Urinary Tract Metabolic Disease - Module 4
1/258
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
259 Terms
Stones in the urinary system (general term referring to a stone anywhere in the renal system)
Define urolithiasis
Stones in the renal collecting system
Define nephrolithiasis
Calyces, pelvis, ureter, or bladder
Where would a stone be located in the case of nephrolithiasis
Calcifications in the renal parenchyma
Define nephrocalcinosis
Cortex or medulla of the kidney
Where would the stone be located in the case of nephrocalcinosis
Very common
Is nephrolithiasis common or rare
Age
An increased incidence of nephrolithiasis has been seen with:
Caucasian males
What type of patients more commonly are affected by nephrolithiasis
Don't really know why they form but there are certain things that can increase your risk
Do we know the etiology of nephrolithiasis
Hereditary, limited water intake (chronic dehydration), diets high in animal protein, urinary stasis
What are some risk factors for nephrolithiasis
12%
What % of the population will have urinary stones at some point in their lifetime
True
T/F: stones can move through the collecting system
UPJ, at iliac vessels, UVJ
What are the 3 location of natural narrowing in the
Uretopelvic junction, located where the ureter attaches to the kidney pelvis
What does UPJ stand for and where is it located
When the ureters cross over the iliac vessels they are narrowed a little bit
Why does the ureter narrow at the iliac vessels
Ureterovesicular junctions, is where the ureter connects to the bladder
What does the UVJ stand for and where is it located
UVJ
Where is the most narrowest portion of the ureter
80%
