geography- Resource management - Paper 2
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
May - Year 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
food miles define
the distance that food travels from producer to consumer
carbon footprint define
the measure of the impact human activities have on the environment in terms of the amount green house gases they produce
How much wayter does the average person in UK use per day + percentage pf what is used for
150 Liters
30% toilet flushing
21% bath + taps
13% clothes washing
12% showers
8% washing up
7% outdoor
5% other
4%v drinking
how many people in the world live without access to clean water
240 million +
how many people globally face hunger on a daily basis
how many people, globally, lack essential micronutrients
795 million
2 billion
which energy source is non renewable but doesnt give off CO2 when producing energy
main challange of using this energy source to produce electricity
Nuclear power
if it goes goes wrong radioactive leaks causes changes to human DNA which causes cancer
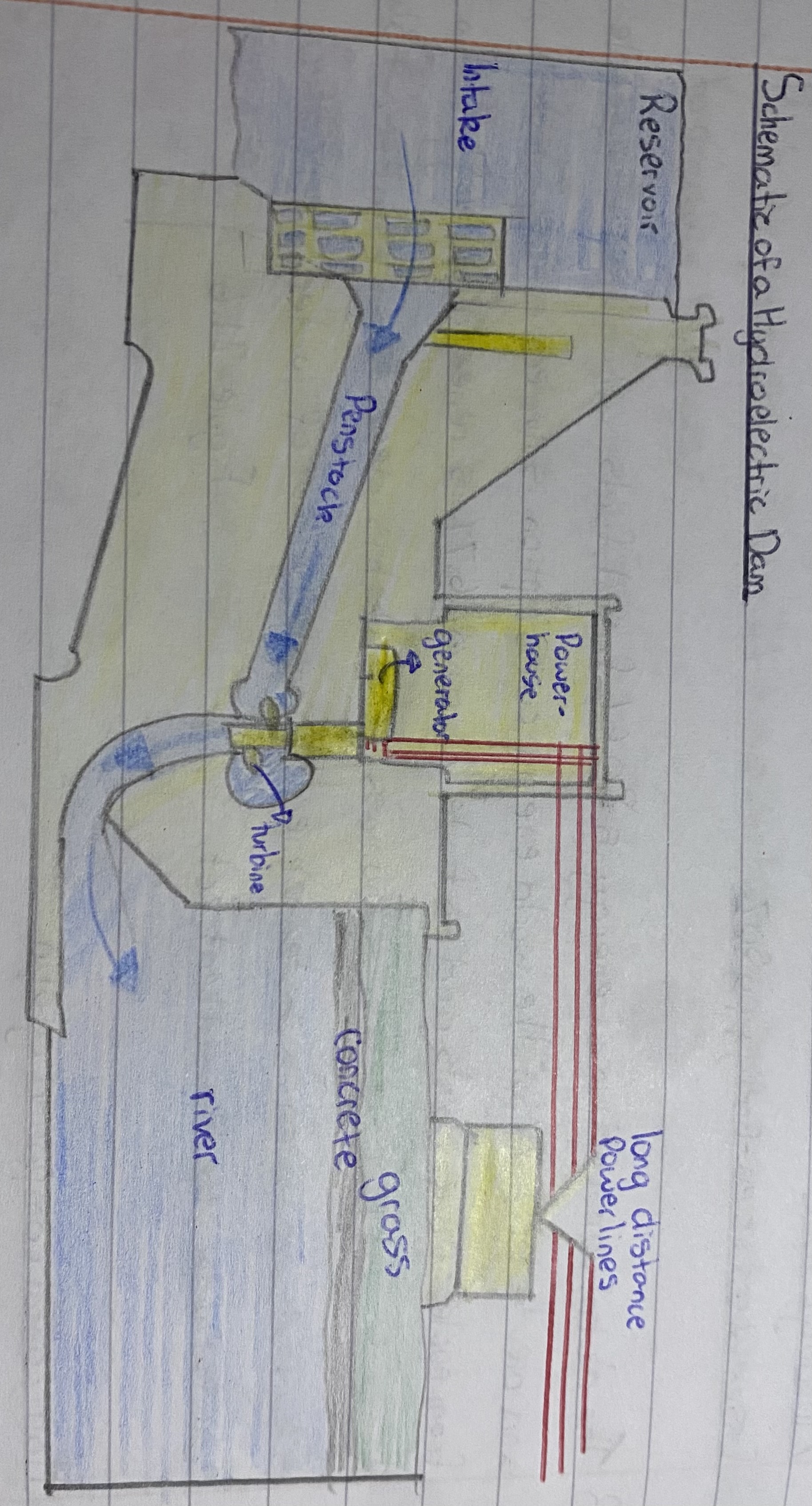
pros and cons of hydroelectric power (1,1)
pro
-lowe maintanance
cons
use lots of concreate- not renewable
schematic of a hydro electric dam
MONDAY 20 JUNE LOOK IN VOOK
How has demand for food changed since 1950s (4,3)
1950s
-used to eat seasonaly - resrticted in winter - so people would preserve food by pickling or in jam
-eat simpler - as you grow your own
-healthier
-families didnt have a car - norm man would work and wife would walk to shops + cook - buy locally
Now
-not eating seasonally - importating food from other countries - more variety
-chefs incourage us to eat more exotically
-in 2013 47% 0f UKs food supply was imported - carbon footprint is increased because of food miles
why should you eat seasonally (5)
-reduces energy (+CO2 emissions) needed to grow and transport the food
-avoid paying a premium for food that is scacer
-support local economy
-to reconnect with natures cycles + passing of time
-seasonal food is fresher + so tends to be tastier + more nutritious
whats the aim of organic farming
to protect the environment + wildlife by using natural predators to control pests
How does Organic farming avoid using pesticides
chemical fertilisers
cemical weed killers
animal rearing differ
