membrane function - ion gradients
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
why are there ion gradients across cell membranes
to maintain cell volume
gives rise to the membrane potential
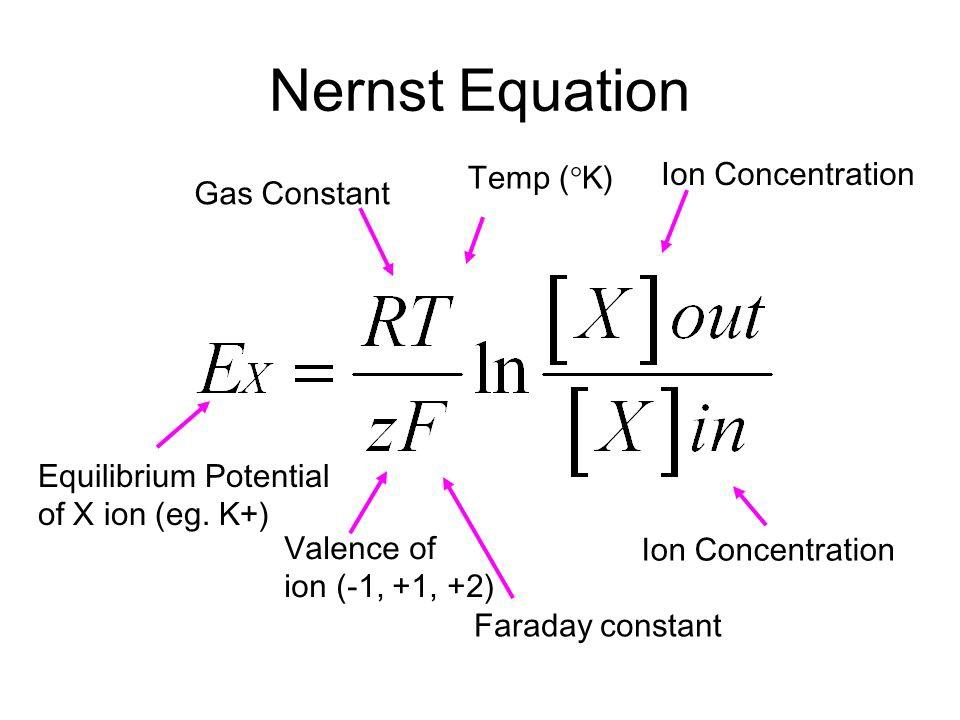
purpose of nernst equation
translates the chemical gradient in mM to an electrical gradient mV
osmoregulation
major limiting factor in evolution
challenges met in vertebrates with gills and or kidneys
so cells are subject to an extracellular environment
extracellular environment
total ion composiiton - 296.5mM
each ion generates an osmotic potential
extracellular is 296.5 and intracellular must be the same
change in these values causes movement by osmosis and change of cell volume
what happens if inc of extracellular osmolarity
hypertonic extracellular
cell volume will decrease
what happens if dec extracellular osmolarity
hypotonic
increase in cell volume
why do volume changes not reach theoretical values
osmotically inactive volume - 15-30% does not respond
cell volume regulatory mechanisms are activated before cell change is complete
regulatory volume increase mechanism
due to accumulation of K+ and Cl-
water follows
transport driven by Na+ gradient with ATPase
regulatory volume decrease mechanism
extrusion of potassium and chloride
transport driven by K+ and or Cl- gradient
most cells use ion channels or some cells use cotransporter
what happens with chloride ions in most neurons and alpha cells
chloride ions are extruded by active K+ and Cl- cotransporters
opening of chloride ions causes Cl- influx and results in hyperpolarisation of Vm
eg GABAa and glycine receptor inhibition
what happens to chloride in most cells
in most cells chloride ions are accumulated
opening of chloride ion channels results in chloride efflux
causes depolarisation of Vm
changes in intracellular osmolarity
imbalance in ion efflux and influx in transporting epithelia
accumulation of metabolites in metabolically active cells eg liver and pancreatic beta cells
what allows brain tumour (glioma) metastasis
dec cell volume from loss of potassium and chloride allows glioma cells to squeeze between other cells
chlorotoxin
chloride ion channel blocker
inhibits glioma cell migration
used to identify tumour cells in surgery