12.2 Leaves
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:36 PM on 4/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
cuticle
is a waxy layer that covers the epidermis of leaves and stems, which serves as a barrier against water loss, pathogens, and insects. It also reflects sunlight, reducing the amount of heat absorbed by the plant.
2
New cards
upper epidermis
it’s for support and structure
3
New cards
guard cell
controls the opening and closing and regulates gas exchange and water loss through small pores called the stomata.
4
New cards
stoma
where gases pass in and out
5
New cards
Describe how toxic chemicals from plants leaves can be beneficial to humans as a form of medicine.
They’re used to treat cancer and heart disease
6
New cards
Do mature cells of xylem tissue have nuclei? Explain.
Xylem cells that reach maturity become hollow and dead. In this case, it no longer contains cell organelles, such as nucleus.
7
New cards
What are two ways that plants use the glucose they produce during photosynthesis?
Energy source and to make other substances like cellulose, starch or budding material.
8
New cards
Chloraplasts
are organelles that serve as the site of photosynthesis within a plant
9
New cards
Photopigments
are chemicals that undergo a physical or chemical change when they absorb particular wavelengths of light
10
New cards
Label the petiole, blade and veins
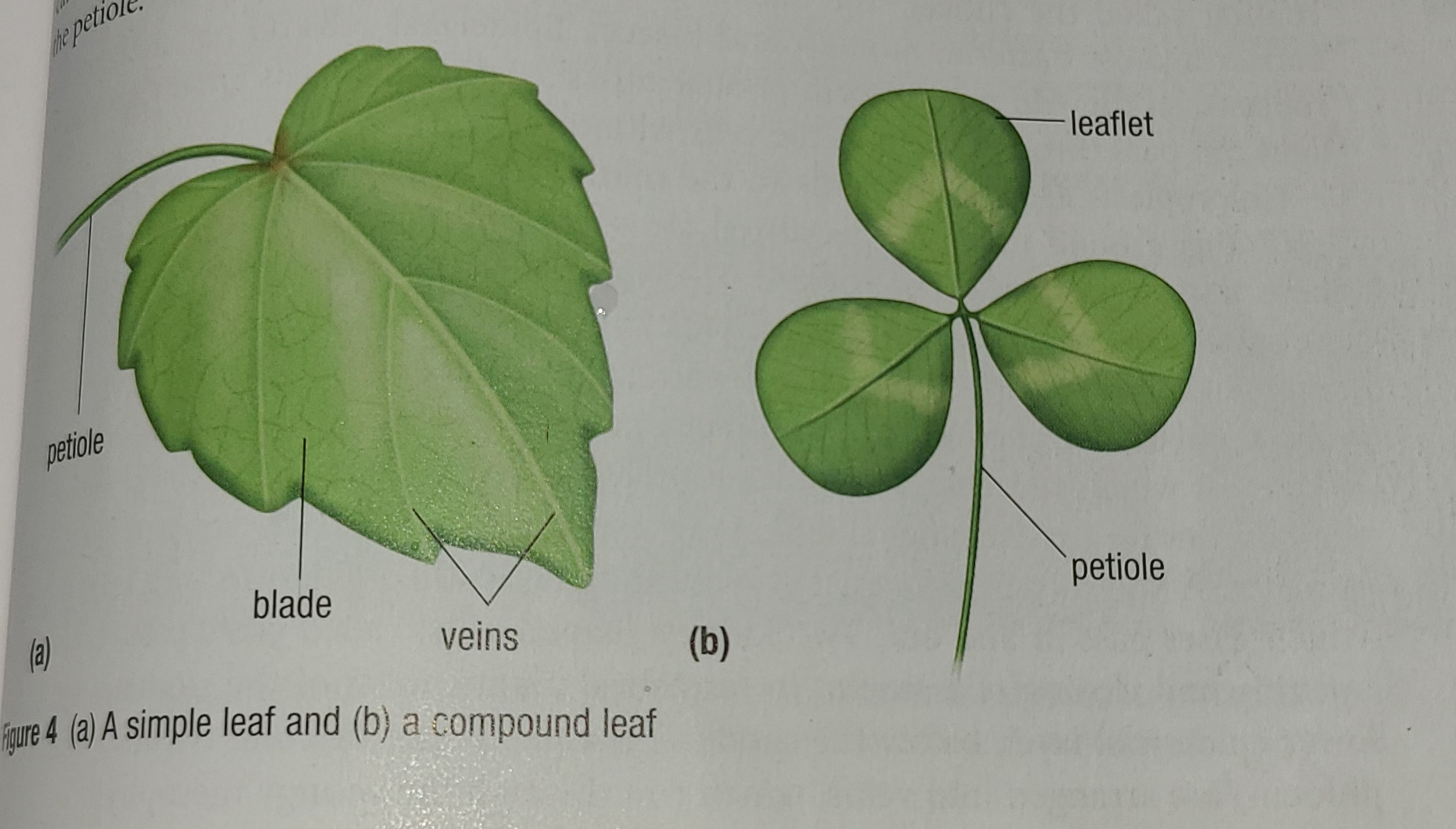
11
New cards
Venation
in monocot is parallel
12
New cards
Eudicot
branching
13
New cards
Label the parts of a cross section of a leaf
14
New cards
In your own words, describe how the leaves of a cacti are adapted to protect the plant from herbivores
Cacti do not have leaves they initially had have to evolved to become spines which protects cactus plant from herbivores and eliminated the problem of water evaporating.
15
New cards
Describe how surface hair can protect plant leaves from being eaten by herbivores.
Surface hair or trichomes are tiny hair-like structures found on the leaves of plants. They act as a protective shield for the plants by making it hard for herbivores like insects and animals to eat the leaves. This is because the hairs can be sharp and uncomfortable, and some can even produce harmful chemicals that deter the herbivores from feeding on the plant. This helps the plants to survive and grow better.
16
New cards
Describe the role of nicotine in tobacco plants
It deters herbivores
17
New cards
Why do some plants lose their leaves in the fall?
In order to help the plant conserve water and nutrients during the winter.
18
New cards
