Chapter 6- Energy, Enzymes, and Biological Reactions
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1. The first law of thermodynamics states that the total disorder of a system always increases.
False - second law of thermodynamics
2. The potential energy in a chemical bond is defined as chemical energy.
True
3. At equilibrium, the concentrations of the reactants equals that of the products.
False - rate of formation
4. Reactions that reach an equilibrium point are reversible.
True
5. ATP synthesis is exergonic.
False-endergonic
6. Enzymes alter the equilibrium point of a reaction.
False - activation energy
7. Enzymes don't change the DG of a reaction.
True
8. The rate of catalysis is proportional to the concentration of the enzyme.
True
9. If an enzyme is bound by an allosteric activator, the enzyme will convert from a low-affinity state to a high-affinity state.
True
10. Ribozymes are enzymes.
False- Biological catalysts
11. The term that best describes all of the chemical reactions of a cell, including acquisition and use of molecules and energy, is ____.
a.
metabolism
b.
anabolism
c.
catabolism
d.
energy budget
e.
thermodynamics
a. metabolism
12. The removal of a phosphate group during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction takes ____.
a.
1012 years
b.
about 10 milliseconds
c.
about 1021 milliseconds
d.
more time than for an uncatalyzed reaction
e.
less time at 1000oC than at 100oC
b.
about 10 milliseconds
13. A child swinging on a swing utilizes which type(s) of energy?
a.
kinetic energy only because the child is in constant motion
b.
potential energy only, because the child has to invest energy to get the swing to move
c.
chemical energy only, because it is the child's metabolism that powers the muscles that make the swing move
d.
kinetic and potential energy only, but in constantly changing ratios: when changing direction it is pure potential energy; at the bottom of the arc, it is pure kinetic energy
e.
kinetic, potential, and chemical energy: the child powers the swing with chemical energy in the muscle, cells and the swing moves like a pendulum with changing ratios of kinetic and potential energy.
e.
kinetic, potential, and chemical energy: the child powers the swing with chemical energy in the muscle, cells and the swing moves like a pendulum with changing ratios of kinetic and potential energy.
14. The ultimate fate of the energy used by organisms is ____.
a.
conversion into heat
b.
transmission onto offspring
c.
to be recycled repeatedly without loss
d.
to be recycled as metabolic energy
e.
move into the environment by conduction
a.
conversion into heat
15. In molecules, the constant motion of the atoms is an example of ____ energy, while the arrangement of atoms and bonds is an example of ____ energy.
a.
potential; chemical
b.
kinetic; potential
c.
potential; free
d.
chemical; free
e.
kinetic; chemical
b.
kinetic; potential
16. Which system is considered a closed system?
a.
a human
b.
a gas-powered automobile
c.
a single-celled organism
d.
a propane furnace
e.
the Earth
e.
the Earth
17. Which system is considered an open system?
a.
a human
b.
a thermos
c.
a wine keg
d.
a greenhouse
e.
the Earth
a. a human
18. According to the first law of thermodynamics, ____.
a.
matter can be created and destroyed
b.
matter only changes forms
c.
energy can be created and destroyed
d.
energy only changes forms
e.
matter and energy can be interconverted
d.
energy only changes forms
19. Which statement is a part of the first law of thermodynamics?
a.
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
b.
Energy cannot be transformed.
c.
The entropy of the universe is constant.
d.
The entropy of the universe is decreasing.
e.
Potential energy is the energy of motion.
a.
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
20. What is the ultimate source of energy for almost all organisms?
a.
catabolism of sugars
b.
ATP
c.
catabolism of fats
d.
the sun
e.
catabolism of sugars, fats, and proteins
d. the sun
21. We can calculate whether a reaction is spontaneous by calculating the change in free energy and accounting for entropy. Your paycheck always lists your gross pay, net (take home) pay, and tax withholdings. Which of the following best correlates your paycheck to the changes in free energy?
a.
gross salary = net salary - tax; total energy = free energy - entropy
b.
net salary = gross salary - tax; free energy = total energy - entropy
c.
tax = gross - net salary; entropy = total energy - free energy
d.
gross salary = tax - net salary; total energy = entropy - free energy
e.
net salary = gross salary + tax; free energy = total energy + entropy
b.
net salary = gross salary - tax; free energy = total energy - entropy
22. During every energy transformation, it can be said that ____.
a.
the entropy of the universe increases
b.
the entropy of the universe decreases
c.
there is an increase in the free energy of the universe
d.
there is a change in the total energy of the universe
e.
the system becomes more organized
a.
the entropy of the universe increases
23. Which example would have a negative change in entropy?
a.
water freezing
b.
fermentation of wine
c.
expansion of the universe
d.
a supernova (stellar explosion)
e.
a frog's life cycle
a. water freezing
24. Which equation is used to calculate the free energy associated with a reaction?
a.
ΔG = ΔH-TΔS
b.
ΔG = ΔH+TΔS
c.
ΔG = - ΔH+TΔS
d.
ΔG = ΔS+TΔH
e.
ΔG = -ΔS-TΔH
a. ΔG = ΔH-TΔS
25. Although energy cannot be created or destroyed, energy transformations are not 100% efficient. Why?
a.
Energy is lost as an increase in heat.
b.
Energy is lost as an increase in entropy.
c.
Energy is lost as a change in free energy.
d.
Energy is lost as a decrease in heat.
e.
Energy is lost as a decrease in entropy.
b.
Energy is lost as an increase in entropy.
26. If a reaction is endergonic, what can we infer about the reaction?
a.
ΔH must be positive
b.
ΔH must be negative
c.
ΔG must be positive
d.
ΔG must be negative
e.
ΔS must be positive
c. ΔG must be positive
27. Which two factors determine whether a reaction is spontaneous?
a.
free energy and activation energy
b.
activation energy and enthalpy
c.
enthalpy and entropy
d.
entropy and activation energy
e.
activation energy and energy coupling
c. enthalpy and entropy
28. If a reaction is spontaneous, then ΔG is ____ and the reaction is ____.
a.
negative; endergonic
b.
negative; exergonic
c.
zero; endergonic
d.
positive; endergonic
e.
positive; exergonic
b.
