Neuro EXAM 1 Case Studies and Photo Recognition
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
14 yo vietnamese girl had a seizure and at ER could not move her right arm or see to her left. She was also quite thin and short and hard of hearing. A month later she was back in the ER and completely unable to move her left arm and hearing was worse; HER DIAGNOSIS IS…
MELAS Syndrome (Mitochondrial Encephalopathy with Lactic Acidosis and stroke) - MITOCHONDRIAL ENERGY FAILURE
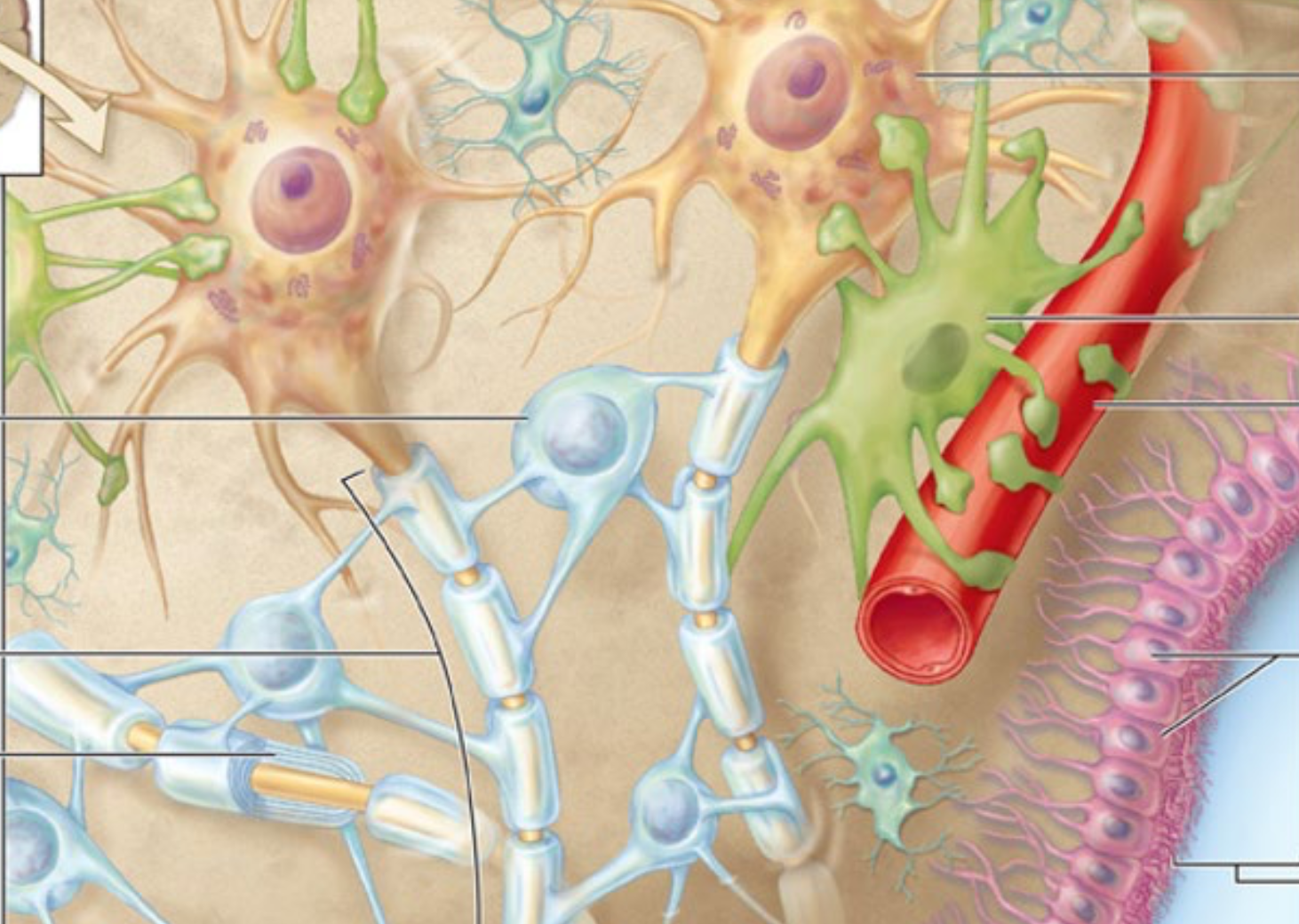
Point out all the glial cells
Proof check
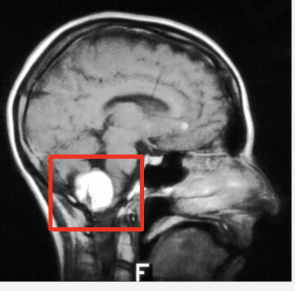
What does this image show
Astrocytoma (excess build up of Astrocytes, forming tumor or mass)
36 year old engineer developed incoordination of his left arm and tendency to fall to his left, along with headaches; his diagnosis IS…
Astrocytoma
15-month-old boy admitted for continual screaming, vomiting, and enlaraging head - he deteriorated and died 3 weeks later; His diagnosis is..
