Table 4.1: Eukaryotic Structures in Animal and Plant Cells (Vocabulary)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key structures listed in Table 4.1 for animal and plant cells.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
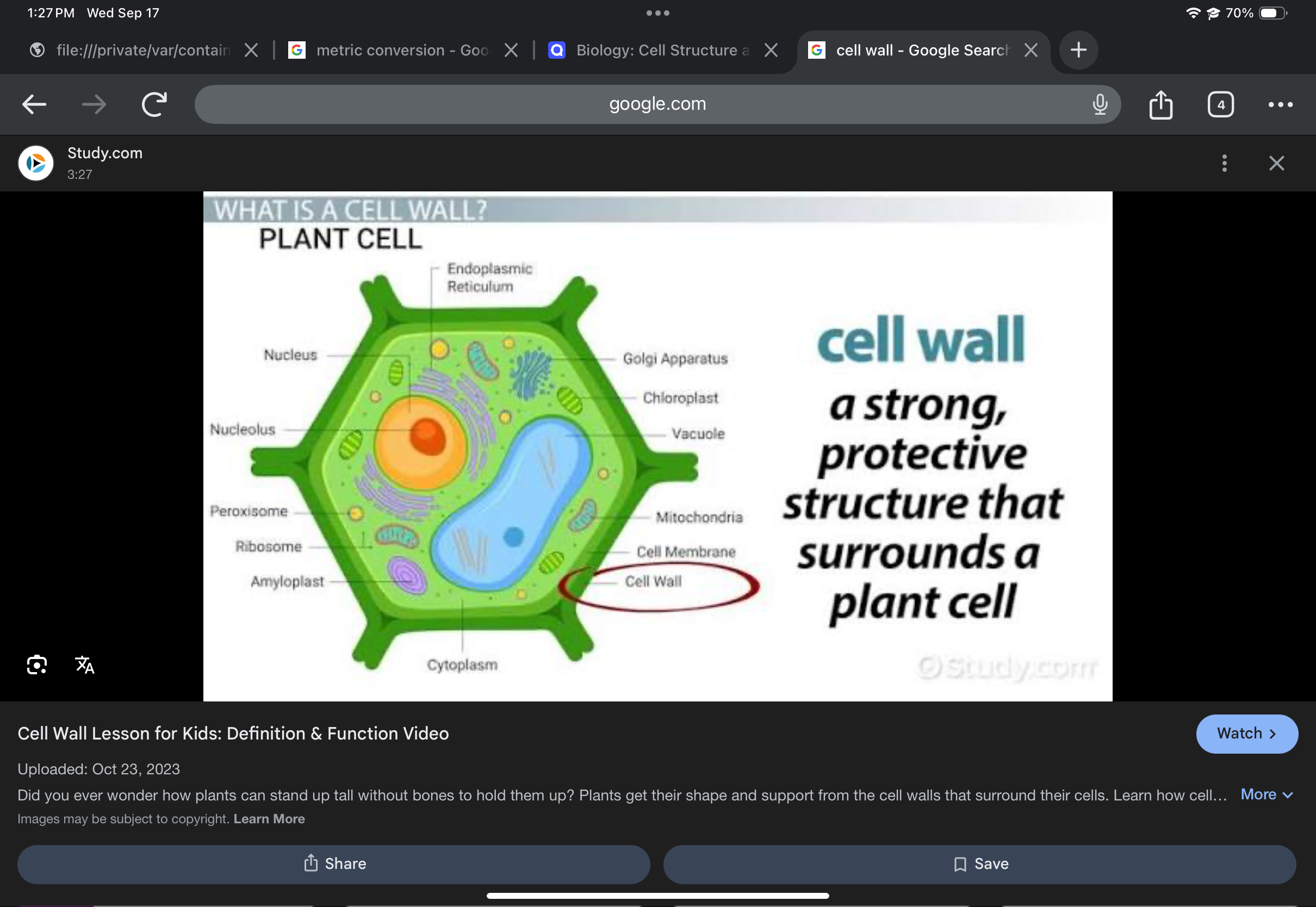
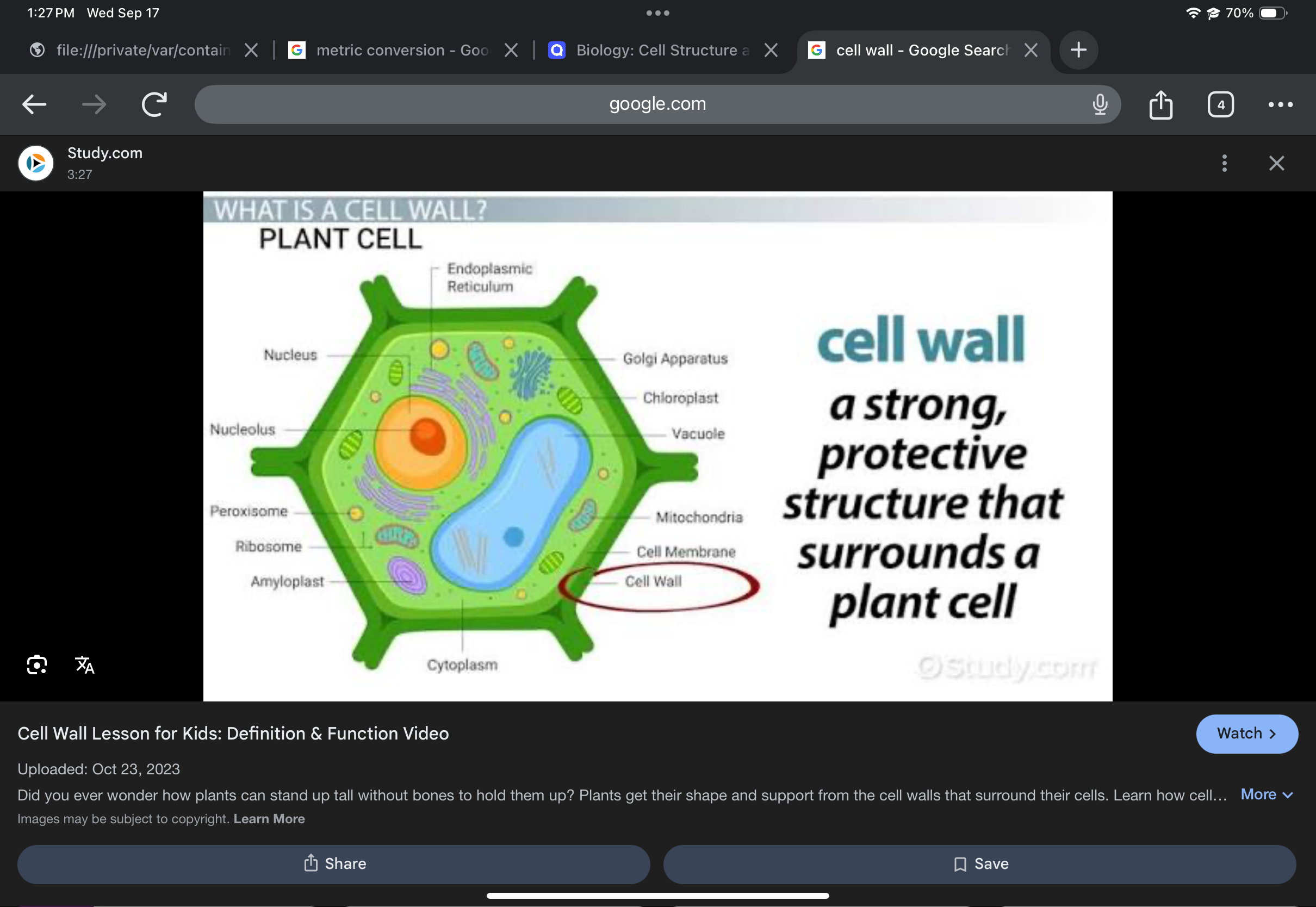