negative; exergonic
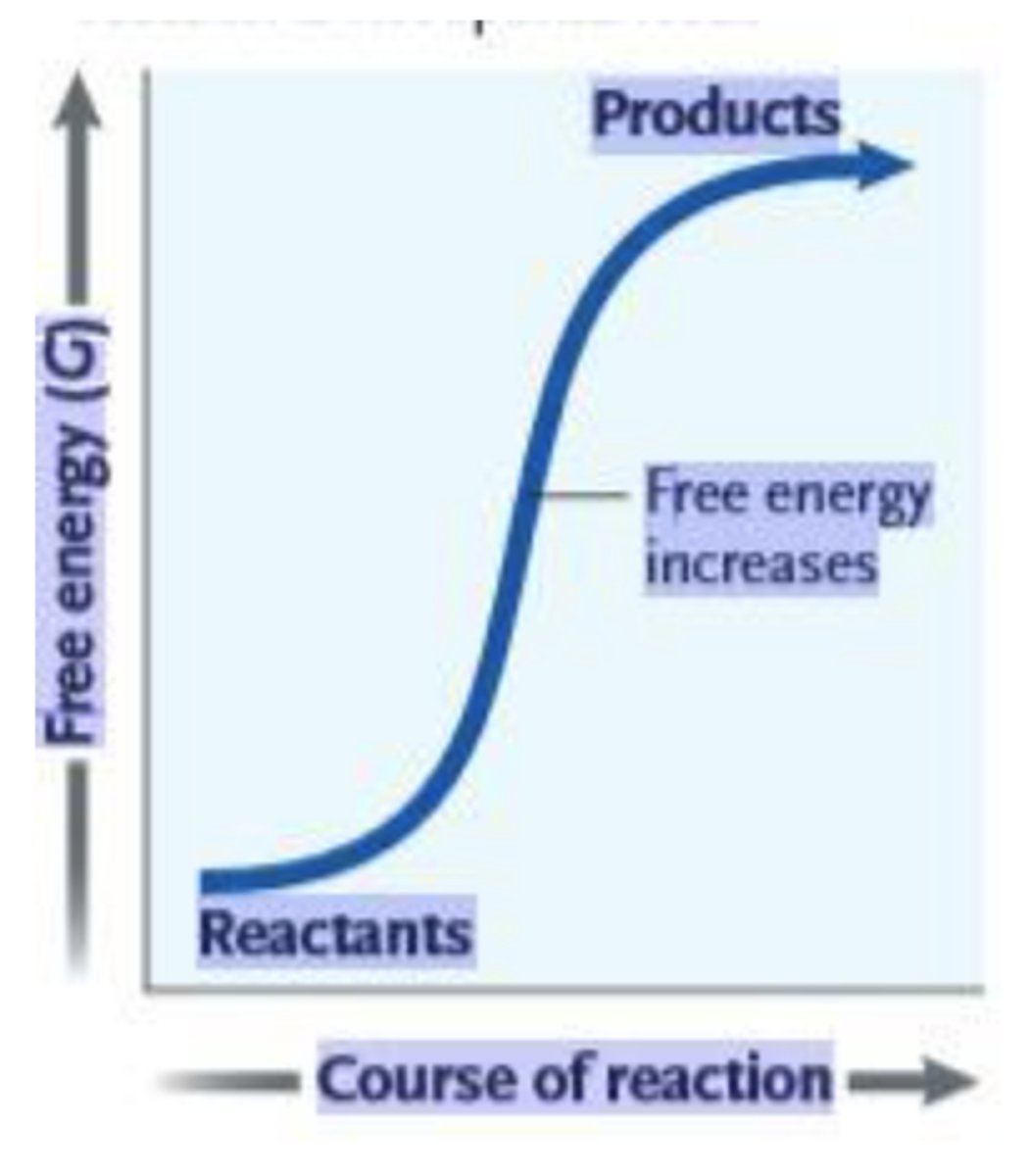
29. What can be inferred from the accompanying graph?
a.
This reaction is endergonic, with a positive ΔG.
b.
This reaction is endergonic, with a negative ΔG.
c.
This reaction is exergonic, with a positive ΔG.
d.
This reaction is exergonic, with a negative ΔG.
e.
There is not enough information to make a determination.
a. This reaction is endergonic, with a positive ΔG.
30. In an exothermic reaction, ____.
a.
ATP is phosphorylated
b.
heat energy is absorbed
c.
the products have less potential energy than the reactants
d.
the reactants have less potential energy than the products
e.
H (enthalpy) = 0
c. the products have less potential energy than the reactants
31. Reversible reactions in a cell rarely reach equilibrium because ____.
a.
the products are generally reactants in other reactions and are thus immediately used
b.
a cell at equilibrium is dead
c.
they are highly regulated to prevent overuse of reactants
d.
cells have no way of measuring the relative ratios of reactants and products
e.
conditions in the cell change too rapidly for any reaction to ever reach equilibrium
a.
the products are generally reactants in other reactions and are thus immediately used
32. When an enzyme-catalyzed reaction reaches equilibrium ____.
a.
the enzymes are now inhibited
b.
the chemical reactions cease
c.
the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
d.
the concentration of reactants equals the concentration of products
e.
ATP is no longer required to drive the reaction
c. the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
33. Identify the exergonic reaction in the list below.
a.
burning wood for a campfire
b.
folding laundry
c.
building a tower out of blocks
d.
synthesizing a protein
e.
storing the third slice of pie in the form of fat
a. burning wood for a campfire
34. Which statement is true for exergonic reactions?
a.
A net input of energy is necessary for the reaction to proceed.
b.
The products have less free energy than the reactants.
c.
The products have more free energy than the reactants.
d.
The reactants will always be completely converted to products.
e.
The entropy of the system is reduced.
b.The products have less free energy than the reactants.
35. Which reaction is most likely to have more products than reactants when it reaches equilibrium?
a.
DG = -25 kcal/mol
b.
DG = -50 kcal/mol
c.
DG = -75 kcal/mol
d.
DG = -100 kcal/mol
e.
They will all have the same ratio of products to reactants regardless of the DG value.
d. DG = -100 kcal/mol
36. An exergonic reaction will have a ____.
a.
negative change in kinetic energy
b.
positive change in enthalpy
c.
negative change in entropy
d.
DG = 0
e.
negative change in free energy
e. negative change in free energy
37. Eating and digesting a candy bar for energy during a sports event is a good example of ____.
a.
catabolism
b.
anabolism
c.
converting kinetic energy into potential energy
d.
metabolism
e.
converting heat energy into chemical energy
a. catabolism
38. The breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP is an example of a(n) ____ pathway.
a.
endergonic
b.
catabolic
c.
cyclical
d.
anabolic
e.
endothermic
b. catabolic
39. Energy from ATP is transferred to the reactant of an endergonic reaction by addition of a(n) _____ group to that molecule..
a.
nitrate
b.
ribose
c.
deoxyribose
d.
acetyl
e. phosphate
e. phosphate
40. The free energy of ATP hydrolysis is -31.0 kJ/mol. The free energy of glucose phosphorylation by hexokinase is +14.3 kJ/mol. These two reactions are coupled to allow them to proceed spontaneously. What is the overall free energy associated with this coupled reaction?
a.
-45.3 kJ/mol
b.
-31 kJ/mol
c.
-16.7 kJ/mol
d.
16.7 kJ/mol
e.
45.3 kJ/mol
c.
-16.7 kJ/mol
41. How does energy coupling allow chemical reactions that are not spontaneous to proceed?
a.
the energy from both reactions increases the total free energy
b.
the energy from the endergonic reaction is transferred to the substrate to stabilize it
c.
the energy from the endergonic reaction is transferred to the enzyme to stabilize the transition state
d.
the energy from the exergonic reaction is transferred to the substrate to stabilize it
e.
the energy from the exergonic reaction is transferred to the substrate to destabilize it
e.
the energy from the exergonic reaction is transferred to the substrate to destabilize it
42. How do cells overcome the energy requirement of endergonic reactions?
a.
coupling ATP synthesis with phosphorylation reactions
b.
coupling endergonic and exergonic reactions
c.
coupling endothermic and endergonic reactions
d.
coupling ATP transport with endergonic reactions
e.
coupling ATP synthesis with endergonic reactions
b.
coupling endergonic and exergonic reactions
43. Where does the energy for ATP synthesis come from?
a.
anabolism of complex molecules into simpler molecules
b.
catabolism of complex molecules into simpler molecules
c.
anabolism of simple molecules into complex molecules
d.
catabolism of simple molecules into complex molecules
e.
anabolism of complex molecules directly into ATP
b. catabolism of complex molecules into simpler molecules
44. Approximately how many ATP molecules are hydrolyzed and resynthesized each second in a typical cell?
a.