What % of stones get stuck at the UVJ
<5mm
What size of stones typically are able to be passed unassisted
80%
What % of stones <8mm can be pass without assistance
>5mm
What size of stones more commonly require intervention to be passed/get ride of
UPJ
What is 1
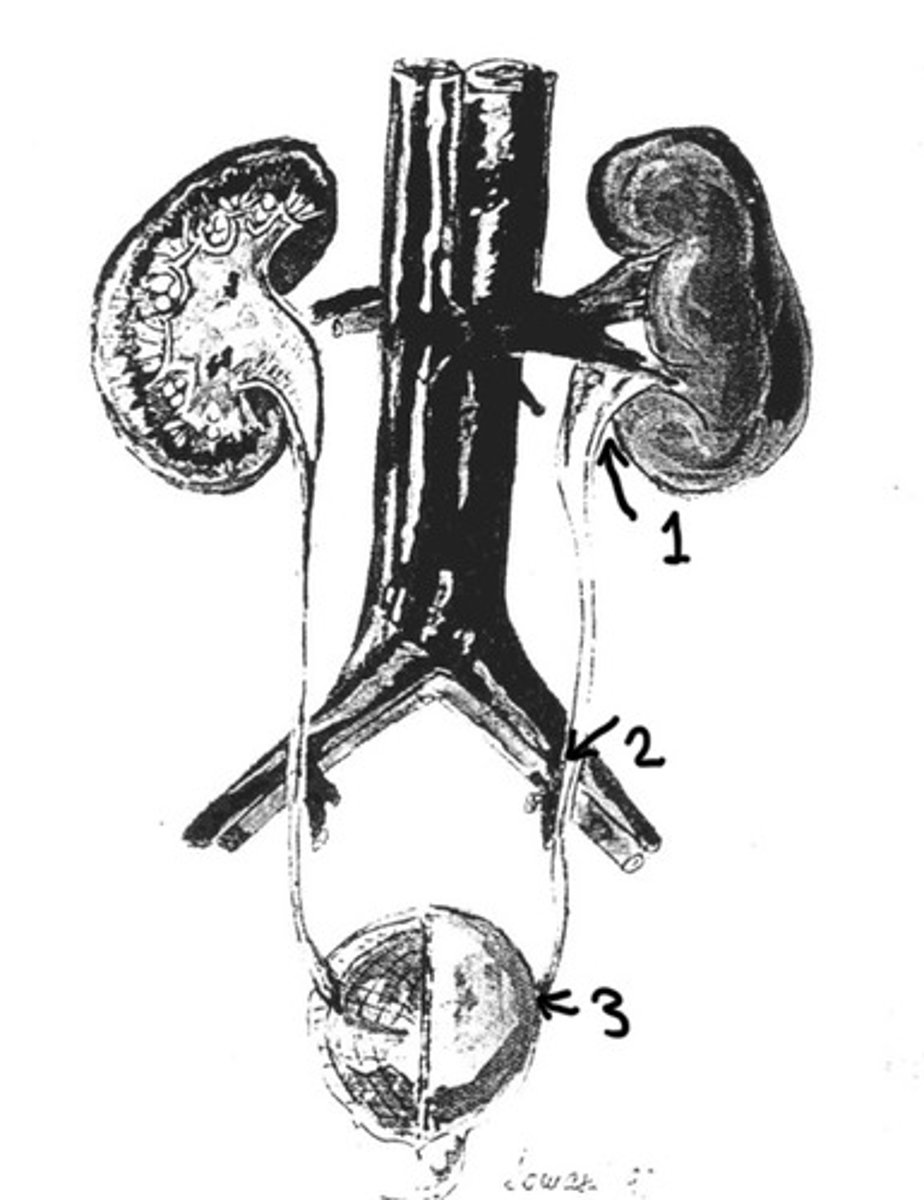
Ureters crossing over the iliac vessels
What is 2
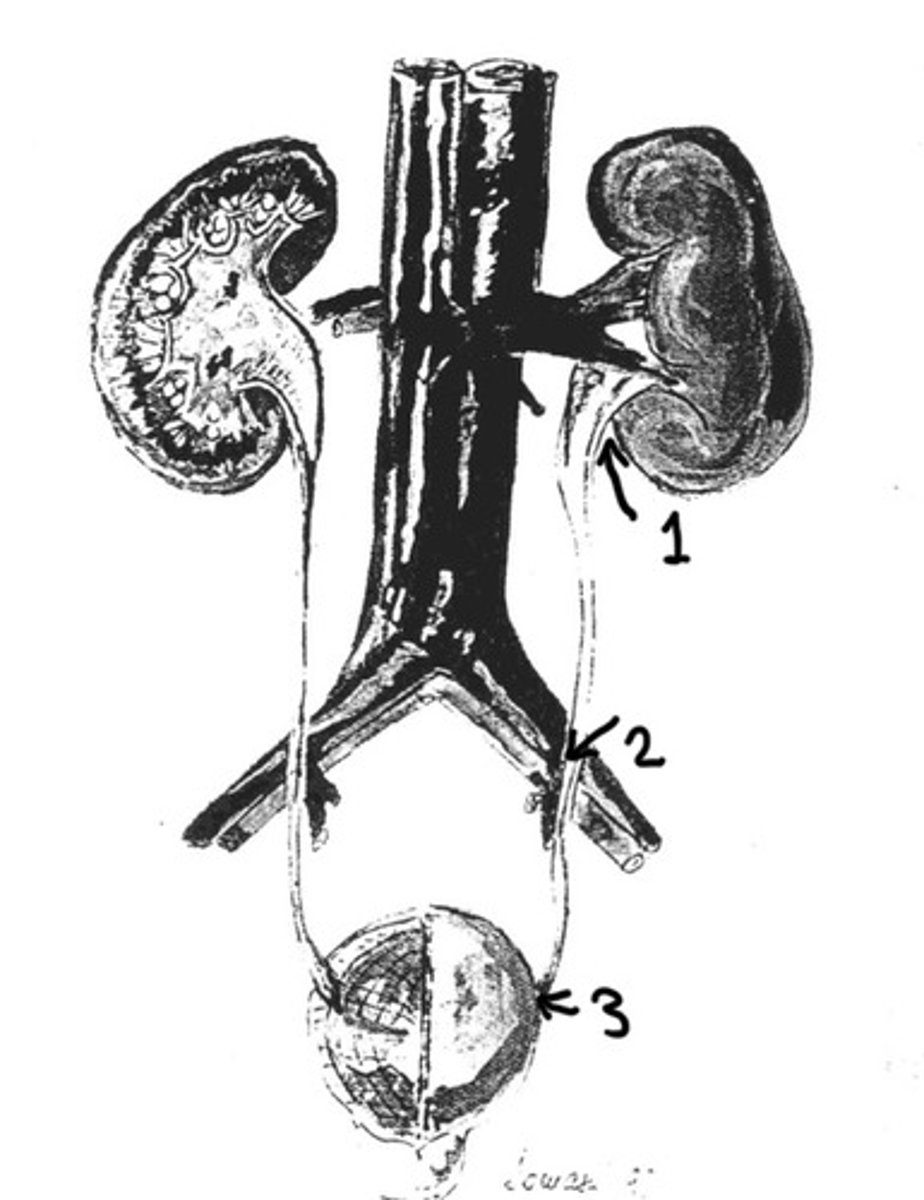
UVJ
What is 3
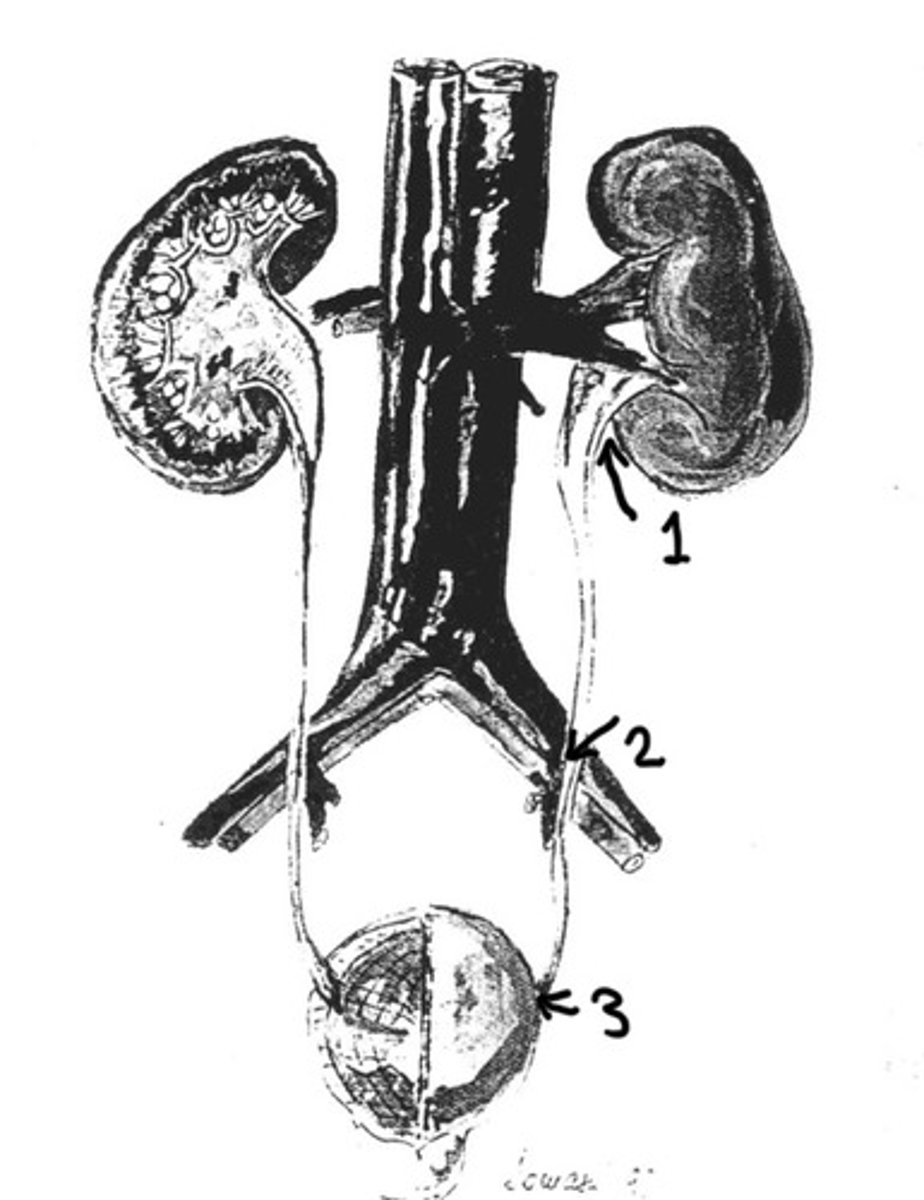
Often asymptomatic
What is the usually presentation of nephrolithiasis
Hematuria and flank pain
What are some other symptoms of nephronlithiasis
If the stone is just sitting in the calyces and not moving will probably not cause much problems but once it starts going down the ureter and get stuck is when it usually causes pain
Describe the the location of a kidney stone may affect the symptoms
Microscopic or gross/frank
What are the 2 types of hematuria that may be seen with nephrolithiasis
Visualized in urine (the urine is visually red/brown)
What does gross or frank hematuria mean
Only can see the blood under the microscope (wont be able visually see a colour change)
What is microscopic hematuria
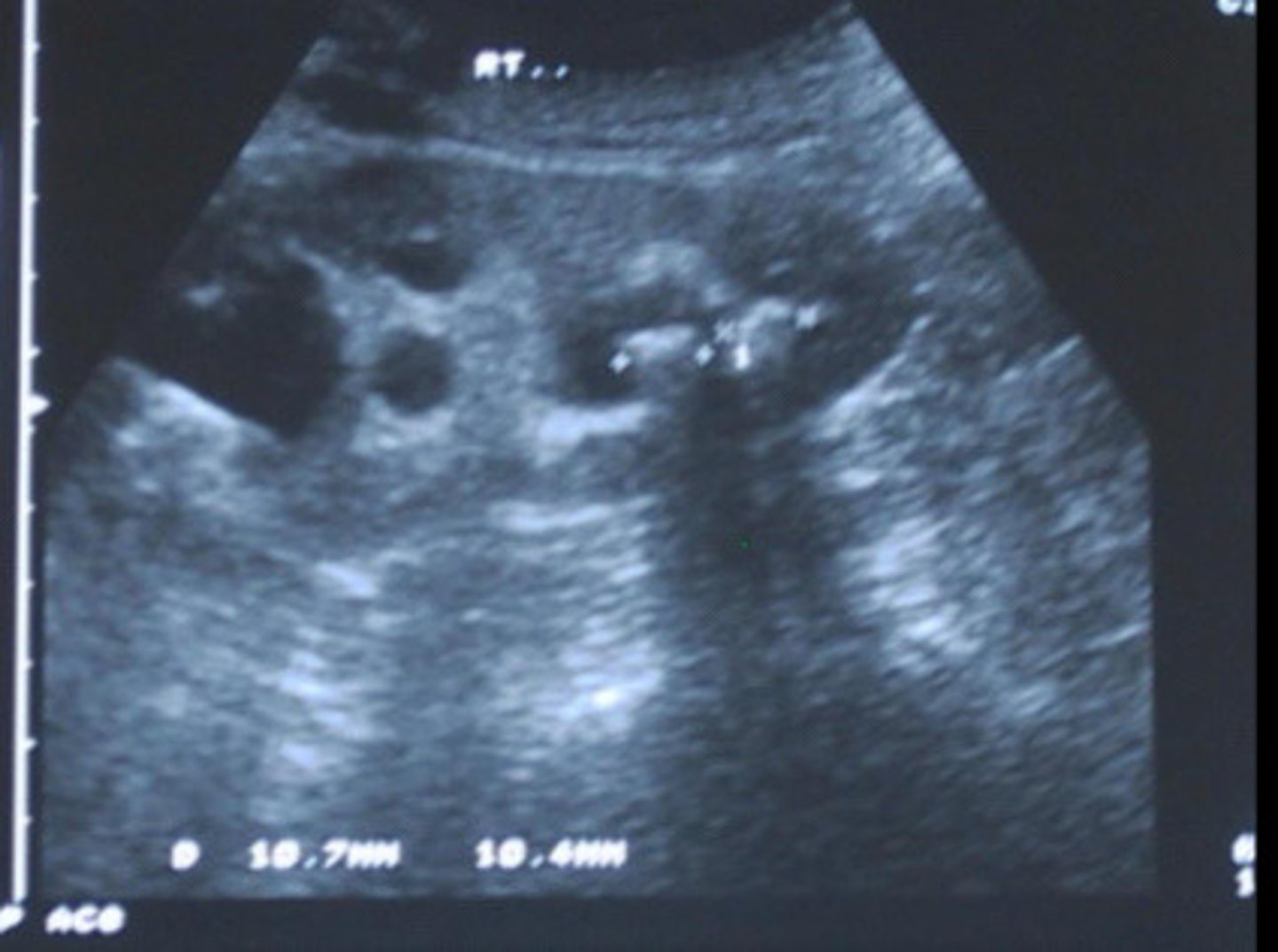
Echogenic focus or foci with posterior shadowing
Describe the sonographic appearance of nephrolithiasis
Nephrolithiasis
What does this image show
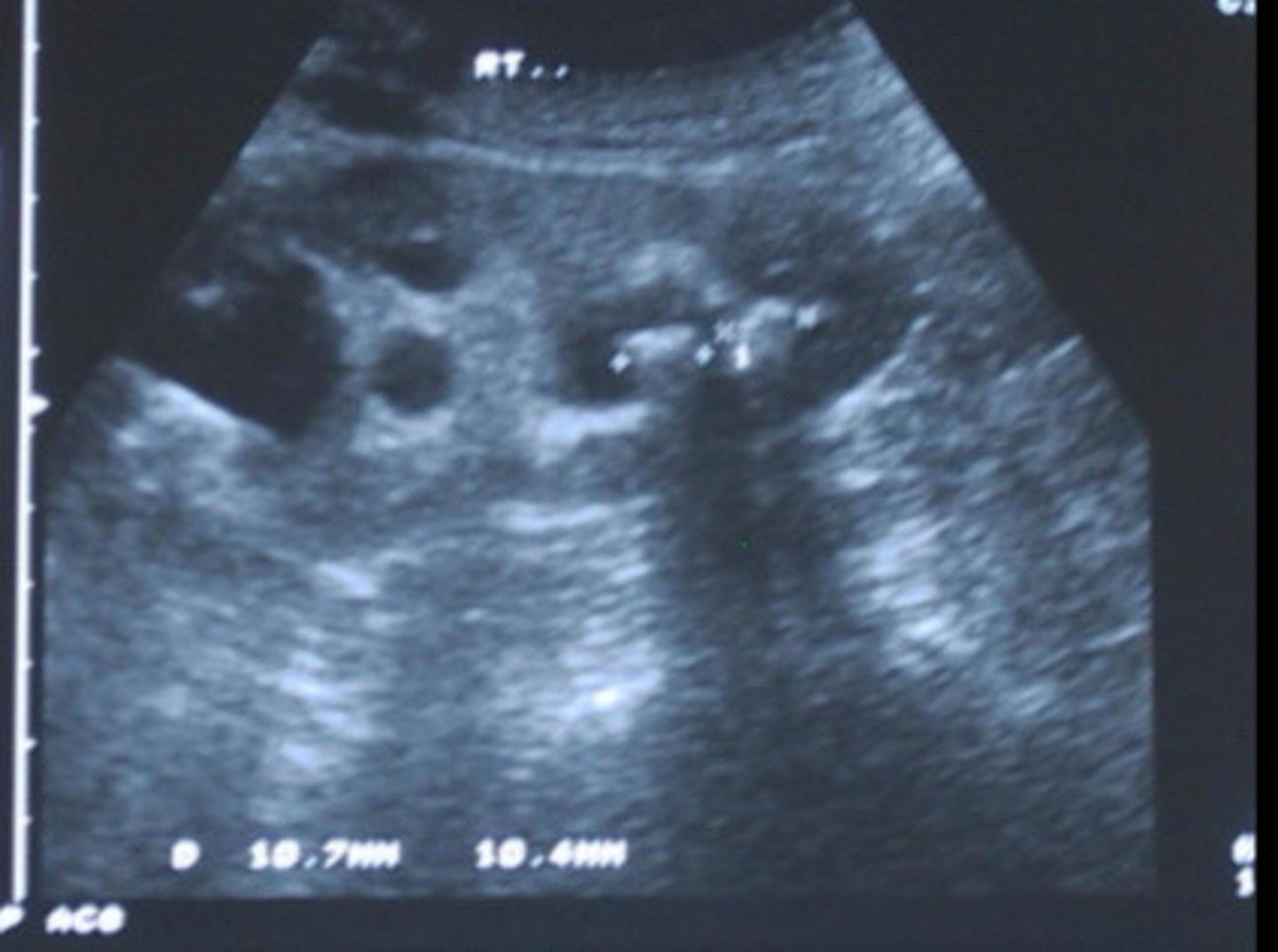
Nephrolithiasis
What does this image show
Number, size, location, and complications
What are the 4 main pieces of info that you should try to answer when you find nephrolithiasis
To determine if the stone can pass or if the patient will need intervention
Why is it important to determine the size of the stone
