chemistry of life
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has weight; composed of elements
Elements
composed of chemically identical atoms
bulk elements
required by the body in large amounts
Trace elements
required by the body in small amounts
Atoms
smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element and consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
proton
a subatomic particle with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom, contributing to the atom's mass.
neutron
carries no electrical charge
electron
a subatomic particle with a negative charge that orbits the nucleus of an atom and is involved in chemical bonding.
Nucleus
central part of the atom, composed of protons and neutrons, electrons move around the nucleus
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of one atom, equals the number of electrons in the atom and determines the element's identity.
Atomic weight
the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in one atom. electrons do not contribute to the weight of the atom
Isotopes
atoms with the same atomic numbers but with different atomic weights. atoms with the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons: EX: oxygen. unstable isotopes are radioactive; they emit energy or atomic fragments
molecule
particle formed when two or more atoms chemical combine
compound
particle formed when two or more atoms of different elements chemically combine
molecular formulas
depict the elements present and the number of each atom present in the molecule EX: H2, C6H12O6 (glucose), H2O
Bonding atoms first shell
2 electrons
Bonding atoms Second shell
8 electrons
Bonding atoms third shell
8 electrons
ion
an atom that gains or loses electrons to become stable, an eclectically charged atom
Cation
a positively charged ion, formed when an atom loses electrons
Anion
A negatively charged ion, formed when an atom gain electron
ionic bond