Describe the adaptations of onions that help them store water and carbodhydrates?
It is made up of leaves that can hold/store the water and carbohydrates.
19
New cards
How do humans use the waxes produced in leaf cuticles?
They use it for car and furniture polish
20
New cards
cuticle
prevents water loss and provides barrier against bacteria
21
New cards
Toxins that have a psychotropic effect on humans can be beneficial adaptations for plants in several ways:
they can be beneficial adaptations for plants by providing defense mechanisms against herbivores, attracting pollinators, fending off competitors, and resisting pathogens and pests.
22
New cards
Palisade mesophyll
is a special part inside the leaves of a plant where it makes food by using sunlight. It has a lot of green structures called chloroplasts that help it to do this. The cells in the palisade mesophyll are tall and shaped like columns, and they are found near the top of the leaf.
23
New cards
spongy mesophyll
is another special part inside the leaves of a plant where it makes food by using sunlight. It is found just below the palisade mesophyll and is made up of cells that are more loosely packed. The spongy mesophyll helps the plant to breathe by allowing gases to move around. It also stores food made by the plant during photosynthesis.
24
New cards
Aerenchyma
is a is a term used in botany to describe a type of plant tissue that contains air spaces, which allows for the exchange of gases between the roots and the atmosphere. It is commonly found in aquatic or wetland plants, and serves to transport oxygen to the roots and other parts of the plant that are below the waterline.
25
New cards
mesophyll
It is composed of two layers, the palisade mesophyll, and the spongy mesophyll, which contain specialized cells called chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll
26
New cards
describe how sub-zero can affect leaves.
Freezing damage, dehydration,reduced photosynthesis and changes in pigment
27
New cards
Adaptations angiosperm trees
includes deep roots that can reach water sources, leaves that can capture sunlight efficiently, and the ability to produce flowers and fruits that attract pollinators and seed dispersers.
28
New cards
vascular bundle
vascular bundles are plant tissues that trasport water, minerals and nutrients throughout the plant. They consist of xylem and phloem.
29
New cards
Lower epidermis
is a layer of cells on the underside of a plant leaf that helps with gas exchange and contains stomata.
30
New cards
Upper epidermis
is a layer of cells on the top of a plant leaf that protects against water loss and damage. It also contains the cuticle.