Biology Exam 3
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Kingdom Plantae
Complex, multi-cellular organisms that use photosynthesis to make food.
Sessile
An organism that does not move. It remains attached to one place.
Plants develop from
a protected embryo
Alteration of generation (in plants)
a life cycle that involves a switch between two multicellular stages: the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte
Gametophyte
gamete-producing plant; multicellular haploid phase of a plant life cycle
sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism
Evolution of land plants
- Required adaptations that allowed photosynthetic organisms to move from aquatic to terrestrial environments
- Plants had to adapt to living and reproducing in a dry environment
Formula for photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O + Sunlight --> C6H12O6 + O2
Advantages for land plants
1. More Sunlight
2. More CO2
3. More access to nutrients in the soil
Adaptations of land plants: Roots
Absorbs H2O and nutrients, as well as, anchoring the plant to the ground
Adaptations of land plants: Shoots (stems & leaves)
Absorbs sunlight
Cuticle
A waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves
Adaptations of land plants: Cuticle
Prevents water loss
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move in and out of the plant
Adaptations of land plants: Stomata
Maintains water balance within the plant, as well as, assisting in photosynthesis by exchanging gases
Does CO2 go in or out of a plant?
In
Does O2 go in or out of a plant?
Out
Does H2O go in or out of a plant?
Out
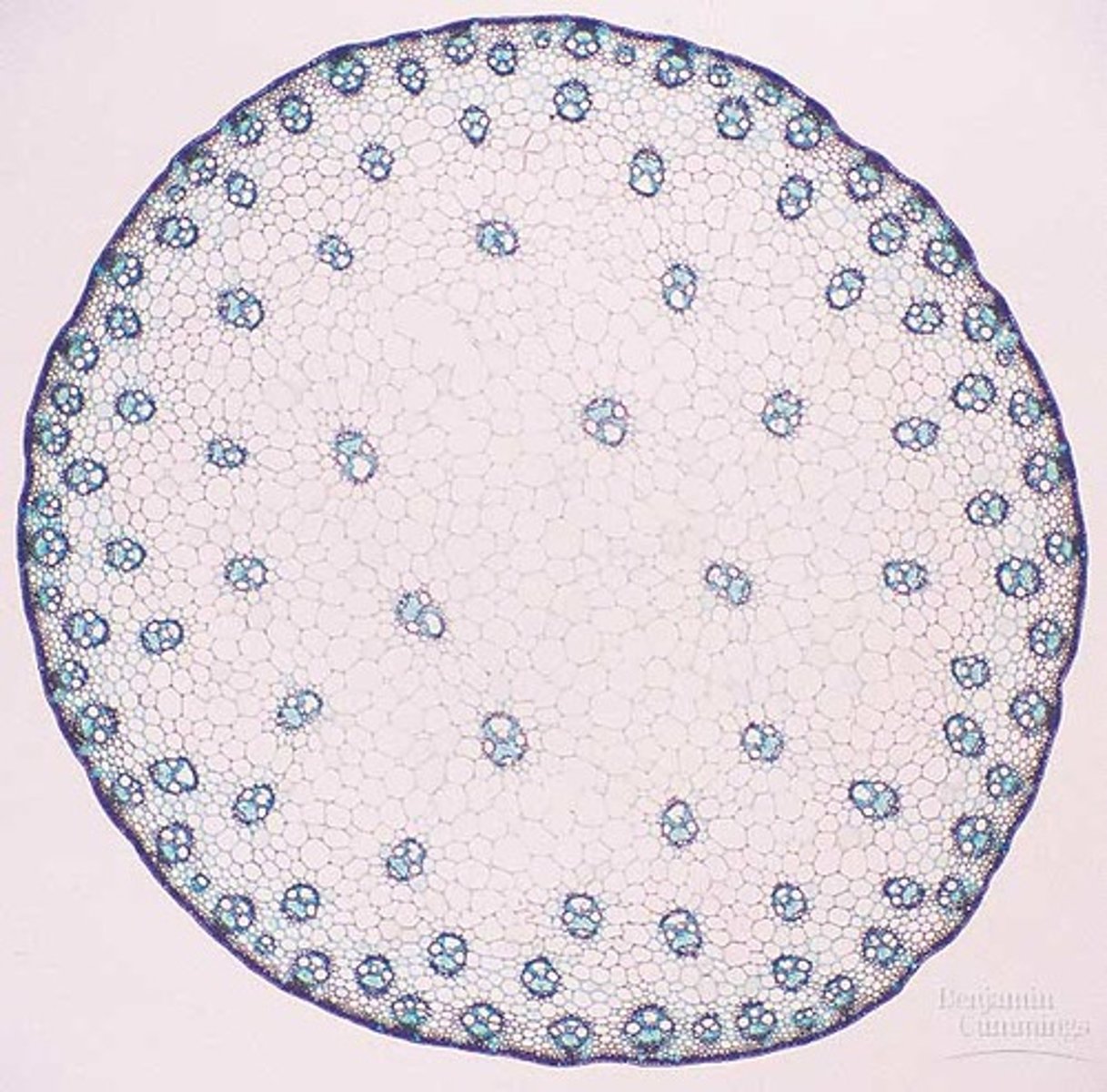