Assess where the urine is backed up, it will back up proximally to the level of the stone
How can you determine the location of the stone if the stone is not well visualized
Hydronephrosis or small/absent urine jet in the bladder
What are some supporting findings/complications of nephrolithiasis
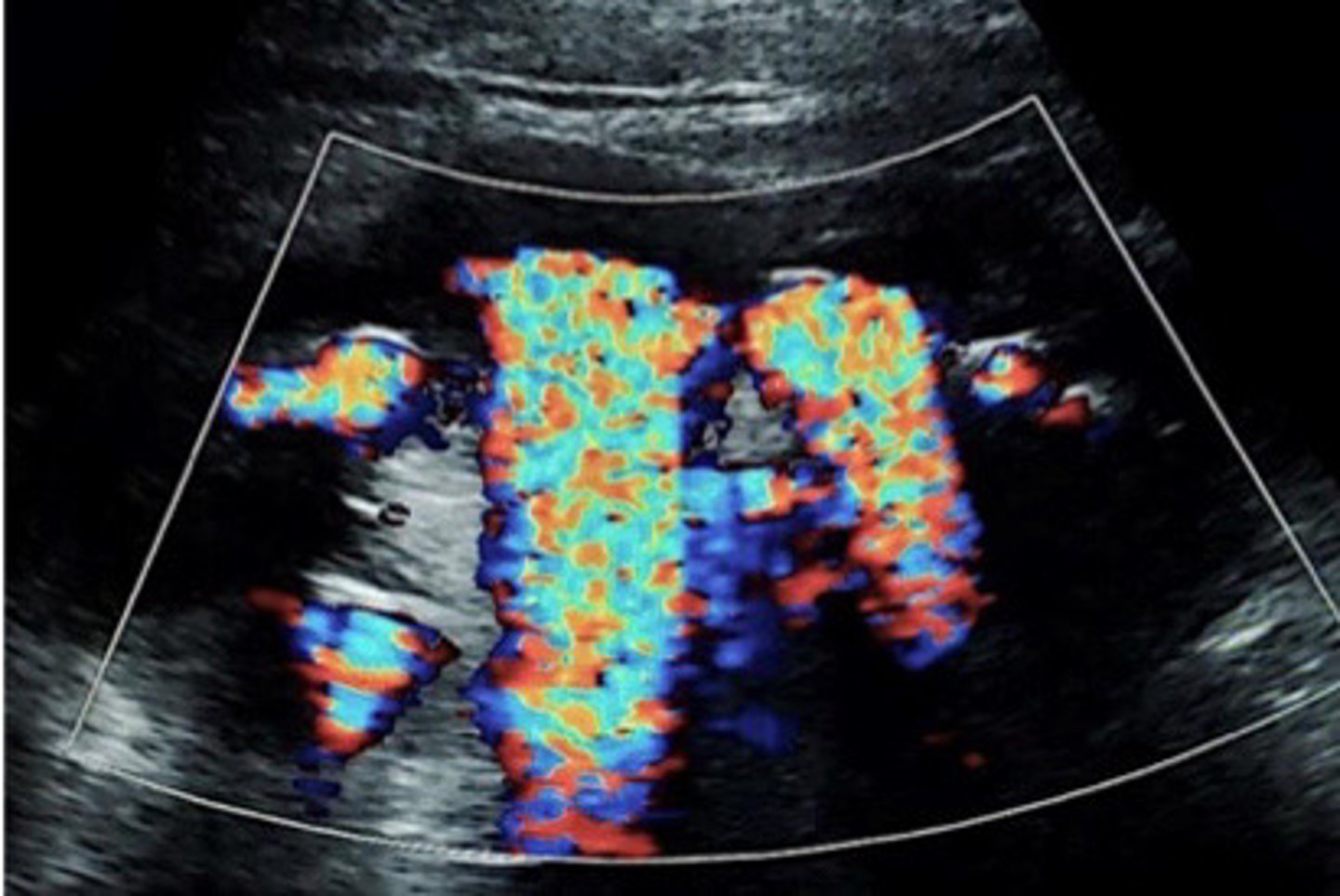
Twinkle artifact
What is an artifact that a stone may produce
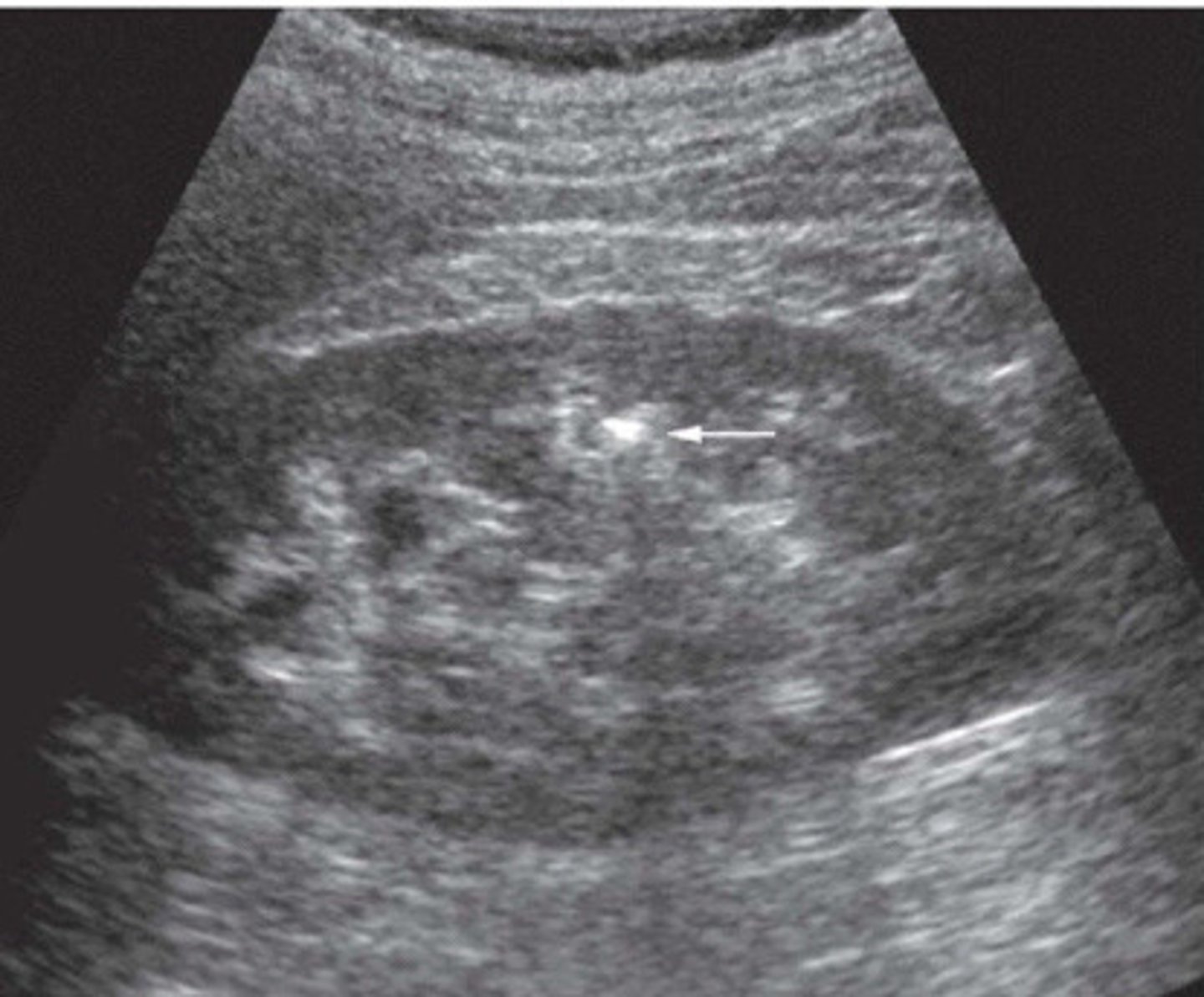
When a stone is located in the sinus region, it is hard to determine if it is a stone bc it will blend into the hyperechoic sinus. You can use colour or power Doppler to look for a twinkly artifact a stone will give off
Explain how you can use the twinkling artifact to your advantage when suspicious of a stone in the sinus region
Stone difficult to identify in the sinus region
What does this image show
Stone now identified with the twinkle artifact
What does this image show
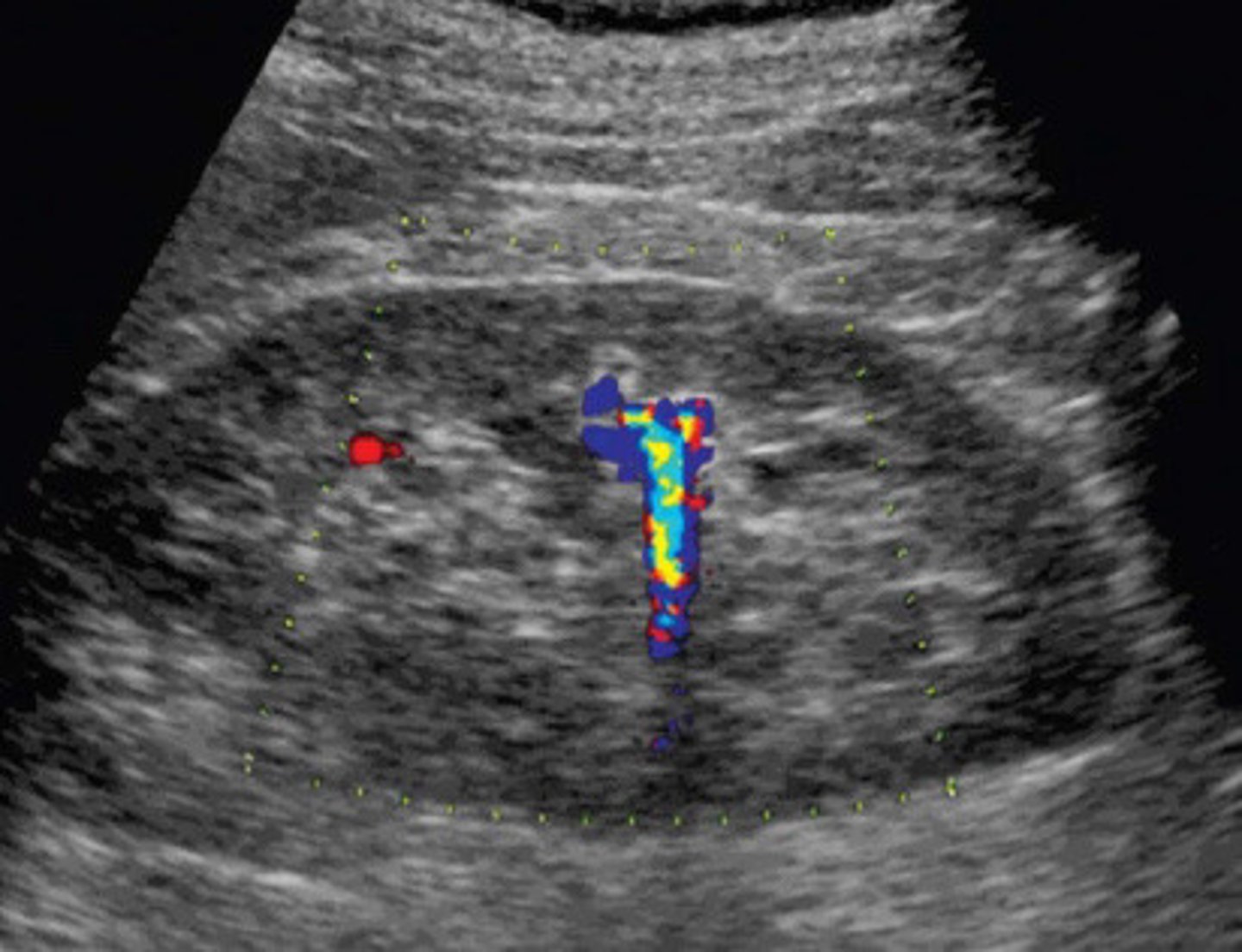
Colour reverberation
What is the twinkling artifact
Colour or power Doppler
What mode do you have to use in order to be able to see the twinkling artifact
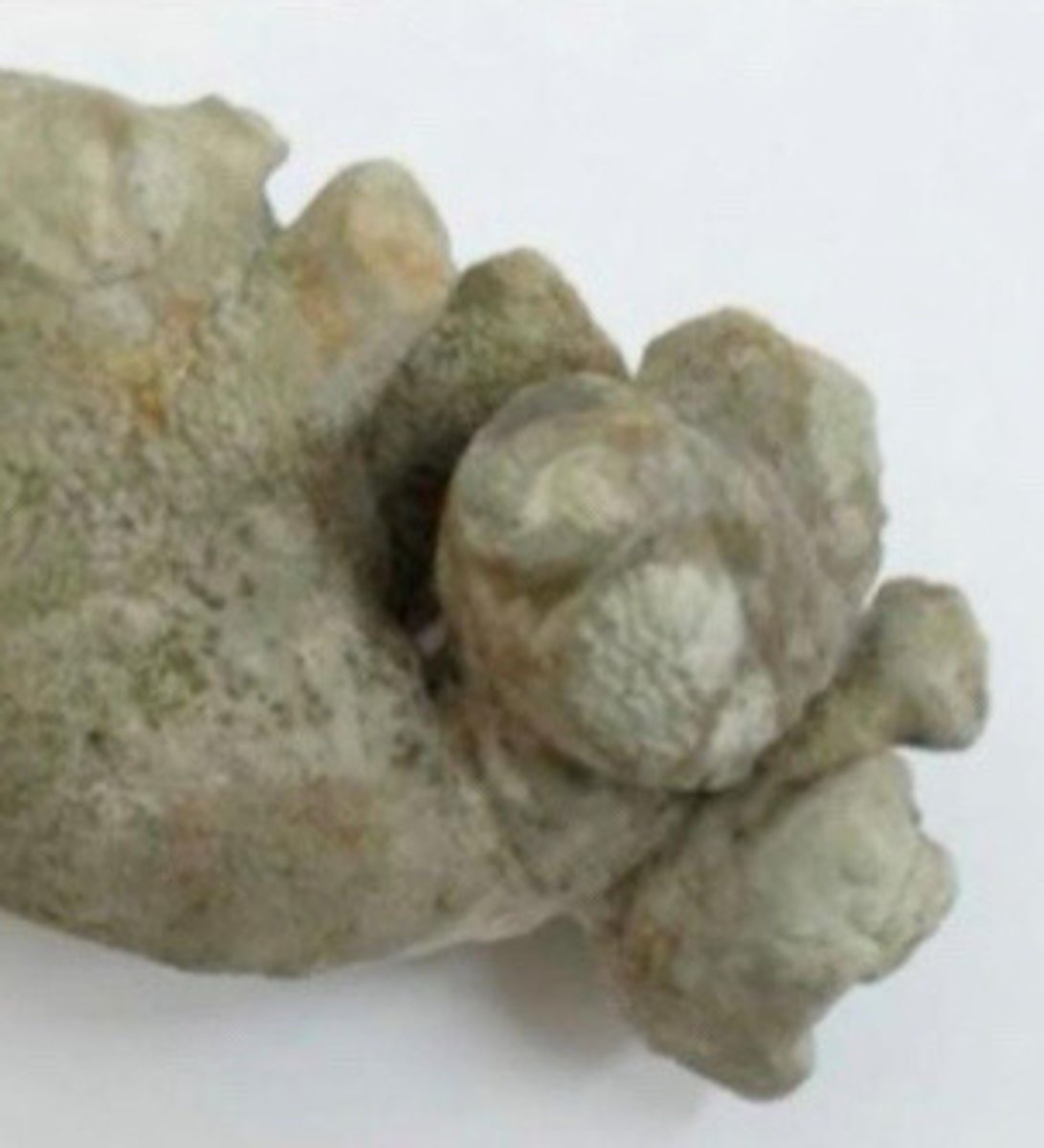
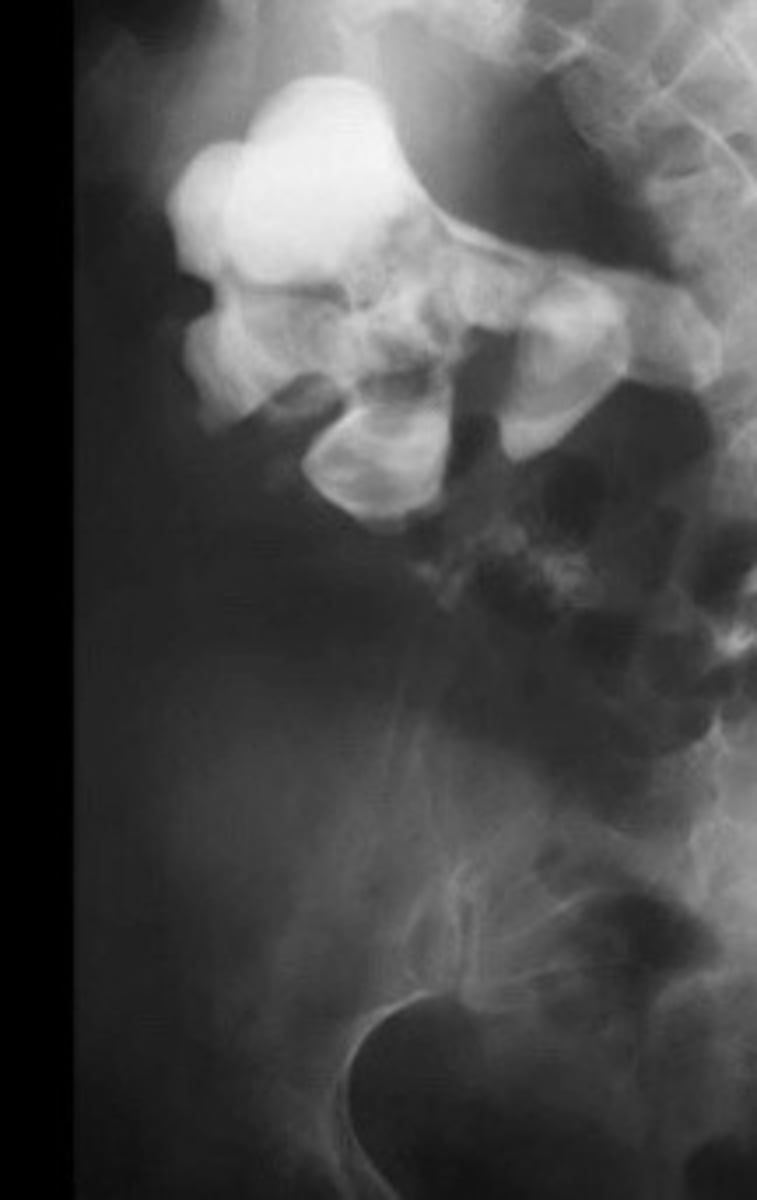
Staghorn calculi
What does this image show
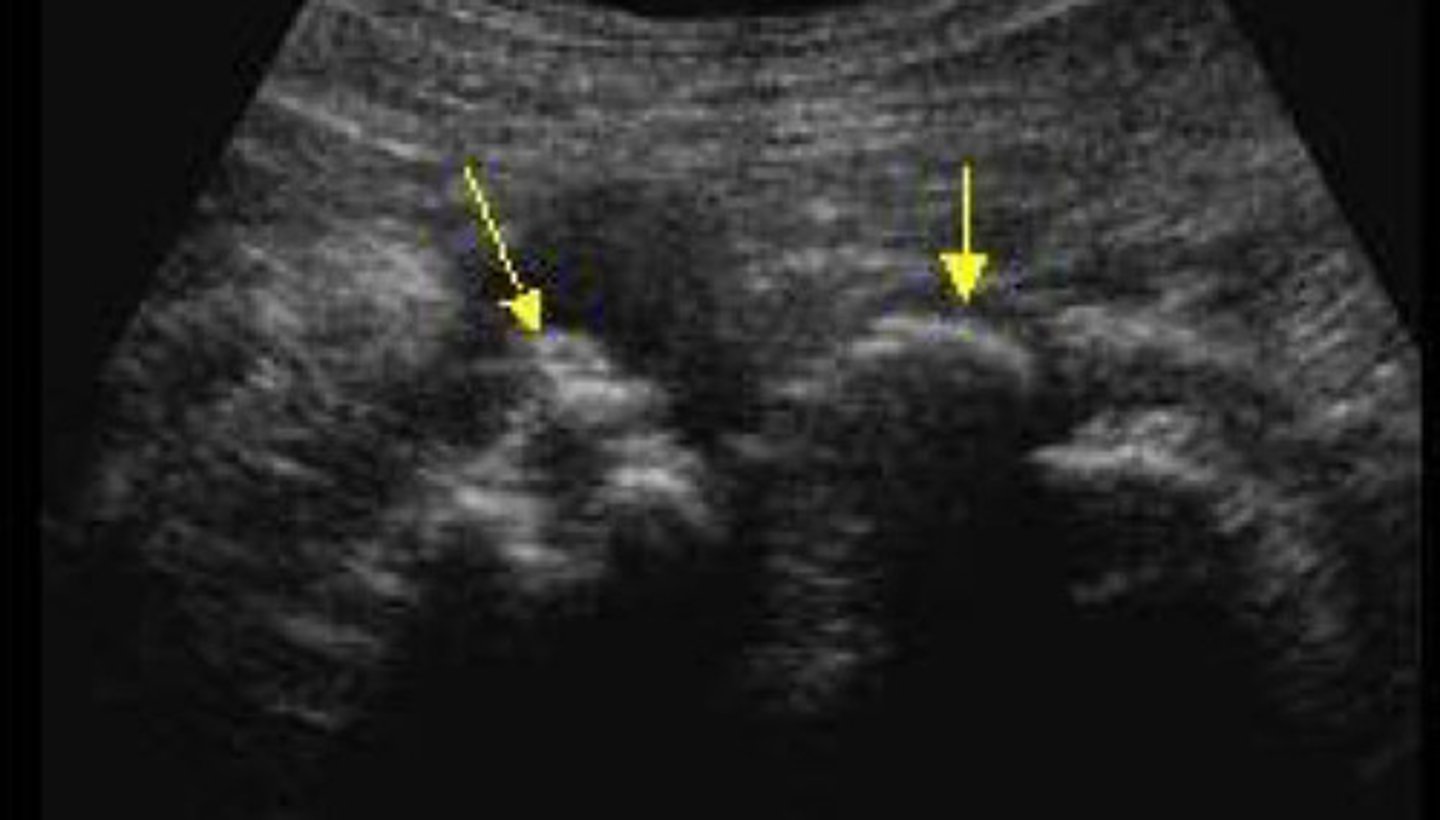
Calcifications filling all or most of the renal collection system/calyces
What is staghorn calculi
Staghorn calculi
What does this image show

X-ray of staghorn calculi
What does this image show
Twinkle artifact from staghorn calculi
What does this image show
Staghorn calculi
What does this image show
Intrarenal gas, renal artery calcifications, calcified sloughed papilla, calcified tumours, ureteric stent
What are some false positives for nephrolithiasis (things we may mistake for a stone in the collecting system)
Bacteria in the collecting system may be gas production and appear as an echogenic focus with dirty shadowing
Explain how intrarenal gas can be mistaken for stones in the renal collecting system and what causes it to
Small vessels of our renal arteries can calcify as we age, and may look echogenic and mimic a stone (i dont think it would really have shadowing tho)
Describe when renal artery calcifications occur and how the can be mistaken for nephrolithiasis
Apex of the pyramids
Papilla=
In some disease processes, the pyramids becomes calcified and sloughed off. Since they are calcified they will look like echogenic foci
What is calcified slough papilla and how can they mimic nephrolithiasis
When someone has a stone in their ureter, the ureter can become very inflammed. This can cause the wall of the ureter to stick together and even scar togethe. They will often put a stent in to keep the ureter wall away from each other while they are healing
Describe when a ureteric stent would be used
The stent may be bright and shadow so can mimic a stone
Why may a ureteric stent be confused for nephrolithiasis
Try to follow the dilated tube (ureter) until you find an echogenic focus or the end of the dilation
What is a tip to help you determine the location of a stone in the ureter
Very hard to follow the ureters at all their length bc of bowel gas
Why is it sometimes hard to identify the location of a stone in the ureter
Posterior aspect at the trigone of bladder
Where do the ureters connect into the bladder
