CH 10: Vital Signs
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
always remember to follow these standard precautions

for vital signs... you measure these 4 things....
1. temperature
2. respiratory rate
3. pulse
4. blood pressure
what is 40.0C in F?
104F
what is 37.0C in F?
98.6F
What is 35C in F?
95F
rectal temp measure _____-____C higher than oral
() reading is the most accurate/close to core temp but invasive
() is preferred for critical care bc of its accuracy
() readings are in between oral and rectal
() readings are the most variable/unreliable
0.4-0.6
rectal
rectal
temporal
tympanic
for rectal temp position pt _____ _____ , don gloves, place cover on thermometer probe, apply lubricant, insert _____inch ifor adults and ____inch for infants <6months, leave until beep DO NOT LET GO, then clean pt
left lateral, 1 inch, 1/2 inch
mean oral temp in a resting adult
temperature above _____ is considered febrile
97.7F
100.4F
should you report in C or F (usually C unless your agency uses F
document temp and _____
route
oral temp is the most convenient and commonly used. sublingual pocket has rich blood supply from carotid arteries that quickly responds to changes in inner core temp. wait no less than ___ min if pt has recently eaten, had hot/cold liquid, smoked
15
electronic thermometers are used for oral, axillary, and rectal temps. blue tipped is for () red tipped is for ()
blue is oral and axillary. red is rectal.
__________ temp used in peds often due to ease
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
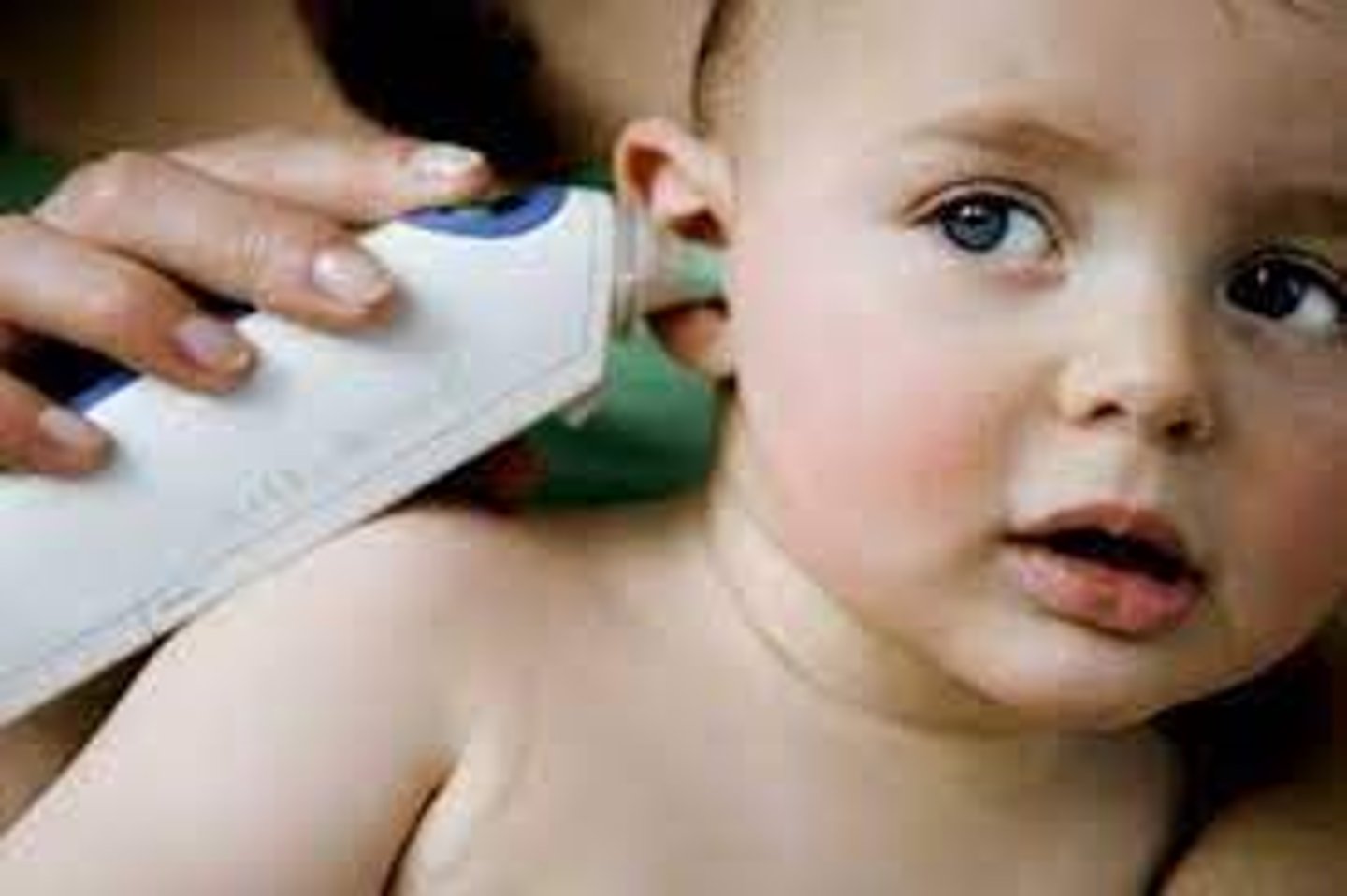