an attraction between a cation and an anion, formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom: EX sodium Ion (Na+) and Chloride ion (Cl-) they bond to make sodium chloride
covalent bond
a type of bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms. this sharing allows each atom to attain a full balance shell, leading to better stability. EX two hydrogen atoms form single bonds
structural formulas
show how atoms bond and are arranged in various molecules
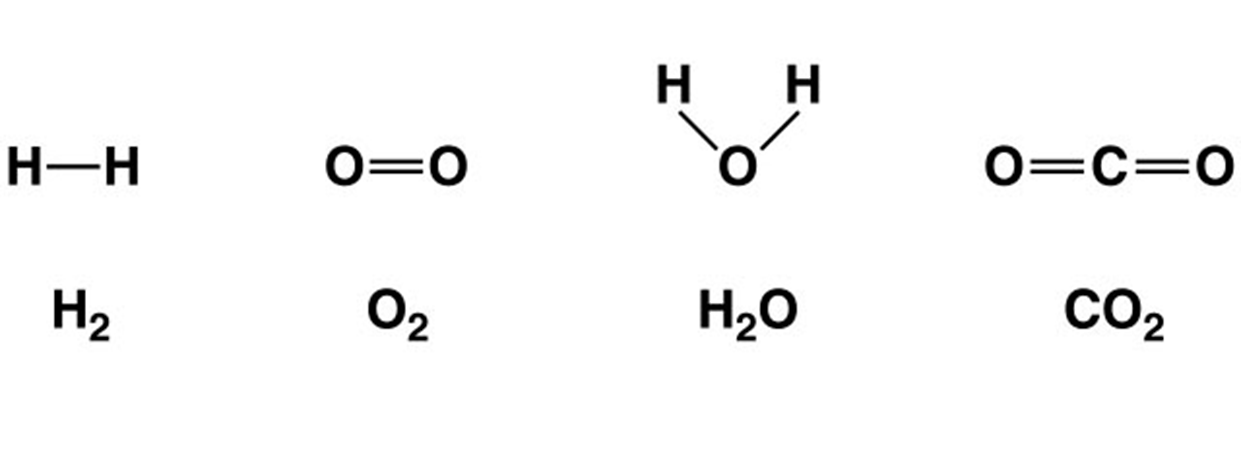
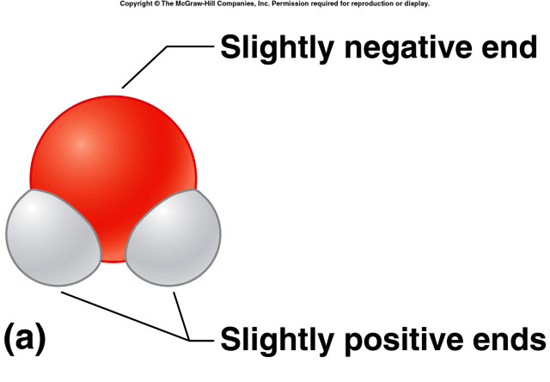
polar molecules
molecule with a slightly negative end and a slightly positive end, results when electrons are no shared equally in covalent bonds water is an important polar molecule
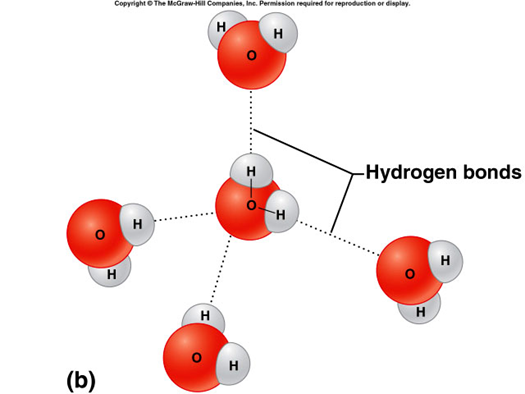
hydrogen bond
a weak attraction between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule, formed between water molecules, important for protein and nucleic acid structure
Chemical reactions
occur when chemical bonds form or break among, ions, or molecules
reactants
the starting materials of the reaction - the atoms, ions, or molecules ex: NaCl
products
substances formed at the end of the chemical reaction EX: Na+ + Cl-
synthesis reaction
also known as a direct combination reaction, occurs when two or more simple elements or compounds combine to form a more complex product. EX: A+B —> AB
decomposition reaction
chemical bonds are broken to form a simpler chemical structure EX: AB —> A+B
exchange reaction
chemical bonds are broken, and new bonds are formed EX: AB + CD —> AD + CB
reversible reaction
the products can change back to the reactants
electrolytes
substances that release ions in water, they have a natural positive or negative charge EX:
NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
Acids
electrolytes that dissociate to release hydrogen ions in water Ex: HCL → H+ +Cl-
Bases
substances that release ions that can combine with hydrogen ions EX: NaOH → Na+ + OH-
Salts