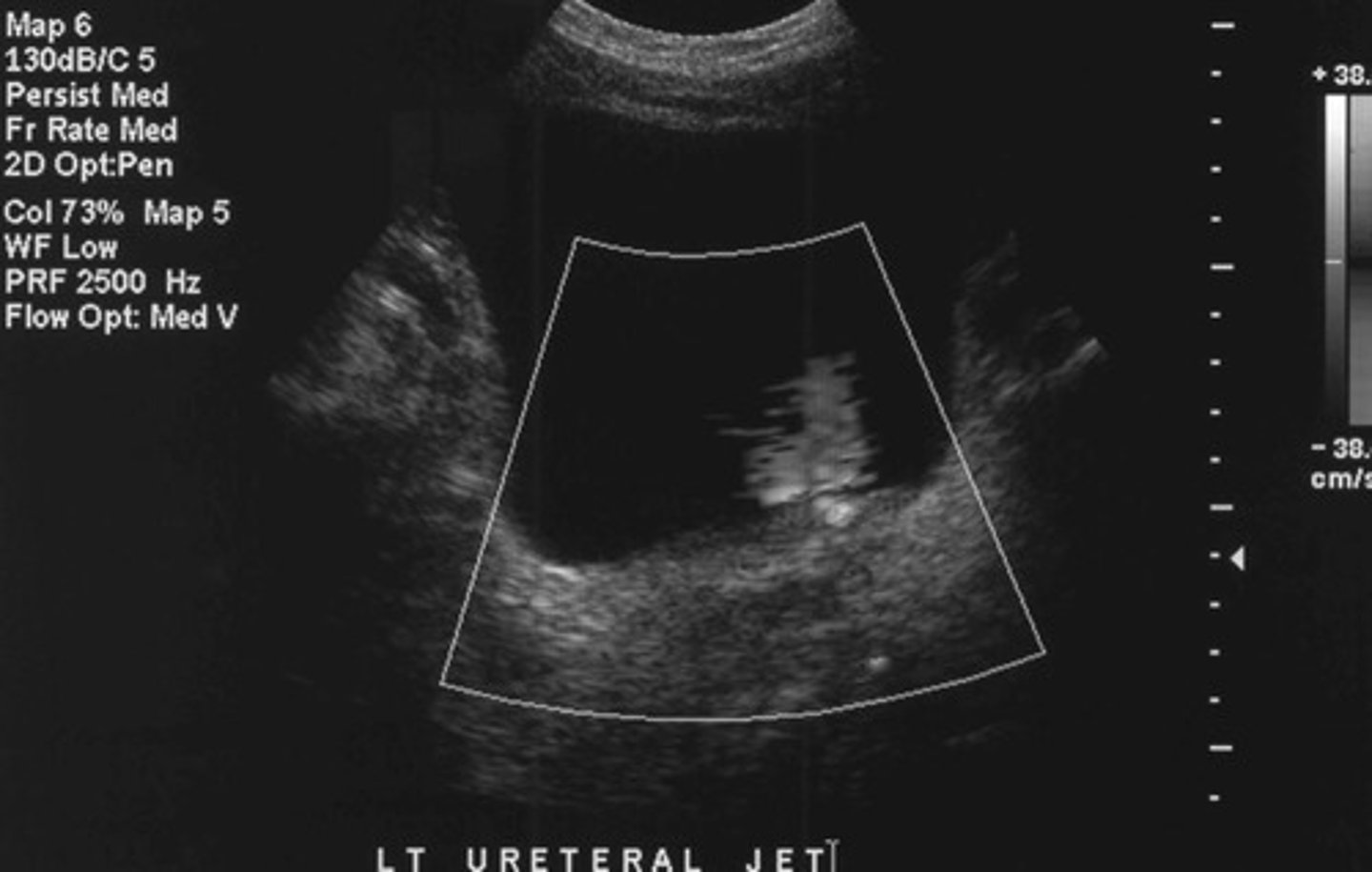
Want to determine if the stone is completely or just partially obstructing an ureter
Why do you ALWAYS want to asses a urine jet when you find a stone in the ureter
Urethral jet
What does this image show
One
How many bladder calculi does a patient usually have
Asymptomatic
What is the usually symptoms of bladder calculi
Hematuria and pain
What are some over possible s/s of bladder calculi
Stone formed in the kidney and went down the ureter into the bladder OR a stone that formed in the bladder itself (due to urinary stasis)
What are the 2 possible causes of bladder calculi
Mobility
What feature of a bladder calculi do you need to confirm
Bc if it doesn't move it may be more concerning for a calcified mass
Why should you try as hard as you can to get the bladder calculi to move
Depending portion of the bladder (gravity dependent)
Where would a bladder calculi be located
Dilation of the renal collection system
What is hydronephrosis
True
T/F: hydronephrosis may be asymptomatic and an incidental finding
Obstructive and non obstructive
What are the two types/causes of hydronephrosis
Renal atrophy
What can hydronephrosis lead to eventually if it is left untreated for a long amount of time
Intrinsic or extrinsic obstruction of urine flow
Define obstructive hydro
Something obstructing urine physically in the collecting system
What would intrinsic obstructive hydro be
Something of the outside of the collecting system putting pressure on the system
What would extrinsic obstructive hydro be
Masses, enlarged lymph nodes, etc
What are some examples of extrinsic obstructive causes of hydro
Ureteral jets (is it fully or partially obstructive?)