for tympanic membrane temp place covered probe tip in ear canal, aim infrared beam at tympanic membrane, straighten ear canal for adults do this by ______ for children under 3 ________. activate device and read temp in 2-3 seconds.
pull pinna up and back, pull pinna straight down
temporal artery thermometer slides probe ()
reading takes 6 seconds
questionable reliability and not as accurate as other methods
across forehead then behind ear
what about those non-contact infrared thermometers that are common now?
BAD, less accurate than other measures and are not sensitive to temperatures above 37.5°C
pulse, use the pads of your first 3 fingers, palpate the radial pulse at the flexor aspect of the wrist laterally along the radius bone
30 sec interval most accurate/efficient when hr is regular
REGULAR RHYTHM: count number of beats in 30sec then multiply by 2
IRREGULAR RHYTHM: count for a full min
make sure to start your first count as "zero"
assess () () and ()
rate, rhythm, force
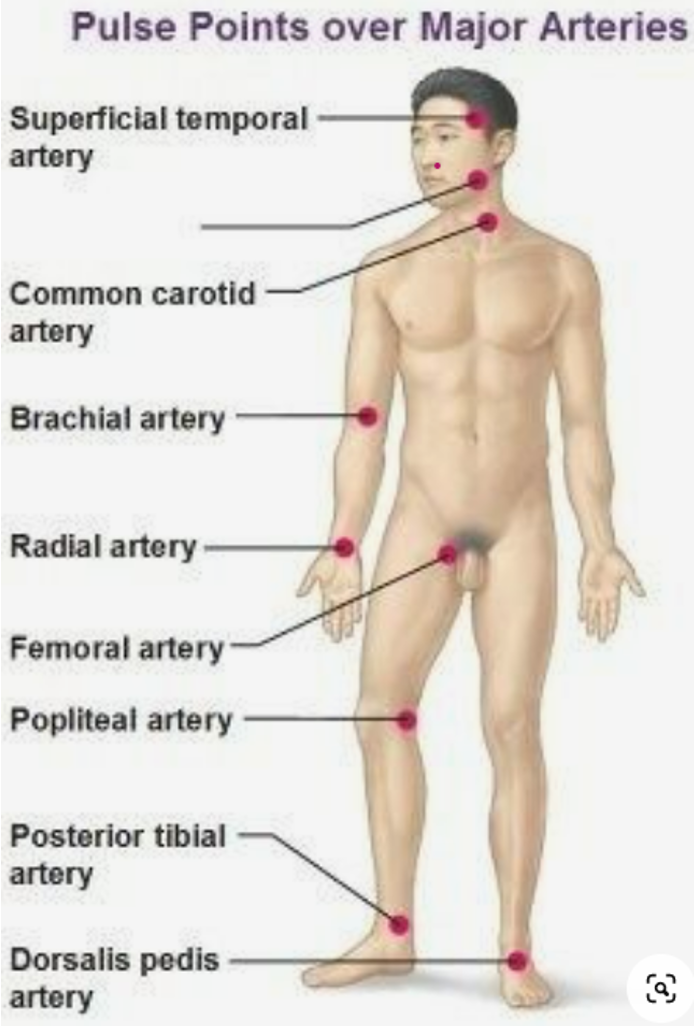
diff pulse locations
superficial temporal artery, common carotid artery, brachial artery, radial artery, femoral artery, popliteal artery, posterior tibial artery, dorsalis pedis artery
bradychardia is ______bpm in adult
< 50 bpm
bradycardia can be caused by
meds, well-trained athlete (they have a stronger more efficient heart that pushes larger stroke volume w each beat)
tachycardia is _______bpm in audlts
> 95 bpm
tachycardia can be caused by
anxiety, exercise, fever, sepsis, stress, pain and more
can low pulse be normal?
