DNA transcription
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
the process by which a sequence of DNA nucleotides is used as a template for the synthesis of an RNA molecule
what is transcription?
messenger RNA
transfer RNA
ribosomal RNA
noncoding RNA
what are the major RNA molecules?
to encode the amino sequences of polypeptides
what is the function of mRNA?
read the mRNA and transfer the appropriate amino acid to the polypeptide chain
function of tRNA
forms ribosomes which read mRNA to make proteins
what does rRNA do?
everything
how much of the chromosome is transcribed?
catalytic, structural, regulatory
what are the functions of non-coding RNA
the sum of all the RNA molecules produced in a cell
what is a transcriptome?
RNA polymerases
RNA is synthesized by ____
DNA template
RNA synthesis requires a _____
no
does RNA polymerase require a primer
5'-3'
which direction is RNA built in
3'-5'
the DNA template is copied in which direction?
3'-5'
what type of exonuclease proofreading activity does RNA polymerase NOT have
1
which, 1 or 2, is the coding strand?
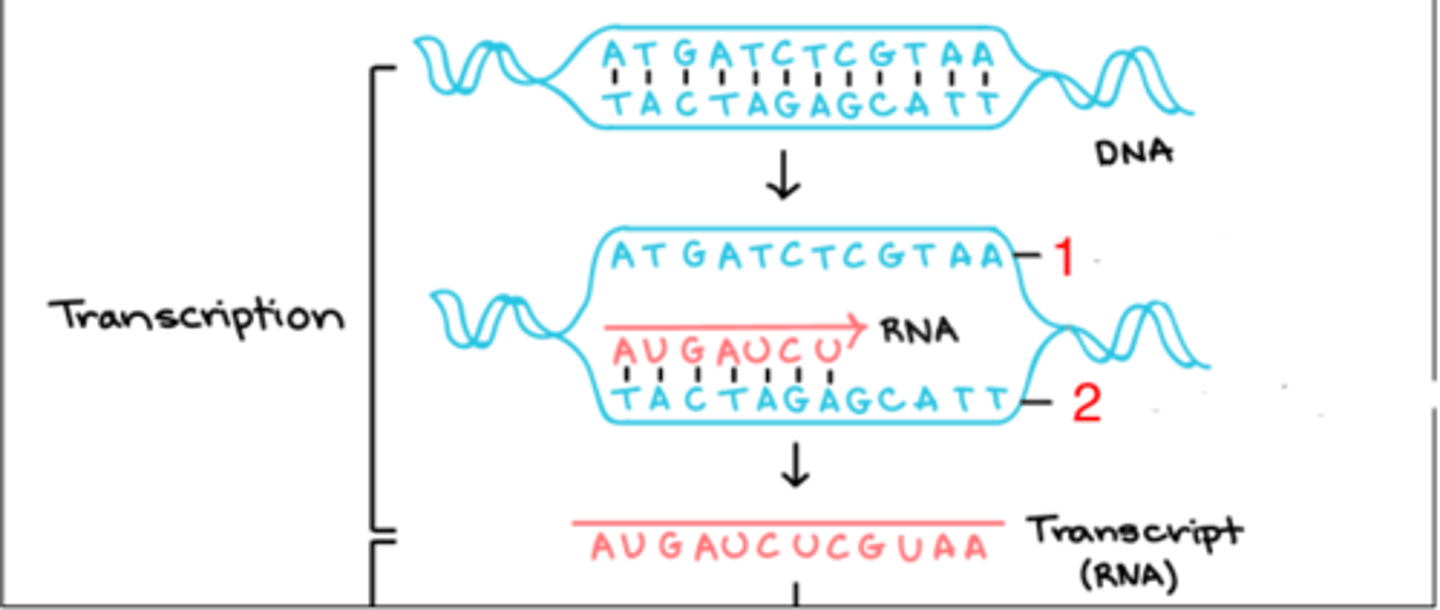
the complementary strand that is identical to the new RNA
what is the coding strand?
2
which is the template strand (1 or 2)?
