Exam 4 review
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Muscle Tissue
Cells Specialized for contraction
Skeletal muscles move body by pulling on bones
Cardiac and smooth muscles control movements Inside body
Common properties of Muscle tissues
Excitability (Responsiveness)
Contractility (Ability of cells to shorten)
Extensibility (Stretching)
Elasticity (Recoil)
Functions of skeletal muscles
Producing movement
Maintaining posture and body position
Supporting soft tissues
Guarding body entrances and exits
Maintaining boy temperature
Storing nutrients
Skeletal muscles contain
Skeletal muscle tissue
Connective tissues
Blood vessels
Nerves
What are the three layers of connective tissue Skeletal muscles have?
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
Epimysium
Layer of collagen fibers that surrounds the muscle
Connected to deep fascia
Separates muscle from surrounding tissues
Perimysium
Surrounds muscle fiber bundles (fscicles)
Contains
Collagen fibers
Elastic fibers
Blood Vessels Nerves
Endomysium
Surrounds individual muscle cells (muscle fibers)
Contains
Capillary networks
Myosatellite cells (stem cells) that repair damage
Nerve fibers
Irregular Bones
Complex shapes with short, flat, notched or ridged surfaces. The vertebrae that form the spinal column, the bones of the pelvis, and several bones in the skull are examples of irregular bones.
Short Bones
Boxlike in appearance. Examples of short bones include the carpal bones (wrists) and tarsal bones (ankles)
Flat Bones
Have thin, parallel surfaces. Flat bones form the roof of the skull, the sternum (breastbone), the ribs, and the scapulae (shoulder blades). They protect the underlying soft tissues and offer an extensive surface area for the attachment of skeletal muscles.
Long Bones
Relatively long and slender. They are located in the arm and forearms, thigh and leg, palms, soles, fingers and toes. The femur, the long bone of the thigh, is the largest and heaviest bone in the body.
Structure of a long bone
Diaphysis
Epiphysis
Metaphysis
Diaphysis (shaft)
Wall of compact bone
The central space is called the medullary cavity (marrow cavity)
Epiphysis (wide part at each end)
Mostly spongy bone (trabecular bone)
Metaphysis
Where diaphysis and epiphysis mee
Structure of flat bones
For example, parietal bones of the skull
consist of spongy bone between two layers of compact bone (cortex)
Within the cranium, the layer of spongy bone is called diplo
Characteristics of Bone
Dense matrix due to deposits of calcium salts
Osteocytes (bone cells) within lacunae are organized around blood vessels
Canaliculi
Periosteum
Canaliculi
Narrow passageways that allow for exchange of nutrients, wastes, and gases
Periosteum
Covers outer surfaces of bones (except at joints)
Consists of outer fibrous and inner cellular layers
Membrane that cover outside of bones
Except within joint cavities
Outer, fibrous layer and inner, cellular layer
Fibers are interwoven with those of tendons
Perforating fibers
Fibers that become incorporated into bone tissue
Increase strenght of attachements
Four types of Bone Cells
Osteogenic cells
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes
Osteoclasts
Osteogenic cells (osteoprogenitor cells)
Mesenchymal cells that divide to produce osteoblasts
Located in inner cellular layer of periosteum and in endosteum
Asist in fracture repair
Osteoblasts
Immature cells that produce new bone matrix during osteogenesis (ossification)
Osteoid - matrix produced by osteoblasts that has not yet become calcified
Osteoblasts surrounded by bone matrix become osteocytes
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that do not divide
Live in lacunae between layers of matrix
Have cytoplasmic extensions that pass through canaliculi
Two major functions
Maintain protein and mineral content of matrix
Help repair damaged bone
Osteoclasts
Absorb and remove bone matrix
Large, multinucleate cells
Secreted acids and protein-digesting enzymes
Dissolve bone matrix and release stored minerals
This osteolysis is important in homeostasis
Derived from the same stem cells that produce monocytes and macrophages
Functions of periosteum
Isolates bone from surrounding tissues
Provides a route for blood vessels and nerves
Participates in bone growth and repair
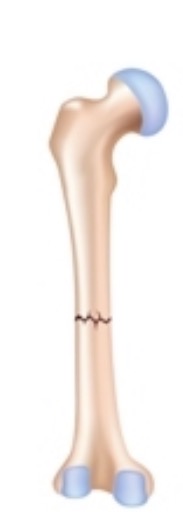
Transverse
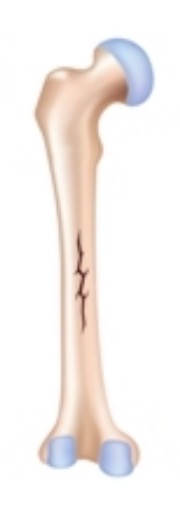
Linear
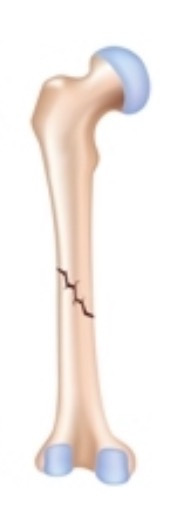
Oblique, nondisplaced

Obilque, displaced
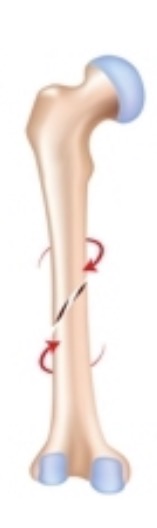
Spiral
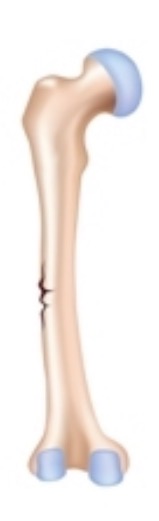
Greenstick

Comminuted
Are Skeletal Muscle Involuntary and Voluntary?
