D2 | Fixed Prosth | Dental Ceramics
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
maxillary anterior teeth are restored with
veneers
ceramic
inorganic, non-metallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling
T/F non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity
T/F non-metals are brittle
TRUE
TRUE
what are the two major components found in ceramics?
refractory crystalline structure
glass
T/F refractory crystalline structures are composed of Si2O and Al2O3
FALSE
glass is composed of Si2O and Al2O3
what are refractory crystalline structures made of?
metallic oxides (silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide)
- retains crystalline identities
what is glass composed of?
Si2O and Al2O3
- do not retain crystalline identities
T/F glass molecules form an amorphous glass gel matrix
TRUE
glass to crystal is like ________ in __________
cement between paved stone

traditional ceramics examples
earthenware, stoneware, domestic porcelain
how does dental porcelain (advanced ceramic) compare to traditional ceramic?
increased/decreased glass
increased/decreased refractory particles
increased/decreased porosity
increased % of glass
decreased % of refractory particles
less porosity
T/F porcelain jacket crown was made from feldspathic porcelain clay. it wasn't particularly esthetic bc of its opacity
TRUE
T/F feldspathic porcelain clay is a traditional ceramic
TRUE
what was feldspathic porcelain clay made of?
equal parts kaolin and fine grains of silica. however, kaolin was phased out and now it's only silica
typical silica glass (noncrystalline solid of SiO2) should be _________ to achieve the "amorphous gel" structure that we desire