What else should you assess if you identify obstructive hydro
The treatment/how fast we need to treat the patient (if fully obstructive may be more emergent)
Why do you need to determine if an obstruction in the collecting system is fully obstructive
Reflux, infection, polyuria
What are some examples of non obstructive causes of hydro
Pt is producing excessive amounts of urine
What is polyuria
DM can cause this, the patient will produce so much urine so quikcly that they can't empty it out fast enough and it will back up into the kidneys (therefore causing hydronephrosis)
Explain an example of polyuria leading to hydronephrosis
Grade 1/mild, grade 2/moderate, grade 3/severe
What are the 3 classifications of hydro
Sonographic appearance
How is the severe of hydronephrosis classified
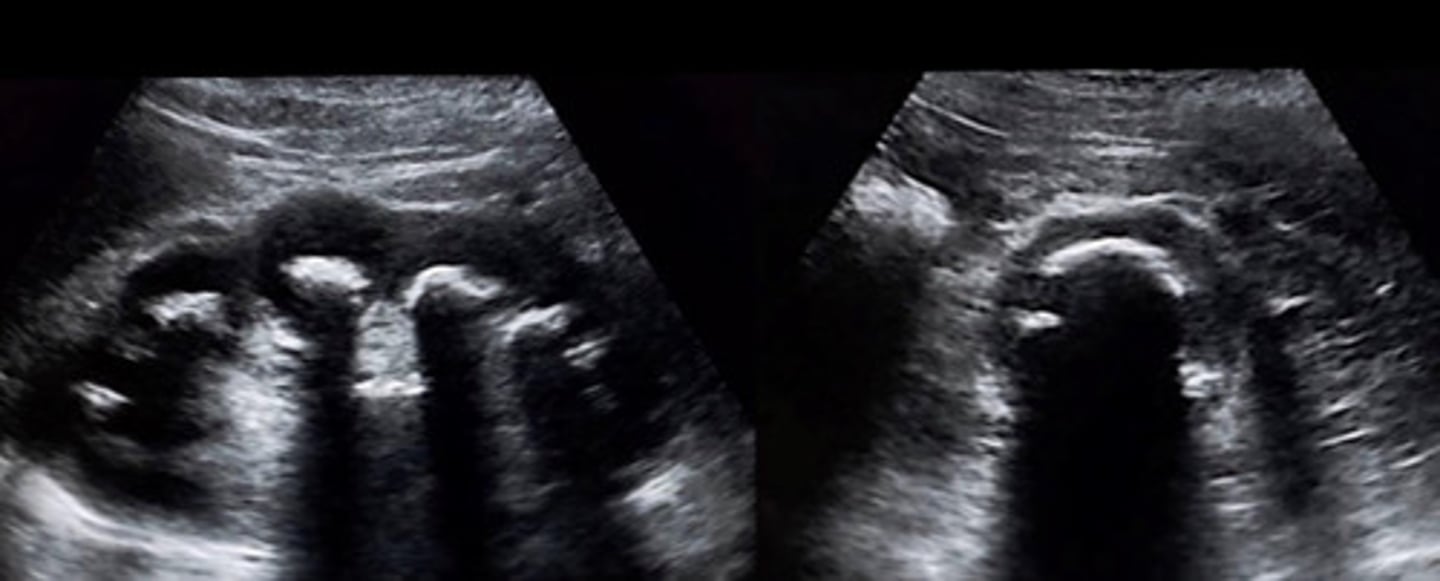
Slight separation (splaying) of sinus echoes (just in the mid sinus region)