pesticides - using natural predators to control pests e.g laderbirds to eat blackfly
chemical fertilisers - rotating crops to maintain fertility and using natural fertilisers
mechanonal weeding
animal rearing - without the use of antibiotics + regular use of drugs to inc growth
when + why did organic produce sale rise
why did it fall in 2009-2011
1990s
people became more concerned about the effect of what they eat on their health
global recession and reduction in incomes for many families made organic food a luxury
why is organic produce more expansive than conventionally
where can you buy organic oriduce
lower yields
supermarkets, farmers markets, vegetable box schemes
how has demand for water inc - only ever 4 marks
domestic appliances
inc hygiene - showering frequently
leisure
industry
food production
inc population
choropleth map define
a map that’s colour coded
when describing the distribution of something what does
TEA stand for
T- trends
È- evidence
A-anomalies
water surplus areas define
places where yhey have more water than theu need for the population
water deficit areas define
places where they do not have enough water for the needs of the population and may suffer shortages
causes of water pollution
sewage containing bacteria may be pumped into rivers and the sea
pollution such as oil from boats and ships can often end up in rivers and coastal waters - impacts economy as government will have to clean it, impacts people as ppl may become ill drom swimming may kill wildlife
rubbish such as supermarket trolleys and bicycles may be dumped - impacts money as some of these items may have been able to use again, impact environment as these items may destroy habitats or kill animals, may impact people as
how is water quality managed in the UK
legislation
strict laws which ensure thaf factories and farms arw limited in the amount and type of discharge they put into rivers.
how is water quality managed in the UK
education campaigns
inform the public about the damage caused by putting inappropriate items into the sewage systems + advise how to dispose of tgem correctly
how is water quality managed in the UK
waste water treatment
local water treatment plants remove suspended solids, to produce clean water for human consumption. They use a number of processes to do this.
