Distance and displacement
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Distance
Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to the total path length traveled by an object, regardless of the direction.
Always positive or zero
Does not consider direction
Displacement
Displacement is a vector quantity (directional) that refers to the change in position of an object from its initial point to its final point. It measures how far out of place an object is in a specific direction.
Speed
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures how fast an object is moving, regardless of the direction. It is the rate at which an object covers distance.
Always positive or zero.
Does not include directional information.
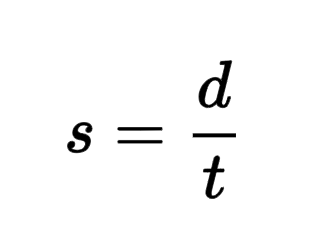
Velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity that measures the rate at which an object changes its position. It includes both the speed and the direction of the object's motion.
For a circular path where an object returns to its starting point, the speed can be non-zero (total distance covered), but the velocity would be zero (no net displacement).
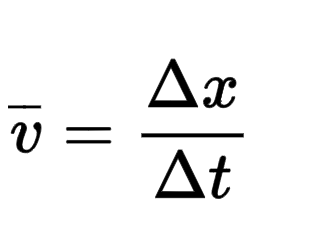
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
Positive Acceleration: Occurs when an object's velocity increases in the direction of motion.
Negative Acceleration (Deceleration): Occurs when an object's velocity decreases in the direction of motion.
Zero Acceleration: Occurs when there is no change in velocity; the object moves with constant velocity.
So as soon as there is a change in velocity (direction or magnitude), there is a change in acceleration
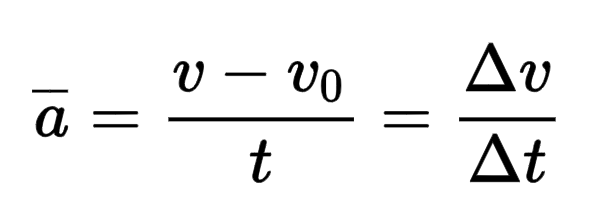
Examples of acceleration
Straight Line Acceleration: A car increasing its speed from 20 km/h to 50 km/h in 5 seconds has a positive acceleration.
Deceleration: A bicycle slowing down from 15 m/s to 5 m/s over 2 seconds is experiencing negative acceleration.
Changing Direction: When a car turns a corner while maintaining constant speed, it still has acceleration due to the change in direction of its velocity.
Gravitational force
the universal force of attraction acting between all bodies of matter.
Gravitational force is exerted by any object with mass, and two objects exert the same magnitude of gravitational force, except most pairs exert a negligible amount of gravitational force compared to things like the earth.
When a pair is formed, they will rotate around a combined center of mass, it lies within the earth for most forces.
They will produce equal pulling forces towards each other
Gravitational force formula
It depends on the masses of the two objects and the radius between them.

Equal gravitational force and acceleration
But just because they have equal forces and it doesn’t mean that they have the same acceleration, as force = mass x acceleration, and they can have different masses and therefore different accelerations
They will often have opposite masses and acceleration but the same force