100
b.
10,000
c.
100,000
d.
10,000,000
e.
100,000,000
d. 10,000,000
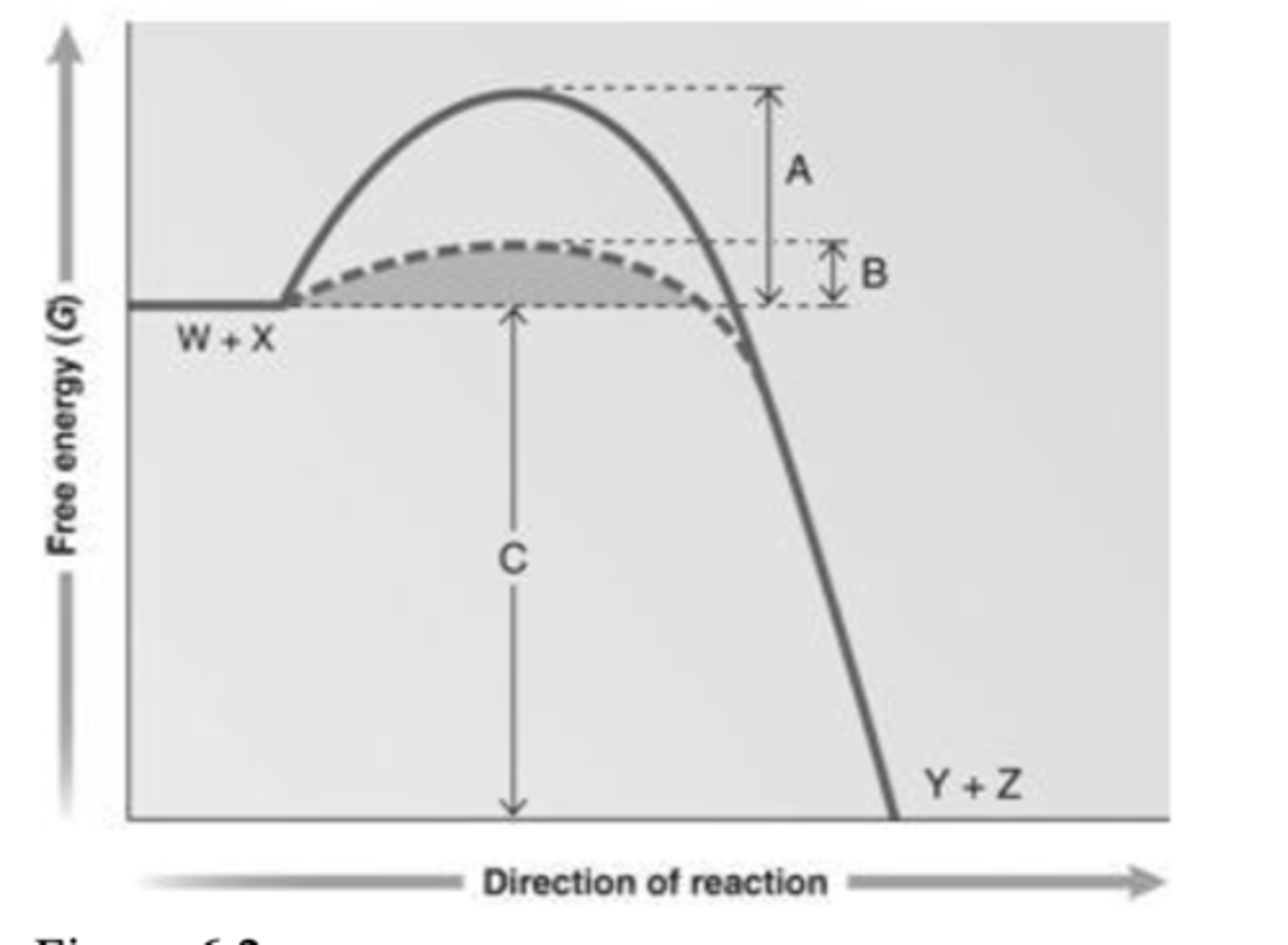
45. Answer the question using the accompanying graph. Which portion of the graph shows the activation energy in the absence of enzyme?
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
W + X
e.
Y + Z
a. A
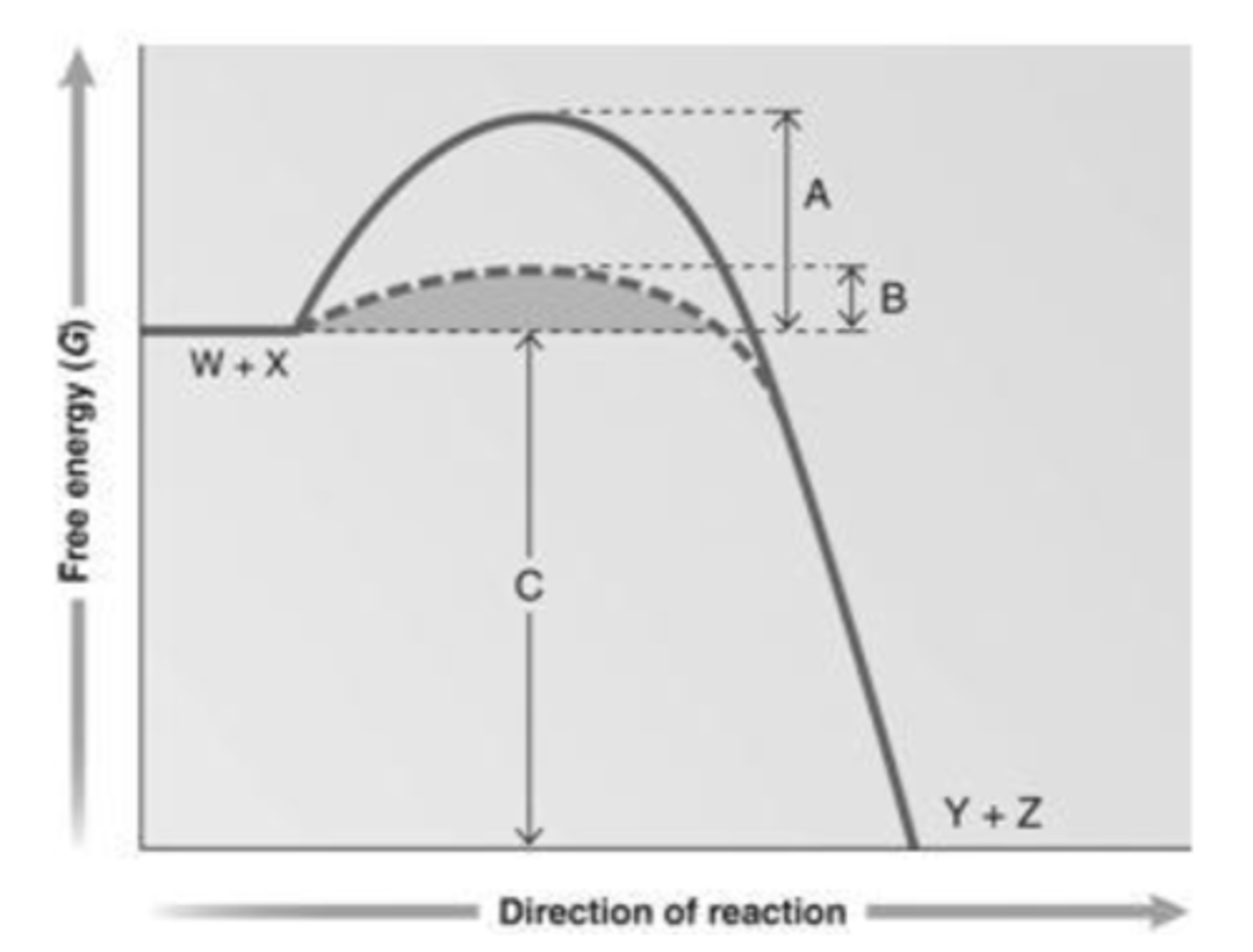
46. Answer the question using the accompanying graph. Which portion of the graph shows the activation energy in the presence of enzyme?