vascular tissue in plants
Made up of xylem and phloem, it transports fluid and nutrients internally
Adaptations of land plants: Vascular tissue in plants
Transports important things like nutrients and fluid (similar to veins)
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
Phloem
the vascular tissue in plants that conducts sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves.
Liginin
Secondary support for the cell wall
Adaptations of land plants: Liginin
Creates support, structure, and strength for the plant
Secondary plant structures
Flowers, fruits, and seeds
The two divisions of kingdom plantae
Bryophytes & Tracheophytes
Bryophytes
nonvascular plants where gametophytes are the dominant stage and sporophyte is retained
Example of Bryophytes
mosses, liverworts, hornworts
What do bryophytes lack?
vascular tissue, lignin, & roots, stems, or leaves
What do bryophytes rely on to transport things?
Diffusion
bryophytes attributes
-less than 1 inch in size; very small
-restricted to watery environments
What do bryophytes need for fertilization?
water; the sperm need to swim
Rhizoids
A thin, rootlike structure that anchors a moss and absorbs water and nutrients.
Why are bryophytes sensitive to pollution?
Because they are very absorptive
the most common bryophytes are
peat moss
peat bog
A wetland area with an accumulation of dead plant material, especially moss. This area is very acidic and doesn't allow many things to grow there.
What can grow in peat bogs
cranberries and blueberries
Tracheophytes
vascular plants where sporophyte is dominant & gametophyte is not retained
What do tracheophytes have?