Alexander disease (Astrocytes fill with GFAP protein and fail)
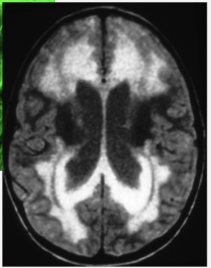
what does this image show
Build up of GFAP in astrocytes (Alexander Disease)
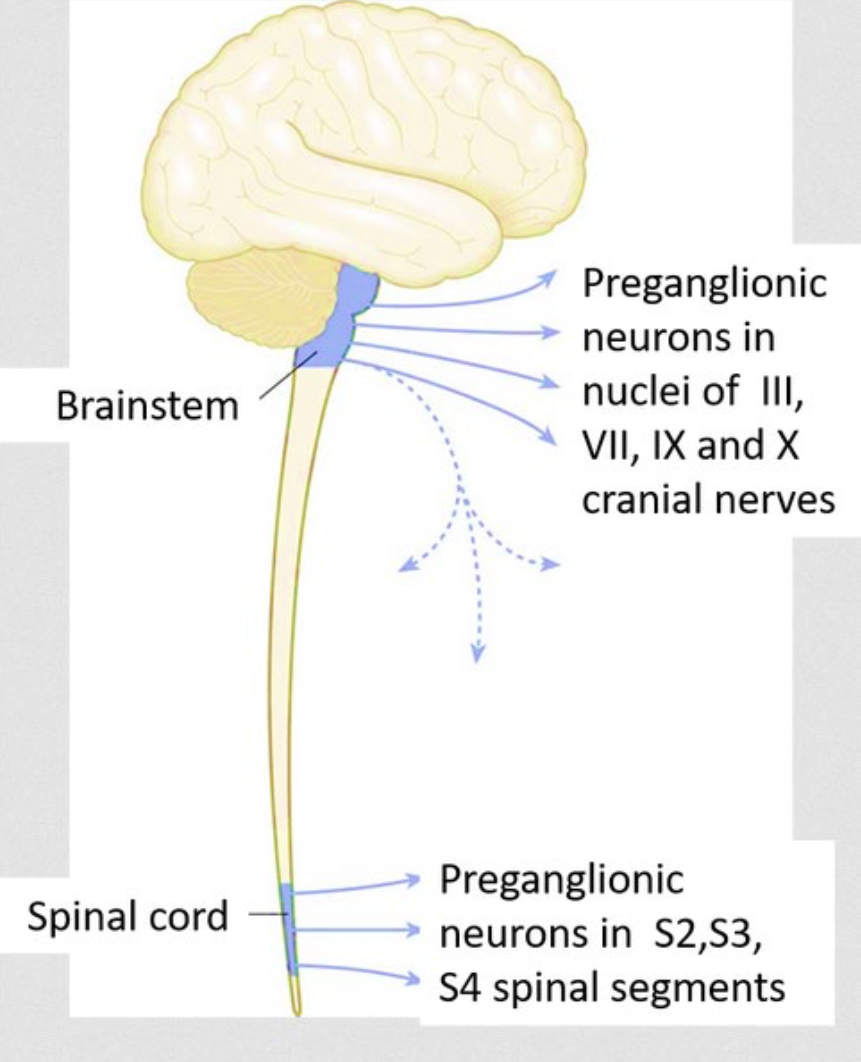
What system is shown in this image
Parasympathetic System (rest and digestion)
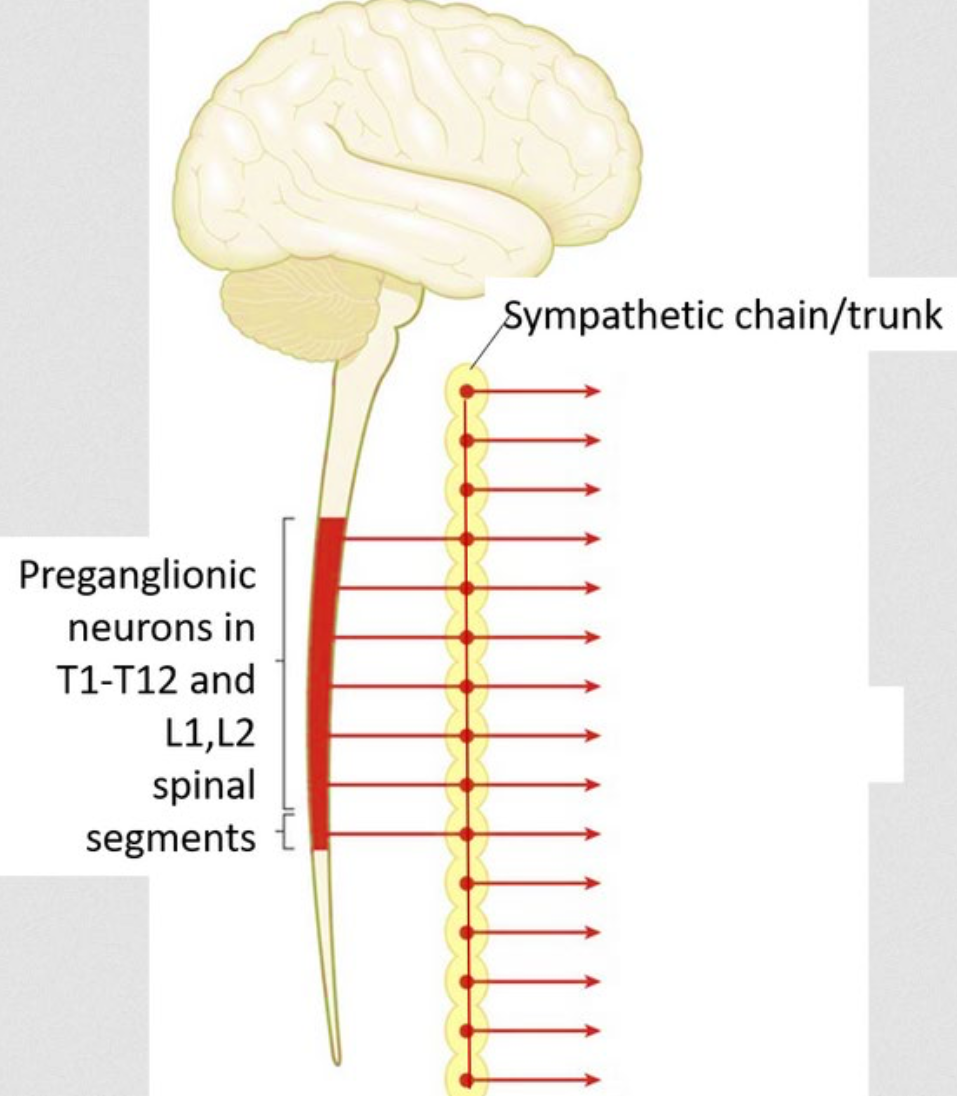
What system is shown in this image
Sympathetic System (prepares body for action)
Medial
toward middle
Ipsilateral
same side
Anterior vs. Posterior
Head side and Tail end