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
W + X
e.
Y + Z
b. B
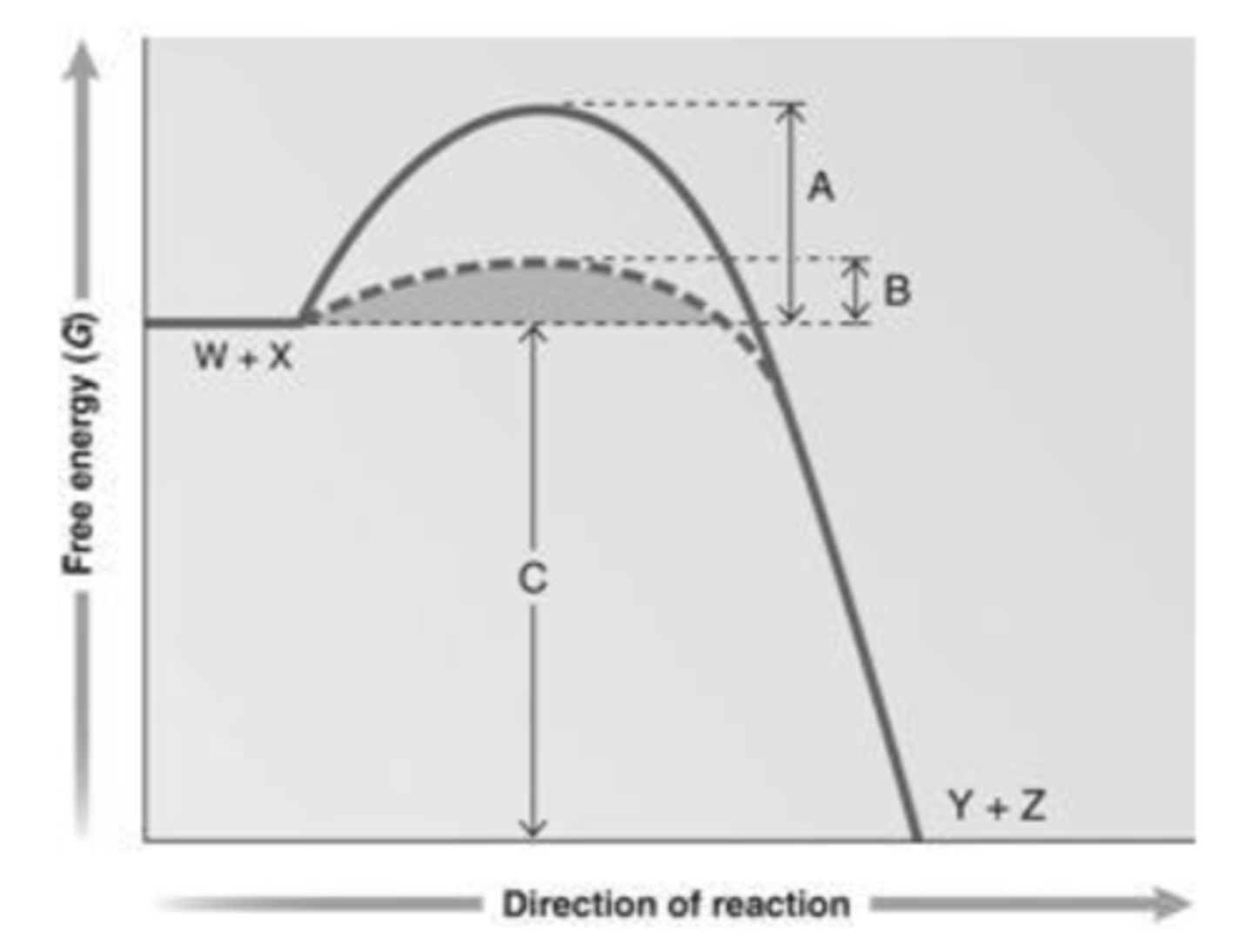
47. Answer the question using the accompanying graph. Which portion of the graph shows the free energy of the reaction?
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
W + X
e.
Y + Z
c. C
48. The conversion of a diamond into graphite is a spontaneous reaction. Why are most women walking around with diamond rings and not graphite rings?
a.
inorganic substances, like diamonds, do not react like organic substances
b.
the transition state is very stable
c.
the energy of activation is very high
d.
the free energy of this reaction is too low
e.
the free energy of this reaction is too high
c. the energy of activation is very high
49. Enzymes aid in metabolism by ____.
a.
changing the DG of the reaction
b.
adding additional reactants to the system
c.
slowing the rate of some reactions and increasing the rate of other reactions
d.
stabilizing the transition state
e.
removing unused reactants from the system
d. stabilizing the transition state
50. Enzymes ____.
a.
change the rate of a reaction
b.
change the direction of a reaction
c.
change the free energy of a reaction
d.
are used up in a reaction
e.
are present in concentrations approaching their substrates' concentrations
a. change the rate of a reaction
51. What is the primary determinant of the function and specificity of an enzyme?
a.
the cofactors bound to the enzyme
b.
the presence or absence of an allosteric regulator
c.
prosthetic groups
d.
the enzyme's conformation
e.
the pH of its environment
d. the enzyme's conformation
52. Enzymes function primarily by ____.
a.
forcing the reactants into an altered environment which in turn creates a change in the free energy of the reactants relative to the products
b.
altering the equilibrium point of a particular reaction to favor the formation of products
c.
increasing the probability that the reactants will come into close proximity to each other in the proper orientation for forming the transition state molecule
d.
removing reactants from solution in a set ratio to increase the chances of the remaining individual reactants interacting with each other
e.
changing the ratio of reactants to products so that the forward reaction is favored
c. increasing the probability that the reactants will come into close proximity to each other in the proper orientation for forming the transition state molecule
53. Enzymes are ____ catalysts.
a.
protein
b.
lipid
c.
nucleic acid
d.
inorganic
e.
ionic
a. protein
54. You modify the primary sequence of an enzyme in a region that will be the active site when the protein is properly folded. What is the predicted outcome of this change?
a.
