Determinants of Permeability (Stevens)
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SG5 (lecture)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Jv=LpS [(Pc - Pt)m- sigma (pic- pit)
Starling equation
Jv= transendothelial fluid flux
Lp = hydraulic permeability
S= surface area
P= hydrostatic pressure
Sigma= protein reflection coefficient (negative charge barrier or epithelium)
pi= colloid osmotic pressure
C= capillary
T= tissue
Increased permeability. What do you measure?
Lung weight - not easily done clinically
Lymph flow- not done clinically
Alveolar flooding- can be clinically done
How we can get increased permeability
Disruption of the barrier
Increased hydrostatic pressure difference (increased BP)
Decreased colloid pressure difference
When left atrial pressure exceeds ___ mmHg of pressure, the lung fluid increases. J point increase. Lung becomes edematous
25
With half normal protein, when left atrial pressure exceeds __ mmHg of pressure, the lung fluid increases. Lung becomes edematous.
10
Low protein ______ sensitivity to fluid accumulation
greater
On the evening before admission, the patient suddenly became dyspneic while seated. Later, while walking, he had moderate, dull, nonpleuritic substernal pain, which subsided five minutes after he sat down. That night he was orthopneic. In the morning he was brought to the hospital.
The temperature was 36.9°C, the pulse was 88, and the respirations were 26. The blood pressure was 130/90 mm Hg. The physical examination revealed a pale, obese man propped up in bed who had dyspnea while breathing oxygen at 5 liters per minute.
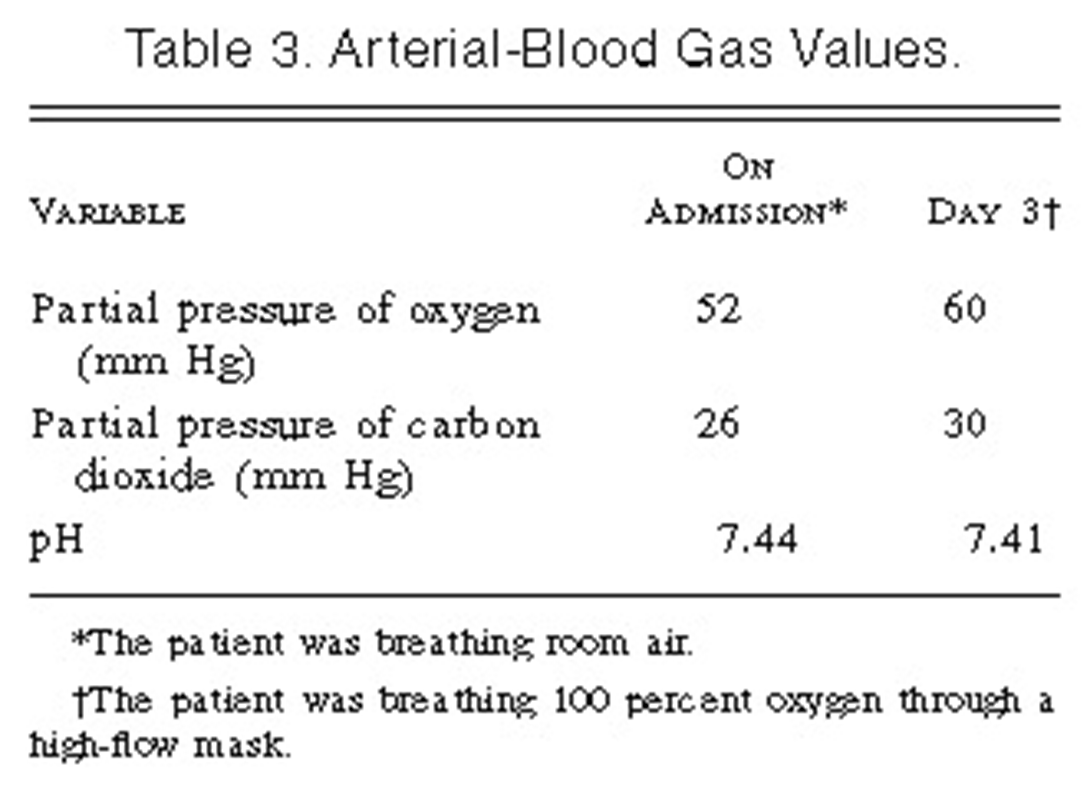
In this case, the most likely cause of increased permeability is:
A) Increased surface area (S)
B) Decreased capillary colloid osmotic pressure (pc)
C) Increased microvascular hydrostatic pressure (Pt)
D) Increased hydaulic permeabilty (Lp)
C
How can we disrupt the endothelial cell barrier?
