Ecology: Desert and Grassland
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
xerocoles
animals that can live in deserts
erg
sand dune region
largest desert in the world
antarctica - 5.5M square miles
also largest cold desert
5.4M arctic then sahara
xerophytes
desert plants
map of deserts
plus antarctica and arctic
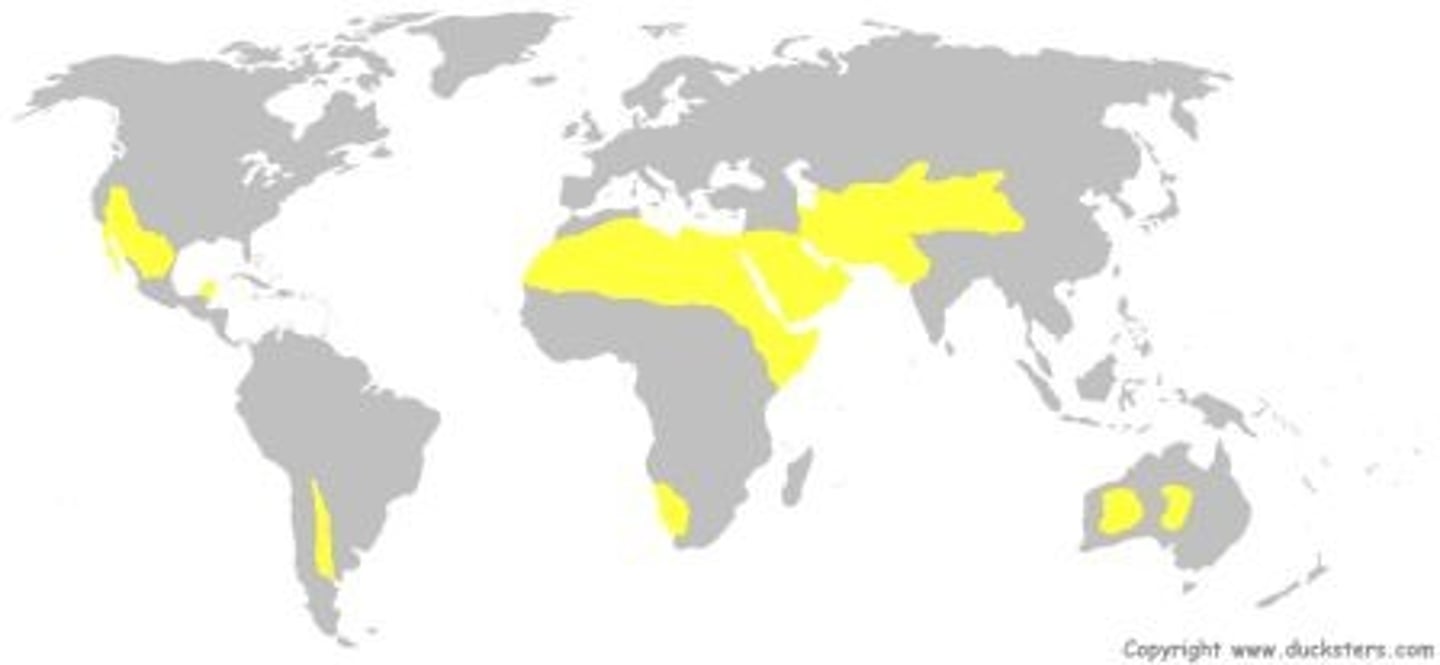
area of earth w/ desert
1/3 of earth (30-33%) including polar
20% is true desert, the 33% is climactic 10in rain defn
hottest temp ever
54C in death valley and also in kuwait
desert defn
less than 10in (25cm) of rain per year
xerophyte adaptations
annuals: short lived during rains, winter annual
succulents: store water in stem so no transpiration, thick waxy cuticle resist water loss, CAM, recessed stomata;
deep roots to tap groundwater or shallow to get as much rain as possible
where do grasslands form
in areas where too little precip for forest but too much for true desert
aridity index
A = P/PET = average annual precip/potential evapotranspiration
<0.05 = hyperarid
0.05-0.20 = arid
0.20-0.50 = semiarid
generalizations about grassland plant species
grasses of multiple species and genera but mostly dominated by a few species
most with rhizomes (underground spreading stems that send up shoots and nodes and store starches up to 1/2 of biomass); wind pollination
perennial bunchgrasses don't have rhizomes and come back from base (not spreading)