transport vessels, xylem, phloem, lignin, and roots, stems, & leaves
seedless vascular plants
Plants that have vascular tissue but reproduce by spores (ferns, club mosses, and horsetails)
Rhizomes
horizontal underground stems
Club Mosses (Lycophyta)
the earliest group of seedless vascular plants; tiny scale-like leaves, have rhizomes, resemble tiny pine trees, with sporangia at the base of the leaves, and are typically 8 inches in height
sporangia
multicellular organs that produce spores
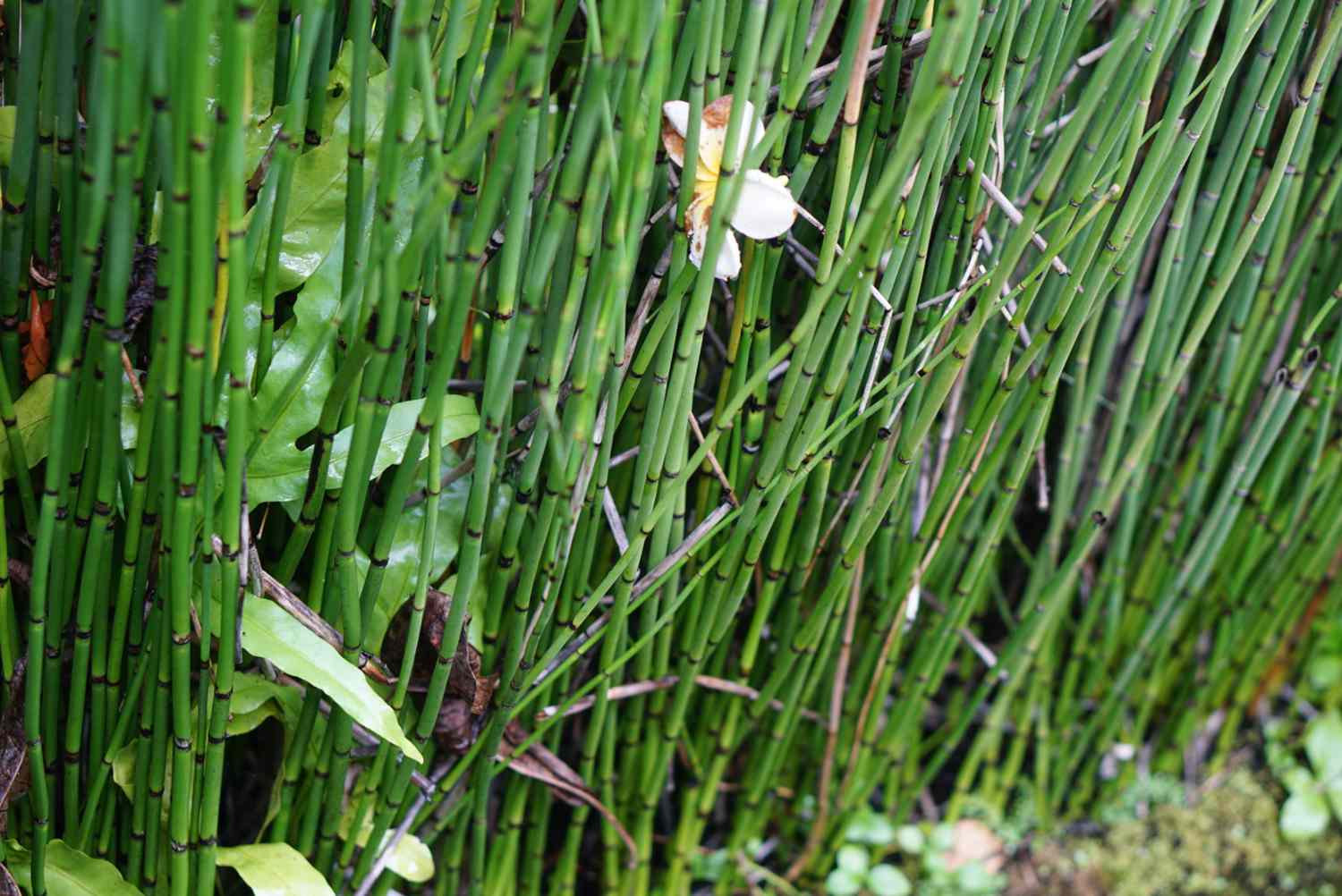

Horsetails (scouring rushes)
less than 3ft tall hollow, ribbed stems that are jointed at nodes. Stems, branches, and leaves are green (photosynthetic) and have rough texture due to silica (SiO2).
strobilus
The technical term for a cluster of sporophylls known commonly as a cone, found in most gymnosperms and some seedless vascular plants.