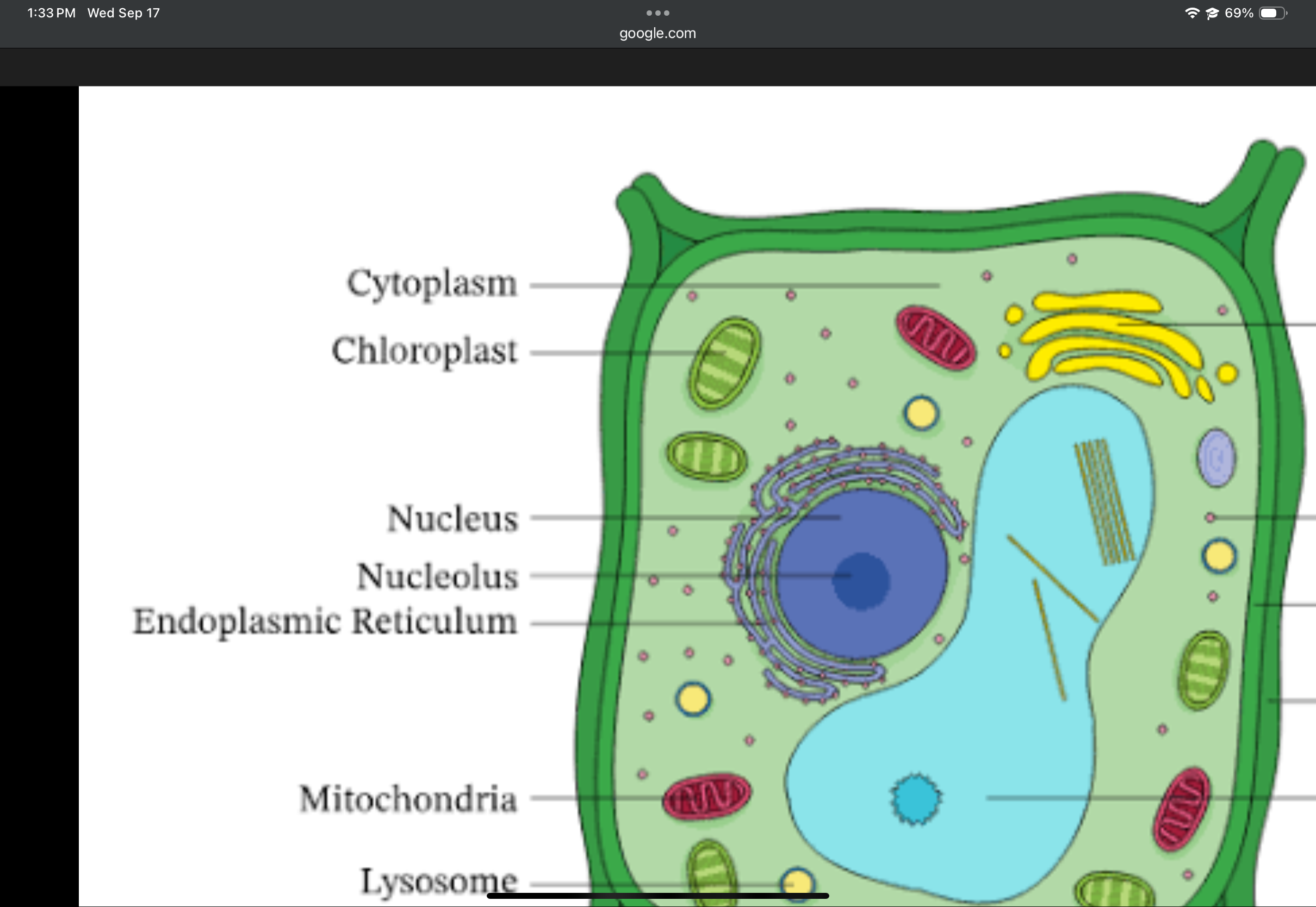
Cell wall
Provides support and protection; contains cellulose fibrils.
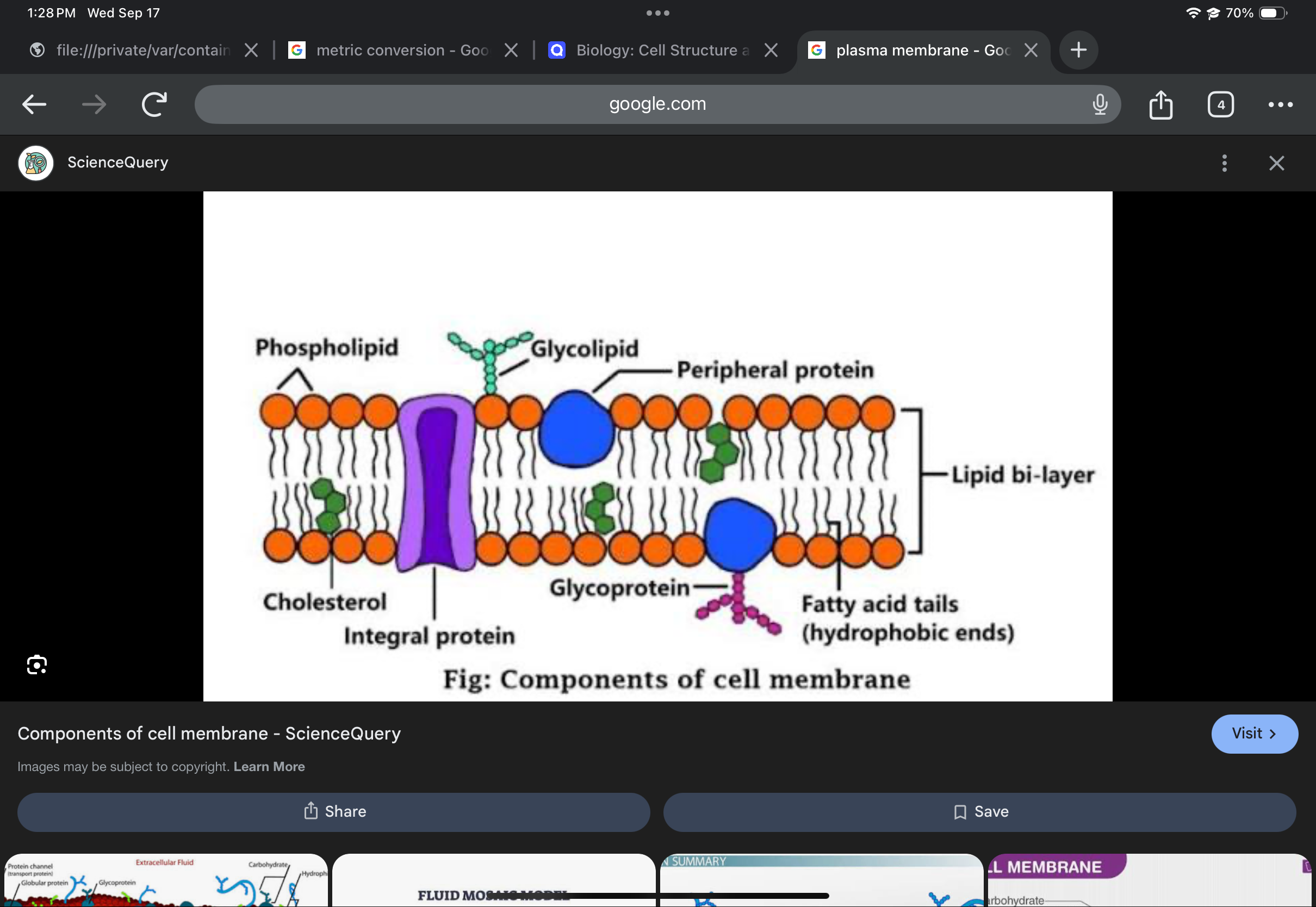
Plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; regulates entry and exit of molecules.
Nucleus
Stores genetic information; enclosed by a nuclear envelope; site of DNA and RNA synthesis.