will grow back after fire, grazing, wind, extreme temp
temperatures in grasslands
huge range from seasons often deep into the negs in winter (more to north), 110 to -20
grassland precipitation
24-40in
steppes often include semiarid lands 10-24in
whole range is 6-40in (generally)
grassland precipitation season
scattered thunderstorms (convective storms) in summer but most rain/snow in winter and cooler times
grassland soils
mollisols (basic, hummus rich, dark, productive, Ca/Mg)
mollisols are most common soil type in US (21.5%) and 7% of ice free land worldwide
found in W great plains and scattered rest of west
grassland growing season
typically 120-200 days
grasslands topography
flat, some rolling hills, steep canyons
grasslands fire
frequent due to summer thunderstorms
necessary to maintain ecosystem and keep back trees and shrubs, grasses have survival mechs
grasslands fauna
grazing animals like deer, elk, bison in large herds
songbirds and small burrowing mammals very common
Grassland animal adaptations
fast, colony burrowers, jumping, strong flying birds, camoflage, good vision,
tallgrass prairie
usually around 1-3m, deep roots, nearest eastern deciduous forests
precip around 25-40in, usually around 35in
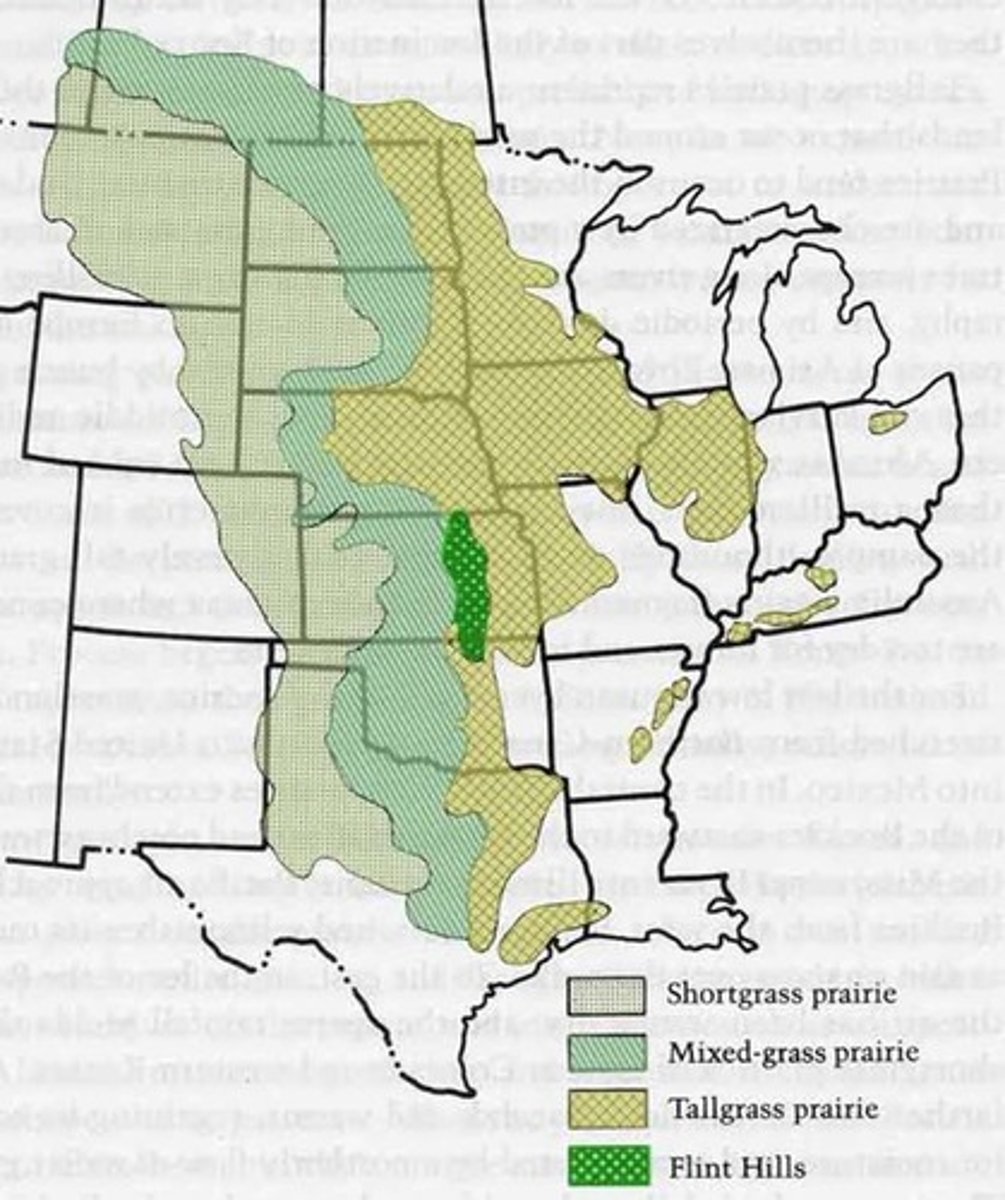
Tallgrass prairie problems
most plowed and planted w/ wheat/corn; increased drainage and runoff reduces moister areas
Tallgrass prairie plants
Big bluestem (image), sand bluestem, indian grass, slough grass, switchgrass