The enzyme will not bind to the substrate properly.
b.
The enzyme will not be able to bind an allosteric inhibitor.
c.
The enzyme will have an increased rate of activity.
d.
There will be no change in the enzyme's function.
e.
The enzyme will bind the substrate but not be able to release the products.
a.
The enzyme will not bind to the substrate properly.
55. What is the difference between cofactors and coenzymes?
a.
cofactors are not necessary for enzyme function, but coenzymes are
b.
cofactors can be inorganic or organic, coenzymes are always inorganic
c.
cofactors can be inorganic or organic, coenzymes are organic cofactors
d.
cofactors are always vitamins, coenzymes are always ions
e.
cofactors help with essential metabolic reactions, coenzymes assist with nonessential metabolic reactions
c. cofactors can be inorganic or organic, coenzymes are organic cofactors
56. What is the name of the specific region of an enzyme responsible for catalysis?
a.
functional domain
b.
active site
c.
binding site
d.
allosteric site
e.
reaction domain
b. active site
57. Coenzymes that bind tightly to enzymes are called ____.
a.
cofactors
b.
appendages
c.
regulatory groups
d.
prosthetic groups
e.
magnetic groups
d. prosthetic groups
58. What happens to an enzyme after it has catalyzed a reaction?
a.
it is sent to the proteasome for degradation
b.
it is inactivated by phosphorylation
c.
it is inactivated by dephosphorylation
d.
it releases the cofactor to get a new one ready for catalysis
e.
it returns to its original state
e. it returns to its original state
59. What is the purpose of ionic groups in the active sites of enzymes?
a.
to alter the substrate in a way that favors catalysis
b.
to catalyze an acid/base reaction required for synthesis
c.
to promote the binding of substrates that otherwise would not fit
d.
to generate an electronic current to provide the energy for the reaction
e.
to increase the salt concentration required for the chemical reaction to occur
a.
to alter the substrate in a way that favors catalysis
60. If an enzyme is saturated, ____.
a.
it cannot continue to catalyze the reaction
b.
the reaction is at equilibrium
c.
the rate of the reaction will slow and the reaction will stop
d.
it recruits more reactants
e.
the reaction is being catalyzed at the maximum rate
e. the reaction is being catalyzed at the maximum rate
61. You do an experiment in the laboratory and add increasing amounts of substrate to a solution containing an enzyme and a pH buffer. You incubate the container at the optimal temperature for your enzyme. Each time you add more substrate, you measure the rate of the reaction. If you graph the results with substrate concentration on the x-axis and reaction rate on the y-axis, what will you find over time?
a.
The rate of the reaction will proceed with a slope of 1 and continue in a linear fashion indefinitely or until you run out of reactants.
b.
The rate of the reaction will increase rapidly, taper off, and plateau.
c.
The rate of the reaction will increase slowly, plateau, and then drop sharply back to zero.
d.
The resulting graph will be a perfect bell curve.
e.
There is no way to predict what the graph will look like without more information.
b.The rate of the reaction will increase rapidly, taper off, and plateau.
62. In competitive inhibition, the ____.
a.
products block the active site of the enzyme
b.
products bind to a site other than the active site of the enzyme and block enzyme activity indirectly
c.
substrate and cofactors compete for the active site
d.
inhibitor binds to and directly blocks the active site of the enzyme
e.
inhibitor binds to the enzyme at a site other than its active site
d. inhibitor binds to and directly blocks the active site of the enzyme
63. How does the cell overcome inhibition from irreversible inhibitors?
a.
by binding a second inhibitor, which forces the enzyme's conformation to dislodge the first inhibitor
b.
by phosphorylating the enzyme, altering the enzyme's conformation to dislodge the inhibitor
c.
by altering the cellular pH, which will decrease the bonding between the enzyme and the inhibitor
d.
by degrading the enzyme-inhibitor complex and generating new enzyme
e.
by upregulating the expression of other enzymes with similar catalytic functions
d.
by degrading the enzyme-inhibitor complex and generating new enzyme
64. In order to prevent hair loss in men, one popular treatment is to use an inhibitor of the enzyme that converts testosterone to a different androgen (DHT). The inhibitors are steroids similar to testosterone that cannot be converted into DHT. How would you classify this type of inhibition?
a.
competitive inhibition
b.
noncompetitive inhibition
c.
allosteric inhibition
d.
feedback inhibition
e.
ionic inhibition
a. competitive inhibition
65. Allosteric inhibitors are often ____.
a.
substrates of the reactions they regulate
b.
products of the reactions that they regulate
c.
charged amino acids in the active site
d.
large, complex organic molecules
e.
competitive inhibitors
b. products of the reactions that they regulate
66. What happens when an enzyme is bound by an allosteric activator?
a.
The enzyme transitions from an activate state to an inactive state.
b.
The enzyme transitions from a low affinity state to a high affinity state.
c.
The enzyme transitions from a high affinity state to a low affinity state.
d.
The enzyme can now bind to the cofactors necessary for the reaction.
e.
The enzyme can no longer bind to inhibitors.
b.
The enzyme transitions from a low affinity state to a high affinity state.
67. In the accompanying figure, why does the curve sharply drop after approximately 45°C instead of mirroring the slope of the line going from 0-40°C?
a.
At high temperatures, the reactions proceed so quickly that enzymes are no longer helpful or required.
b.
This is true of all catalysts and is not due to any special features of enzymes.
c.
The kinetic energy of the reactants is so great that it destabilizes the enzyme and diminishes the enzyme's activity.
d.
The kinetic energy of the reactants is lower than that of the products, forcing a change in enzyme activity.
e.
The enzyme begins to denature above a certain temperature, eliminating all catalytic activity of the protein.
e. The enzyme begins to denature above a certain temperature, eliminating all catalytic activity of the protein.
