Biology - Chapter 1 (copy)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Observation
Things you experience through the senses, by seeing, hearing, tasting, touching, or smelling.
Fact
Two people can observe the same thing, and if they are careful observers they can use their observations to come up with facts about the situation that are not subject to their opinion.
Inference
Drawing conclusions about the things you have observed. Inferences depend greatly on personal opinions and ideas. Two people may observe the same series of events but infer very different things from them.
Theory
General explanations are based on a large amount of data. The way we know something works is based on a lot of tested hypotheses which we can use to make predictions.
Hypothesis
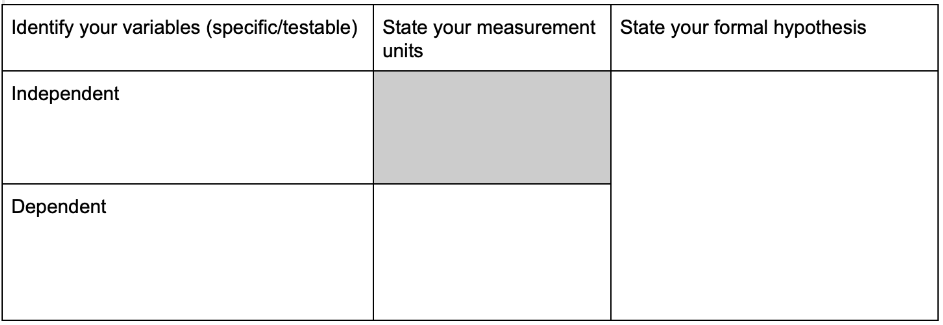
Educated guess based on an inference. A hypothesis is a tentative statement that is specific, testable, and measurable. It proposes a possible explanation for some phenomenon or event.
If there is a relationship between ____________ (independent variable) and __________ (dependent variable), then I think _______________ will happen because of ______________.
Theory vs. Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a tentative explanation of an observation that can be tested. It is the starting point for further explanation. However, a Theory is an explanation of aspects of the natural world, that has been tested by many hypotheses, proven in laws, and justified through facts.
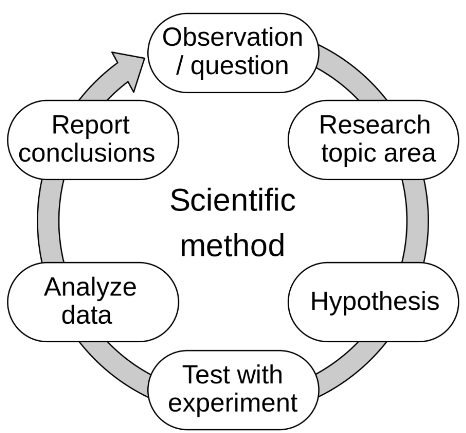
Scientific Method (on wall)
Obervation/Question, Reasearch the Topic, Create a Hypothesis, Test the Hypothesis with an Experiment, Analyze the Collected Data, and Report Your Conclusions
Qualitative Data
Qualitative data is information that cannot be counted, measured or easily expressed using numbers. It is collected from text, audio and images and shared through data visualization tools, such as word clouds, timelines, graph databases, concept maps and infographics.
Quantitative Data
Quantitative data is data that can be counted or measured in numerical values.
Controlled Experiment
A controlled experiment actually consists of two experiments run side by side.
Experimental / Control Group
The original experiment is called the control. The second experiment duplicates the first, except for a single factor which you purposely change.
Independent Variable
Variable that Stayed the Same
Dependent Variable
Variable Measured
Constants
What you needed to stayed the same when you conducted your experiment from the class demonstration.
Graduated Cylindar
Graduated cylinders are long, slender vessels used for measuring the volumes of liquids. Measure from meniscus - lowest point.
Beaker
A lipped cylindrical glass container for laboratory use. Mainly used for chemistry.
Erlenmeyer Flask
It is generally used for the purpose of mixing, cooling, incubating, filtrating, storing, and other solution handling processes.
Prediction Statement
A prediction is an outcome that is expected if the hypothesis is true. Prediction statements typically use the words 'if' or 'then'.
Phenomenon
An observable event
Data Table
A data table includes the independent and dependent variables, it shows the measurement one is using in the data table, the amount of trials, and the average. Purpose: These are used to record and summarize data. They allow relationships and trends in data to be more easily recognized.
Claim
A claim is a complete statement of what is known.
Evidence
Data that supports a claim is evidence.
Reasoning
Reasoning explains why the data set supports the claim.