mixed grass prairie
usually under 0.5-1.3m in height; usually around 3ft
precip around 14-25(35-65cm)
mixed with taller grasses growing in slightly wetter areas and shorter ones in drier areas
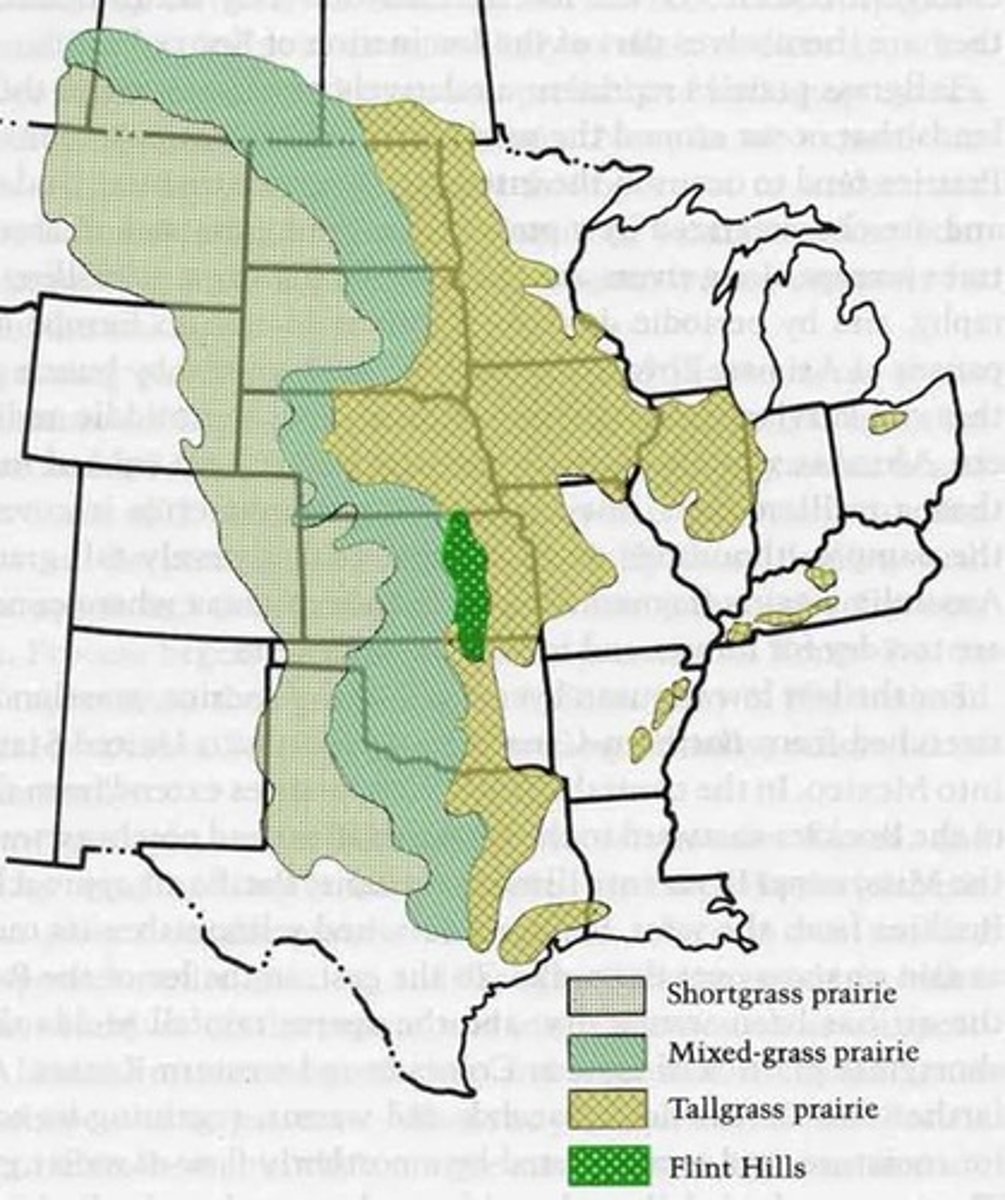
mixed grass prairie species
little bluestem grass, june grass, needle grass, dropseed grass, wheatgrass, wild rye
mixed grass prairie problems
almost entirely planted over with crops such as corn and soybean
shortgrass prairie
nearest to western deserts, cover most area of the 3 groups in N america; mostly W of latitude 100W
most less than 20in high; fewer forbs because lower rain favor grasses; can't grow bigger bc no water
precip usually around 10-15in
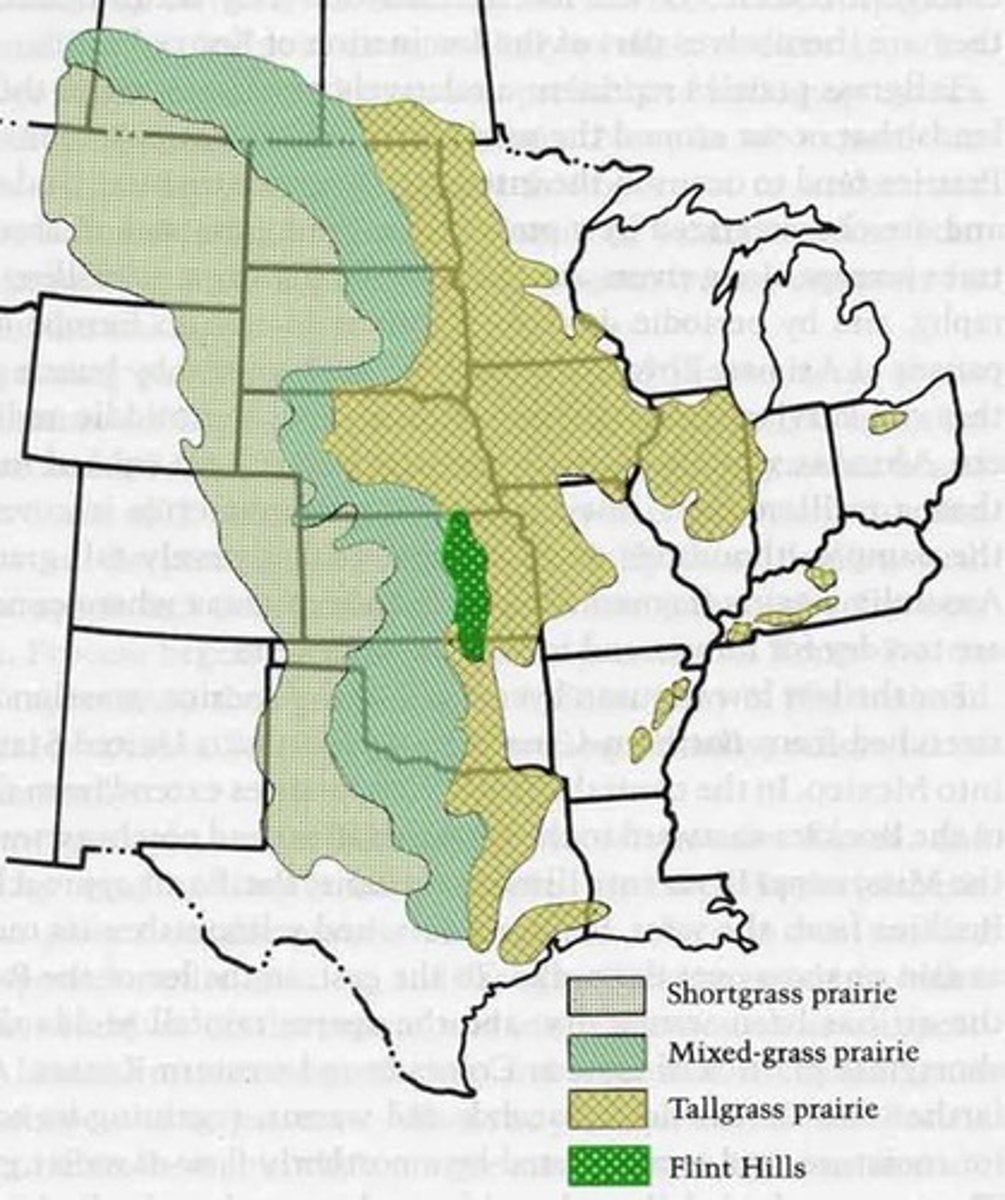
shortgrass prairie problems
some takeover for irrigated corn and crops; mostly just overgrazed for cattle, fenced from native grazers, invasives on ranges
shortgrass prairies species
buffalo grass, galleta grass, needle grass, grama grass, penn sedge

bunchgrass prairie
also called palouse prairie (near palouse river in WA)
found in plains N of great basin, colorado, UT, CA, WY, MT

bunchgrass prairie species
purple needlegrass, sagebrush, bluebunch wheatgrass
bunchgrass vs. typical plains grass
bunchgrass sends up new shoots from its base forming a clump
Most prairie grasses have mat-like roots that spread and produce new shoots spread out from one another
characteristics of grassland birds