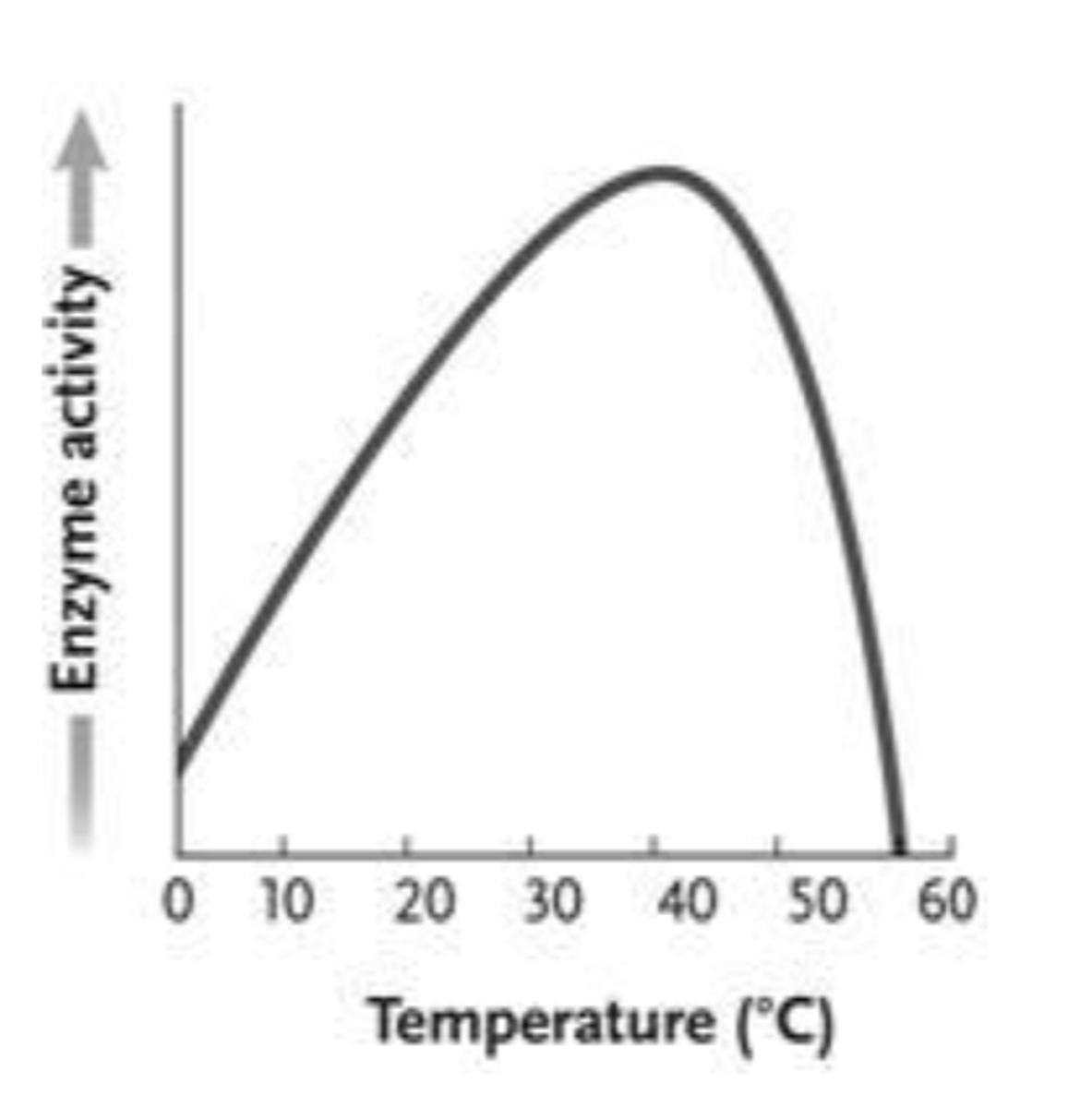
68. If an enzyme's optimal temperature is 37°C, then the enzyme ____.
a.
has a cofactor
b.
is likely to catalyze the reaction at the same rate at 30°C
c.
will probably be inactive at a pH below 4.5
d.
will completely denature at 38°C
e.
activity will drop at temperatures above 37°C and likely be eliminated by 60°C
e.
activity will drop at temperatures above 37°C and likely be eliminated by 60°C
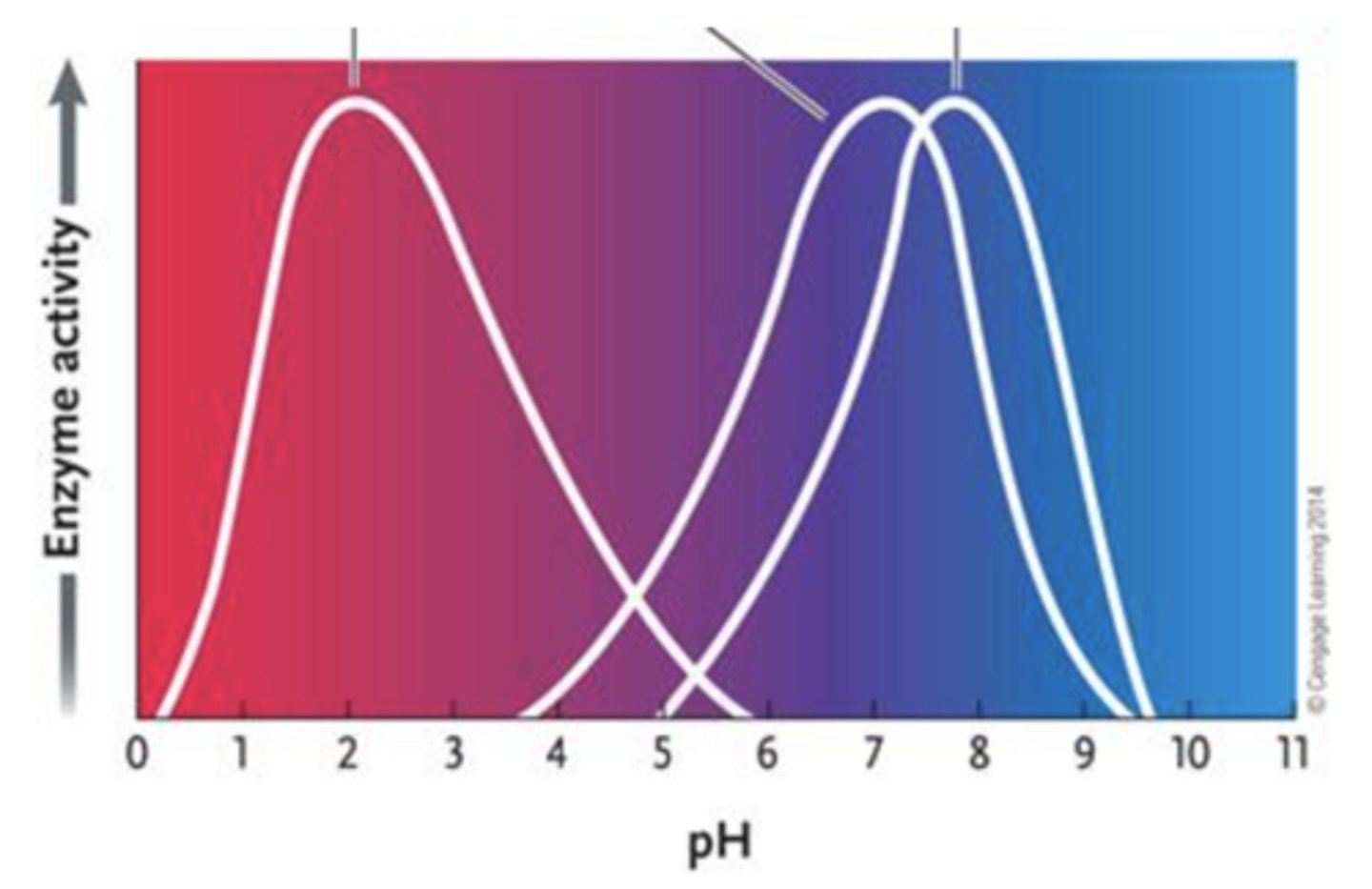
69. Answer the question by using the accompanying graph. The optimal pH for enzyme 1 is ____.
a.
2
b.
3
c.
4
d.
7
e.