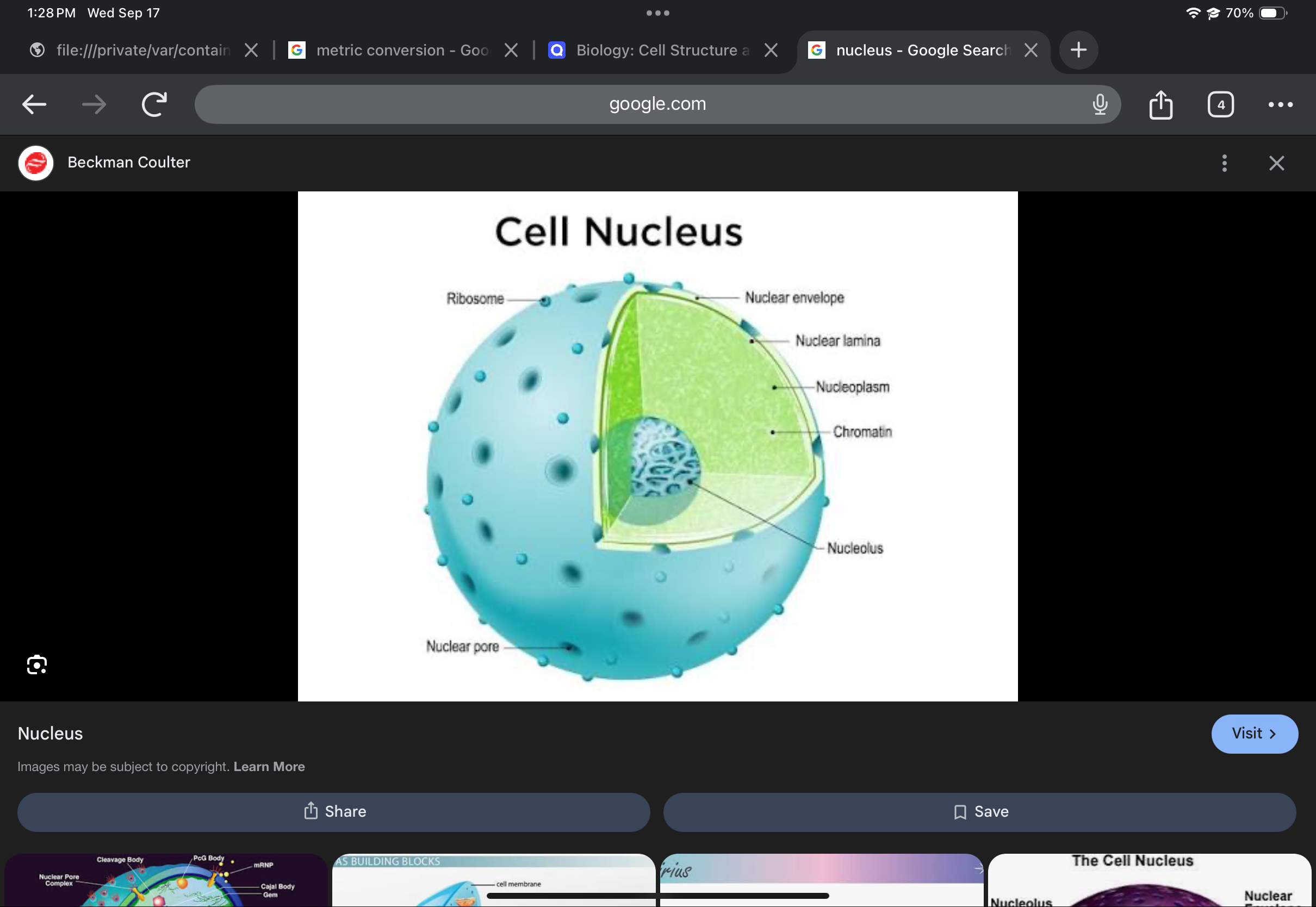
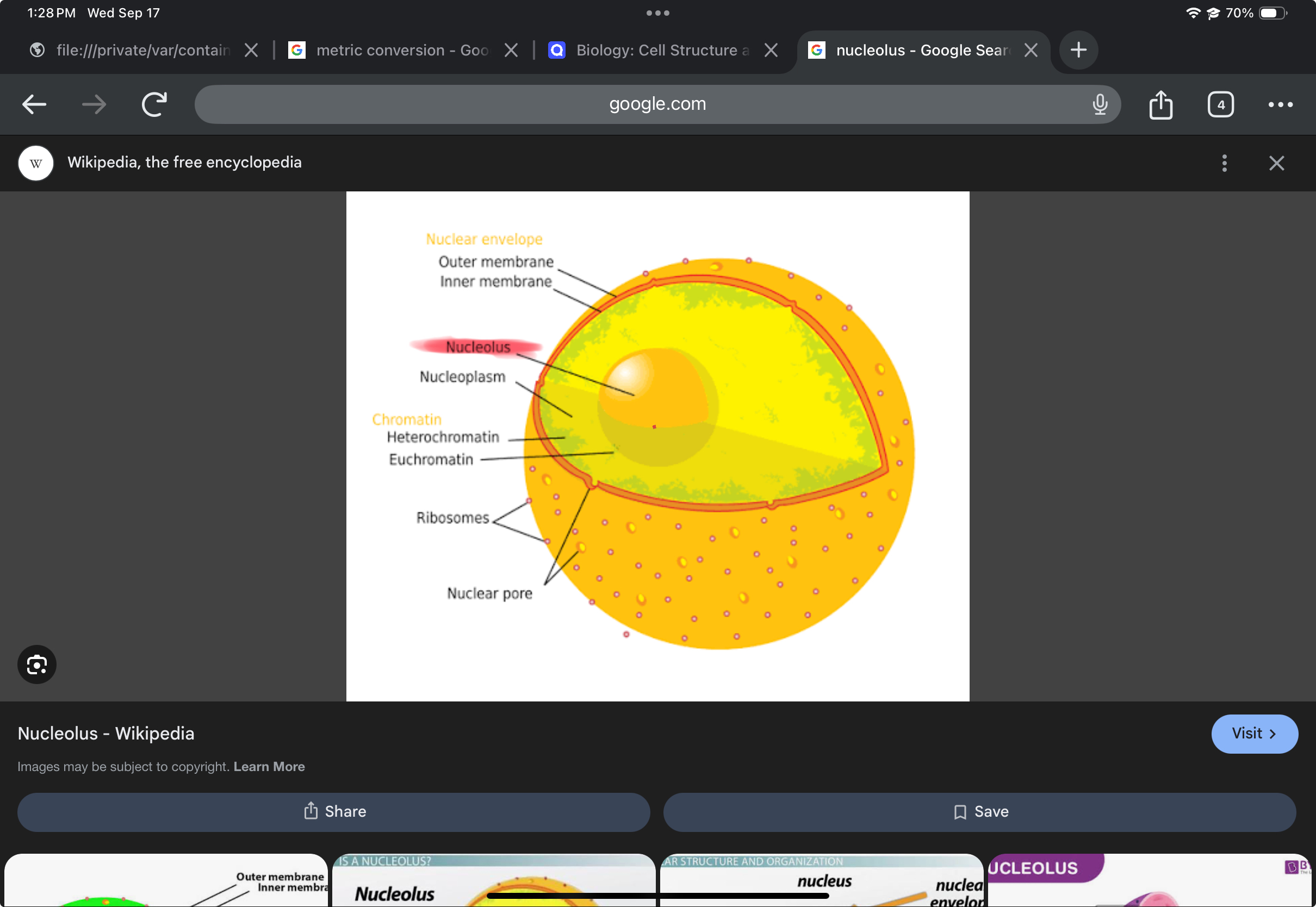
Nucleolus
Concentrated region within the nucleus where ribosome subunits are produced.
