Chapter 17 - Gluconeogenesis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Gluconeogensis
The synthesis of glucose from pyruvate.
What is the major site of gluconeogenesis?
The liver, although gluconeogenesis can occur in the kidney.
What important role does gluconeogenesis serve?
Especially important during fasting or starvation, as glucose is the primary fuel for the brain and the only fuel for red blood cells.
Pyruvate can also be formed by what alternative means…
Lactate by lactate dehydrogenase
Carbon skeletons of some amino acids
Glycerol (—>dihdroxyacetoneTriacylglycerols
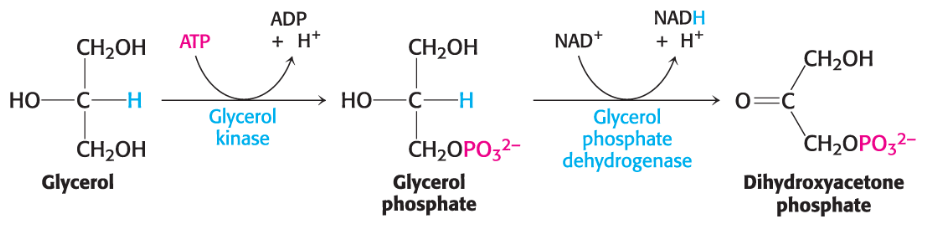
What is the model Oxaloacetate?

Do the disgram of gluceogenesis.

What are the Six High-Transfer-Potential Phosphoryl Groups Are Spent in Synthesizing Glucose from Pyruvate.
2 pyruvate
4 ATP
2 GTP
2 NADH
2 H+
H2O
What are the three irreversible steps of gluconeogensis"?
Glucose + ATP -Hexokinease→ glucose 6-phosphate + ADP
Fructose 6-phosphate + ATP -Phosphofructokinase→ Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + ADP
Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP -Pyruvate kinase→ pyruvate + ATP
The formation of phosphoenolpyruvate from pyruvate
requires two enzymes…
Pyruvate carboxylase
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
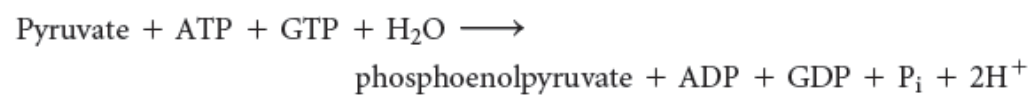
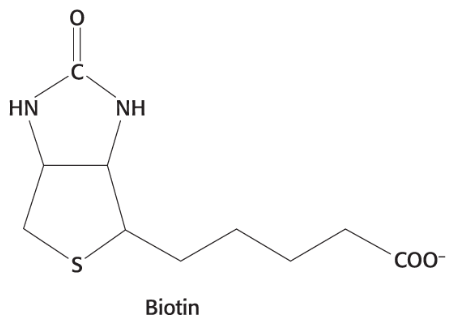
Pyruvate carboxylase requires what as a
cofactor
the vitamin biotin (B7)
Glucose 6-phosphate is transported into the
…the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Glucose 6-phosphatase, an integral membrane on the inner surface of the endoplasmic reticulum, catalyzes the formation of glucose from glucose 6-phosphate.
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are regulated so that within a cell, one pathway is relatively inactive while the other is highly active.
The rationale for reciprocal regulation is that glycolysis will predominate when glucose is abundant, and that gluconeogenesis will be highly active when glucose is scarce.
The glucagon signaling pathway leads to the
phosphorylation of the bifunctional enzyme, which
inhibits the kinase and stimulates the phosphatase