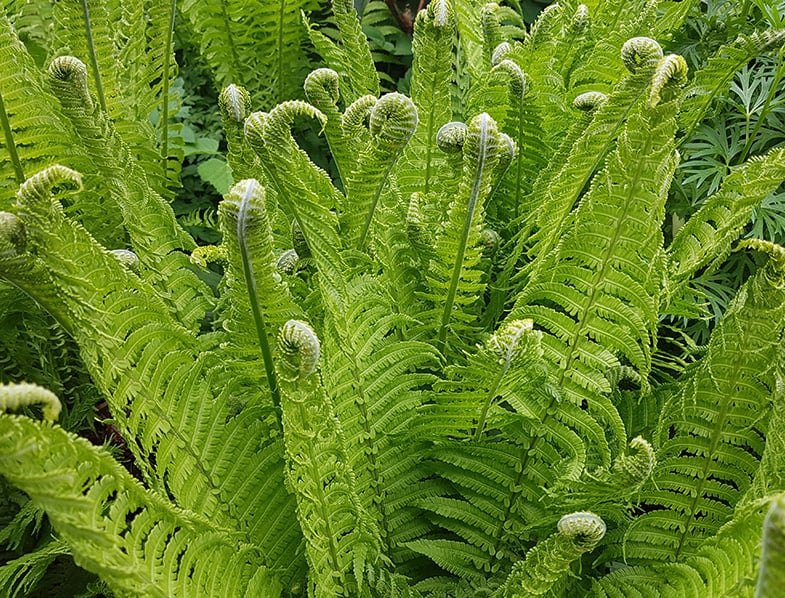

Ferns
Any of numerous flowerless, seedless vascular plants having roots, stems, and fronds and reproducing by spores.
What is the only seedless plant to have big broad leaves?
