Welding A
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
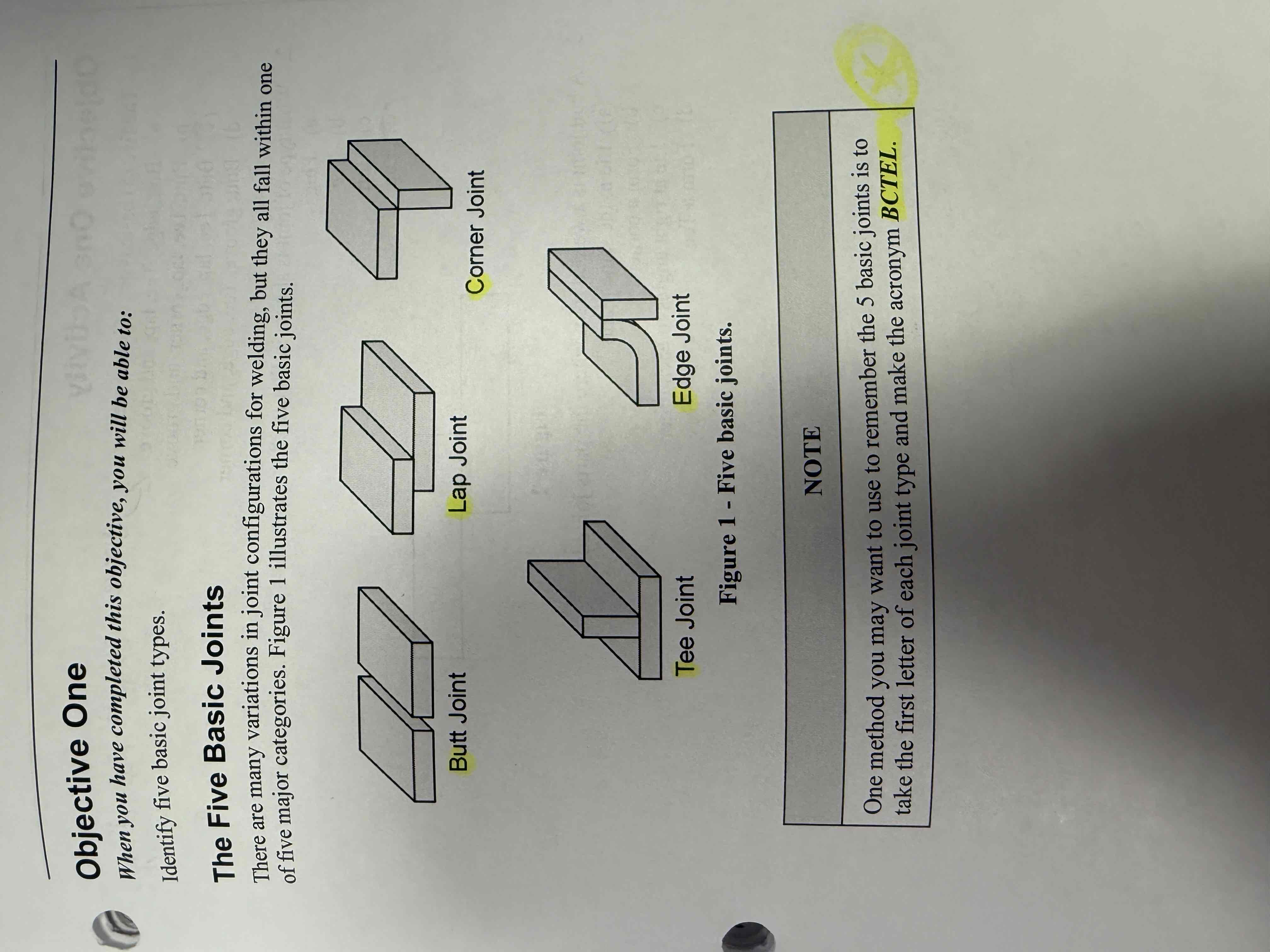
List the 5 basic joint types and application
Butt joint
used extensively in welding industry
Gives maximum strength of joint (full strength weld)
Used when joint is subject to high stress, cyclic, changing loads, critical applications.
