2. Benign Tumors of the Jaws
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
slide 1-6
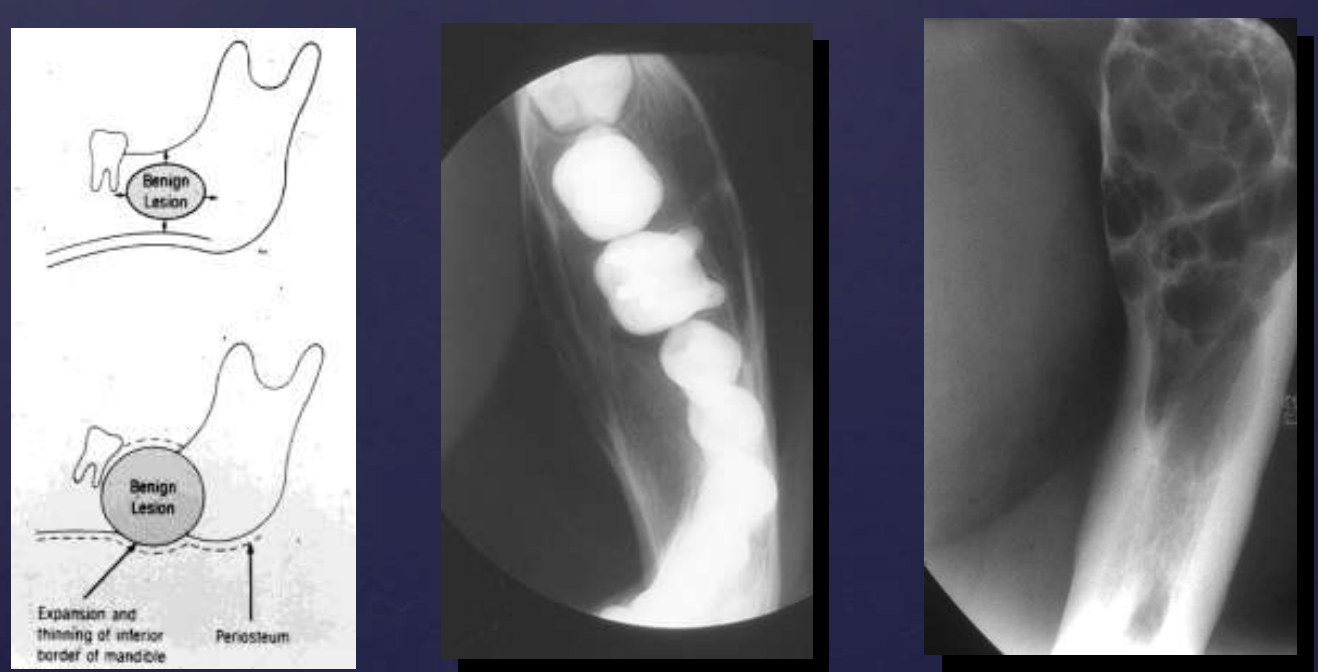
how do benign tumors effect surrounding structures: cortical bone?
expansion
thinning
erosion (in case of aggressive benign lesions)
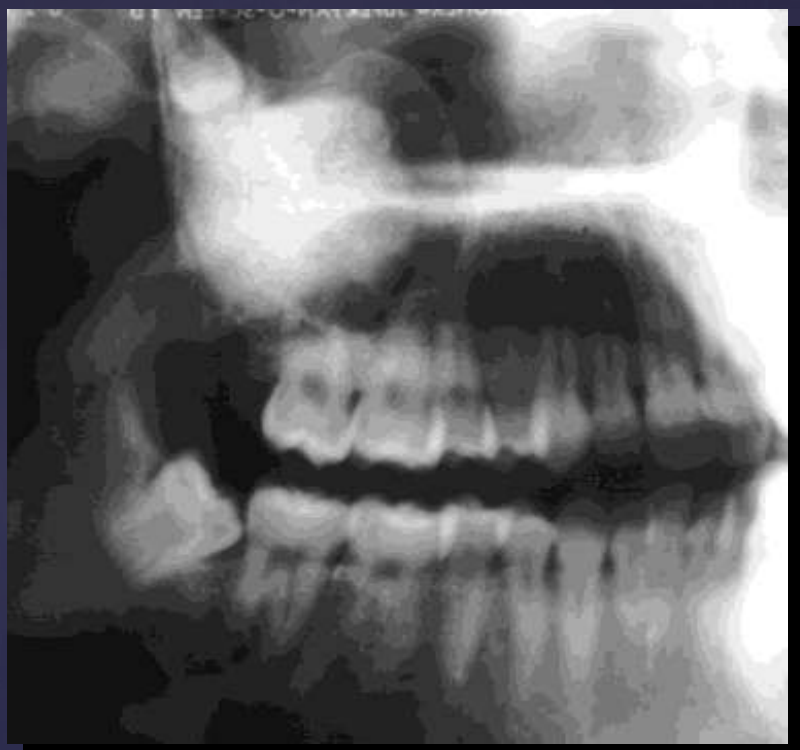
how do benign tumors effect surrounding structures: maxillary sinus?
