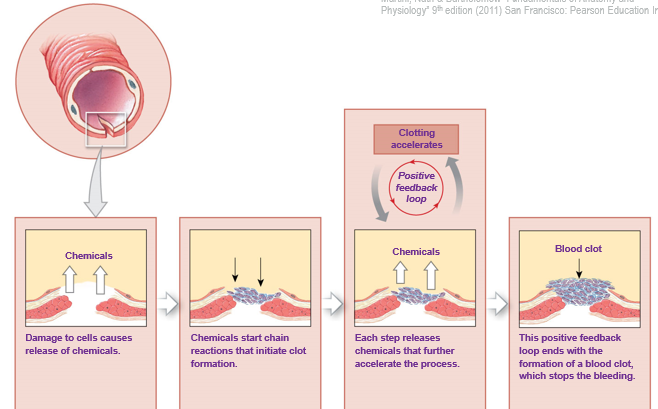
Positive feedback - exaggerates variation
Negative feedback
thermoregulation
Positive feedback
blood clotting