Module 9: Social Psychology
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Social Influence
Changes in beliefs due to social pressure.
Conformity
Adjusting behaviors to match group norms.
Sherif's Autokinetic Effect
Illusion of light movement in darkness.
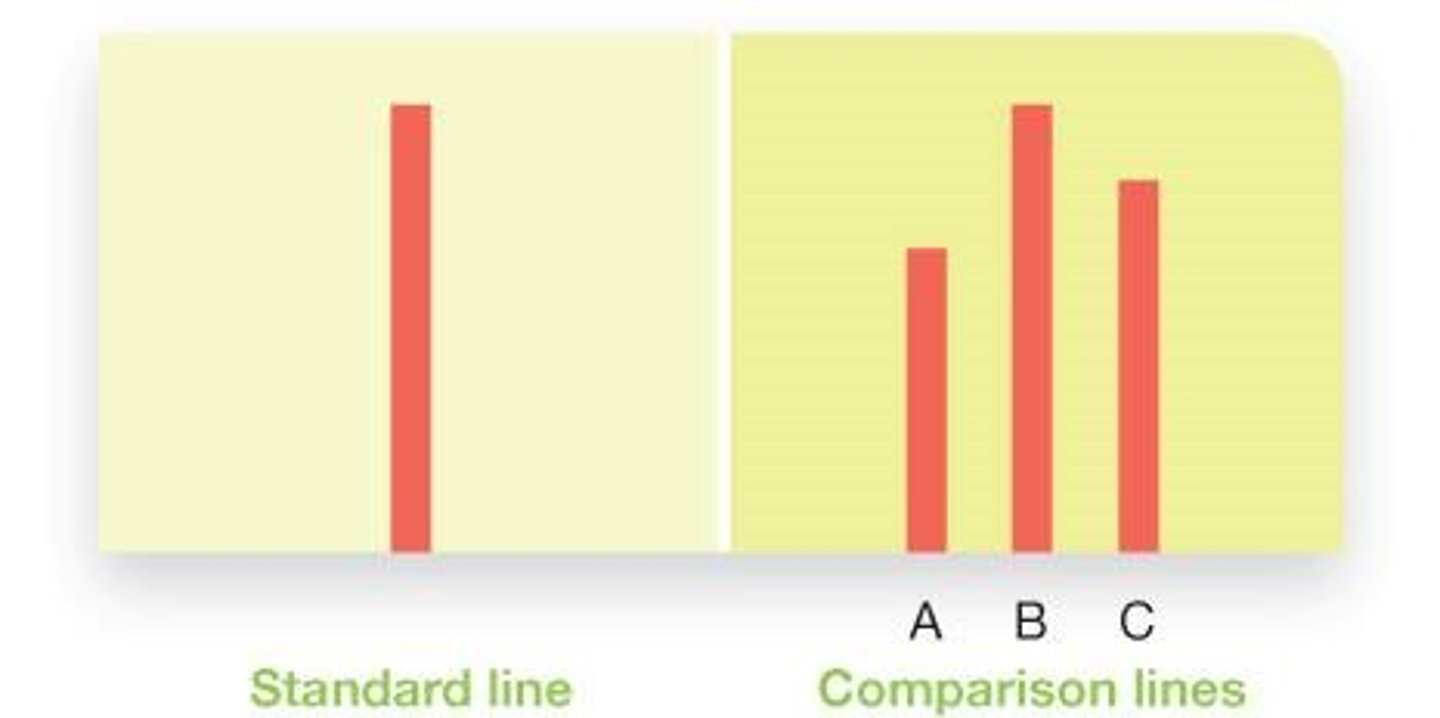
Asch's Line Study
Experiment demonstrating group pressure on judgments.
Normative Influence
Conforming to be liked or accepted.
Informational Influence
Conforming to be correct or accurate.
Private Acceptance
Changing beliefs privately and publicly.
Public Compliance
Changing public behavior without private belief change.