displacement
what surrounding structures can be affected by benign tumors?
manidbular canal (displaced)
maxillary sinus (displaced)
cortical bone (expansion, thinning, erosion)
teeth (displaced)
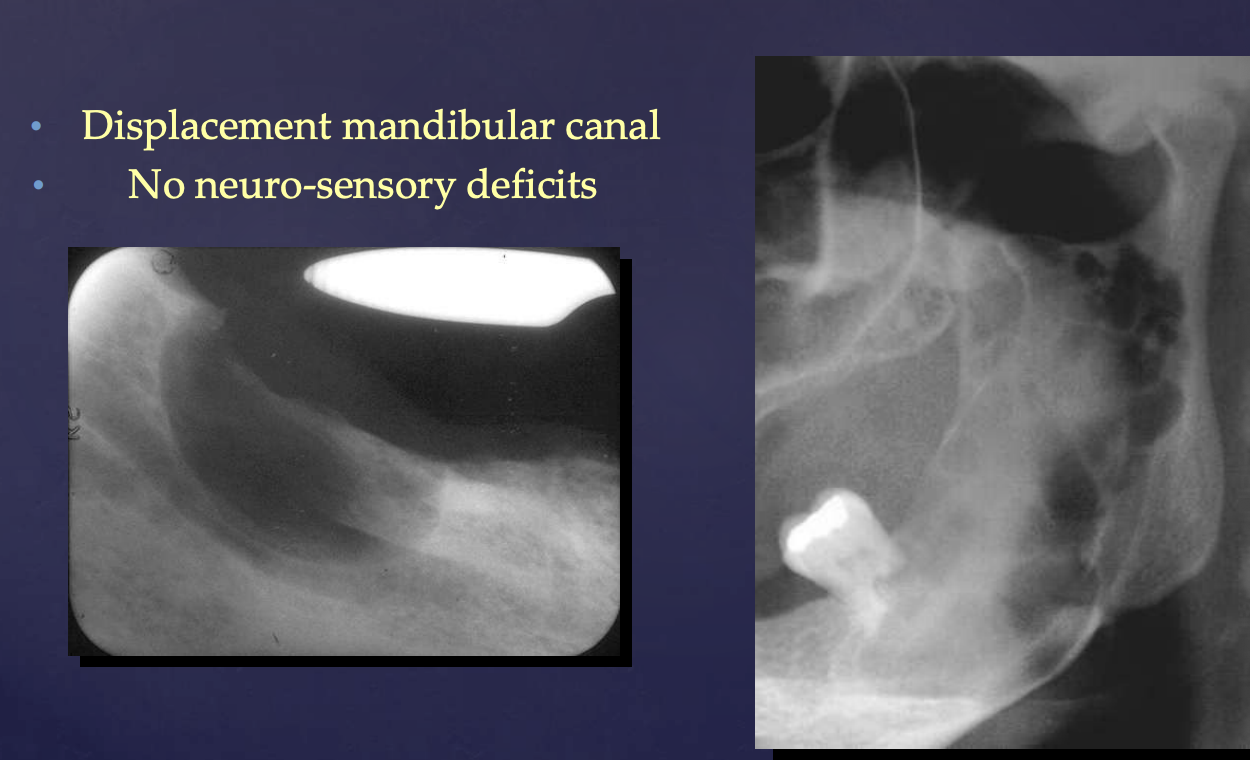
Displacement mandibular canal (No neuro-sensory deficits)
how do benign tumors effect surrounding structures: teeth?