Voluntary
What type of Appearance does Cardiac and Skeletal Muslce has?
Straited Muscle
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
Surrounds the sarcoplasm (cytoplasm of a muscle fiber)
A sudden change in membrane potential initiates a contraction
Myofibrils
Lengthwise subdivisions within a muscle fiber
Responsible for muscle contraction
Made of bundles of protein filaments (myofilaments)
Two types of myofilaments
Thin Filaments
Thick Filaments
Thin Filaments
Composed primarily of actin
contains F-actin, nebulin, tropomyosin, and troponin proteins
Filamentous actin (F-actin)
Twisted strand composed of two rows of globular G-actin molecules
Active sites on G-actin bind to myosin
Nebulin
Holds the F-actin strand together
Tropomyosin
Troponin
Thick Filament
Composed primarily of myosin
Each contains about 300 myosin molecules
Each myosin molecule consists of
Tail
Binds to other myosin molecules
Head
Made of two globular protein subunits
Projects toward nearest thin filament
Core of titin recoils after stretching
Sarcomeres
The smallest functional units of a muscle fiber
Interactions between filaments produce contraction
Arrangement of filaments accounts for the striated pattern of myofibrils
Dark bands (A bands )
Light bands (I bands)
A band
M line
H band
Zone of overlap
M line
In center of A band
Proteins stabilize positions of thick filaments
I band
Contains thin filaments but no thick filaments
Z lines
Titin
Tropomyosin
Covers active sites on G-actin
Prevents actin-myosin interaction
Troponin
A globular protein
Binds tropomyosin, G-actin, and Ca2+
Sliding-filament theory
During a contraction:
H bands and I bands narrow
Zones of overlap widen
Z lines move closer together
The width of the A band remains constant
Thus, thin filaments must slide toward the center of sarcomere
Isotonic Contractions
Skeletal muscle changes length
Resulting in motion
Isotonic concentric contraction
Muscle tension > load (resistance)
Muscle shortens
Isotonic eccentric contraction
Muscle tension < load
Muscle elongates
Isometric Contractions
Skeletal muscle develops tension that never exceeds the load
Muscle does not change length
Cardiac Muscle Cells
Found only in the heart
Have excitable membranes
Striated like skeletal muscle cells
Structural characteristics of cardiac muscle tissue
Are small
Are typically branched with a single nucleus
Have short, wide T tubules
No triads
Have SR with no terminal cisternae
Are almost totally dependent on aerobic metabolism
Contain lots of myoglobin, many mitochondria
Contact each other via interclated discs
Intercalated discs
Specialized connections
Join sarcolemmas of adjacent cardiac muscle cells by gap junctions and desmosomes
Functions include:
Stabilizing positions of adjacent cells
Maintaining the three-dimensional structure of tissue
Allowing ions to move from one cell to another
So cardiac muscle cells beat in rhythm
Functional characteristics of cardiac muscle
Automaticity
Contraction without neural stimulation
Controlled by pacemaker cells
Nervous system can alter pace and tension of contractions
Contractions last 10 times longer than those in skeletal muscle, and the refractory periods are longer
Wave summation and tetanic contractions are prevented due to special properties of sarcolemma
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Integumentary system
Arrector Pili muscles erect hairs
Cardiovascular and respiratory systems
Regulates blood pressure and airflow
Digestive and urinary systems
Forms sphincters
Moves materials along and out of the body
Reproductive system
Transports gametes and expels fetus
Structural characteristics of smooth muscle
Long, slender, spindle-shaped cells
– Single, central nucleus
– No T-tubules, myofibrils, or sarcomeres
• Non-striated muscle
– Scattered thick filaments with many myosin heads
– Thin filaments attached to dense bodies
• Dense bodies connect adjacent cells, transmitting contractions
– No tendons or aponeuroses
Functional characteristics of smooth muscle tissue
• Excitation–contraction coupling
• Length–tension relationships
• Control of contractions
• Smooth muscle tone