Axial Skeleton: Skull
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
skull, vertebral column, and rib cage
the axial skeleton consists of…
8 cranial bones
how many cranial bones are there?
14 facial bones
how many facial bones are there?
calvaria
the roof of the cranial cavity
nasal septum
the bone and cartilage that divides the nasal cavity in half
spheniodal, maxillary, frontal, ethmoidal
what are the four paranasal cavities?
maxillary sinus; it drains at the top
which sinus is the most commonly infected?
frontal bone
the bone located at the anterior roof of the cranium
supraorbital margin
the prominent bony ridges over the orbits, typically covered in hair
supraorbital foramen
a hole at the midpoint of each supraorbital margin, that allows for passage of small nerves and blood vessels
frontal sinuses
sinuses that are shaped like a butterfly, not everyone has, and are a unique biological identifier
frontal crest
a ridge on the internal anterior surface of the frontal bone that is the anterior attachment site for the falx cerebri
falx cerebri
a sickle shaped sheet of connective tissue that partially separates the left and right sides of the brain
parietal bones
paired bones forming the lateral walls and roof of the cranium
sagittal suture
the midline suture that divides the left and right parietals
coronal suture
the suture that separates the parietal bones from the frontal bone
temporal bones
paired bones that form the lower sides and part of the floor of the cranium
squamosal suture
the suture that divides the temporal bones from the parietal bones
petrous region
the region of the temporal bone that houses the structure of the middle and inner ear
internal auditory canal (internal acoustic meatus)
the space that allows nerves and blood vessels to travel to and from the inner and middle ear
otitis media
infection of the middle ear
carotid canal
a space that allows the entry of the internal carotid artery into the cranial cavity
foramen lacerum (FLOST)
an opening that is closed off by connective tissue in a living person, and is located between the petrous portion of the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone, and the occipital bone
jugular foramen
an opening just posterior to the carotid canal, and allows blood to drain from the brain via the internal jugular vein
mastoid region
a region of the temporal bone that is a rounded projection and can be felt behind the ear
mastoid process
the large bony part of the temporal bone that allows for muscle attachment that can flex the neck or rotate the head
mastoiditis
an infection of the mastoid bone, due to prolonged otitis media
squamous region
the region of the temporal bone that is the lateral flat surface directly inferior to the squamosal suture
zygomatic process
the forward projection of the temporal bone that forms the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch
mandibular fossa
the inferior portion of the squamous region that receives the articulating condyle of the mandible
temporomandibular joint (mandibular condyle)
the condyle that articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
tympanic region
the region of the temporal bone that is a small area surrounding the outer entrance to the external auditory canal
styloid process
the spiney process just inferior to the tympanic region that serves as a muscle attachment site for several muscles associated with the tongue and hyoid bone
occipital bone
the bone that forms the back and much of the base of the skull
lambdoidal suture
the suture that separates the occipital bone from the parietal bones
foramen magnum
the large opening at the base of the occipital bone that the spinal cord passes through to attach to the brain
occipital condyles
the rounded knobs on each side of the foramen magnum that articulate with the atlas vertebrae, they work as a “rocking chair” and allow the head to nod yes
nuchal lines (superior and inferior)
the two prominent horizontal ridges on the posterior of the occipital bone that are attachment sites for neck muscles
internal occipital crest
a ridge on the internal posterior surface of the occipital bone that is the posterior attachment site for the falx cerebri
sphenoid bone
the bone that contributes to the base of the skull and resembles a bat, sometimes it is referred to as the bridge bone because it connects several facial and cranial bones
sella turcica
the prominent depression on the superior medial portion of the sphenoid bone that holds the pituitary gland
head into the dashboard syndrome
when trauma to the brain sends it forward, severing the pituitary stalk
optic foramen
a foramen in the sphenoid bone that allows passage of the optic nerve (CN II)
foramen rotundum
a foramen in the sphenoid bone that allows for passage of the second branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) that conveys sensations from the teeth and gums of the maxillae
foramen ovale
a foramen in the sphenoid bone that allows for passage of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) that conveys sensation from the teeth and gums of the mandible
foramen spinosum
a foramen in the sphenoid bone that is a small opening for meningeal blood vessels
superior orbital fissure