a) slowly cooled
b) rapidly cooled
b) rapidly cooled
PFMs came about bc of what two patents?
patent 1:
- identified the formulations of feldspathic porcelain that enabled systemic control of the sintering temp and coefficient of thermal expansion
patent 2:
- described components that could be used to produce alloys that bond chemically to and that are thermally compatible with the feldspathic porcelains
advanced ceramics are often classified as _________ ceramics
oxide or non-oxide ceramics
- further divided into structural/engineering, function, or nuclear ceramics
the majority of ceramics used in restorative dentistry belong to what category of ceramics?
structural or engineering ceramics
dental ceramics can be classified based on what characteristics (8)
- microstructure
- principle crystal phase/matrix phase
- processing method
- firing temp
- translucency
- fracture resistance
- uses/indications
- abrasiveness
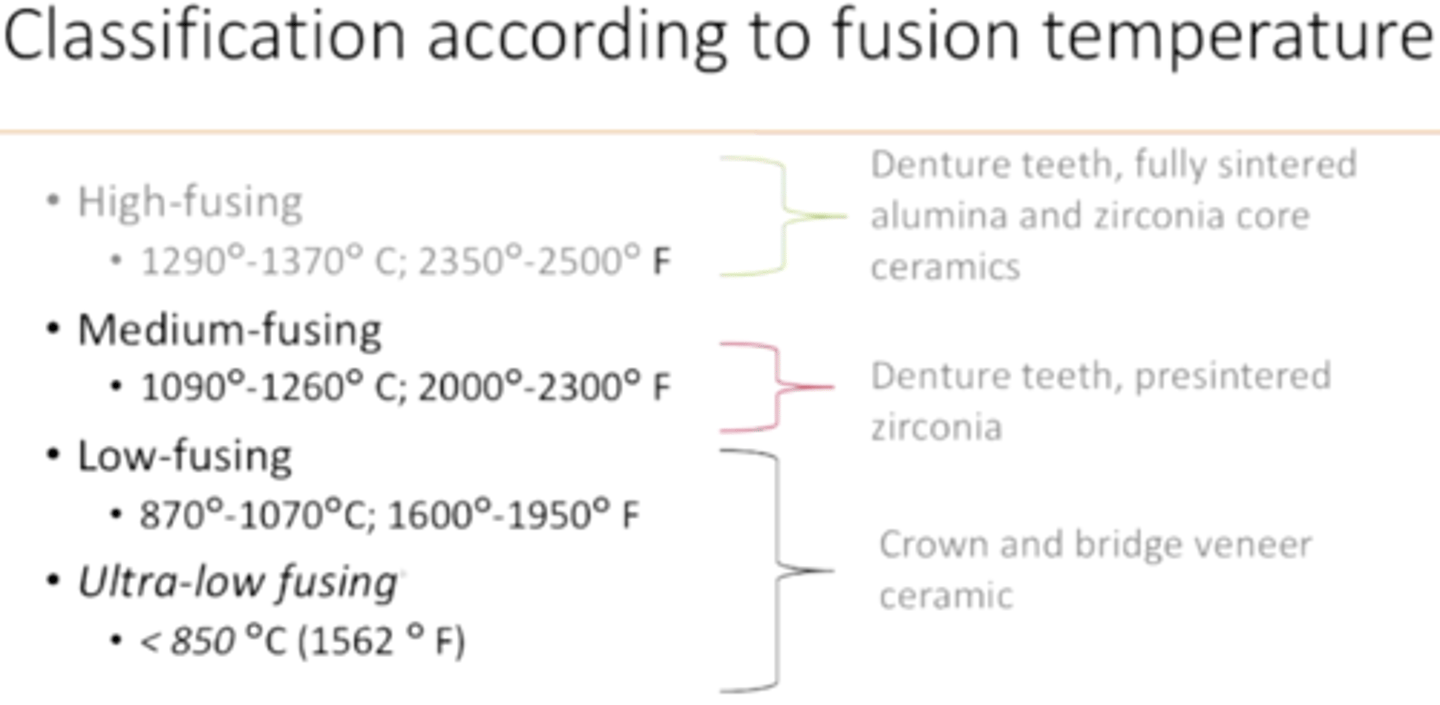
classification of ceramics according to fusion temperature
when adding porcelain onto existing crown, you should
a) add porcelain with higher fusing temp
b) add porcelain with lower fusing temp
b) add porcelain with lower fusing temp -- so you don't melt the OG crown while heating up
summary of fusion temperatures for different ceramic types
how do you manufacture feldspathic porcelain?
frit the glassy mass - each fritting lowers temp at which particles will fuse and coalesce
_____mm is needed where function is great and some esthetics are required
1.0-1.5mm
____mm is needed when esthetic needs are minimal
0.8-1.0mm
____mm is needed when optimum esthetics are needed
1.5-2.0mm
how does the metal bind to the ceramic for PFM? which one is the primary bonding mechanism?
mechanical entrapment (22%)
chemical bonding (51%)
- covalent bonding
compressive forces (26%)
T/F many restorations made from metal and porcelain combinations having contraction coefficient differences between 0.5 and 1.0x10^-6/K are known to survive for many years. coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) must be within 0.1% over solidification/fusion and cooling temp range
TRUE
adhesive failure?
cohesive failures?
adhesive: failures at dissimilar layers
cohesive: failures at similar layers

JR Kelly classifies dental ceramics into what 3 main composition categories?
1) predominantly glassy materials
2) particle-filled glasses
3) polycrystalline ceramics
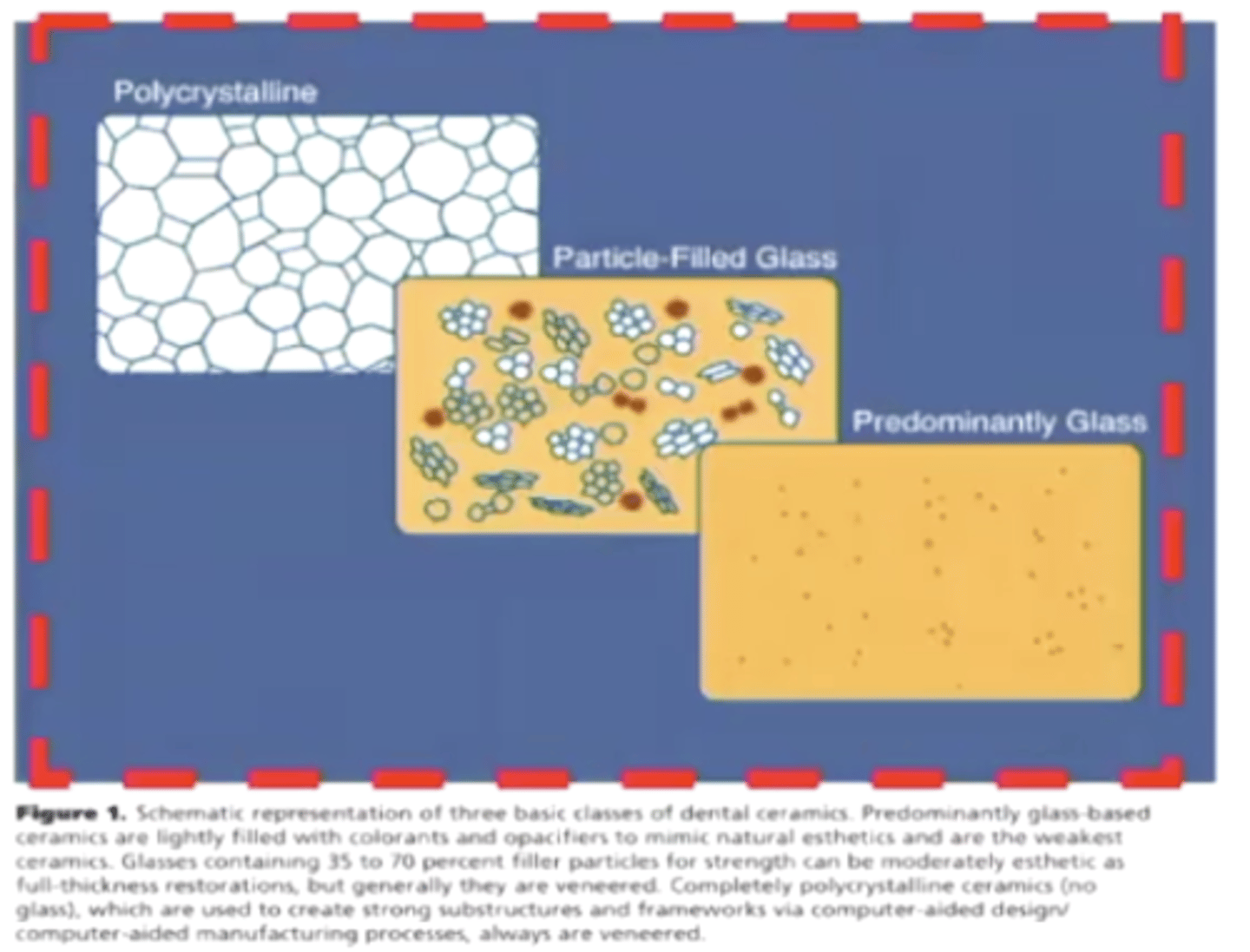
T/F highly esthetic dental ceramics are glassy
T/F highly strengthed ceramics are crystalline
TRUE
TRUE
glass matrix ceramics are a special subset of
a) predominantly glassy materials
b) particle-filled glasses
c) polycrystalline ceramics
b) particle-filled glasses
how are glass matrix ceramics made?
1) they contain >50% fine and uniformly distributed crystals and is formed into desired shape as a glass.
2) subjected to heat treatment to induce partial devitrification (loss of glassy structure by crystallization of glass)
this 2-stage heat treatment (nucleation and crystallization process) is called ceramming
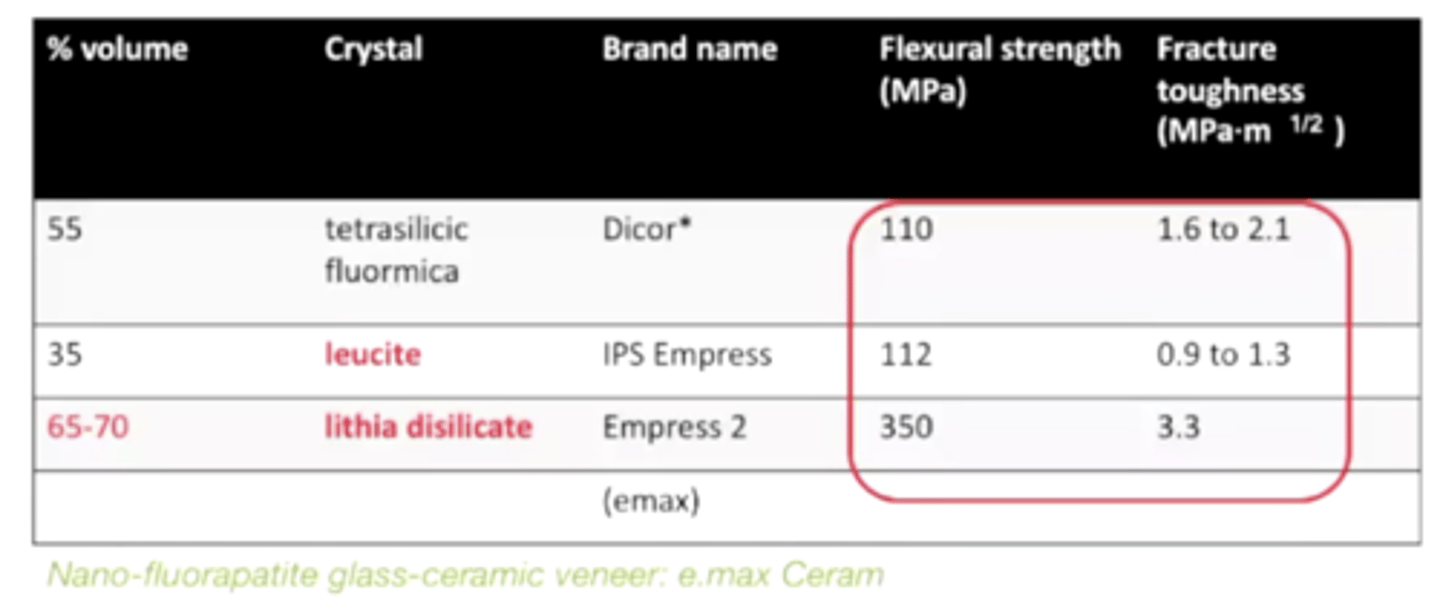
emax, the most popular glass-matrix ceramic, is formed with what crystal?
lithia dislicate
T/F emax has superior flexural strength and fracture toughness to its other glass-matrix ceramic competitors
TRUE
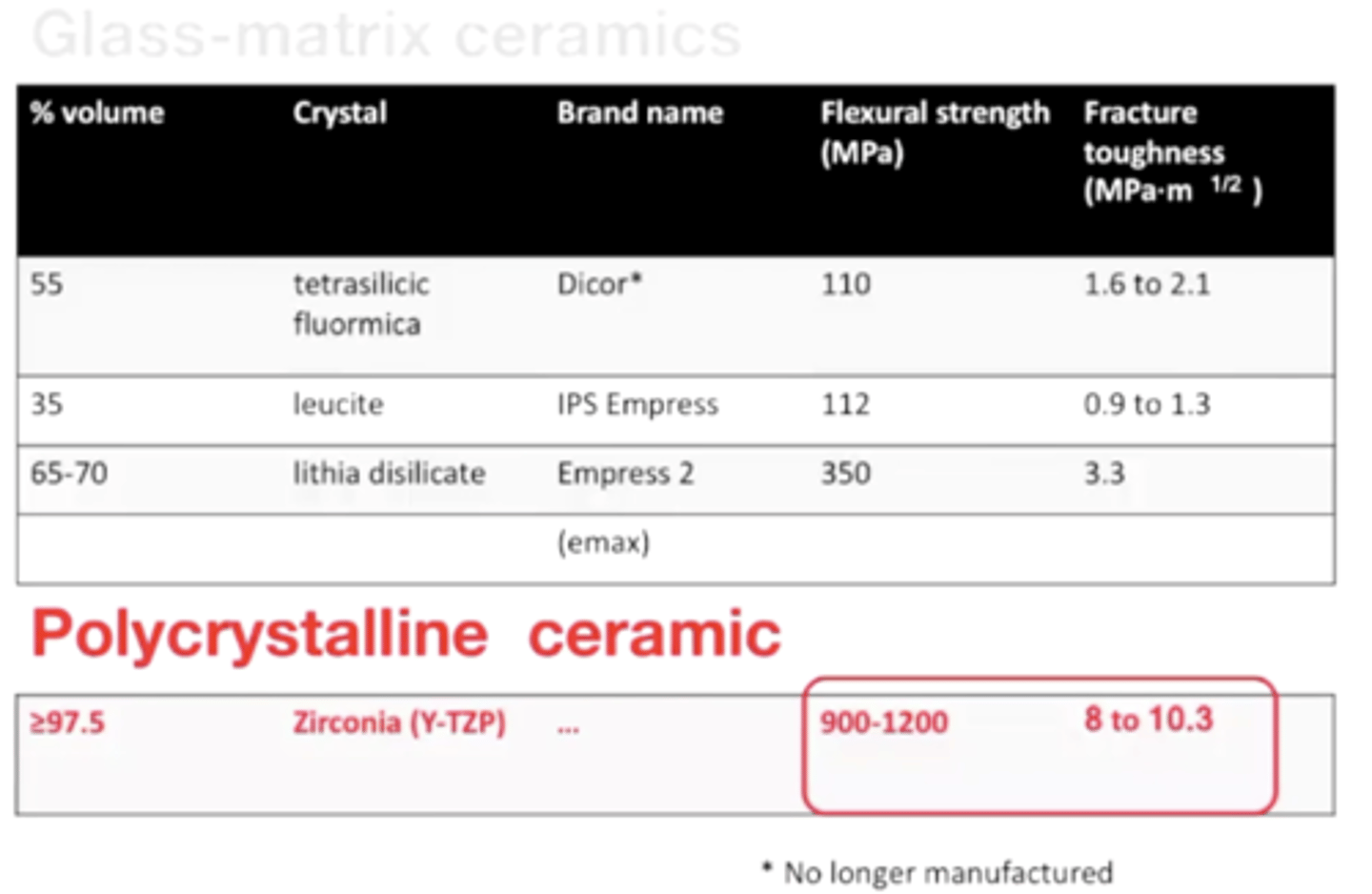
which of the following about polycrystalline ceramics is false?
a) no glassy components, making it difficult to etch
b) tougher and stronger than glassy ceramics
c) limited translucency, known for its relative opacity
d) silica oxide or aluminum oxide
e) shrink by around 30% in volume when made fully dense during firing
d) silica oxide or aluminum oxide -- it is made of alumina and zirconia* (more common)
T/F polycrystalline ceramics are almost 3x stronger than glass-matrix ceramics (also review: what's the glass-matrix ceramic called)
TRUE
zirconium dioxide aka zirconia is a polymorphic material that occurs in three different forms depending on ___________
temperature
what are the different forms zirconia takes?
monoclinic (m) at room temp
tetragonal (t) above 1170ºC
cubic (c) beyond 2370ºC
tetragonal to monoclinic phase transformation causes what?
shear strain
volume expansion (4%)
closes cracks
T/F tetragonal to monoclinic phase can lead to large increases in fracture toughness of the material but also cause cracks during cooling of the material
TRUE
ok this zirconia shi is hellaaa unstable... what do you add to stabilize it?
yttria (Y2O3)
zirconia restorations milling process

layered vs monolithic all ceramic restorations
monolithic:
- one huge hunk of porcelain
layered:
- core material (glass matrix or polycrystalline aka emax or zirconia)
- luting cement
- different layers of porcelain
T/F PFM and PFZ (porcelain-fused-zirconia) have similar bonding attachments, with chemical bonding playing the major role
FALSE
while PFM's main bonding mechanism is chemical, PFZ's main bonding mechanism is mechanical bonding.
T/F there is no clear evidence that there is chemical bonding between zirconia and veneering ceramics
TRUE
the strength of the PFZ bond depends on ________(3)
- type of veneering ceramic used
- number of firings
- cooling rate after firing
T/F PFZ is good for areas where there's not much functionality involved bc it's only held by mechanical bonds
TRUE
how are metal ceramics fabricated? (PFM)
sintering
heat pressing on metal
how are all ceramics made? (3)
- heat pressing
- hard machining
- hard machining + heat treatment
flexural strength
strength test of a bar supported at each end or a thin disk supported along a lower support circle under a static load
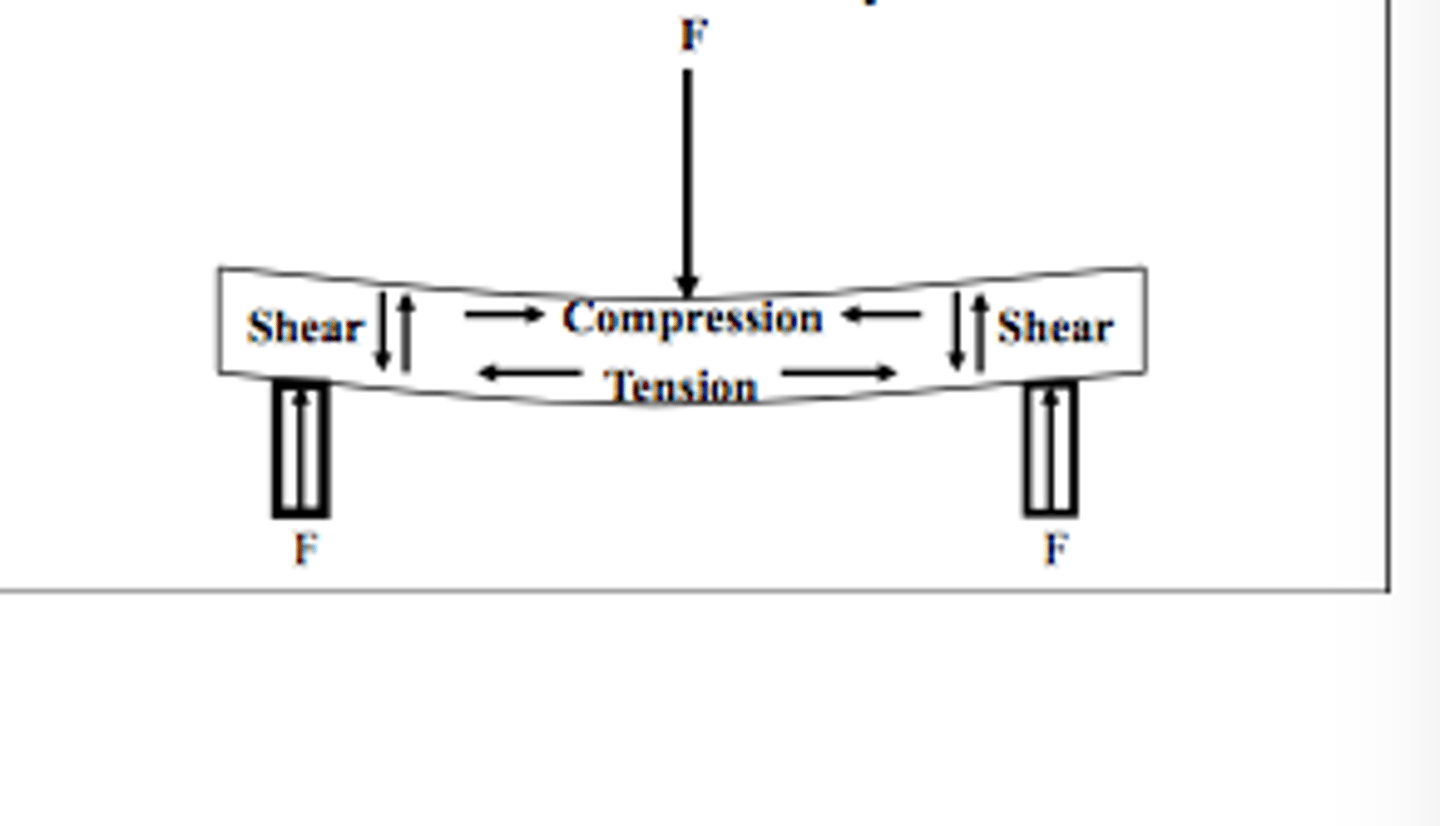
typical specimen dimensions to test flexural strength are a minimum span length of ____mm, a width of ____mm and a thickness of ____mm
minimum length of 20mm
width of 4mm
thickness of 1.2-2.0mm
fracture toughness is also known as
critical stress intensity
what is fracture toughness?
measure of the energy required to propagate critical flaws in the structure
mechanical property that describes the resistance of brittle materials to the catastrophic propagation of flaws under an applied stress
failures in dental ceramic prostheses are usually associated with ________
structural defects or flaws
how might flaws within prostheses arise?
during fabrication and preparation
from post-insertion functional activity
T/F vacuum firing reduces porosity (something air-firing naturally has). this increases strength and decreases translucency
FALSE
while vacuum firing does reduce porosity, this serves to increase strength and increase translucency
T/F compressive stresses close up flaws, while tensile stresses open up flaws
TRUE
T/F surface cracks can be induced by machining or grinding
TRUE
a crack's stress will be reduced by all the following except:
a) another crack
b) pore
c) crystalline particle
d) glass
d) glass
crack propagation theory
as the crack propagates through the material, the stress concentration is maintained at the crack tip, until the crack moves completely through the material, or until it meets another crack, a pore, or a crystalline particle, which reduces the localized stress
thermal shock is caused by __________
uneven heating or cooling -- crown's surface may expand or contract more quickly than the interior, and due to the differential thermal expansion, stresses will develop
thermal shock is more severe upon
a) cooling it
b) reheating or glazing a crown
b) reheating or glazing a crown
in glass, silicates, and other oxide ceramics, ________ break the strained bonds at the crack tip
water molecules
slow crack growth (subcritical)
precedes final catastrophic fracture in brittle materials, unless load is applied very quickly or high magnitude.
- progresses steadily over time, accelerating at higher stress levels and ultimately leading to failure
to maximize durability...
T/F avoid stress raisers like sharp lines in prep
T/F provide maximum occlusal thickness for ceramic
T/F use lowest elastic modulus substrate as possible
T/F bond the restoration
T/F develop broad, not pinpoint, occlusal contacts
TRUE
TRUE
FALSE - use highest elastic modulus (stiffness)
TRUE
TRUE