how is water quality managed in the UK
building better treatment plants and investing in new infrastructure
better sewers abd water mains can prevent spills abd accidents but can lead to higher water and sewage bills to pay for the investment
how is water quality managed in the UK
pollution traps
for example when roads and motorways are built close to rivers and watercourses, pollution traps such as red beds often installed to ‘catxh’ and filter out pollution
how is water quality managed in the UK
green roofs and walls
in cities, new buildings often have green roofs, which filter out the pollutant naturally jn rainwater. green roofs also offer excellent sustainabile water management. This reduces the risk of flooding by reducing runoff from the roof. green roofs can also help to combat climate change by increasing the absorption of CO2 from the atmosphere
what are our main energy sources (9)
are tgey renewable or non renewable
1 power stations - type burns coal, oil, gas(fossil fuels) - NR
2 nuclear - NR
3 solar - R
4 wind - R
5 tidal -R
6 waves - R
7 hydroelectric- using dams -R
8 geothermal - magma + heat + hotspots - R
9 biofuel - waste products - R
Location of kielder water transfer scheme
Northumberland, North East England
Built in the 1970s–1980s
Kielder Water is the largest man-made reservoir in the UK by volume
🏗
Why Was It Built
To ensure water security in the North East of England
Designed to transfer water from areas of surplus (Kielder, NW) to areas of deficit (Newcastle, Sunderland, Middlesbrough)
Anticipated increased demand from industry (which didn’t grow as much as expected)
How Does the Transfer Work
Water is stored in Kielder Reservoir
Transferred via rivers and tunnels to River Tyne, River Wear, and River Tees
Can supply up to 1.2 billion litres per day
Also supports hydroelectric power generatio
Benefits / Positive Impacts
Water Security: Supplies reliable water to cities and industries in NE England.
Hydroelectric Power: Generates renewable energy (enough for 10,000 homes).
Tourism & Recreation: Kielder Forest and Water Park attract over 250,000 visitors/year.
Jobs: Created employment during construction and in tourism.
❌
Problems / Negative Impact
2,000 hectares of forest and habitats flooded
Affected local wildlife and river ecosystems
Cost: Very expensive to build (over £160 million)
Social Impact:
A small number of people (less than 100) displaced
Some farmland lost
Overestimated Demand: Industry didn’t grow as expected, so not all water was needed
define fracking
when water is pumped into the rocks underground which then releases gas
pros and cons of fracking
PRO
creates jobs
we gain gas which can be used for energy we couldn’t extract a couple years ago
CONS
environmental - heavy lorry traffic in rural areas + contamination kf water supplies
economic- extraction is expensive (uses lots of water), energy bills for ppl wouldn’t decrease because of this
social- multinational companies gain profit, nit the local owners consenting in fracking their land sì less ppl will consent to it
food security define
when all people at all times have access to sufficient, safe, nutritious food to maintain a healthy active life
why is food demand growing
inc population
there’s a clear correlation between areas of greatest population growth abd areas which have the lowest calorie intake (è.g africa )
why does calorie intake snd diet change wheb GDP changes in a country
when someone gains money, theu are able to buy more luxury items è.g meat abd fast food. For example jn china in the 1980s 6% of their diet was meat but 30 yrs later it was 17% and their GDP had increased
causes of inc global food demand (2)
inc population
urbanisation
factors affecting food supply (6)
pests/diseases - diseases can worsen food insecurity as tgey reduce the available workforce agriculture
war/conflict - food supplies can be siezed by soldiers or destroyed
water supply - water stress can occur making water dirty
climate - è.g floods caused by tropical storms causes losses kf crops
technology - HICs can manage water stress by using water transfer schemes and irrigation
poverty - some ppl can’t afford nutritious food for them abd their family’s - makes them weak and unable to work on labd or earn money to support themselves
impacts there would be if people didn’t have enough food
are they social economic or environmental
decrease in population - social
health decrease- social
famine + under nutrition - social
rising prices - economic
conflict and social unrest - social
pesticides/fertilisers - water pollution - environmental
over grazing snd soil erosion - environmental
strategy - irrigation
description
advantages
disadvantages
description
watering of land using water moved from somewhere else
Most methods take water from rivers/lakes
Irrigation needed whether our water shortages during growing season
advantages
Can increase crop yield and income - helps reduce poverty - major cause of food insecurity
disadvantages
sometimes problems with irrigation - certain large scale schemes can push people off the land to be used for reservoirs and the cost involved with setting up the method for delivering water