electrolytes formed by the reaction between an acid and a base EX: HCL + NaOH → H2O +NaCl
pH Scale
indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
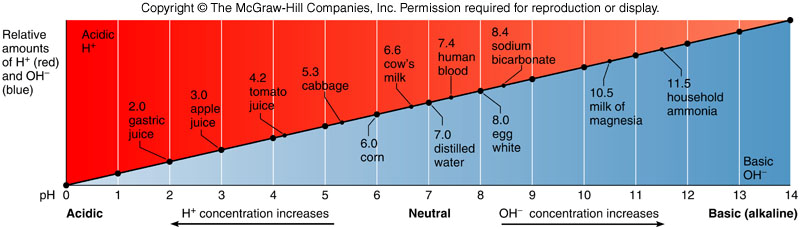
neutral
pH 7; indicates equal concentration of H+ and OH-
Acidic
pH less than 7; indicates a greater concentration of H+, to reduce this you add a base
Basic or alkaline
pH greater than 7; indicates a greater concentration of OH-
organic molecules
contains C and H, usually larger than inorganic molecules dissolve in water and organic liquids EX: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
inorganic molecules
generally, do not contain C, usually smaller than organic molecules, usually dissociate in water, forming ions EX: water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and inorganic salts
water (inorganic)
two thirds of the weight of an adult human major component of all body fluids, medium for most metabolic reactions, important role in transporting chemicals in the body, absorbs and transports heat
oxygen (inorganic)
used by organelles to release energy from nutrients in order to drive cell’s metabolic activities, necessary for survival
carbon dioxide (inorganic)
waste product released during metabolic reactions, must be removed from the body, the exception contains carbon but is still inorganic
inorganic salts
abundant in body fluids, sources of necessary ions (Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+), play important roles in metabolism
Carbohydrates (organic)
provide energy to the cells, supply materials to build cell structures, water soluble, contains C, H, and O, ratio of H to ) close to 2:1 (C6H12O6)
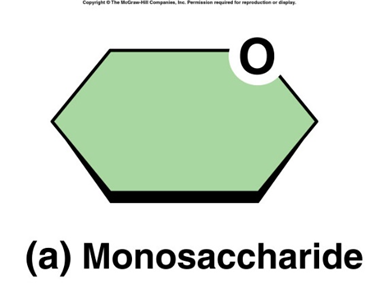
monosaccharides
single sugar molecules that cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller carbohydrates. they are the most basic units of carbohydrates. consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CH2O) EX: glucose, fructose
