Biology: Plasma Membrane Structure, Function, and Transport Mechanisms
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
primary function of the plasma membrane
Acts as a boundary between the cell interior and the extracellular environment, controlling what enters and exits the cell.
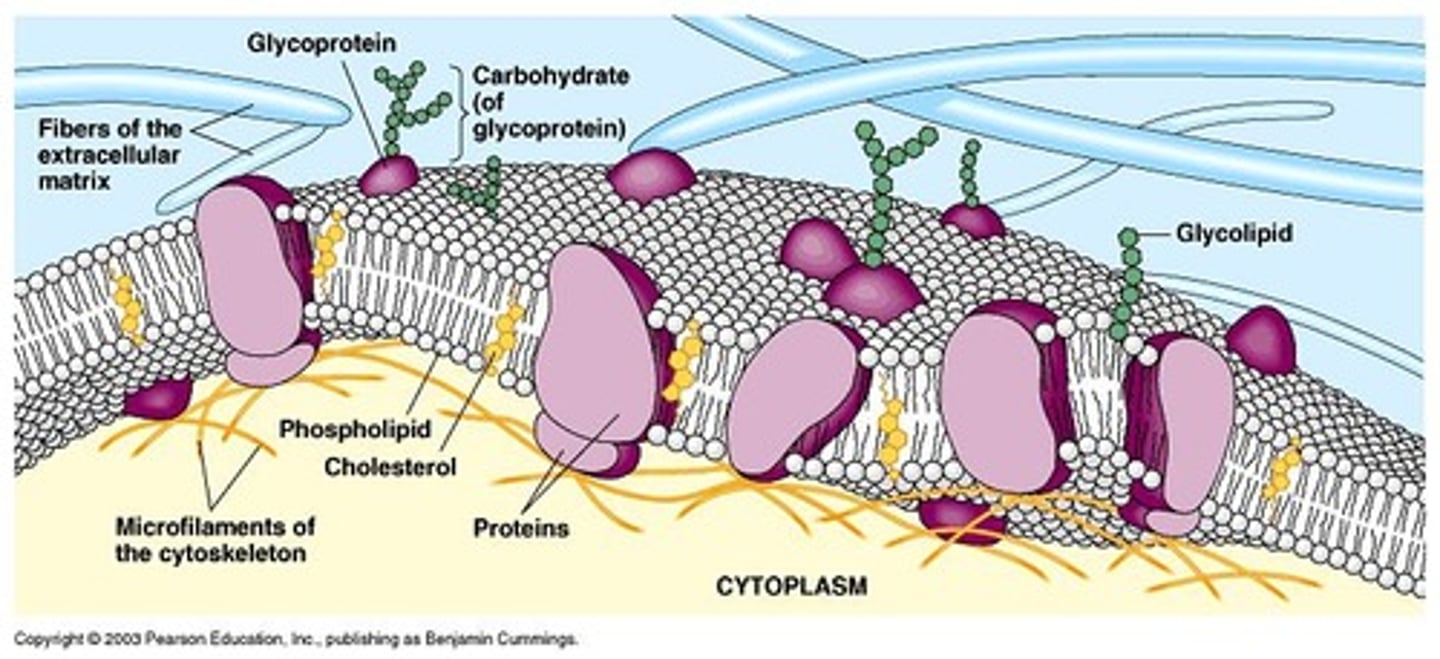
structure of the plasma membrane
A fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins.
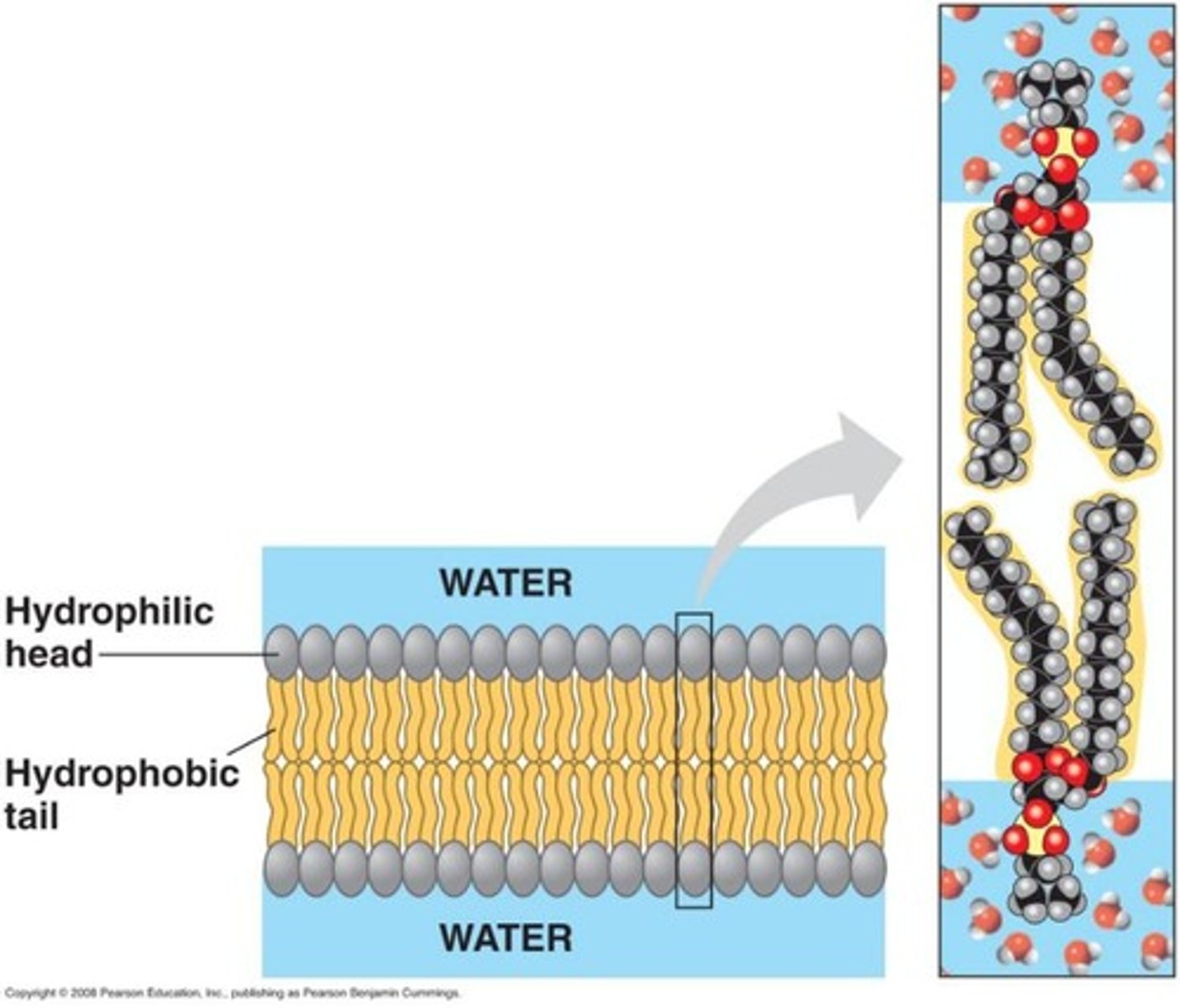
What do lipid molecules form in the plasma membrane?
A flexible bilayer.
role carbohydrates play on the plasma membrane
They act as cell identification tags on the surface.
