Population health and epidemiology EXAM
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Communicable disease
can be spread from person to person
indirect contact
virus/bacteria
noncommunicable disease
cannot be transmitted between people
developed bc of lifestyle factors; set, genetics, enviormental exposure
Social determinants
education, socioeconomic
healthcare, neighborhood
physical enviorment
resources available
SNAP, foodstamps
medicare/medicaid
helplines, support groups
shelters, free clinics
social justice
belief that all people have equal rights, opportunities, and treatment
Morbidity
having a specific illness
mortality
number of deaths a specific illness has caused
prevalance
proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition at a specific time.
incidence
measure of disease that allows us to determine a person's probability of being diagnosed with a disease during a given period
case fatality
The proportion of people who die from a specified disease among all individuals diagnosed with the disease over a certain period.
proportion
The risk of developing a disease during a specified period
It can be used to describe the percentage of a population that has a particular characteristic.
life expectancy
how long someone is expected to life
quality of life
how well someone lives
vital statistics
quantitative data about important life events, such as births, deaths, marriages, and divorces
primary intervention
Implemented before the onset of a health issue
secondary intervention
Focuses on early detection and intervention
tertiary intervention
Addresses existing conditions
cost effectiveness
a way to measure how well resources are used to achieve a desired outcome
HIV
A virus that attacks and destroys the human immune system.
false positive
Incorrectly identifies a trait or characteristic when it does not acutally exist
false negative
Incorrectly identifying the absence of a characteristic or train when it DOES exist
culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
Haly
Health-adjusted life expectancy: This is calculated by subtracting the life expectancy (# of years lived) with disability multiplied by a weighting to represent the effect of the disability
daly
Disability-adjusted life year: DALYs are years in perfect health lost. This measurement is used to determine how a disease or injury affects your length and quality of life in a population
informed consent
An ethical principle requiring that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate.
informed decision
a decision that is based on information not just feelings
socioeconomic status
status in society based on level of education, income, and occupational prestige
Healthy People 2030
a national initiative that sets data-driven objectives to improve health and well-being over the next decade.
It focuses on a wide range of public health issues, including social determinants of health, health disparities, and leading health indicators.
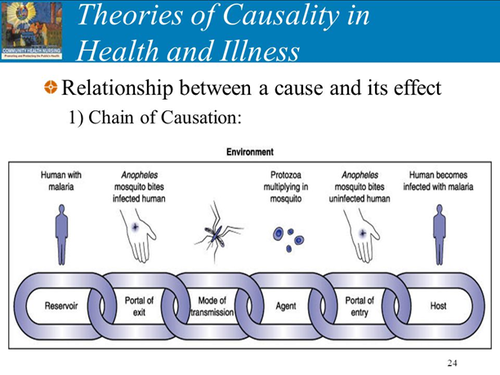
chain model
evidence based data
based on information collected through various research methods which are used to design, implement, and evaluate public health programs and policies.
Evidence-based public health refers to the practice of using the best available scientific evidence to guide public health decision-making and interventions.
17 goals
no poverty
- zero hunger
- good health and well being
- quality education
- gender equality
- clean water and sanitation
- affordable and clean energy
- decent work and economic growth
- industry, innovation, and infrastructure
- reduced inequalities
- sustainable cities and communities
- responsible consumption and production
- climate action
- life below water
- life on land
- peace, justice, strong institutions
- partnerships for the goals
shared decision making
both the patient and physician contribute to the medical decision-making process and agree on treatment decisions.
research study
first step is INFORMED CONSENT
order of research study
Informed Consent
Study Design
Formulation of Research Questions/Hypotheses
Sampling
Data Collection
Data Analysis
Interpretation of Results
Reporting and Dissemination
Ethical Considerations (including follow-up and participant care if needed)
healthcare disparities
differences in the quality and access to healthcare services between groups of people
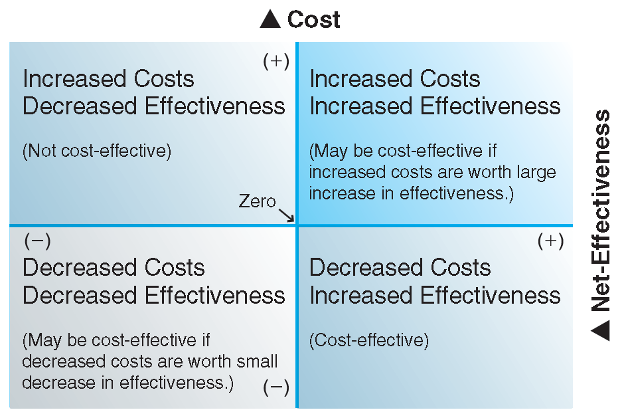
cost net effectiveness
passive immunity
It is temporary immunity that occurs when antibodies are transferred from one person or animal to another. The recipient's immune system doesn't produce its own antibodies; instead, it "receives" them from an outside source.
active immunity
occurs when an individual’s immune system is exposed to a pathogen, either through natural infection or vaccination, and produces a response that includes the production of antibodies and memory cells.
herd immunity
occurs when a large portion of a population becomes immune to a specific infectious disease, either through vaccination or previous infections, making the spread of the disease from person to person less likely