strategy - aeroponics
description
advantages
disadvantages
description
process of using air instead of soil to grow plants
Grown in a closed environment E.G.greenhouses
Nutrients and water are sprayed in a fine mist onto to roots abd lower stem every few minutes
advantages
Plants grow faster as roots are more exposed to oxygen
Easier to ensure the plants have all nutrients needed
Enable seasonal crops to be grown all year around
disadvantages
People think these foods don’t taste as good
Cost of heating and lighting can be high
strategy - hydroponics
description
advantages
disadvantages
description
plants grow in water roots of plants are in nutrient rich water bath throughout their life is
advantages
Plants receive more nutrients - grow faster
Uses less space - plants can be stacked on top of one another
Increases freshness as crops can be shipped to a alive in the water
disadvantages
Technical knowledge is important on the system is very expensive to set up and run
strategy - the new green revolution
description
advantages
disadvantages
description
scientist developed new types of seeds which produce higher yields
Known as high-yielding varieties (HYV)
advantages
Development brought new chemical pesticides herbicide and fertilisers-help plant growth
Agriculture industries is able to produce larger quantities of cheaper food
disadvantages
Since 50s/60s the global population has continued to grow and cocky aren’t growing with it
now a ‘ new green Revolution’ focusing on Africa and instead of Asia-major part of this new green revolution is the role of biotech
strategy - biotechnology
description
advantages
disadvantages
description
when plants animals and fish are genetically modified (GM)for crops - injects the genes of one plant to another-giving the new plant the other plants characteristics
advantages
many potential benefits for LIC farmers - can design drought resistant plants- don’t catch diseases
disadvantages
People concerned about the effects of GM crops on the environment as well as on human health
strategy - appropriate technology
description
advantages
disadvantages
description
using cheap skills/materials that are easily available to increase crop production without putting people out of work
Low tech strategy E.G.harvesting equipment
advantages
Appropriate LIC as other methods (aeroponics) is too expensive
Can produce power
disadvantages
Not as efficient as other strategies - therefore won’t be enough to solve the problem
example: “large scale agriculture”
Almeria, Spain
how many acres of greenhouses does Almeria, Spain have
45,000 acres of greenhouses
world’s largest area of greenhouses
how would you describe Almeria, Spain
dry climate - arid - 200m of rainfall a year
turning into a desert
where is Almeria, Spain
southeast of spain
in europe
by the coast of meditaranean sea
facts + figures
almeria, spain
who are the greenhouses owned by
what crops are grown here
how much income does tgis scheme bring - ehy
how are the plants grown
greenhouses owned by a mixture of large businesses and individual farmers
most of out of season UK crops are grown here
scheme brings over US$1.5billion per year in income - as it delivers over half of Europe’s fruit and veg
almost all plants grown by hydroponics
so successful tgey moved up the valleys of the nearby Alpujarra hills - one of spains most unspoilt areas
ehy did they develop this large scale agricultural scheme (6)
changes in ppls diet - ppl eat more veg
development of suitable plastic to build the greenhouses
new + fast transport methods - lowered shipping cost
average temp in region is 20C without 3,000 hours of sun per year
lower costs from immigrants
funding from EU abd spanish gov.
disadvantages of Almeria (6)
large amounts of cheap labour
immigrant labour is paid very low wages and often live abd work in poor conditions
many immigrants are working illegally and so have little control over their working conditions
local environment has been badly affected - large areas of land have been covered with plastic, destroying the natural ecosystems + plastic is dumped in sea and is affecting marine ecosystems
increased use of pesticides in the area has led to increased health risks for those who work or live near the greenhouses
greenhouses reflect sunlight baxk into the atmosphere + contributed to the cooling of the area - temp has dropped by 0.3C per 10 years
advantages of Almeria, Spain (8)
large amounts of cheap temporary labour
the immigrant labour is paid very low wages and often live and work in poor conditions
the advance of hydroponic growing techniques
less water is used due to drip irrigation + hydroponics
a new desalination plant supplying fresh water from sea water to the region
low energy costs due to the all-year-round-warmer temperatures
additional jobs created in packing plants
relatively cheap fresh fruit and veg provided all year
sustainable food production define
maintains food supplies for future generations without damaging the land,water, energy resources. Provides social benefits and doesn’t contribute to climate change.