Corner joint
Widely used on sheet metal fab
Can be flush corner, half open corner, open corner
Tee joint
often joined via fillet welds
Edge joint
Used extensively to join light gauge sheet metal fabs
Less danger of burn through and reduce distortion
Limitation is that it cannot withstand heavy or dynamic loads
Often welded autogenously (without filler metals)
Lap joint
fillet welds
Highly successful of joining materials of different thicknesses
No special prep
Can be single or double welded
(BCTEL)
What are the 4 weld types
Surfacing weld
beads over a surface
Usually to economically reclaim a metal surface or to return original equipment thickness
2 step: 1. Layer softer and less expensive metal to get thickness required, 2. Layer of hard surface metal over first layer for durability
Plug or slot weld
Drill or flame cut a hole or slot in the plate
common on lap joints
Difference between plug or slot is the shape of the hole in the metal
Fillet weld
Used extensively because no prep needed, but do not produce the highest possible weld strength
found on lap, tee, corner joints
One or more layers of weld metal
Shape of triangle
Groove weld
common on butt joints
Several variations (square groove, bevel groove, vee groove, U groove, J groove)
Fillet weld anatomy image (see answer)

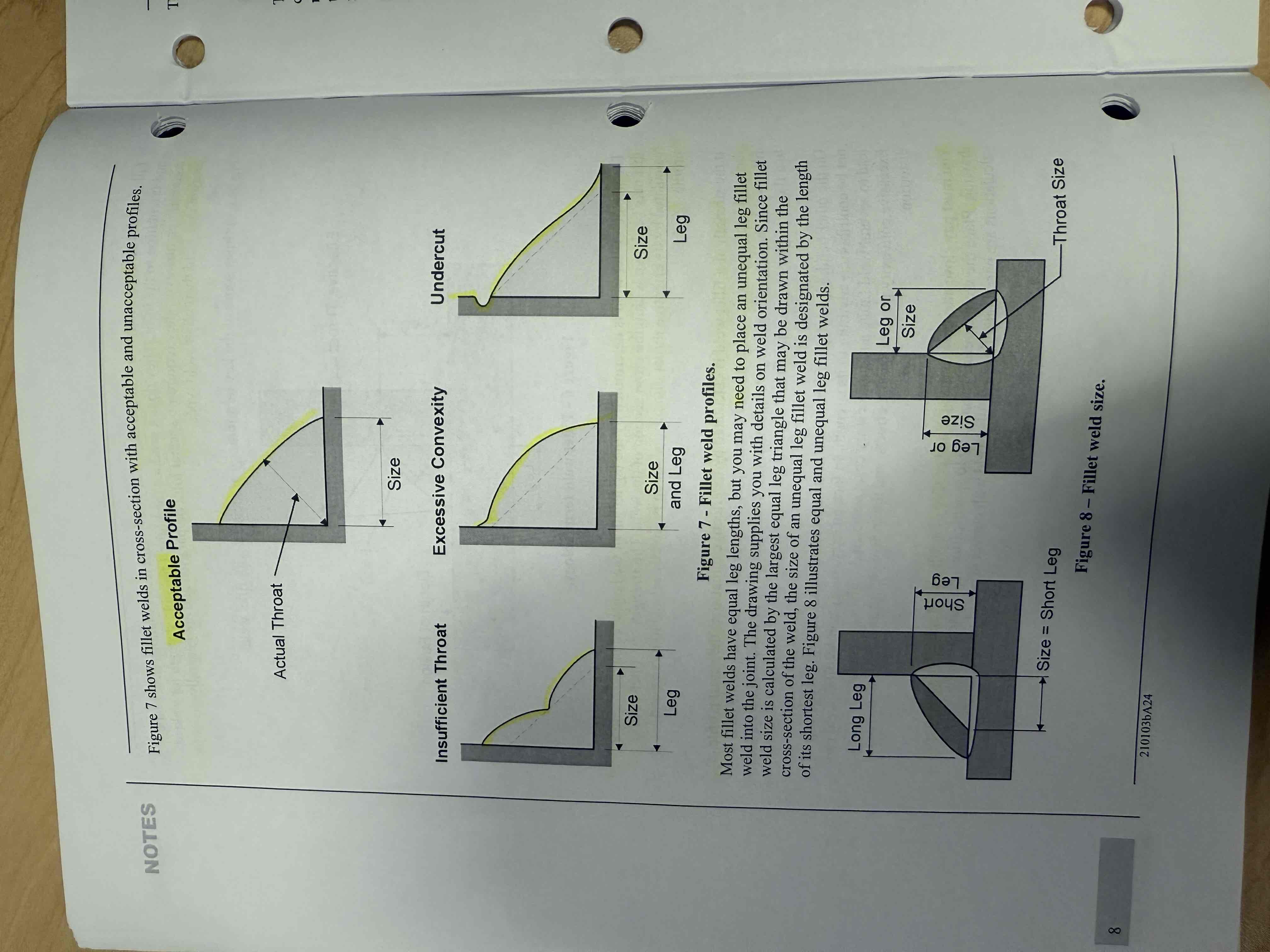
How is the size and strength of a fillet weld determined?
Strength: calculated by “effective throat dimension” which is based off the size and profile of it.
Size: determined by leg length of largest “equal leg triangle” Both legs of the triangle need to be equal for the weld to mean something. You can do this by “stacking welds”
Undercut vs excessive convexity vs insufficient throat image
What are the 4 basic variations of a fillet weld?
Continuous
Intermittent
Chain intermittent
Staggered intermittent
based on strength, joint economy, control of distortion/stress
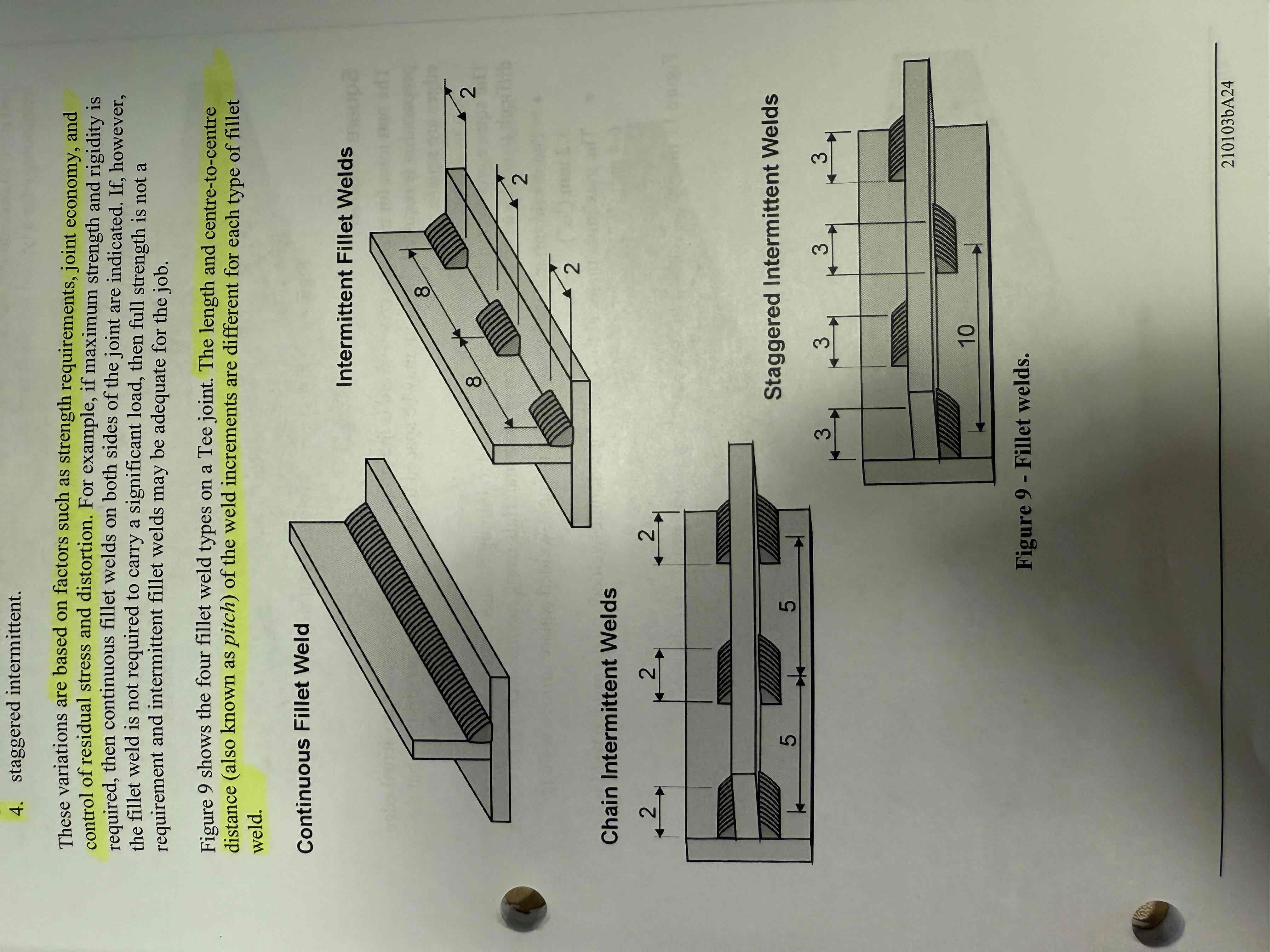
What is the length and centre to centre distanced of weld increments called (when fillet welding)