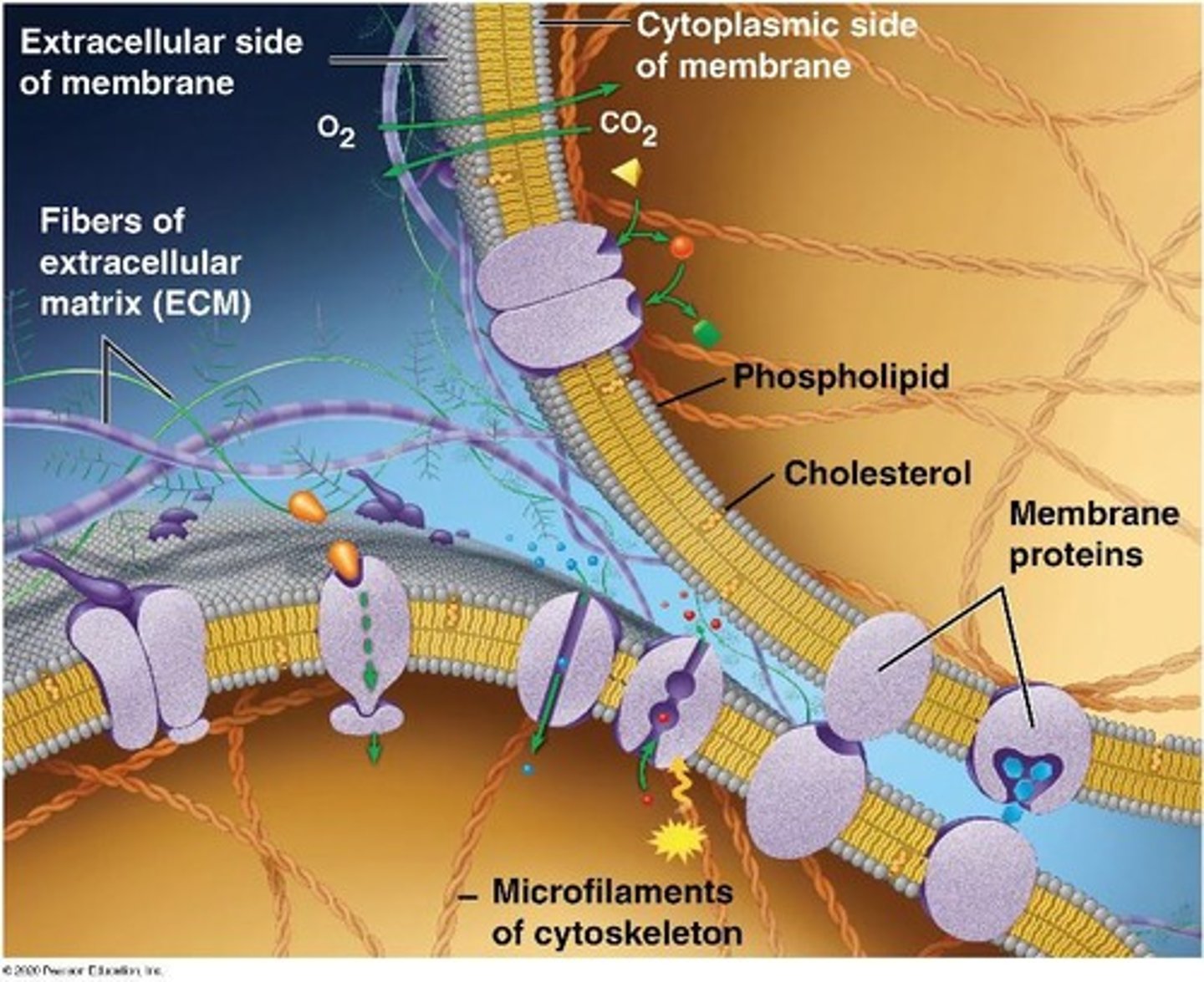
difference between the cell membrane and the cell wall
The cell membrane is flexible and selectively permeable, while the cell wall is rigid and provides structural support.
phospholipid arrangement in water
They form a stable bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing the water and hydrophobic tails facing away.
amphipathic
Molecules that have both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties.
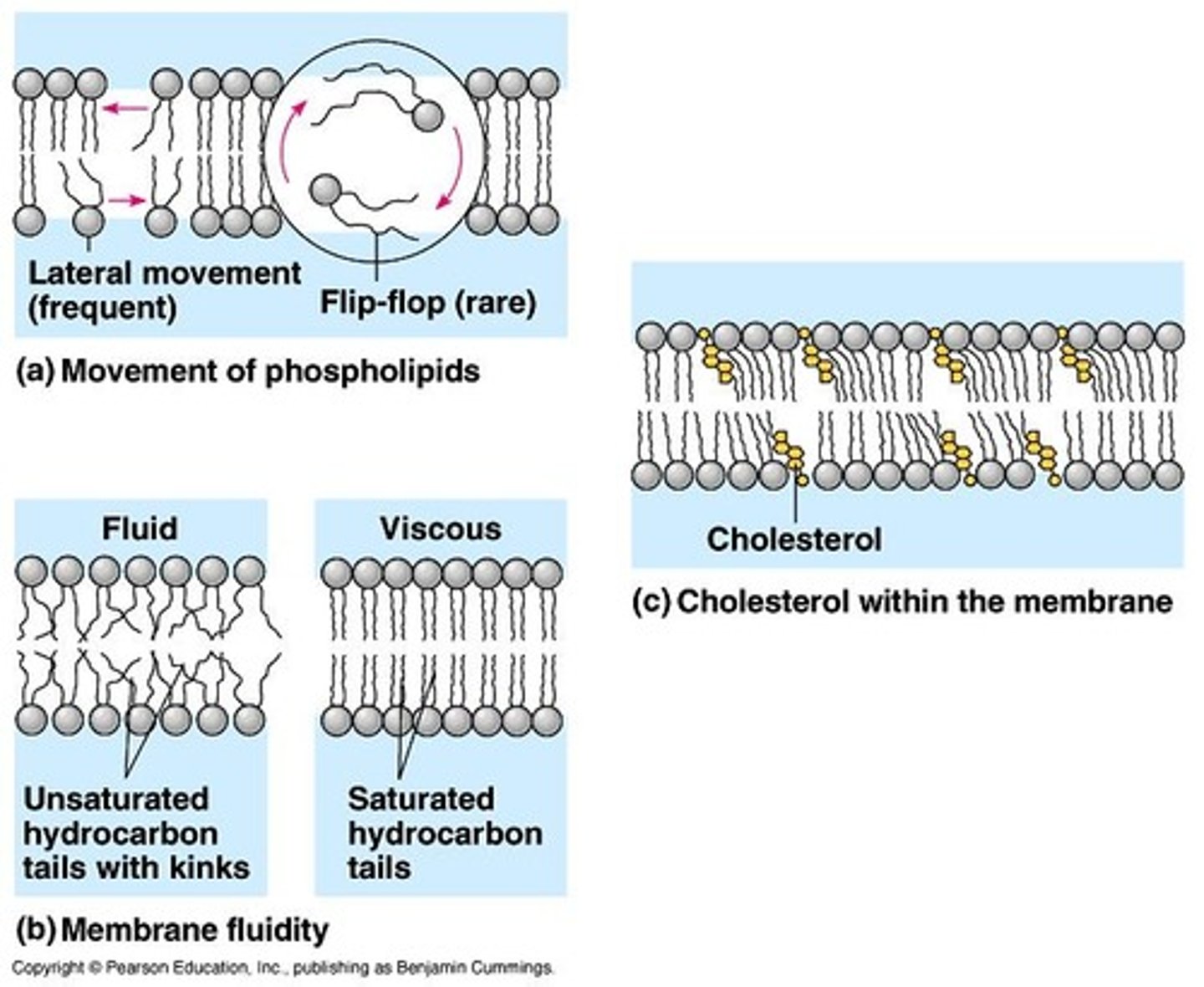
consistency of cell membranes at room temperature
Similar to salad oil, allowing for rapid lateral movement of lipids.
Why are flip-flops of lipids in the membrane rare?