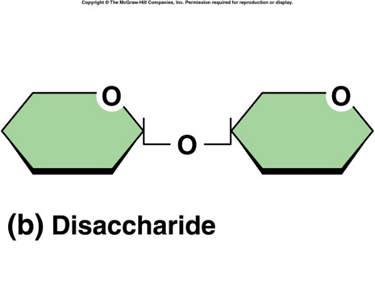
disaccharides
sugars formed by the combination of two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond, general chemical formula of C12H22O11 EX: Sucrose, lactose
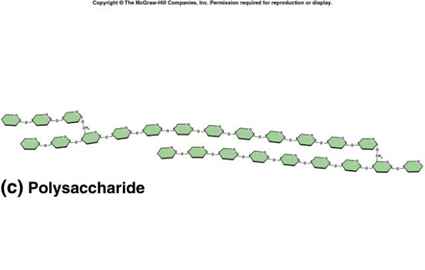
polysaccharides
polymers of simple sugars connected together by glycosidic linkages, which are covalent connections, general formula C6H10O5 EX: Glycogen, cellulose
building block to polysaccharide
monosaccharide
building block to lipids
fatty acids, glycerol
building block to nucleic acids
nucleotides
building block to proteins
amino acids
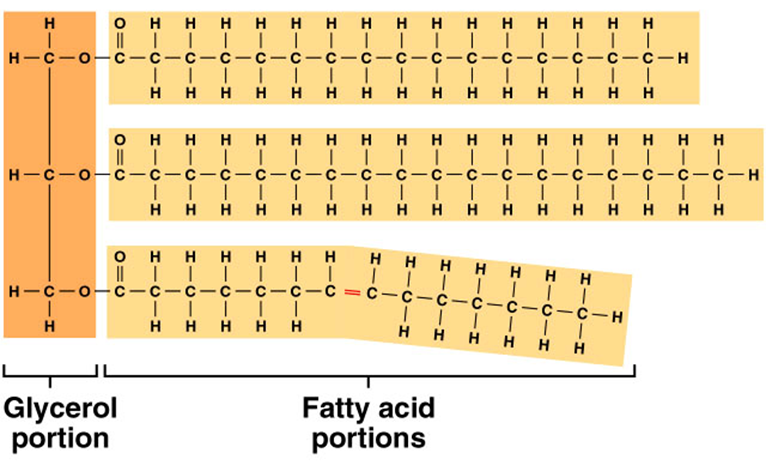
lipids (organic)
soluble in organic solvents; insoluble in water, used primally for energy. most common lipid in the body contains C, H, and O but less O than carbohydrates (C57H110O6), building blocks are 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids per molecules, saturated and unsaturated
phospholipids (organic lipids)
building blocks are 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and 1 phosphate per molecule, hydrophilic, and hydrophobic, major component of cell membranes
steroid (organic lipids)
four connected rings of carbon widely distributed in the body, various functions, component of the cell membrane, used to synthesis hormones, cholesterol
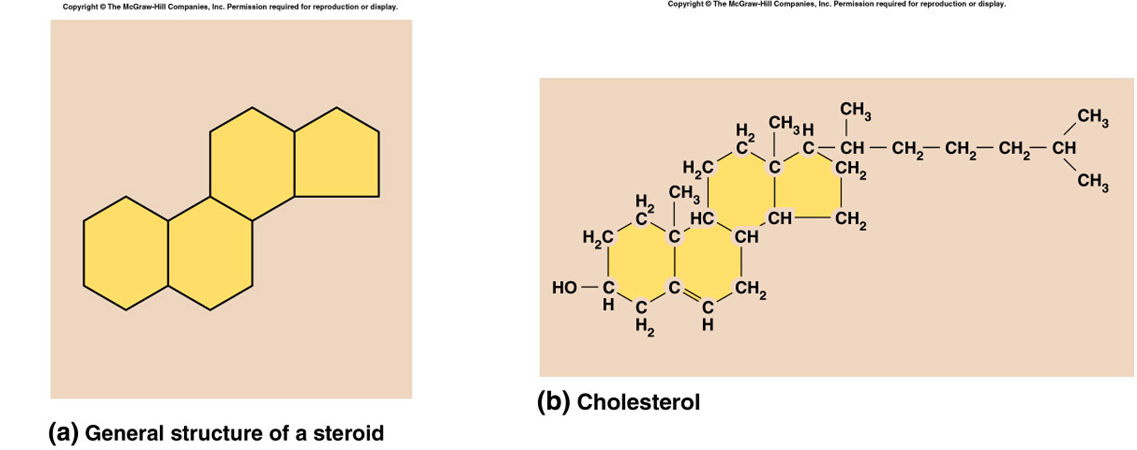
proteins (organic)
structural material, energy source, hormones, receptors, enzymes, antibodies, building blocks are amino acids
amino acids are held together by what
peptide bonds
proteins structure
primary structure, 2. secondary structure, 3. tertiary structure, 4. quaternary structure
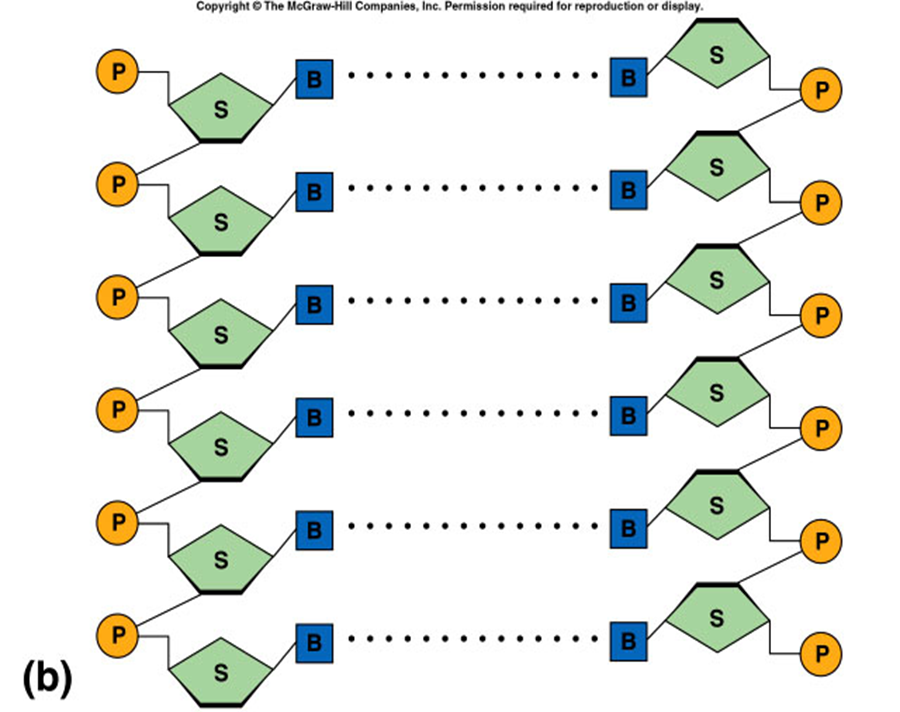
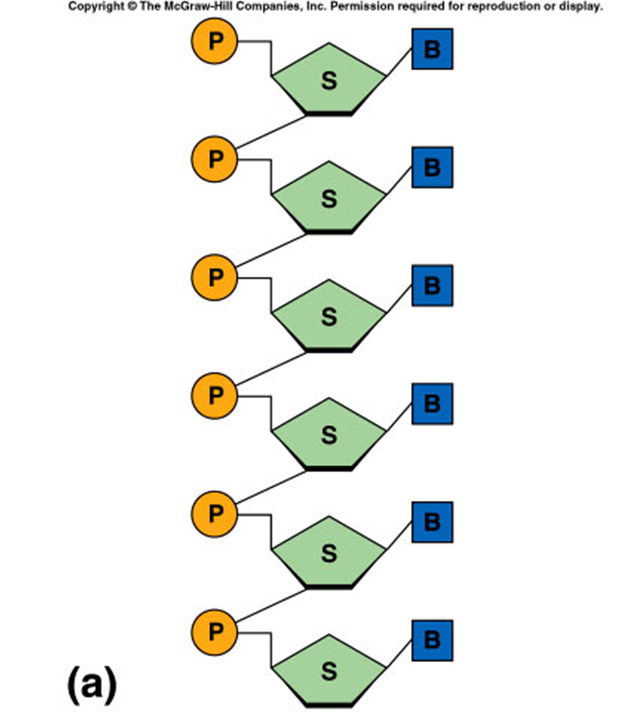
nucleic acids (organic)
carry genes, encode amino acid sequences of proteins, building blocks are nucleotides
DNA
double polynucleotide
RNA
single polynucleotide
nitrogenous bases
Adenine pairs with thymine
cytosine pairs with Guanine