Paracellular (most common)
Apoptosis/necrosis
Trancellular
Paracellular endothelial cell disruption
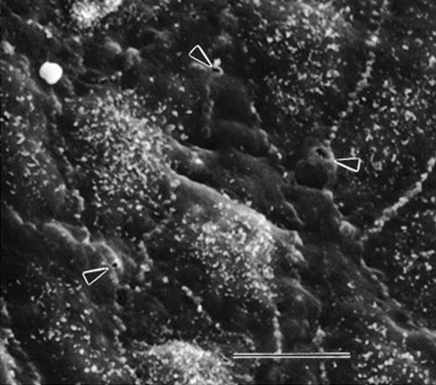
Normal
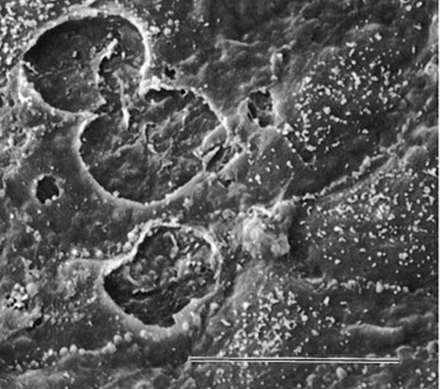
Disrupted
Junctions of the cell pull apart secondary to inflammation proteins and fluids can flow through
Most common way
Apoptosis/necrosis endothelial cell disruption
Common finding in acute lung injury
Transcellular endothelial cell disruption
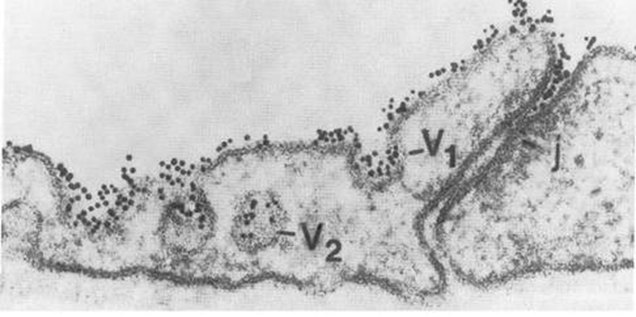
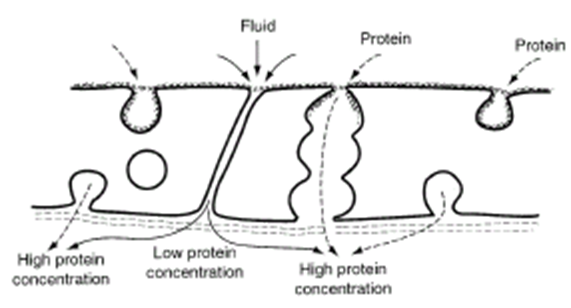
Endothelium very active
Overlying junctions proteins are caught
However, endocytic vesicles can move them (caveolae)
Albumin in interstitial is normal finding but lower than the plasma
Inflammation increases endothelial transport of albumin
______ in interstitial is normal finding but lower than the plasma
Albumin
Elevated pulmonary venous pressure due to:
Increase LV end diastolic pressure
Increased LA pressure
Increases in hydrostatic pressure causes
Elevated pulmonary venous pressure
High flows
High blood volumes
Only __% of the lung capillaries are perfused at any time.
20
In response to increased CO, you recruit more circulation in the lungs, recruiting more surface area . If flows get too high, you will increase _______
permeability
If the blood volumes go up, you recruit more capillary surface area, drives fluid out of the vasculature
This one does not make sense to me.
More fluid moves out when more ____ is recruited because of the higher capillary pressure. It is just because there are more capillaries actually engaged.
SA
_______ lymphatic clearance can also increase permeability
Decreased
A 22-year-old woman whose blood culture was positive for Streptococcus pneumoniae, causing pneumonia complicated by septic shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Diffuse alveolar infiltrates appear patchy and bilateral with air bronchograms
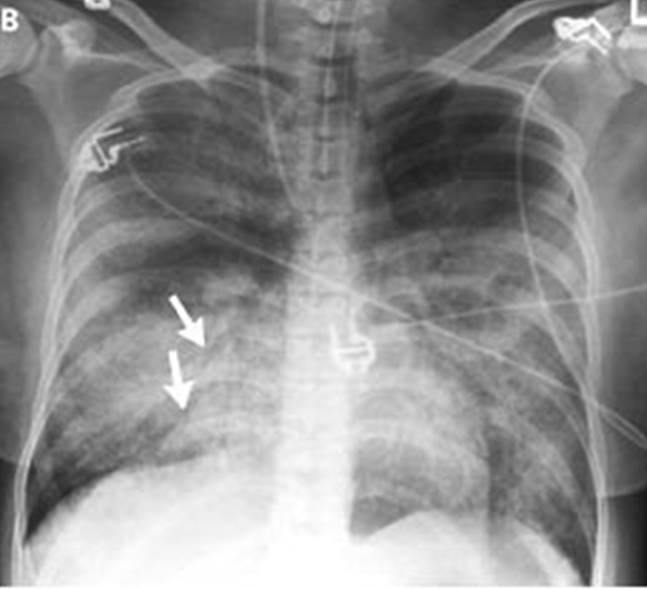
alveolar flooding leads to arterial hypoxemia and may be associated with cough and expectoration of frothy edema fluid
what is the most likely cause of increased permeability?