Pitch
Anatomy of a groove weld image
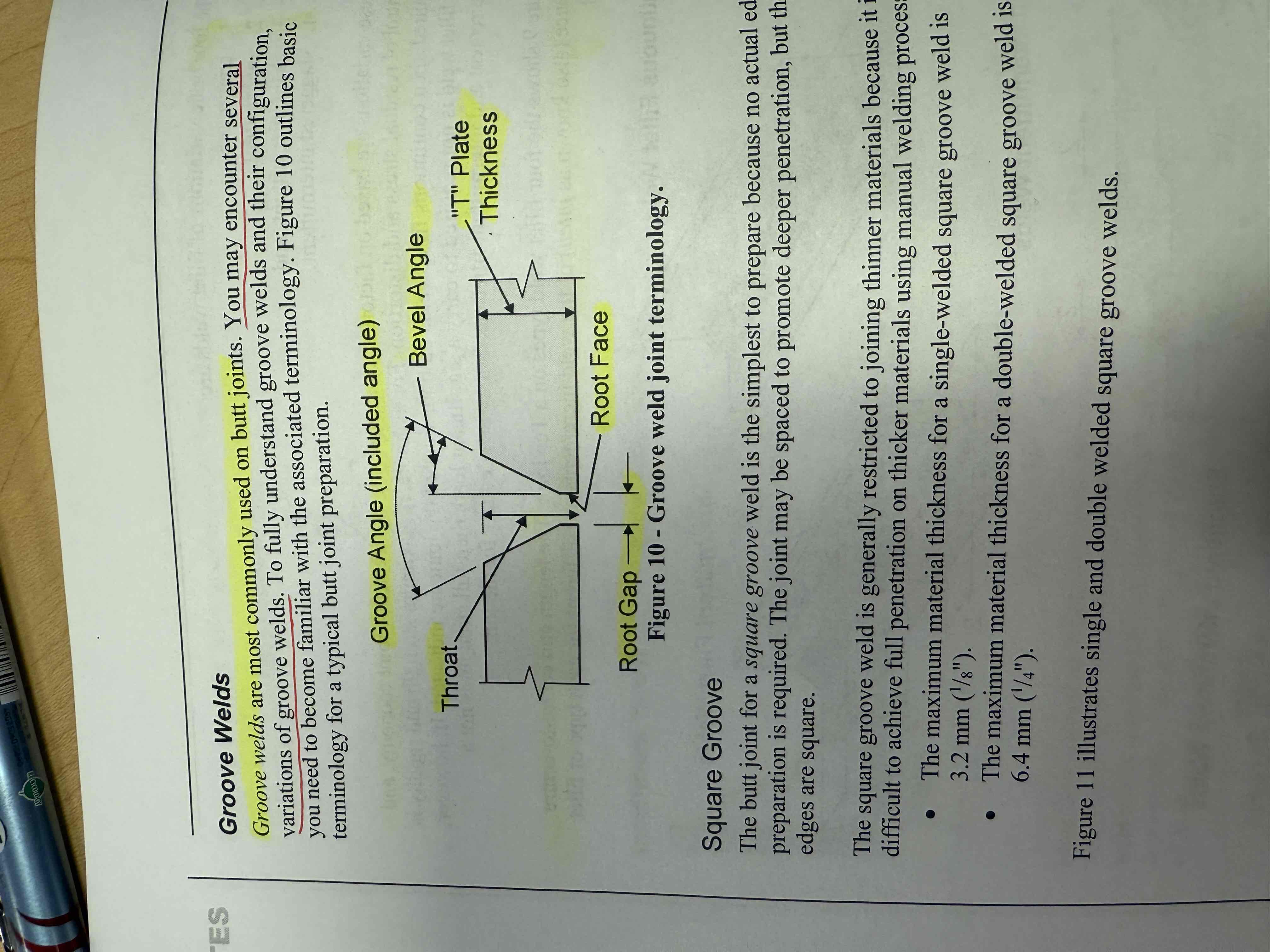
What are the 5 variations if groove welds and applications?
Square groove
simple to prepare as there is no edge prep
Thin material only (difficult to achieve full penetration)
single welded square groove max material thickness (1/8”)
Double welded square groove max material thickness (1/4”)
Bevel groove
only one side is beveled and the other is square
When you have access to only one member of the joint.
Less prep and welding time
You must ensure complete fusion.
Can be single or double bevel
Vee Groove
3/8 to 1” thickness range
Easy to prepare and good accessibility for full penetration
Double vee used if thicker material and access to both sides- minimizes distortion by equalizing shrinking forces
U groove
similar to vee groove but smaller included angle (less filler than a Vee groove)
J Groove
used if access to only one member of joint in horizontal position
J groove is better than bevel as it gives better welding access for better penetration at bottom of joint
Usually expensive prep. Generally used on thicker material
Which vee groove welds uses less material? Single or double?
Double Vee Groove weld uses less weld metal than a single.
Vee Groove vs U Groove weld?
U groove is smaller included angle which uses less filler metal than a Vee groove. BUT a U groove takes longer to prepare.
It is generally cheaper to prepare Vee groove but it uses more filler metal compared to a U groove. Ensure you factor in prep time and material costs.
What is a backup strip in a butt joint?
Used where welding can take place from one side only. Or where root opening is too wide to join easily across open gap.
What does CSA and ASME stand for?
Canadian Standards Association
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
What is the CSA and ASME designation for joint types and positions?
Number denotes position, letter denotes weld type.
Ex: 1GF: G groove weld, F is fillet weld, R at the end stands for rotating.
