BIOL-K 325 Lab: LAB 11 - Hill Reaction
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:31 AM on 3/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
1
New cards
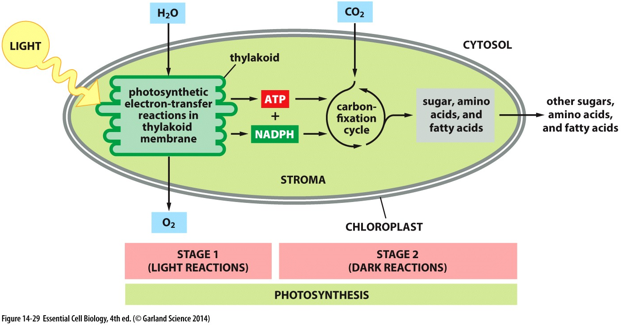
Photosynthesis
* Light + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 +6O2 +H2O
* Light energy is captured and turned into chemical energy.
* Light (photons) drives the oxidation of electron donors and produces organic sugars.
* Light-dependent reactions (photo-phosphorylation):
* Light + H2O + NADP → O2 + NADPH + ATP
* Thylakoid membranes.
* Requires light to excite electrons, which reduces NADP and generates ATP.
* The excited electrons are replaced by splitting water resulting in oxygen evolution.
* __Photo-phosphorylation:__
* Light-isolated chloroplasts can generate ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
* __Z-scheme:__
* When photosystems, complexes of proteins, chlorophyll, and other pigment molecules collect light energy via the excitation of electrons and pass the high energy electrons to the Hill reagent (NADP).
* Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle):
* CO2 + H2O +NADPH + ATP → glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
* Stroma.
* Carbon dioxide is fixed by rubisco to generate G3P, which is then processed into sugars within the stroma of the chloroplasts.
* *NADPH and ATP are used to fix carbon dioxide into glucose.*
* Light energy is captured and turned into chemical energy.
* Light (photons) drives the oxidation of electron donors and produces organic sugars.
* Light-dependent reactions (photo-phosphorylation):
* Light + H2O + NADP → O2 + NADPH + ATP
* Thylakoid membranes.
* Requires light to excite electrons, which reduces NADP and generates ATP.
* The excited electrons are replaced by splitting water resulting in oxygen evolution.
* __Photo-phosphorylation:__
* Light-isolated chloroplasts can generate ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
* __Z-scheme:__
* When photosystems, complexes of proteins, chlorophyll, and other pigment molecules collect light energy via the excitation of electrons and pass the high energy electrons to the Hill reagent (NADP).
* Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle):
* CO2 + H2O +NADPH + ATP → glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
* Stroma.
* Carbon dioxide is fixed by rubisco to generate G3P, which is then processed into sugars within the stroma of the chloroplasts.
* *NADPH and ATP are used to fix carbon dioxide into glucose.*
2
New cards
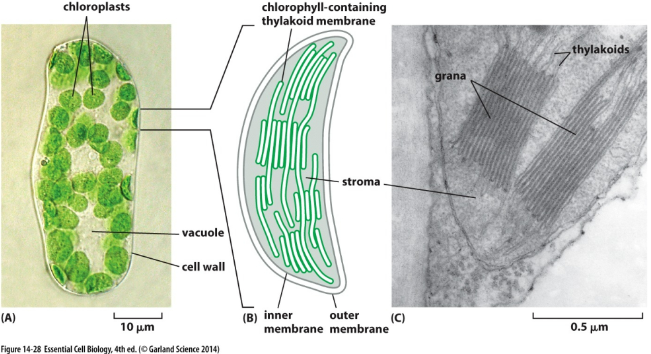
Chloroplast
* Organelle where photosynthetic reactions occur.
* Chlorophyll.
* Gives plants their green color.
* Captures light to drive photosynthesis.
* Stoma vs. grana (thylakoid membranes).
* The stroma is the internal matrix of chlorophyll.
* The inner membrane is called the thylakoid, which is arranged in stacks called grana.
* Chlorophyll.
* Gives plants their green color.
* Captures light to drive photosynthesis.
* Stoma vs. grana (thylakoid membranes).
* The stroma is the internal matrix of chlorophyll.
* The inner membrane is called the thylakoid, which is arranged in stacks called grana.
3
New cards
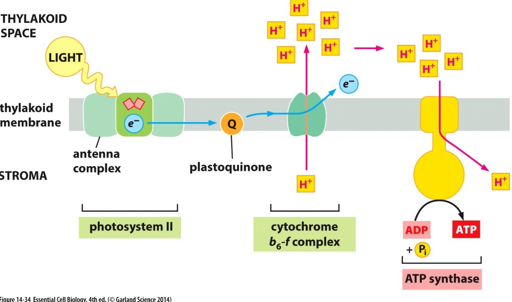
Light-dependent reactions
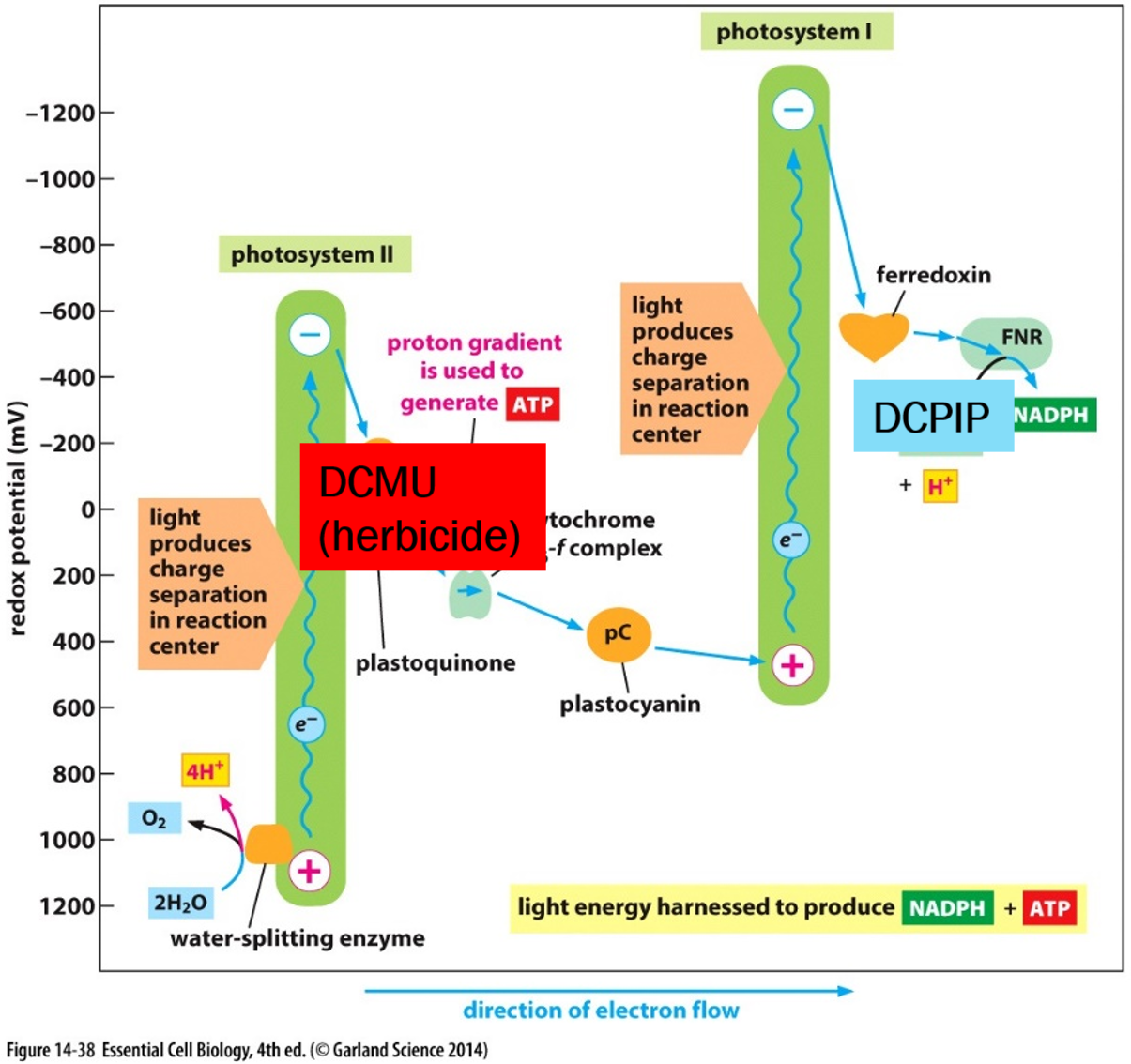
* Hill reaction:
* H2O + A(oxidized) → AH2 (reduced) +O2
* H2O is the electron donor, and A is the electron acceptor (Hill reagent).
* Robert Hill was the first person to prove that photosynthesis had two sides: one that requires light and one that does not.
* He demonstrated the Hill reaction using purified chloroplasts, where water and an oxidized electron acceptor are reduced, and oxygen is evolved without carbon dioxide. He used light only.
* This can be demonstrated with many different reagents called Hill reagents.
* Hill reagent:
* Reduced by electron transport of photosystems II & I.
* In plants: NADP.
* In this experiment: DCPIP.
* Blue when oxidized and colorless when reduced.
* Can measure the rate of photosynthesis by the oxidation of DCPIP over time.
* The Proton gradient created across the thylakoid membrane drives ATP synthase.
* H2O + A(oxidized) → AH2 (reduced) +O2
* H2O is the electron donor, and A is the electron acceptor (Hill reagent).
* Robert Hill was the first person to prove that photosynthesis had two sides: one that requires light and one that does not.
* He demonstrated the Hill reaction using purified chloroplasts, where water and an oxidized electron acceptor are reduced, and oxygen is evolved without carbon dioxide. He used light only.
* This can be demonstrated with many different reagents called Hill reagents.
* Hill reagent:
* Reduced by electron transport of photosystems II & I.
* In plants: NADP.
* In this experiment: DCPIP.
* Blue when oxidized and colorless when reduced.
* Can measure the rate of photosynthesis by the oxidation of DCPIP over time.
* The Proton gradient created across the thylakoid membrane drives ATP synthase.
4
New cards
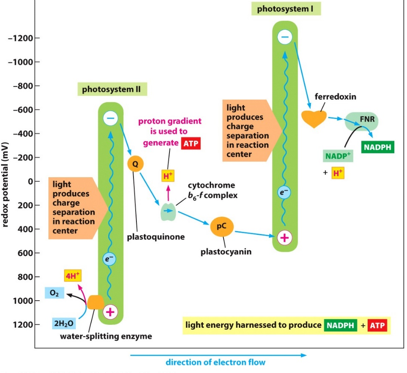
Non-cyclic electron flow
* Light excites electrons in special chlorophyll in photosystems II & I.
* The excited electron in PSII is replaced by splitting water.
* PSII electron is passed via plastoquinone and plastocyanin to replace excited electron in PSI.
* PSI electron is used to reduce NADP into NADPH.
* The excited electron in PSII is replaced by splitting water.
* PSII electron is passed via plastoquinone and plastocyanin to replace excited electron in PSI.
* PSI electron is used to reduce NADP into NADPH.
5
New cards
Where do they fit?
* In this experiment, we will use DCPIP as our Hill’s reagent, thus it will be the final electron acceptor replacing NADP.
* We will also use DCMU, a pre-emergent herbicide, which uncouples photosystem II and I, preventing electrons from passing between them.
* We will also use DCMU, a pre-emergent herbicide, which uncouples photosystem II and I, preventing electrons from passing between them.
6
New cards
Tasks
* Label cuvettes and make a data chart:
* You will measure absorbance at 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 minutes.
* Add 0.3M surcose, DCPIP, and DCMU as applicable to each cuvette.
* Set the spectrophotometer to 620 nm, add chloroplasts to blank, mix gently, and blank.
* Add chloroplasts to tubes 1-4 and mix gently.
* Put cuvettes 1 & 3 10 cm from the light source and cuvettes 2 & 4 20 cm from the light source.
* Measure the absorbance at intervals after exposing it to light.
* Graph absorbance and calculate the photosynthetic rate to compare the different conditions.
* Use post-lab questions to guide dicsussion.
* You will measure absorbance at 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 minutes.
* Add 0.3M surcose, DCPIP, and DCMU as applicable to each cuvette.
* Set the spectrophotometer to 620 nm, add chloroplasts to blank, mix gently, and blank.
* Add chloroplasts to tubes 1-4 and mix gently.
* Put cuvettes 1 & 3 10 cm from the light source and cuvettes 2 & 4 20 cm from the light source.
* Measure the absorbance at intervals after exposing it to light.
* Graph absorbance and calculate the photosynthetic rate to compare the different conditions.
* Use post-lab questions to guide dicsussion.
7
New cards
Add-on from Introduction
* Organisms capable of creating their own food are **autotrophic organisms.**
* Two main types:
* Photoautotrophs:
* Use photosynthesis.
* Chemoautotrophs:
* Use chemosynthesis.
* The evolution of photosynthesis by cyanobacteria shaped the Earth to be the oxygen-rich, life-supporting atmosphere that it is today.
* Two main types:
* Photoautotrophs:
* Use photosynthesis.
* Chemoautotrophs:
* Use chemosynthesis.
* The evolution of photosynthesis by cyanobacteria shaped the Earth to be the oxygen-rich, life-supporting atmosphere that it is today.