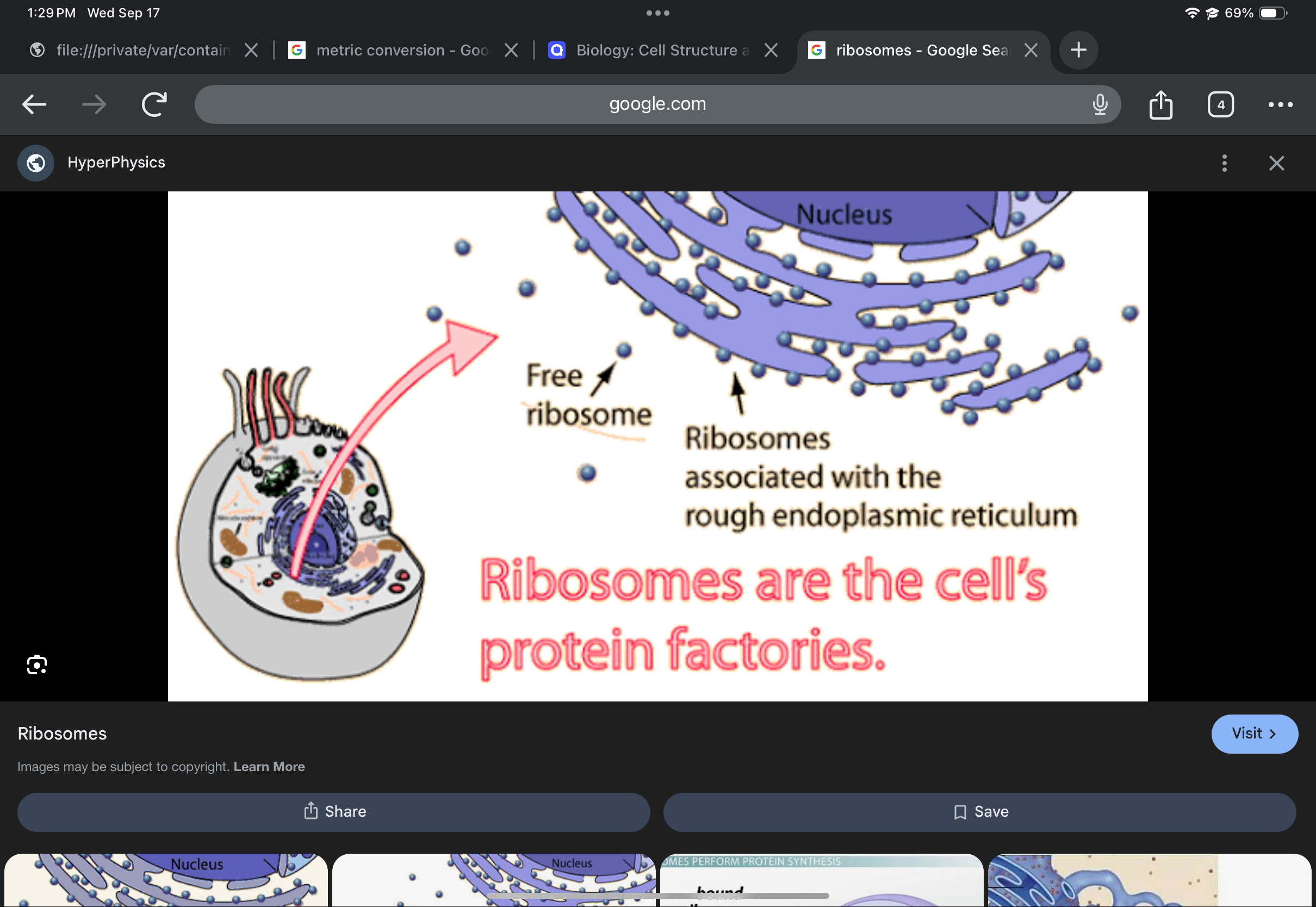
Ribosome
Protein and RNA complex that synthesizes proteins; composed of two subunits.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Membranous network of channels; site of protein and lipid synthesis; includes rough and smooth ER.
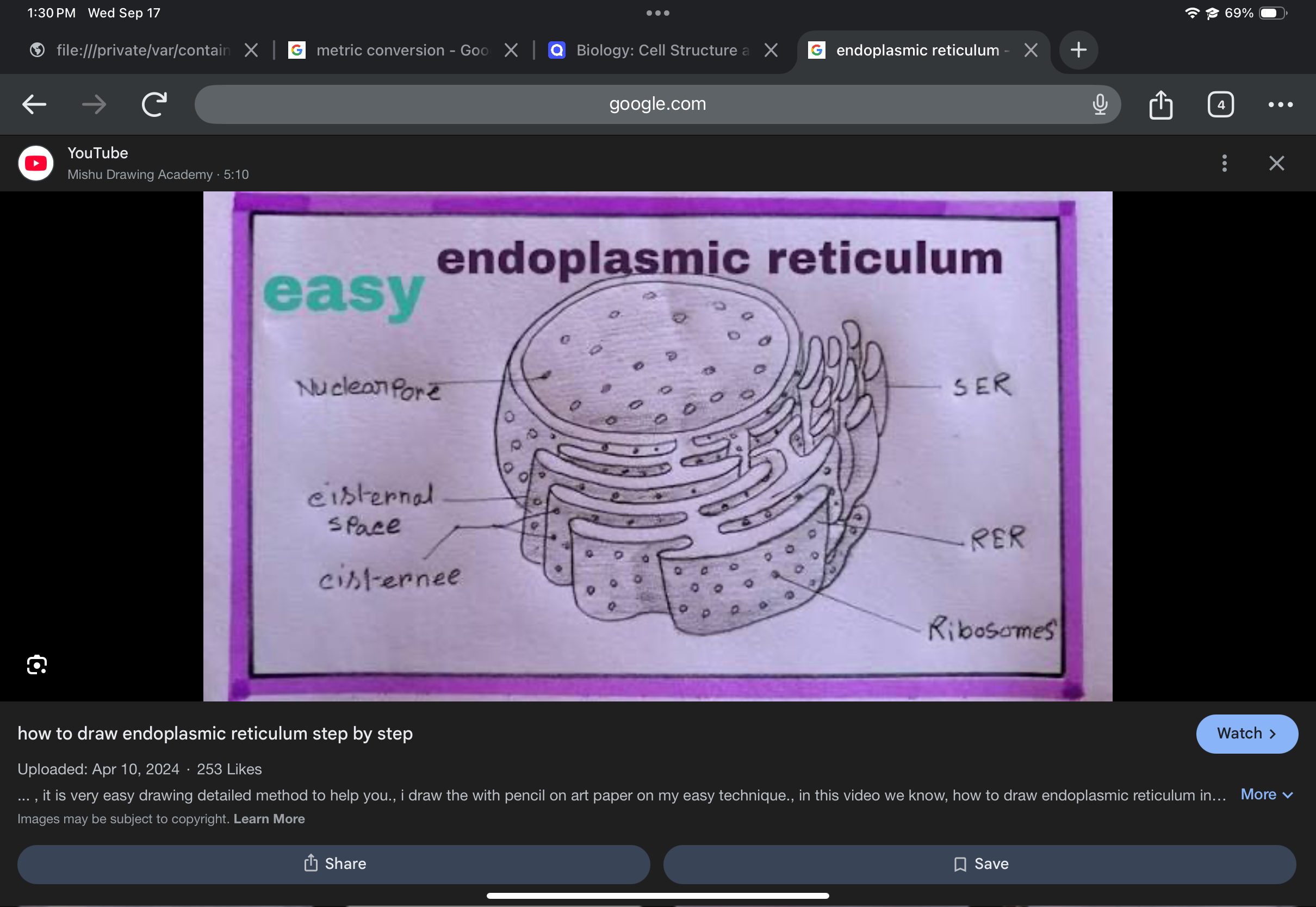
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER)
ER studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins destined for secretion or membranes.
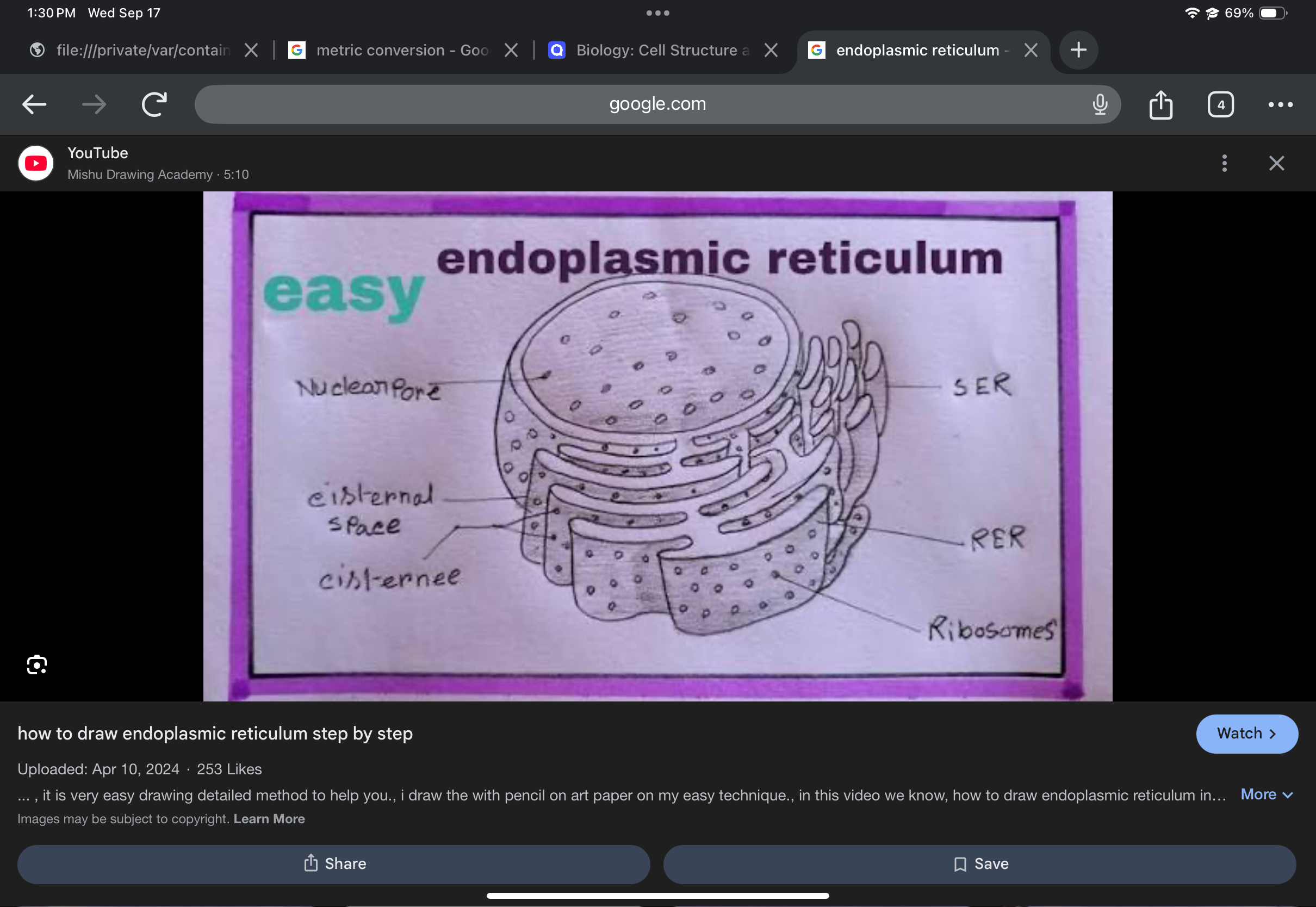
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER)
ER lacking ribosomes; synthesizes lipids and detoxifies certain substances.