Ferns
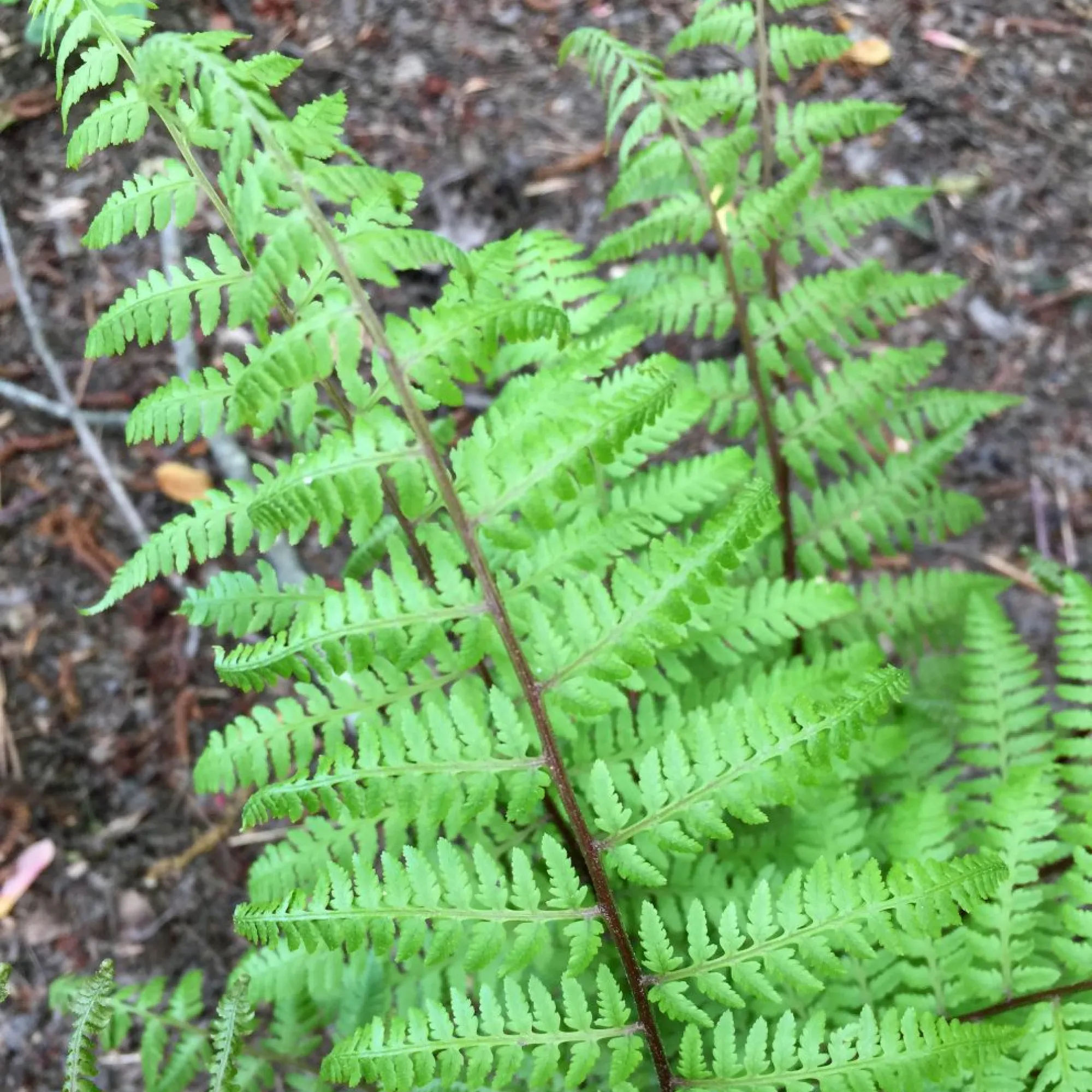

Frond
The leaf of a fern plant
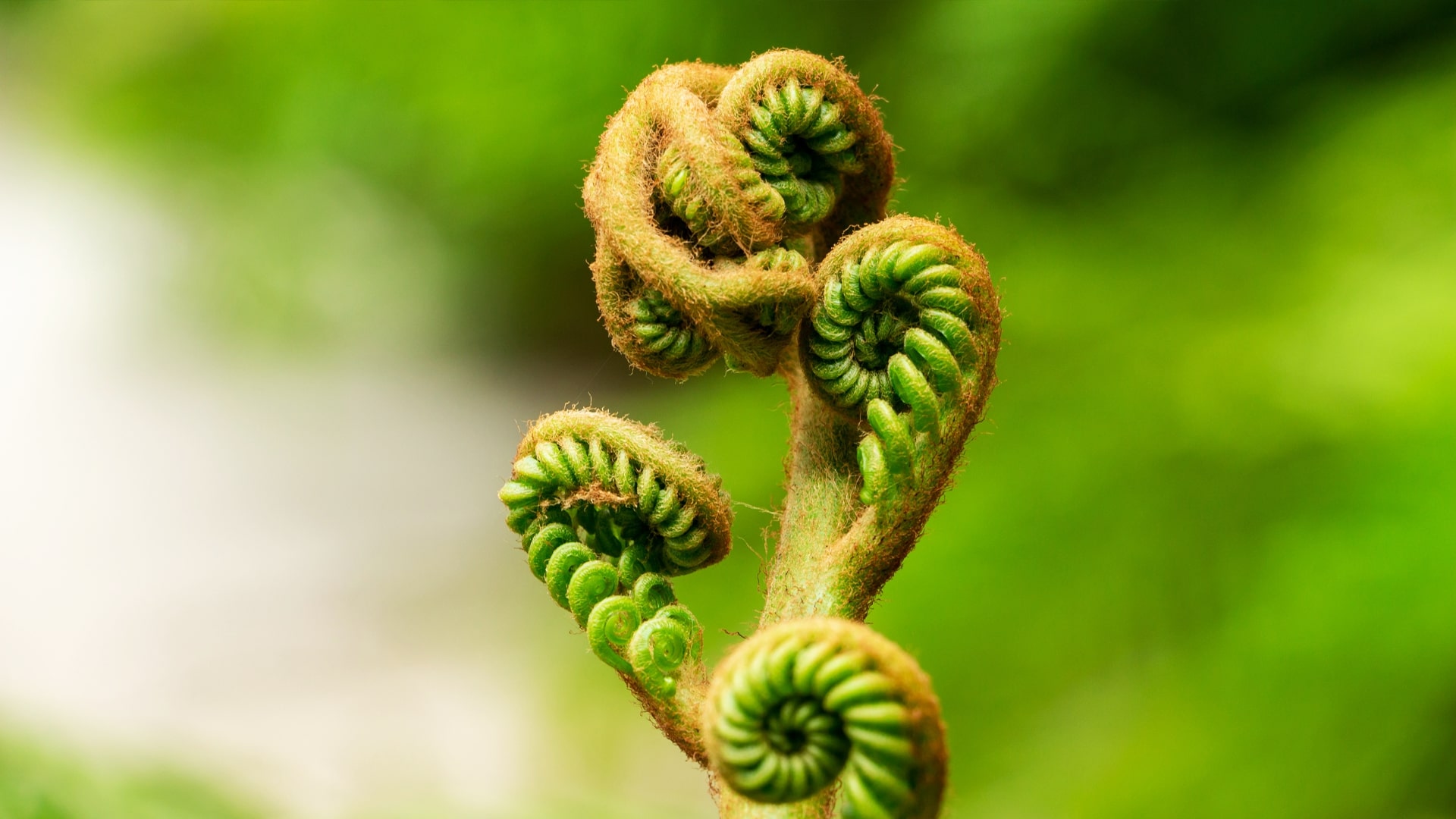

Fiddlehead
tightly coiled new leaves of ferns
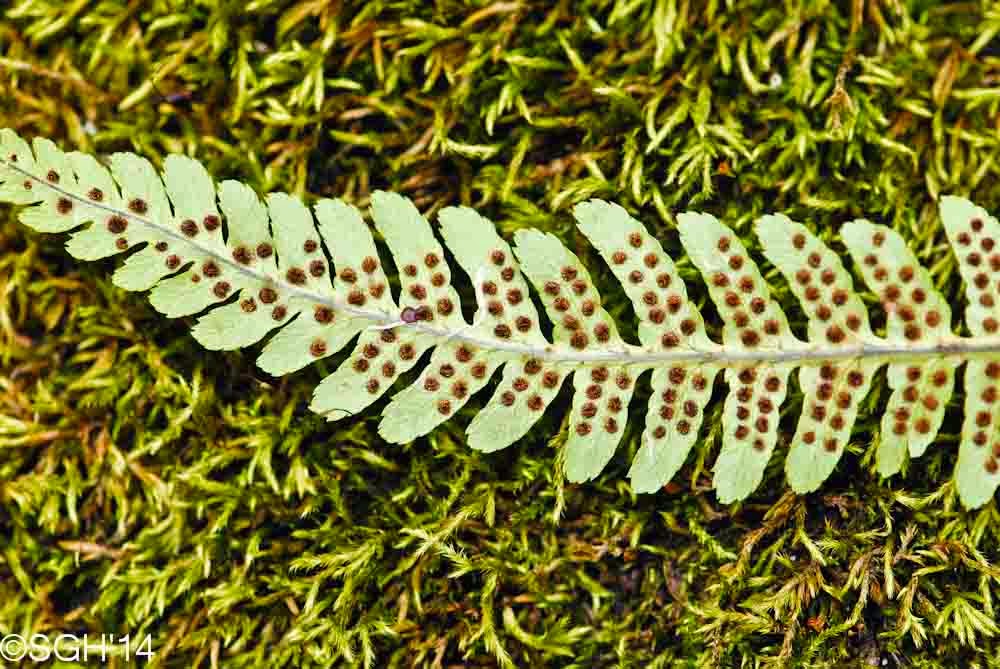

Sori
raised spots located on the underside of sporophyte ferns, clusters of sporangia
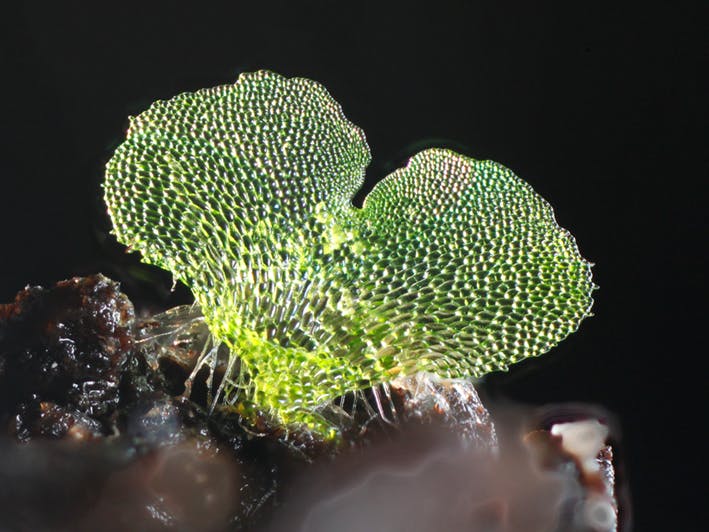

What shape is a ferns gametophyte?
A very distinguished heart shape
Epiphyte
a plant that uses another plant for support, but not for nourishment
What do all seedless vascular plants have?
Rhizomes
seed plants
vascular plants that produce seeds
Which of these two are most successful, seedless plants or seed plants?
Seed plants
Why are seed plants most successful
because they have seeds and pollen that they use for reproduction
Pollen
(male) A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants
Seed
(female) plant embryo and a food supply encased in a protective covering
Seed coat
A tough outer covering of a seed, formed from the outer coat of an ovule.
Gymnosperms
A plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than seeds enclosed in fruits; Non-flowering plants
Conifers
cone bearing trees
Conifers examples
pines, firs, spruces, junipers, redwood, hemlock, cyprus
Evergreen
a tree that does not lose its leaves in the winter and stays green all year round
Conifers are adapted to
cold and dry weather
Conifers reproductive cycle
Conifer reproduction is a simple process of wind pollination where male cones release pollen, which travels on the wind to female cones. Once inside the female cone, the pollen fertilizes the ovules (immature seeds).
male cones are
small; it holds pollen & later disintegrates
female cones are
your typical large pine cone
Cycads
Gymnosperms that grow in tropical or subtropical areas; look like palm trees with cones
Cycads example
Sago Palms (toxic)
cycads male
a tight cone
Cycads female
"fluffy"/leafy and has seeds
Strobilus
a compact cluster of spore-bearing structures
dioecious
Having male and female reproductive organs in separate plants or animals
monoecious
having male and female reproductive organs in the same plant or animal
Ginkgo
a long-lived, disease-resistant, dioecious tree with unique fan-shaped leaves, capable of clonal reproduction, and known for its striking yellow autumn foliage and resilience in disturbed environments
Ginkgoes are cultivated in Asia for
their medicinal properties and for ornamental purposes
Why are ginkgos planted in cities?
They are seen as beautiful and are resistant to pollution and insects
The female ginkgoes produce a
vomit/stinky smelling fleshy looking seed
Gnetophytes
Live in hot deserts and tropical rain forests; can be a tree, vine, or shrub
Gnetophytes example
Ephedra Plant- used for weight loss
Angiosperms
A flowering plant which forms seeds inside a protective chamber called an ovary.
Angiosperm adaptations: Flowers
Purpose: Hold the reproductive structure; to increase pollination increase fertilization
Angiosperm adaptations: Fruit
Seed bearing organ of the plant; Purpose: seed dispersal
Angiosperm adaptations: Broad leaves
Purpose: to increase photosynthesis
Pollination syndrome
a set of flower characteristics associated with a particular type of pollinator; how pollen is spread
pollination syndrome: birds
usually tube shaped red flowers w/ little or no fragrance & lots of nectar
Pollination Syndrome- Bees
bright yellow or blue flowers w/ nectar spurs and landing platforms (don't see red)
Pollination syndrome: bat
large, dull-colored, night-blooming flowers that offer abundant nectar
Pollination syndrome: wind
Forgo color and often have no petals, but dangle for maximum wind pick up (grass)
Pollination syndrome: fly
Have strong, bad odors- red/pink coloration
decidous
A plant that sheds its leaves during a particular season and goes dormant for a short time period annually
Angiosperms defense mechanisms
Prickles, briars, and toxins
How many groups of angiosperms are there?