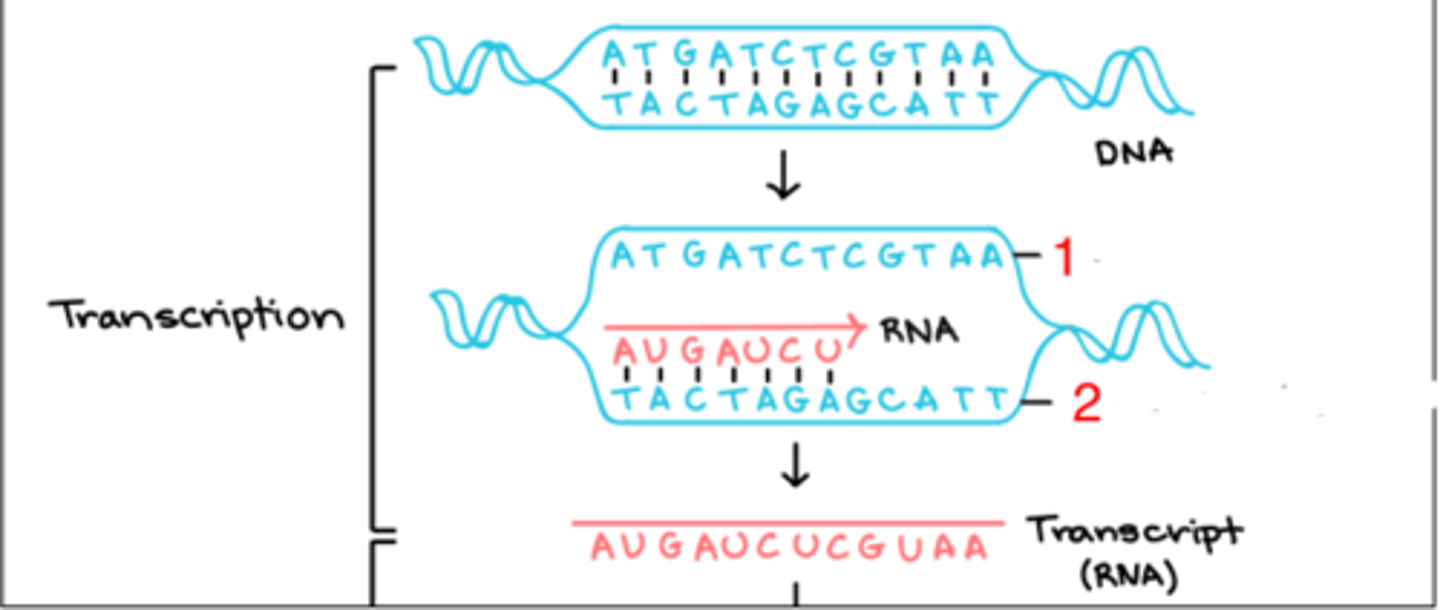
it serves as the template for RNA synthesis
what is the purpose of the template strand?
RNA polymerase, DNA, and transcript (mRNA)
what does the transcription bubble contain?
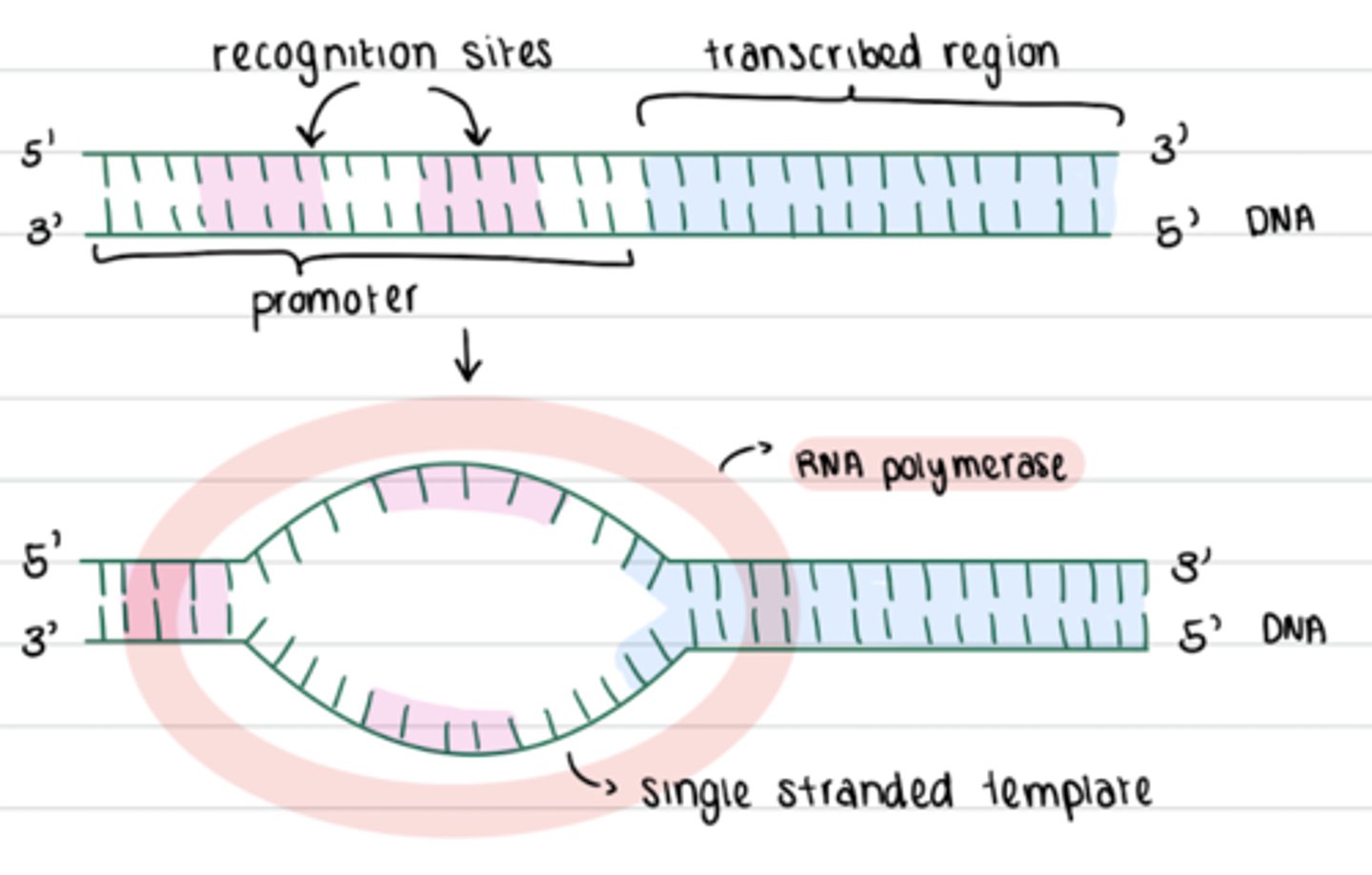
the sequence of DNA needed for the RNA polymerase to recognize the starting point
what is a promoter?
the sequence of the promoter that is common in most DNA and is recognized by the RNA polymerase
what is a consensus sequence?
-10 TATAAT
-35 TTGACA
promoters of prokaryotes
-30 TATAA
+1 Inr
promoters of eukaryotes
initiation
elongation
termination
what are the three transcription stages?
- RNA polymerase recognises and binds to recognition sites of promoter region
- closed complex --> open complex
what happens in initiation
