701: Endocrine Neck & Larynx
1/320
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
321 Terms
Subclavian veins or make connections with external jugular
Anterior jugular veins begin in mental triangle and empty into...
External jugular v.
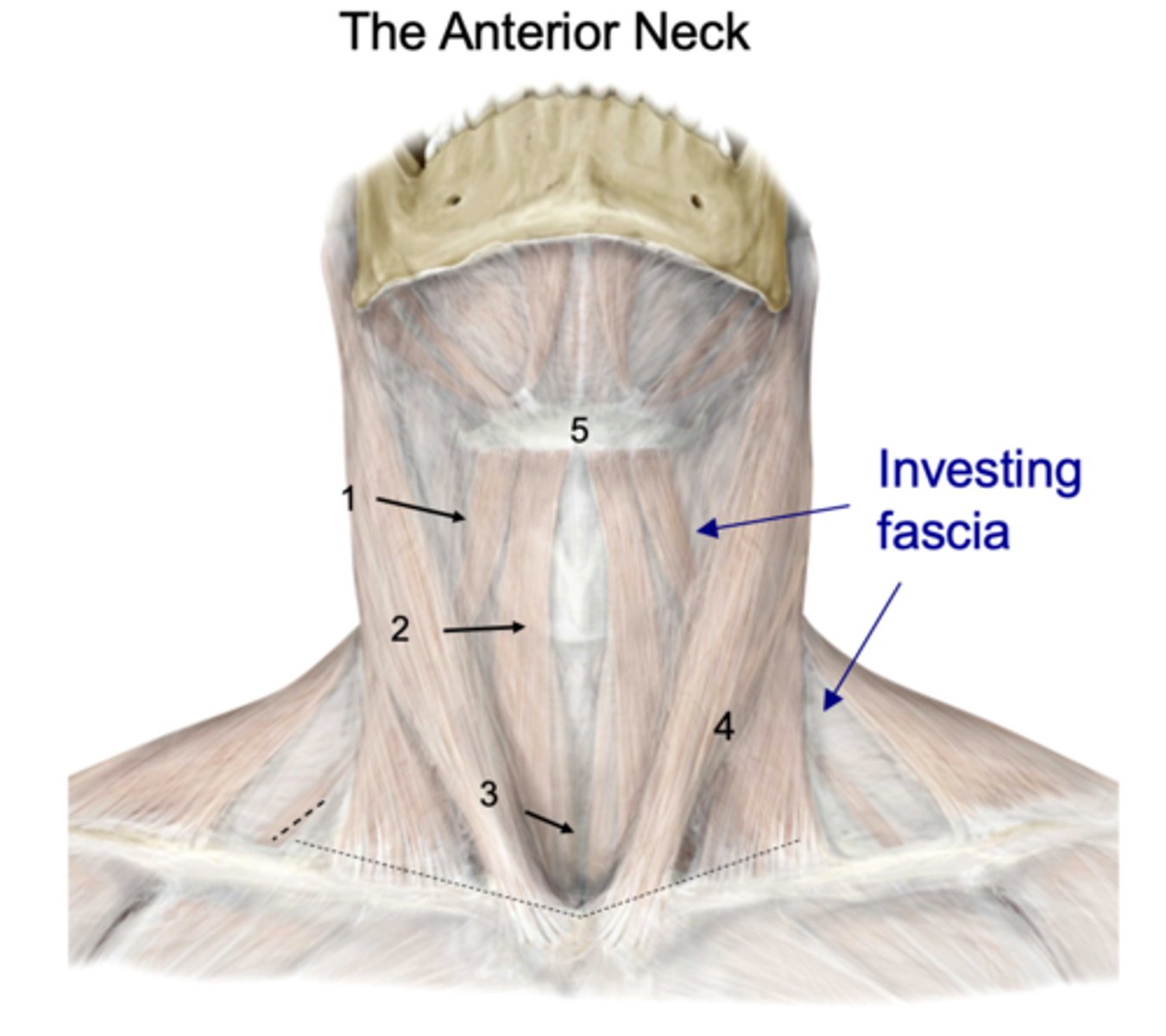
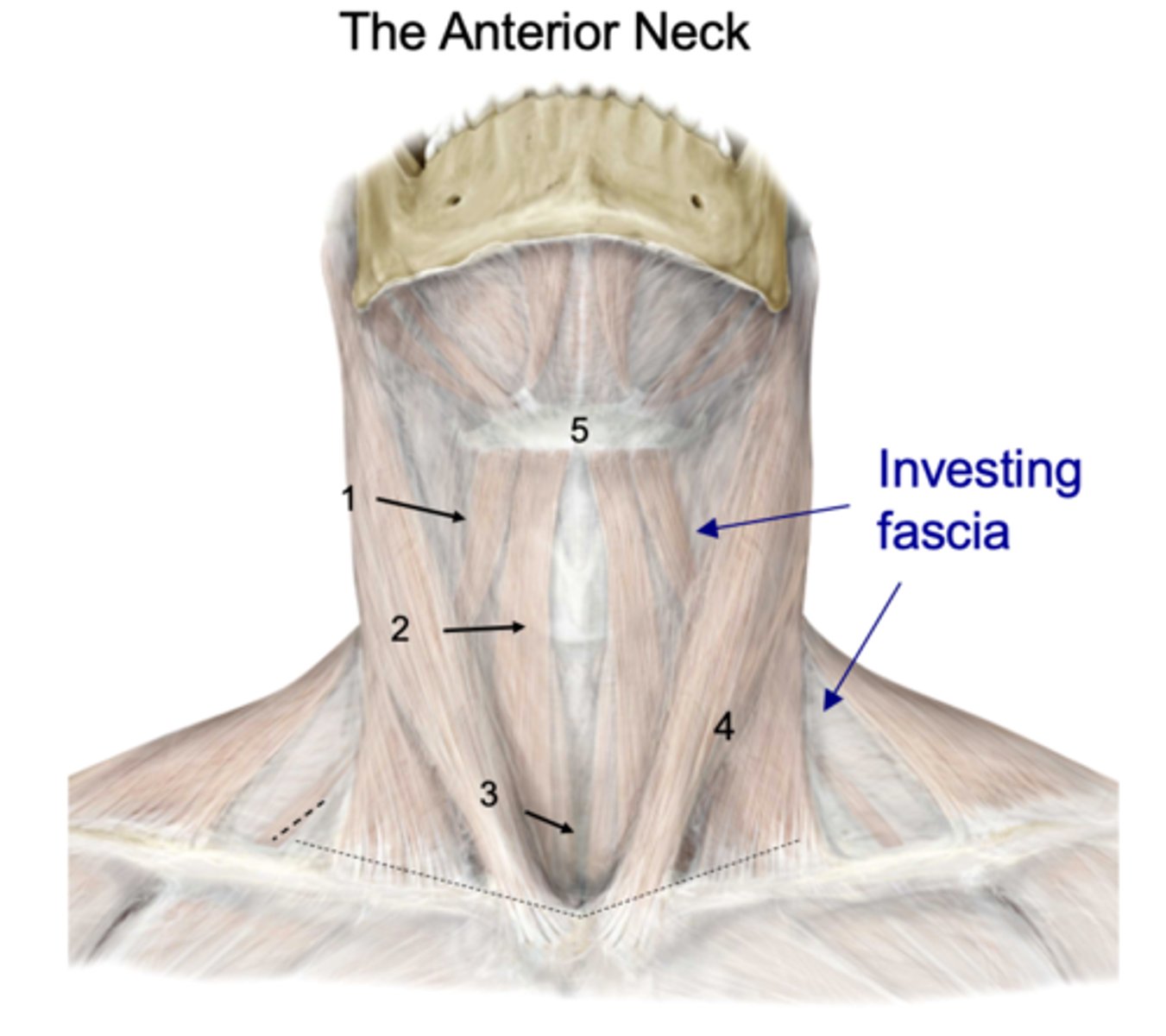
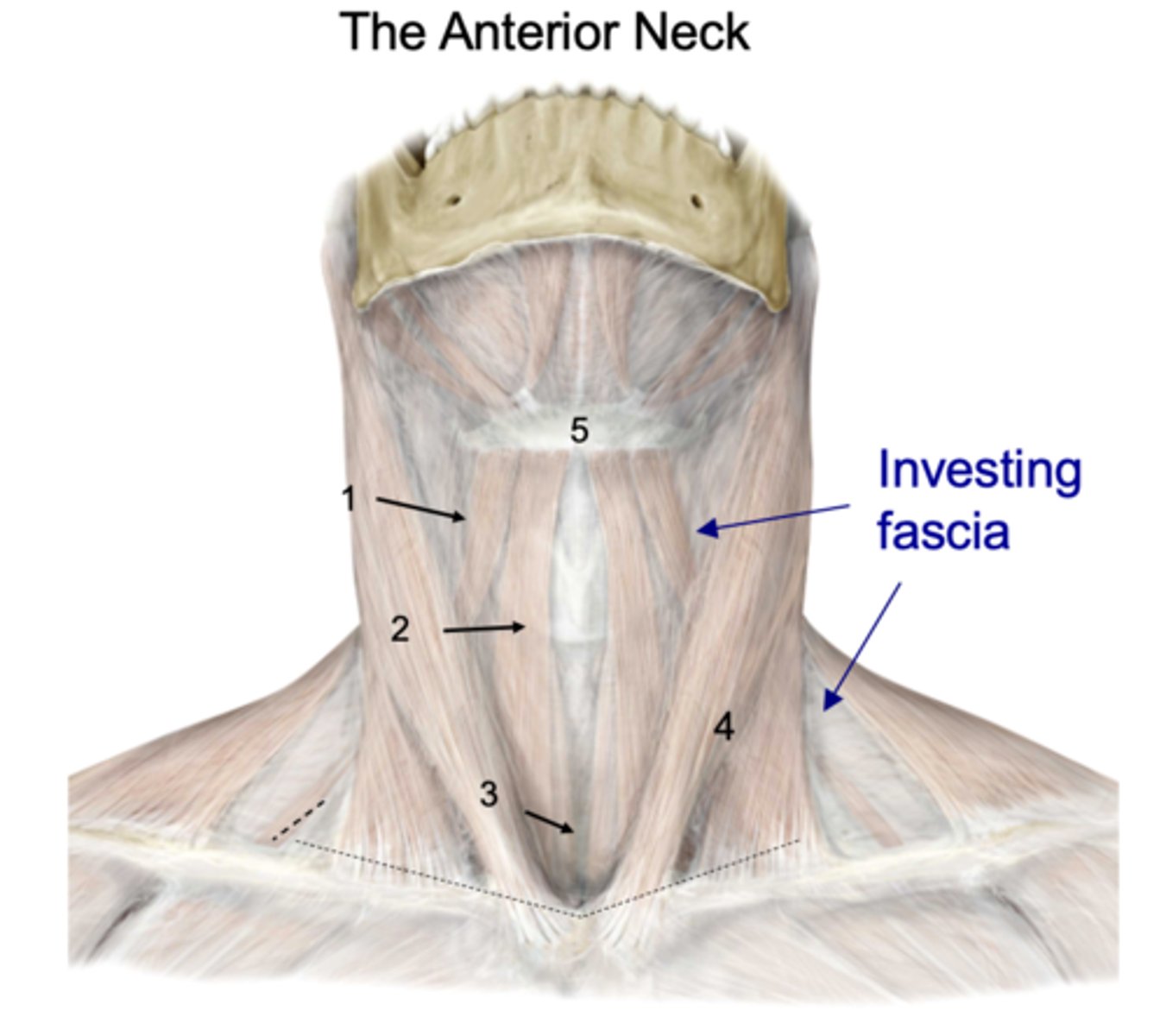
Identify the structure at #1
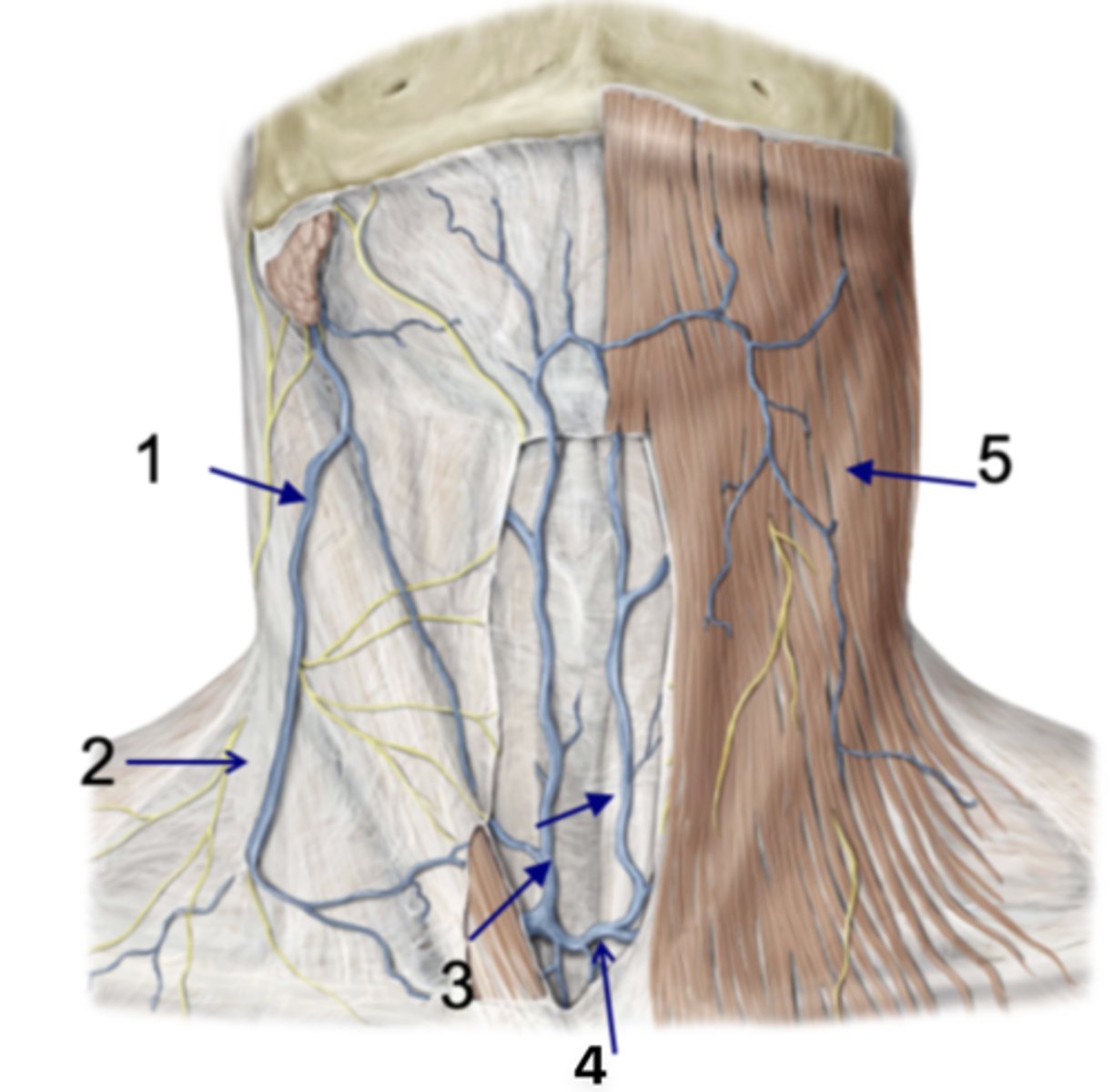
Investing fascia
Identify the structure at #2
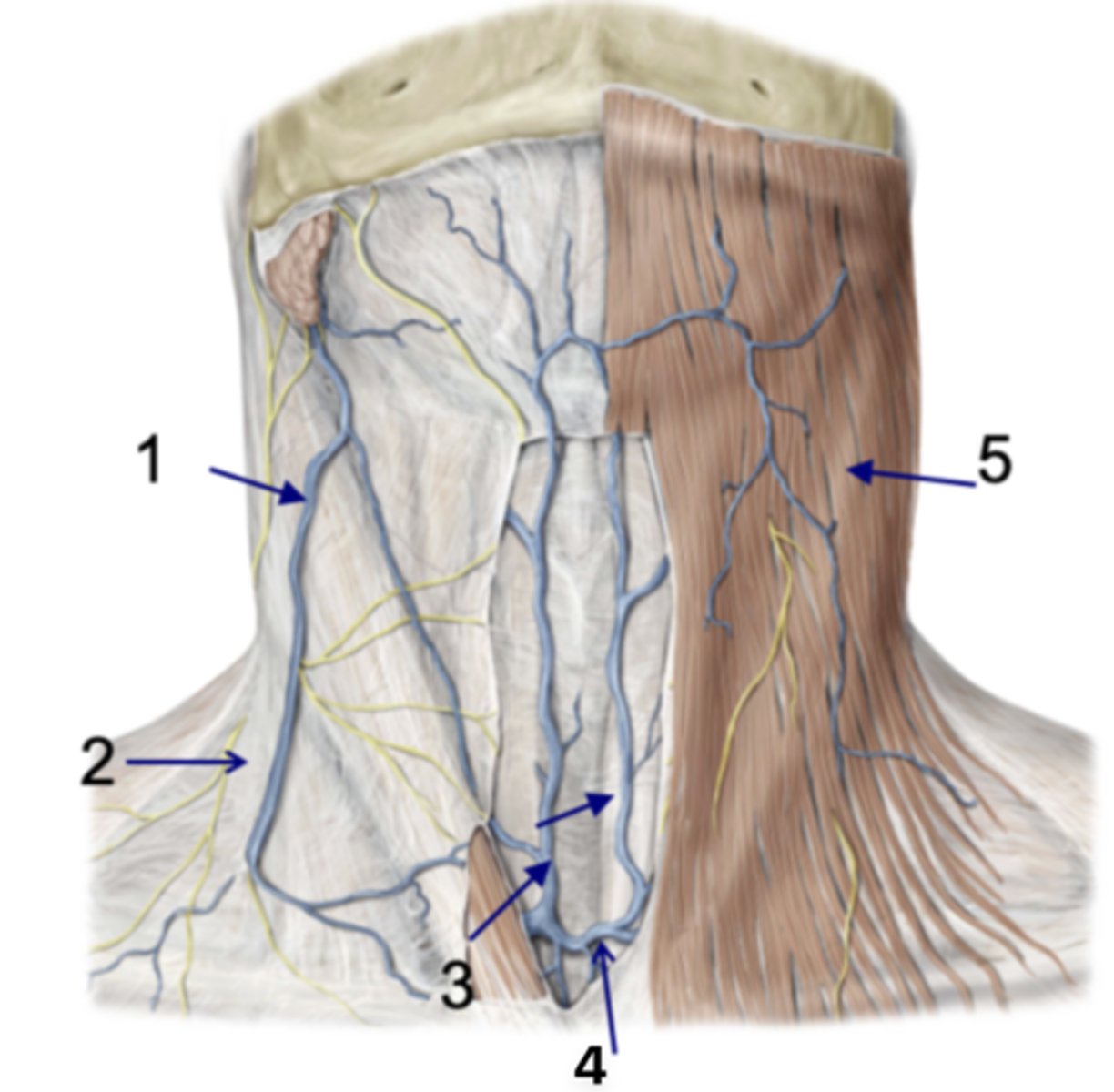
Anterior jugular vv.