yes (ie., well trained athletes)
if a pulse is not palpable, a _________ may be used
doppler
______________ pulses run higher and have a different scale of normal readings
pediatric
what is a regular pulse tempo?
even tempo
what is an irregular pulse tempo?
uneven tempo
the _______ ________ reflects the strength of the heart's stroke volume
pulse force
what scale number pulse force is considered regular
2+
_______ pulse force is considered absent
0
______ pulse force is considered weak/thready
1+
_______ pulse force is considered bounding or full. is this normal?
3+. no, normal is 2+ bounding pulse is not super worrisome though pregnancy can cause it but so can hyperthyroidism...
for respirations, breathing should be relaxed/regular/automatic/silent
- do not tell pt u are counting their resp
-count for at least 1 full min
-record # of breaths per min and character of breaths (even, shaky,etc
yay
respiratory rate normal range
12-18 breaths/min
is respiration faster or slower in infants and children
faster
newborn resp rate immediatley post birth
30-50 breaths/min
at age ___ when alveolar development is complete, resp rate slows to the same as adults and you can use adult normal ranges
8
pulse:respiratory rate RATIO
4:1
tachypnea is ______breaths/min
above 25
bradypnea is ________breaths/min
8-12
() Force of blood pushing against the side of its container, the vessel wall
() Maximum pressure felt on the artery during left ventricular contraction, or systole
() Elastic recoil, or resting, pressure that the blood exerts constantly between each contraction
() Difference between systolic and diastolic pressures and reflects the stroke volume
() Pressure forcing blood into the tissues averaged over the cardiac cycle
blood pressure
systolic blood pressure (SBP)
diastolic blood pressure (DBP)
pulse pressure
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
if you get an abnormal reading on a pulse oximeter, you should
move it around because it could be due to placement, dark nail polish, etc.
pulse oximeters show
both the pulse and oxygen saturation