Hydrogen bonds with water must be broken, requiring specific conditions for the phosphate heads to move correctly.
saturated fatty acids affect on membrane fluidity
They result in straight chains that allow for maximum interaction, making membranes more viscous.
effect cholesterol has on membrane fluidity
At warm temperatures, it restrains phospholipid movement; at cool temperatures, it prevents tight packing to maintain fluidity.
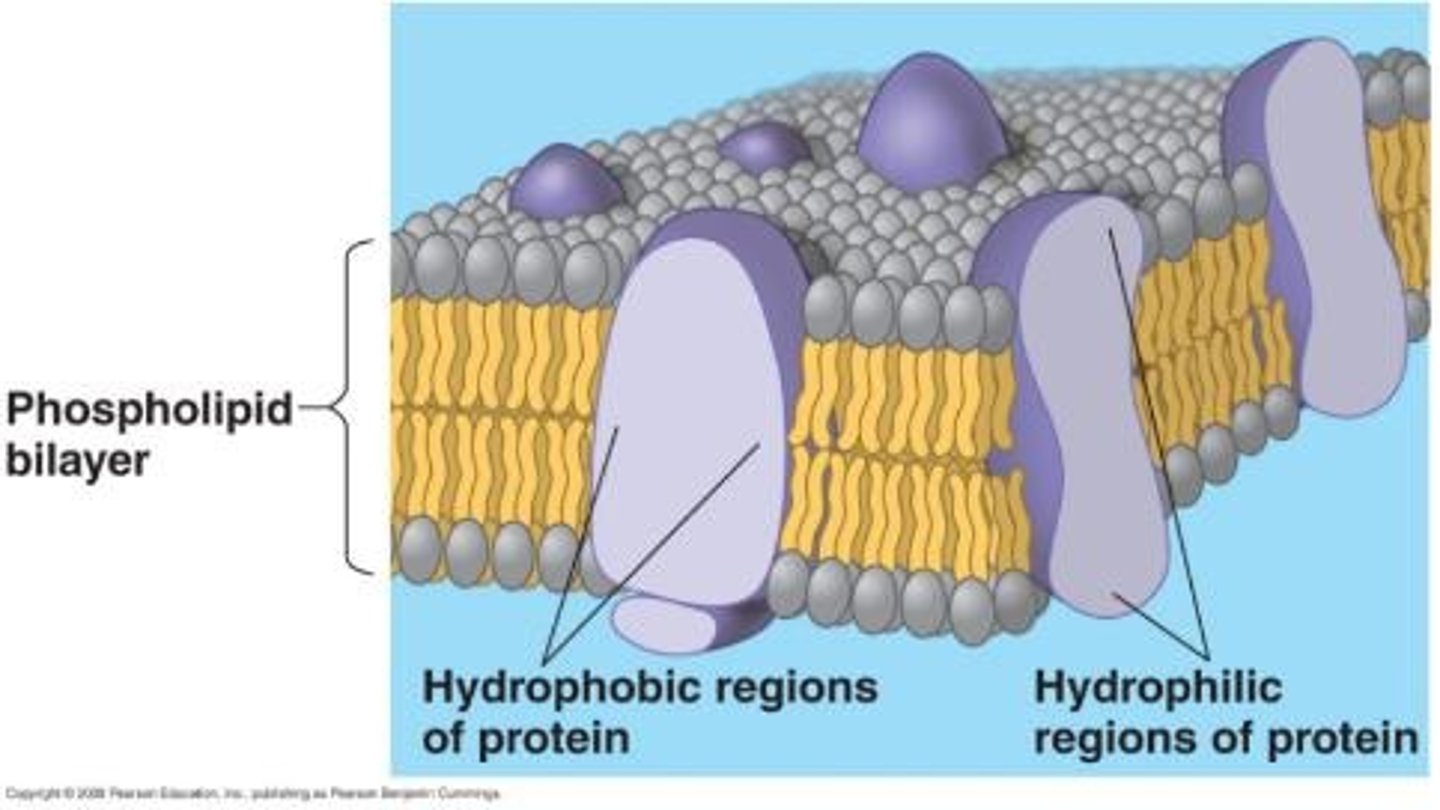
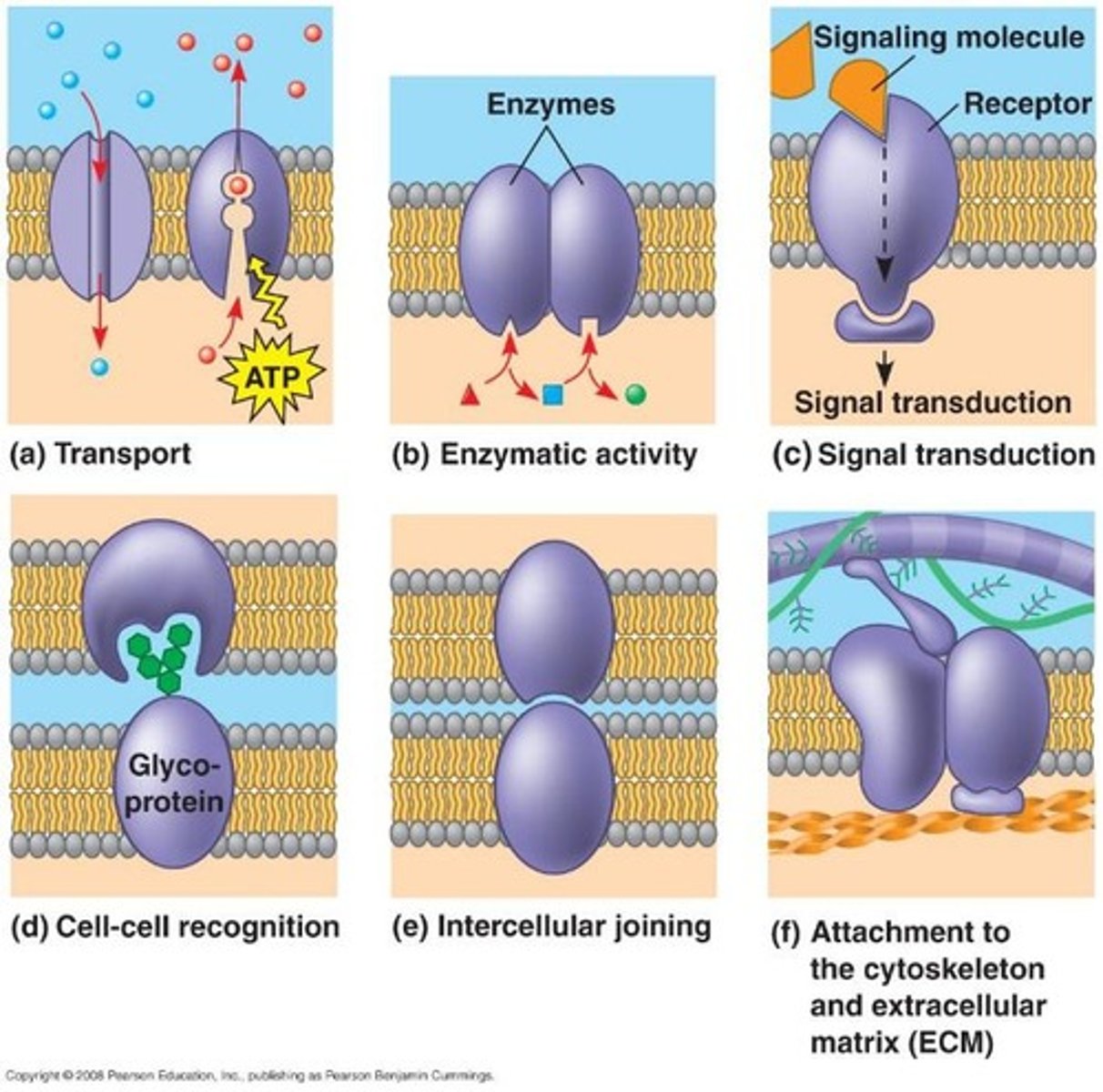
two types of membrane proteins
Peripheral proteins (on the membrane surface) and integral proteins (anchored to hydrophobic lipids).
transmembrane proteins
Integral proteins that span the membrane and have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
role of membrane carbohydrates
They provide specificity for cell-cell or cell-protein interactions.
glycolipids and glycoproteins
Glycolipids are sugars attached to lipids, and glycoproteins are sugars attached to proteins.
type A blood
A type antigens and B type antibodies.
