HLS histology 2 : Hematopoiesis II
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
The growth factor that produced by cells in the kidneys and stimulates production of mRNA for globins is ….
The glycoprotein erythropoietin
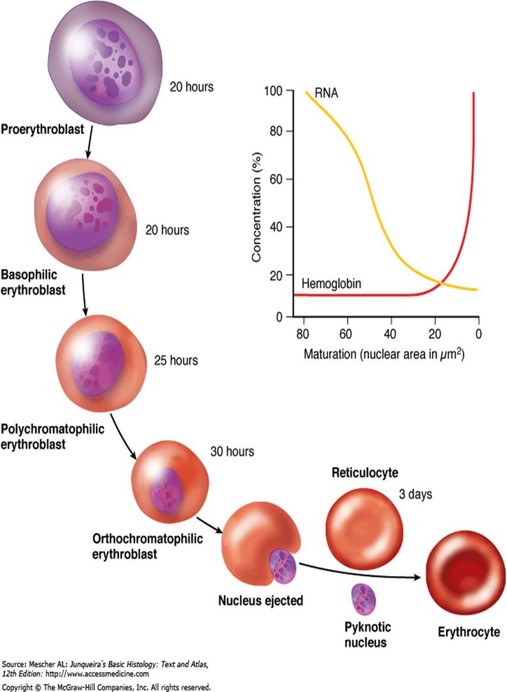
stages of Erythropoiesis?
1-Pluripotential stem cell ——> myeloid multipotential
2-Erythrocyte colony forming unit (CFU-E) (progenitor)
3-Pro-erythroblast
4-Basophilic erythroblast
5-Polychromatophilic erythroblast
6-Orthochromatophilic erythroblast (normoblast)
7-Reticulocyte
in erythropoiesis , the cytoplasm is deeply basophilic in …..
Basophilic erythroblast
in erythropoiesis , the cytoplasm shows areas of acidophilia and basophilia in …
Polychromatophilic erythroblast
(T/F)
in the cytoplasm of orthochromatophilic erythroblast (normoblast) there is no ribosomes and polyribosomes
false
The cytoplasm of orthochromatophilic erythroblast contains ribosomes and polyribosomes.
in erythropoiesis ,The nucleus condensed pyknotic and extruded peripherally in…
Orthochromatophilic erythroblast
(T/F)
Reticulocyte is non-nucleated immature erythrocyte.
True
Reticulocyte is stained with…
Brilliant cresyl blue
In erythropoiesis , what changes will happen to the following:
1- cells size
2- nucleus
3- ribosomes and polysomes
4- hemoglobin
5- Mitochondria and other cell organelles
1) The cell size becomes smaller
2) The nucleus becomes smaller, condensed, pyknotic and finally extruded from the cell
3) Decrease in free ribosomes and polysomes (decrease of basophilia)
4) increase of hemoglobin (increased acidophilia)
5) Mitochondria and other cell organelles gradually disappear
shape of the nucleus in megakaryoblast …
large kidney-shaped nucleus with numerous nucleoli
The characteristic of megakaryoblast nucleus is…
- polyploidy nucleus [multiple sets of haploid number (23 chromosomes)
- endomitosis (multiple nuclear divisions without separation)
(T/F)
Both megakaryocyte and megakaryoblast have basophilic cytoplasm
True
shape of the nucleus in megakaryocyte …
Irregular lobulated nucleus with coarse chromatin
The process of Megakaryopoiesis is driven by …. hormone
Thrombopoietin
Platelets originate by …..
Fragmentation of cytoplasm of mature megakaryocytes
Whole process :
With maturation of megakaryocytes, they extend several long, wide branching processes called proplatelets These cellular extensions penetrate the sinusoidal endothelium and are exposed in the circulating blood of the sinusoids.
Numerous demarcation channels formed throughout the cytoplasm (fracture lines) for the release of platelets
Platelets originate by fragmentation of cytoplasm of mature megakaryocytes and the remainder of cells degenerated and phagocytosed by macrophages.
stages of Granulopoiesis?
1-Pluripotential stem cell ——> myeloid multipotential
2-Granulocyte colony forming unit (CFU-G)
3- Myeloblast
4- Promyelocyte
5- Myelocyte
6-Metamyelocyte
initial production of specific granules occur in which stage of granulopoiesis?
the myelocyte stage
intermediate stage Before granulocytes complete its maturation called,,,
the band cell
stages of monocytopoiesis?
1- Pluripotential hematopoietic stem cell ——> myeloid multipotential stem cell
2- Colony forming unit of monocyte (CFU-M) (M-CSF)
3- Monoblasts: identical to the myeloblast morphologically
4- Promonocytes: a large cell with basophilic cytoplasm and a large, slightly indented nucleus
5- Monocytes: circulate for three days then enter C.T and become macrophages.