APES EXAM (ULTIMATE STUDY PACKET)
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
Endangered Species Examples
- Bald Eagle: recovered and removed from list
- Red Wolf: low point was 17 indv
- Cali Condor: most expensive conservation project ever in US
The Greenhouse Effect
warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere by greenhouse gases
Biomes
large regions characterized by distinct climate and organisms, made up of many ecosystems
Ectones
regions where two ecosystems merge
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy (6CO2 + 6H20+Sun => C6-H12-O6+6O2 + energy)
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen
anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen, creates methane gas/ethyl alcohol/acetic acid/hydrogen sulfide
Energy lost per trophic level
90%
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
GPP (gross primary productivity)
rate at which producers convert solar energy to chemicals
NPP (Net Primary Productivity)
GPP - R(respiratory loss)
law of tolerance
Degree to which living organisms are capable of tolerating changes in their environment
limiting factor principle
Too much or too little of any abiotic factor can limit or prevent growth of a population of a species in an ecosystem, even if all other factors are at or near the optimal range of tolerance for the species.
Hydrological Cycle
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Precipitation
- Transpiration (evaporation from plants)
- Infiltration (water into soil)
- Percolation (downward flow of water through soil to aquifers)
- Runoff (downslope water movement to sea)
Photosynthesis (Carbon Cycle)
plants take CO2 and convert to carbohydrates
Respiration (Carbon Cycle)
Consumers breathe, and turn carbohydrates into CO2
Decomp (Carbon Cycle)
Decomposers turn carbohydrates into CO2
Compaction (Carbon Cycle)
biomass is buried and compressed into fossil fuels
Combustion (Carbon Cycle)
fossil fuel biomass is burned, releases CO2
Absorption (Carbon Cycle)
Oceans absorb massive amounts of CO2, convert to Carbonic Acid, lowering their PH
How much of the atmosphere is nitrogen?
78%
Why do bacteria/lightening need to convert Nitrogen gas into other compounds?
So that multicellular organisms can take it in
All compounds in the Nitrogen Cycle (6)
N2 (Nitrogen Gas)
NH3 (Ammonia)
NH4 (Ammonium)
NO3 (Nitrate)
NO2 (Nitrite)
Protein
Nitrogen Fixation (Nitrogen Cycle)
Process of converting nitrogen gas (N2) into ammonia (NH3)
Nitrification (Nitrogen Cycle)
Ammonia ->NO2 (nitrite) -> NO3 (Nitrate) by bacteria
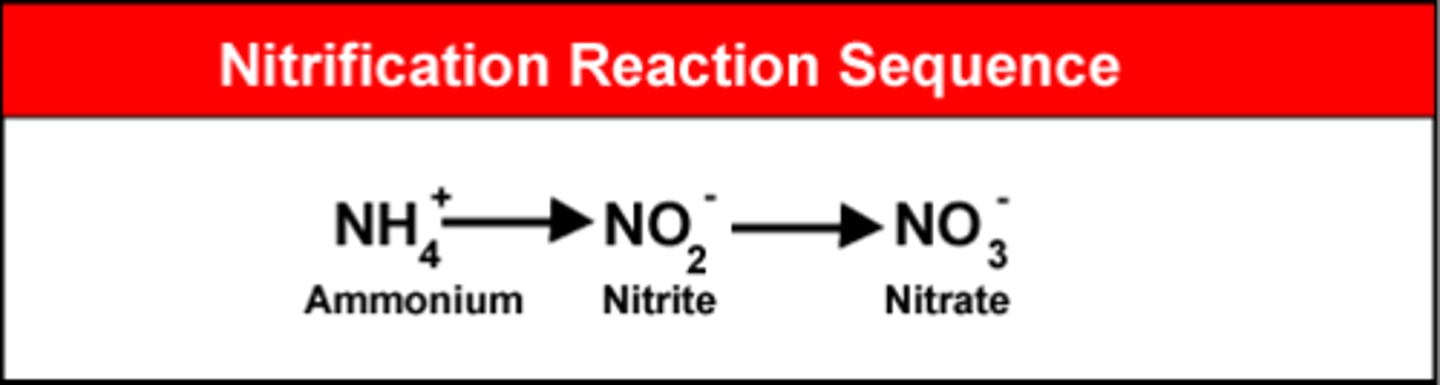
Assimilation (Nitrogen Cycle)
plant roots take up NH3/NH4/NO3, convert into complex organic molecules
Ammonification (Nitrogen Cycle)
Decomposers break down complex organic molecules -> NH3/NH4 (Ammonium)
Denitrification (Nitrogen Cycle)
process by which bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas (N2)
Phosphorus Cycle
- weathering (slow breakdown of terrestrial phosphate)
- runoff (phosphate into aquatic systems through percipitation)
- assimilation (producers take up phosphorus, then consumers eat producers)
- deposition (return of phosphorus to soil through decay)
Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community