8
b. 3
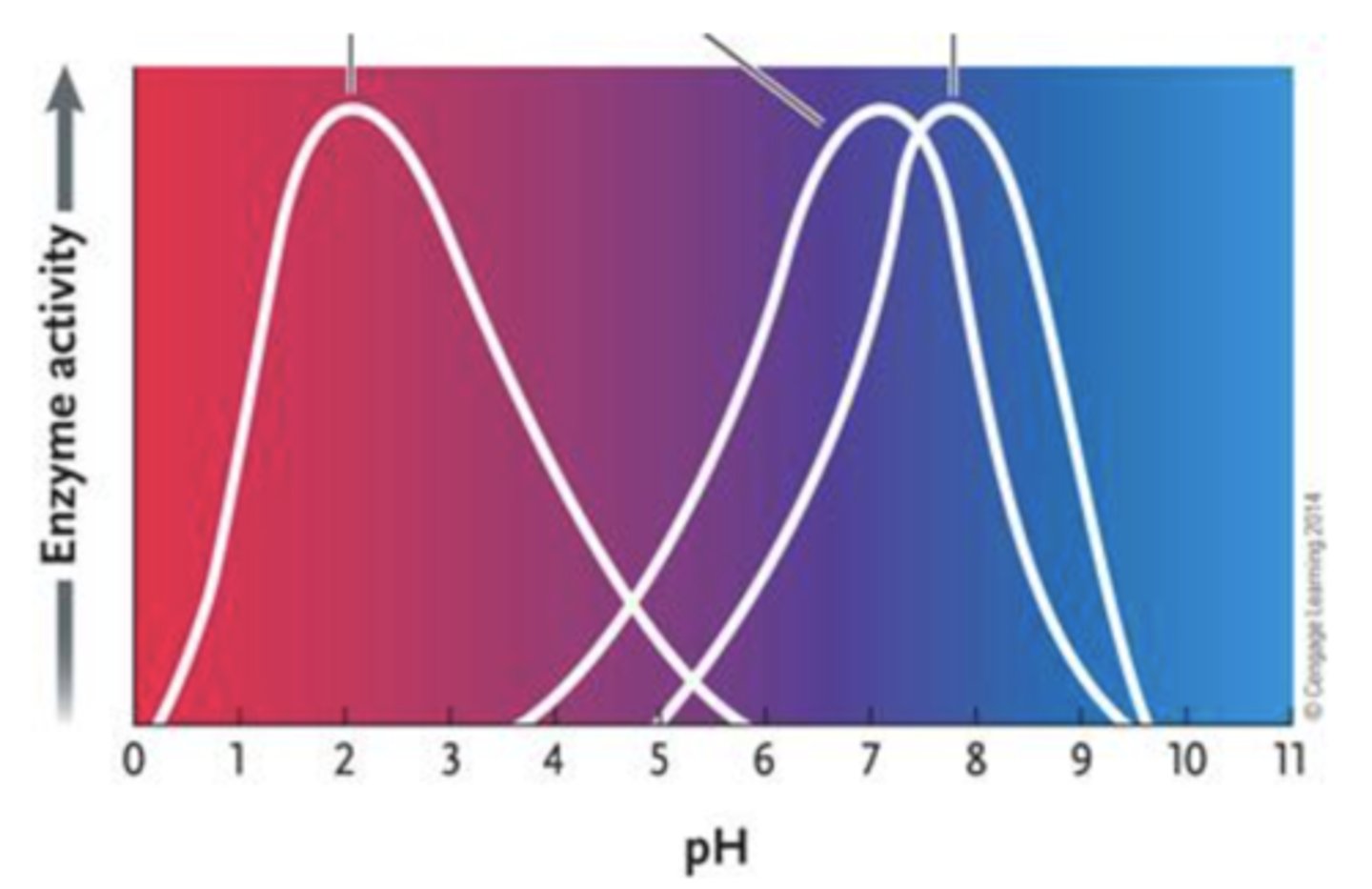
70. Answer the question by using the accompanying graph. The optimal pH for enzyme 2 is ____.
a.
2
b.
3
c.
4
d.
7
e.
8
d. 7
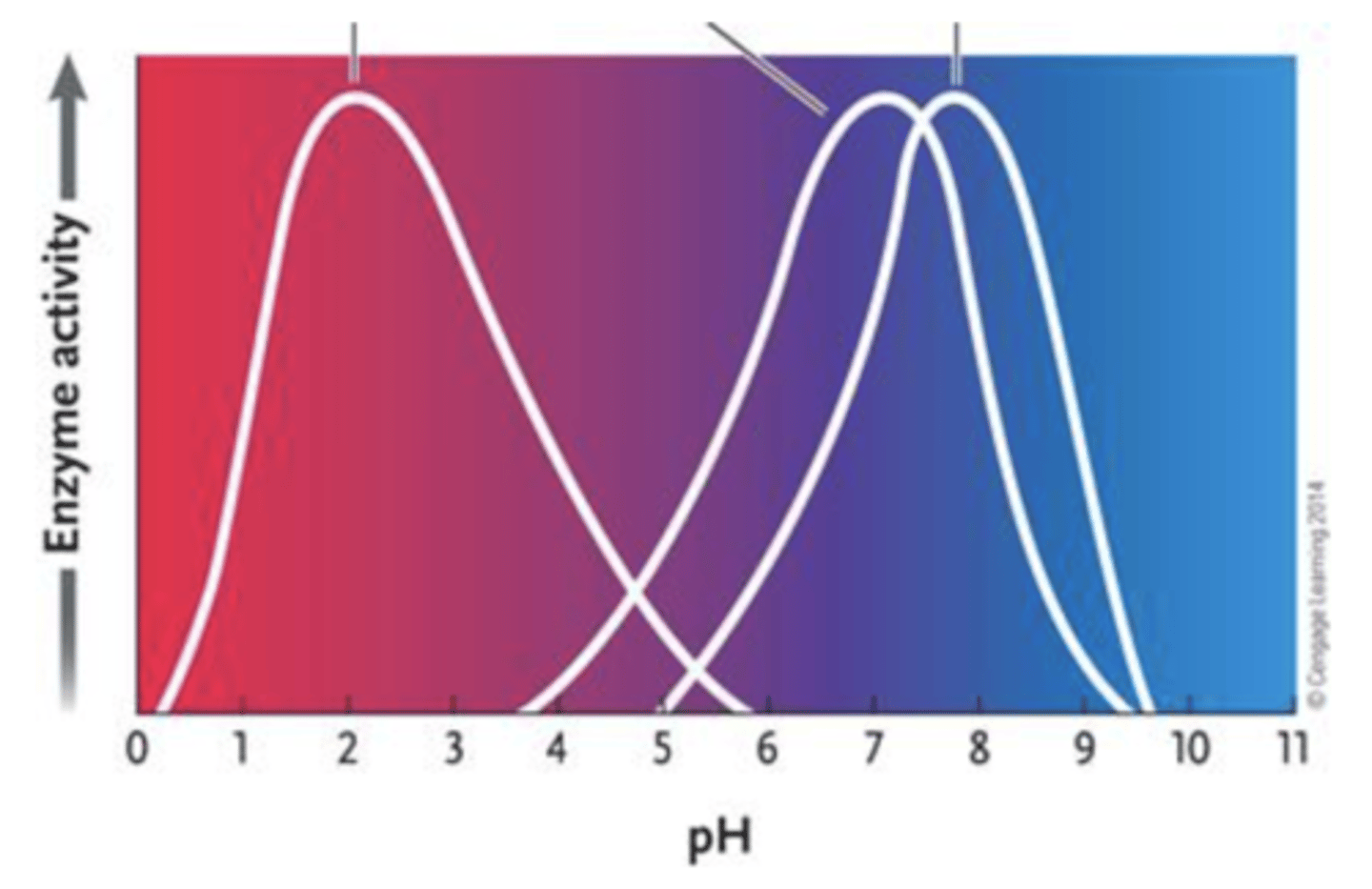
71. Answer the question by using the accompanying graph. If all three enzymes catalyze the same reaction and your experimental conditions require a pH of 8, which enzyme would you choose?
a.
enzyme 1
b.
enzyme 2
c.
enzyme 3
d.
either enzyme 2 or 3
e.
both enzymes 2 and 3
c. enzyme 3
72. Why do Siamese cats have brown ears, nose, tails and paws?
a.