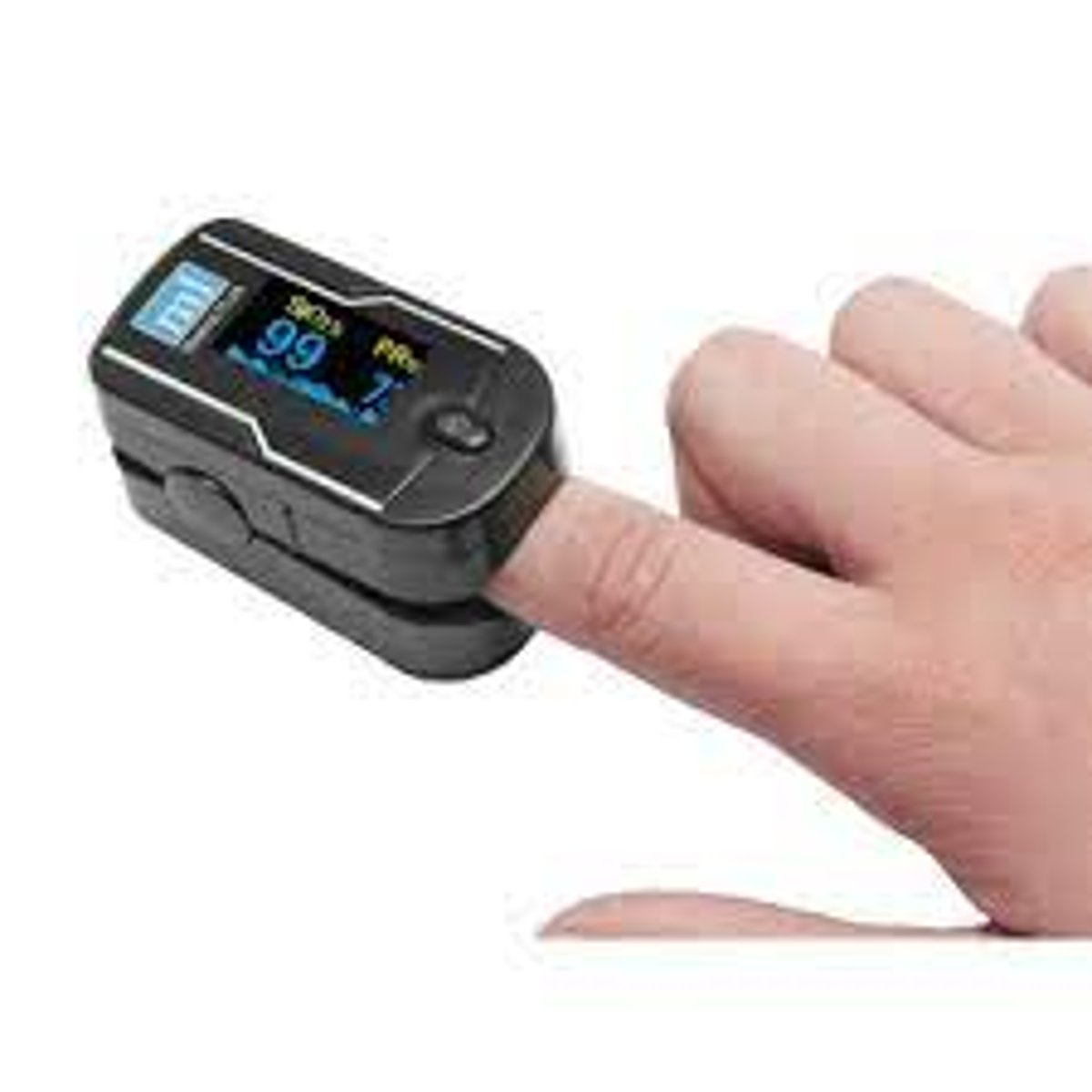

what is a normal oxygen saturation reading for an adult?
95-100% on room air
a measure of how much hemoglobin is currently bound to oxygen compared to how much hemoglobin remains unbound in the blood
oxygen saturation
abnormal oxygen saturation
<95% on room air
maximum pressure during left ventricular contraction
systole
the top blood pressure reading
systolic
the bottom blood pressure reading
diastolic
recoil/resting pressure between each contraction
diastole
systolic BP minus diastolic BP = () this reflects the stroke volume
pulse pressure
_______ _______ reflects stroke volume
Pulse pressure
when performing a blood pressure cuff reading, you should make sure the cuff is
the correct size and inflated to maximum level
how should you deflate the blood pressure cuff?
slowly and evenly
generated when a blood pressure cuff changes the flow of blood through the artery
Korotkoff sounds
Korotkoff sounds
systolic and diastolic which is first sound which is last
systolic first, diastolic laste
delete
delete
do not obtain blood pressure readings on
mastectomy arms or other injured areas
syncope

when should you take serial measurements of pulse and BP? (3)
1. you suspect volume depletion
2. when the person is known to have hypertension or is taking antihypertensive medications
3. when the person reports syncope or near syncope (ie., dizziness)
describe how you would take orthostatic (or postural) vital signs
-have person rest supine for 3-5 min
-then take baseline BP and pulse
-have patient sit up, assess BP and pulse
-have patient stand up, assess BP and pulse
-after an extra 3 minutes, take BP and pulse again
when performing an orthostatic vital sign measurement, a patient would have orthostatic hypotension is their systolic pressure drops _______ or if their diastolic pressure drops _________ after standing
20 mm Hg or more
10 mm Hg or more
__________ ___________ blood pressure changes are caused by abrupt peripheral vasodilation without a compensatory increase in cardiac output.
orthostatic hypotension

Orthostatic changes commonly occur with.... (4)
-prolonged bed rest,
-older age,
-hypovolemia,
-some medications
you perform an orthostatic vital sign assessment on a patient. their systolic pressure decreased 8 mm Hg when they changed from sitting to standing. do they have orthostatic hypotension?
no bc for systolic it has to drop 20 mm Hg or more from sitting to standing
normal bp range audlt
120/80 or less
Systolic: 120 or less
Diastolic: 80 or less
Elevated BP range adult
120-129 / less than 80
Systolic: 120-129
Diastolic: 80 or less
high blood pressure hypertension stage 1
130-139 / 80-89
Systolic: 130-139
Diastolic: 80-89
high blood pressure hypertension stage 2
140+ / 90+
Systolic: 140+
Diastolic: 90+
hypertensive crisis range (when doctor needs to be immediately consulted)
180+ / 120+
Systolic: 180+
Diastolic: 120+
underweight BMI
normal BMI range
overweight BMI
obesity class 1
obesity class 2
extreme obesity
<18.5
18.5-24.9
25-29.9
30-34.9
35-39.9
40+
ADULT VITAL SIGNS
normal oral temp range
normal rectal temp range
normal mean oral
abnormal fever/hyperthermia
abnormal hypothermia
normal oral range: 96.4-99.1 f
normal rectal temp: 97.1-100.1 f
mean oral: 97.7 f
fever: 100.4 f more
hypothermia: 96.4f less
ADULT VITAL SIGNS
normal pulse rate
abnormal bradycardia
abnormal tachycardia
normal pulse rhythm
abnormal pulse rhythm
normal pulse force
abnormal pulse force (3 answers)
50-95 bpm
less than 50
more than 95
even tempo, regular
irregular, uneven tempo
2+
0=absent, 1+=weak/thready, 3+=bounding/full
ask the prof if i need to memorize this pic
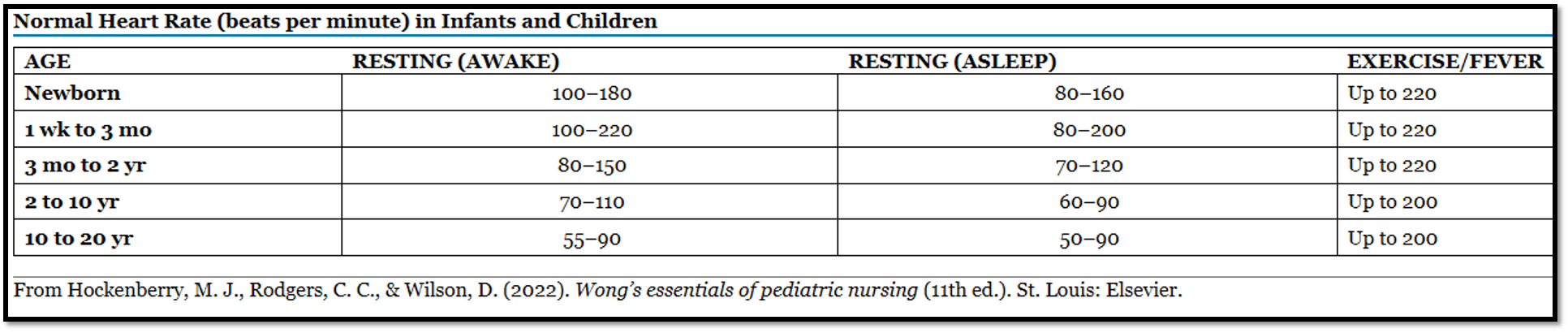
ask prof if i need to memorize vital signs in f and c
did u?