lots of them (lots of songbirds)
strong fliers due to high winds, nest in tall grasses,
characteristics of small grassland mammals
many in colonies, many burrow, many hop for visibility
grassland history
during pleistocene/miocene (50-3.5MYA) mountains in N amer make grassland climate more favorable
after pleistocene ice ages, drier/warmer climate expand grasslands
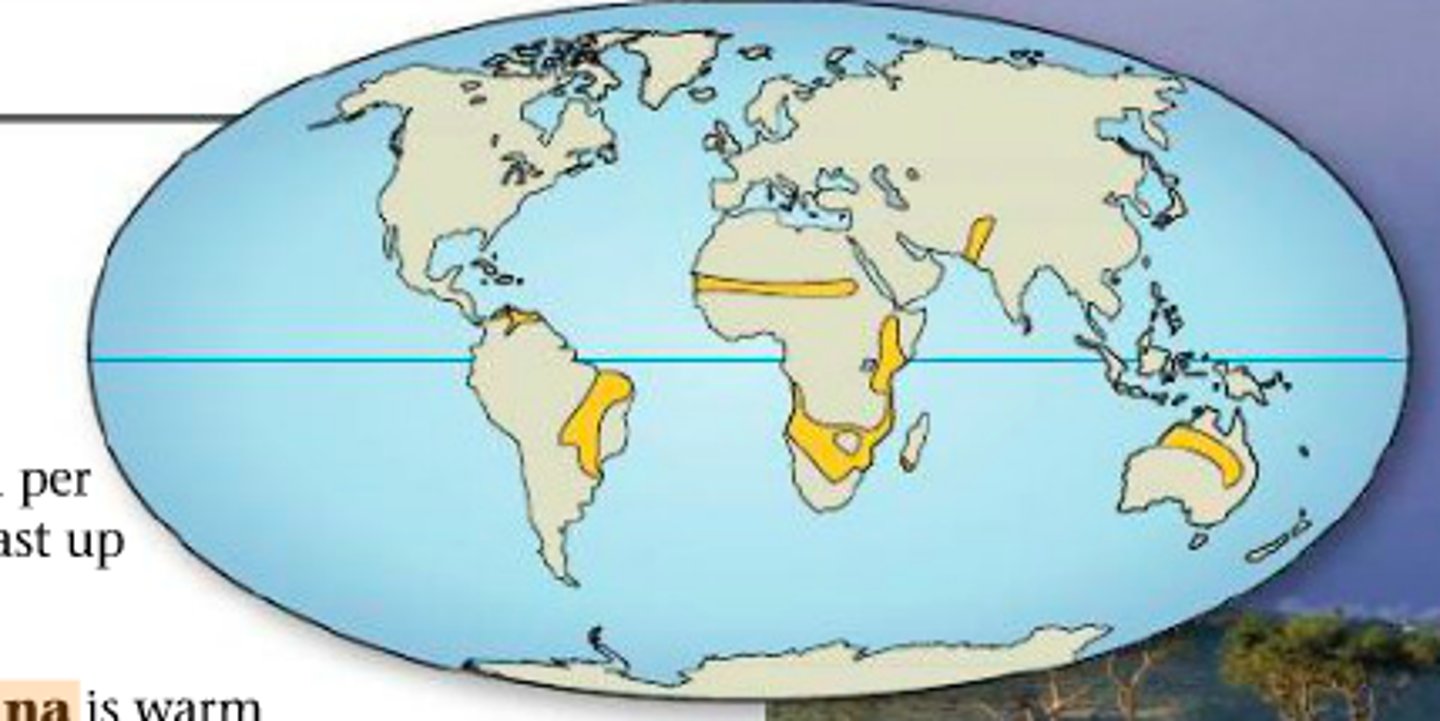
savanna
tropical grassland with few uniformly dispersed trees that aren't dense enough to form a closed canopy
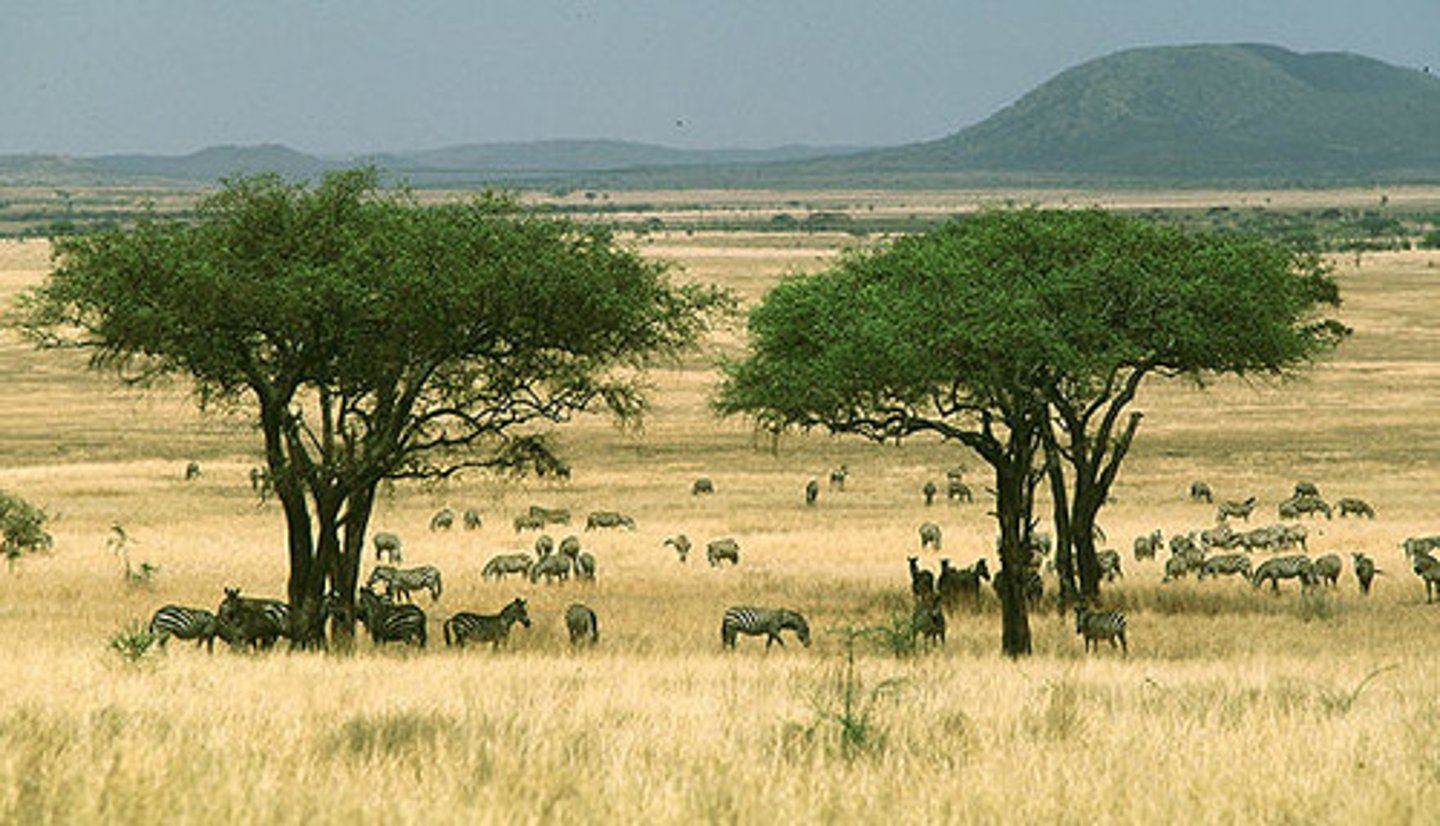

savanna reqs
20-50in of rain concentrated in 6-8 months followed by long hot drought where fires are common; average daily temp never drop below 64F
types of savanna
climactic savannas - classic all rain in one season and fire and drought maintain in rest of year
edaphic savannas - thin or clay soils that inhibit tropical forest growth
derrived savannas - human or elephant deforestation creates critical mass of grass to burn away tree sprouts
savanna plants
generally has a dominant grass or few grass/forb species and scattered deciduous trees
grasses: includes elephant grass which is like 10ft
trees: acacia, baobab, candelabra
savanna seasons
winter is dry starting October with strong winds, little rains, few lightning
summer is wet
neither season is very cold
savanna fires
during winter dry season
small animals in burrow, big out run, insects die, grades burn but roots ok