Type AB blood
It has both A and B type antigens and no antibodies, making it a universal receiver.
Type O blood
It has both A and B type antibodies but no antigens, making it a universal donor.
selectively permeable
The membrane allows some substances to cross while restricting others.
types of molecules that pass through the membrane rapidly
Small hydrophobic molecules like CO2, O2, and steroid hormones.
passive transport
The movement of substances across membranes without the use of cellular energy.
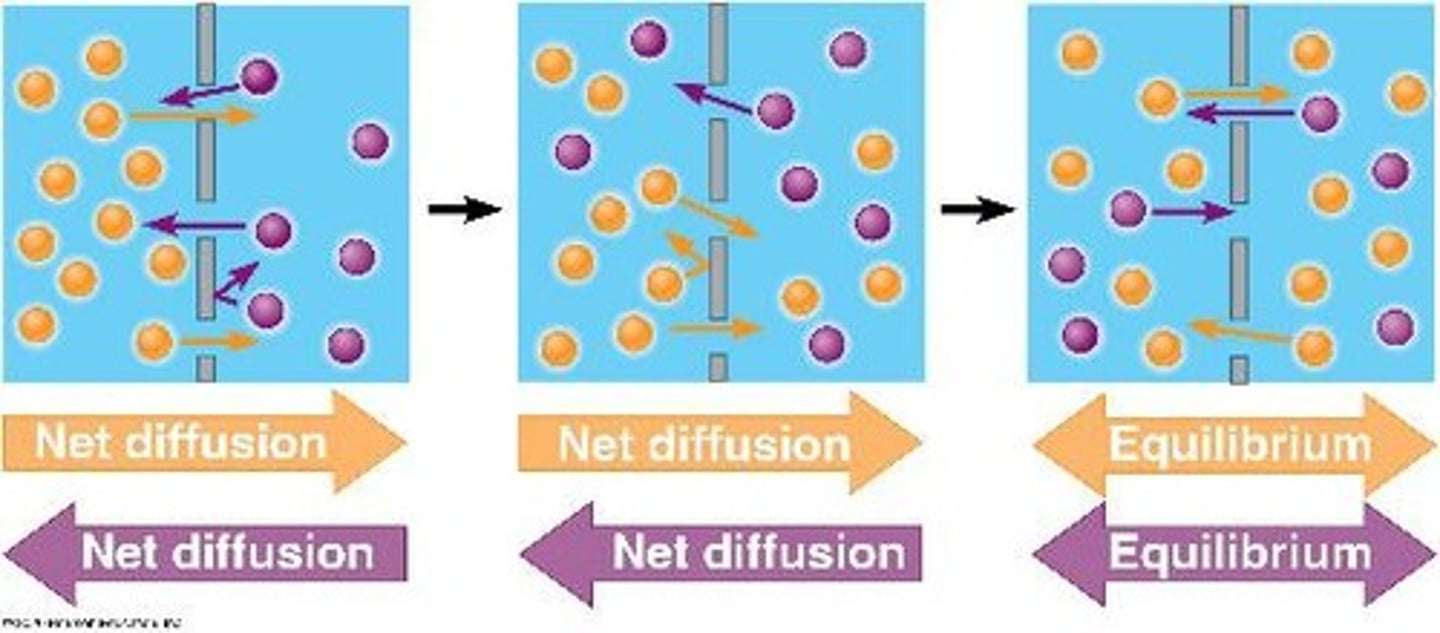
diffusion
The tendency for particles to spread out from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
relationship of rate of diffusion to the concentration gradient
The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the steepness of the concentration gradient.
dynamic equilibrium
A state where solutes move back and forth across a membrane, but there is no net change in concentration.
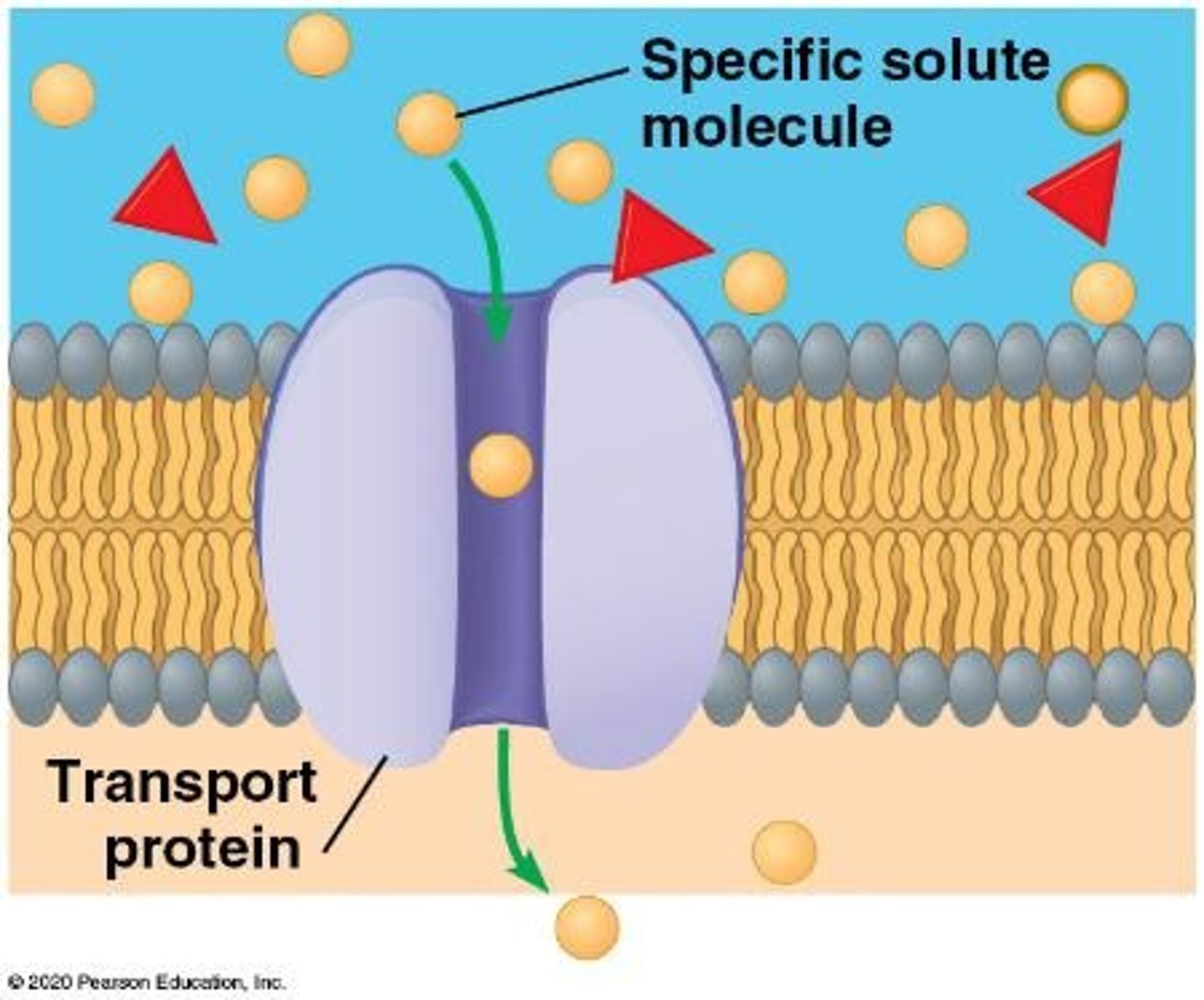
facilitated diffusion
The process where substances move down a concentration gradient through selective protein pores without requiring energy.
type of molecules that can easily diffuse through the lipid bilayer
Only small non-polar molecules.