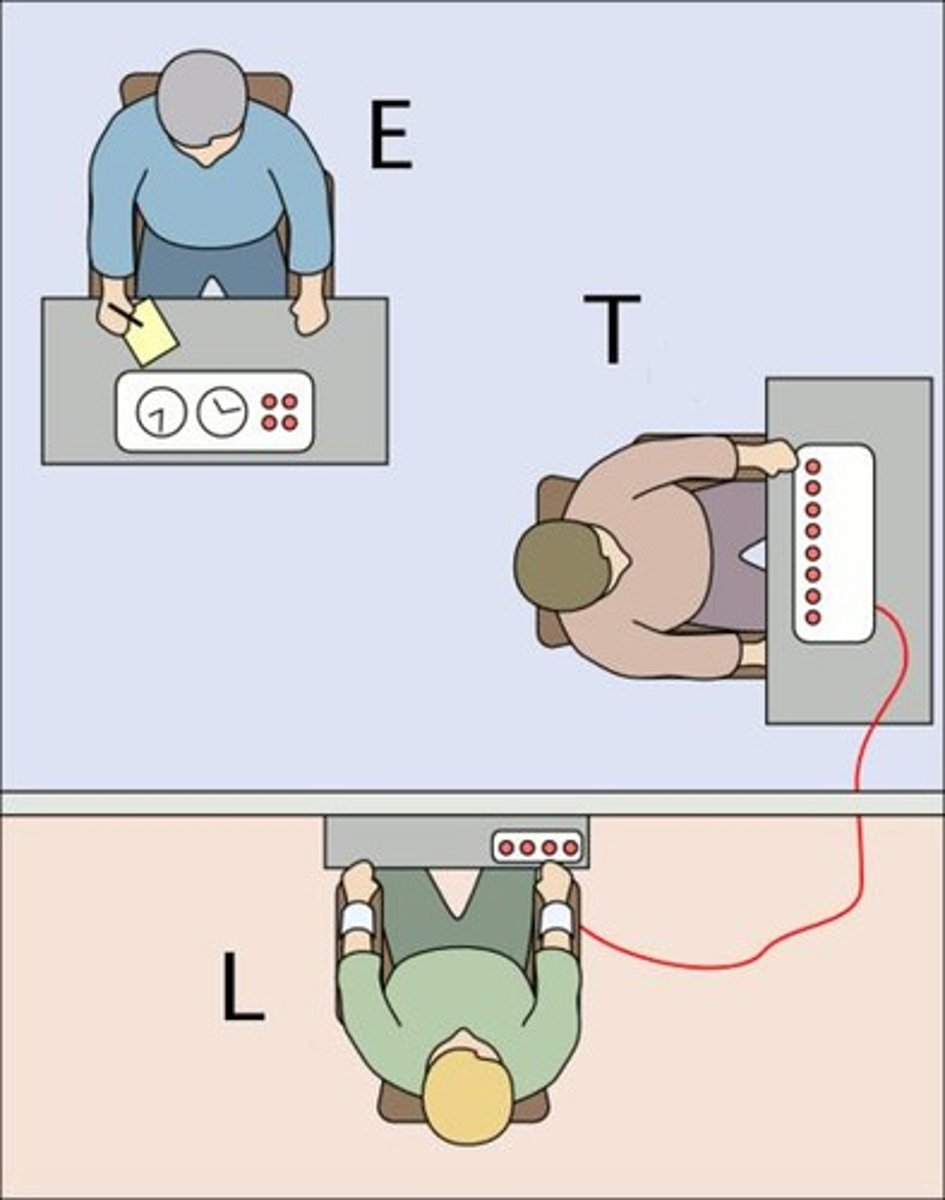
Milgram Experiment
Study on obedience to authority figures.
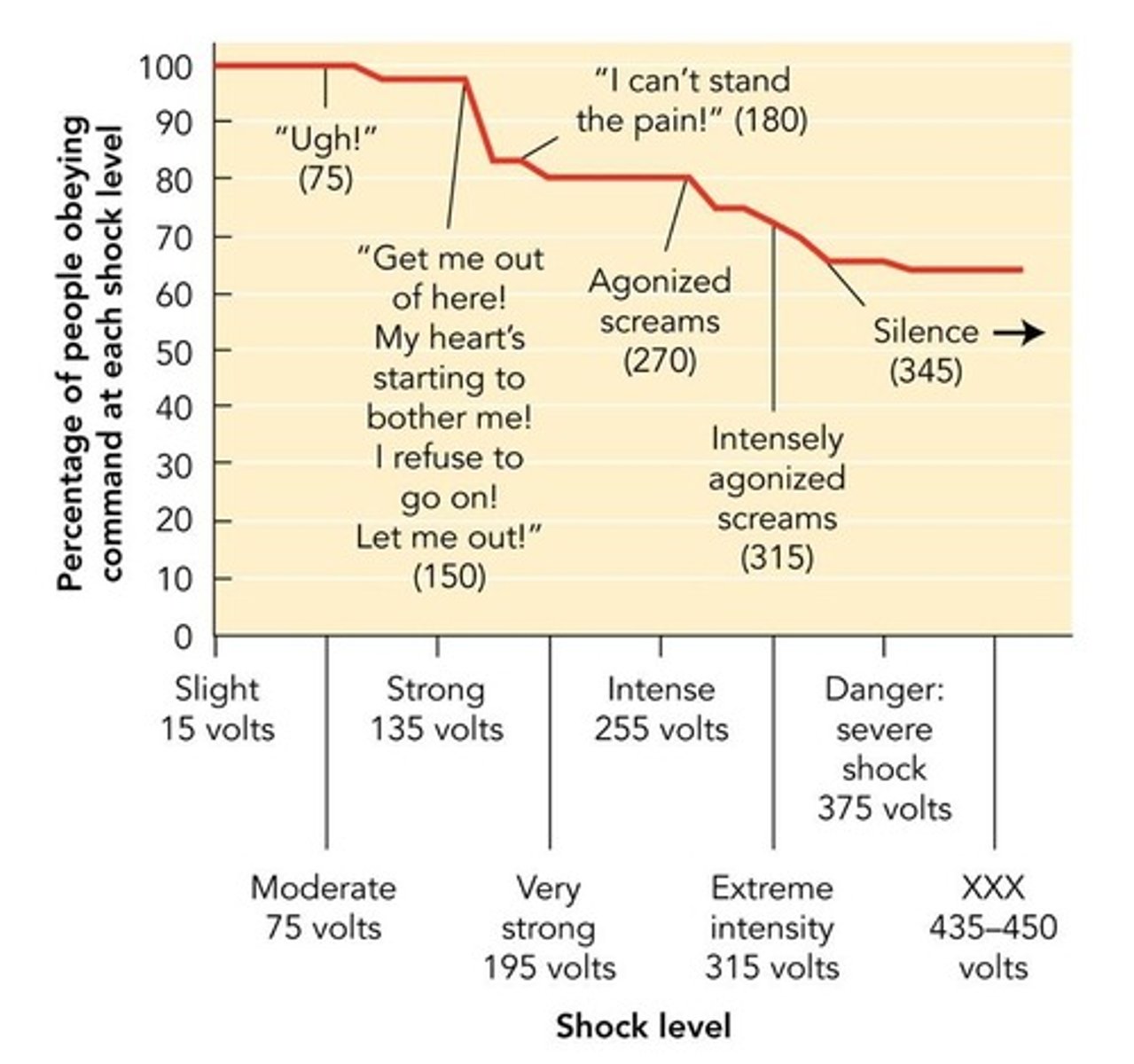
Shock Levels
Range from 15 to 450 volts administered.
Teacher-learner Role
Participants act as teachers administering shocks.
Experimenter Prompts
Commands to continue the experiment despite distress.
Deception in Studies
Misleading participants about study's true nature.
Psychiatric Follow-ups
Post-study assessments for long-term effects.
Destructive Obedience
Obeying commands leading to harmful outcomes.
Distance of Victim
Influences likelihood of obedience in experiments.
Legitimacy of Authority
Authority figure's perceived legitimacy affects obedience.
Cog in a Wheel
Feeling of being part of a system.
Group Pressure
Influence exerted by majority on individual responses.
Critical Trials
Key trials in Asch's study with incorrect answers.
Control Participants
Individuals tested alone with minimal errors.
Conformity Rates
Percentage of participants conforming in studies.
Attribution
Explaining causes of behavior in others and ourselves. (Why'd they do that?)
Post Talk Rationalization
Assigning cause to behaviour after the fact. (not always accurate)
Personal/Internal Attribution
Behavior caused by individual characteristics. (doesn't change from situation to situation)
Situational Attribution
Behavior caused by external circumstances. (could easily change from situation to situation)
Actor-Observer Bias
Differing perceptions of own vs. others' behavior. (biased)
Fundamental Attribution Error
Overemphasis on personal factors for others' behavior, and situational factors for our own. "He didn't do well on the test because he isn't smart, I just didn't sleep well"
Self-Serving Bias
Attributing successes to personal factors and failures to situational factors. (protects self esteem)
Is influenced by culture and psychological state. (eg. depression)
Cultural Influence on Attribution (individualistic vs Collective cultures)
Individualistic cultures - tend to adopt self serving bias more often
Collectivist cultures - tend to not do so