A) Increased surface area (S)
B) Decreased capillary colloid osmotic pressure (pc)
C) Increased microvascular hydrostatic pressure (Pt)
D) Increased hydaulic permeabilty (Lp)
D
A 51-year-old man who presented with acute anterior myocardial infarction and acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Note the enlargement of the peribronchovascular spaces (arrowheads) and the prominent septal lines (Kerley's B lines) (arrows) as well as acinar areas of increased opacity that coalesce into frank consolidations.
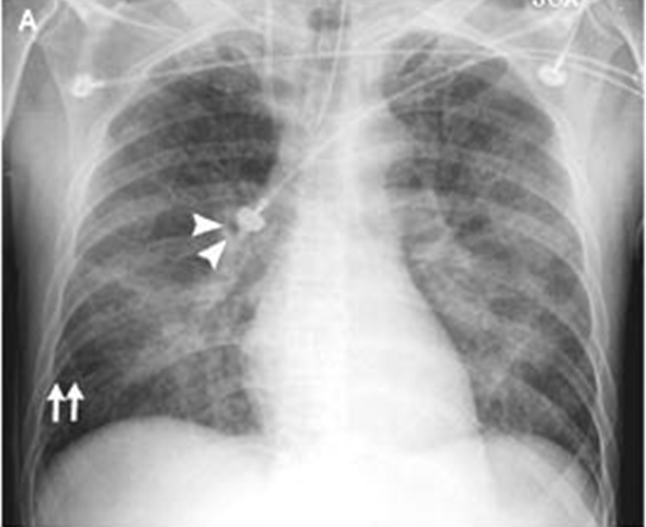
interstitial edema causes dyspnea and tachypnea
what is the most likely cause of increased permeability?
A) Increased surface area (S)
B) Decreased capillary colloid osmotic pressure (pc)
C) Increased microvascular hydrostatic pressure (Pt)
D) Increased hydaulic permeabilty (Lp)
C
alveolar flooding leads to arterial hypoxemia and may be associated with cough and expectoration of frothy edema fluid
Why?
Fluid in the airways prevents efficient gas exchange
interstitial edema causes dyspnea and tachypnea
Why? Activation of J receptors in the interstitial space.
Activation of J receptors in the interstitial space.
What is the gold standard for determining the cause of pulmonary edema?
A) Pulmonary artery catheterization
B) Chest x-ray
C) Doppler imaging of the mitral valve annulus
D) Transesophageal echocardiography
E) Transthoracic echocardiography
A
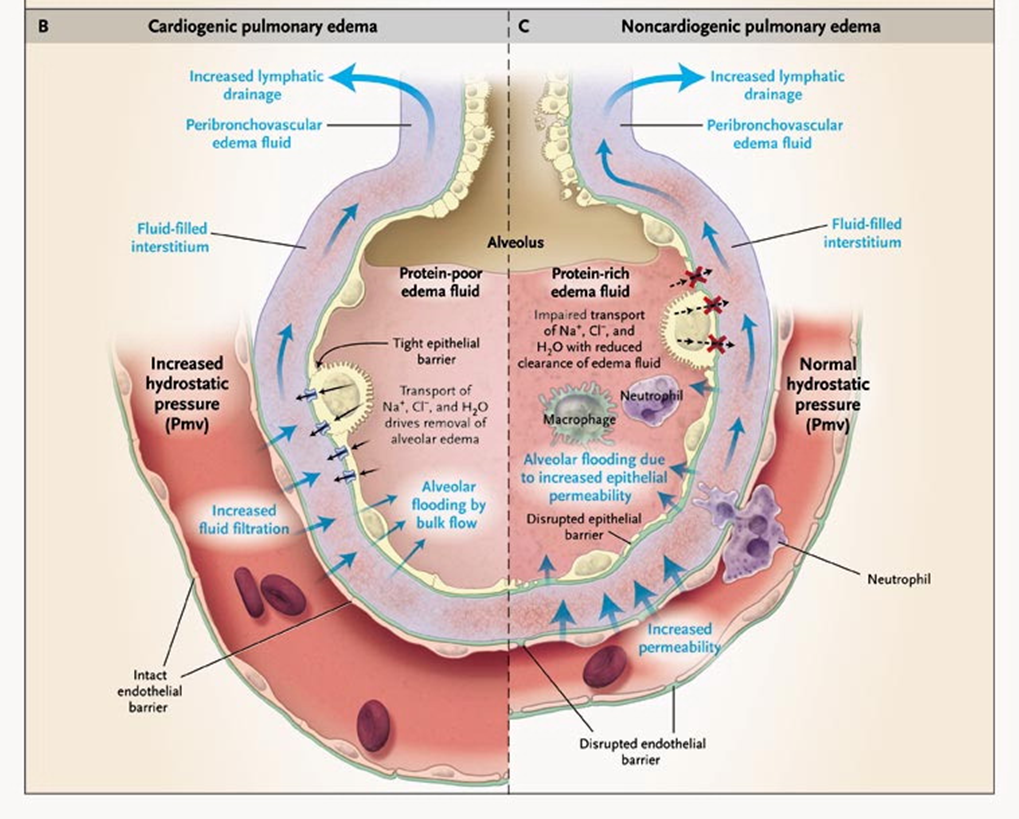
Cardiogenic vs non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Fluid filtered from capillaries to interstitial space is drawn by _______ interstitial pressure through the interstitial highway into the broncho vascular cuff where edema fluid can accumulate and gain access to lymphatics for clearance back out of lymphatics into general circulation
negative
Left Increased LA pressure increases pressure in capillaries hydrostatic- no disruption of endothelial level. Pressure is driving fluid out, protein poor, transudate.