savanna problems
desertification, clearing for farming, poaching, overgrazing
savanna locations
brazillian horn highlands, venezualan campos, sahel (lot thicker than shown), E africa and S africa, parts of india and SE asia; N australia
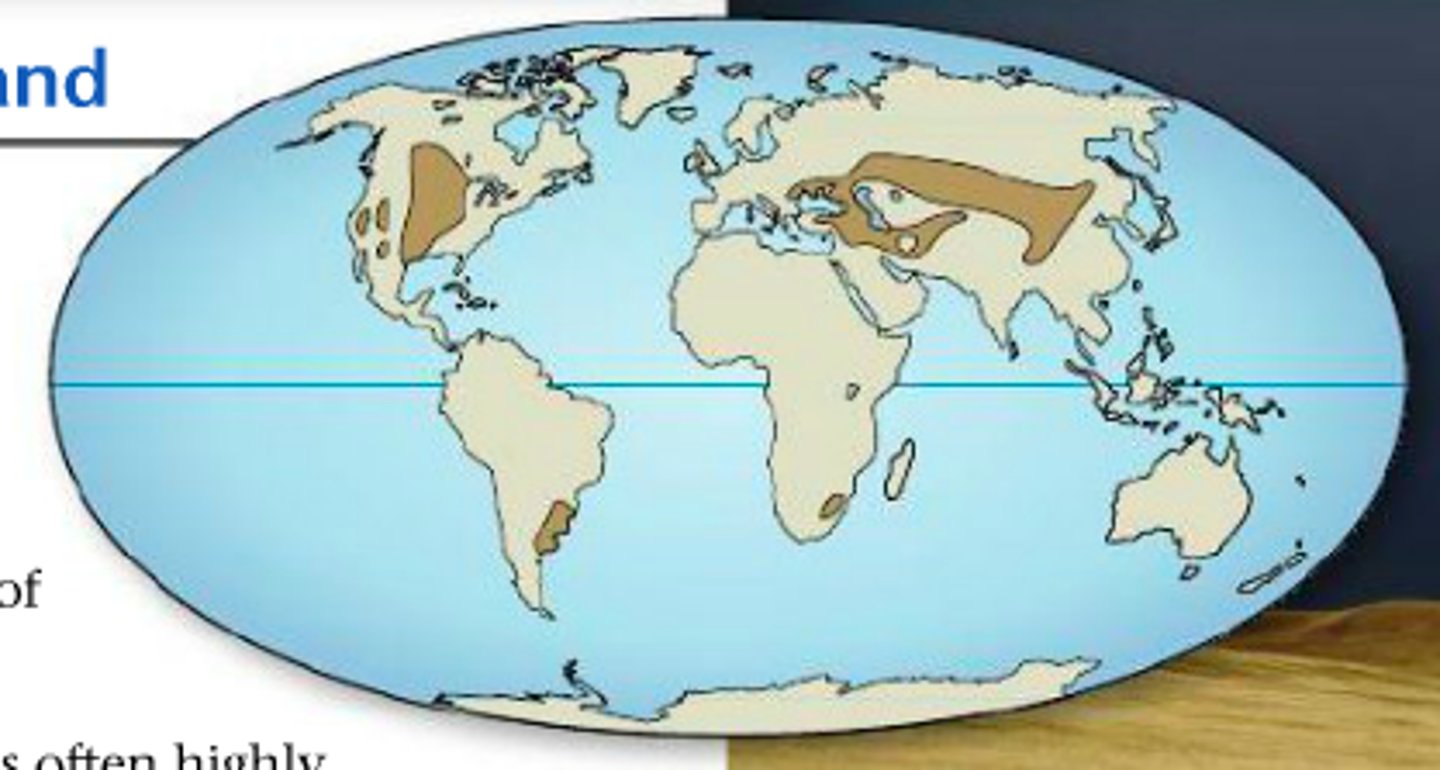
temperate grasslands definition
clearly defined hot summer and cold Winters
temperate grasslands distribution
plains of US, pampas in Argentina, eurasian steppes from ukraine through balkash, mongolia and manchuria area, turkey
rainfall in temperate grasslands
moderate: 20-35in per year (more rain is taller grass)
mostly late spring early Summer
temperate grasslands soil
mollisols dark and Rich
savanna soils
rich ish but often leached
temperate grasslands fire
there is some fire in the drought season in fall or summer, but not as much or as important as savannas
temperate grasslands seasons
very hot summer and cold winter
rains in late spring and early Summer and drought for the rest of the year
trees in temperate grasslands
some riparian but basically nonexistent in actual grass unlike savanna
steppe rain
10-20in in winter (30-50cm), can be as low as 6in
steppe problems
wheat and grazing destroying it, salinization from irrigation
desert fires
uncommon, most of the time there isn't enough vegetation
flash flooding mechs
earth is hard baked so all the water just runs off immediately after it falls
desert classification systems
common: hot/subtropical, cold, semiarid, coastal
cause based: trade wind, midlatitude, rainshadow, monsoon, polar, coastal
stupid-ass far-left soinc classification: hot, warm, cold
hot and dry desert
little rain but varies; mean temps 20-25C; often over 40C; can drop into -C
plants w/ thick cuticle and sometimes CAM; small animals (lizards mostly)
include major N amer deserts of chihuahua-sonoran, sahara, australia
semiarid desert
cooler (20-25 in summer, 10C at night, cooler winters); precip 10-20in (between desert and grasslands); sort of includes steppes and more vegetated areas
gravelly in hills with hardpan bottoms
plants are larger shrubs like creosote; brickelbrush; somewhat more animals (small mammals)
cent asia, great basin, montana, mojave in some parts
coastal deserts
cool (15-20C in summers) summers and moderate winters; very little precip, often years between
cold W coastal currents block rain
atacama and namib
very dry adapted animals and plants
cold/polar deserts
cold (below freezing winter, 20C in summer); higher precip (15-25cm) mostly as snow in winter; air too cold to hold moisture
antarctica/arctic
silty soil
trade wind desert
encompasses most hot and dry deserts
found closer to the equator at less than 30 latitudes
hottest and driest; ie: sahara
midlatitude deserts
encompasses some hot deserts and most semi-arid colder ones
found towards the poles from 30 latitude
bit cooler and wetter than trade wind deserts; ie: great basin, talkamakan, gobi