why are organix farming and permaculture similar because…
they are both sustainable because…
the most sustainable approach is … because…
they both avoid using chemicals
they are better for environment
permaculture because they don’t disturb wildlife and is less wasteful è.g use of water
organic farming
variety of crops layout of crops
irrigation
pest control
souo preparation
plant one variety of crop (monoculture)
large scale singular crop
use wasteful irrigation systems - use sprinklers which jet out gallons of water - most evaporates
may use organic compounds to kill or control insects snd weeds
dig the soil to create raised rows
permaculture
variety of crops layout of crops
irrigation
pest control
souo preparation
mixed variety + large varieties at once!!
variety of plants are grown together in helpful ways - one revitalise the soil anither to provide ground cover sì soil foesnt dry out, one to deter pests, one to attract beneficial insects è.g ladybugs + large varieties at once!!!
rainwater rather than hosepipes connected to public water supplies hoses in small supply
create an ecosystem for all plants and animals - including pests
pile on compost without distributing soil and worms
seasonal food
eating food tgat is in season locally reduces food miles + also reduces energy used in producing out kf season food locally in greenhouses
urban farming initiatives
when gardens are created on unused land in towns and cities
aim is to increase the connection people have with food production and contribute to a sustainable system kf food production
HICs- run locally/voluntarily to contribute to a sustainable future
LICs-important part of food security + contribute to income + nutrition by providing fresh fruit, veg + meat
many major cities in USA have wrll established urban farming communities
other countries allocate allotments, allowing people with small or no gardens to produce their own food
local food
local food consumption in HICs can benefit people in LICs
this reduces the crops grown by LICs for export
sustainable meat
there are many views on whether the production of meat dor human consumption is sustainable esp considering the huge cost to the environment
feeding animals grains and concentrated feeds indoors is less sustainable than the traditional method of grazing animals è.g sheep outdoors on grass (pasture fed)
grazing livestock outdoors can also be a good way to maintain the landscape such as moorlands in the UK
producing other meat è.g chicken + pork, using free-range methods where the animals are able to go outside for at least part of their lives + exhibiting more natural behaviours, is also seen as more sustainable than rearing tgem intesively indoors
many countries have developed labelling systems to enable consumers to identify meat produced by more sustainable methods è.g freedom food logo used in UK
sustainable fish
sustainable sourcing of fish = whrn fish are farmed/fished in a place where the species can maintain its population indefinitely, and without impacting on other species in the ecosystem by removing their food source or damaging the ohysical environment
identifying fish that are sustainable is very difficult due to the difficulties in accurately assessing fish populations
in addition, methods used to catxh the fish can impact on the sustainablity of the fish
large-scale purse seine net fishing for tuna catches many other species due to the small hikes in nets not allowing them to escape - these other species are often returned to the sea dead = by catch
more sustainable fishing method è.g using pole snd line
seabed dredging or bottom trawling for shellfish can destroy the entire sea floor ecosystem
diving is more sustainable - only selecting the mature ones
sustainable fishing for tuna + shellfish can also come from fish farms, including mussels + freshwater fish
HOWEVER some large scale fish farming has caused inc problems for marine ecosystems by introducing diseases to the wild fish population + polluting the surrounding waters wiyh chemicals, antibiotics + vaccines used to control diseases in intensively farmed fish
why do we waste food - UK (3)
farmers - grow more than they need so they don’t have to pay fines to supermarkets (for not growing enough) unwanted food goes in bin