Proximal
near center
Dorsal
toward back
Lateral
toward side
Contralateral
Opposite side
Distal
toward periphery
Ventral
toward belly
Afferent
carries impulses INTO region of interest (sensory)
Efferent
carries impulses AWAY from a region of interest (Motor)
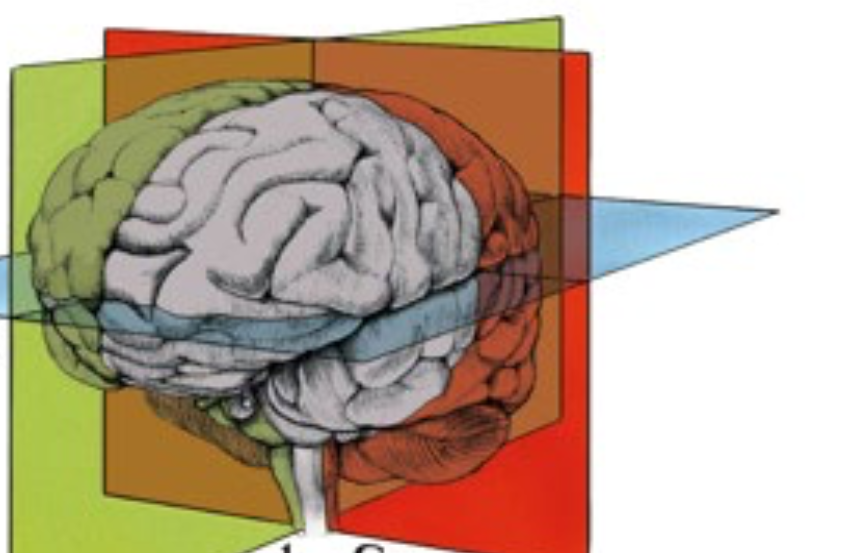
Name the 3 planes and point to them
check for accuracy
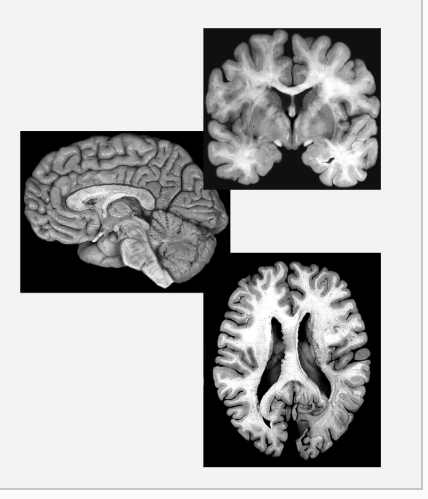
Name the 3 splits
Check for accuracy
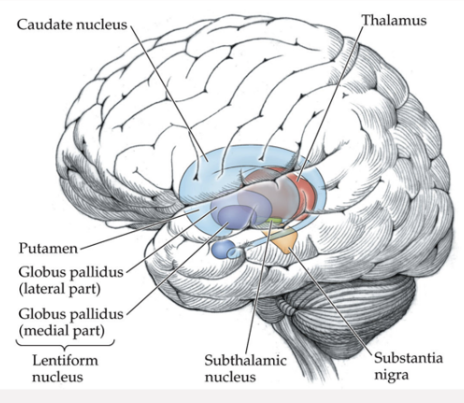