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Could be secondary to infection
endothelial junction disrupted
Des not require increase in BP to drive fluid out
High protein exudate
Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Lung lymph flow is measured under different conditions. Closed symbols represent experimental subjects, and open symbols represent control subjects. Each line is indicative of lung lymph flow in a single subject. Which of the following would best explain the lymph response depicted by the attached graph?
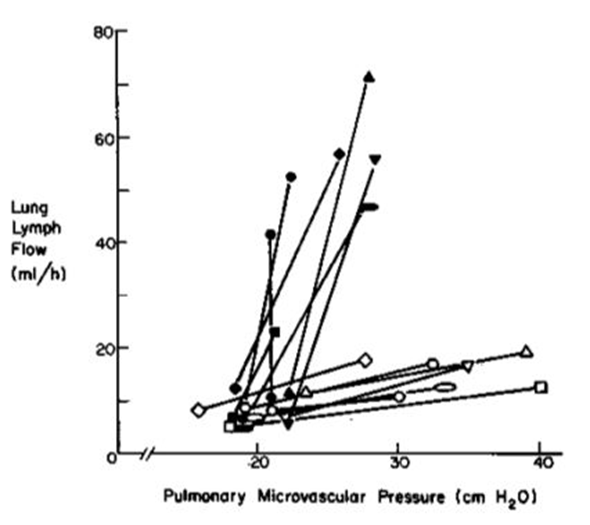
A. The individuals represented by closed symbols are infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa
B. The individuals represented by closed symbols have suffered a myocardial infarction
C. The individuals represented by closed symbols have hyperalbuminemia (an increase in serum albumin)
D. The individuals represented by the closed symbols have volume overload
E. The individuals represented by the closed symbols have pulmonary arterial hypertension
A
Histamine infusion resulted in an increase in lung lymph flow (see attached figure), but it did not change cardiac output. Based upon information provided in the accompanying figure, which of the following most likely accounts for the histamine-induced increase in lung lymph flow?
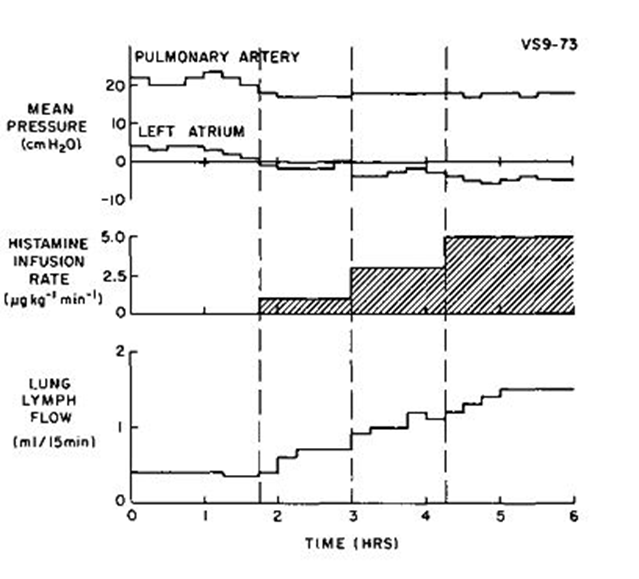
A. An increase in left ventricular end diastolic pressure
B. An increase in alveolar flooding
C. An increase in pulmonary arterial vascular resistance
D. A decrease in the reflection coefficient of albumin (σ)
E. A decrease in pulmonary blood volume
D
Histamine increases capillary permeability to both fluid and protein.