Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances with different properties
Property
Physical of chemical characteristic of a substance
Atom
The smallest particle of an element (element and its atoms have the same name)
Atomic symbol
One or two letters that represent the name of an element
3 Main Subatomic Particles
Protons, neutrons, electrons
Protons
Positively charged subatomic particles
Neutrons
Neutrally charged subatomic particles
Electrons
Negatively charged subatomic particles
Electron Shell
The circle that represents the average location of electrons
Atomic Number
Number of protons in the nucleus
Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
Atomic mass
Average mass number for all isotopes of an element
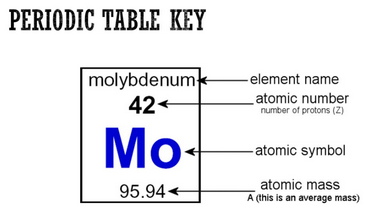
Atom on a periodic table
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Tracer
A substance added to a biological system to track its behavior, distribution, and processes at the molecular, cellular, or systemic level
Neutral atom
Positive charges are balanced by equal amount of negative charges
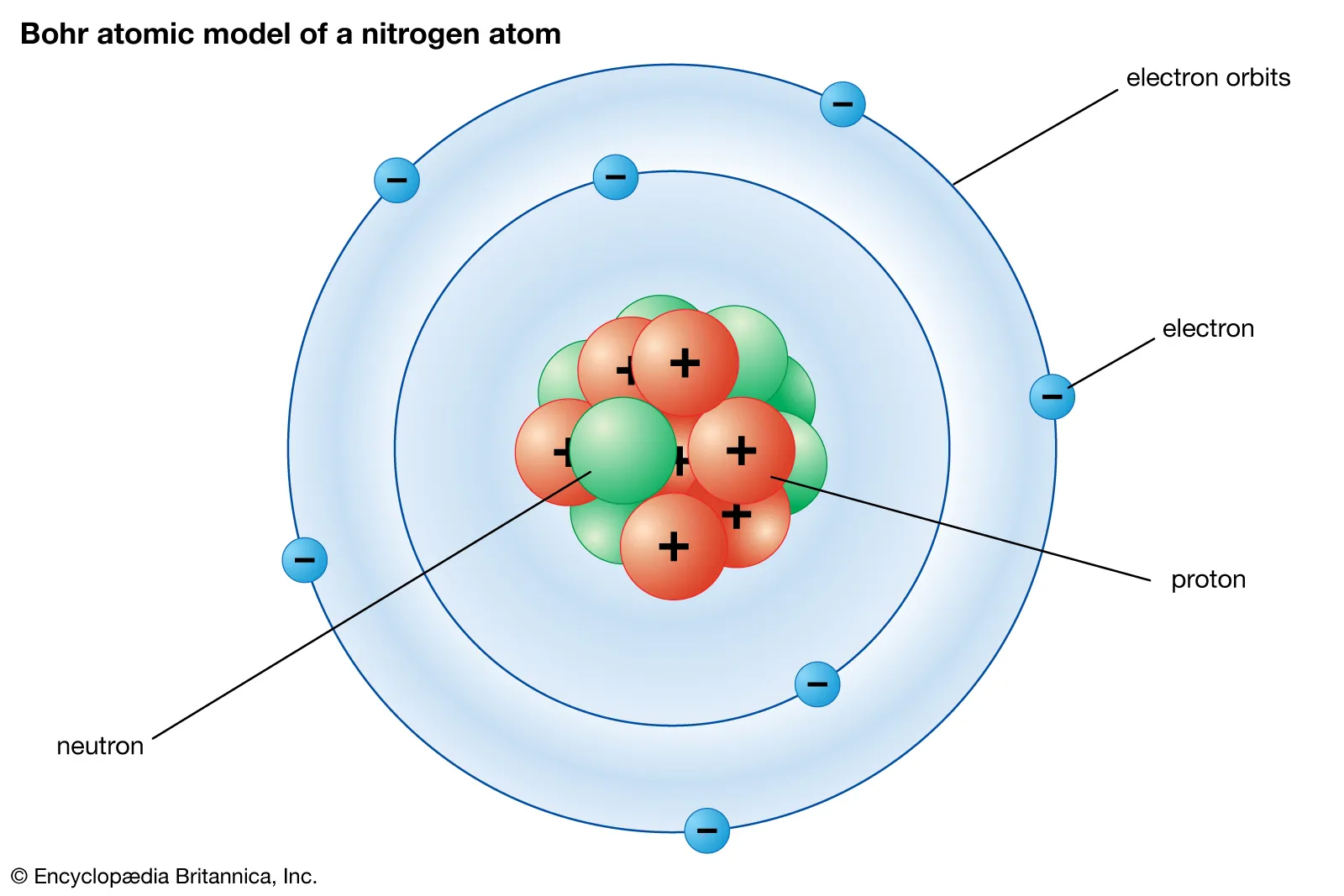
Bohr model
Image
Octet rule
If an atom has more than one shell: the outermost shell is most stable when it has 8 electrons
Which element does not follow the octet rule?
Hydrogen and Helium
How many electrons do hydrogen and helium need to be most stable?
Two electrons (duet rule)
Valence shell
Atoms outermost shell, determines whether atom gives up or accepts electrons
Molecule
Two or more elements bonded together, smallest part of a compound that retains its chemical properties
Compound
A molecule containing at least 2 different elements
Formula
Tells you the number of each kind of atom in a molecule (ex. C6H12O6)
Ions
Charged particles
Ionic Bond
Ionic compounds held together by a strong attraction between negatively and positively charged ions
Salts
Solid substances that usually separate and exist as individuals, formed from reaction of an acid and a base
Ionic bond vs ionic compound
Ionic bond is the process of electrons being transferred between two atoms, while ionic compound is the connection between those atoms as a result
Covalent bond
Two atoms have a STRONG connection and share electrons in such a way that each atom has an octet of electrons in the outer shell
Nonpolar covalent bond
The sharing of electrons between two atoms is equal due to low difference in electronegativities
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract and hold electrons toward itself in a chemical bond
Polar covalent bond
Electrons are not shared equally among atoms due to different electronegativities
Hydrogen bond
The weak attraction of a slightly positive hydrogen to a slightly (electro)negative atom near it (like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine)
Calorie
A unit that describes the amount of heat energy need to raise the temperature of 1g of water to 1 degree C
Solution
Combination of solutes
Solute
Dissolved substances
Hydrophilic
Molecules that can attract water
Hydrophobic
Nonionized and nonpolar molecules that cannot attract water
Surface tension
Force that holds moist membranes together due to the attraction of water molecules through hydrogen bonds, allowing liquid to resist external force
Hydrogen ions (H+)
One of two ions that results when a water molecule separates, hydrogen ion that has lost is electron, causing it to have a positive charge
Acids
Substances that separate in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+)
Hydroxide ions (OH-)
One of two ions that results when a water molecule separates, it has gained an electron, has a negative charge
Bases
Substances that either take up hydrogen ions or release hydroxide ions
pH scale
Scale used to measure the acidity or basicity/alkaninity of a solution
Buffer
A mixture of molecules that release or bind H+ in order to keep pH within normal limits, removes or accepts hydrogen ions
Cohesion
Water molecules are attracted to each other
Adhesion
Water molecules stick to other substances
Specific heat
The amount of heat that is needed for the temperature of 1g of a substance to increase by 1 degree celsius
Water has a ___ specific heat capacity
High
Nonpolar covalent bond electronegativity
Difference is less than 0.5
Polar covalent bond electronegativity
Difference is greater than or equal to 0.5, but less than or equal to 2.0
Ionic bond
Difference is greater than 2.0
If a molecule is symmetrical in 3D, it is a ________ ________ ____
Nonpolar covalent bond
Chemical reaction
The process of bond formation
Ionic compounds are _____ substances that usually ______ and exist as _______ ions in water
solid, separate, individual
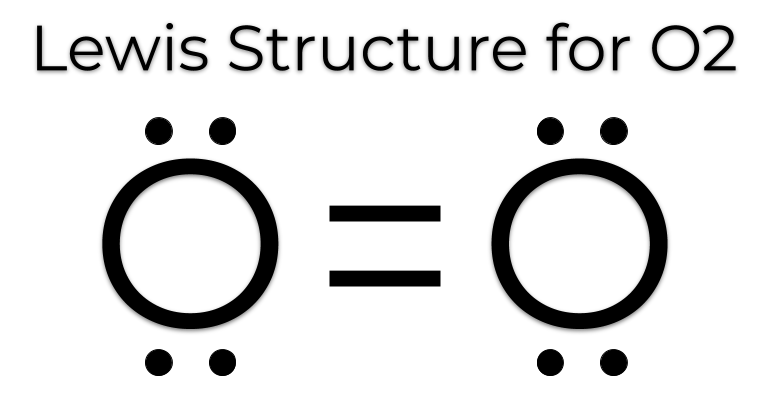
Lewis dot diagrams
Representations of molecules showing all the gained or lost electrons
Is water a polar or nonpolar molecule?
Polar
Why is water polar?
Oxygen is electronegative and hydrogen is electropositive
What makes hydrogen bonding so special?
It is a very weak attraction between two atoms, allowing for special characteristics
broken, strong
A single hydrogen bond is easily ______ while multiple hydrogen bonds are collectively quite ______
Capillary action
Movement of water up the roots of plants
large, little
Water having hydrogen bonds allows water to absorb _____ amounts of heat with _____ temperature change
Allows organisms to keep their internal temperatures stable
How does water having a high specific heat help organisms maintain homeostasis?
broken
For water to evaporate, hydrogen bonds must be ______, which requires a lot of energy
Evaporative cooling
Sweating and transpiration (plants absorbing water through their roots) are examples of cooling
hydrogen/hydronium (H2O+), hydroxide (OH-)
When water dissociates, it breaks apart into a ______ ion and a ________ ion
less, expands
Ice is _____ dense than liquid water because water ______ when cooled
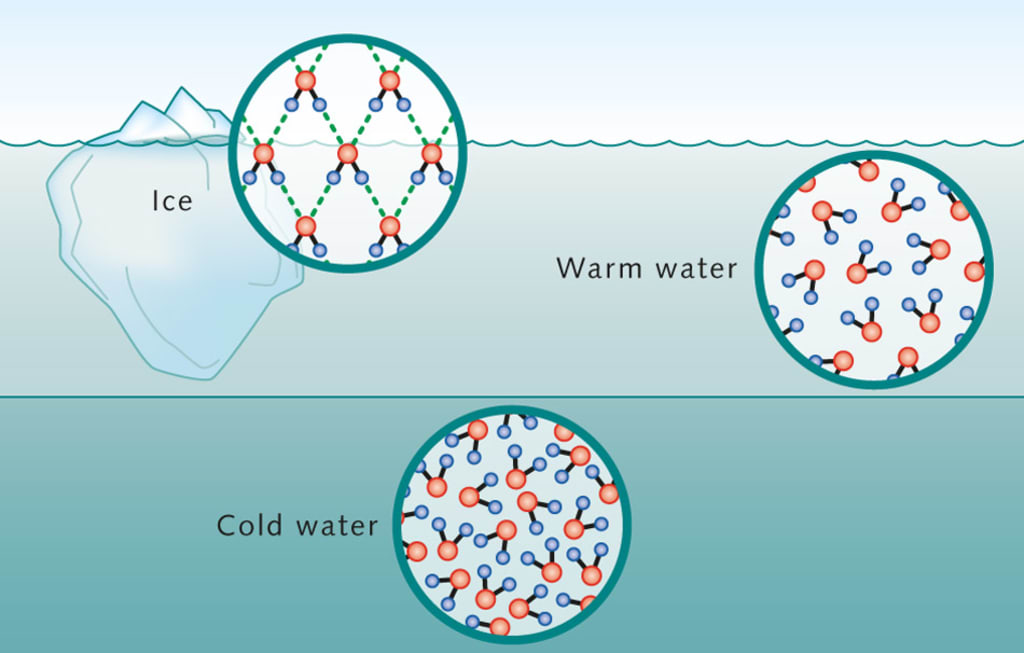
Hydrogen bonds form a stable crystal lattice structure, so the molecules are farther apart
Why does water expand when frozen?
survives
Ice insulates lakes=life ______ under ice
Potential Energy
A form of energy which can do work
Entropy
Energy released as heat
Buffer system
Two components that work together to resist changes
Most buffers consist of a…
weak acid (which releases H+) and a weak base (which binds H+)
minimize the change in pH
The function of a buffer is not to keep a solution neutral, but to
Most biochemical processes proceed normally only when the pH remains within a fairly narrow range
Why are buffers important to living organisms
Alkalosis
The pH goes above the normal range, leading to low acidity
Acidosis
The pH goes below the normal range, leading to high acidity
Hydroxide ions (OH-)
What does a base release when it is dissolved?