1: flat or pipe
2: horizontal
3: vertical
4: overheat
5: pipe fixed horizontal plane
6: pipe fixed 45 deg plane

Weld design considerations (7)
Joint using least amount of filler metal with complete penetration.
Joint config must be suitable for thickness of material
Different thicknesses - size weld by thinnest material to avoid over welding
Joint accessibility for welding
Welded flat if possible
Consider joint prep needed
Consider Double joint if accessible from both sides.
Define Tensile strength and how it’s calculated.
How much pull a material stands without fracture.
Tested by pulling material apart with machine
Divide the load by cross sectional area of test specimen:
If it takes 15,000 lbs to break a ½ by ½ “ square →
15,000 / 0.25inch area= 60,000
Define Yield Strength and how it is tested.
Stress point at which permanent deformation takes place. Tested with a tensile strength machine.
Define ductility and how it is tested?
Ability of a material to stretch or deform under load without breaking.
Tested during tensile or a bend test and expressed in % elongation. (If it is 2” and breaks after stretching to 2 1/2”, it is at 25% elongation).
Define Elasticity
Ability of metal to return to original shape and dimension once load is removed.
Define Malleability
Metal ability to be cold worked without alot of resistance.
Define Impact Strength. How is it tested?
Ability of a metal to withstand sharp, fast blows.
2 Ways to test - Izod and Charpy tests
Both use a weighted swinging pendulum to break specimen.
Define Toughness. How can it be increased?
Ability of a metal to withstand a rapidly applied load and deform without breaking. Ability to absorb energy without fracturing.
Tempering usually reduces hardness to promote toughness
Define Hardess, how can the max hardness be pre-determined, how is it tested?
-Hardness: ability to resist penetration or indentation (scratching and abrasion)
-Max hardness can be pre-determined by the carbon content in the metal
-2 ways of testing is the Rockwell or the Brinell tests.
What 2 types of loading can a weld be subjected to?
Dynamic- vibration, movement, shock
Static - storage, supports
What are the 5 characteristics of most metals?
Solid at room temp
Opaque
Conduct heat and electricity
Reflect light when polished
Expands when hot, contracts when cold
What are the 3 ways to identify metal?
Visual appearance and color:
hot roll with black mill scale vs cold rool shiny and smooth
Aluminum oxidizing rapidly
Copper and brass are reddish/yellowish
Fractured Surface
examine exposed grain structure
Aluminum fractures whiter than othwrs
Low carbon steels bright grey fracture, high carbon steel whiter and finer grain structure
Relative weight
magnesium 109 lb/ft3, carbon steel 490, copper 558, gold 1205
What tests can you do to identify metals if the other methods don’t work?
Chip test
chisel and see how the chips look
Softer material = longer chip pieces
More carbon = steel is more difficult to cut and chips are smaller and brittle
Spark test
studying spark stream when grinding, mainly used to test carbon content in steels
Low carbon steel: bright, long, straight, yellow. Little branching and few carbon bursts
High carbon steel: darker, yellow-orange, burst near wheel. More branching and sparks follow wheel
Cast iron: red bursts near grinder, orange-yellow further out. Spark stream is shorter. Needs considerably more pressure
File Hardness Test
scratching the metal and using the Rockwell or Brinell scale to accurately measure hardness.
Lower carbon = lower number on scale
What is a Mill Test Report
-Most precise method of identifying a metal
-Required for some specific jobs
-Contains heat number stamped into material- should be transferred if the material is ever cut!
-Metal identification tags usually accompany it.
How can you reinforce welds on a lap joints.
Place plug or slot welds along the joint
A lap joint should overlap by?
Thickness of the work piece.
Main factor in determining type of joint for welding?
Strength and loading req.
Size of groove weld is determined by ?
Throat dimension
What do ferrous metals contain?
Iron
What does a higher carbon content do for the metal?
Increases the hardness and strength but decreases ductility
What steel is harder than a file?
Hardened tool steel
When welding edge joint on thin gauge, how much filler is usually used?
Usually none