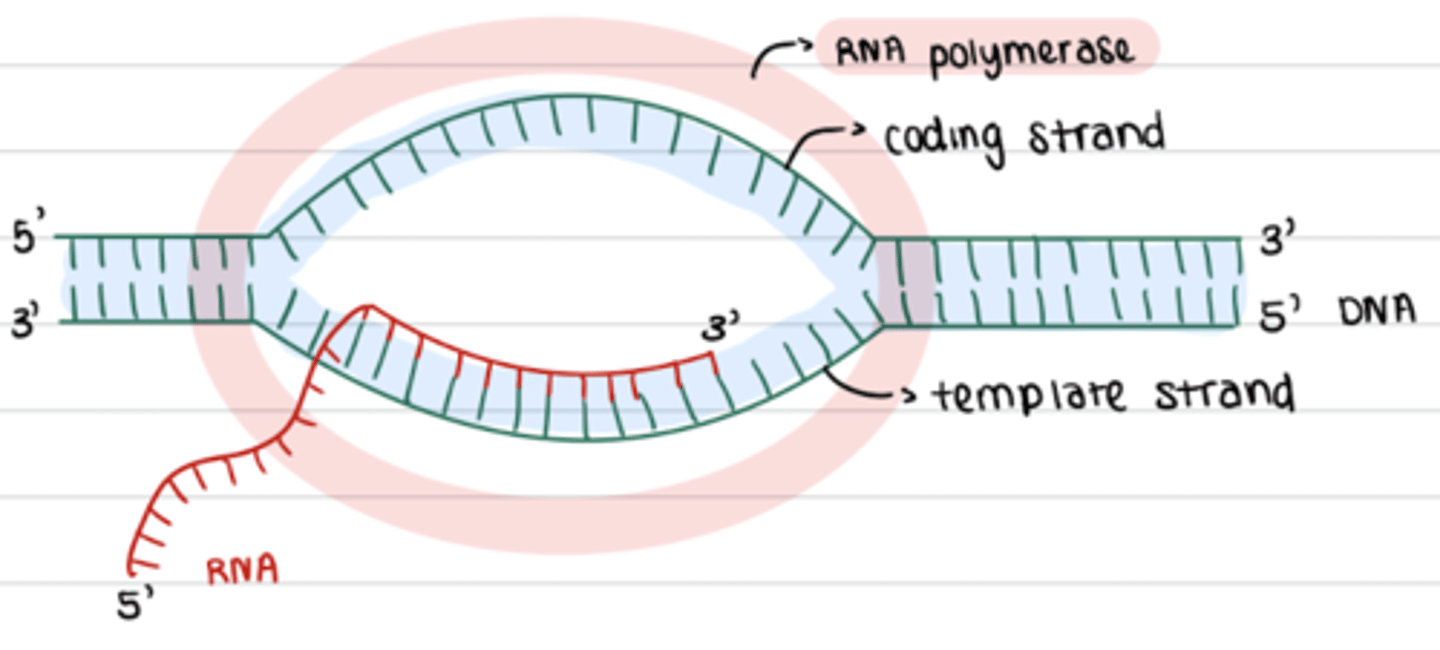
- transcription bubble
- mRNA transcribed
what happens at elongation
- termination sequence in template RNA signals RNA polymerase to end mRNA sequence
- mRNa base pairs with itself forming a loop
Rho independent termination
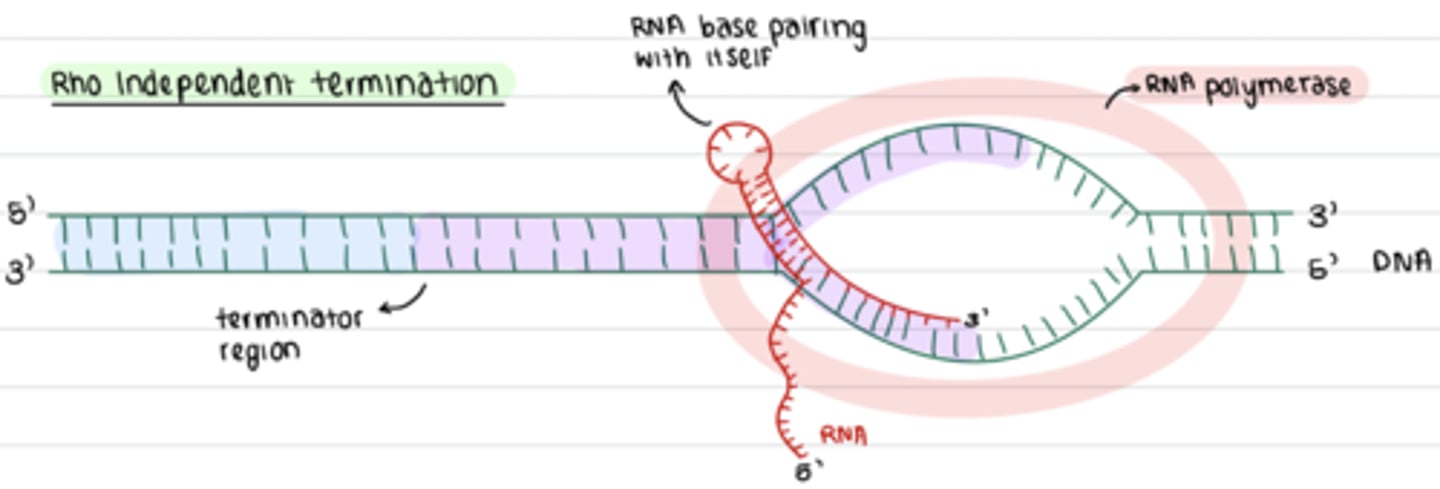
- termination sequence in template RNA signals RNA polymerase to end mRNA sequence
- Rho binds to specific mRNA sequence
- mRNa does not loop around itself
Rho dependent termination

eukaryotic
which, prokaryotic or eukaryotic transcription is more complex?
eukaryotic
which, prokaryotic or eukaryotic transcription has several RNA polymerases?
- necessary for initiation
- recognise specific sites on promoters
transcription factors
pre-mRNA --> mature mRNA
RNA maturation
prokaryotes
mRNA maturation does not occur in ...
5' cap is added
3' poly tail is added
introns are spliced
what occurs during mRNA processing?
eukaryotes
mRNA maturation only occurs in....
protects mRNA from enzymatic destruction
what does the 3' poly tail do?
to protect mRNA from ribonucleases and bind mRNA to ribosome
the function of the 5' cap is....
exon
which, exon or intron, is the coding segment?
both
which, introns or exons, are transcribed by RNA polymerase?
exons
a mature mRNA is only made up of ...
a specific exon may or may not be included into the mature mRNA
allows us to get more than 1 protein from the same gene depending on exons
what does alternative processing mean?
when a gene can give rise to multiple different proteins
what is differential mRNA processing
DNA ligase
after splicing how are exons stuck back together