Siamese cats contain heat sensitive enzymes that are more active in the extremities.
b.
Siamese cats contain heat sensitive enzymes that are more active in the core body.
c.
Siamese cats contain pH sensitive enzymes that are more active in regions of the body exposed to UV radiation.
d.
Siamese cats contain pH sensitive enzymes that are more active in regions of the body that are not exposed to UV radiation
e.
Siamese cats contain pH sensitive enzymes that are more active in regions of the body that contain nerve endings.
a.
Siamese cats contain heat sensitive enzymes that are more active in the extremities
73. What is the optimum pH of most enzymes?
a.
1
b.
3
c.
5
d.
7
e.
9
d. 7
74. Is a ribozyme a true enzyme?
a.
Yes, because it is a catalyst.
b.
No, because it is not a protein.
c.
No, because it cannot catalyze a reaction.
d.
Yes, because it can synthesize a protein.
e.
No, because it doesn't require cofactors.
b. No, because it is not a protein.
75. Zhang and Cech's experiments confirmed which feature of ribozyme activity?
a.
Ribozymes inhibit rates of biological reactions.
b.
Ribozymes catalyze formation of bonds between amino acids in protein synthesis.
c.
Ribozymes catalyze formation of the fundamental linkage tying nucleic acids to proteins.
d.
Ribozymes can link nucleic acids together even if their proteins are removed.
e.
Ribozymes provide a possible solution to the question of whether proteins or nucleic acids appeared first in evolution.
b.
Ribozymes catalyze formation of bonds between amino acids in protein synthesis.
76. Ribozymes are ____.
a.
RNA catalysts
b.
proteins that catalyze RNA synthesis
c.
RNA molecules that slow the rate of protein synthesis
d.
the products of RNA degradation
e.
amino acids that catalyze RNA synthesis
a. RNA catalysts
77. Harry Noller's experiments in which he extracted the ribosomal proteins and found that RNA molecules could catalyze protein synthesis had one major flaw. What was the flaw?
a.
the extraction process may have altered the RNA molecules
b.
protein synthesis may have occurred prior to extraction
c.
coenzymes, which were not extracted, might have been responsible for the reaction
d.
the extraction process may have altered the pH of the environment
e.
undetectable amounts of protein may have remained
e. undetectable amounts of protein may have remained
78. How did Zhang and Cech purify the RNA molecules that were able to catalyze the linkage between two amino acids?
a.
passing the reaction mixture through a column that binds biotin
b.
passing the reaction mixture through a column that binds all proteins
c.
passing the reaction mixture through a column that binds RNA
d.
centrifuging the reaction mixture to concentrate the proteins
e.
centrifuging the reaction mixture to concentrate the RNA molecules
a.
passing the reaction mixture through a column that binds biotin
79. The discovery of ____ suggested that nucleic acids likely existed prior to proteins.
a.
RNA
b.
ribozymes
c.
RNA polymerase
d.
peptide bonds
e.
endoplasmic reticulum
b. ribozymes
80. Because of some of the problems with explaining how the first RNA organisms originated, an alternative possibility has been proposed in which ____.
a.
proteins and RNA evolved simultaneously
b.
DNA existed before RNA
c.
lipids functioned as enzymes
d.
a different form of life existed before the RNA world
e.
viruses functioned as carriers for RNA
d. a different form of life existed before the RNA world
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
a.
The product of the reaction interacts with an enzyme in a noncompetitive way to inhibit or enhance enzyme activity
allosteric regulation
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
b.
The linking of an exergonic reaction with an endergonic reaction that allows a cell to drive a nonspontaneous reaction to completion
coupled reaction
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
c.
A series of chemical reactions where the products of one reaction are the reactants for a subsequent reaction
metabolic pathway
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
d. A substance that facilitates a chemical reaction without itself being consumed by the reaction
catalyst
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
e. The energy needed to start a reaction, be it endergonic or exergonic
activation energy
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
f. The portion of the enzyme that binds to a reactant or reactants
active site
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
g. A state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction
equilibrium point
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
h. An intermediate arrangement of unstable bonds between atoms that can proceed towards either the reactants or products of a reaction
transition state
Match each of the following terms with its correct definition.
I.
The reactant molecule that binds to an enzyme
substrate
For each of the following situations, choose the most appropriate term. Some choices may be used more than once.
a.
endergonic
b.
exergonic
c.
equilibrium
90. protein synthesis
a. endergonic
For each of the following situations, choose the most appropriate term. Some choices may be used more than once.
a.
endergonic
b.
exergonic
c.
equilibrium
91. digestion of a candy bar
b. exergonic
For each of the following situations, choose the most appropriate term. Some choices may be used more than once.
a.
endergonic
b.
exergonic
c.
equilibrium
92. a dead cell
c. equilibrium
For each of the following situations, choose the most appropriate term. Some choices may be used more than once.
a.
endergonic
b.
exergonic
c.
equilibrium
93. a reaction where DG is positive
a. endergonic
For each of the following situations, choose the most appropriate term. Some choices may be used more than once.
a.
endergonic
b.
exergonic
c.
equilibrium
94. a reaction where DG is negative
b. exergonic
For each of the following situations, choose the most appropriate term. Some choices may be used more than once.
a.
endergonic
b.
exergonic
c.
equilibrium
95. the rate of synthesis equals the rate of degradation
c. equilibrium
96. Why is energy defined as "the capacity to do work"?
Energy cannot be directly measured or weighed, and can only be detected through its effects on matter, including its ability to move objects against opposing forces, such as friction, gravity, or pressure, or to push chemical reactions toward completion.
97. Define metabolism.
Metabolism is the total of all of the chemical reactions in a cell. These reactions can be catabolic or anabolic and are used to synthesize new molecules or extract energy from molecules to power cellular work.
98. What is the significance of activation energy?
Activation energy is the initial energy investment required to start a reaction. Without this initial energy, reactions will not start.
99. Why is using heat to speed up biological reactions problematic?
Although increasing the temperature increases the rates of all reactions, high temperatures destroy the structural components of cells, particularly proteins, and this can result in cell death.
100. Why does the existence of ribozymes offer a possible solution to the question of whether nucleic acids or proteins appeared first in evolution?
Because nucleic acids contain the required genetic information, enzymes are required for the duplication of this information. Because ribozymes are both nucleic acids and enzymes, this suggests that they could have served both roles in early life forms.