Identify the structure at #3
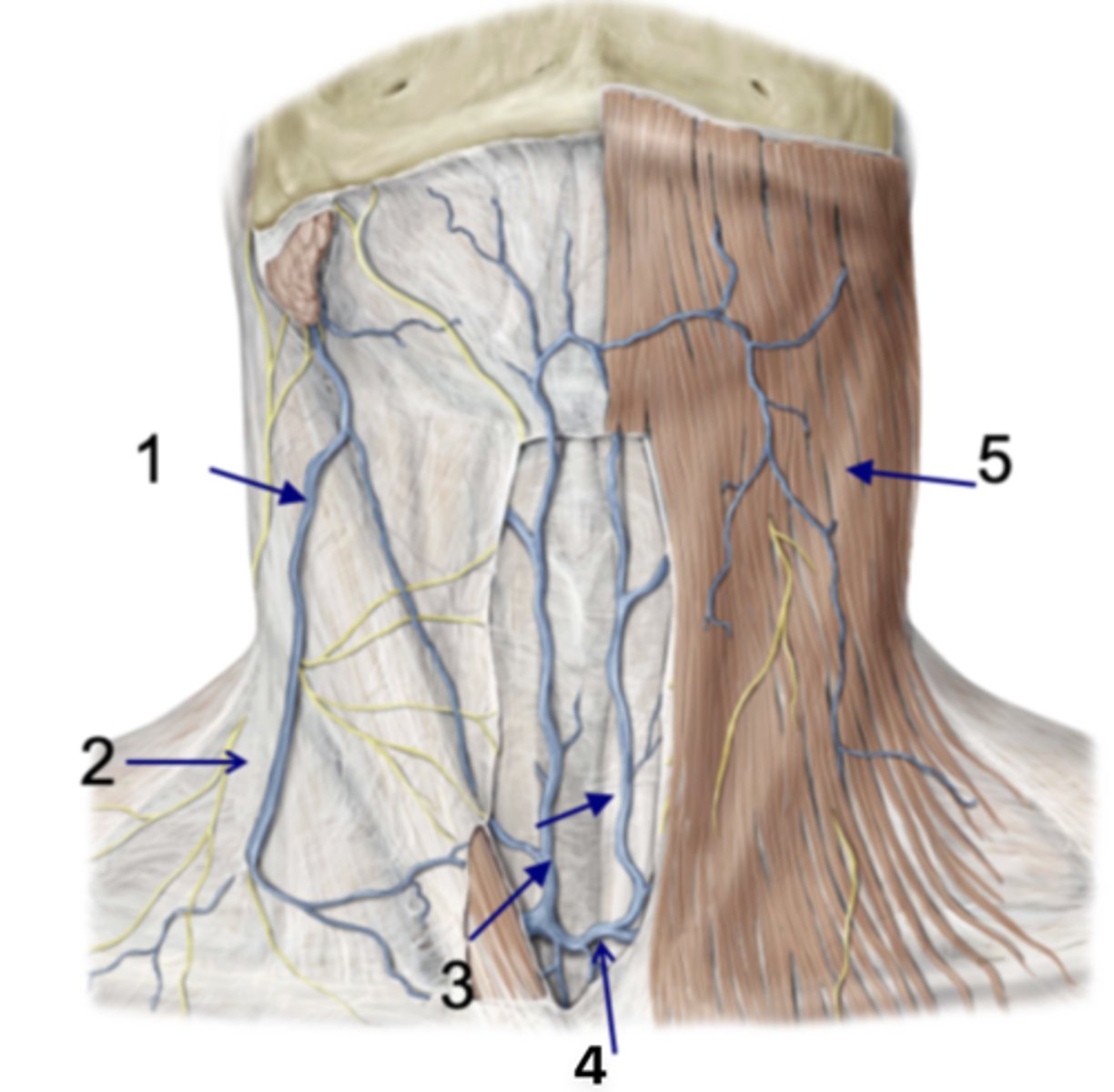
Jugular venous arch
Identify the structure at #4
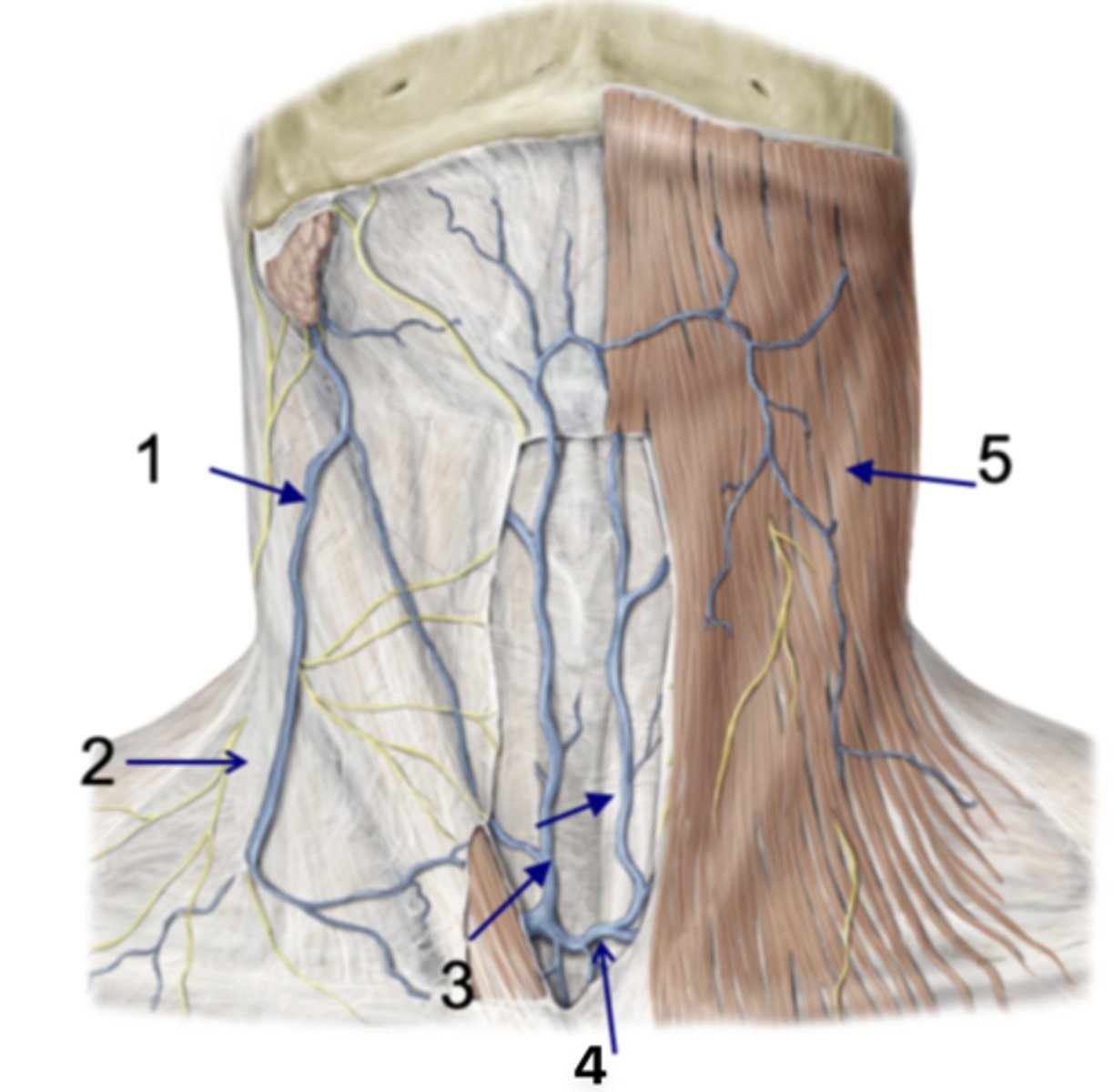
Platysma
Identify the structure at #5
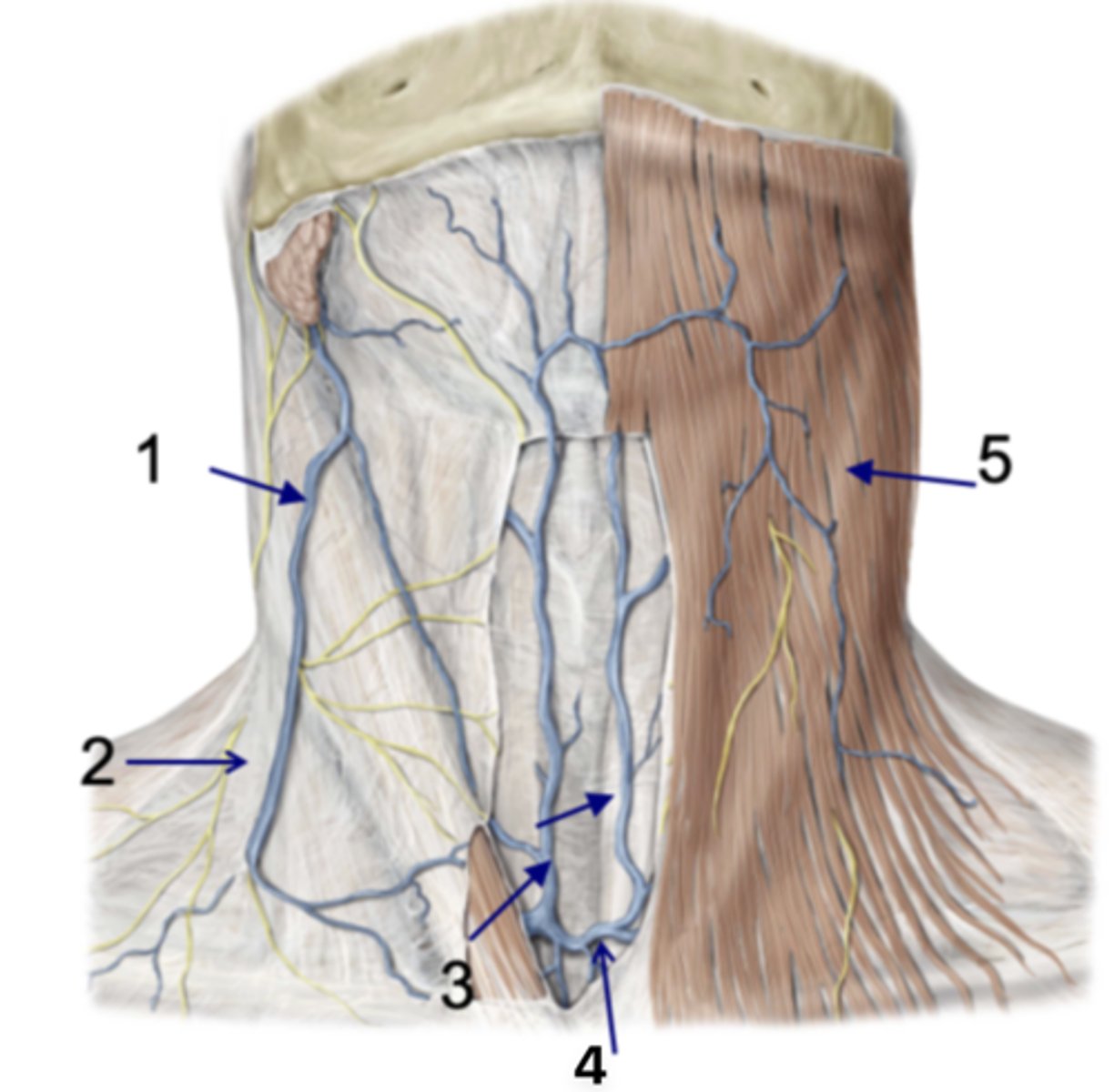
infrahyoid and suprahyoid muscles
What muscles are deep to the platysma and investing fascia?
Omohyoid
Identify the structure at #1
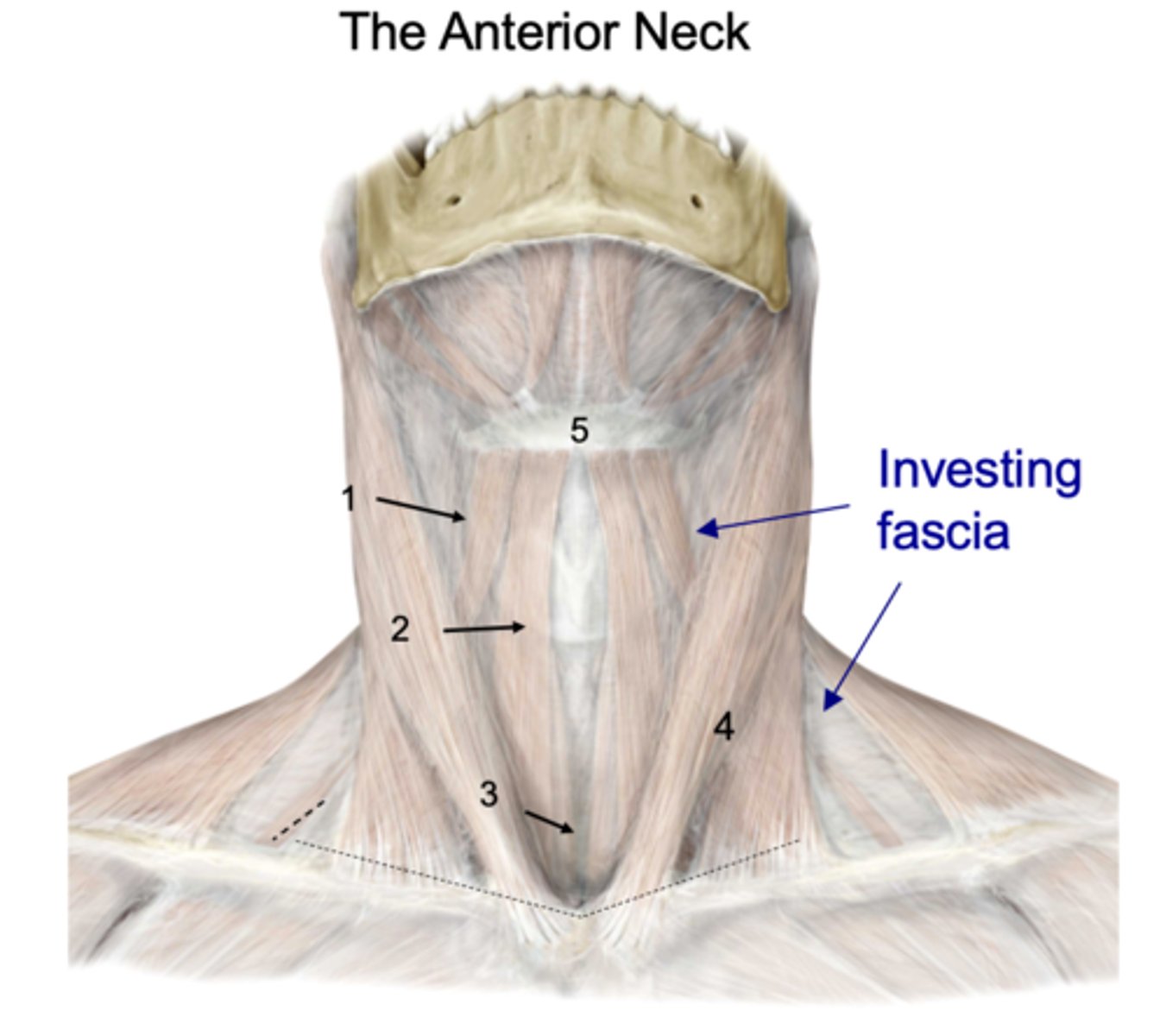
Sternohyoid
Identify the structure at #2
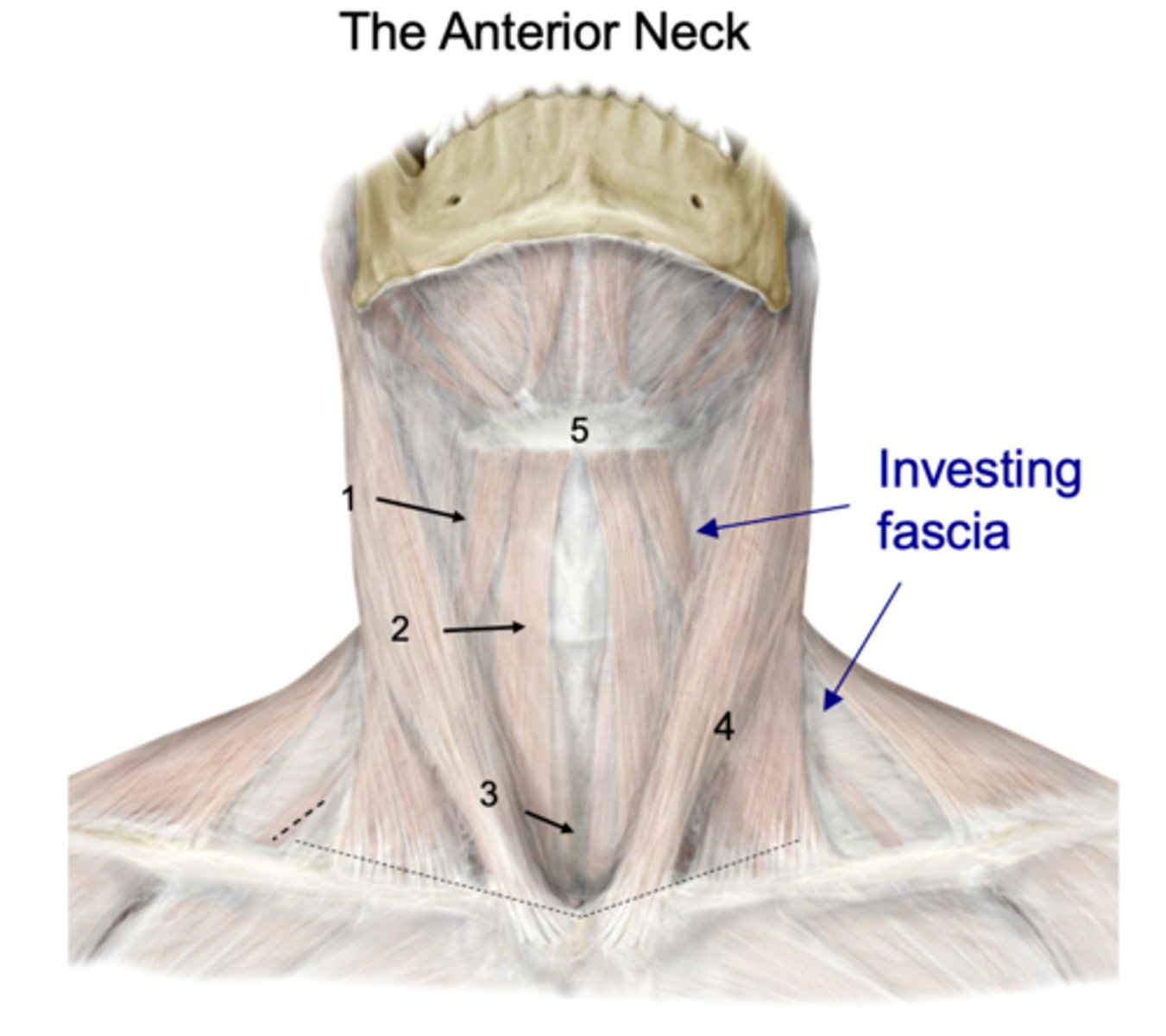
Sternothyroid
Identify the structure at #3
SCM
Identify the structure at #4
Hyoid
Identify the structure at #5
thyroid gland
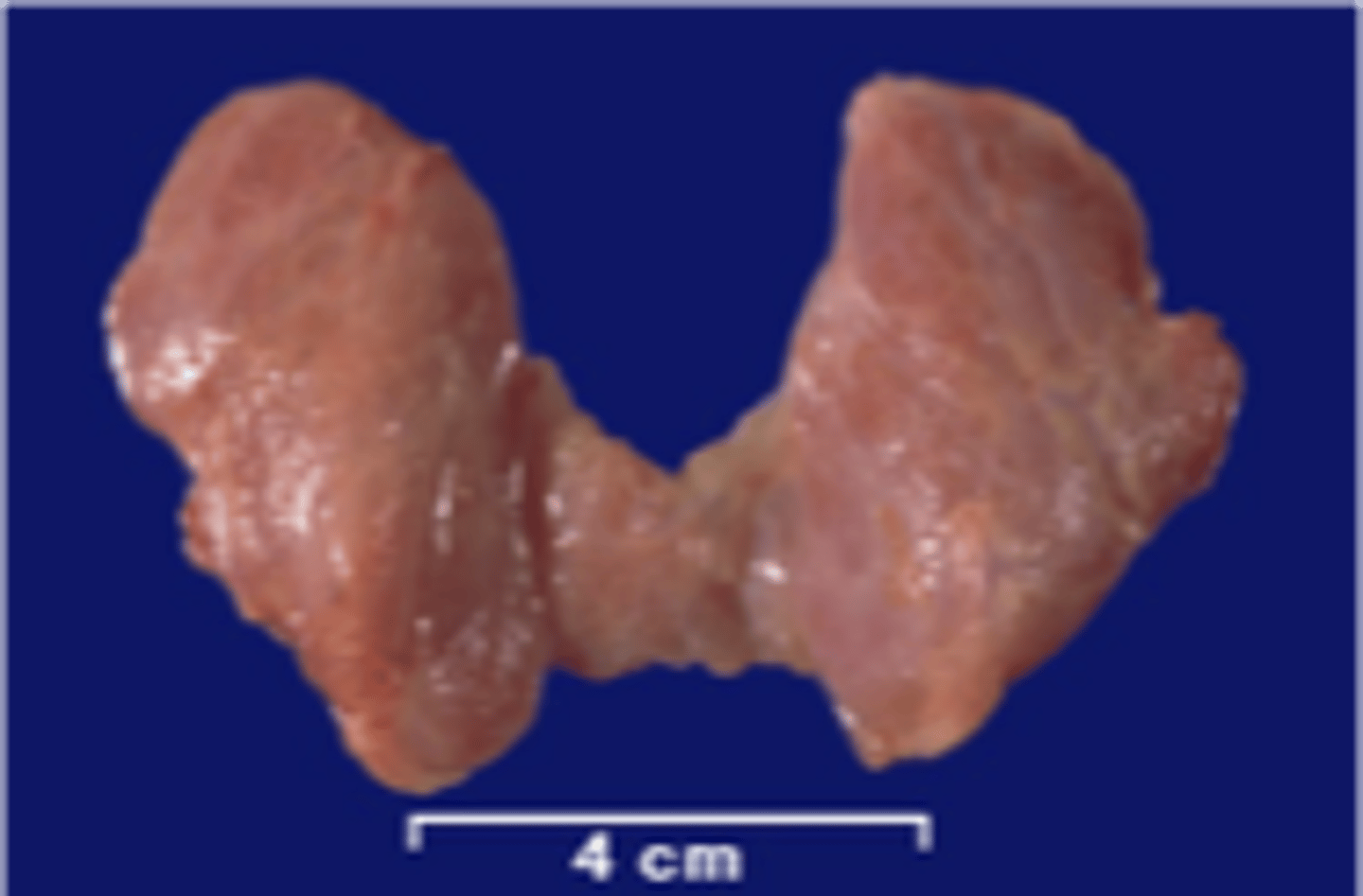
what is the largest endocrine gland in the body?
platysma m.
sternothyroid m.
sternohyoid m.
what 3 muscles must be reflected to view the thyroid gland?
cricothyroid m.
the thyroid gland lies posterior to all these muscles except:
-platysma m.
-cricothyroid m.
-sternothyroid m.
-sternohyoid m.
thyroid gland
produces T3, T4 & calcitonin in the body:
T3, T4
hormone that regulates metabolism:
calcitonin
hormone that regulates calcium levels:
Thyroid gland
Identify the structure
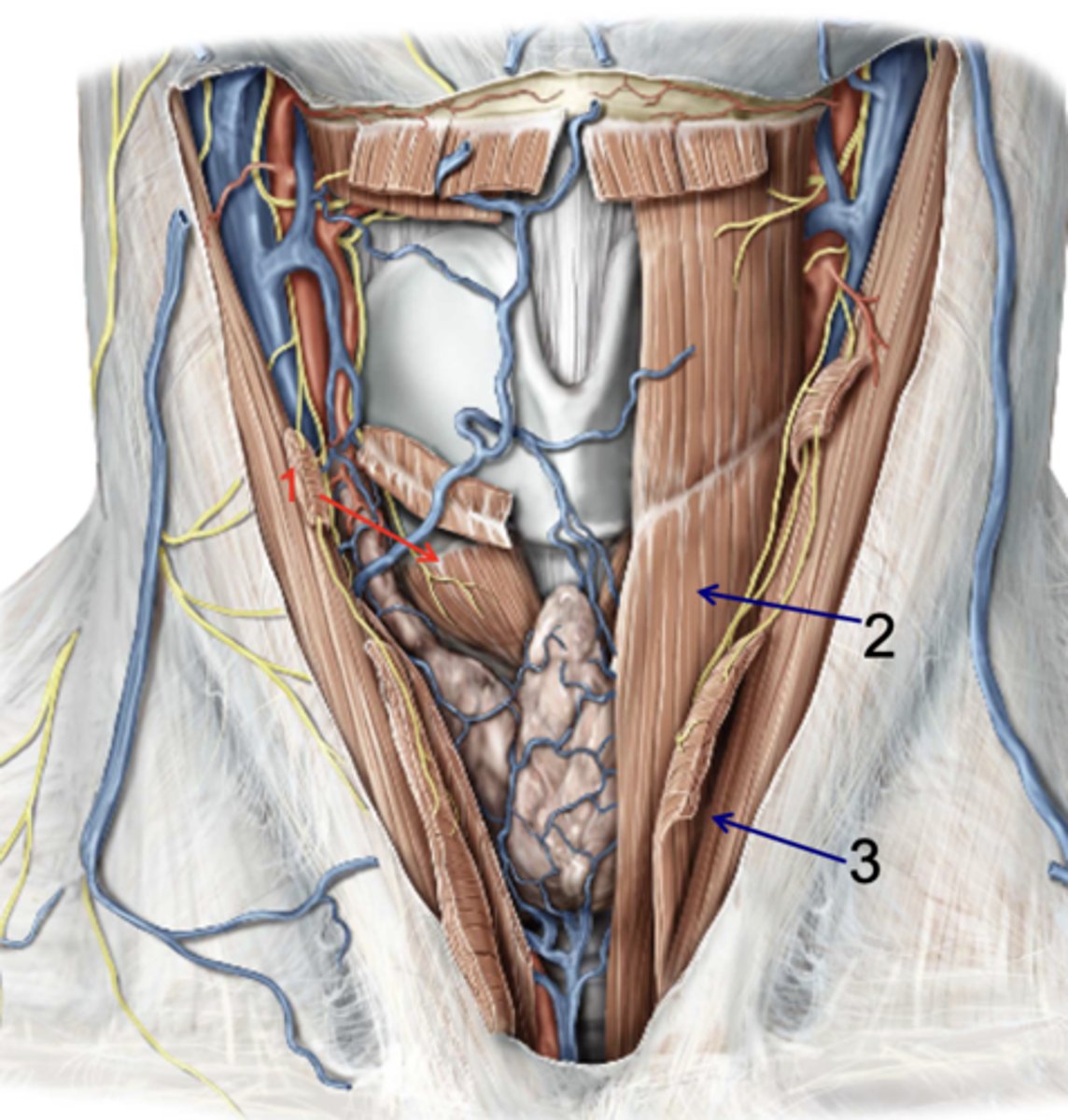
Cricothyroid
Identify the structure at #1
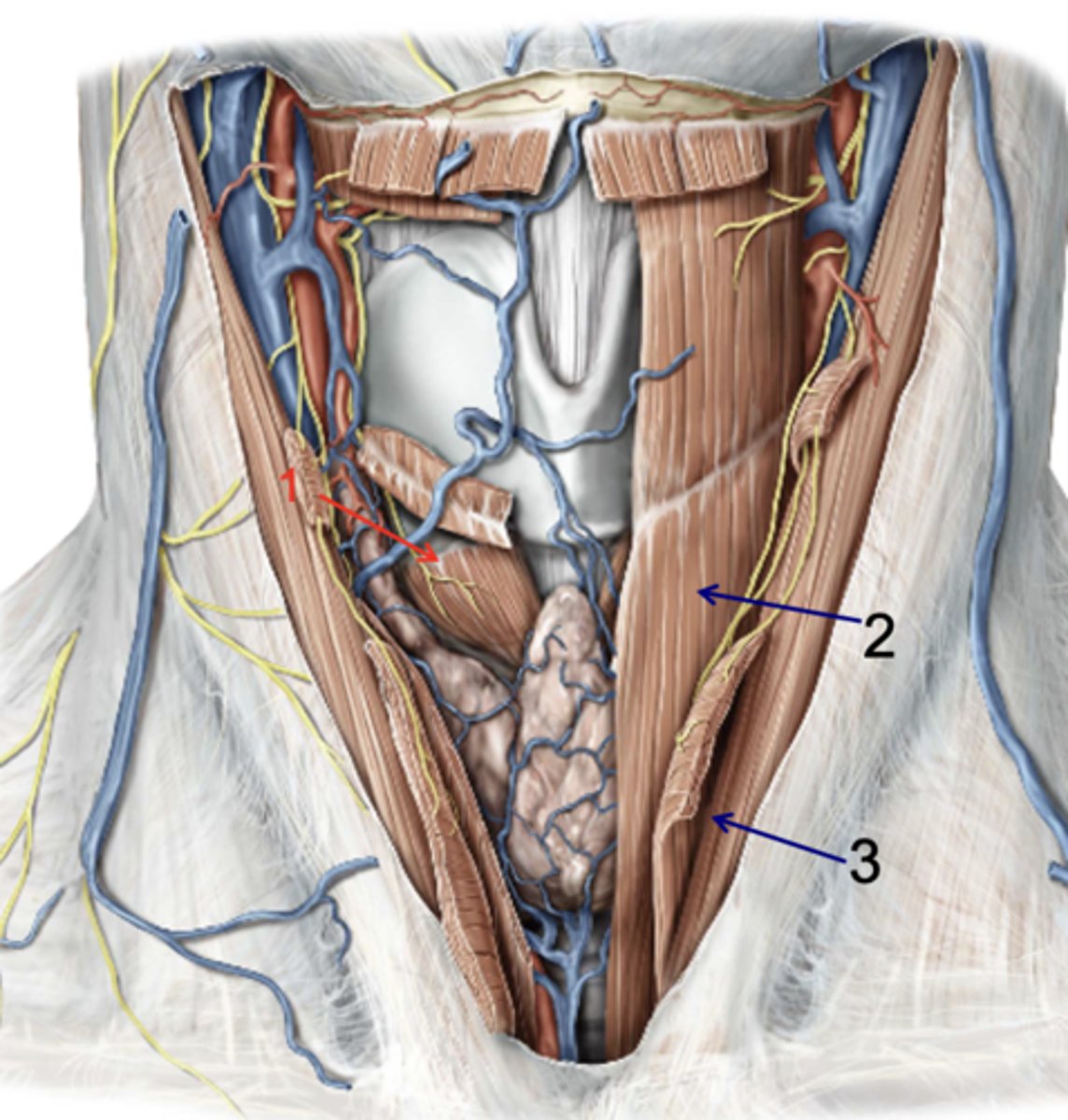
Sternothyroid
Identify the structure at #2
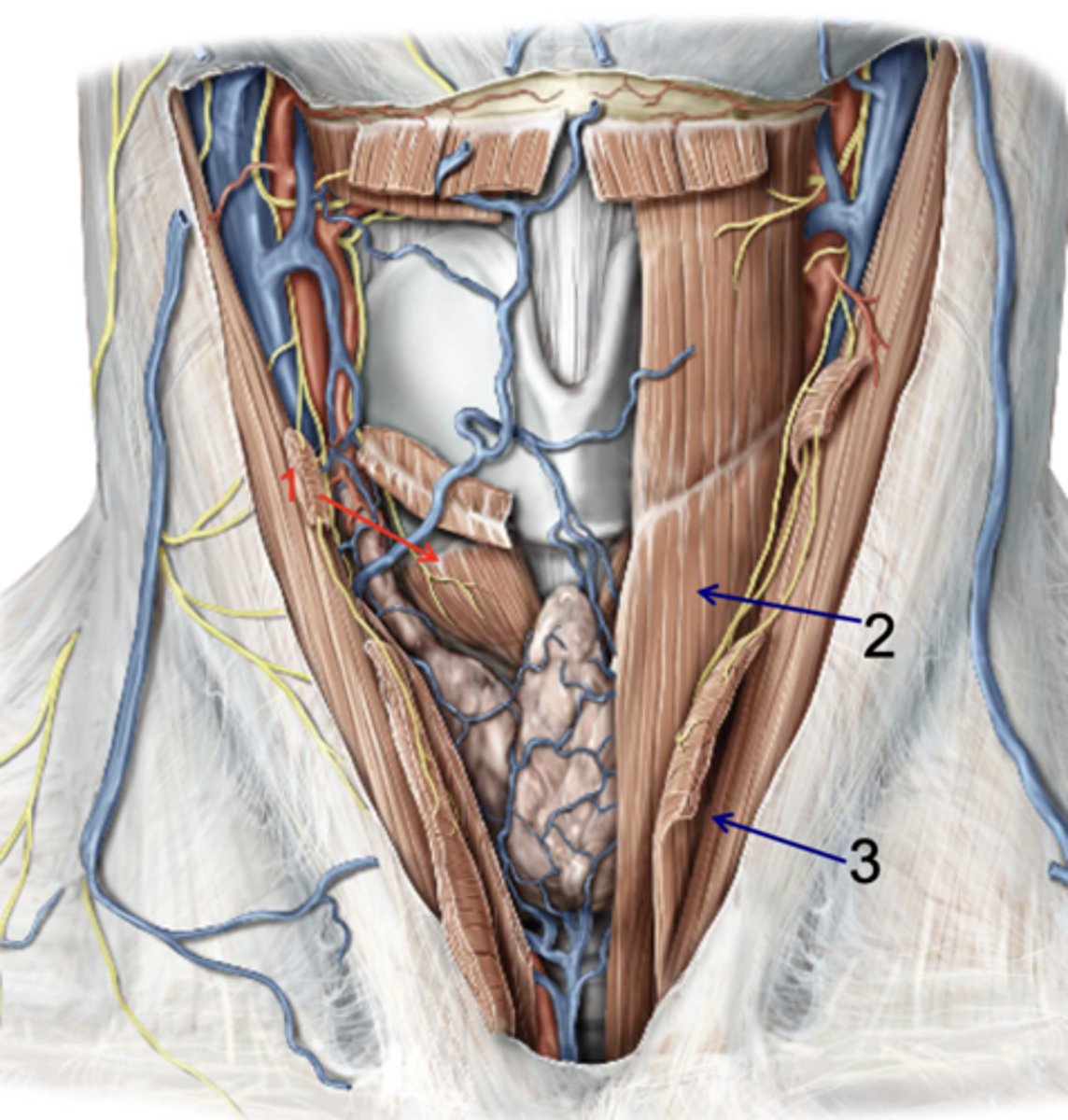
Sternohyoid
Identify the structure at #3
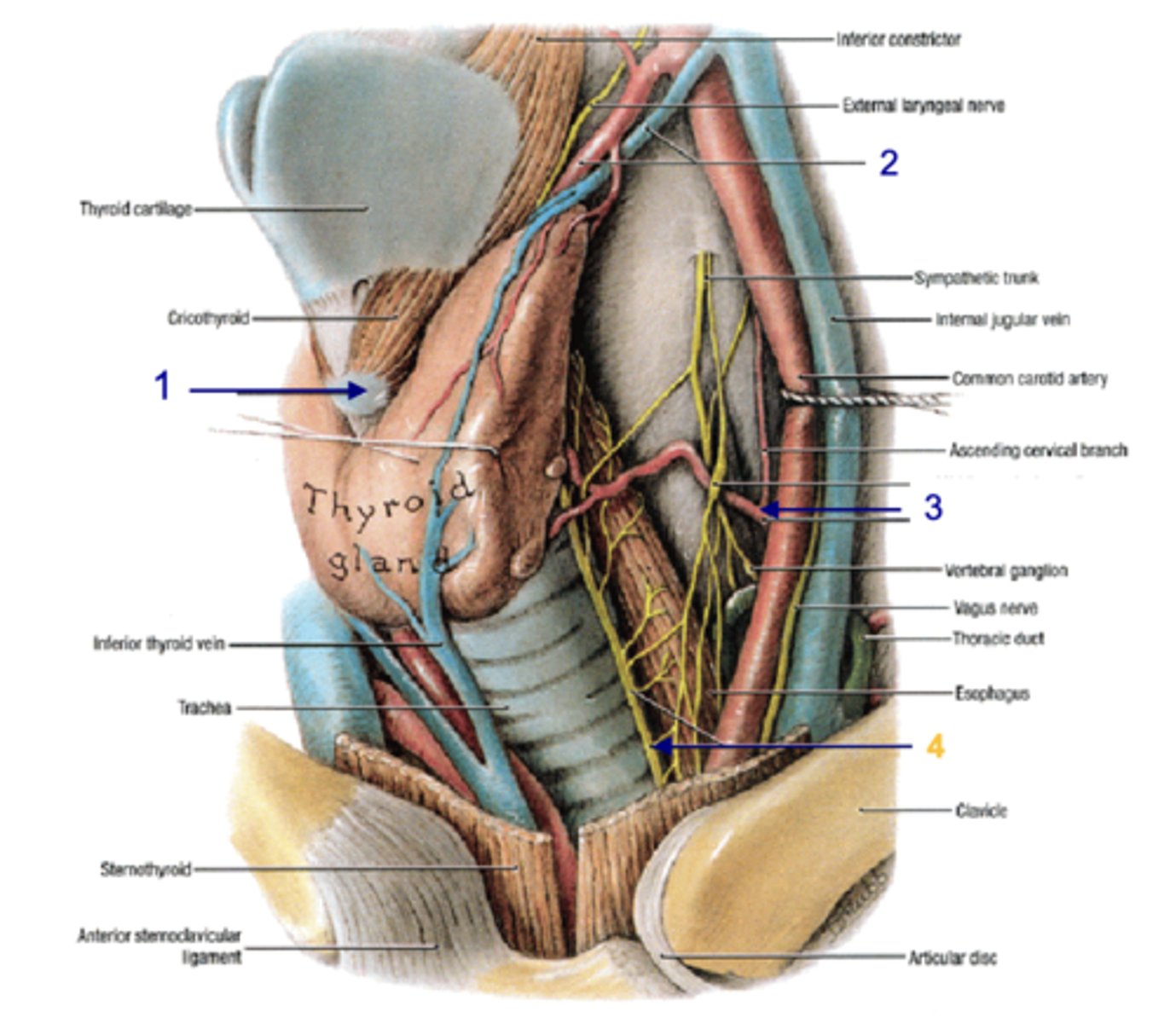
common carotid a.
the thyroid lies medial to what artery?
internal jugular v.
the thyroid lies medial to what vein?
vagus n.
the thyroid lies medial to what nerve?
external carotid a.
the superior thyroid artery is a branch of the:
thyrocervical trunk
the inferior thyroid artery is a branch of the:
brachiocephalic trunk
the thyroid ima artery is a branch of the:
isthmus
the thyroid ima artery supplies the _______
Trachea
Esophagus
The thyroid gland is anterior and lateral to what structures?
Common carotid a.
Identify the structure at #1
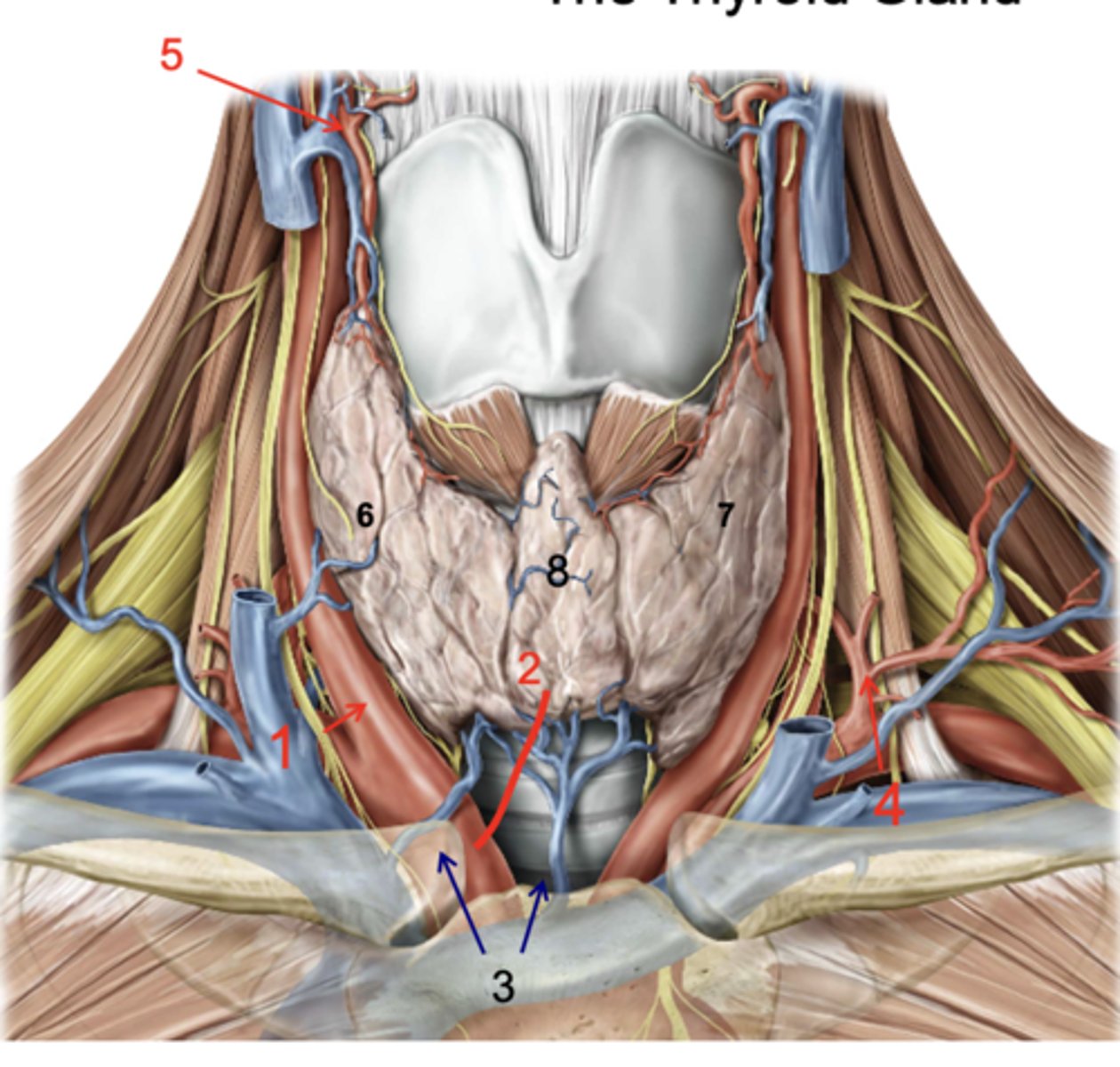
Thyroid ima a.
Identify the structure at #2
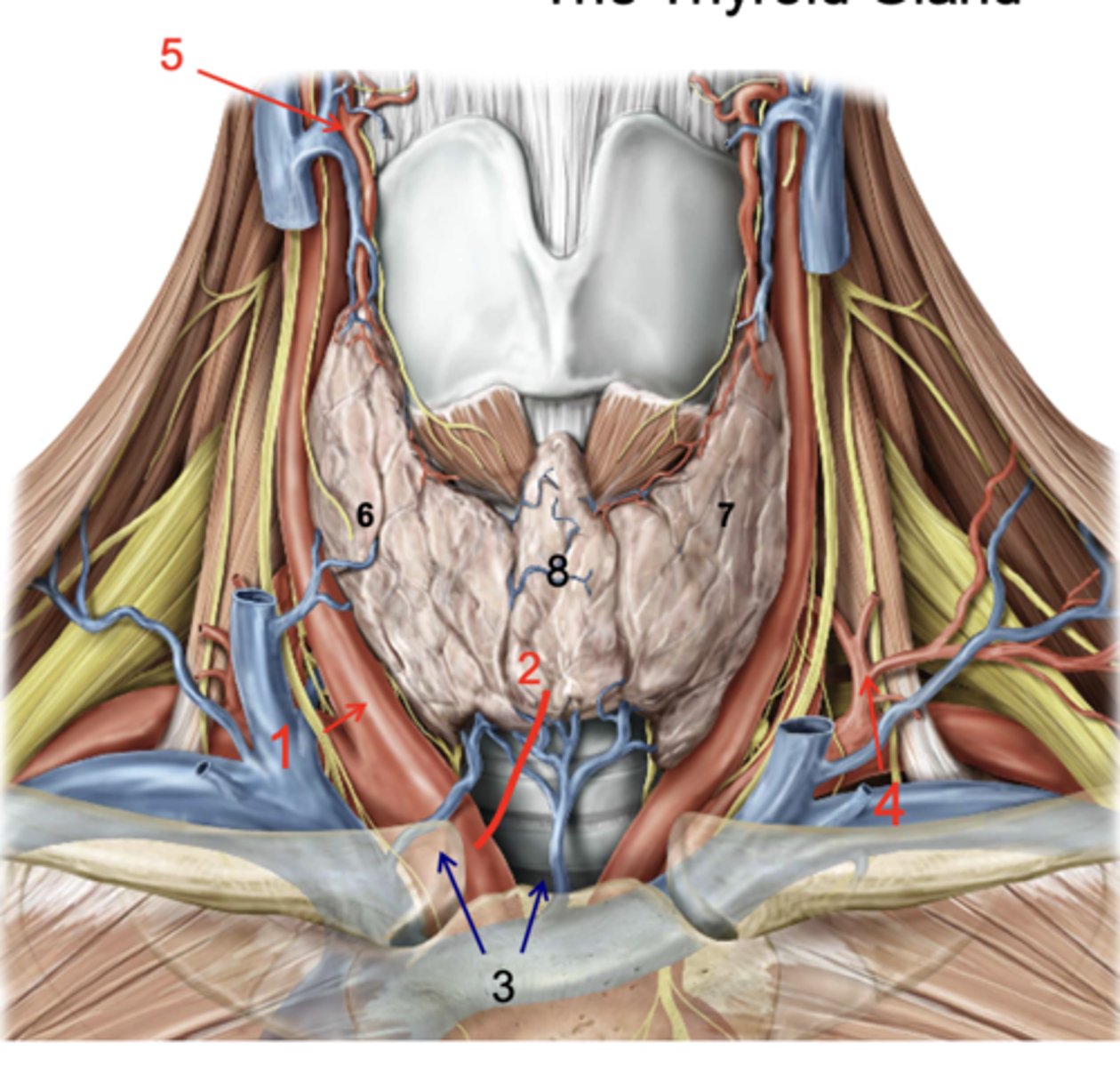
Inf. thyroid vv.
Identify the structure at #3
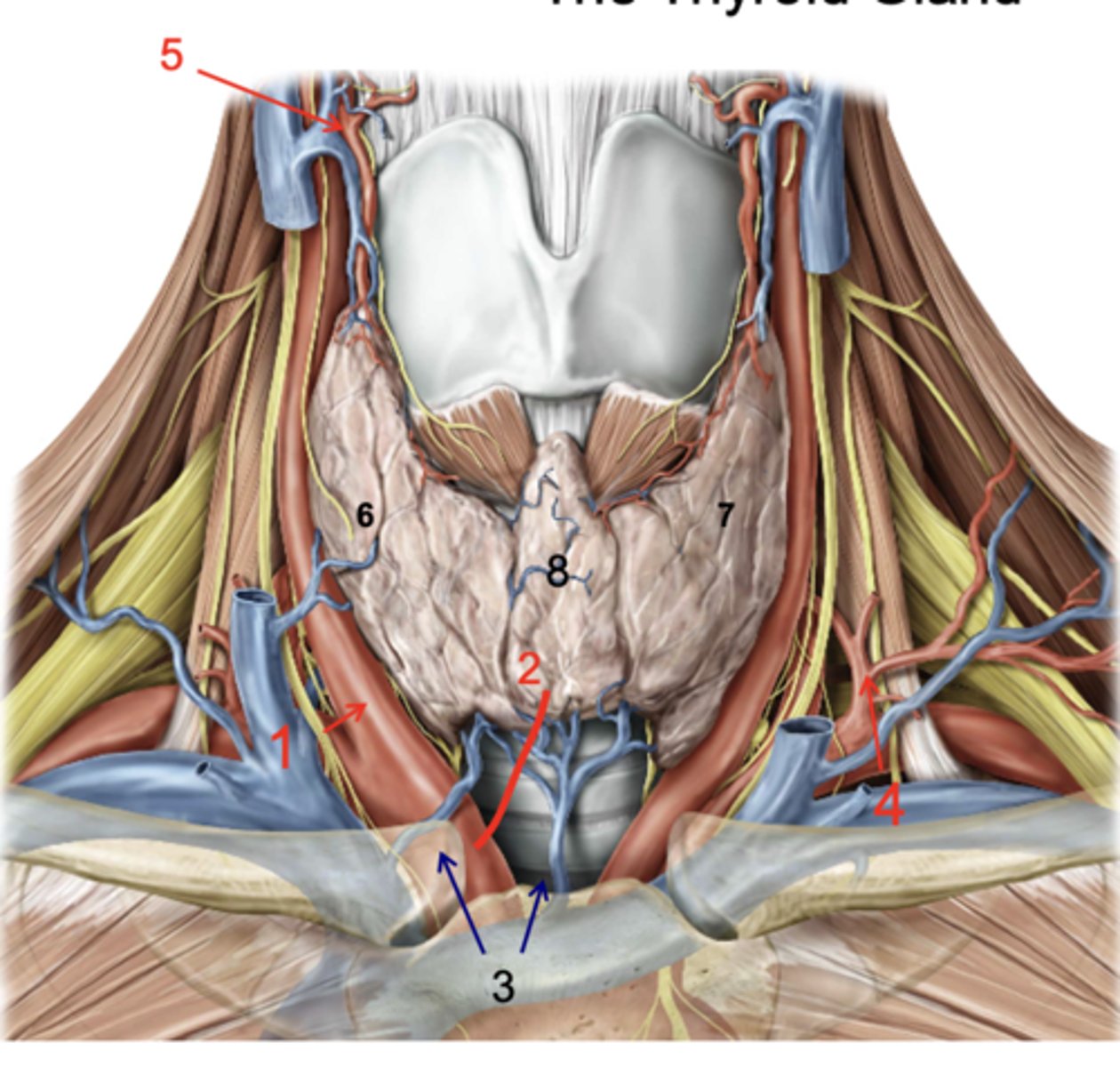
Inferior thyroid a.
Identify the structure at #4
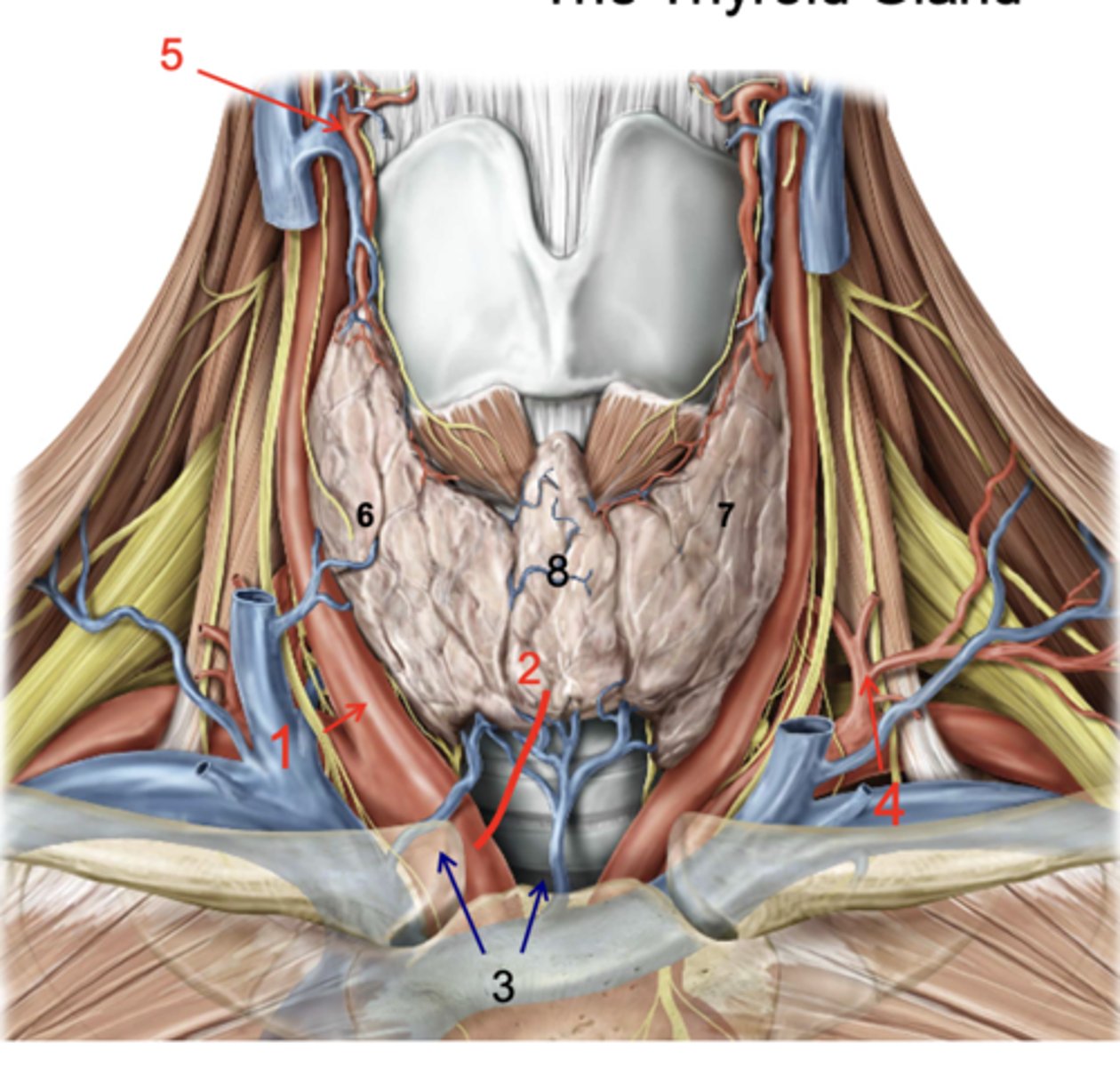
Superior thyroid a.
Identify the structure at #5
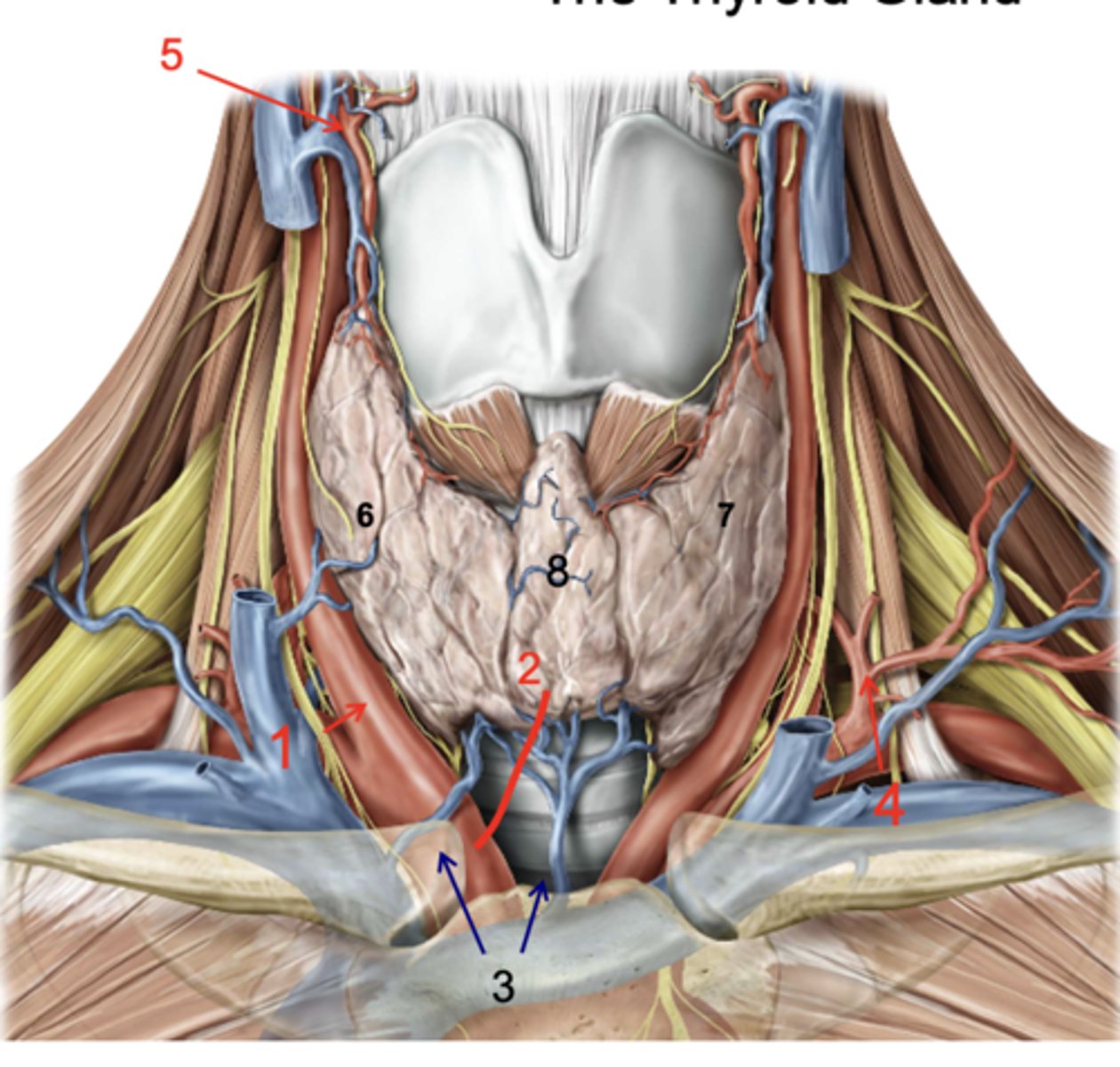
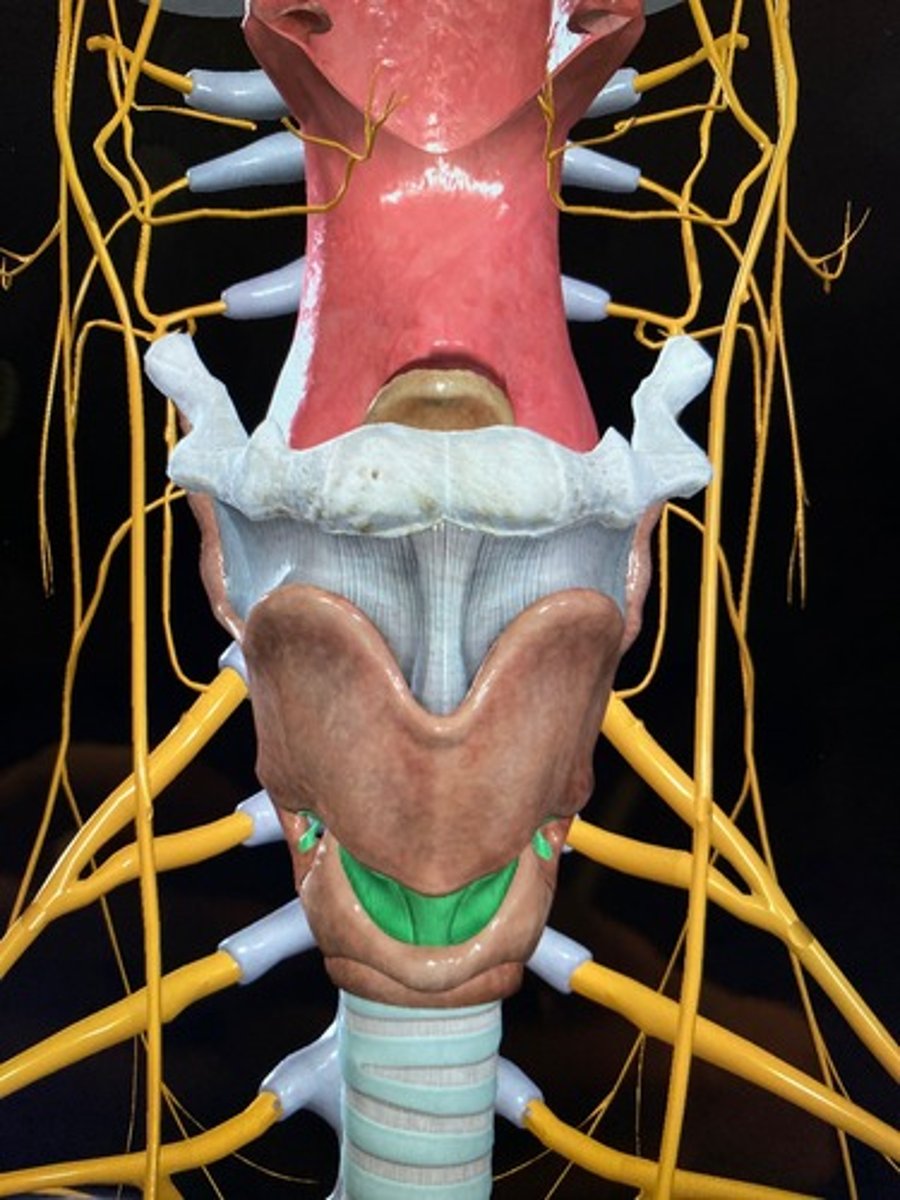
Right lobe of thyroid gland
Identify the structure at #6
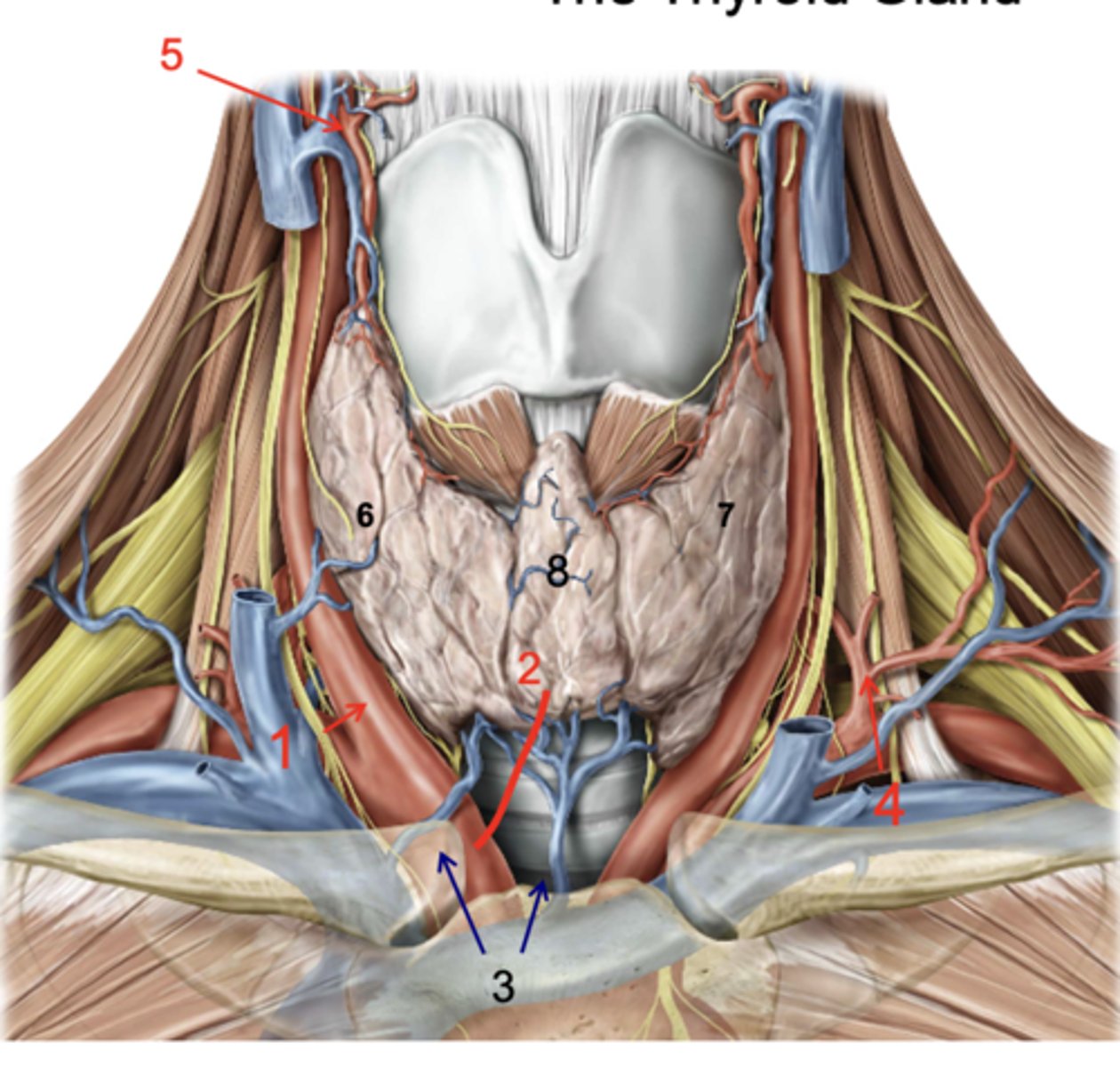
Left lobe of thryoid gland
Identify the structure at #7
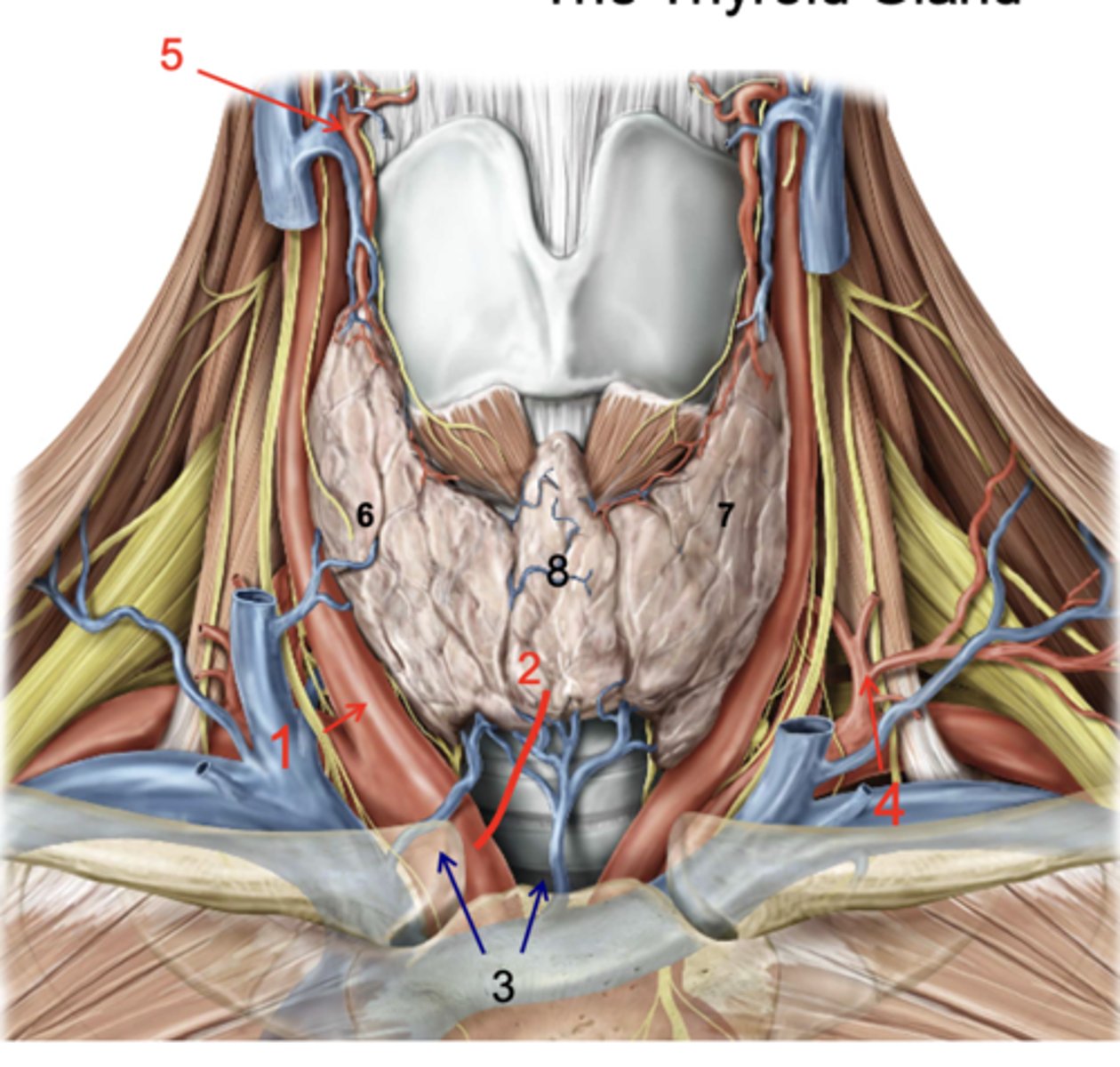
Isthmus
Identify the structure at #8
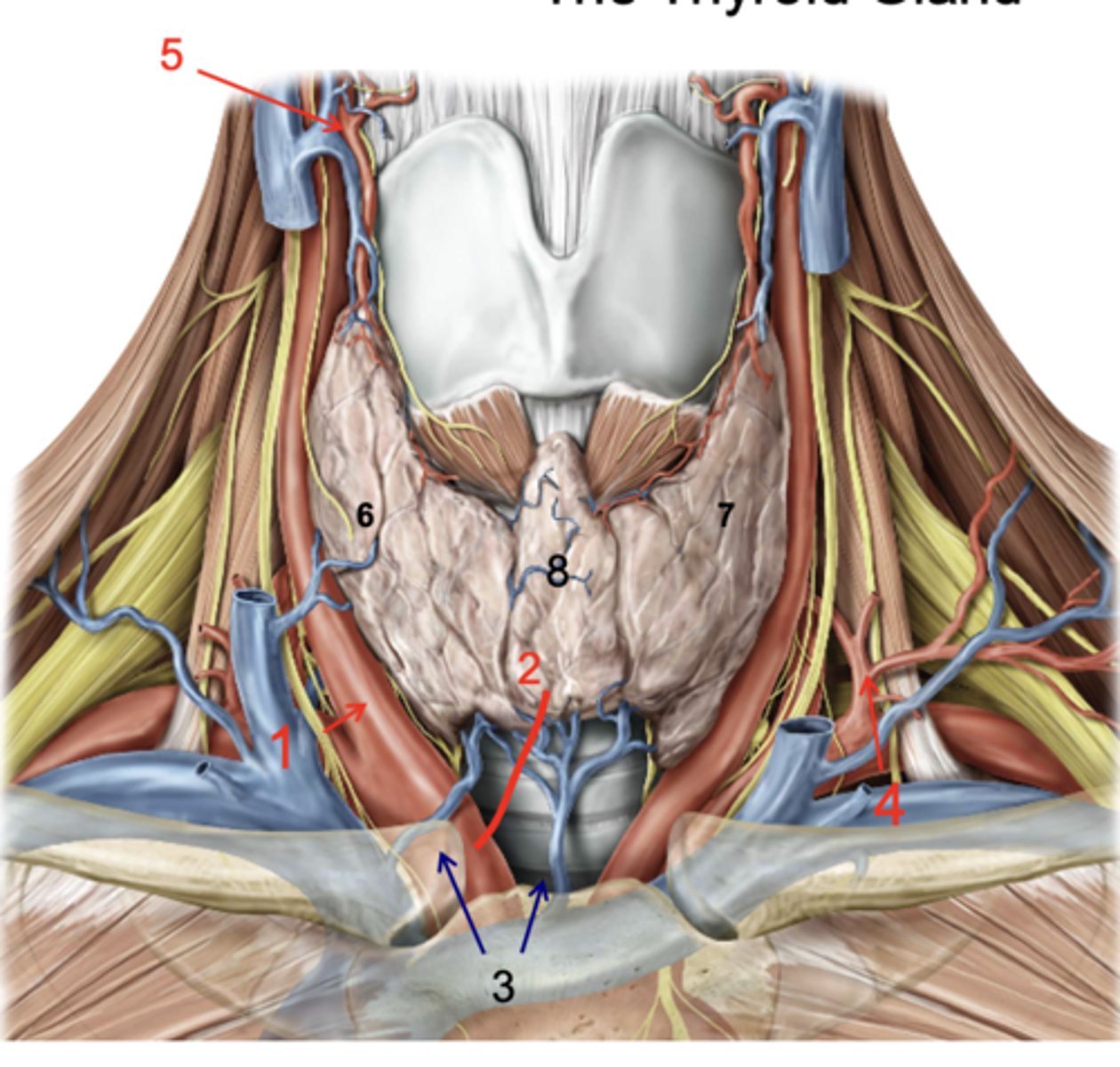
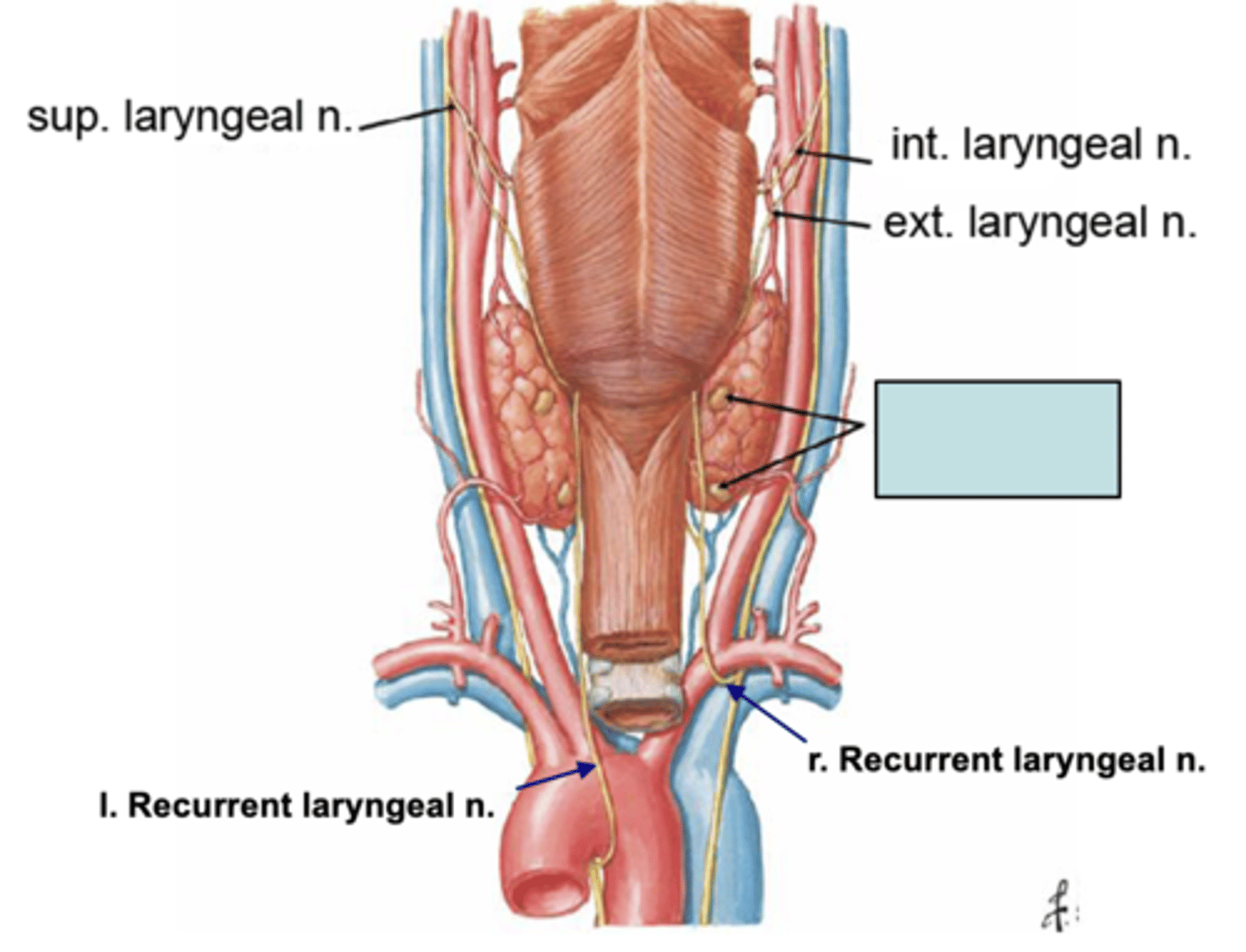
recurrent laryngeal n.
what structure runs in the groove between the trachea and the esophagus?
inferior thyroid a.
patient presents with the inability to speak after a thyroid removal surgery. You know that the surgeon must have nicked the recurrent laryngeal n. What artery was the surgeon ligating when he cut the recurrent laryngeal n.?
Sup. thyroid a.
Identify the structure at #1
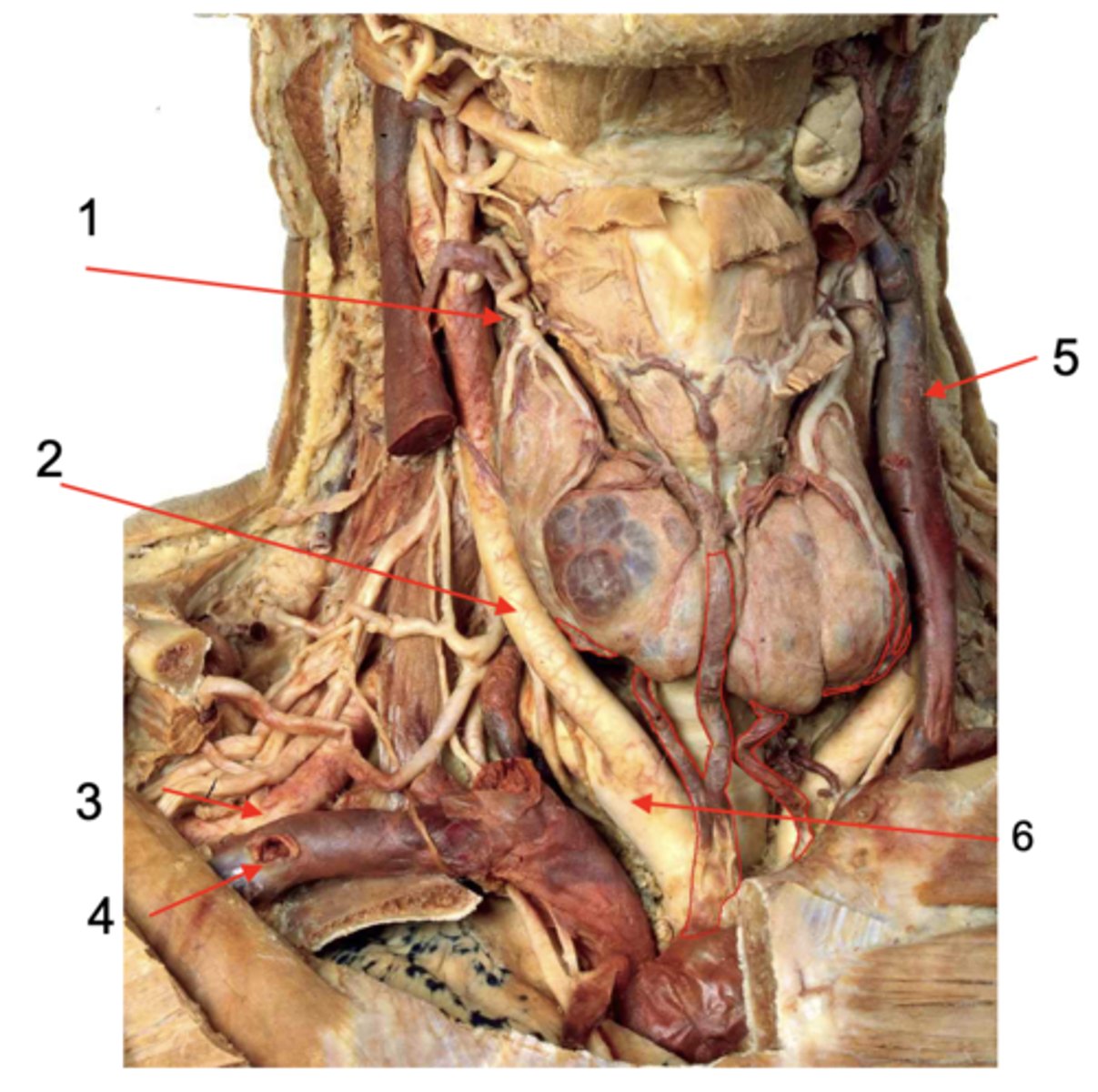
Common carotid a.
Identify the structure at #2
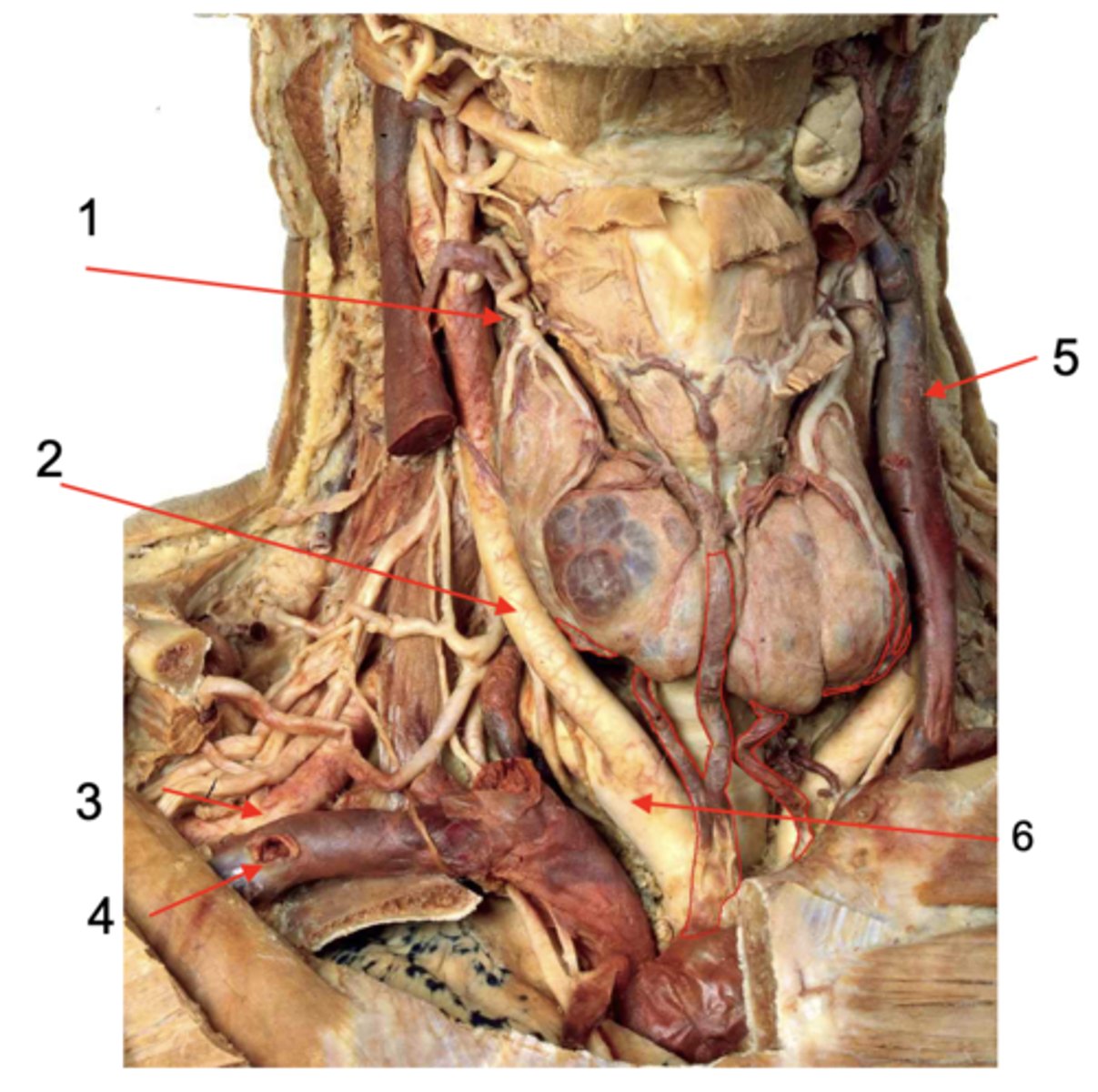
Subclavian a.
Identify the structure at #3
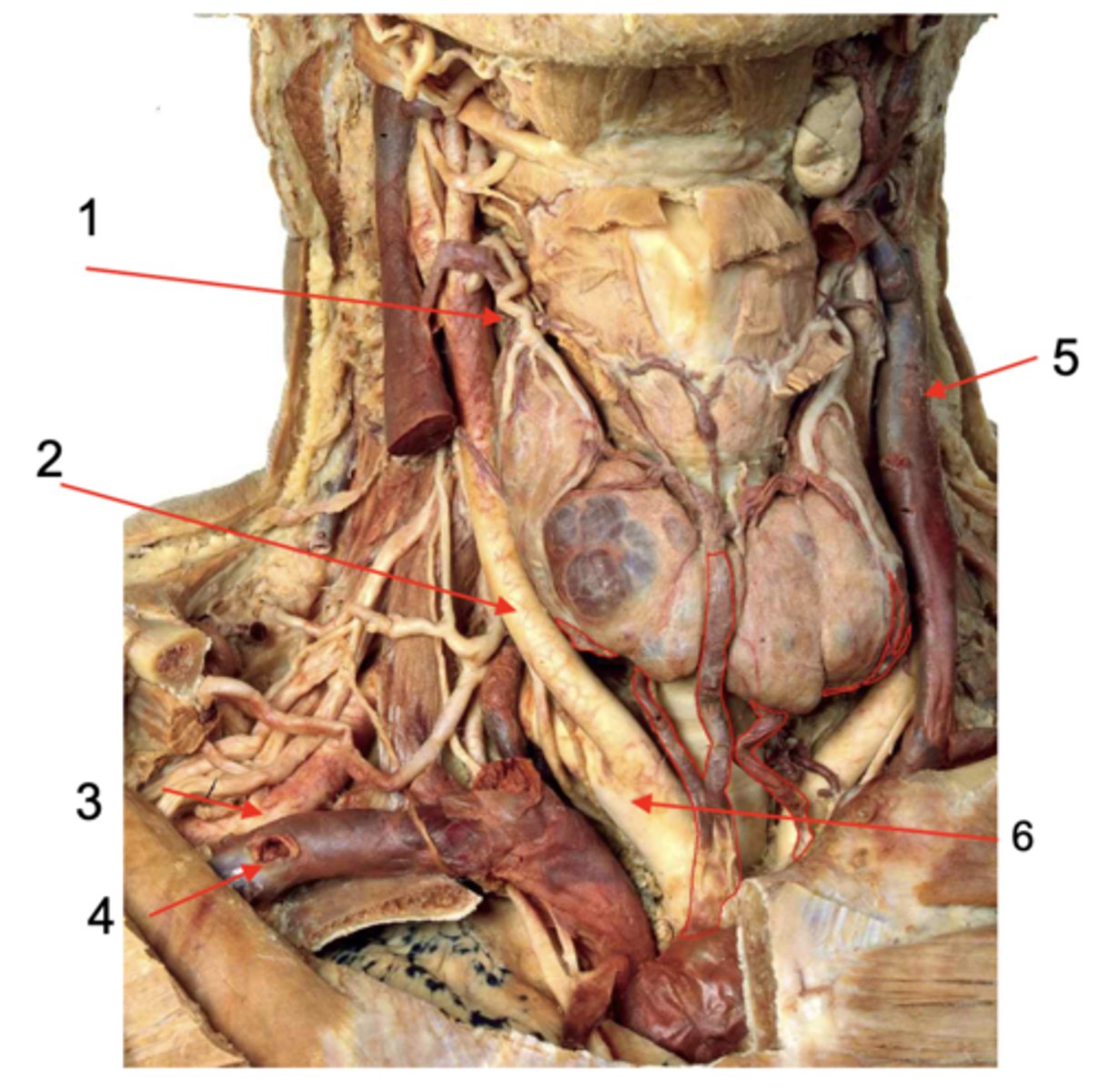
Subclavian v.
Identify the structure at #4
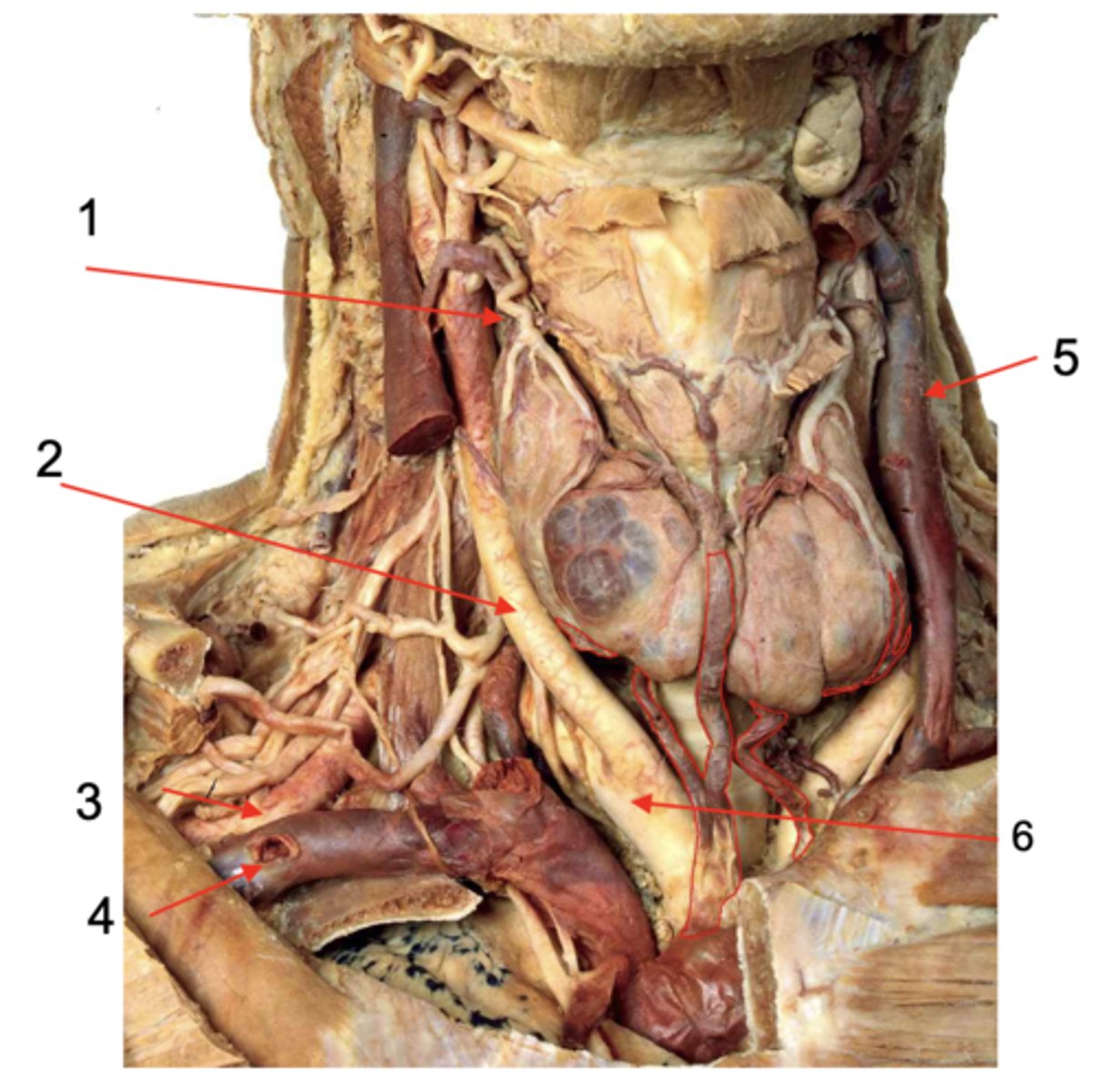
Internal jugular v.
Identify the structure at #5
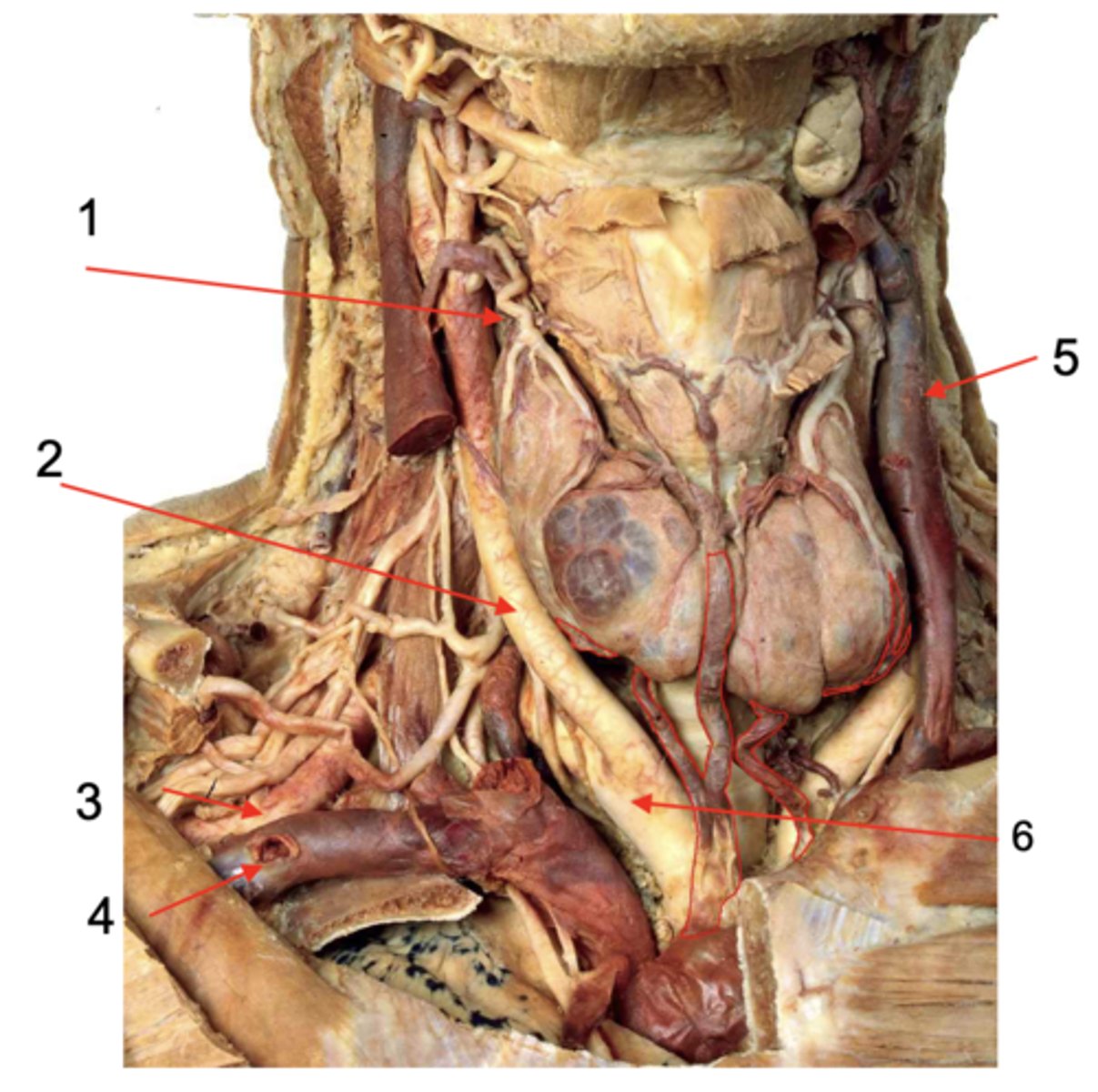
Brachiocephalic trunk
Identify the structure at #6
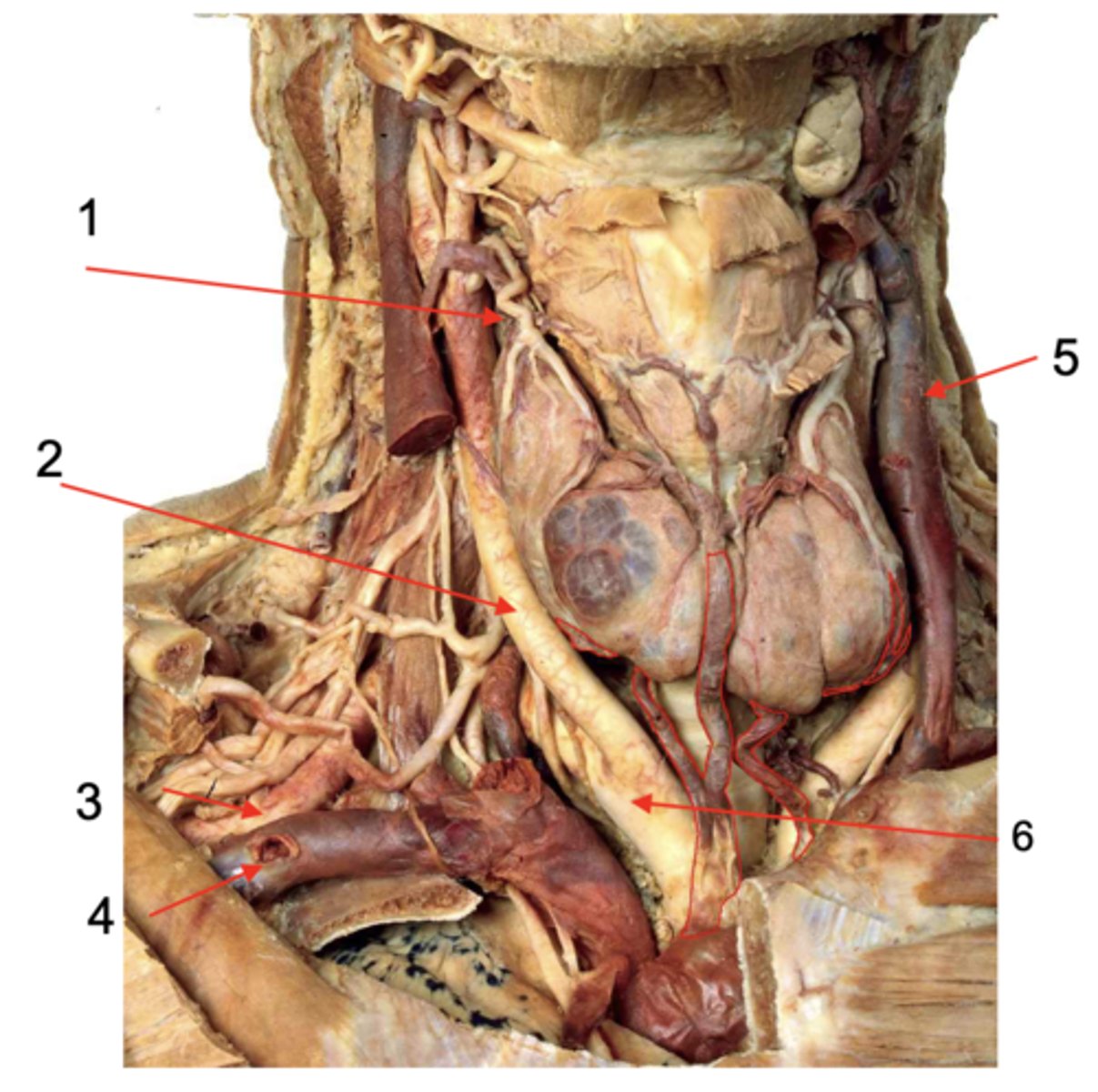
Cricoid cartilage
Identify the structure at #1
Superior thyroid a.
Identify the structure at #2
Inferior thyroid a.
Identify the structure at #3
Left recurrent laryngeal n.
Identify the structure at #4
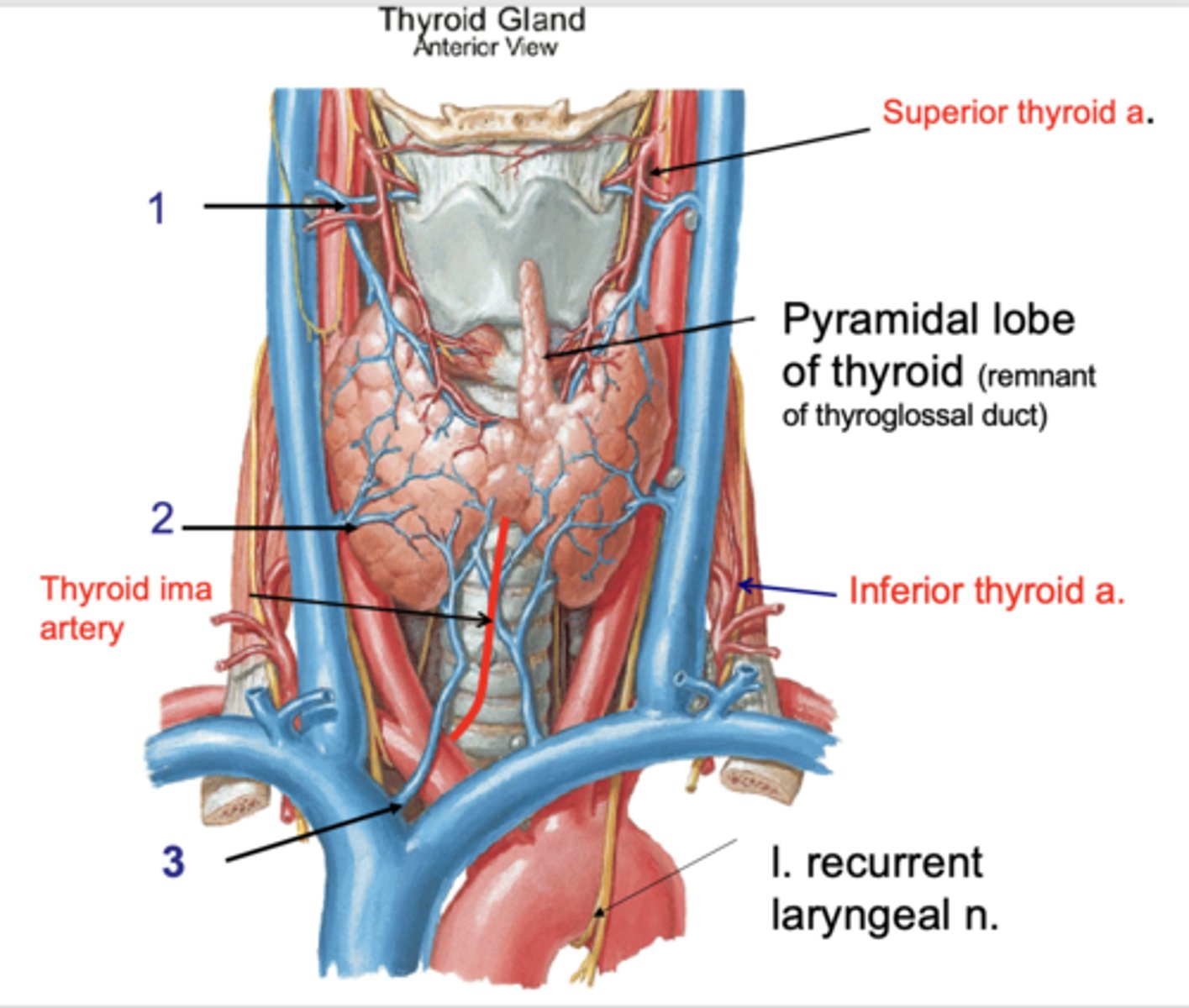
Superior thyroid v.
Identify the structure at #1
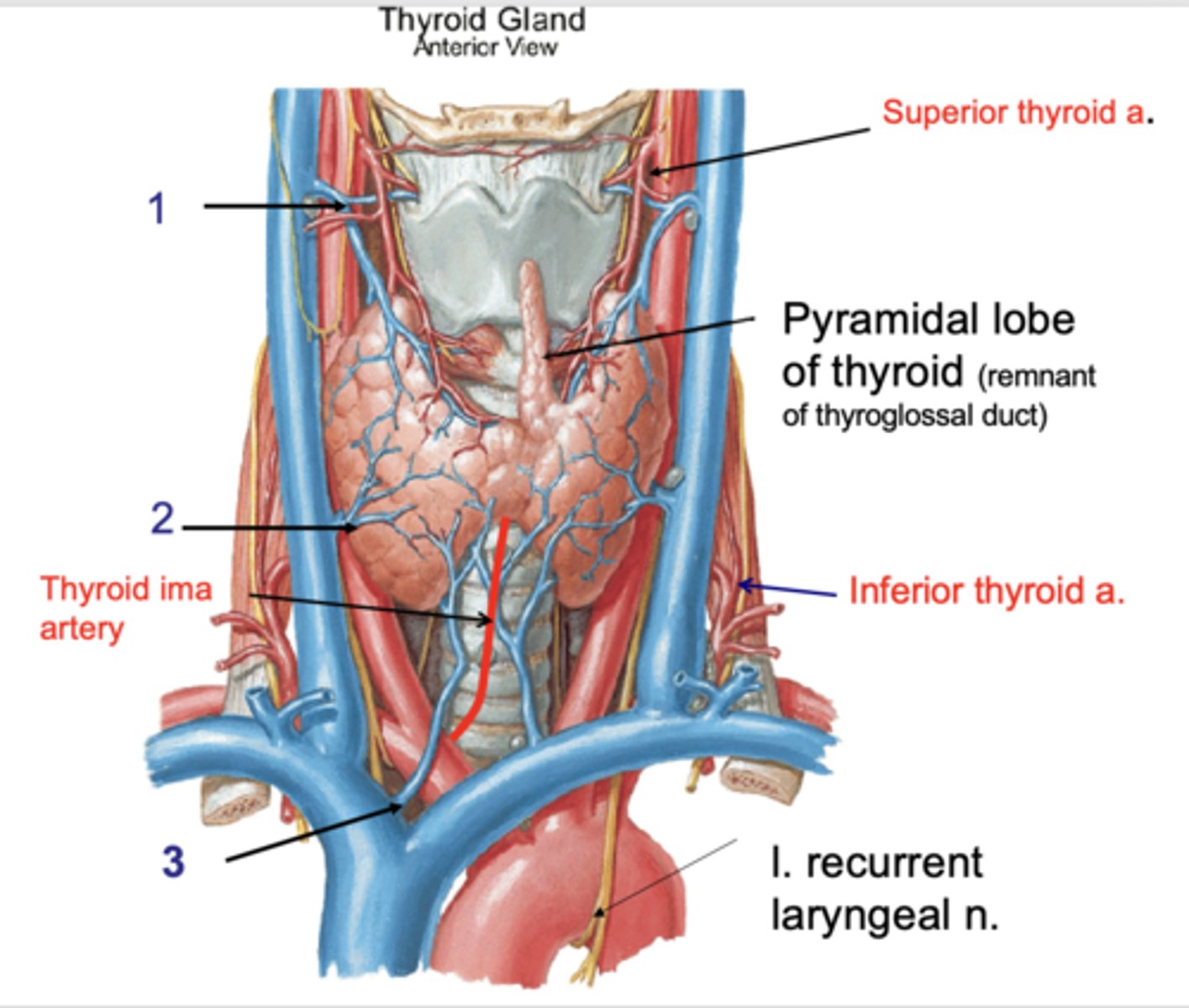
Middle thyroid v.
Identify the structure at #2
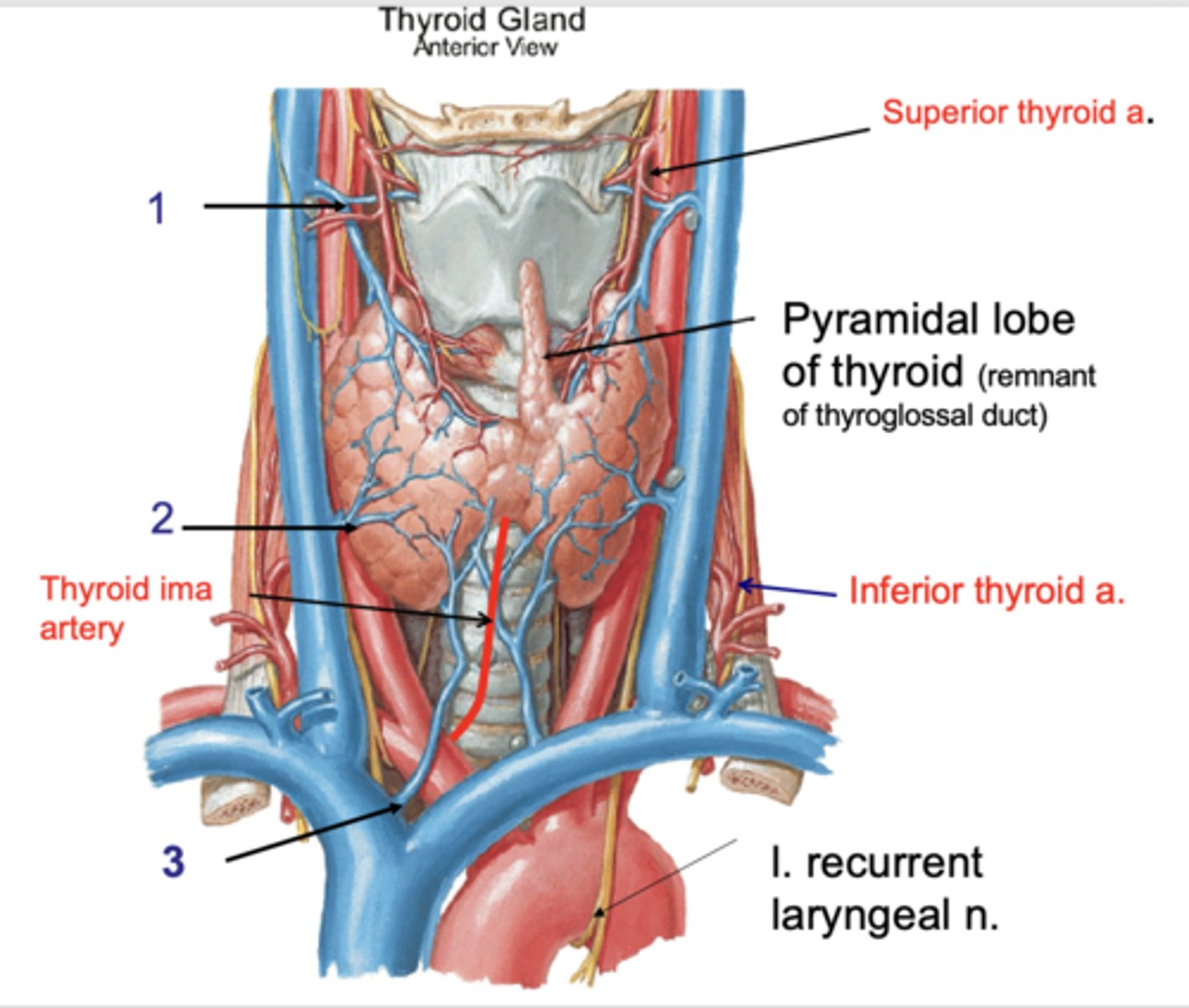
Inferior thyroid v.
Identify the structure at #3
3-4 weeks
At what gestational age does the thyroid gland first appear in the embryo?
At the base of the tongue
Where does the thyroid gland initially develop in the embryo?
Thyroglossal duct
Which structure connects the thyroid gland to the tongue during its migration?
It degenerates and disappears
What happens to the thyroglossal duct by the fifth week of development?
Thyroglossal duct
The pyramidal lobe is a vestigial remnant of which structure?
internal jugular v.
the superior thyroid vein drains into the:
internal jugular v.
the middle thyroid vein drains into the:
brachiocephalic v.
the inferior thyroid vein drains into the:
Ectopic thyroid
What is the term for a thyroid gland that develops in an abnormal location?
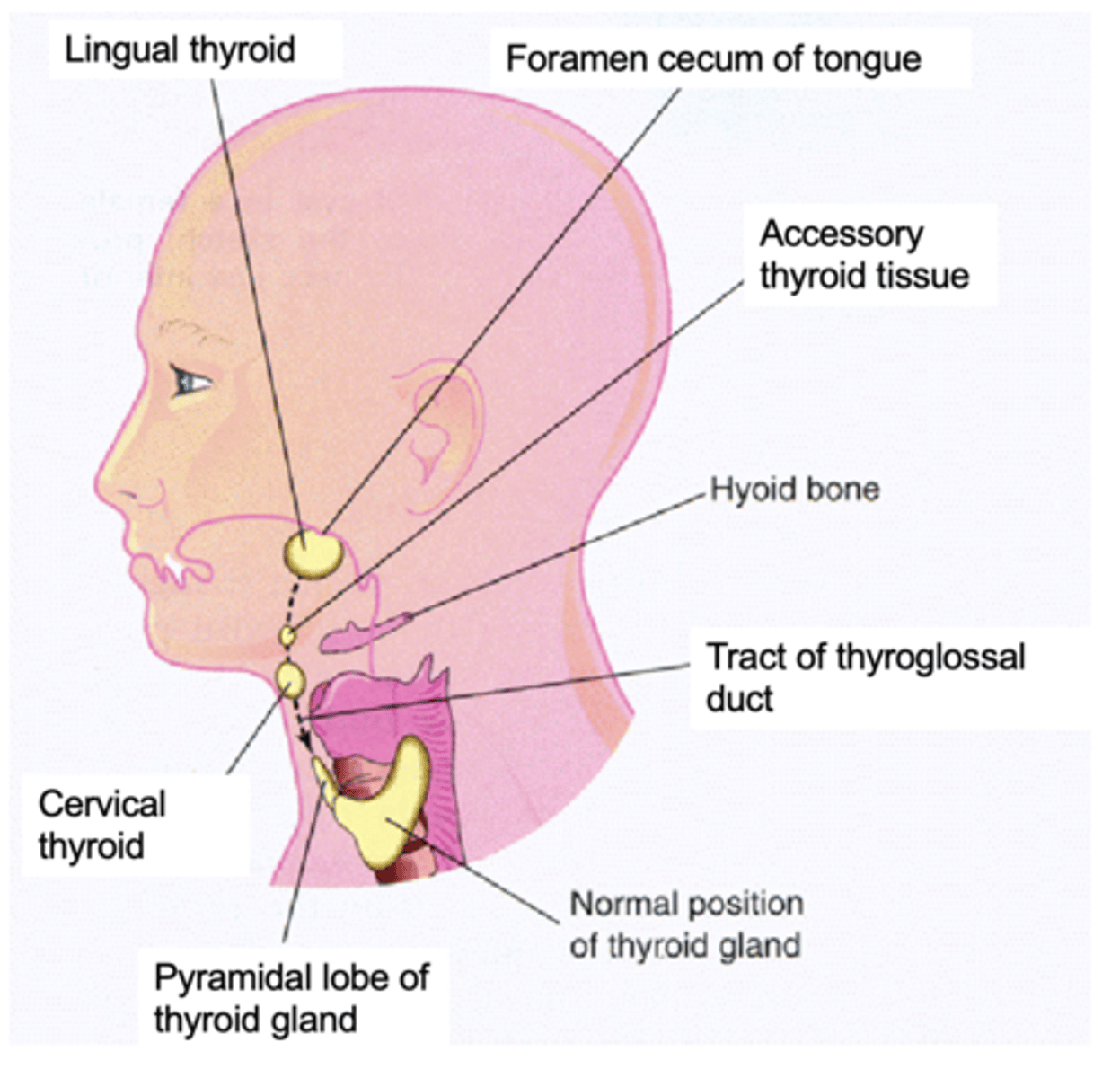
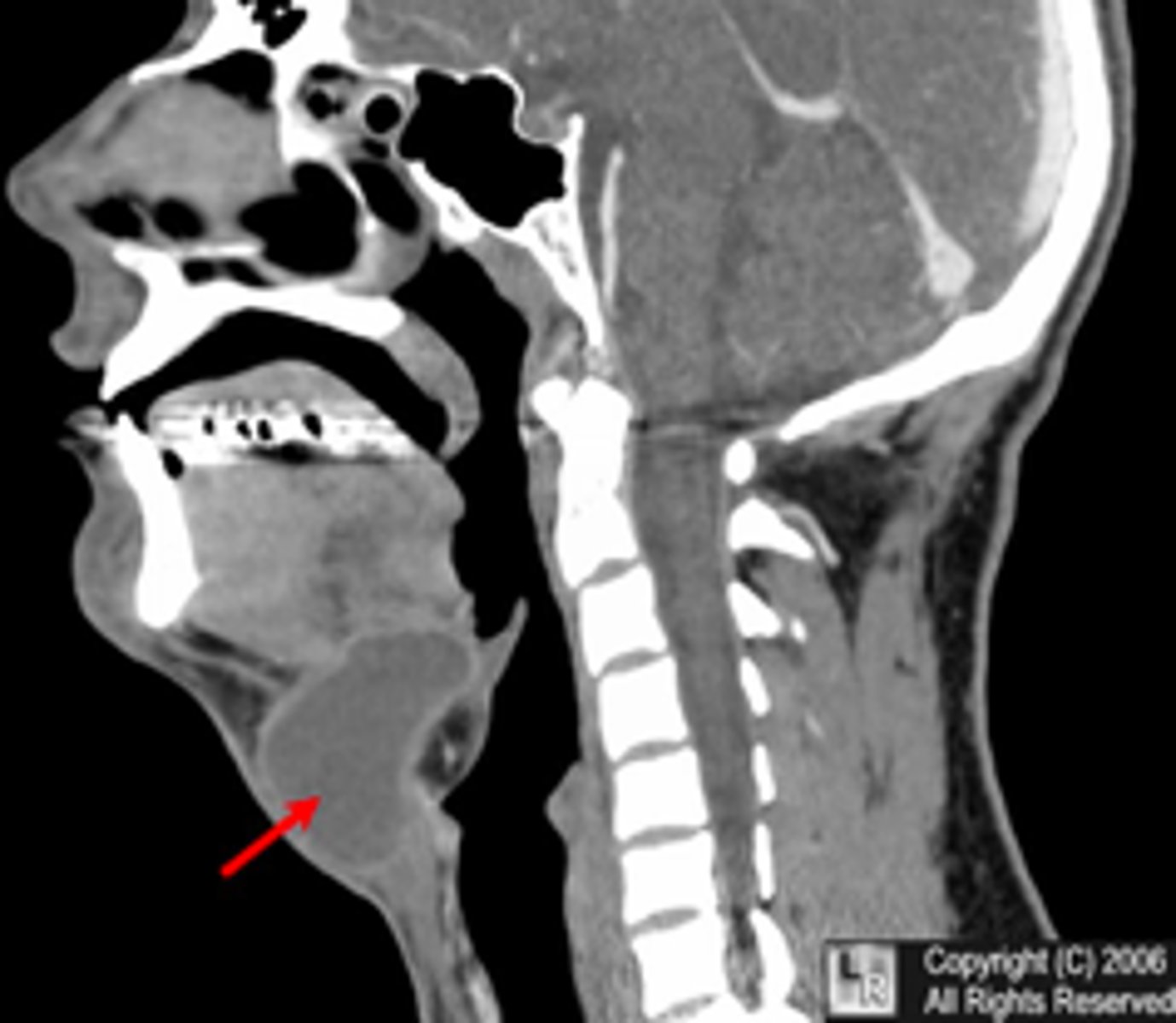
Lingual region
Which of the following is a common location for ectopic thyroid tissue?
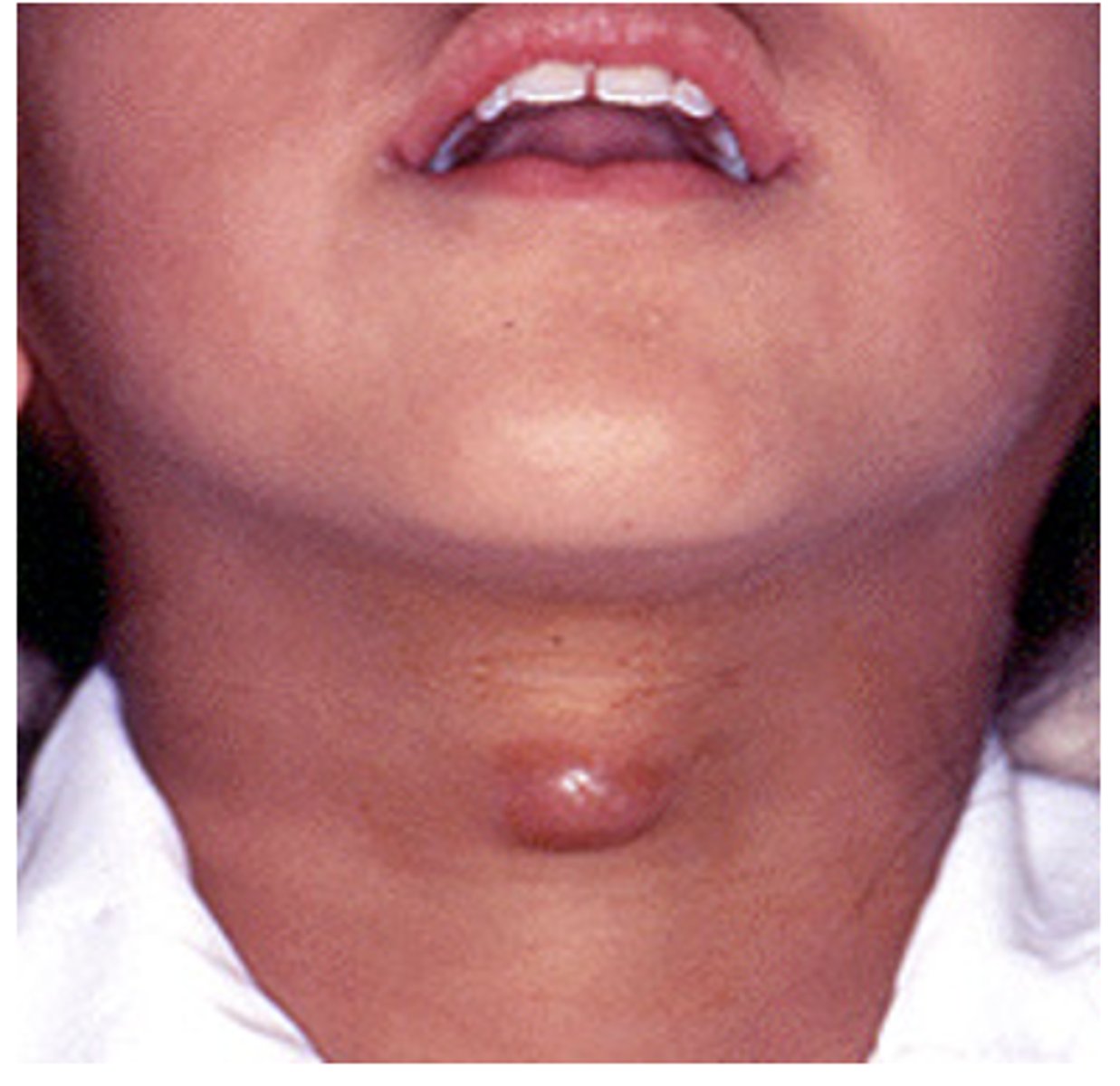
thyroglossal duct cyst
The thyroglossal duct may persist and form a fluid filled cavity called a...
thyroglossal duct cyst
Presents as a painless swelling in the midline near hyoid bone that moves when swallowing. What is the diagnosis?
Sistrunk Procedure – surgical resection of the duct to base of tongue including the body of hyoid bone to ensure complete removal of the duct
What is the treatment for a thyroglossal duct cyst?
Iodine
One of the fundamental ingredients of thyroid hormones T3 and T4
Thyroid Releasing Hormone (TRH) and Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) in the hypothalmus and pituitary gland.
The thyroid gland is stimulated to secrete T3, T4 and calcitonin by what hormones?
goiter
patient presents with abnormal enlargement of the neck. Patient experiences swelling in the front of the neck (just below the Adam's apple) feeling of tightness in the throat area and hoarseness. Blood screening shows a normal calcium levels and low iodine levels. What is the diagnosis?
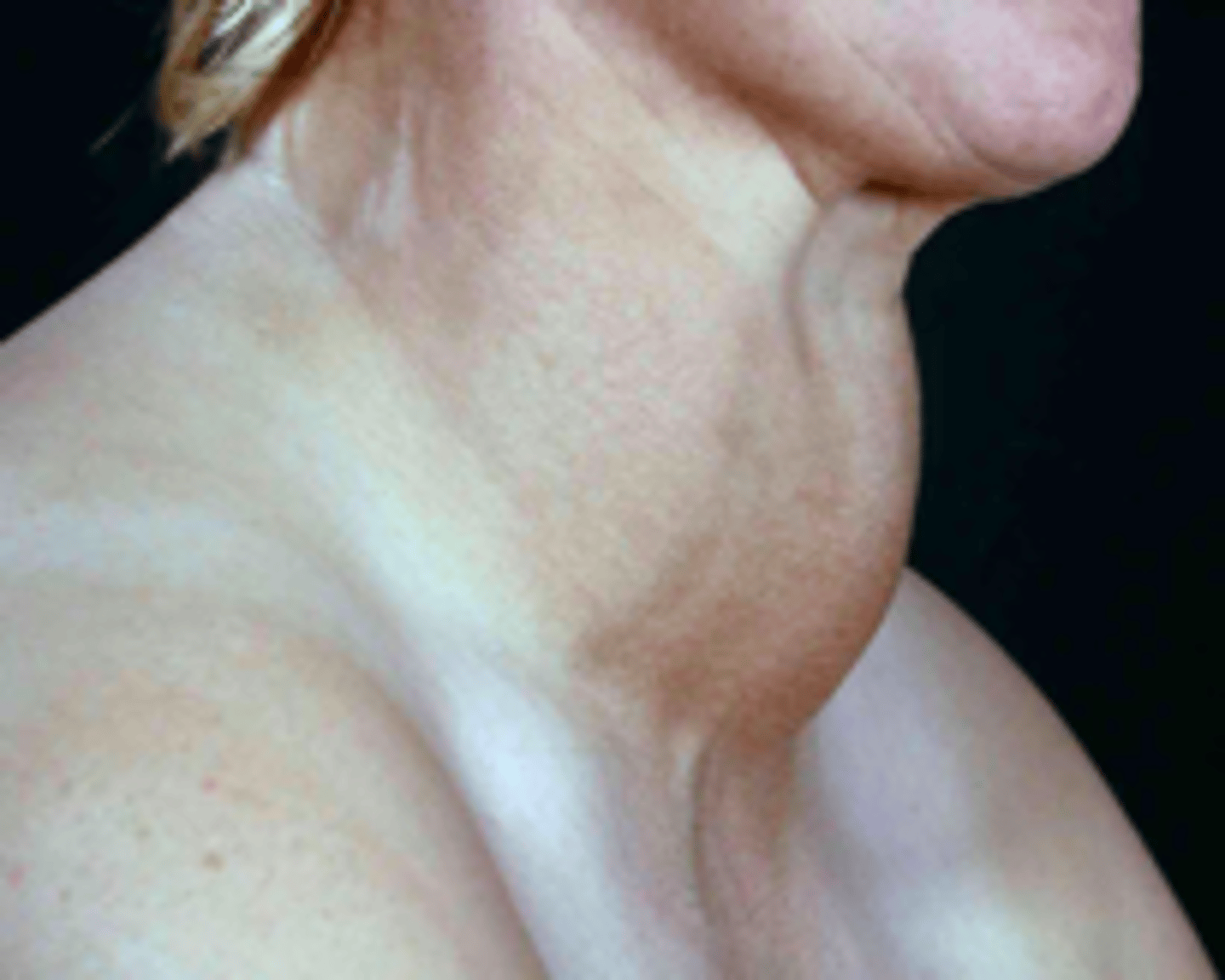
goiter
patient presents with the following CT and X-Ray. What is the diagnosis?
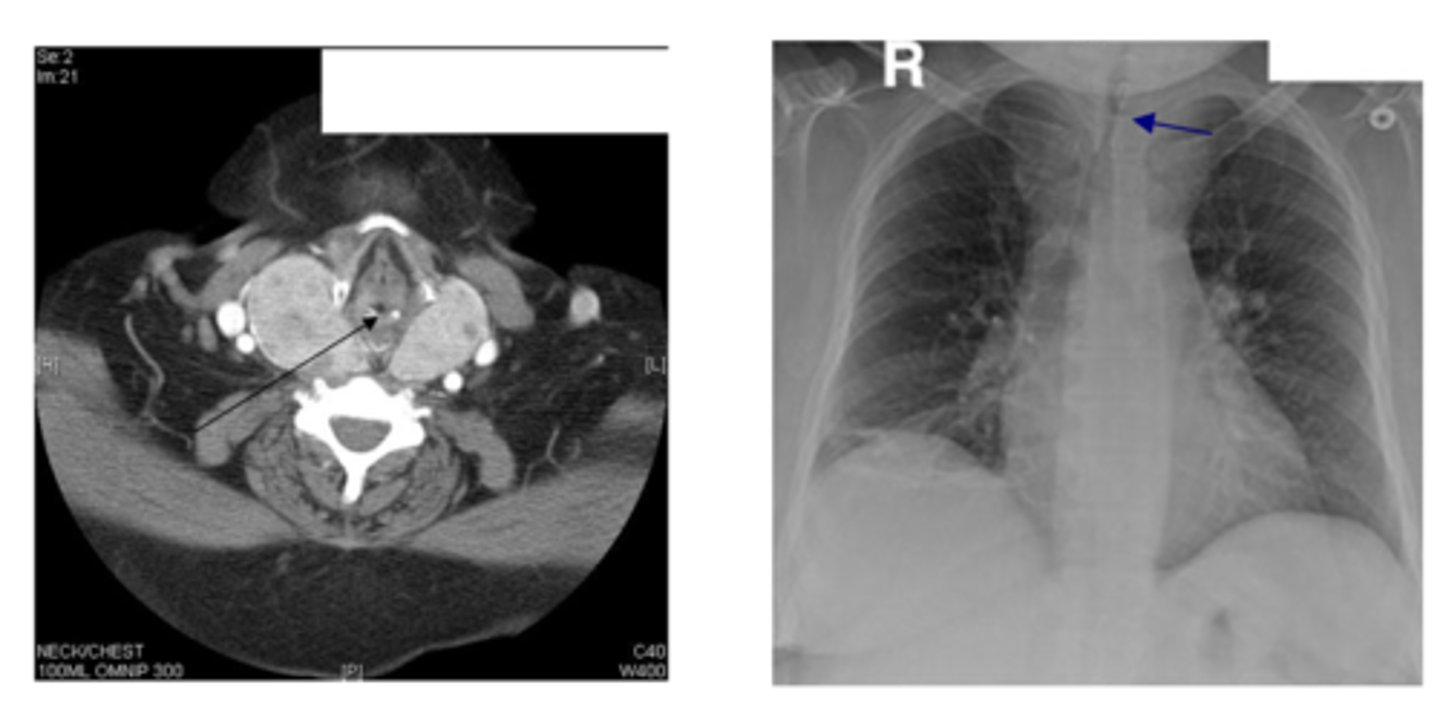
Goiter
In the absence of Iodine, T3 and T4 cannot be produced, and TRH and TSH will increase, causing cells in the thyroid gland to hypertrophy, producing a...
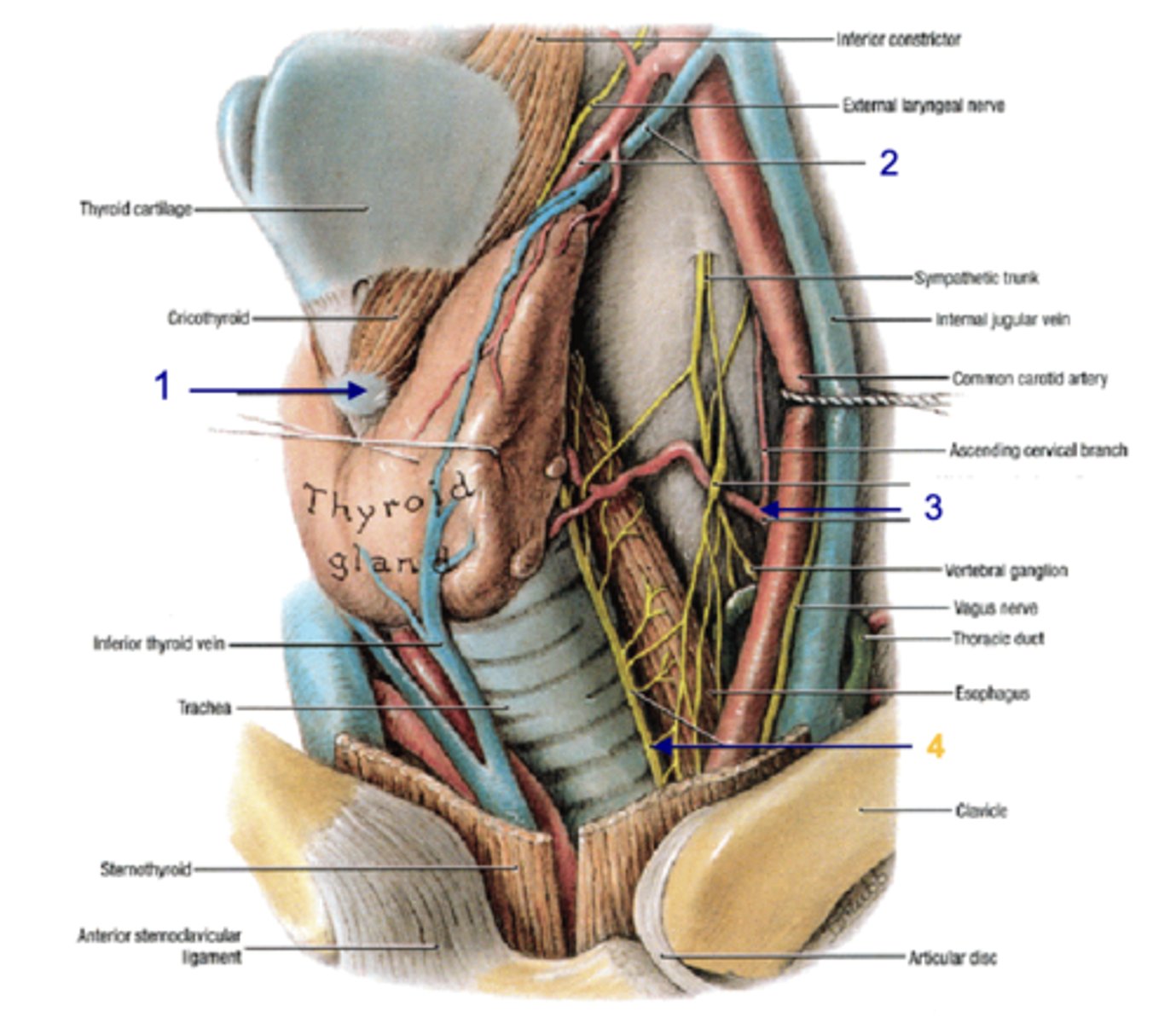
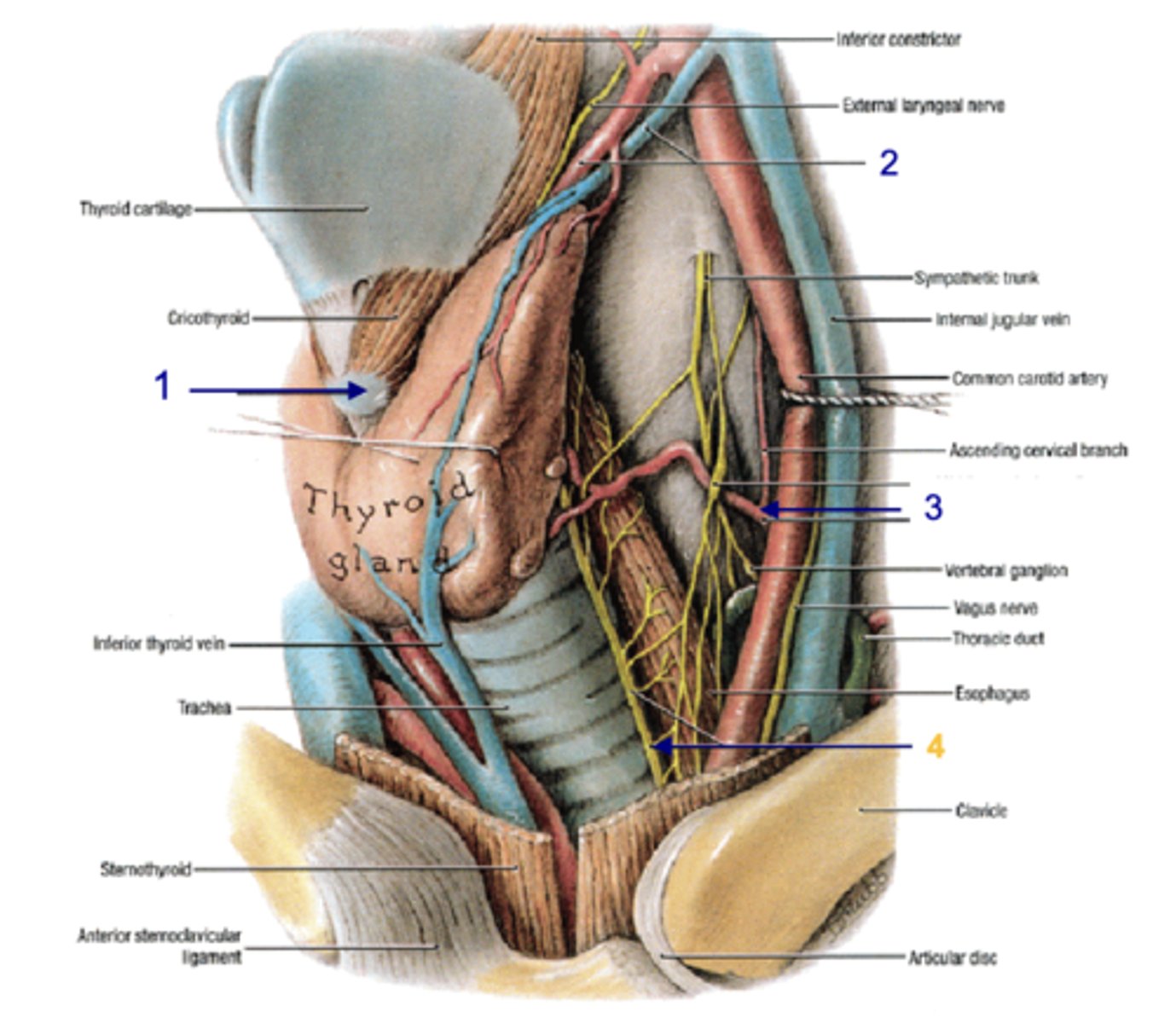
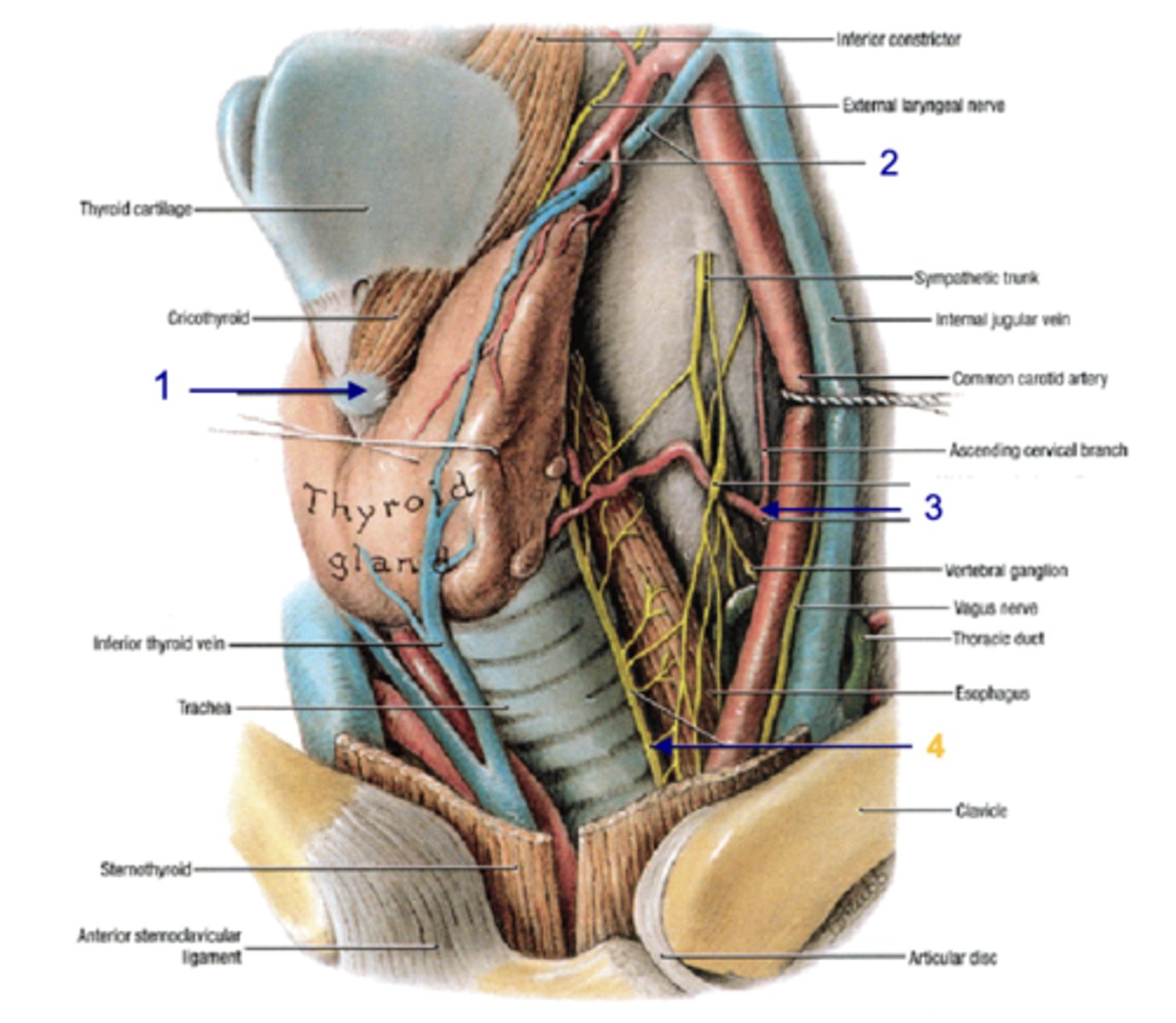
parathyroid hormone (usually 2 superior, 2 inferior)
hormones that regulates level of calcium in blood, bones, GI system
parathyroid glands
Identify the structure
posterior
the parathyroid glands lie on the _______ aspect of the thyroid gland
1. Phonation – production of sound
2. Acts as a sphincter for respiratory system – regulates amount of air to and from lungs -allows increase in abdominal pressure (Valsalva maneuver)
3. Also acts with oral cavity, oral pharynx in the process of deglutition (swallowing)
The larynx consists of cartilages connected by ligaments and moved by muscles. What are the three main functions of the larynx?
larynx
what part of the respiratory system contains the vocal cords?
tip of epiglottis
upper boundary of the larynx:
lower level of cricoid cartilage
lower boundary of the larynx:
C3-C4
the epiglottis lies at what vertebral level?
C6
the cricoid cartilage lies at what vertebral level?
inferior
the larynx is located _______ to the hyoid bone
superior
the larynx is located _______ to the thyroid gland
The epiglottis
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
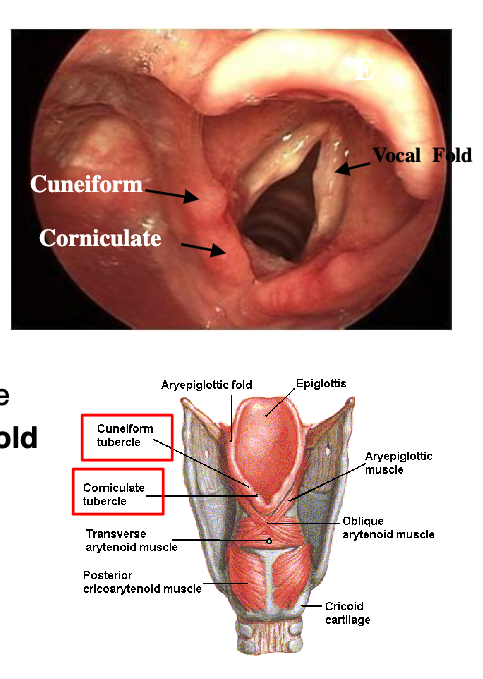
Arytenoid
Corniculate
Cuneiform
Hyoid bone
The structural rigidity of the larynx is provided by
unpaired
is the epiglottis cartilage a paired or unpaired cartilage?
unpaired
is the thyroid cartilage a paired or unpaired cartilage?
unpaired
is the cricoid cartilage a paired or unpaired cartilage?
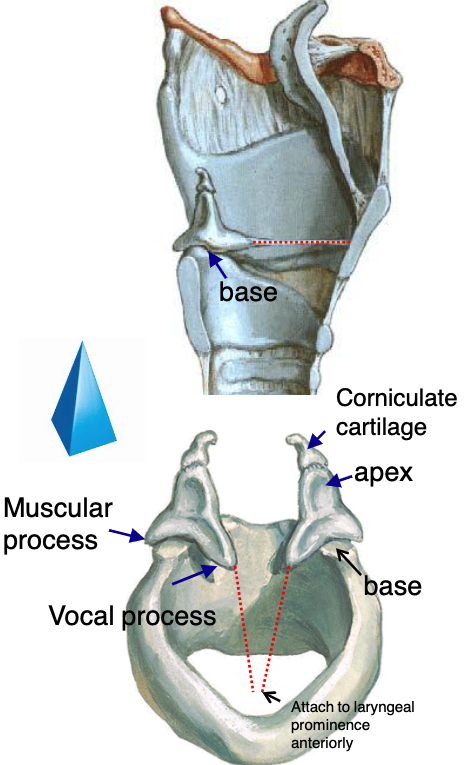
paired
is the arytenoid cartilage a paired or unpaired cartilage?
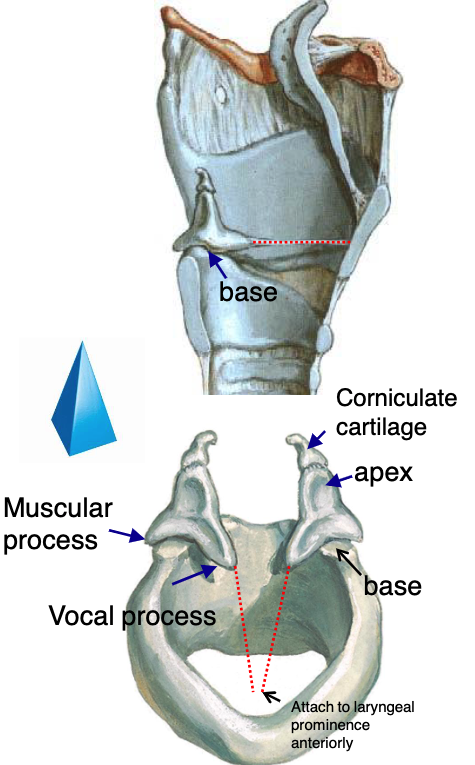
paired
is the corniculate cartilage a paired or unpaired cartilage?
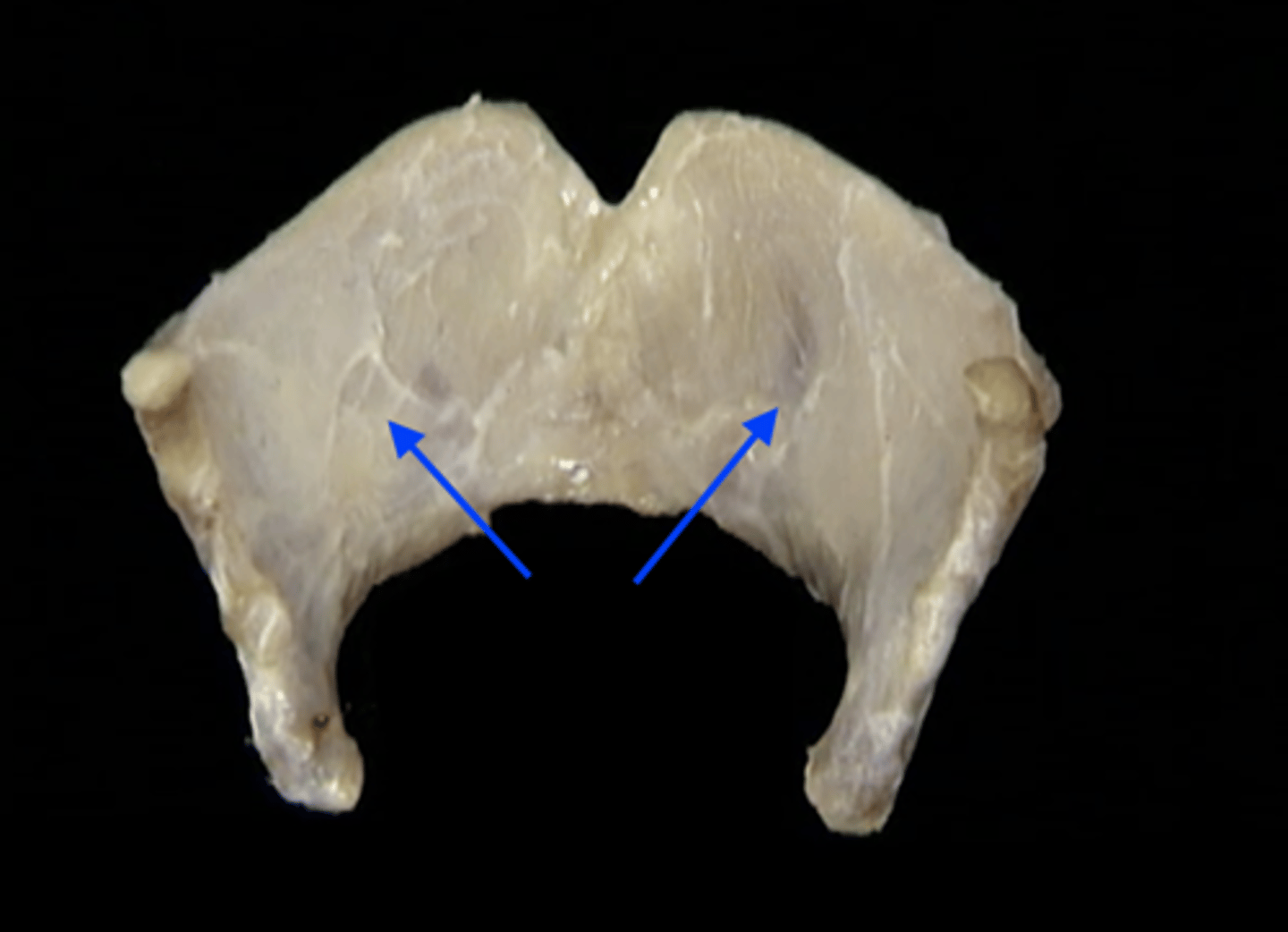
paired
is the cuniform cartilage a paired or unpaired cartilage?
- Connected by joints, membranes and ligaments
- Moved by muscles
The cartilages that maintain the structural rigidity of the larynx are connected by what? How do they move?
thyroid cartilage
what structure forms the Adam's apple?
thyroid cartilage (laryngeal prominence is aka Adam's apple)
the laryngeal prominence is located on which cartilage?
thyroid laminae
identify the structure:
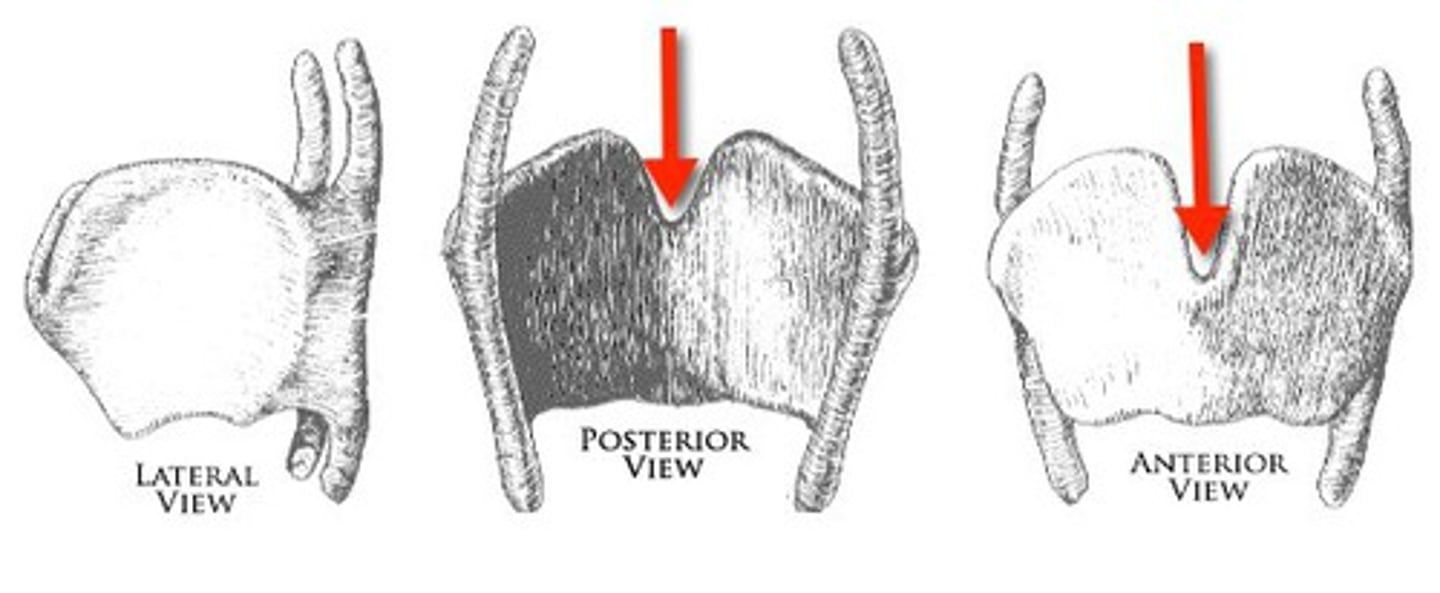
laryngeal prominence
identify the structure:
superior thyroid notch
identify the structure:
superior horn of thyroid cartilage
identify the structure:
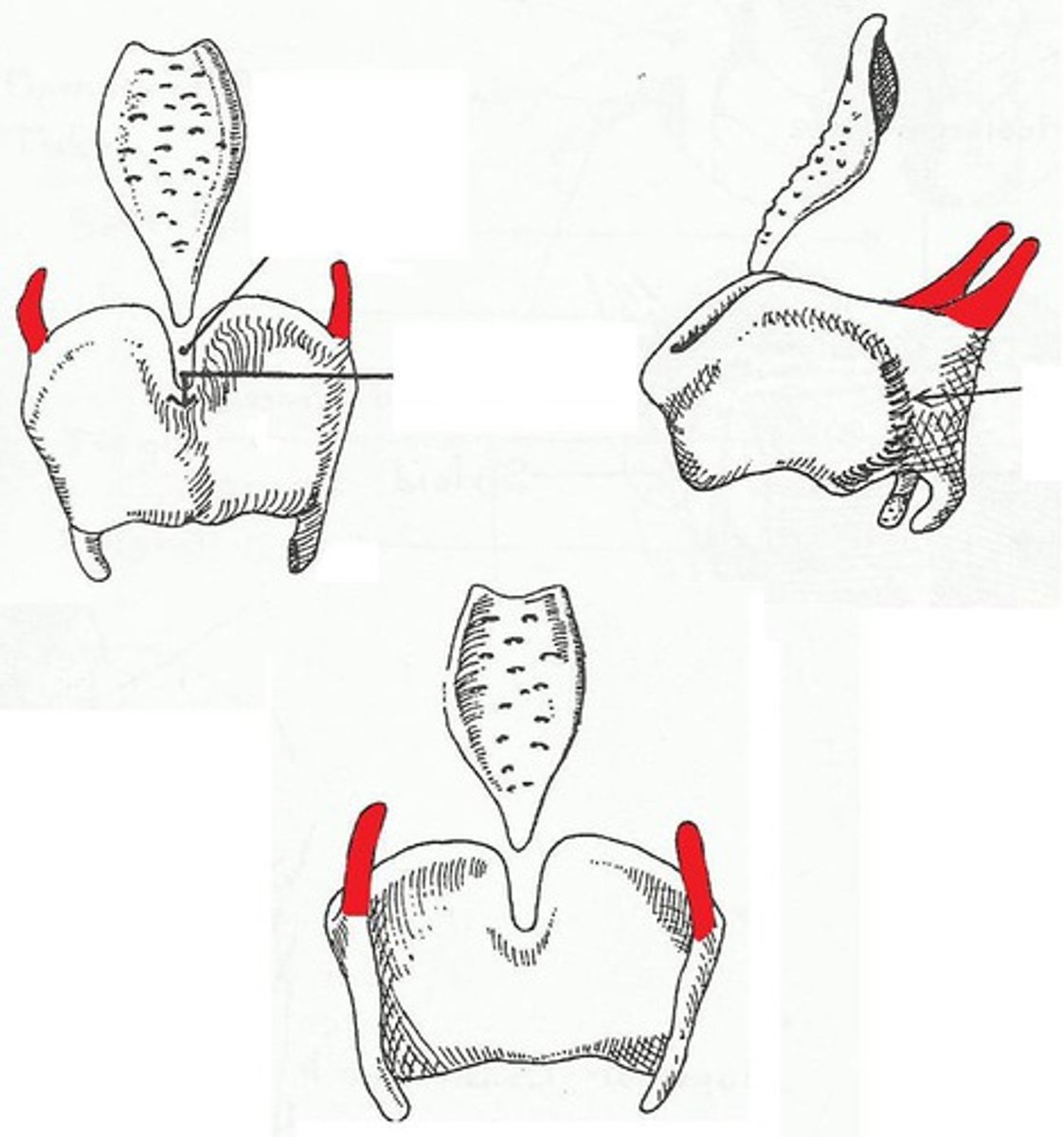
inferior horn of thyroid cartilage
identify the structure:
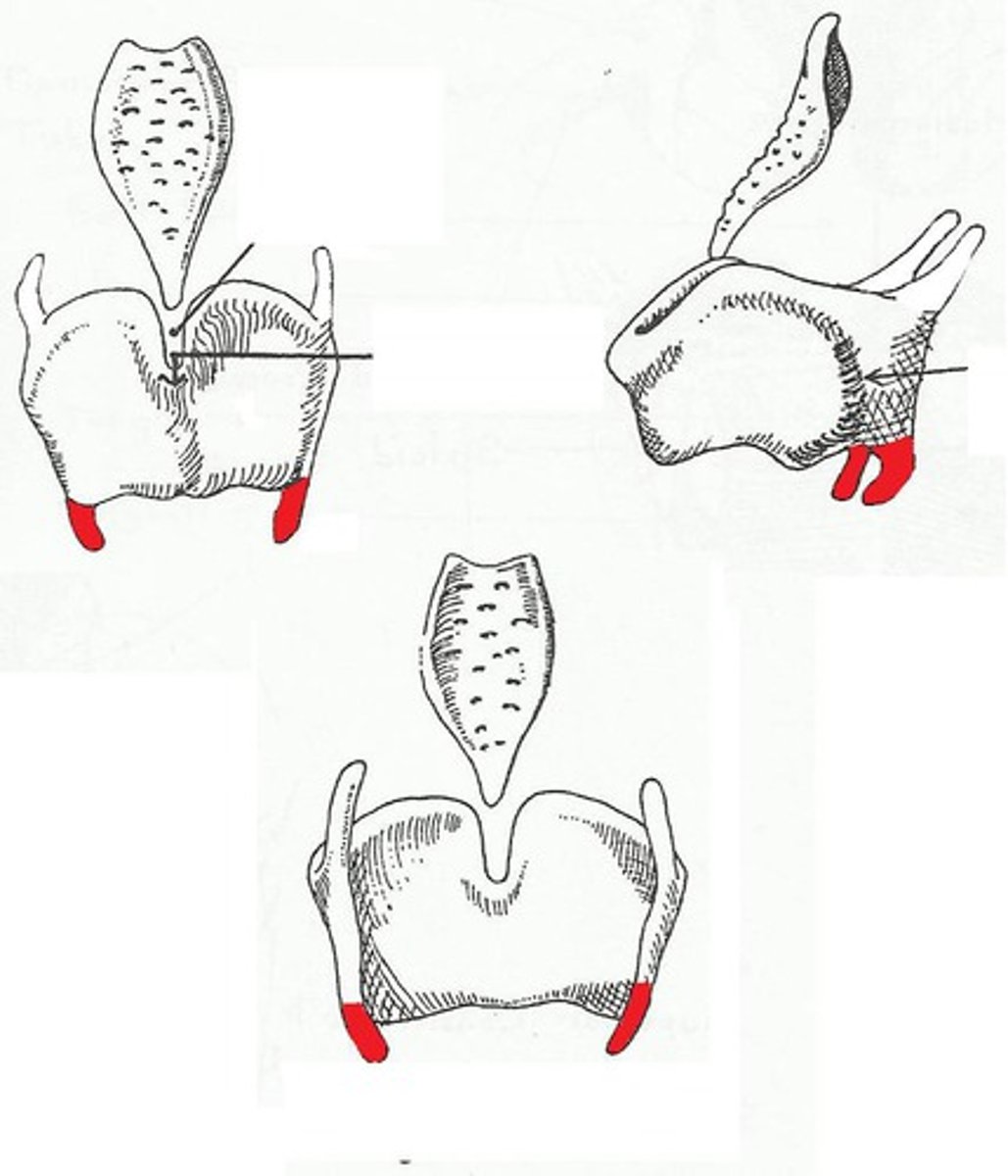
oblique line of thyroid cartilage
identify the structure:

thyrohyoid membrane
identify the structure:
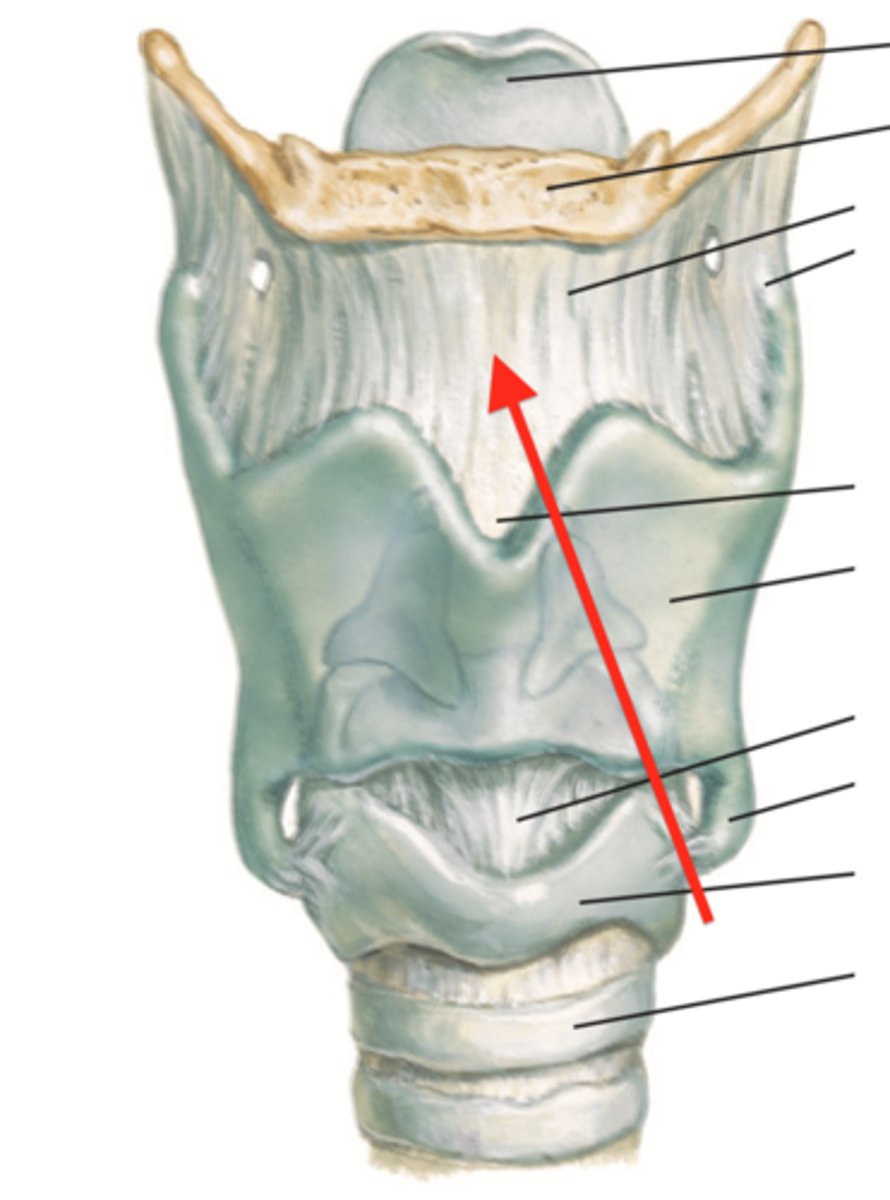
cricoid membrane
identify the structure: