Lesson 11
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Simple Random Sampling (SRS)
A simple random sample (SRS) of size n consists of n individuals from the population chosen in such a way that every set of n individuals has equal chance of being selected
Sampling Frame
In order to perform random sampling we need a record of the entire population. The sampling frame is the list of individuals in the population from which a sample is drawn.
Might not necessarily be the same as population
Example: Want to sample businesses in Toronto and use Yellow Pages as sampling frame; but not all businesses are necessarily listed!
Try to use sampling frame that is as close as possible to population of interest
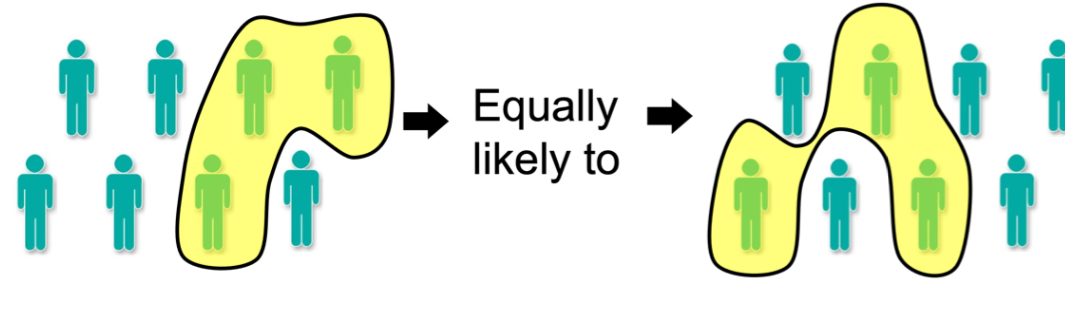
Stratified Sampling
Sometimes population is divided into groups of similar individuals, called strata
Example: Student population w/ 40% males and 60% females
With SRS you could end up with all female sample
Could be a problem, especially if strata are very different from each other (in terms of parameter)
To ensure more representative sample, use Stratified random sampling
Stratified Random Sampling: Select separate SRS’s within each stratum (w/ separate sample sizes relative to stratum sizes), and combine them to get stratified sample
▶ Example: Total size n = 5
▶ Males: n ×0.4 = 2
▶ Females: n ×0.6 = 3
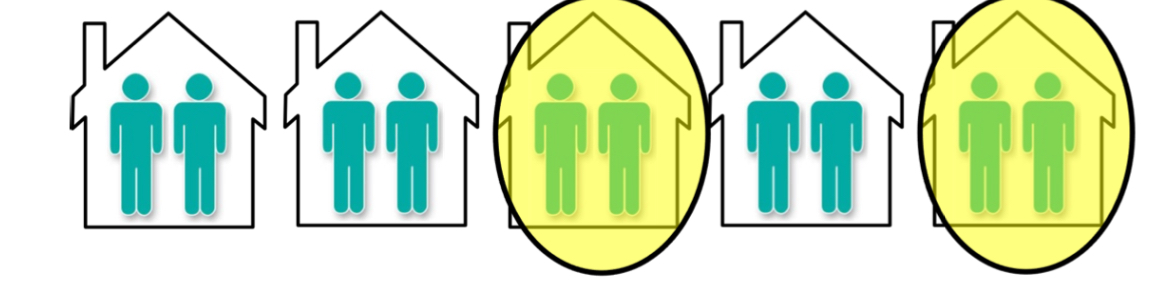
Cluster Sampling
SRS can sometimes be impractical
Example: SRS of n Torontonians −→might have to visit n different households
If population is divided in clusters, by geography or other boundaries, it is easier to perform SRS of clusters, i.e. cluster sampling
Example: SRS of Toronto households (clusters)
Multistage Sampling
Population might be divided into a hierarchy of clusters
Example: Province > City > Neighborhood > Household
Multistage sampling: use SRS within each stage of hierarchy to collect sample
Note: Cluster/Multistage sampling is mainly used for convenience, unlike stratified sampling which is used for improving accuracy
Systematic Sample
Individuals in population are often ordered
Example: Students in alphabetical list, customers exiting store, etc
If order is not associated with response, can use systematic sampling: sample every i-th individual, starting at random
Example: Sample every 5th customer
What Can Go Wrong?
Mistake 1: Sample Volunteers
The resulting voluntary response bias invalidates the survey. More likely to leave store review if you didn’t like the service provided.
Mistake 2: Sample Conveniently
In convenience sampling we simply include the individuals who are convenient for us to sample.
Unfortunately, this group may not be representative of the population.
Mistake 3: Use a Bad Sampling Frame
An SRS from an incomplete sampling frame introduces bias
Mistake 4: Undercoverage
In many survey designs, some portion of the population is not sampled at all or has a smaller representation in the sample than it has in the population.
Non response bias
a significant portion of those who are selected for the sample do not respond to the survey or study.
People who do not respond to a survey or study differ in important ways from those who do.
Imagine a survey sent to 1,000 university students asking about mental health:
Only 400 students respond.
Most responses come from students already engaged with mental health services.
If students not struggling or those too busy to respond are underrepresented, the results may overestimate the prevalence of mental health issues.
response bias
favoring certain answer in way question is asked
Make sure wording is neutral; use pilot (trial) study
Participants give inaccurate or untruthful answers, often in a systematic way that skews the data, usually to be more socially desirable
Difference between cluster and stratified sampling
In cluster sampling, the population is divided into groups (clusters), and then entire clusters are randomly selected for inclusion in the sample. In stratified sampling, the population is divided into subgroups (strata) based on shared characteristics, and then individuals are randomly sampled from each stratum