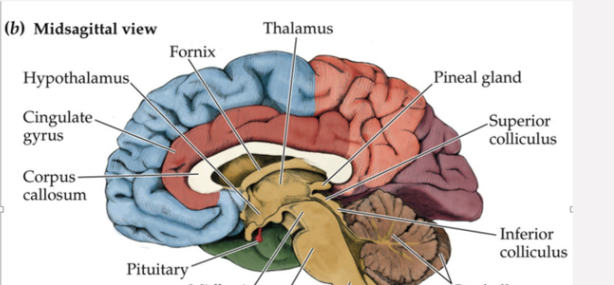
Which area of the brain is shown in this image; what does it do?
Basal Ganglia - in charge of movement control
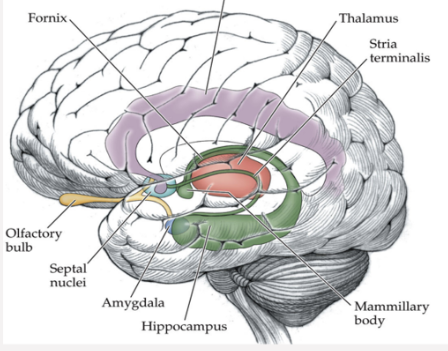
What area of the brain is shown in this image; what does it do?
Limbic System - in charge of emotional memory regulation
Point out the cerebellum in this image; what does it do?
in charge of motor coordination and learning
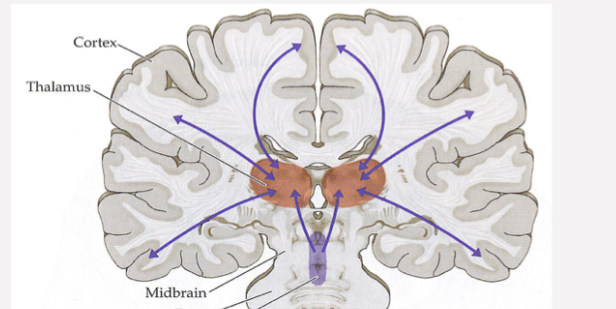
What area of the brain is shown in this image; what does it do?