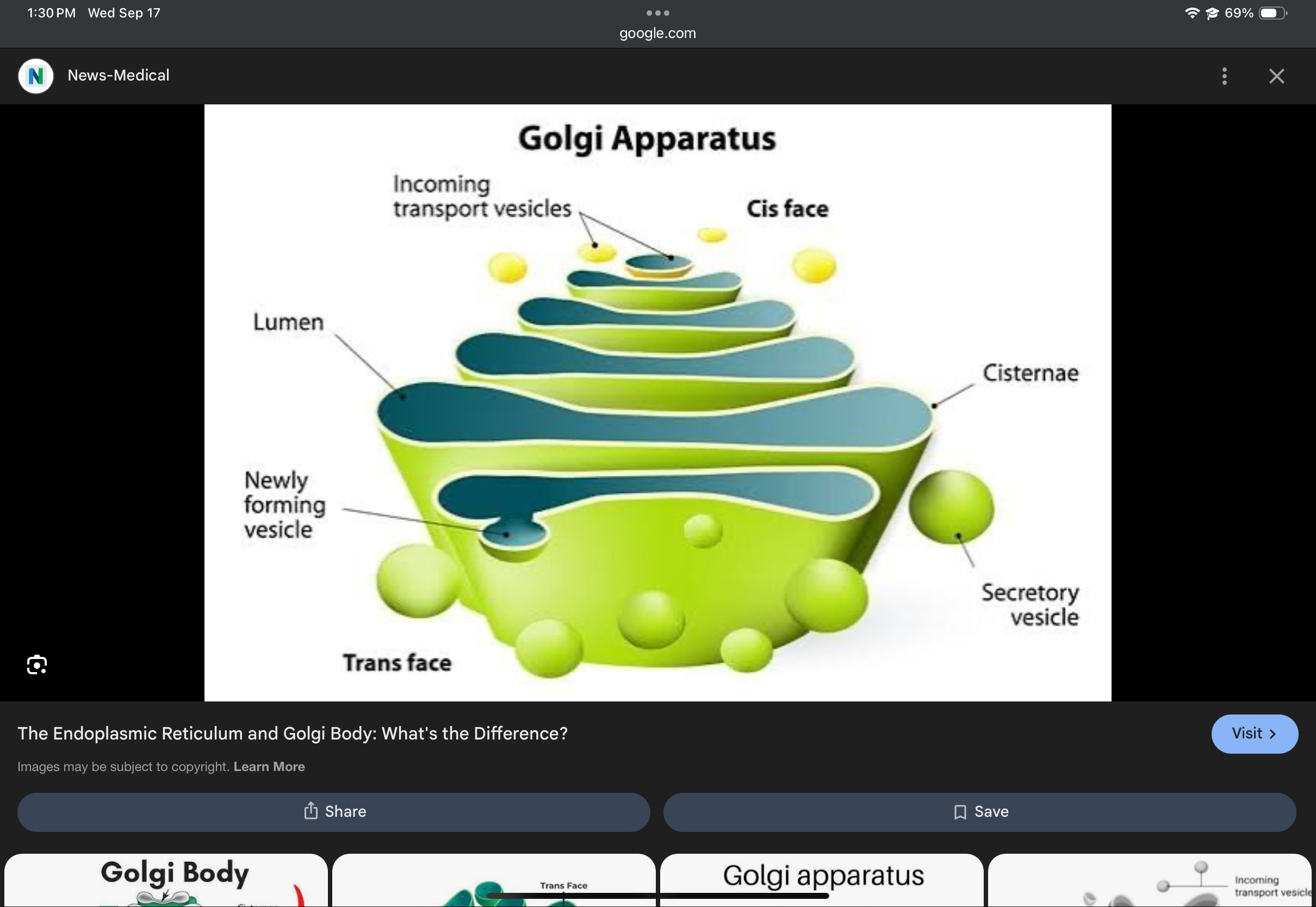
Golgi apparatus
Processes, packages, and distributes proteins and lipids via vesicles.
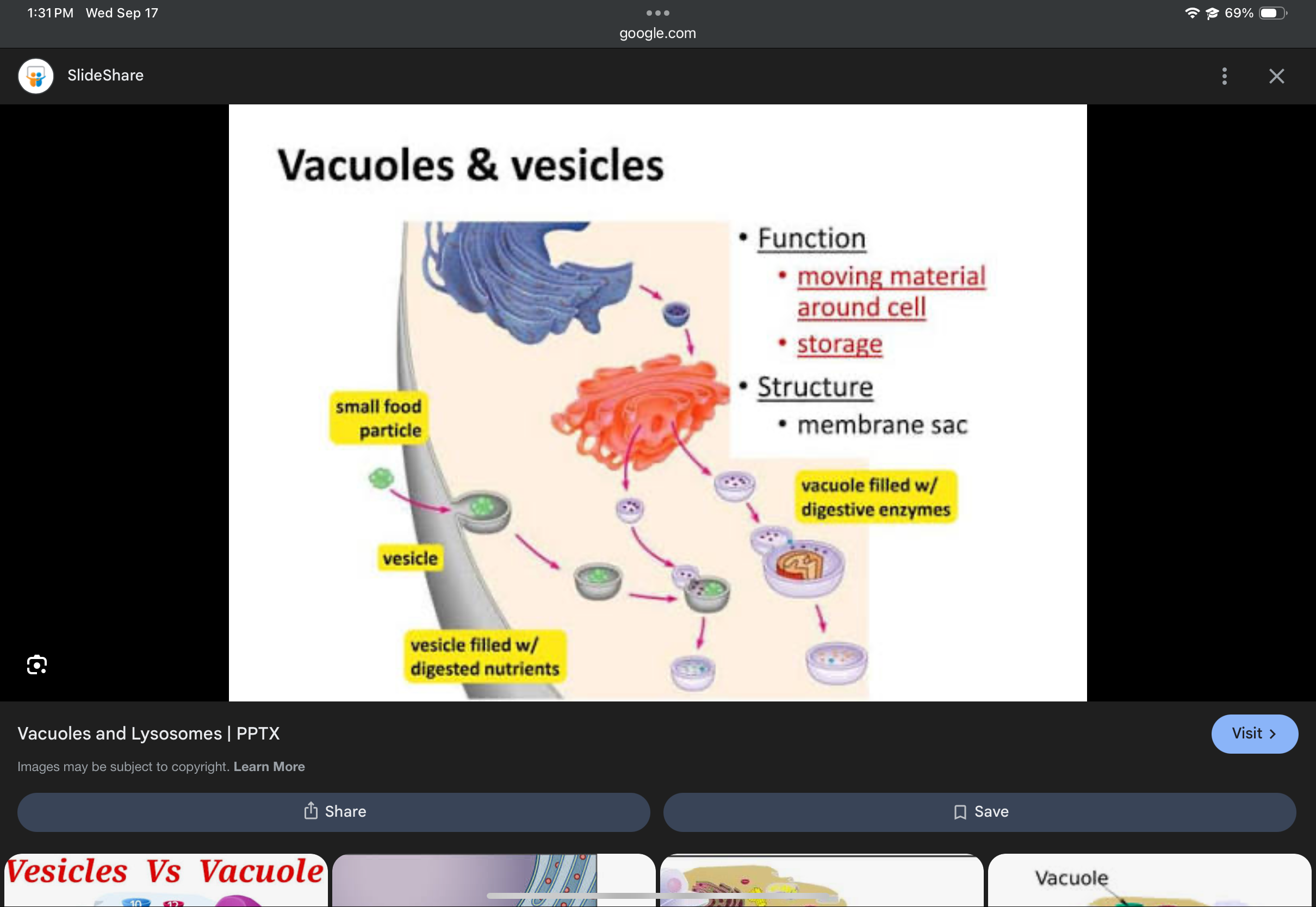
Vesicle/vacuole
Membrane-bound sac that stores and transports substances.
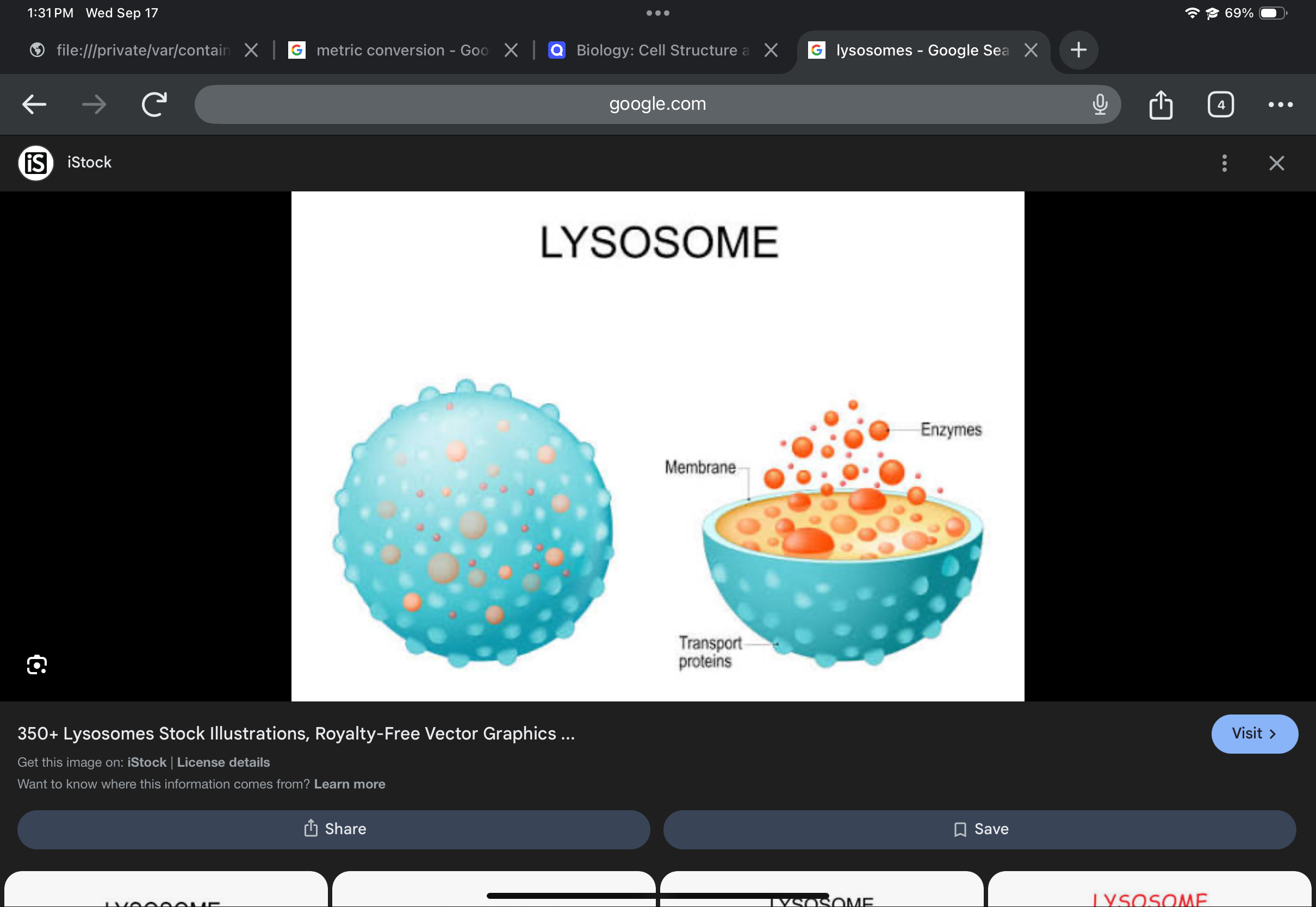
Lysosome
Vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes; digests macromolecules and cellular components.
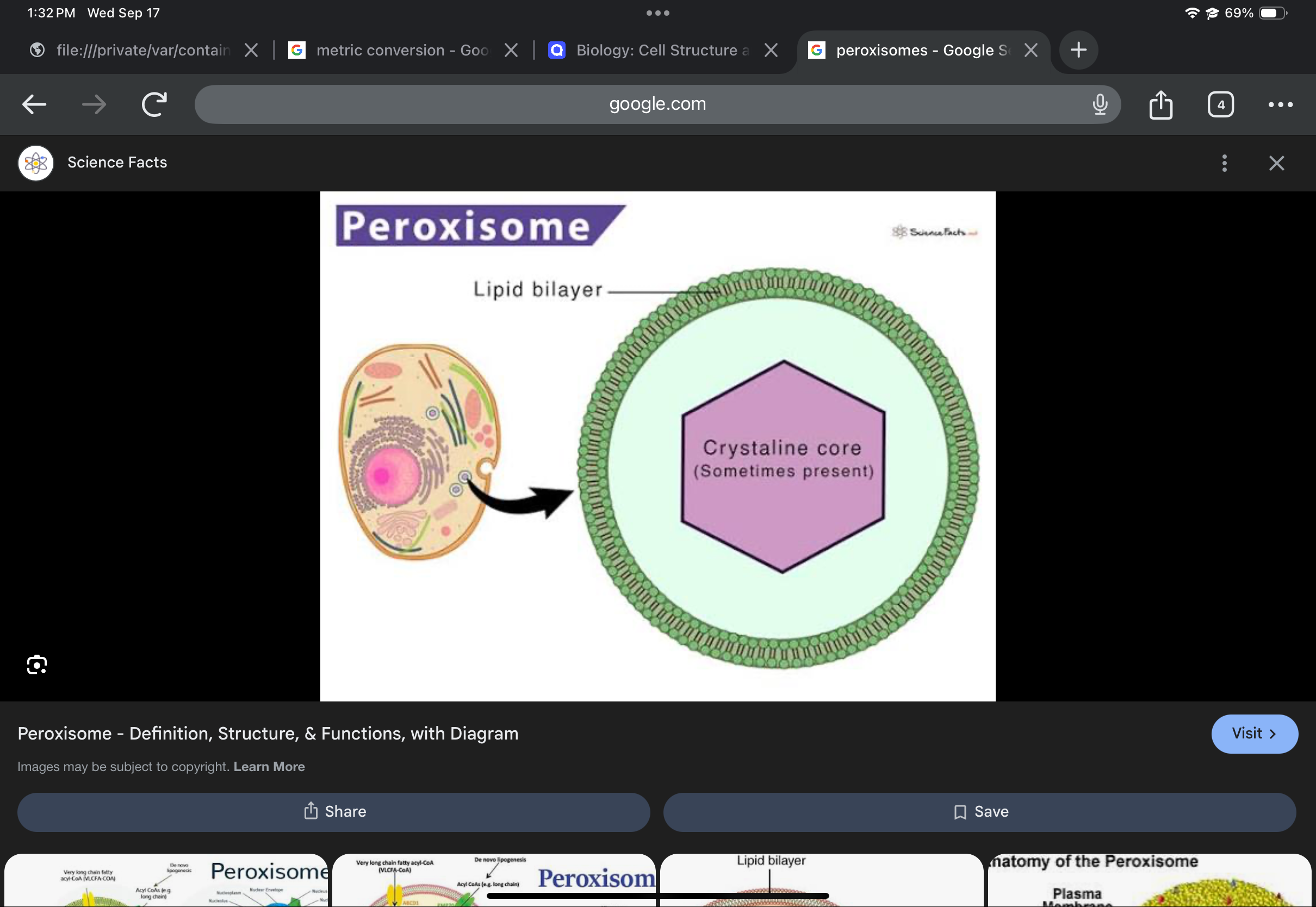
Peroxisome
Vesicle containing enzymes; breaks down fatty acids and detoxifies hydrogen peroxide.