supermarkets - put up offers so they gain more money and makes consumers buy more than whst they need
consumers - buy more than ehat tgey need - end up throwing away kots of food - stick to use by dates and throw food away if it’s passed its date - even if tgey are still safe to eat
difference between food waste and food loss
food waste is food that is food bought by consumers and is then wasted in the home. food loss is food that is lost in any stage kf production before it enters the home
ways of reducing food waste
eat smaller portions
learn to preserve products jn season - freeze, pickle, can, make jam
shop more carefully - buy exactly what you need or plan meals
look carefully at use by dates
but odd shaprd veg tgen expecting perfect ones + encourage supermarkets to stock them
supermarkets need to reduce confusion over ‘best before’ and ‘use by’ dates on packaging
compost peelings + other veg waste - ensuring they don’t go to landfill sites - vut return nutrients to the soil
example - local sustainable food production
Jamalpur district
where is Jamalpur district
south of asia
bangladesh
india almost completely surrounds Jamalpur and Myanmar is on the East kf Bangladesh
bangladesh opens into the ocean and is only a few meters above sea level
bangladesh has a river running through bangladesh into the ocean
what does NGO stand for
and what is it
N-non
G-governmental
O-organisation
charity
è.g red cross and practicle action aim is to fix poverty through technology practicle action is working in: india, chile, kenya, etheopia, somalia
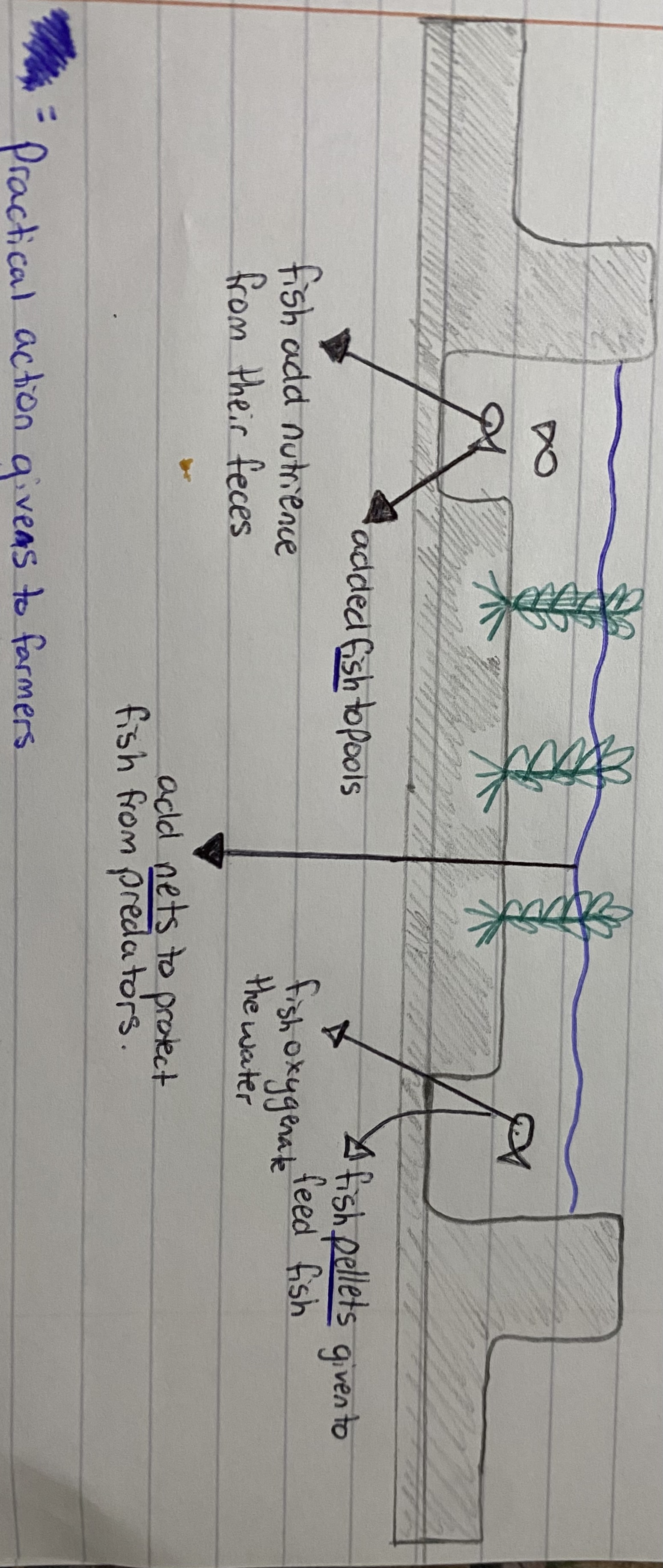
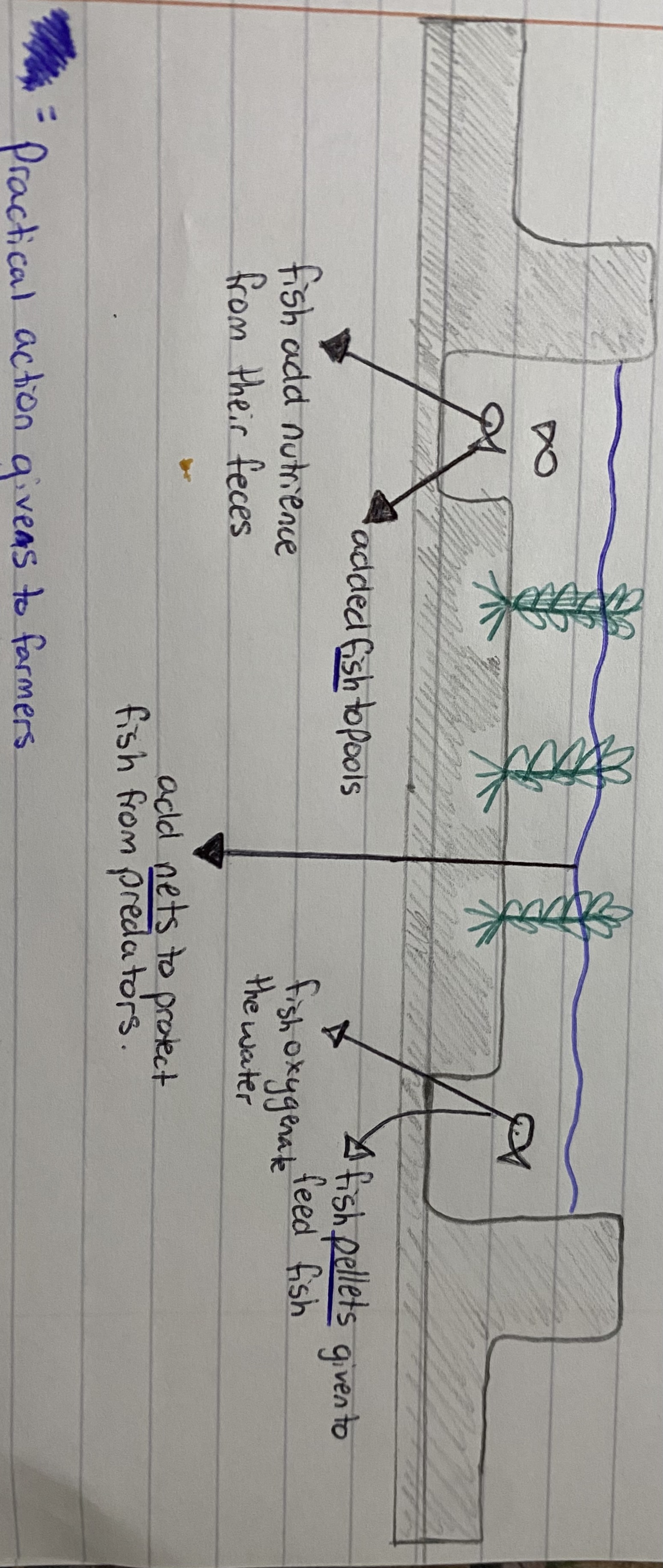
rice-fish culture
sustainability
LOOK IN BOOK 1 OCTOBER
NGO added fish to pools to add nutrience from their fences
NGO added nets to protect fish from predators
NGO added pellets given to feed fish + the fish oxygenate the water
end product is increased yield. More rice = more income
sustainability
environmentalaly - rice and fish benefit + no artificial fertilisers
economically- more money- expanding the business - education
socially- information can be passed on
what is a subsistence farmer
is a farmer who grows just enough for their family