a foramen in the sphenoid bone that allows for passage of several cranial nerves including the first branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) that conveys sensation to the nose, forehead, and anterior scalp
pterion
the portion of the sphenoid bone that articulates with the frontal, parietal, and temporal bones and is named after Hermes wings, this is the weakest part of the skull, and the middle meningeal artery runs underneath
ethmoid bone
the bone that is located in the anterior portion of the floor of the cranium between the orbits
crista galli (cock’s comb)
the midsagittal elevated superior part of the ethmoid bone, and is an anterior attachment site for the falx cerebri
cribriform plates
the parts of the ethmoid bone lateral to the crista galli that have numerous foramina that allow passage of fibers for the olfactory nerves (CN I) to travel from nose to brain
meningitis
fracture and leakage of of spinal fluid following trauma to the face, allowing bacteria to enter the meninges
perpendicular plate
the superior part of the nasal septum, the inferior midline projection of the ethmoid bone that divides the nasal cavity
conchae (turbinates)
two projections of the ethmoid bone on the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
superior nasal conchae and middle nasal conchae
the two projections of the ethmoid bone on the walls of the nasal cavity
erectile tissue
what are nasal conchae made of?
nasal cycle
the turbinates in on fossa fill up with blood while the opposite turbinates decongest by shunting blood away, this cycle is usually 2.5 hours, but varies
zygomatic bones
paired facial bones that form the bony prominence of the cheeks and contribute to the lateral margin of the orbits
zygomatic arch
formed by the articulation of the temporal process of each zygomatic bone with the zygomatic process of each temporal bone
lacrimal bones
paired facial bones that form part of the medial wall of each orbit
lacrimal groove
a passageway for the nasolacrimal duct that drains tears into the nasal cavity
nasolacrimal duct
the duct that opens into the nasal cavity just inferior to the inferior nasal conchae
nasal bones
paired facial bones from the bridge of the nose, support the lateral cartilages
vomer bone
the single facial bone that has a triangular shape and resembles a plow, it contributes to the posterior portion of the nasal septum
inferior nasal conchae
paired facial bones that project into the nasal cavity just below the superior and middle nasal conchae
palatine bones
paired facial bones that are small with an L shape, and form the posterior third of the hard palate
maxillae bones
paired facial bones that unite at the midline to form the upper jaw, they form the anterior portion of the hard palate
anterior portion of the face
anterior portion of hard palate
anterior floor and walls of nasal cavity
inferior parts of the orbits
What parts of the face do the maxillae support?
infraorbital foramen
the foramen located just under the eye, part of the maxillae
palatine processes
projections of the maxillae that move horizontally from the anterior portion of the hard palate
cleft palate
palatine processes fail to join during early prenatal development
maxillary sinus
sinuses that lay lateral to the nasal cavity which drain into the nasal cavity through an opening high and medial within the sinus that exits just inferior to the middle nasal conchae
crepitus
a crackling sound caused by gas or broken bone under the skin
blowout fracture
blows to the eye and orbit that may fracture the floor of the orbit causing the eye, or the muscles to drop down into the maxillary sinus
mandible bone
facial bone that forms the entire lower jaw
body of mandible
the large horseshoe shaped portion of the mandible that is the front and lateral sides
mentum
the anterior point of the body of the mandible
rami (ramus)
the vertical extending portions of the mandible that form the posterior portion of the body
mandibular condyle
the condyle that articulates with the mandibular fossa of the inferior squamous portion of the temporal bone
coronoid
a pointed process of the mandible that allows for muscle attachment that closes the jaw
mandibular notch
the U-shaped depression between the coronoid and mandibular condyle of the mandible
mental foramen
the foramen that penetrates the body of the mandible on each side of the chin for passage of nerves and blood vessels
mandibular foramen
the foramen which penetrate the medial side of each ramus and allows passage of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve
third division nerve block
an injection of anesthetic near the mandibular foramen that will desensitize the mandibular teeth and gums
nasal bones, cribriform plate of ethmoid, parts of the frontal and sphenoid bones
roof of nasal complex
palatine processes of maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones
floor of the nasal complex
ethmoid bone, maxillae, inferior nasal conchae, palatine bones, and lacrimal bones
lateral walls of the nasal complex
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, vomer, and septal cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
nasal septum
maxillae
palatine
sphenoid
zygomatic
frontal
lacrimal
ethmoid
(Mandy Purposely Sees Zebras Falling Like Elephants)
what bones contribute to the orbital complex?
malleus (hammer)
incus (anvil)
stapes (stirrup)
what are the auditory ossicles
hyoid bone
the slender, U-shaped bone located inferior to the skull between the mandible and the larynx, it is suspended by ligaments and is commonly fractured in strangulation homicides
5 years
what age is the skull mostly grown by?
fontanelles (soft spots)
the large membranous areas of the skull that provide spaces between the developing bones
molding
the shifting of cranial bones during parturition that causes a temporary cone head, one parietal bone typically overlaps the other and the occipital bone slides underneath
dehydration (sunken) or meningitis (bulging)
what causes sunken or bulging fontanelles?
dental attrition
the wear down and loss of teeth during aging
coronal
sagittal
lambdoidal
squamosal may or may not fuse before death
in what order do the cranial sutures fuse and become ossified?
Rene LeFort
the man who classified the LeFort fractures
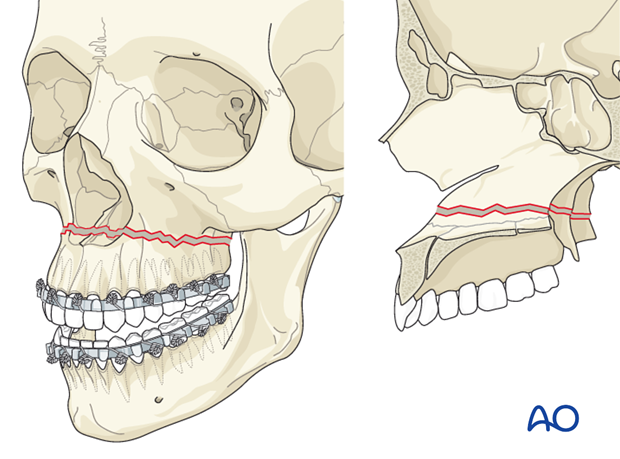
LeFort I fracture (horizontal maxillary fracture)
a horizontal fracture through the pterygoid plates and maxillary bone between the hard palate and orbits
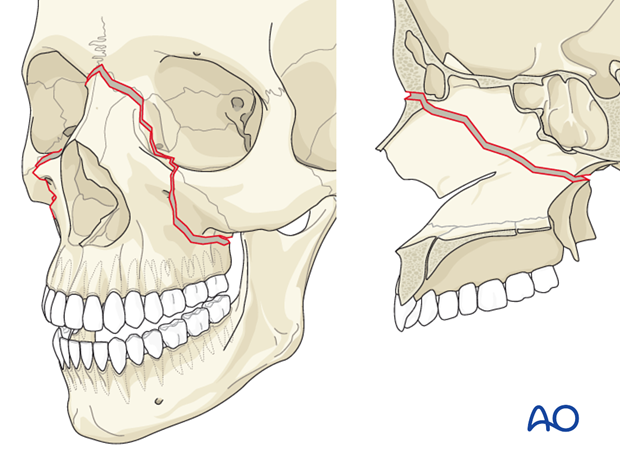
LeFort II fracture (pyramidal fracture)
a fracture line from one of the lateral vertical buttresses across the maxillary bone, extending into the inferior orbital rim and crossing the midline