Describe the appearance of grade 1 hydro
2mm
The sinus echoes must be separated at least ______ to be considered grade 1 hydro
Pt is probably just hydrated, doesn't really mean anything
What does it mean if the sinus echoes are separated by less than 2 mm
Grade 1 hydro
What does this image show
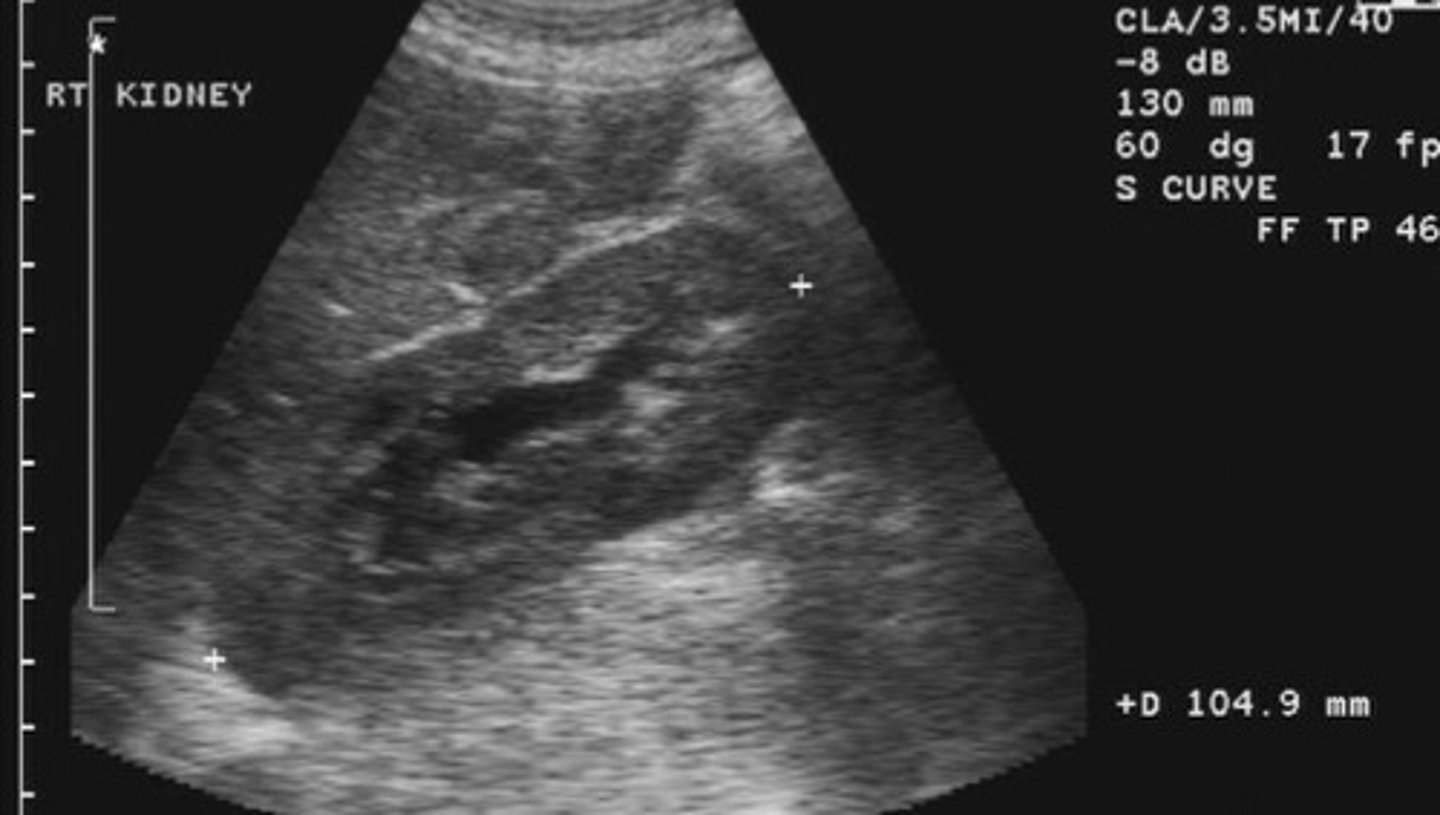
Grade 1 hydro
What does this image show
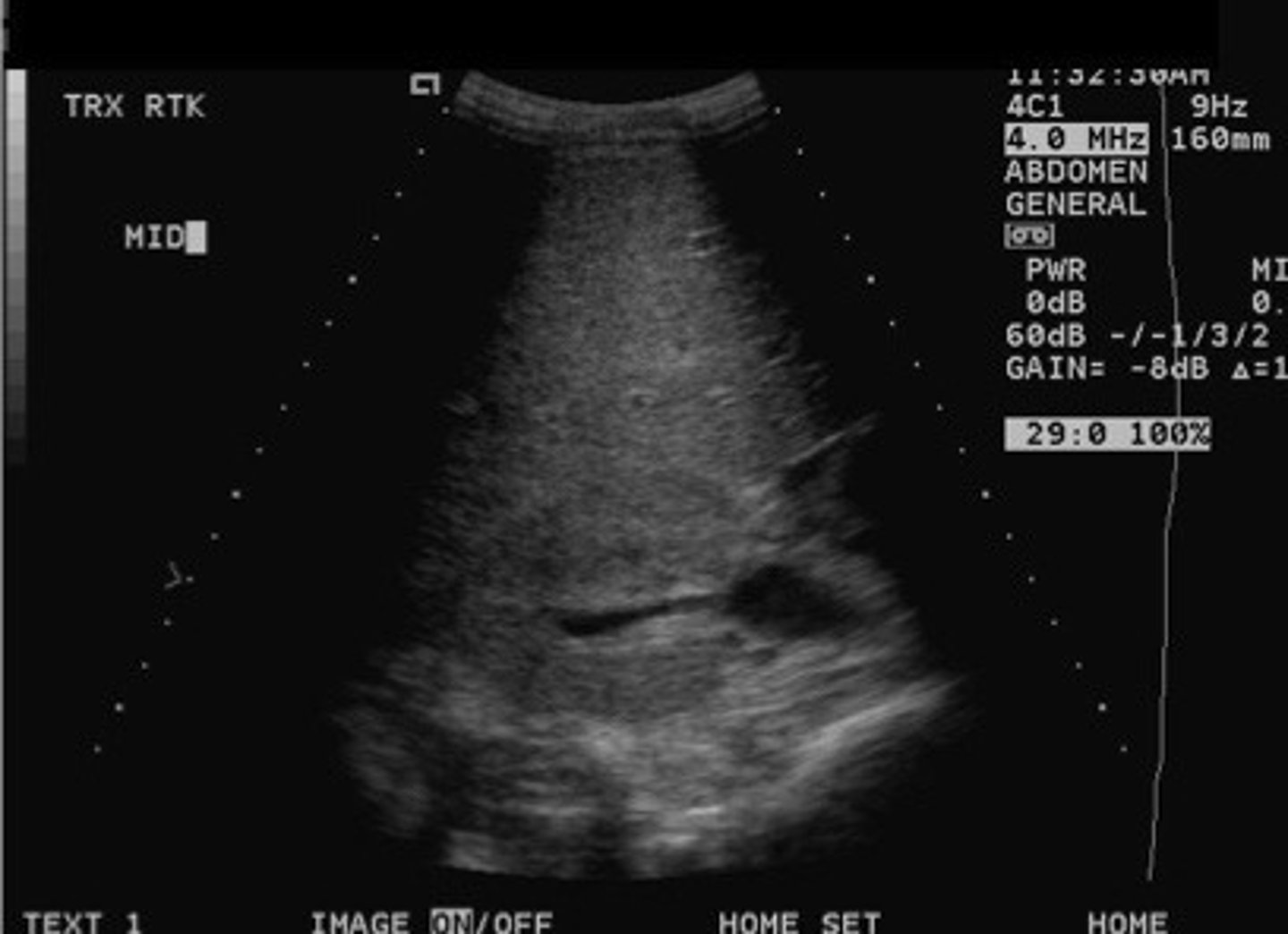
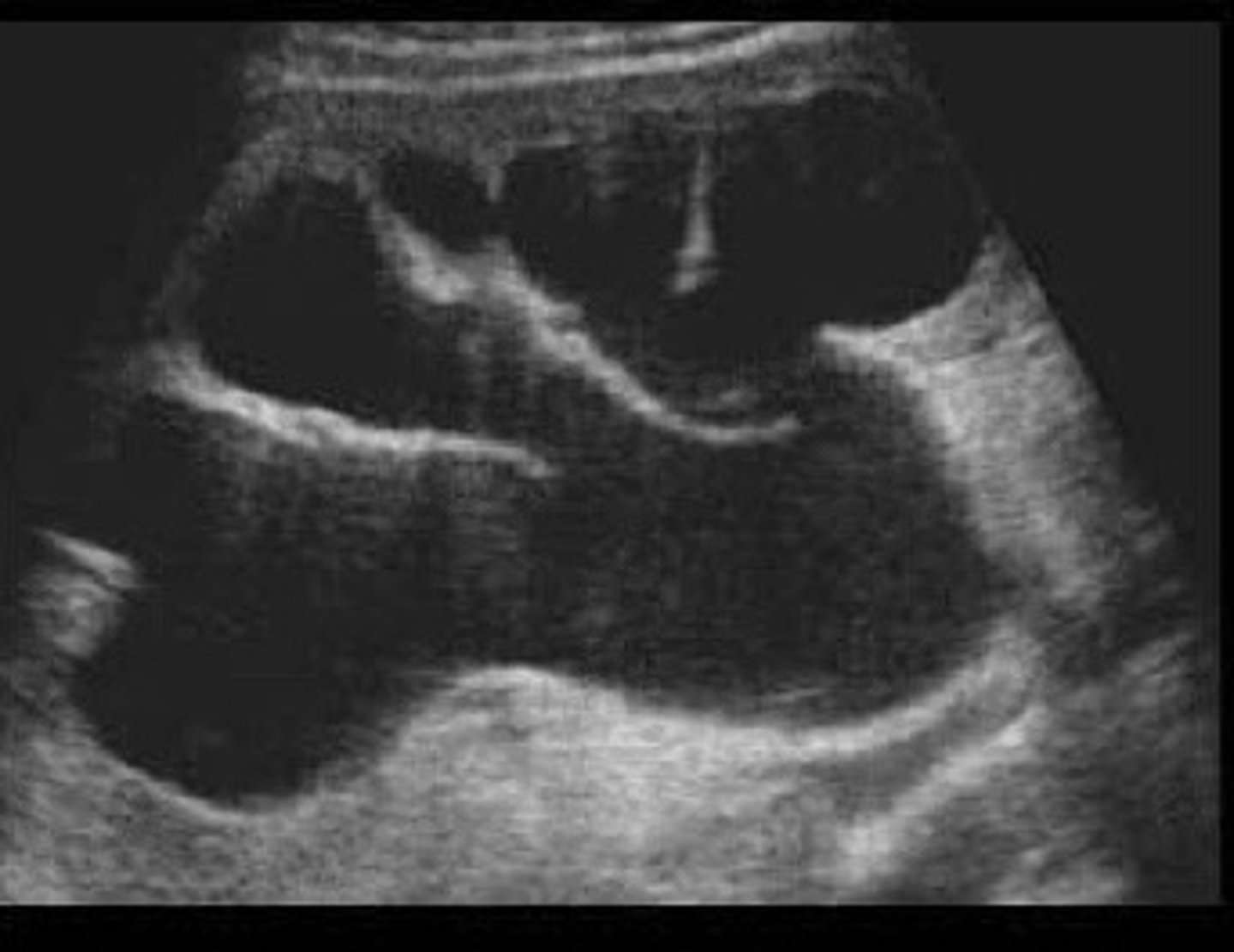
Separation of entire central sinus and club calyces
Describe the appearance of grade 2 hydro
Pelvis, minor and major calyceal system
What is dilated in the case of grade 2 hydro
Rounded like the slubs in a deck of cards (can see an outline of the calyceal system)
Describe the appearance of clubbed calyces
Grade 2 hydro
What does this image show
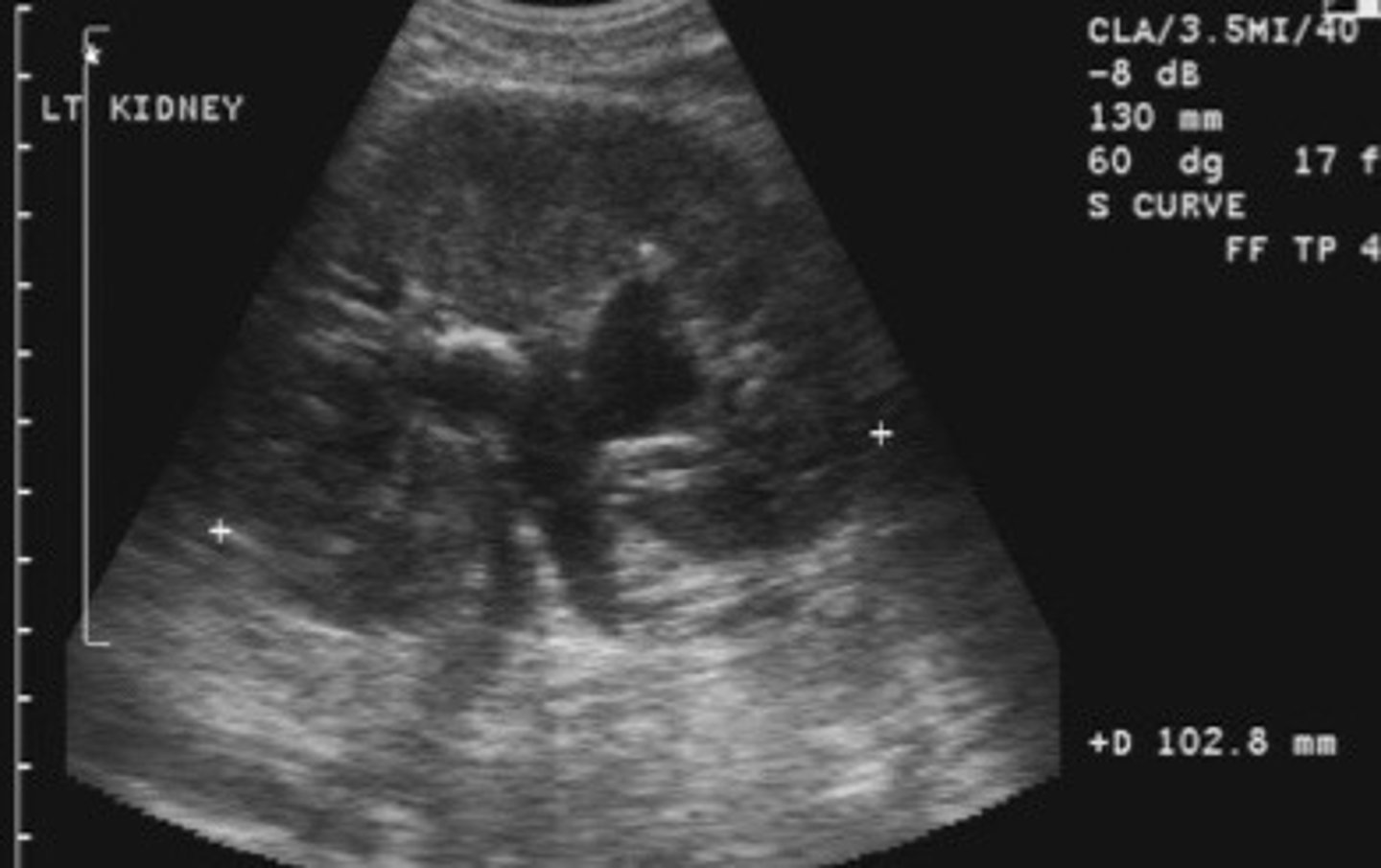
Grade 2 hydro
What does this image show
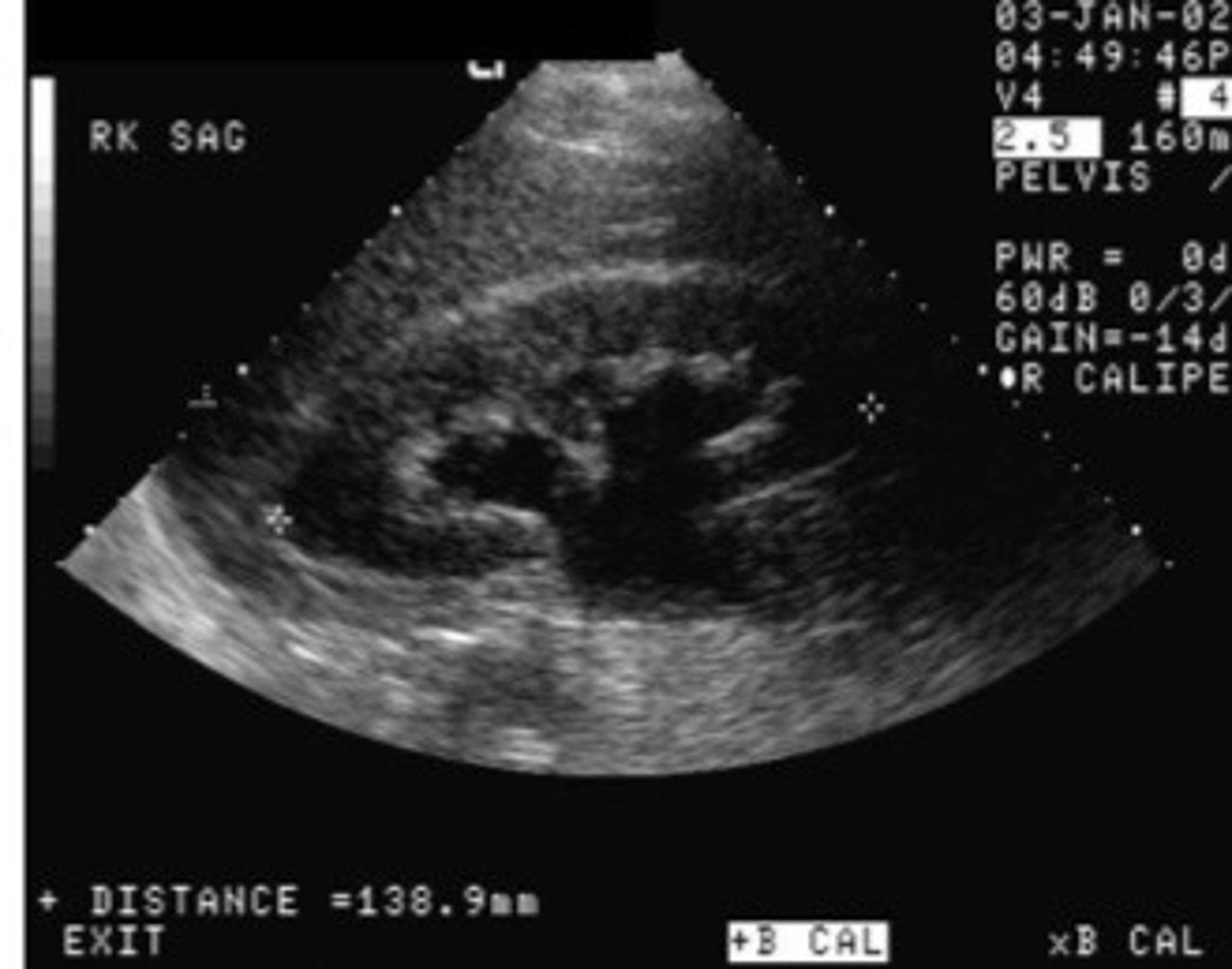
