211 lec 8 sensory contribution II (proprioception and vision)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
M2 is ___ latency, aka ___ reflex
it is sensitive to ___
long latency
polysynaptic reflex
Goal/ intent of the person
M1 is ___ reflex, aka ___ or ___ latency
Monosynaptic reflex
autogenic or short latenchy
describe monosynaptic stretch reflex
1a afferent sends info to motor neuron in spinal cord, which then sends an efferent signal to the muscle
describe M2 (Polysynaptic reflex)
afferent» motor neuron in spinal cord and interneuron (receive descending signal from higher level) » efferent output to muscle fiber
muscle spindles are spindle-shaped receptors oriented in ___ with muscle fibers
parallel
muscle spindles are sensitive to changes in ___ and ____ of muscle fiber
length
rate of change in length
the sensory/afferent neurons in muscle spindle send info to ___ and can excite efferent neurons (aka ___) back to ___
spinal cord
aka Motor Neurons
muscle fiber
M3 is ___
voluntary response
compare loop time of M123
shortest to longest (30-50 vs 50-70 vs more than 120)
compare structures involved in M123
M1= same muscle + muscle spindle
M2= same muscle + muscle spindle + cortex or cerebellum (higher level)
M3= various muscle + various receptor + higher center
which one is modified by instructions from higher center (M123?)
M23
GTO=
golgi tendon organ
GTO is located in the ___ btw ___&__. It detects changes in ___
junction btw muscle & tendons
muscle tension (force)
When theres too much force/tension in muscle, GTO ___
This is considered a ___ close/open loop control
turn in off (inhibit it)
proprioceptive reflexive closed-loop control
GTO and ___ both input to ___ and output back to ___
M1 muscle spindle
spinal cord
muscle
2 types of muscle proprioceptor:
GTO
Muscle spindle
3 type of non muscle proprioceptors:
joint
vestibular
cutaneous
where is vestibular apparatus?
It sends info about ___ and ___
movement of the head
sense of balance
angular acceleration in 3 directions are detected by the ___ movement in ___ of the vestibular apparatus
hair
otolith organs
linear acceleration is detected by the___ movement in ___organs of the vestibular apparatus
hair
otolith organ
cutaneous receptors signals info about _____ (4)
touch
pressure
temperature
pain
joint receptors are embedded within ___
it responds to the ____ and ____
joint capsules
limits of joint range
pressure
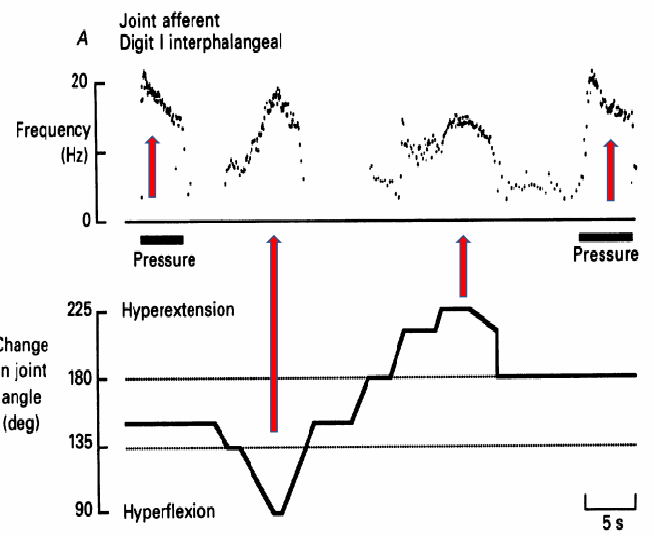
what does this graph illustrate
when applying pressure or approaching limits of hyperextension/flexion, joint receptor sends stronger signals
proprioceptors allow us to make ___, ___ responses to unexpected stimuli such as a sudden stretch/ force
fast and reflexive
describe the closed-loop control model for vestibular proprioceptor
(from muscle) vestibular apparatus » proprioceptive feedback » comparator »error to SI
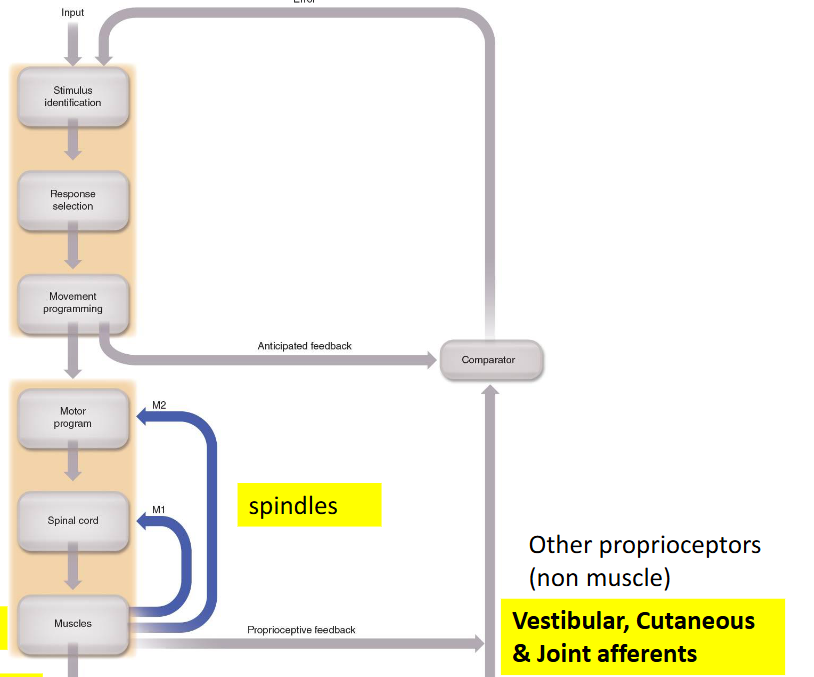
Vision has 2 control component: ___ and ___
dorsal and ventral
visual’s conscious control aspect include ___ stages of info processing
SI, RS, RP
how is the non-conscious/reflexive visual component involved in info processing
(from movement) dorsal vision give exteroceptive feedback back to motor program
whats our preferred source of sensory info
vision
2 visual streams for info procession:
dorsal (non-conscious)
ventral (conscious)
what cortex is linked to dorsal and ventral visual stream
dorsal- parietal cortex (top)
ventral- inferotemporal cortex (bottom)
dorsal stream is linked to vision for ___ (___?).
We use this stream when we ___ with object and ____actions
action (where?)
interact
guiding
ventral stream is vision for ___ (___?)
we use this stream to ___ object and ___
perception (what?)
identify & planning
2 ways we found out that there’s 2 visual stream
dissociation in patients with brain injury
dissociations in seeing and doing in visual illusion research
____ is when you have dorsal stream problem.
meaning that your ___ is fine, but you become disconnected from ___
optic ataxia
vision
guided actions
whats wrong? the patient can see the pencil but continuously miss it
but is lights were off, they could perform accurately
optic ataxia
describe ventral stream function
conscious identification of objects (primarily in center of field-of-vision)
__ is a ventral stream problem.
meaning you can see sth but you can’t make sense of it
visual-form agnosia
what’s wrong? a patient could identify a pictured object only when he starts moving high hands as though he was using it
visual-form agnosia
what is the ebbinghaus illusion
perceptually different looking things that are actually physically identical
illusion give evidence for 2 visual streams: perception is tricked but grasp (vision for action?) is not
IOW, ___ stream is tricked but ___ stream is not
ventral
dorsal
which visual stream is conscious but slower
ventral
which visual stream is non-conscious but fast
dorsal stream
optical flow experiments like the ___and ___ reveals that ____ stream is dominant as shown in the ___ behaviours and ___ control
biking
moving walls
dorsal stream
avoidance behaviour
balance/navigation control
patterns of light=
optical flow
dorsal vision provides info about ___ aka rate of ___ of objects on retina
time to contact (tau)
expension
in the swinging room, the floor is ___ and the walls have objects on them. The movement of walls creates ____ patterns
fixed
optical flow
when the wall swings back, ____ cause the person to ___ despite conflict with other senses
optical flow
fall backward
influence of optical flow (the correction) is very ___
fast
examples that suggest vision dominate other sources of perception
swinging room, McGurk effect, puppets
dsecribe the McGurk effect
you clearly hear ba ba ba
but the lip movement you see fool you to think you heard fafafa instead
compare and contract dorsal vs ventral (table)
consciousness? flexibility? speed?
selective attention?
involved in what stage of motor behaviour?
both:
closed loop
dorsal | ventral | |
unconscious/ reflexive fast/ inflexible | conscious slow/ flexible | |
selective attention | no need (peripheral) adjust motor program | required (foveate) in info process stages |