Three
Magnoliids
share some traits with basal angiosperms but are more closely related to monocots and eudicots; Magnolia, avocado, & black pepper
Monocots examples
lilies, grasses, orchids, palms, grain
Dicots examples
roses, clover, tomatoes, oaks, daisies; most flowering tree, shrubs, and herbaceous plants
Parts of monocots: Flower
Petals in parts of threes; 3, 6, 9...

Parts of monocots: Leaf
blades that are long and slender

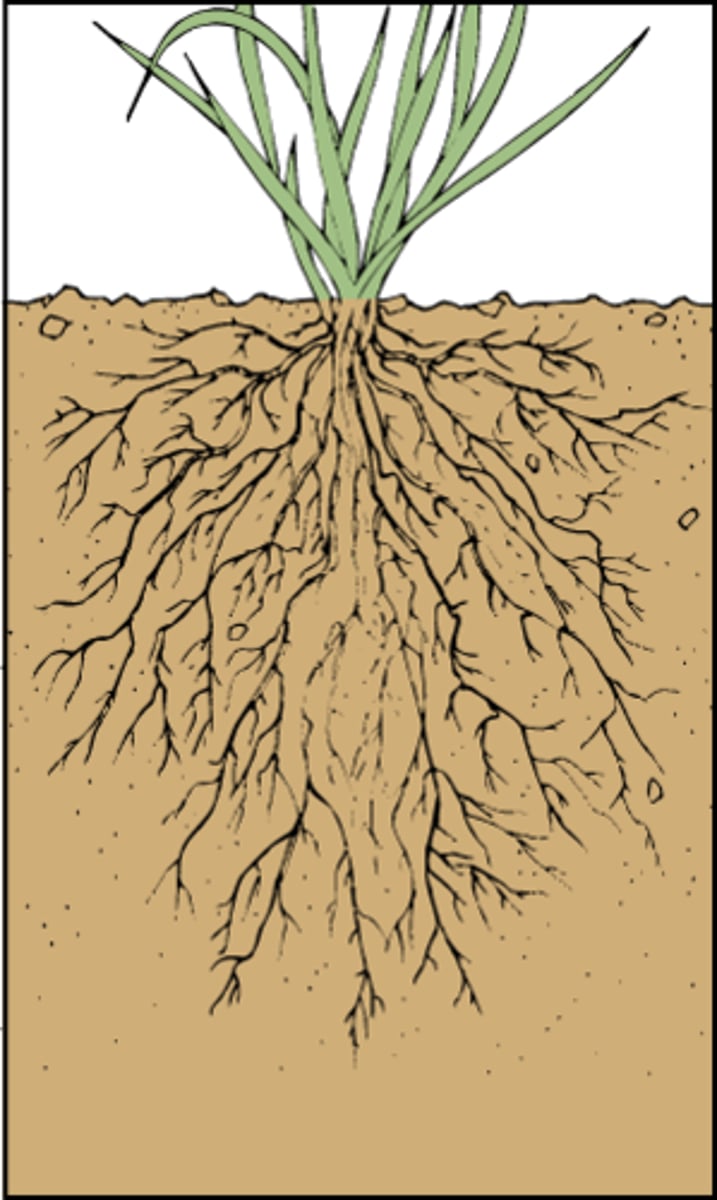
Parts of monocots: Roots
Fibrous root system, all the same size
Parts of monocots: Stem
Vascular bundles throughout