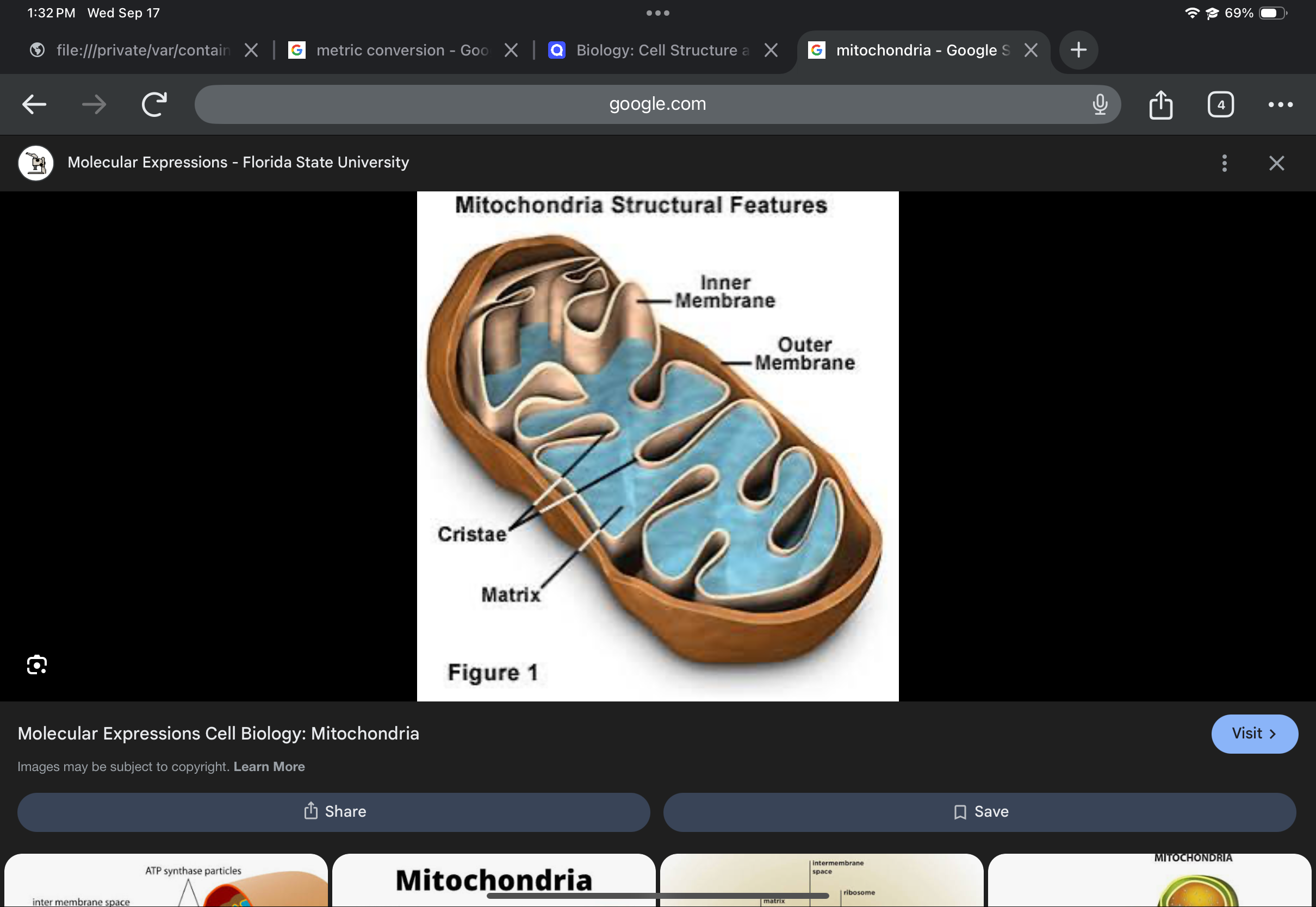
Mitochondrion
Produces energy (ATP) via cellular respiration; has a double membrane with cristae.
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis; contains thylakoids; double membrane.
Cytoskeleton
Network of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and actin filaments that maintains shape and supports movement.
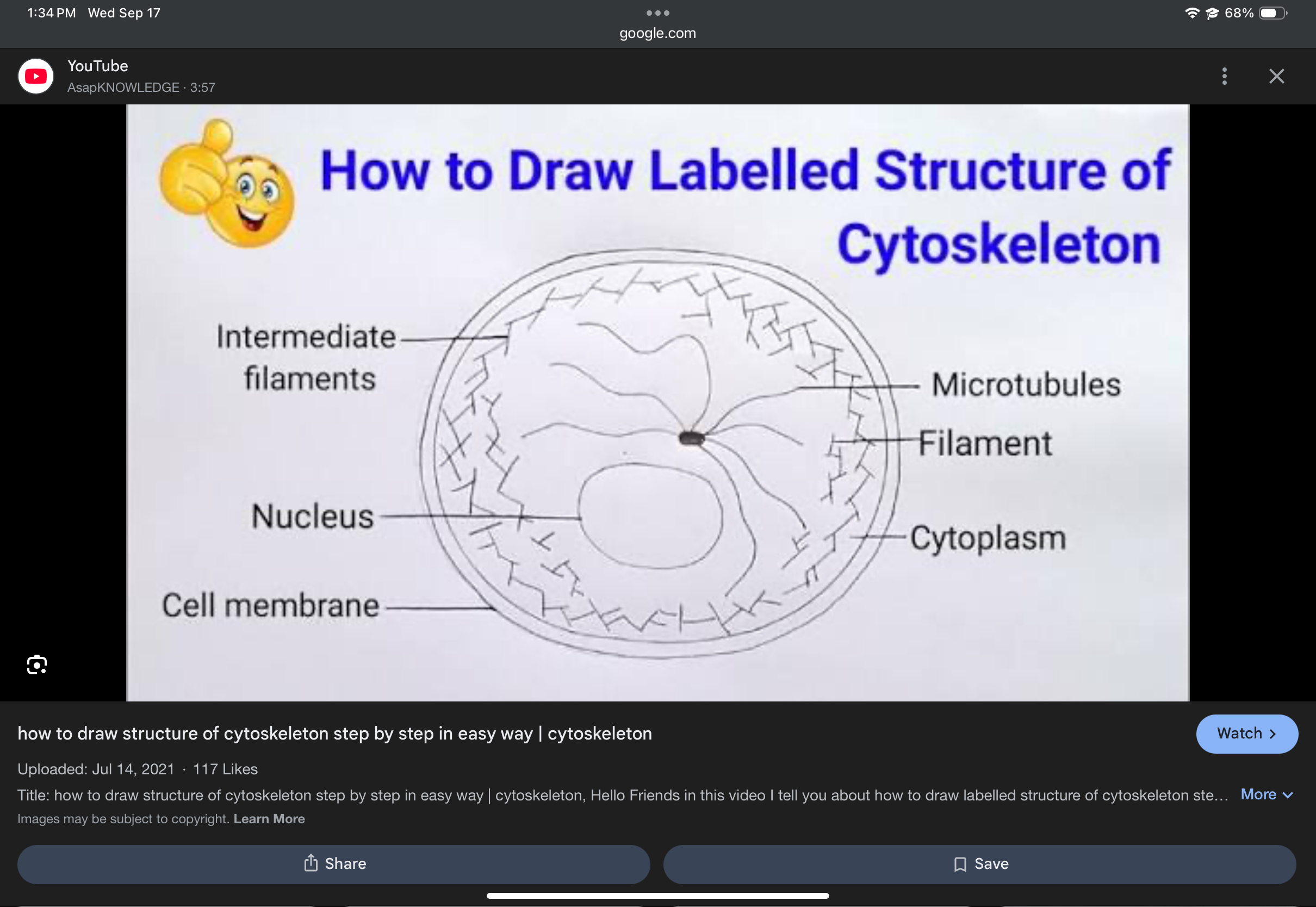
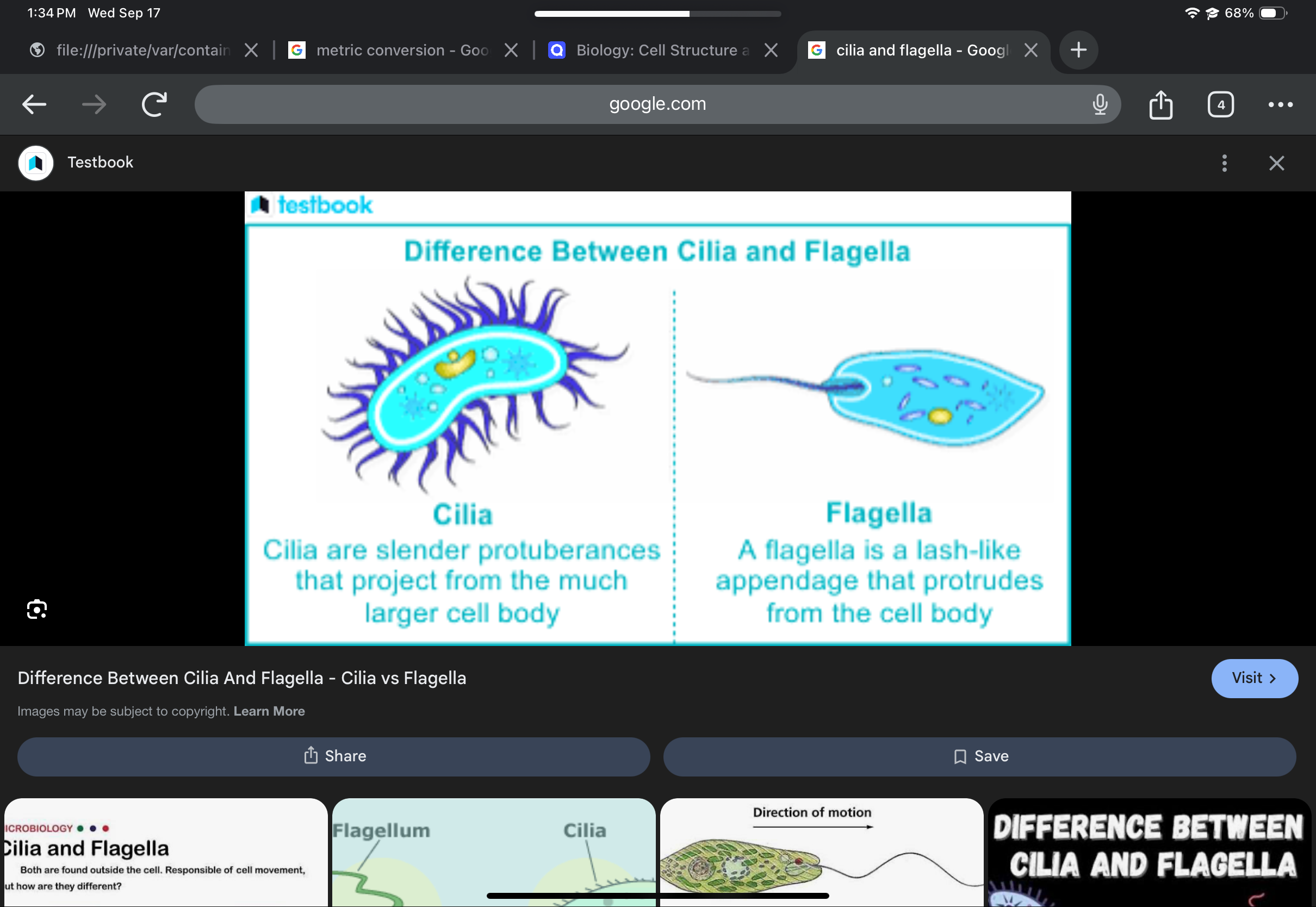
Cilia and flagella
Hair-like structures that move the cell or surrounding substances; supported by microtubules.
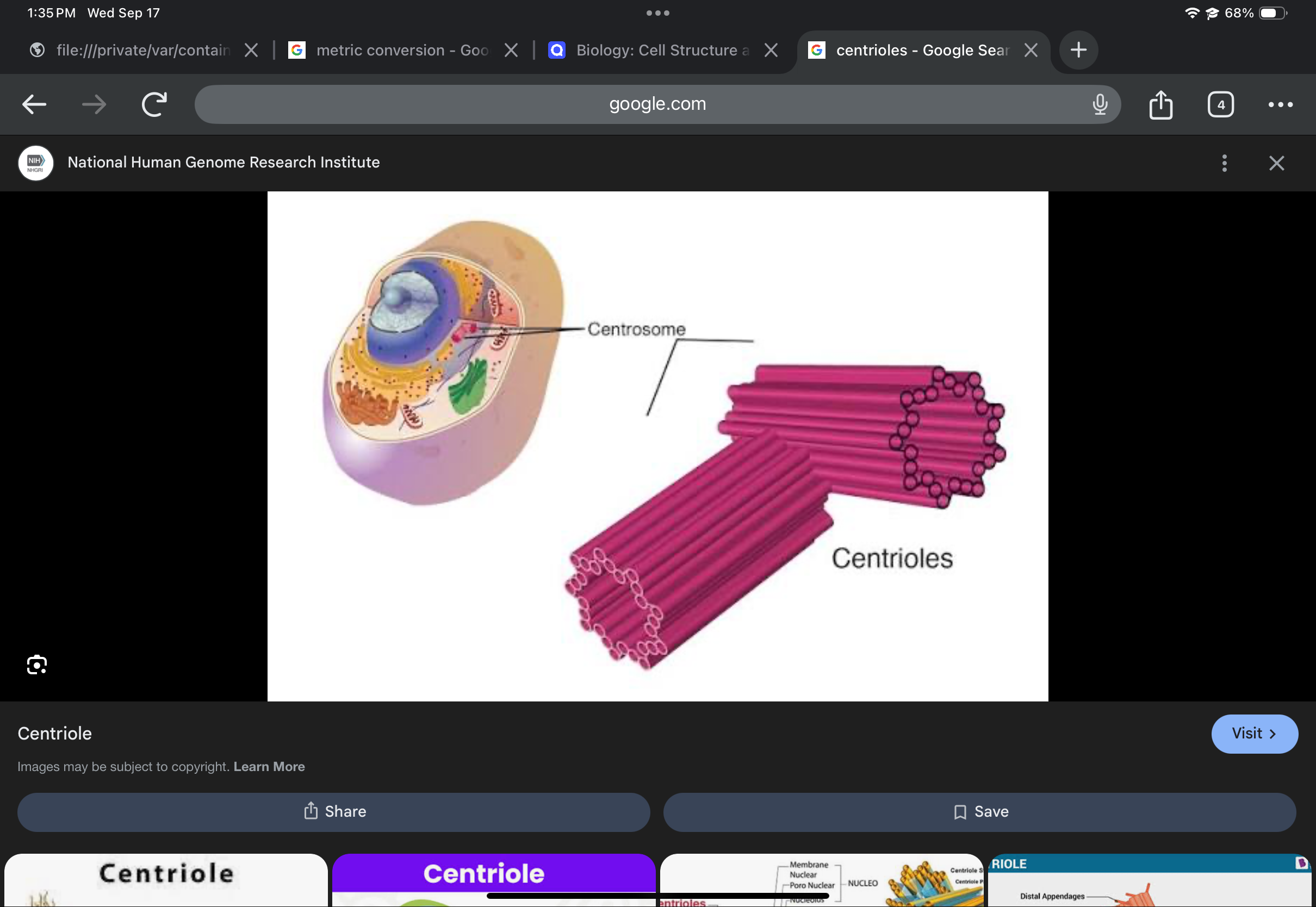
Centrioles (centrosome)
Organize microtubules for cilia/flagella formation; centrosome organizes microtubules during cell division.