Cortical thinning, extensive enlargement of renal sinus and calyces, loss of individual calyx definition
Describe the appearance of grade 3 hydro
How collecting system is blown out and very dilated that it starts pushing on the cortex bc not enough room in the kidney
Why do we see cortical thinning with grade 3 hydro
Loss of the clubbed shape of the calyces, they start to loose their normal shape because so dilated
Describe the appearance of the calyces in grade 3 hydro
Grade 3 hydro
What does this image show
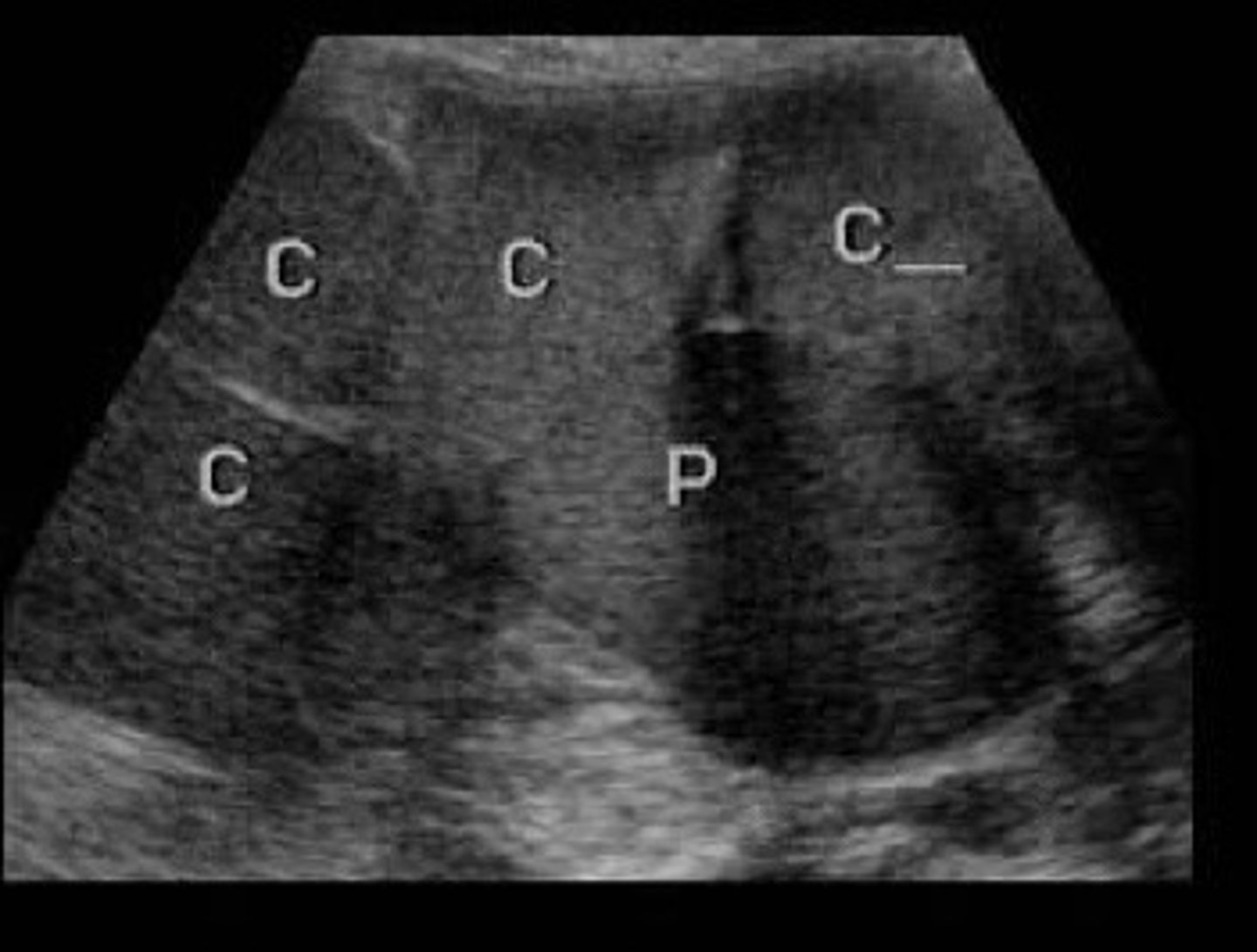
Grade 3 hydro
What does this image show
Look for dilated ureter, then locate lvl of obstruction/cause of hydro, then go to the bladder and look for jets
Describe the next three steps you should take when you find hydronephrosis
Over distended bladder, extra-renal pelvis, multiple parapelvic cysts, AV malformation
What are some false positives for hydronephrosis