Reticular formation - regulates sleep and arousal (makes sure you sleep and wake up), also regulates body temperature
What is Meninges
Brain Wrappings
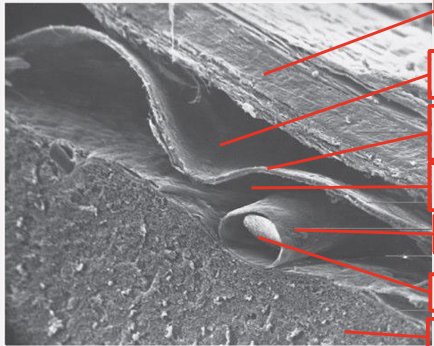
Name what each layer of meninges is
check for accuracy
what connects brain areas?
White matter tracts (axons)
What are the 5 ways of visualizing human brain?
CT, MR, DTI, PET, and fMRI
CT scan
computed tomography scan (uses x-rays absorption to show tissue density)
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging (uses magnetic and radio waves that differ by tissue density)
DTI
Diffusion Tensor imaging (maps white matter pathways of the brain using diffusion of water molecules)
fMRI
function magnetic resonance imaging (uses magnetic and radio waves to produce imaging of brain WHILE it is functioning) - DETECTS changes in brain metabolism like oxygen use in active brain areas
PET
Positron Emission Tomography (uses radioactive tracers (chemicals) to access brain ACTIVITY)
how can denser tissues be identified in brain scan?
whiter image
In a DTI scan what directions are each of the colors of White matter tract pathways?
Blue: up and down
Red: side to side
Green: projecting front and back
doctor found several cataracts in baby when he was a few weeks old and at 4 months he became severely retarded; what is his diagnosis??
LOWE SYNDROME (can’t make golgi sacs so cellular processes are disrupted)
Sheila fell in her garden and cut her leg. She was taken to ER and her wound was cleaned and stitched, but had to return to ER because FACE ACHED and could NOT OPEN MOUTH. She looked unwell and complained of DIFFUSE PAIN - her condition worsened 24 hours later, she developed jaw stiffness and severe back and limb spasms
TETANUS (bacterial infection related to toxin that inhibit glycine release and causes muscle stiffness and spasms)
Intrinsic Proteins
receptors and ion channels; give neuron the necessary properties for SIGNALING
Railtracks of Neurons
Microtubules
STATIC support structure of Neuron
Neurofilaments
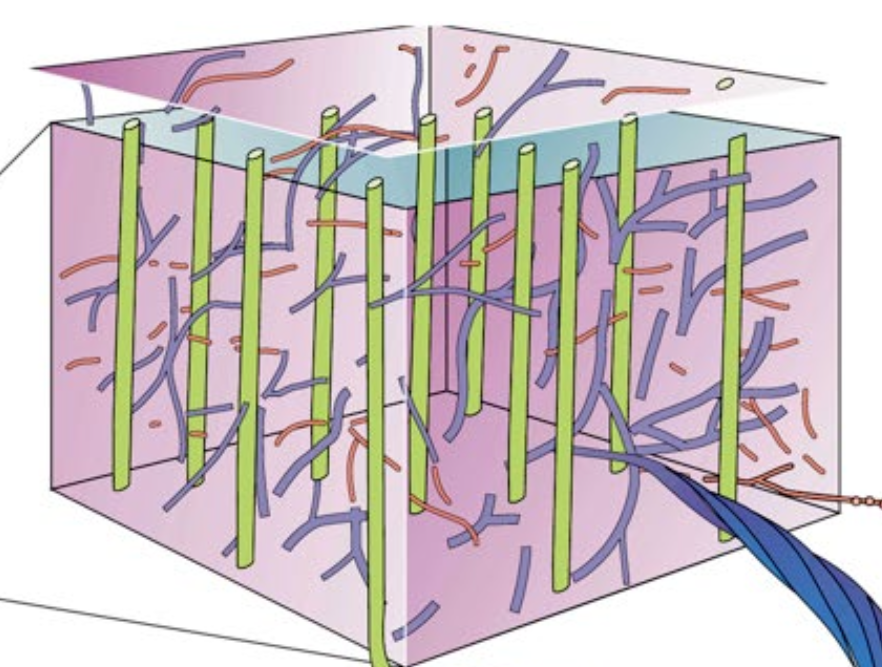
Point out the Neurofilaments and Microtubules
check for accuracy
Explain Anterograde vs. Reterograde transport an proteins involved
SOMA to TERMINA (ant and kinesin involved) - TERMINAL to SOMA (ret, and dynein involved) - > all of this happens along the MICROTUBULES
what do leak channels do
allow potassium to exit the cell more freely than Na+ enters (this is why inside of neuron is more negative)
Ion distribution of Ca2+
many outside cell and fewer inside
Ion distribution of Cl-
many outside the cell and few on the inside
Ion distribution of Proteins (-)
many inside cell and fewer outside cell
Why does sodium potassium pump require energy in the form of ATP?
Because it is moving ions AGAINST concentration gradient (Na+ from inside to outside (low to high) and K+ from outside to inside (low to high))
How does tetrodoxin work?
it comes form pufferfish (fugu) and prevents nerve impulses by blocking voltage gated Sodium channels by binding to them and fails respiratory system. -makes it impossible for Na+ TO ENTER CELL and thus ACTION POTENTIALS cannot be fired preventing nerve signaling.
where do graded potentials occur?
Dendrites
What is true about Na+ gradient ions at the peak of action potential?
the concentration gradient pushing Na+ ions into the cell equals positive charge driving them out.
Saltatory Conduction
signal movement along myelinated axon
What happens when a neurotransmitter bind to an autoreceptor?
autoreceptors are located int he pre-synaptic neuron so it will decrease release
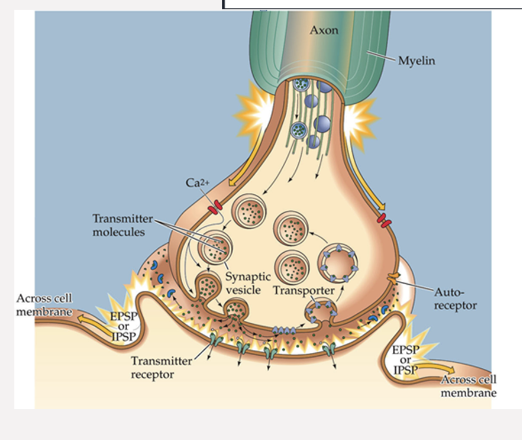
Explain the Chemical Transmission Process
check notes for accuracy
what is 5 HT?
Serotonin
what is MAO?
Monoamine Oxidase - mitochondrial enzyme that breaks down neurotransmitters in the synapse
What leads to alzheimers?
when there is too little acetycholine caused by excess breakdown
Gap Junctions
channels between adjacent cells that allow direct and rapid exchange of small molecules, ions, and electrical signals
HOW does EPSP flow down until it reaches axon hillock?
Passively
What is a Ligand?
It is a term used for any substance that can bind to a targeted protein; in this case a NEUROTRANSMITTER
Absense Seizure
only last few seconds, instant recovey, no weird muscle movements except zoning out and stopping and staring. Brain waves show rhythm.
What does glycine do?
this is an inhibitory NT and its release prevents muscles from being rigid because it stops nerve signals that make muscles contract. TETANUS bacteria blocks the release of glycine.
What is opisthotonus?
weird position where back is arched with head and heels touching the ground; symptoms start with stiff neck, twitchign muscles, feeling of suffocation, then violent convulsions.(that guy in hospital bed that looks like hes doing a back bend)
CAUSED BY: strychnine poisoning which blocks glycine (GLYCINE antagonist)
Explain the different between competitive and non-competitive antagonist?
competitive just takes ligands stop and causes COMPLETE block and non-competitive sits somewhere near ligand binding site so ligand can still bind but it will only have half of the effect its supposed to have (HALF blocked)
List the Amino Acids
Glutamate, GABA, Glycine, Aspartate
2 types of monoamines
Catecholamines and Indolamines
List catecholamines
Dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine
name an indolamine
Serotonin
name the 3 glutamate receptors and agonists
AMPA, NMDA, and Kainate
What is excitotoxicity?
neural injury such as head trauma or stroke causes excess release of glutamate, which kills neurons
List the agonists of GABA
Barbiturate, Benzodiazepine, ethanol, neurosteroids
explain process of catecholamine synthesis STEP by STEP
there are 5 steps - check for accuracy
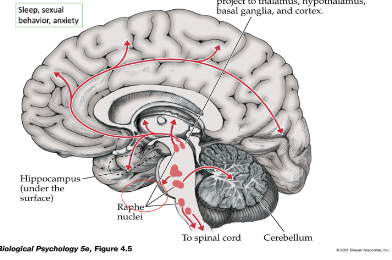
Which pathway is shown here
Serotonin
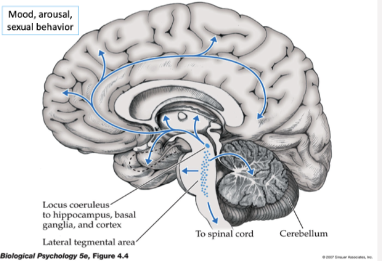
Which pathway is shown here
Norepinephrine
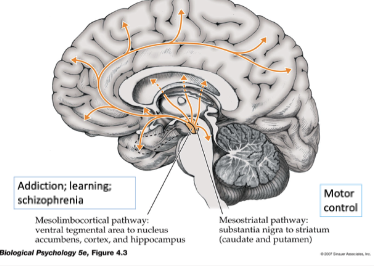
Which pathway is shown here
Dopamine
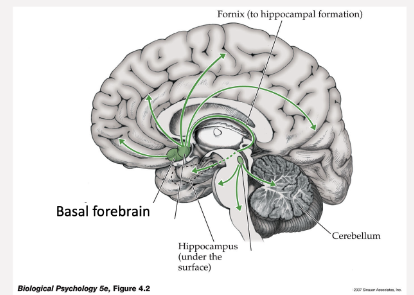
Which pathway is shown here
Cholinergic
Neuroleptic
drug used to treat aggressive behavior and schizophrenia (DOPAMINE antagonist)
Neuromodulator examples
adenosine
What are thee 2 types of antidepressants and what do they do
Tricyclic: increase norepinephrine and serotonin in synapses by blocking reuptake
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors(SSRIs): cause serotonin to build up in the synapses( FEWER SIDE EFFECTS than tricyclics)
Anxiolytic
tranquilizers that reduce nervous system activity
Which anxiolytic is produced by astrocytes?
Diazepum-binding inhibitor
which neurotransmitter is blocked by alcohol and which is enhanced?
Glutamate blocked and GABA enhanced
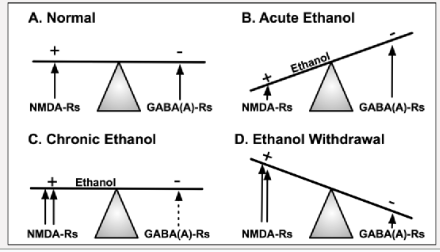
Explain alcohol use and this image
check to make sure
How do opioids work?
GABA inhibition (reduce GABAergic inhibition) in ventral tegmental area causing excess release of dopamine providing feelings of analgesia; also binds to mu-opioid receptors in the CNS, inhibiting pain signaling
What is the Periaqueductal gray (PAG)?
-where opioids relieve physical and emotional pain
How did bayer try to solve his codeine addiction?
he tried to use heroin as a cure but it metabolized into morphine and he got addicted to that instead.
endocannabinoid system
network of receptors, enzymes, and chemical messengers that are in charge of pain perception, digestion, mood/emotion, sleep etc.
which neurotransmitter is ventral tegmental area associated with?
Dopamine
Main mechanism of cocaine
blocks monoamine transporters which enhances effects of dopamine/ - Alertness, energy, and euphoria
main mechanism of marijuana
binds to cannabinoid receptors and mimicks effects of endocannabinoids
main mechanism of nicotine
binds to nicotinic ACh receptor in ventral tegmental region which leads to excess release of dopamine and increases ALERTNESS
what is CART
cocain - amphetamine regulated transcript - peptide involved in pleasure sensations from these drugs and in appetite suppression
main mechanism of amphetamines
block reuptake and increase release of catecholamines - develop conditions like schizophrenia from excess dopamine - long term effects: severe brain damage, cognitive decline, and cardiovascular damage.
What are adderall and Ritalin?
These are both medications for ADHD that improve function; Adderall: increasses dopamine and norepinephrine release and Ritalin: blocks dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake.
what does release of oxytocin do
enhances feelings of TRUST and CONNECTION
stem cells
they self-renew and can convert into different types of cells
a high school student has a seizure at school and was brought to CMC neurology clinic for evaluation - he had red hive like rashes on his face which indicated problem in the BRAIN.
TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS - white part (GLIAL cells excessive in the brain way MORE than neural cells)
Pachygyria
disorders in cell migration step of brain development that cause brain malformation