Human Intervention in Biogeochemical Cycles
- Withdrawing large amounts of water faster than can be replenished
- runoff of phosphate/nitrogen into water from agriculture
- Clearing vegetation: increases runoff, reduces infiltration, decreases CO2 absorption
- Slash/burn agriculture- reduces phosphate in ecosystem, releases CO2
- Burning fossil fuels
Radiometric Dating
elements emit particles/energy at a consistent, measurable rate called a half life
Biological evolution
change to populations genetic makeup through generations
Process of Evolution
- Mutation of dna
- natural selection
- gene flow (movement of genes between populations)
- genetic drift (fluctuations of gene frequency in gene pool)
Speciation
two spiecies arise from one
species diversity/richness
Number of different species in the biosphere
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Island Biogeography
species diversity of island is determined by the immigration/extinction rate. These are affected by SIZE of island and DISTANCE from mainland. Most optimal is large island near mainland.
generalist species
species with a broad ecological niche
specialist species
species with a narrow ecological niche
indicator species
species that serve as early warnings that an ecosystem is being damaged
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem (normally top predator)
foundation species
key role in shaping ecosystem (ex. beavers)
positive/negative feedback loops
positive loops increase effect, negative keep it in balance
ocean acidification
decreasing pH of ocean waters due to absorption of excess atmospheric CO2 from the burning of fossil fuels
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
resource partitioning
dividing up resources so that they are used at diff times/ways, animals dont want competition
parasitism
One organism benefits and the other is harmed
Mutualsim
relationship where both organisms benefit
commensalism
one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Founder effect
genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area
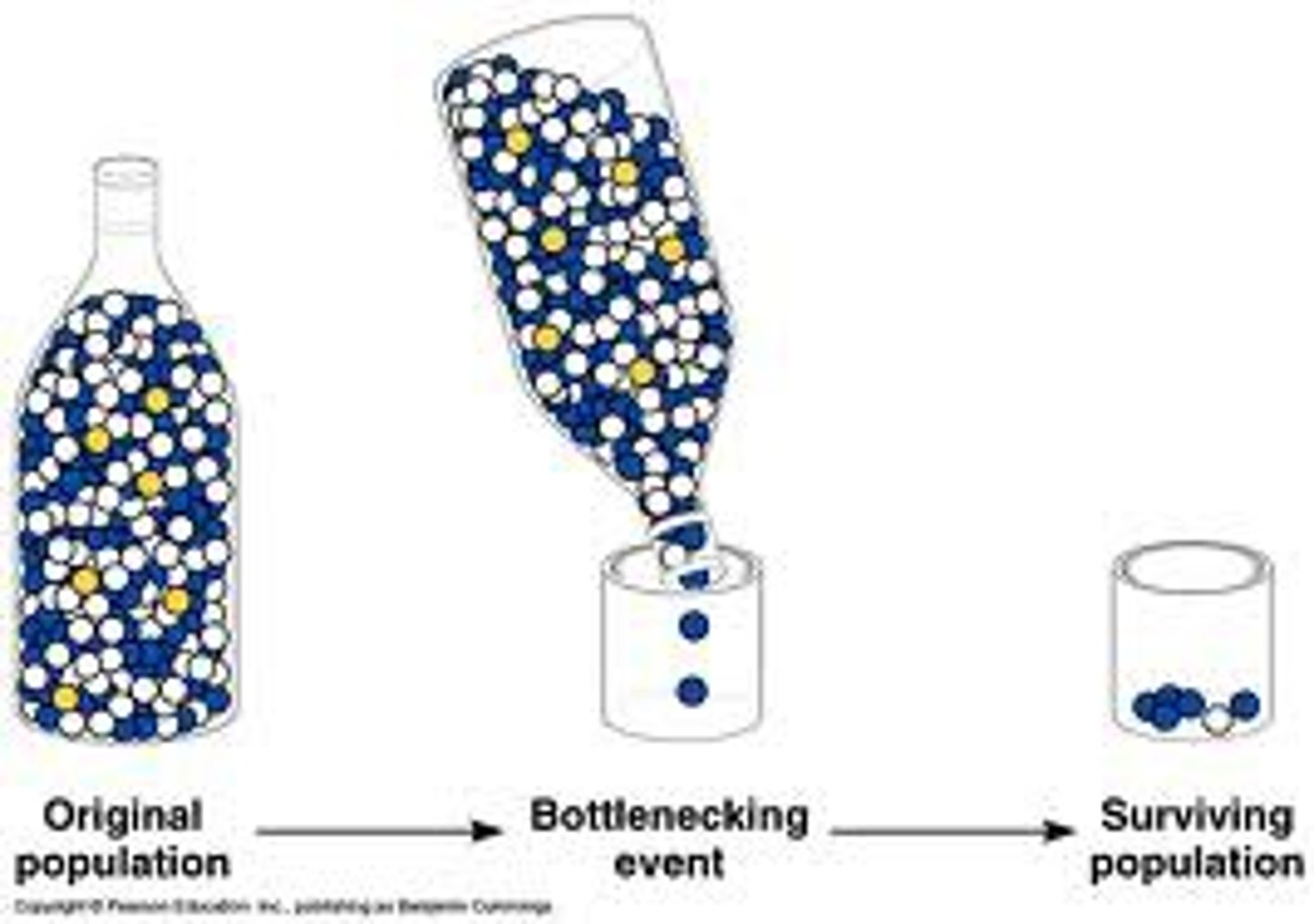
demographic bottleneck
A population founded when just a few members of a species survive a catastrophic event or colonize new habitat geographically isolated from other members of the same species.
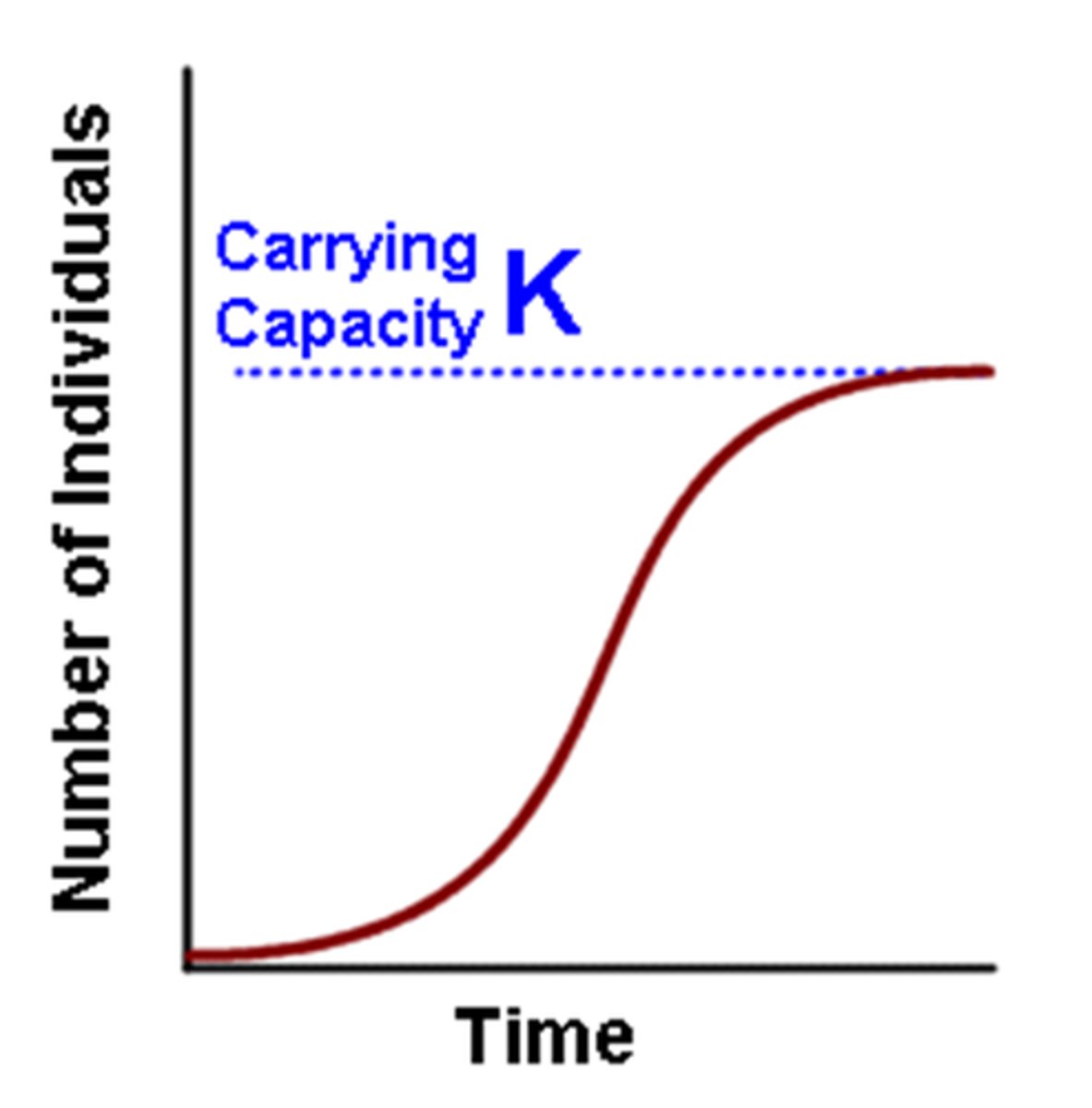
carrying capacity (K)
Maximum population size that a particular environment can support.
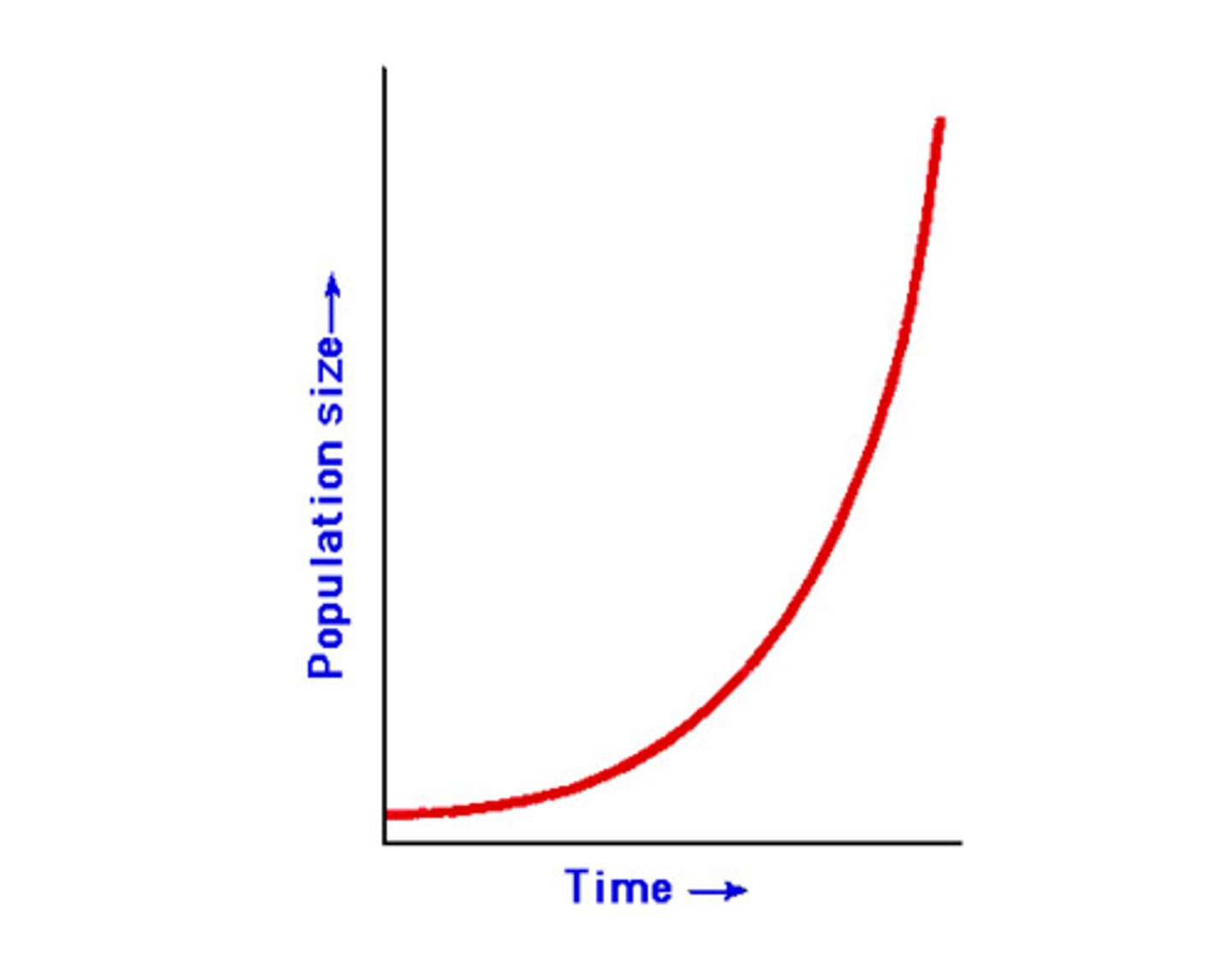
exponential growth
J shaped curve, population has no restrictions
logistic growth
s shaped curve, populations has small/steady increase until k is reached
R selected species
j curve, high increase rate, small, unprotected kids, high mortality, short life
k selected species
s curve, low increase rate, large, slow growing kids, long life
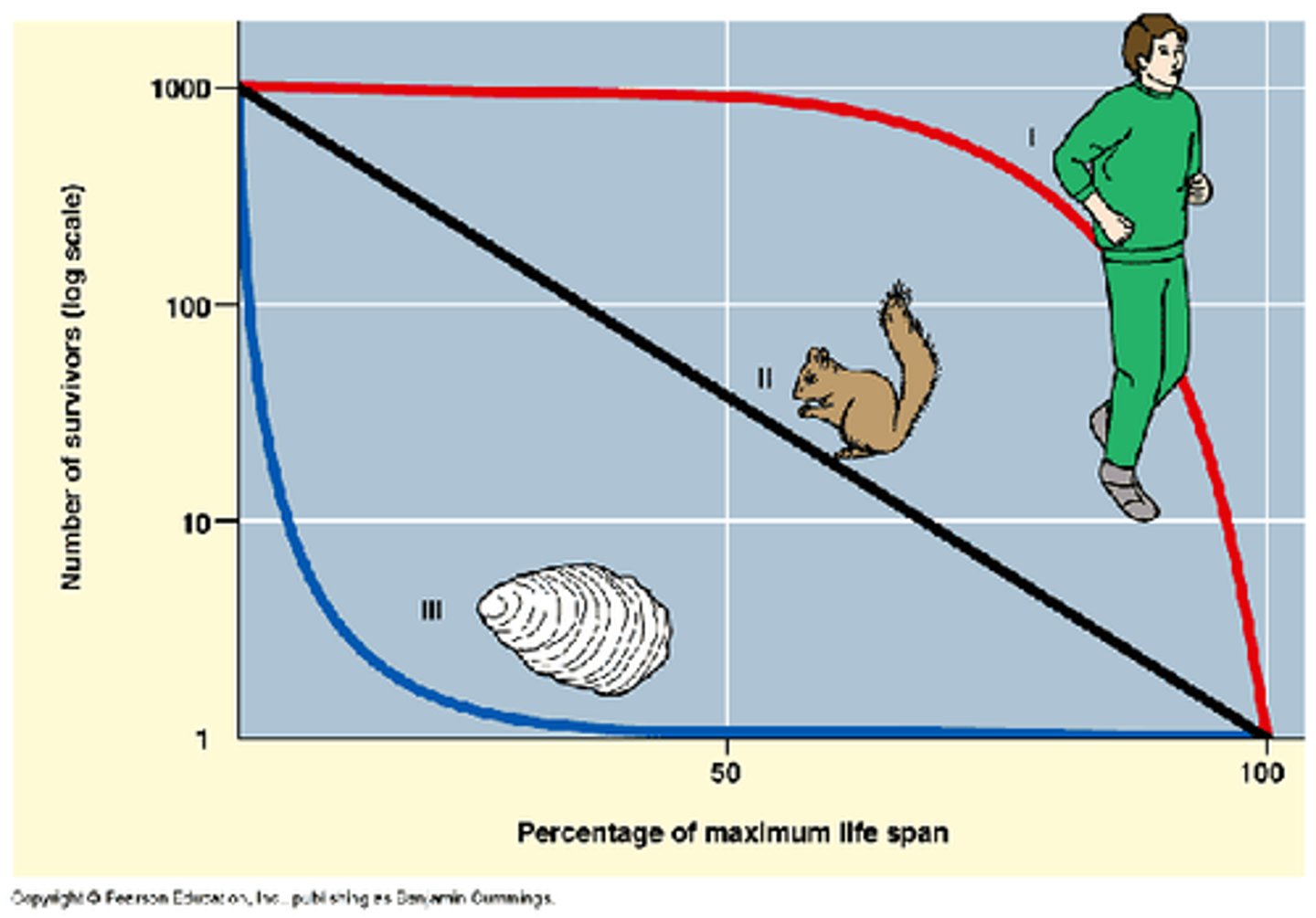
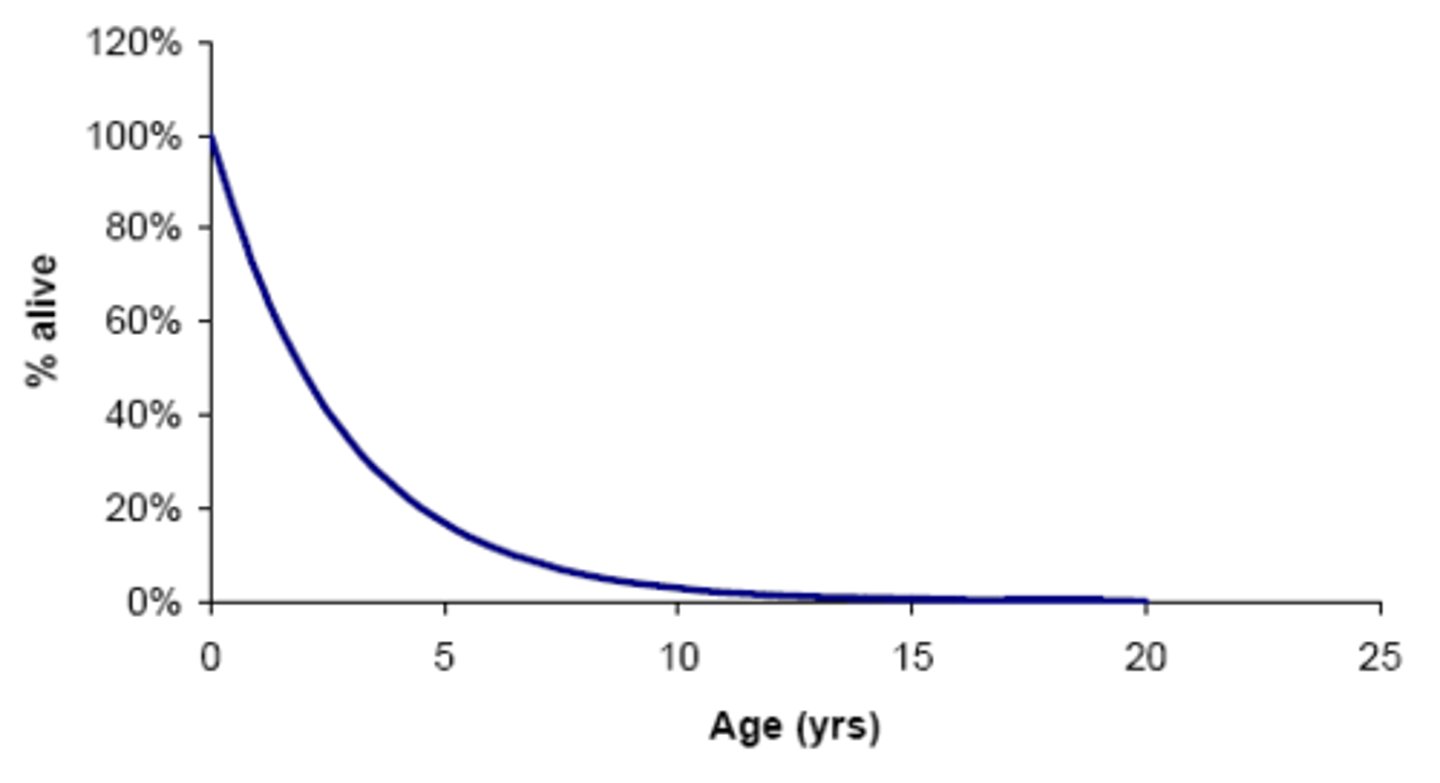
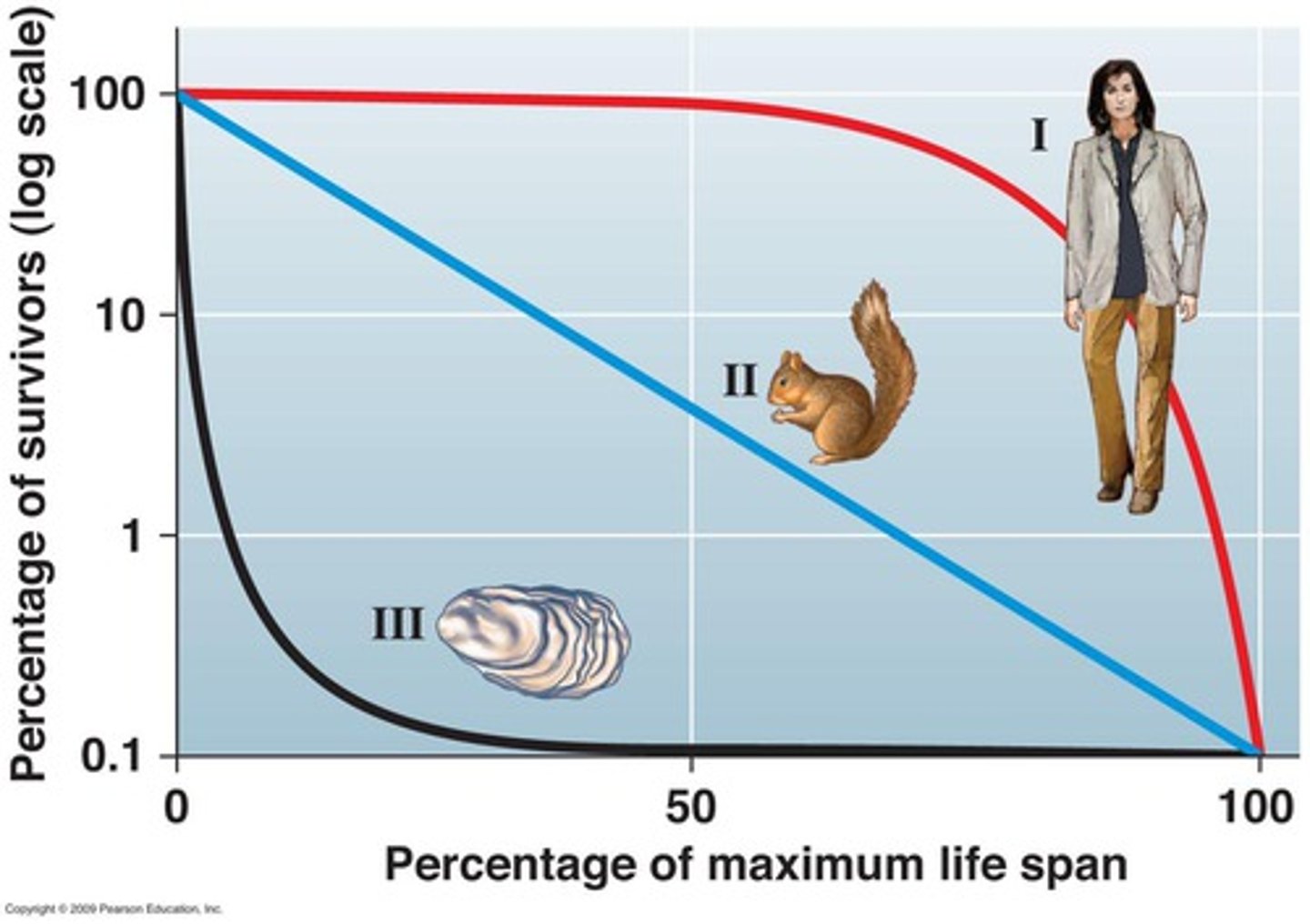
Survivorship Curve
Graph showing the number of survivors in different age groups for a particular species.
primary succession
succession that occurs on surfaces where no soil exists
secondary succession
type of succession that occurs in an area that was only partially destroyed by disturbances
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
climax community
a stable community that no longer goes through major ecological changes