rainshadow deserts
water dumped on windward side of mountains leaving adiabatic heated dry air on leeward side
monsoon deserts
sort of suss; dry but get some rain from monsoon season, mostly fall under other classification and only really found on one site
Great basin gets some monsoon, thar, can prob ignore this term
paleodeserts
places that used to be deserts but aren't anymore
ie: sand hills nebraska
the sun and deserts
lack of moisture means 90% of solar radiation hits ground vs. 40% in humid/tropical
bajada
alluvial fans merge into a gradual slope from mountains in desert to base

different names for grasslands
pampas, prairies, meadows, steppes, savannas, veldt,
list savanna types
tropical, temperate, mediterranean, montane, flooded
montane grasslands
found high up like arctic tundra but not quite
like tibetan plateau, high andes and new guinea
tropical savanna
synonymous with typical savanna
temperate savanna
sketchy term to describe any temperate grassland with sparse trees and shrubs
mediterranean savanna
savannas in mediterranean climates with interspersed trees (med, socal)
ie: oak savannas
flooded grasslands
grasslands that are seasonally/permanently flooded
ie: rann of kutch, okavango
alpine grassland
found above the treeline or polar direction from treeline but not in permafrost
mostly tussock fescue grasses where temperature never tops 50F in summer
drops 6.5C for every thousand feet up of 3 degrees?