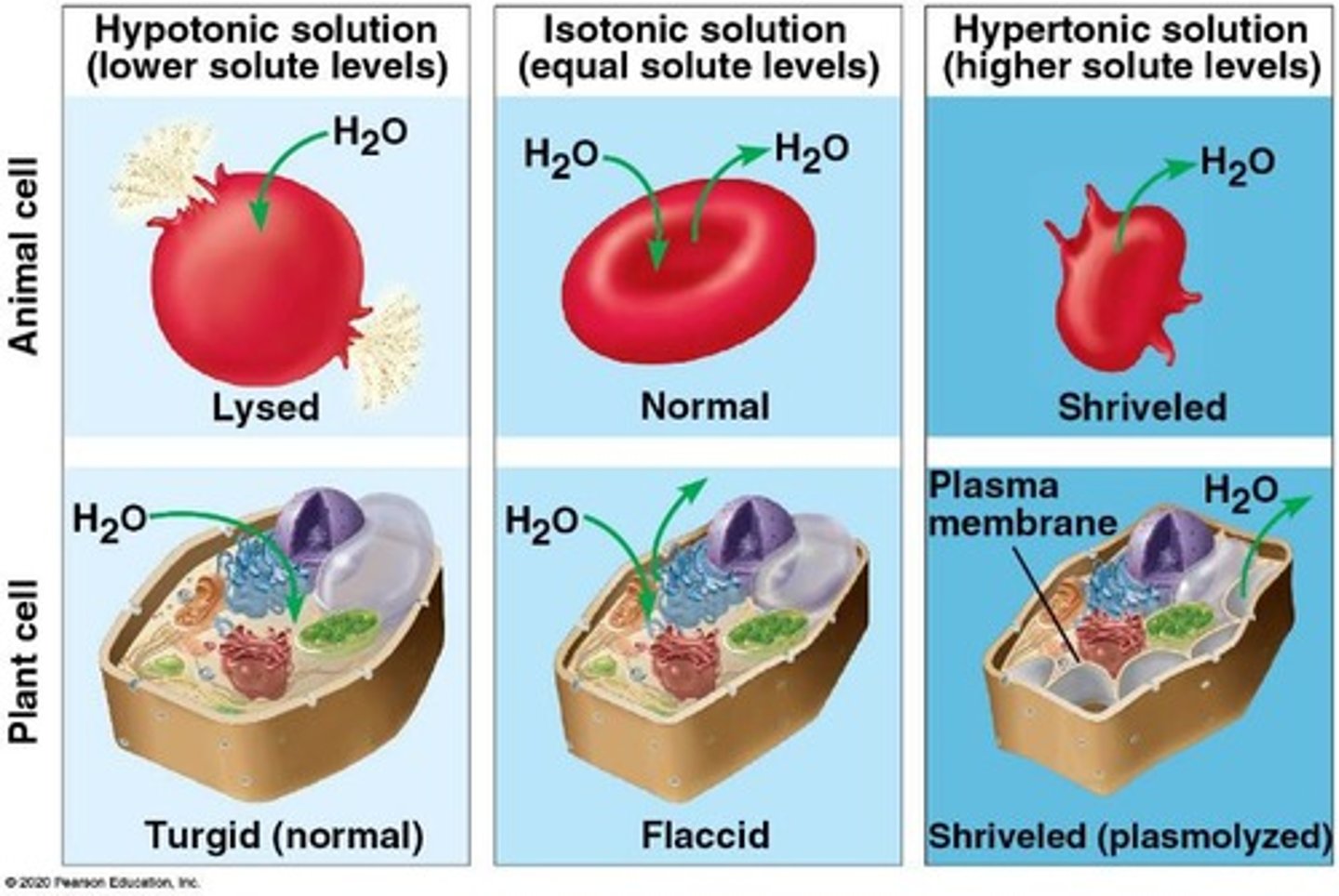
osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
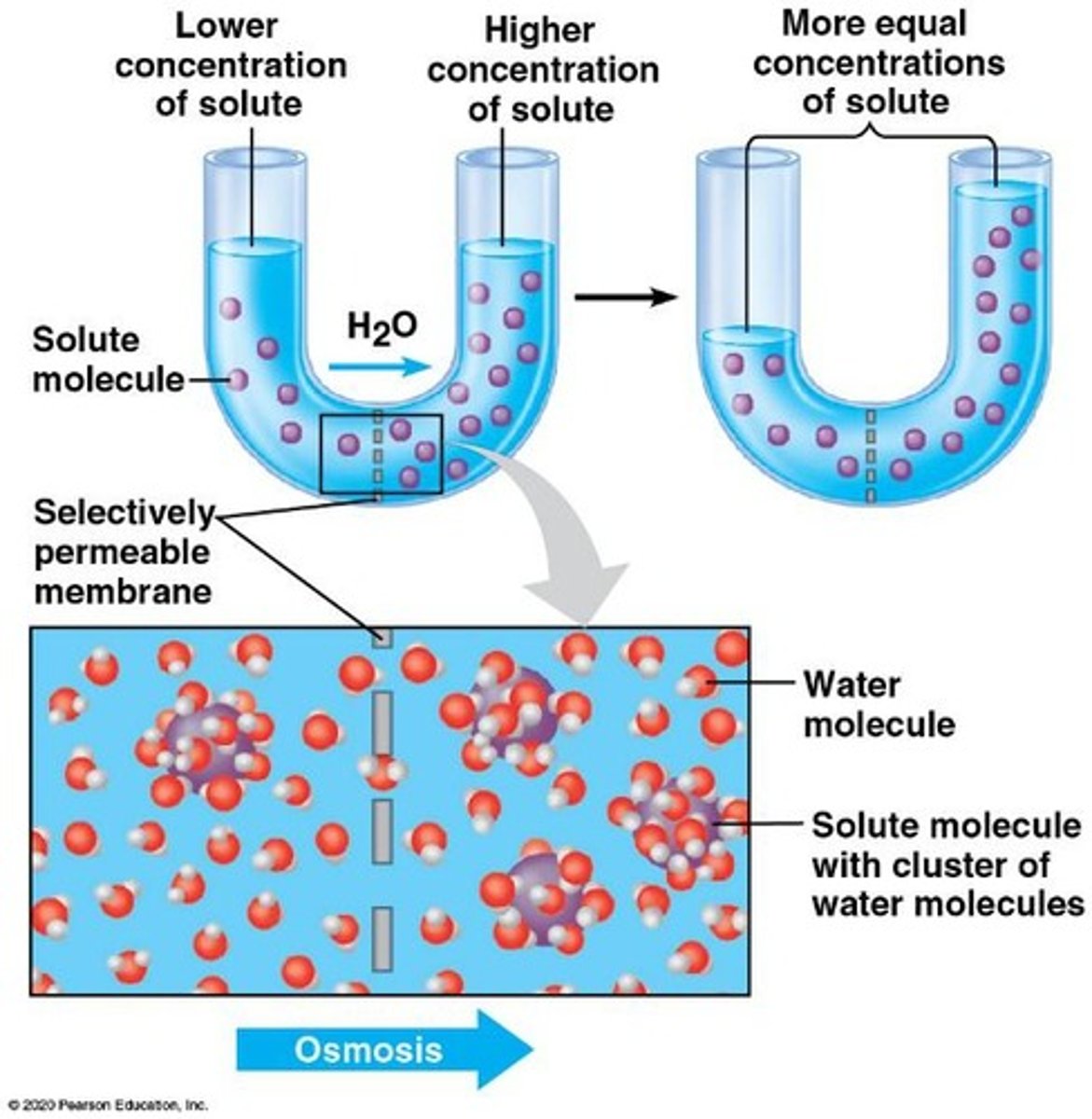
direction water moves during osmosis
From a region of lower solute concentration (high water concentration) to a region of higher solute concentration (low water concentration).
hypertonic solution
An environment with a higher solute concentration compared to the inside of the cell.
hypotonic solution
An environment with a lower solute concentration relative to the inside of the cell.
isotonic solution
An environment with equal concentrations of solutes inside and outside the cell.
osmoregulation
The control of water balance, necessary for organisms living outside marine environments.
plant cells in a hypotonic solution
They become turgid due to the rigid cell wall preventing membrane rupture.
aquaporins
Transmembrane protein channels that facilitate the passive transport of water across the cell membrane.