Natural disturbances to succession
Fire, hurricanes, other natural disasters
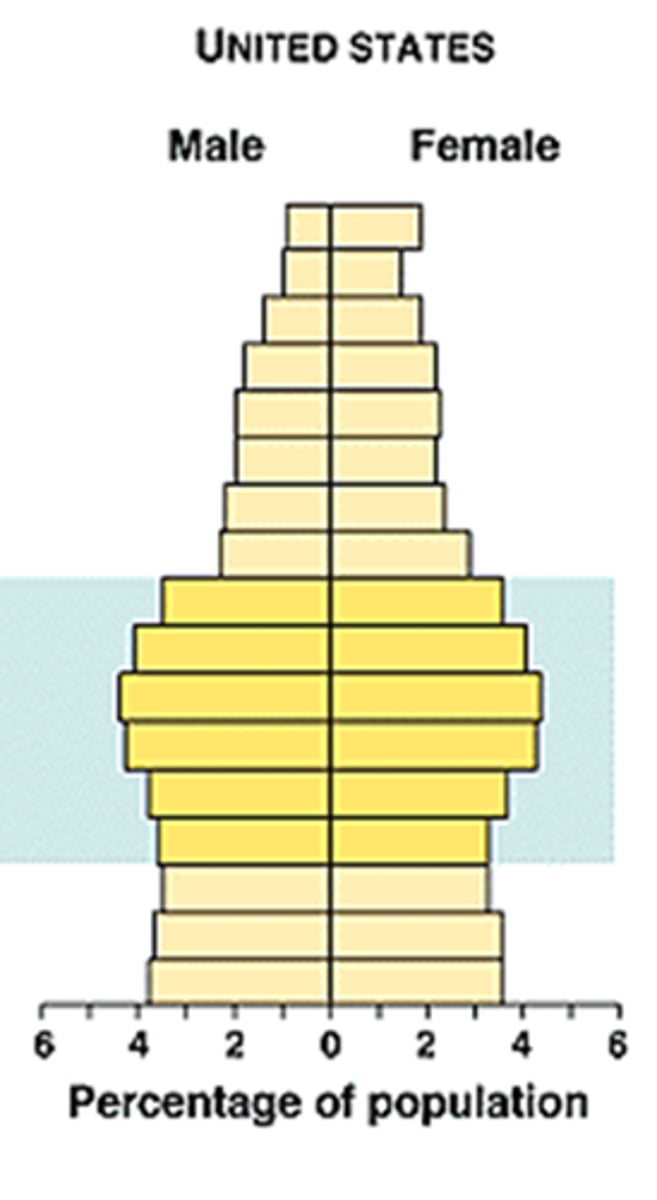
Age structure
the portion of a population at each age level
Factors which determine climate
Average temp and rain
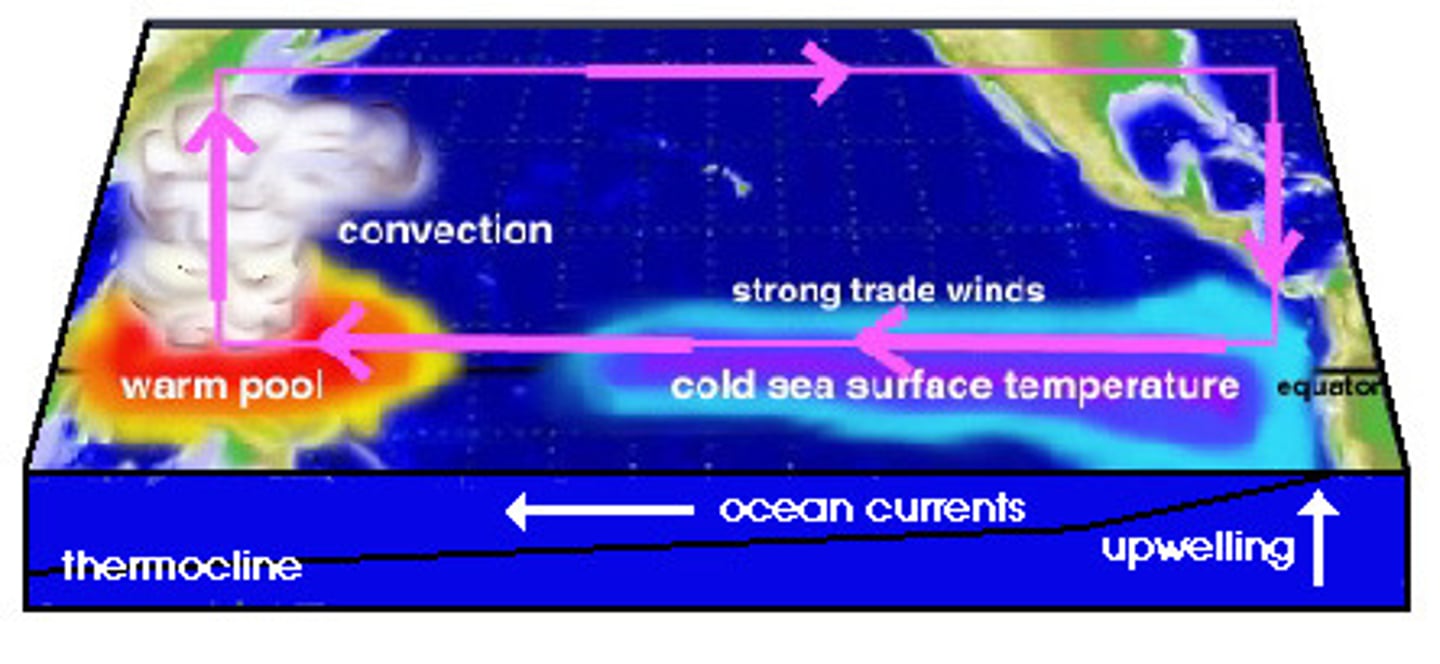
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
The periodic changes in winds and ocean currents, causing cooler and wetter conditions in the southeastern United States and unusually dry weather in southern Africa and Southeast Asia.
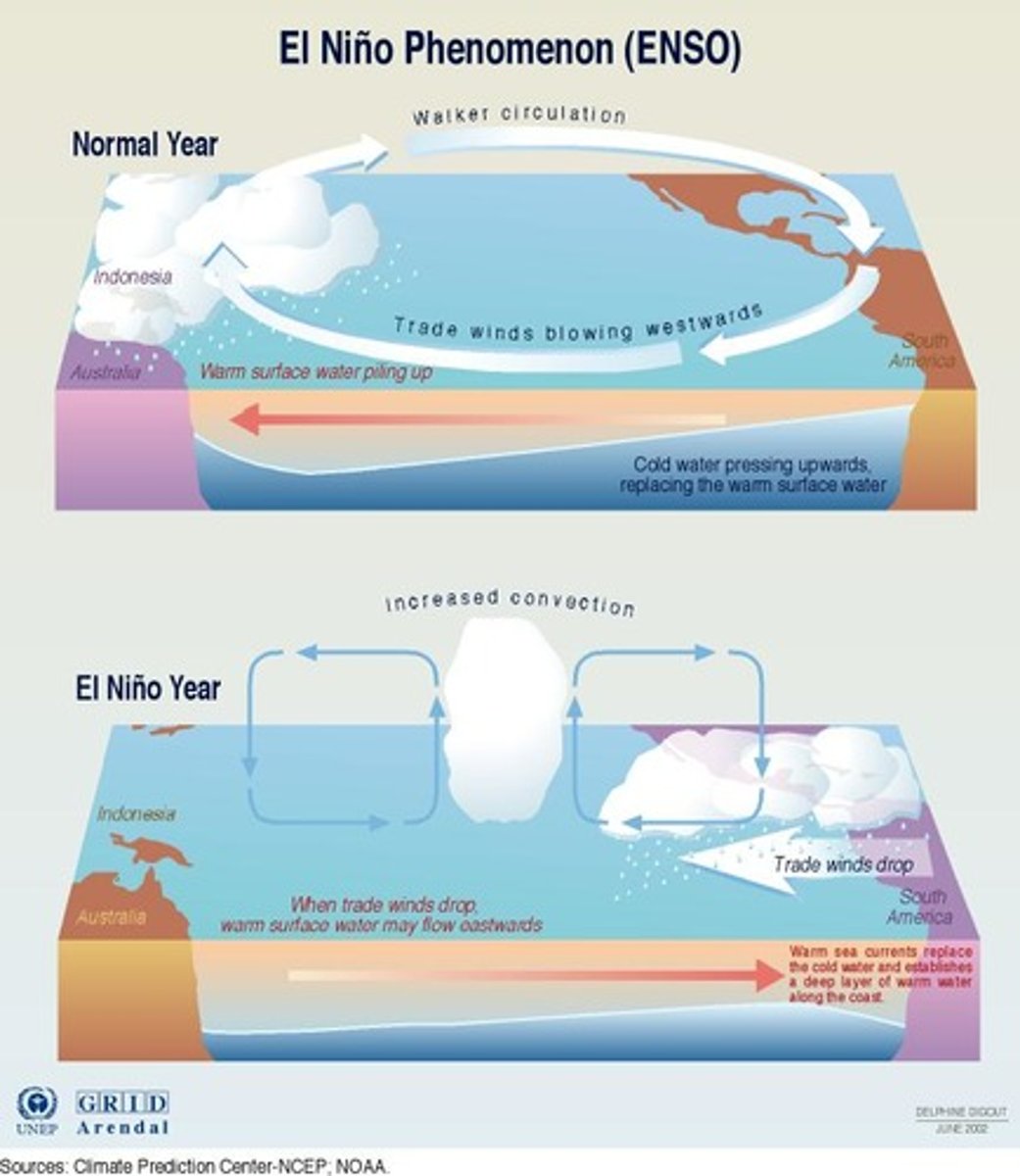
La Nina
Opposite of el nino, A cooling of the ocean surface off the western coast of South America, occurring periodically every 4 to 12 years and affecting Pacific and other weather patterns.
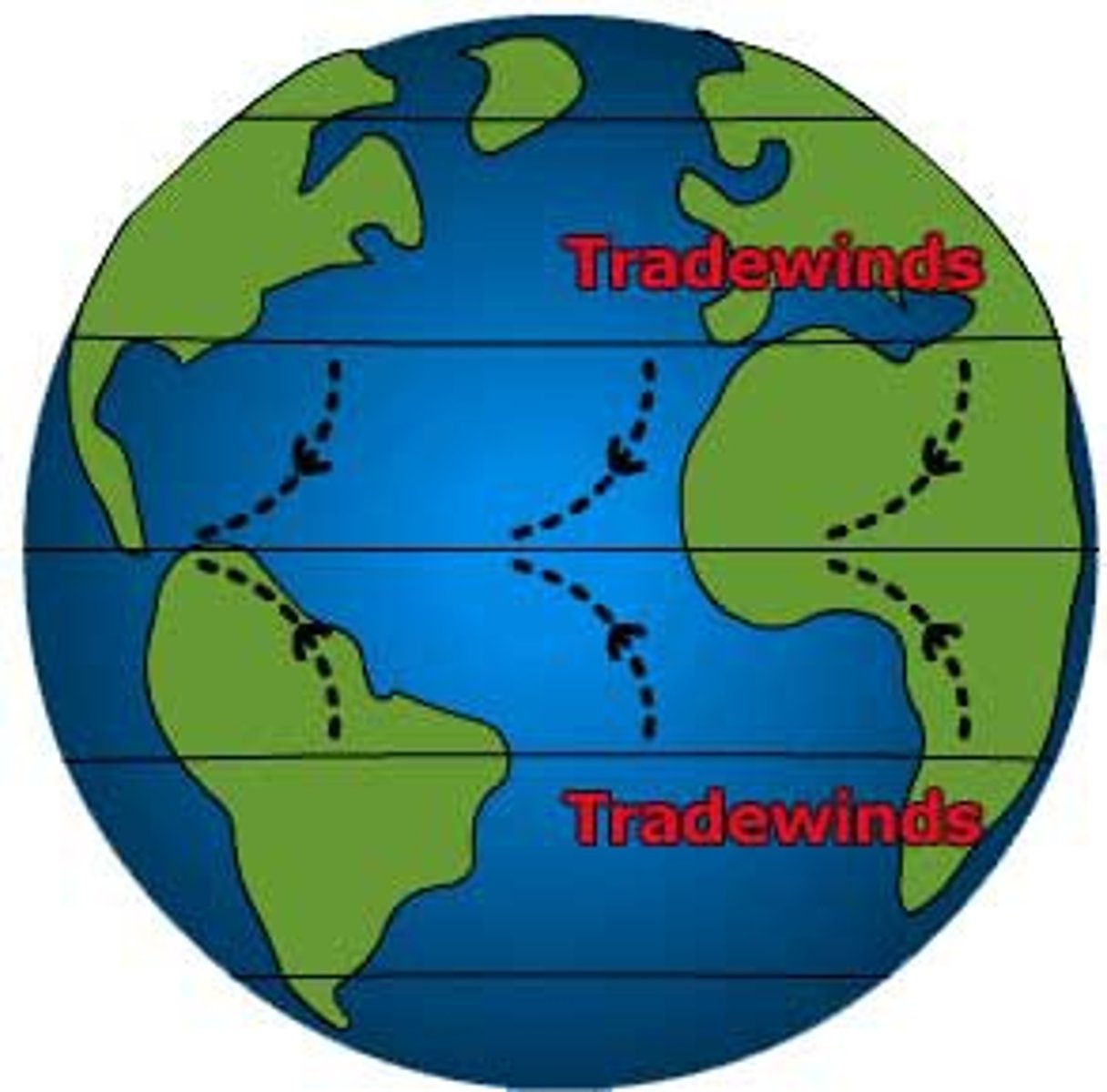
Trade Winds
Winds that blow east to west around the equator
Desert
- evaporation exceeds percipetation
- sparse vegetation, poor soil
- HUMAN IMPACT: Salnization (build-up of salt due to increased evaporation), Aquifer Depletion (causes deserts to sink)
Temperate Grassland
- tall, lush grass and high nutrient soil
- large seasonal temp differences

Grassland
Enough rain for grass, but erratic droughts/fires prevent trees

Tropical Grassland
- higher temps, low/mod rain
- prolonged dry season
- Savannahs: warm all year, alternating wet/dry seasons

Polar Grassland/Arctic Tundra
- cold temperatures, dry
- covered in PERMAFROST (frozen layer of soil, CO2 built up inside)

Chaparral
- Temperate shrubland
- costal areas
- moderate rain, hot and dry summers

Tropical Rain Forest
- warm temp, humidity, heavy rainfall
- most diverse terrestrial biome
- poor soil
- highly stratified, plants grow in layers

Tropical deciduous forest
- warm year round, most rain during monsoon season

Temperate Rainforest
- moderate temp, frequent rain

temperate deciduous forest
- moderate temps w/ strong seasonal changes
- lots of rain
- trees lose leaves in winter
- high nutrient soils
This is our area!

Boreal Forest
- Dry cold climate
- poor soil
- corniferous trees

Oceanic Zones
- epipelagic (photic zone)
- mesopelagic
- bathypelagic
- abyssal pelagic (ocean basins)
- hadalpelagic (deep trenches)
Lake Zones
- littoral (shallow area near shore)
- limnetic (open sunlit water)
- profundal (too dark for photosynthesis)
- benthic (bottom of lake)
Watershed/Drainage Basin
land area that delivers runoff, sediment, and dissolved substances to a stream
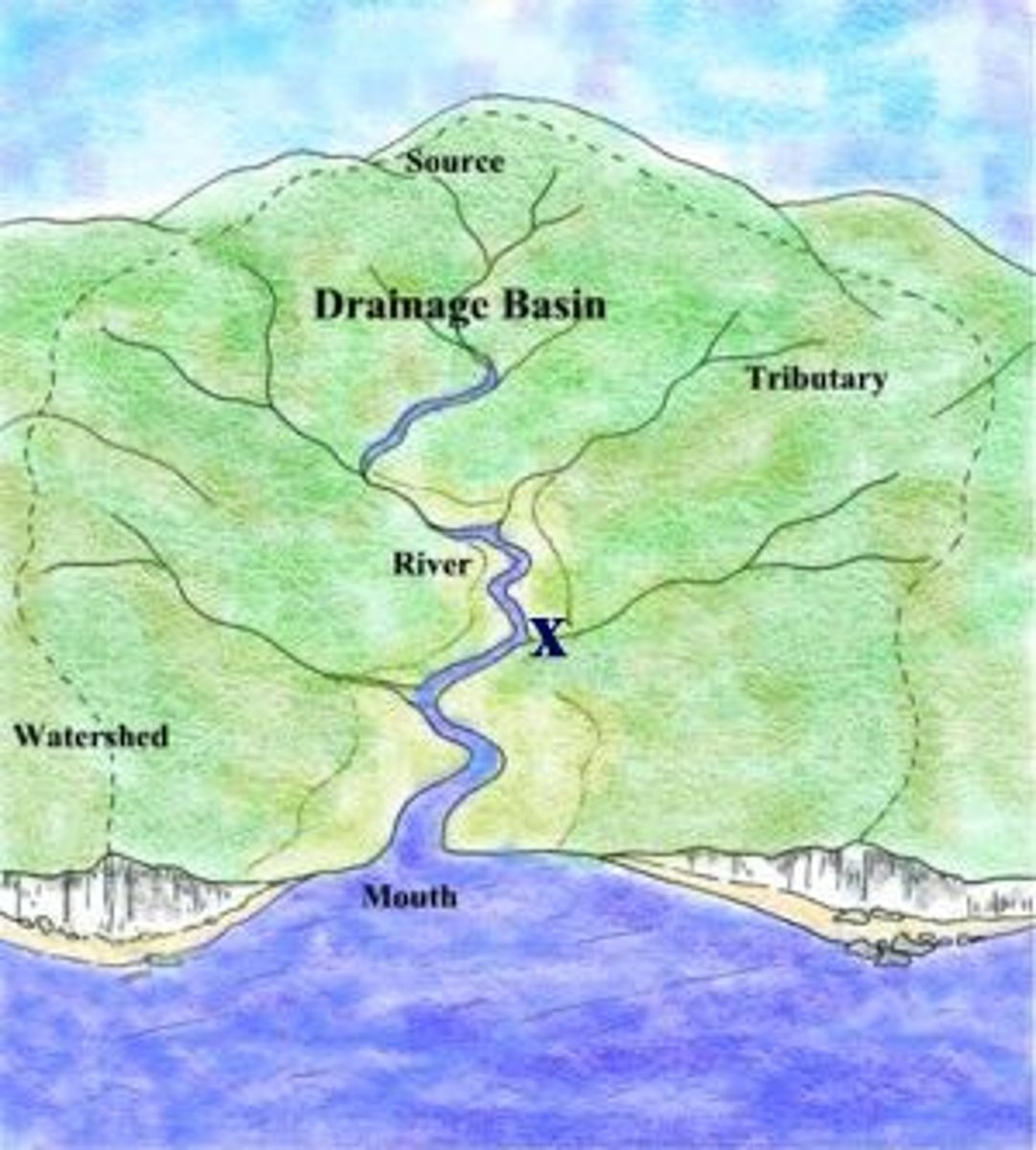
River System
- source (headwaters, cold, nutrient rich)
- transition (streams merge, wider/deeper, warmer slower water)
- flood plain (supports most biodiv)
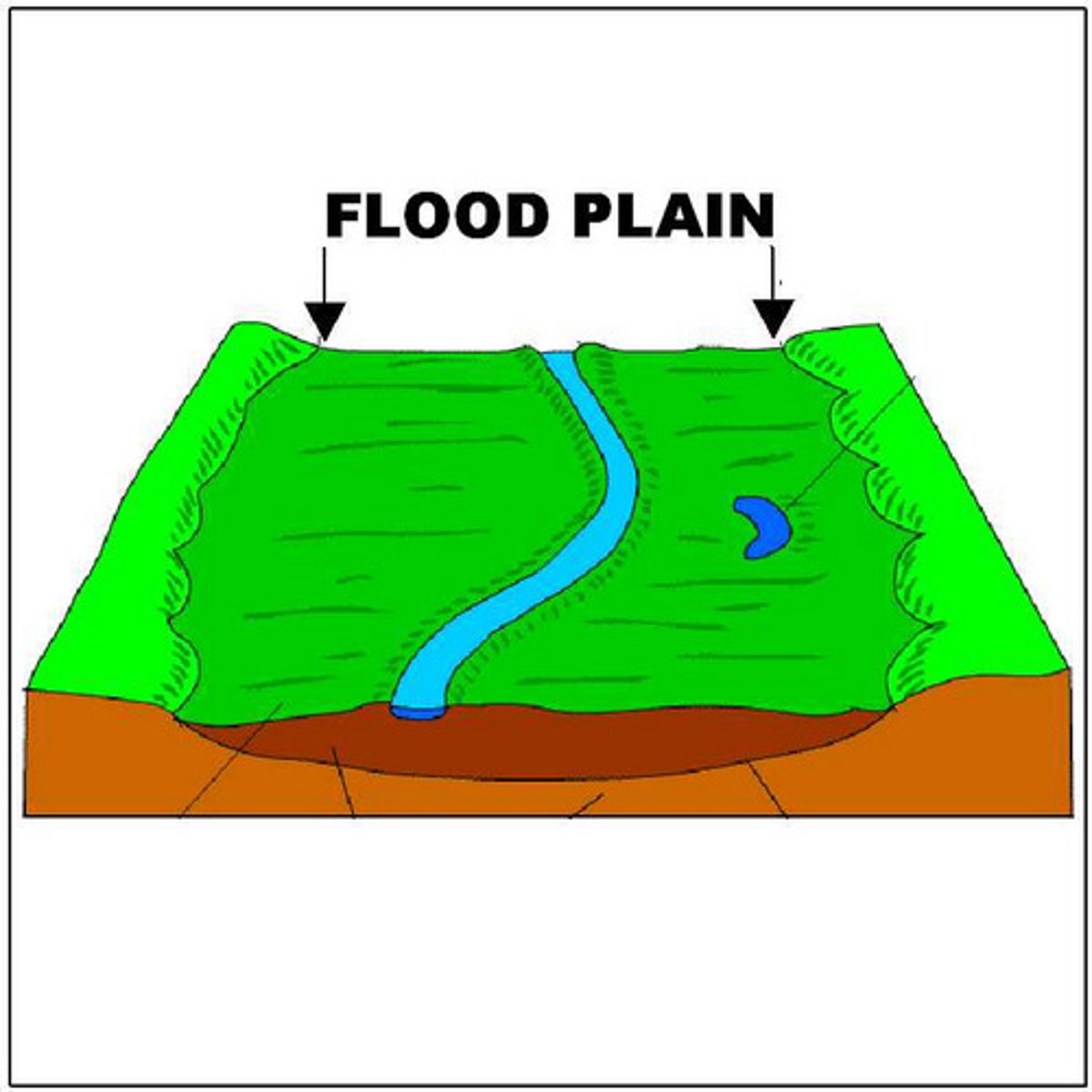
Wetlands
- marshes/swamps/bogs
- water over land
- filter/dilute water pollution
- reduce flooding