successional grasslands
grasslands maintained by fire and grazing and disturbances that would otherwise be taken over by trees and shrubs
temperate vs. savanna
mostly by distance from equator (savanna usually between tropic of capricorn and cancer)
savannas have trees and shrubs while temperate typically little to none
climate: rains and temps
prairie
name given to US grasslands
california grasslands
used to be sagebrush steppes in owens valley and NE and stipa pulchra (purple needlegrass) bunchgrasslands through central and Socal
bunchgrasses disappeared
steppe
treeless, colder, semiarid grasslands

steppe climate
dry (10-20in); drought common summer-autumn; precipitation distributed with rain in summer and some snow in winter but dries out fast in summer rains
cold winters below freezing for 5 months; moderate summers up to around 70's (F)
steppe plants
treeless entirely; feather grasses dominant; feathery flowers, mostly stipa, avena
grasses die back in august and don't revive until spring; most plants less than <0.5m
laterite
hard soil that is clay-like and have iron and aluminum oxides; tropical soil type, low in nutrients and common in savanna
grasslands storms
strong and often short, water evaporates
gullies
large canyons from rills; form in grasslands bc grass usually break force of rain but when gone, erosion rapid into rills then gullies
climate vs. weather
weather is one day; climate is long term patterns
maritime vs continental climates
maritime more stabilized (less seasonal temp variation) and higher rainfall
continental more extreme variation and lower rainfall
intertropical convergence zone
zone around equator where hadley cells meet forcing moist air up and dumping rain
moves around by season (further N in summer)
dust bowl
1931; OK, KA, TX, CO; blow off topsoil in dark clouds across continent; drought caused and fallow fields and dryness mean easy blow away
monsoons
migration of intertropical convergence zone towards poles during their respective summers; cooler air in summers over oceans blows in as land heats into less dense hot air
vast majority of rain falls in summer season with little in winter bc reverses (called anticyclone) where cool air blows out from interior
relative humidity
humidity in air as percent of saturation for that temp
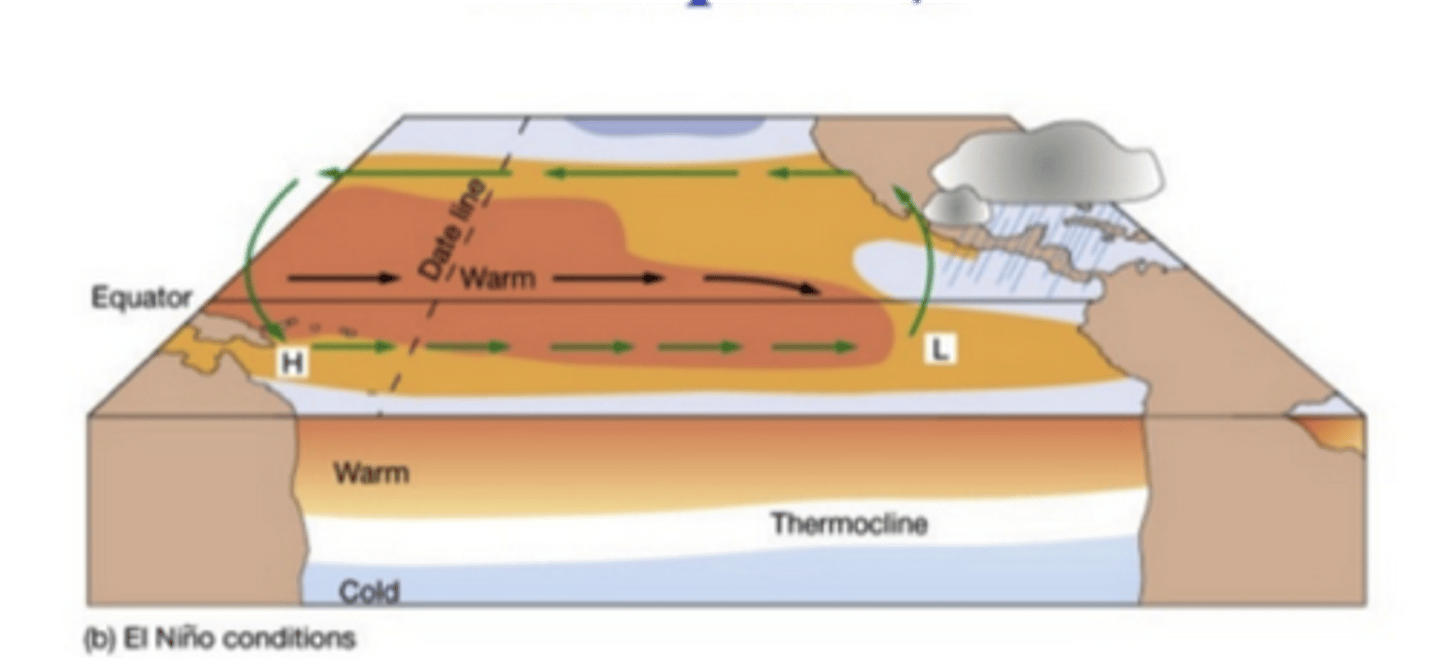
ENSO
el nino southern oscillation
heating of water off peru-chile deepening thermocline; hot air rises drawing in air and rain from E pacific
last glacial period
wisconsinian up until 1mya; interglacial period after is holocene; grasses expand after
sahara
largest non-cold desert; 3.5M square miles
large, some sandy, hot and dry, next to no rain, red sea to atlantic
US deserts
mojave: rainshadow coastal and sierra
colorado: small; around salton sink
sonoran: colorado delta through phoenix and south into mexico
painted: E of little colorado/colorado jnct in NE AZ
chihuahua: little bit into NM but mostly mex
wetting front
rain in deserts leaches down calcium carbonate down to a hardpan layer where it builds up
hardpan
layer of hard material just below surface preventing good drainage

what is sand
bits of silicon dioxide (weathered quartz); erosion resistant
loess
wind blown silt that builds into fertile formations; usually blown from deserts