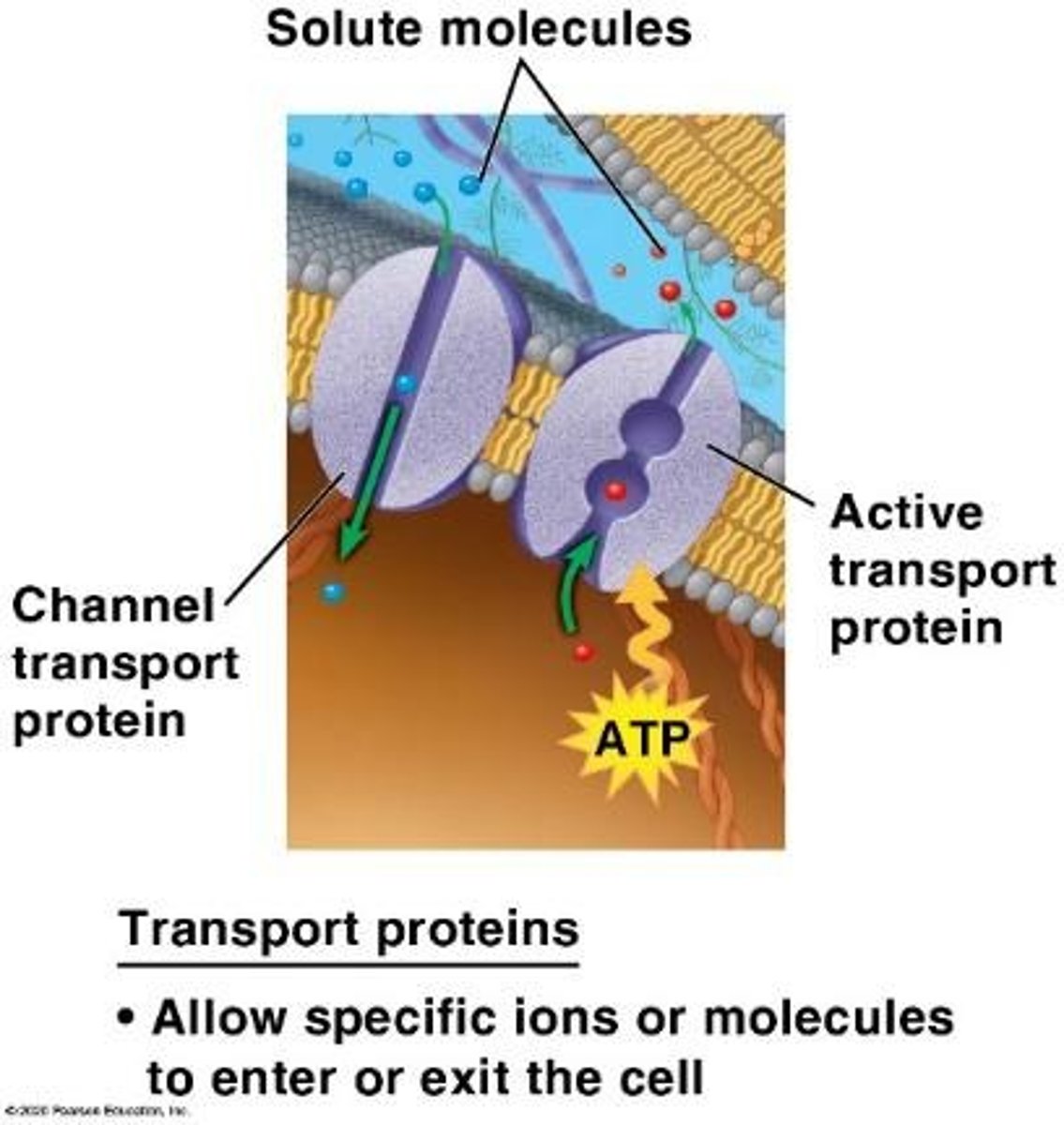
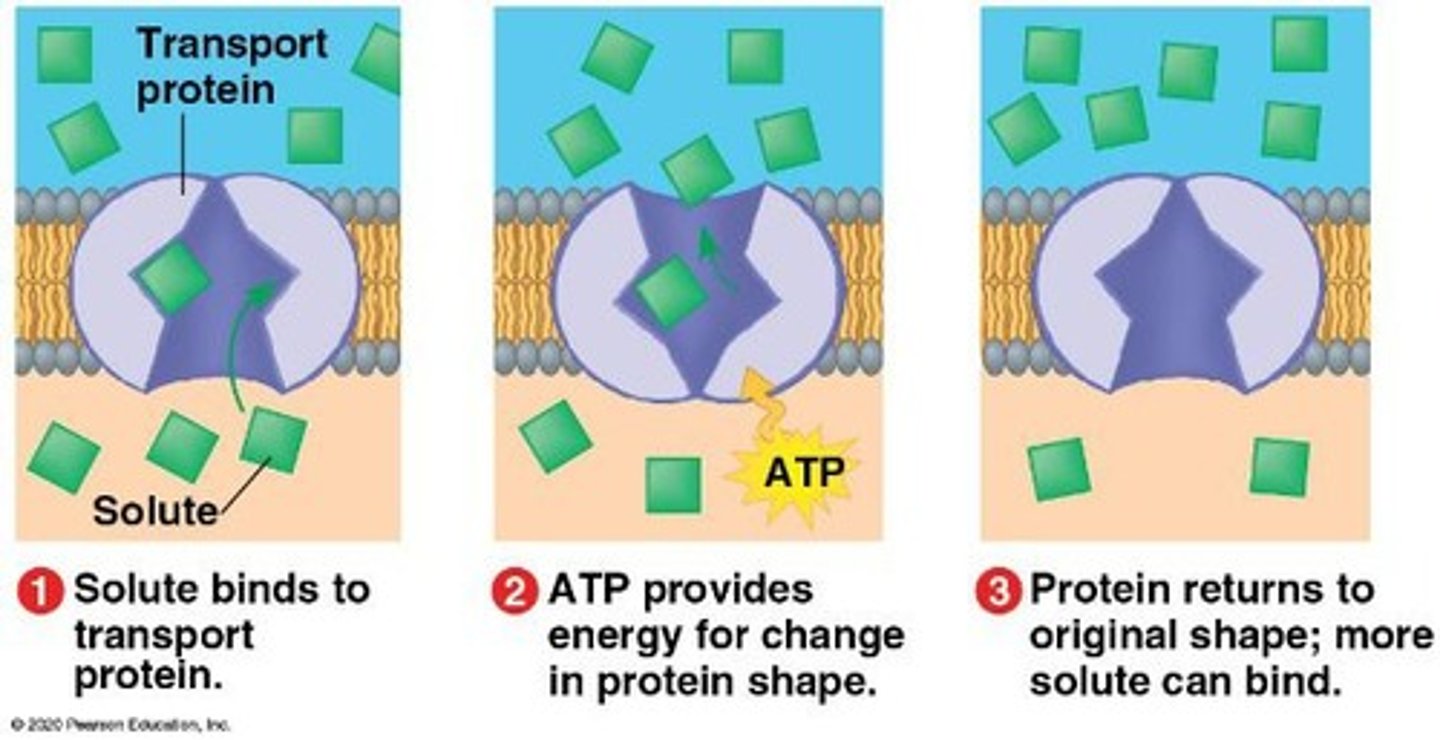
active transport
The movement of solutes across a membrane against a concentration gradient, requiring energy in the form of ATP.
exocytosis
The process where a membrane-bound vesicle fuses with the cell membrane to expel its contents outside the cell.
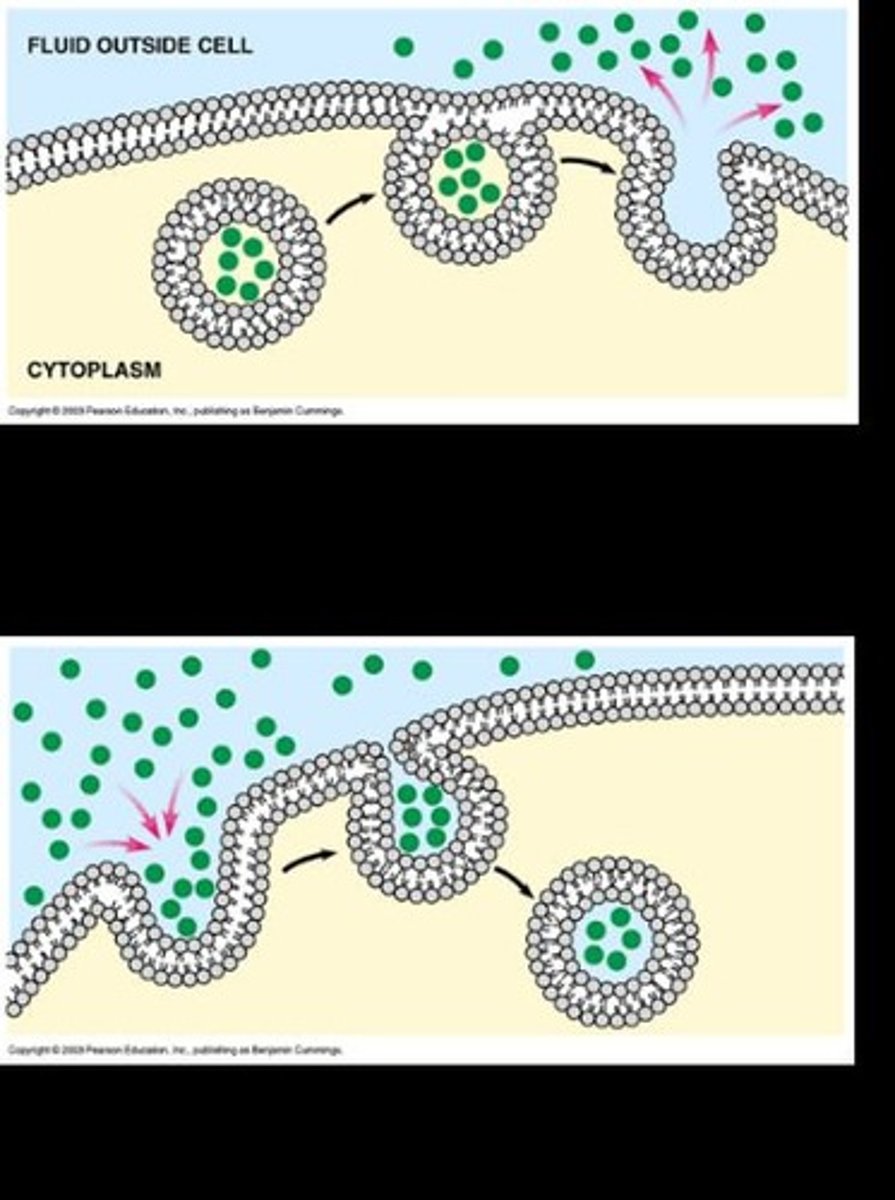
endocytosis
The process where the cell membrane folds inward, trapping material from outside for use inside the cell.
thermodynamics
The study of energy transformations.
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be changed from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
Energy changes are not 100% efficient, and every energy conversion increases the total entropy of the universe.
exergonic reactions
Reactions in which energy is released.
endergonic reactions
Reactions in which energy is absorbed.
cellular metabolism
All the chemical reactions that occur within a cell.
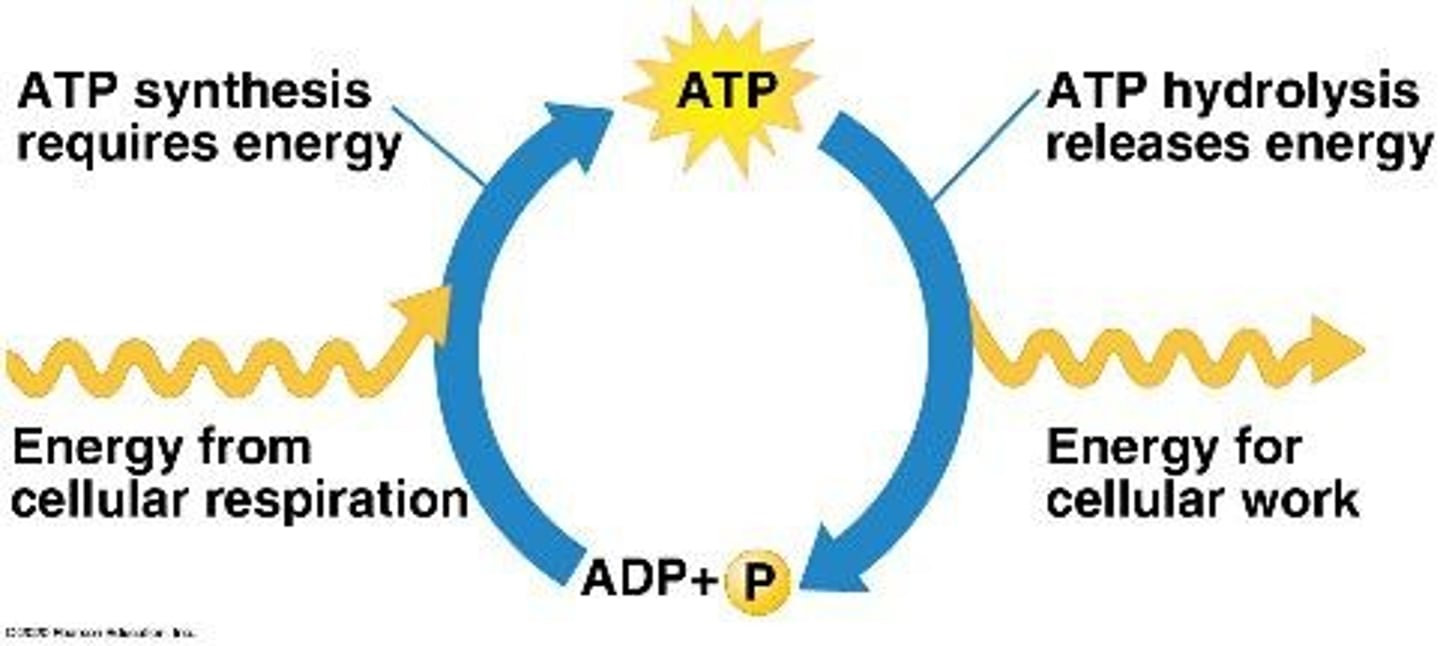
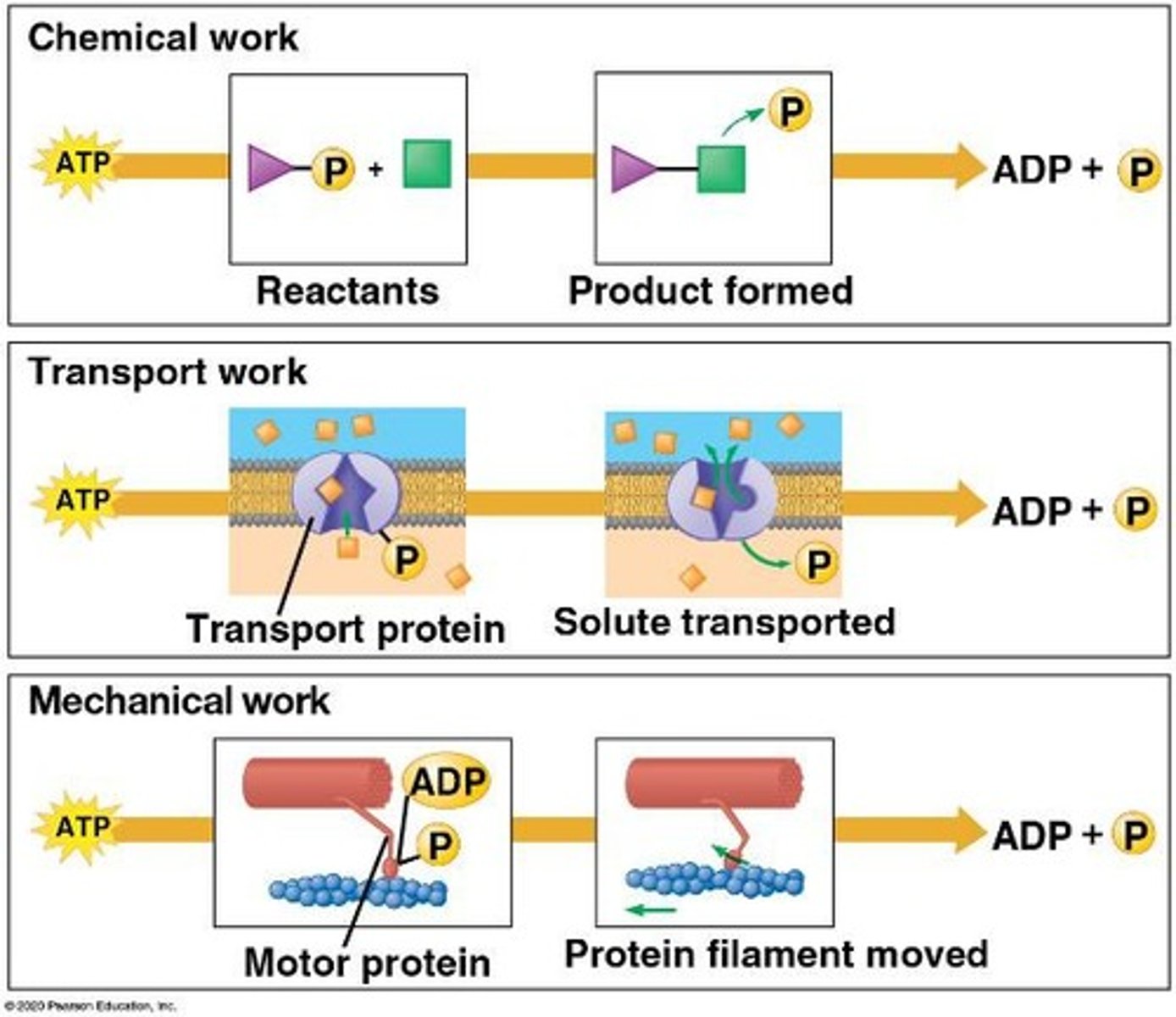
role of ATP in cellular metabolism
ATP couples exergonic reactions to drive endergonic reactions.
enzyme function in cellular reactions
Enzymes act as biological catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy.
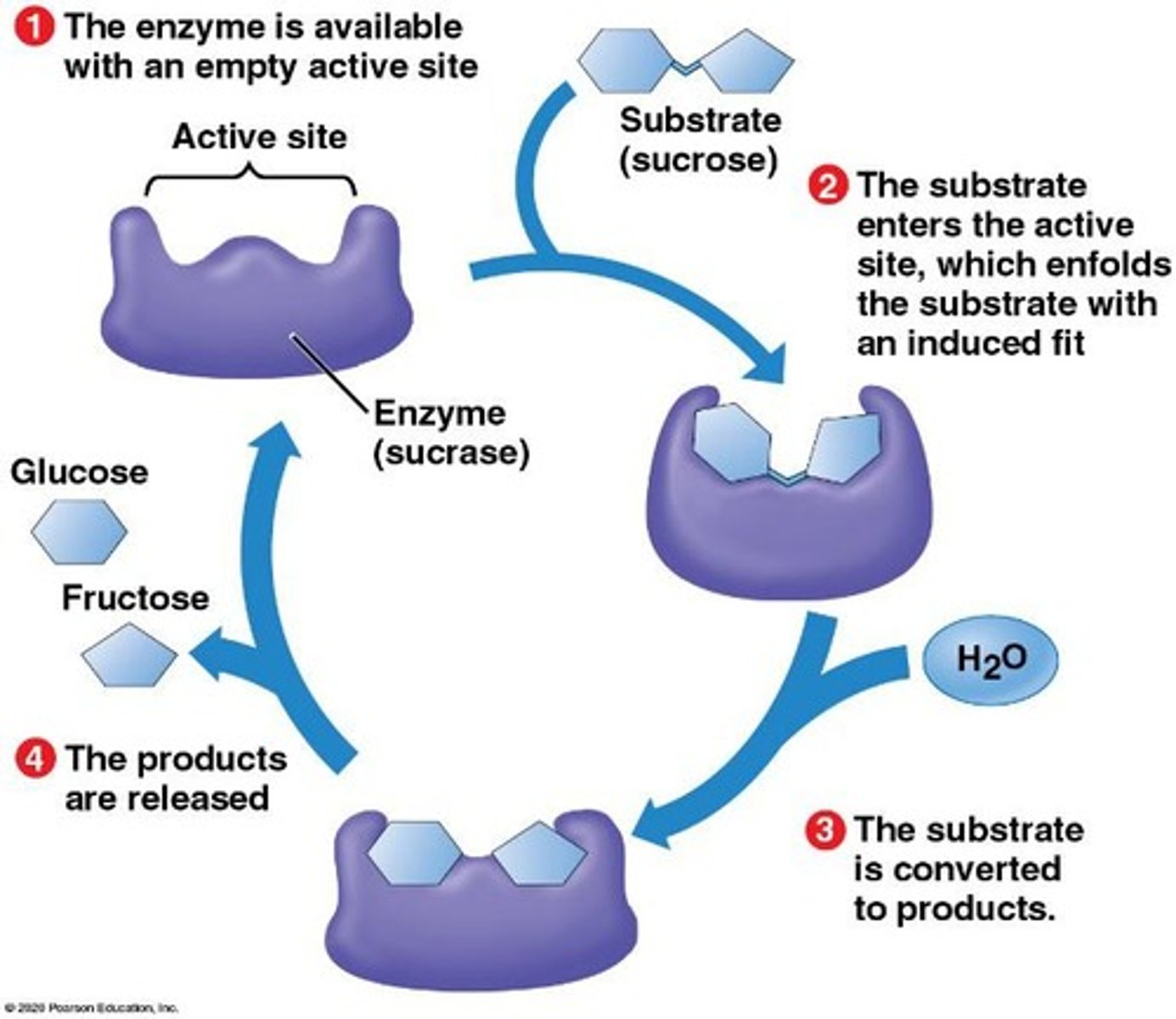
activation energy
The amount of energy reactants must absorb to start a chemical reaction.
specificity in enzymes
The selectivity of enzymes determines which chemical reactions occur in a cell, akin to a lock and key.
ATP cycle
The process where ATP is regenerated from ADP and inorganic phosphate through energy released from exergonic reactions.