Estuaries
- partially enclosed area of costal water
- seawater mixes w/ freshwater
- constant water flow from tides, nutrient rich

Coral Reefs
- Oldest, most productive ecosystems in the world
- Most diverse water ecosystem

ICUN
International Union for Conservation of Nature, leading authority for species conservation. Created the RED LIST of threatend species

CITES
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species, 1975, signed by 183 countries, protects almost 40k species that cannot be traded
Endangered Species Act
(1973) identifies threatened and endangered species in the U.S., and puts their protection ahead of economic considerations
Invasive species
species that have migrated to places where they are not native. Often generalist, r selected.
ex: zebra mussel (chesapeake bay, great lakes, introduced to filter water, but overstepped, killing algea and crayfish), burmese python (everglades)
Selective Cutting (tree harvesting)
mature trees are cut into indv/small groups, creating small gaps
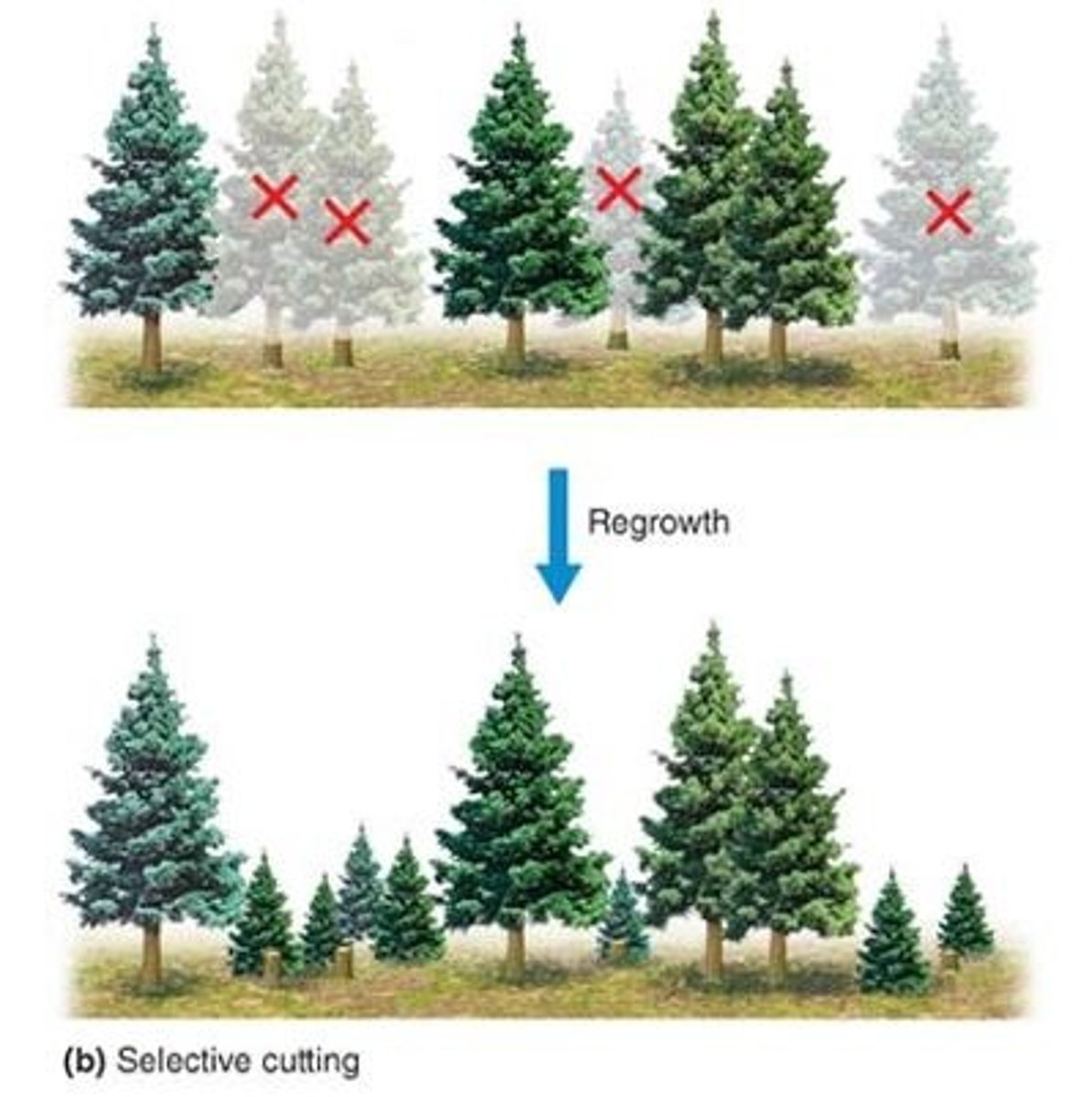
Clear Cutting (tree harvesting)
remove all trees in single cut for $$$

Sustainable Fishing
- reduce bycatch
- fish quotas/regulations
- aquaculture
- reduce invasive species
Bycatch
The unintentional catch of nontarget species while fishing
Aquaculture
The cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions

Biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain
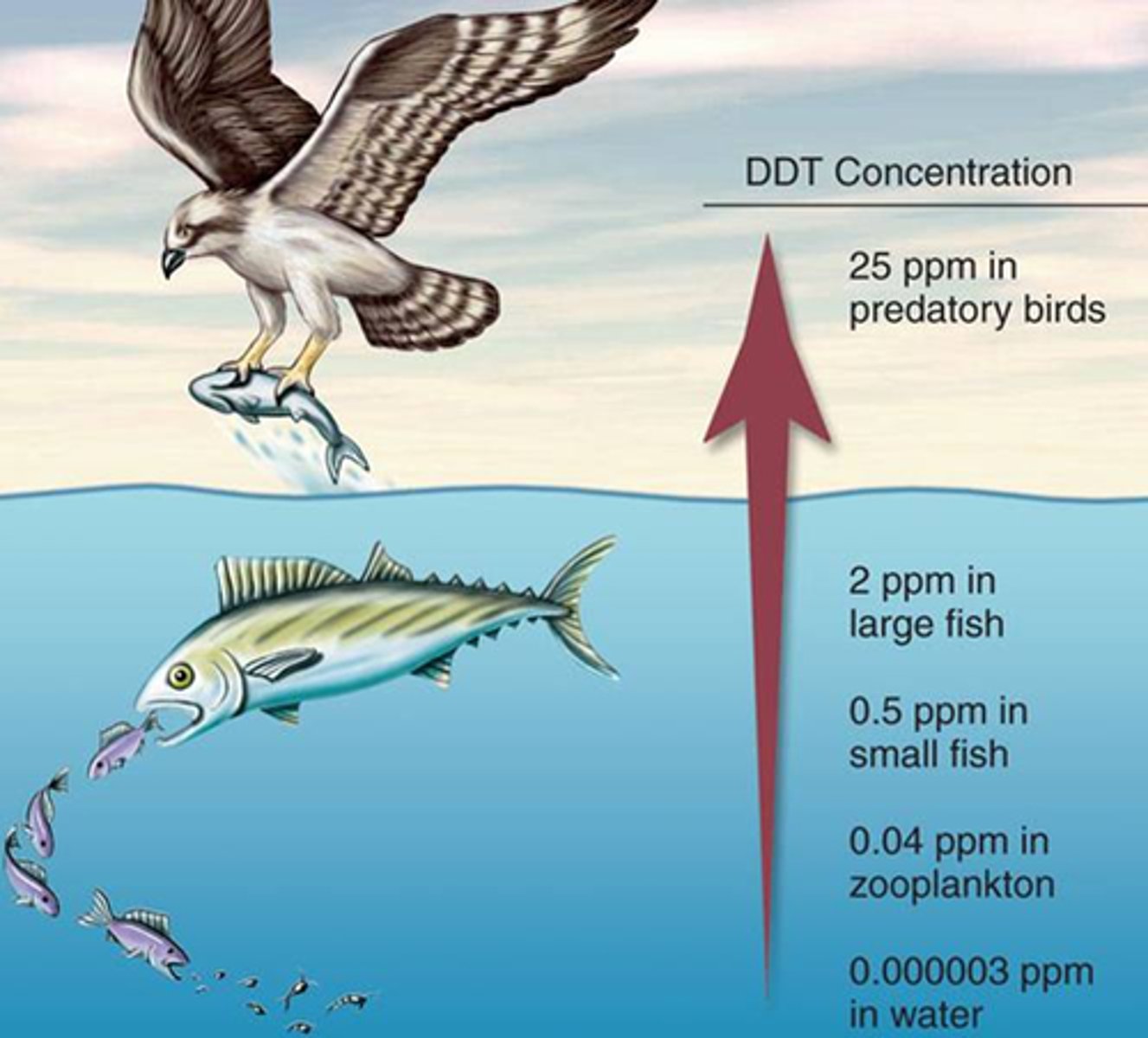
Bioaccumulation
An increased concentration of a chemical within an organism over time
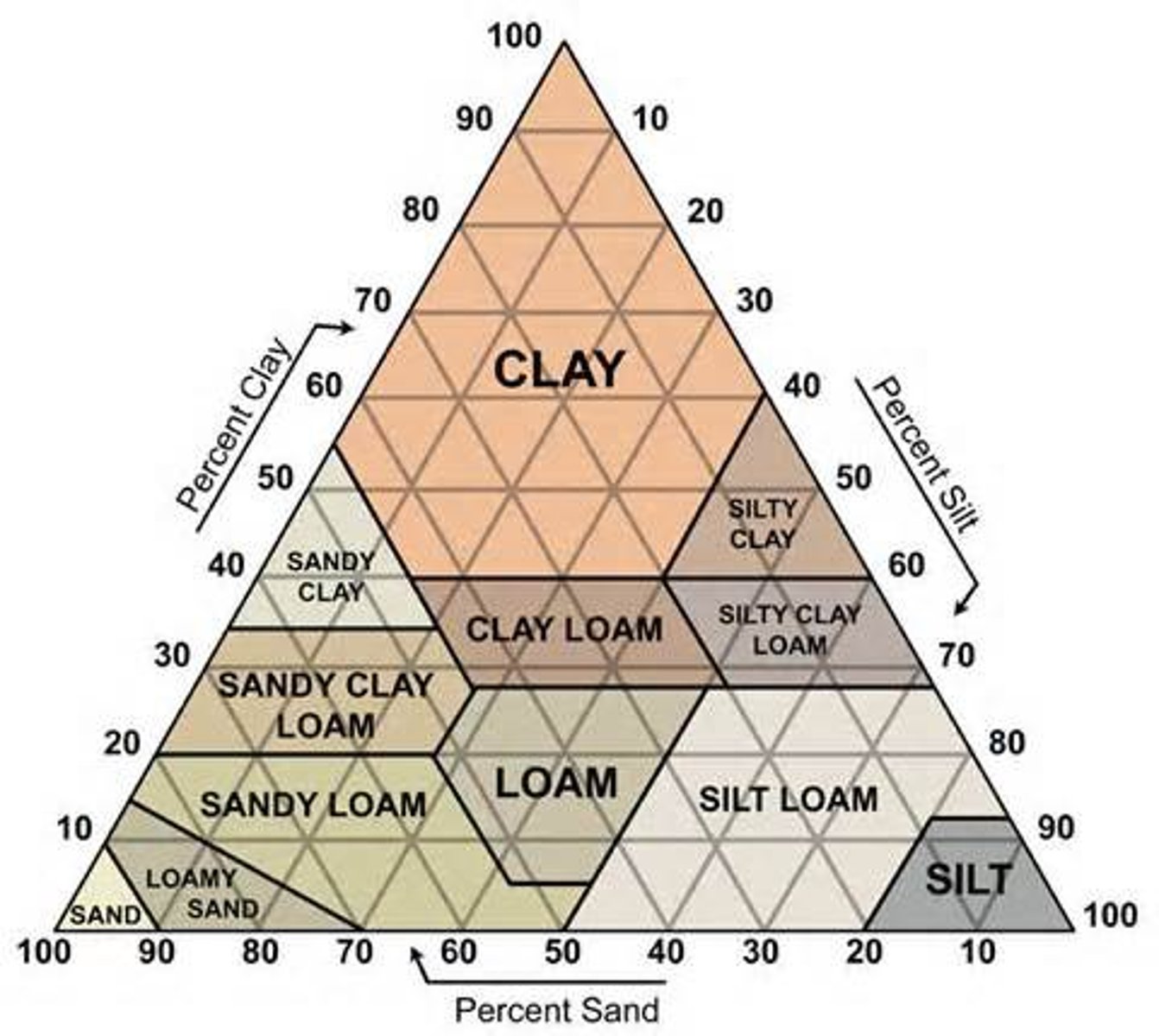
Soil Triangle
a graphic explanation of the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in soil
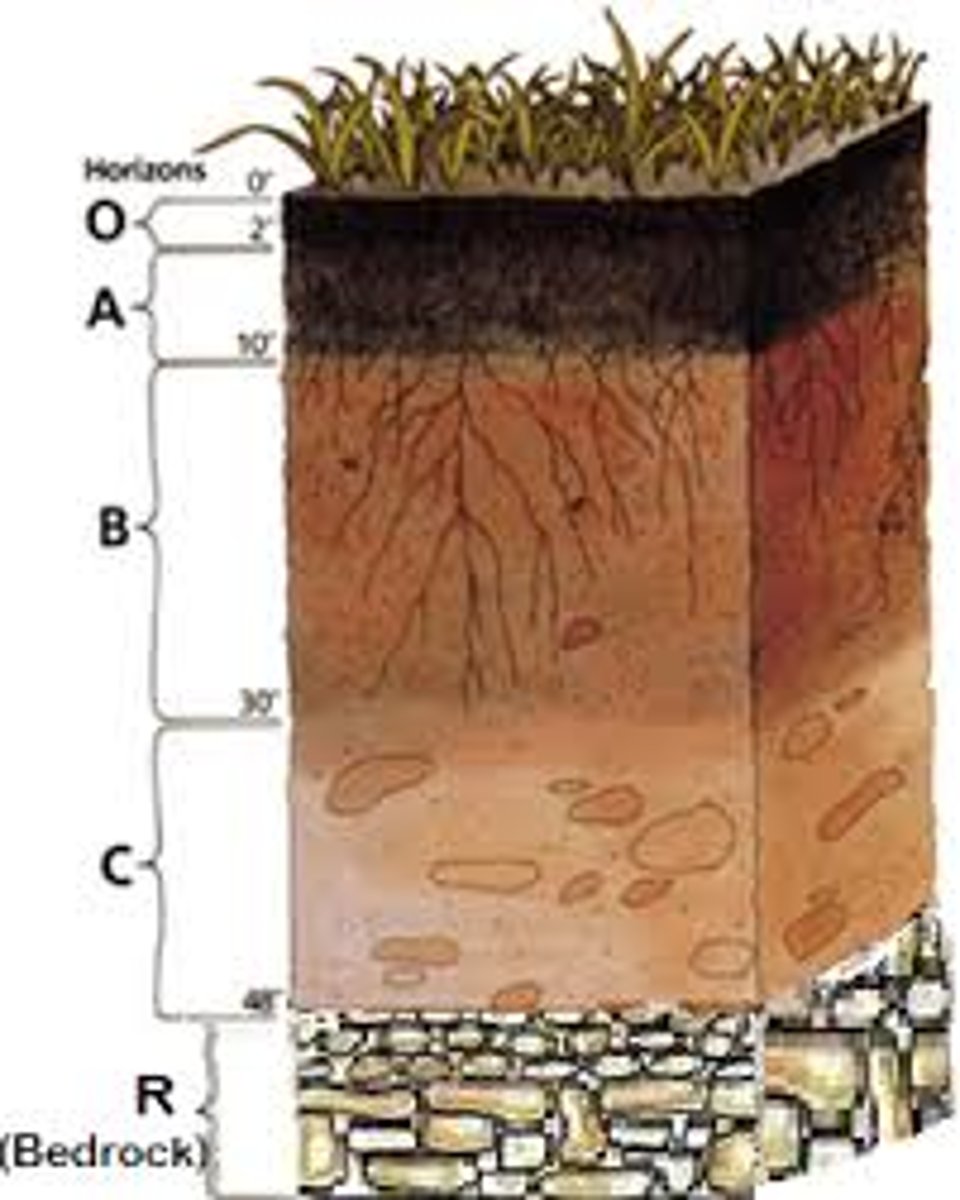
Soil Horizons
- O horizon (surface litter)
- A horizon (topsoil)
- B horizon (subsoil)
- C Horizon (parent material)
Soil Conservation Methods
- No Till Farming (special planter injects seeds/fertilizers in unplowed soil)
- Strip/Intercropping (alternating crop rows with two crops)
-Agroforestry (alternating rows of crops with trees/shrubs)