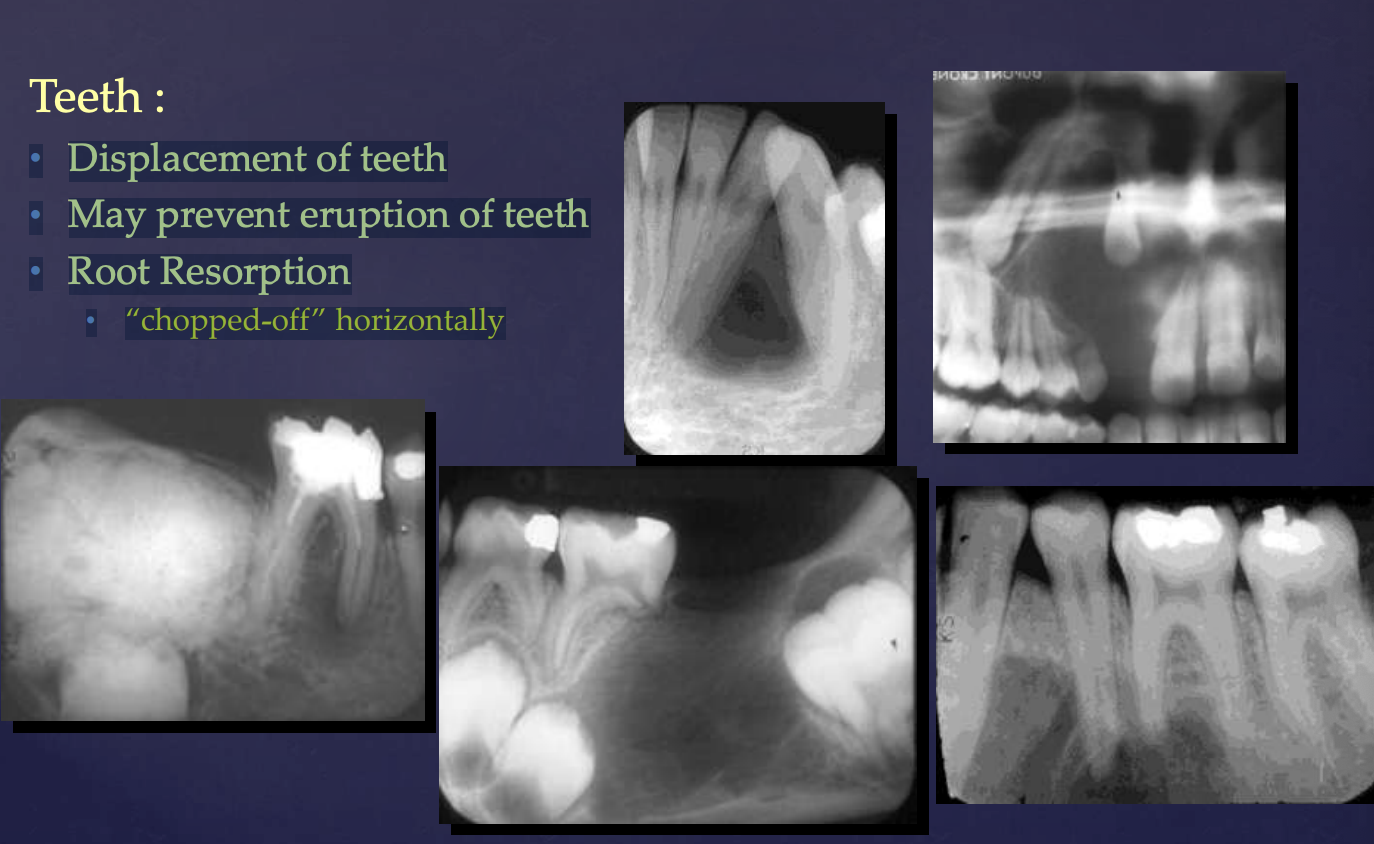
• Displacement of teeth
• May prevent eruption of teeth
• Root Resorption → “chopped-off” horizontally
how do benign tumors effect surrounding structures: mandibular canal?
displacement (no neuro-sensory deficits)
slide 11
• Ameloblastoma
• Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
• Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
• Squamous odontogenic tumor
• Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma
What type of tumors?
epithelial tumors
• Odontogenic myxoma
• Cementoblastoma
• