Photosynthesis Test
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Overall Photosynthesis Reaction
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the point of photosynthesis
Transfer light into chemical energy
Who participates in photosynthesis
Plants, Algae, Some bacteria
3 Main steps to Photosynthesis
Absorption of solar energy = Light reaction
Transformation of light energy into chemical energy as NADPH + ATP = Light Reaction
Storing Chemical energy as glucose sugar = Dark Reaction/Calvin Cycle
Stomata (found in leaves and some stems)
Tiny openings that allow gas exchange
Chloroplasts
Where photosynthesis takes place
Chlorophyll
What absorbs solar energy
Thylakoids
Membrane bound compartments inside chloroplasts that hold the Light reactions
Stroma
Fluid space inside the chloroplasts and between the thylakoids and grant, containing enzymes
Role of Photosystem II
Absorb light energy
Split water into Oxygen, Hydrogen ions, electrons
Releases O2, high concentration of hydrogen as a result
Electron Transport Chain Role
Transports Energized Electrons (plastoquinone and plastocyanin)
Electrons attract hydrogen ions and lose (potential) energy as they are pulled
Photosystem I Role
Electrons are re-energized
2 electrons and a hydrogen ion combine with NADP+ to create NADPH (for Calvin Cycle)
Ferrodoxin Role
Converts NADP+ to NADPH using H+ and e-
Chemiosmosis & ATP Synthase
Hydrogen travels down this opening to leave the thylakoid lumen and enter the stroma
Big Idea for Light reaction
Light energy is stored as chemical energy (NADPH and ATP)
Grana
Stack of thylakoids
3 Steps of Calvin Cycle
Carbon Fixation
Reduction
Regeneration
Carbon Fixation
Carbon + RUBP Makes 6 Carbon Molecule using Rubisco
6 Carbon molecules break into two and make 3PGA
G3P Reduction
Each 3PGA molecule gets a phosphate from ATP and 2 electrons from NADPH
One G3P molecule is saved to make glucose, 5 are recycled
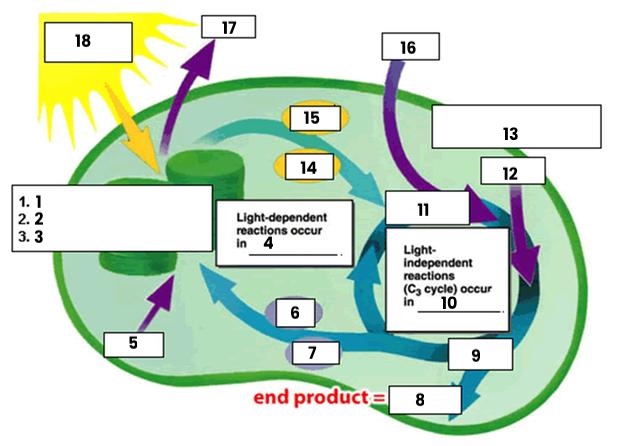
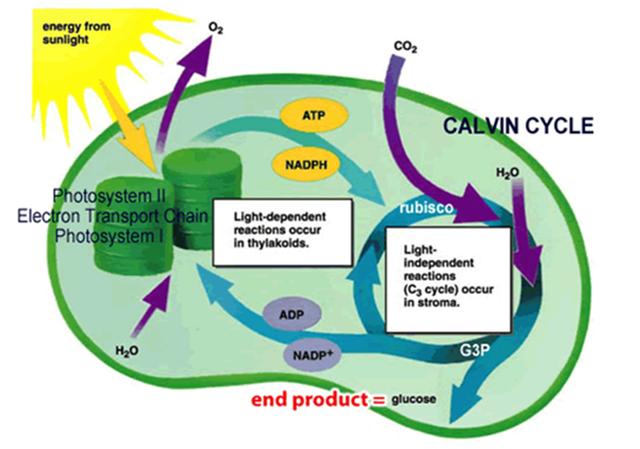
Photosystem II
Electron Transport Chain
Photosystem I
Thylakoids
H2O
ADP
NADP+
glucose
G3P
stroma
rubisco
H2O
Calvin Cycle
NADPH
ATP
CO2
O2
Energy from Sunlight
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
Stores energy in it’s phosphate bonds
Made of Nitrogenous base and ribose (together adenosine)
Also made of phosphate molecules
ATP powers things that consume energy
Active transport
Out of cell - inflammation, pain, shortage of oxygen, empty bladder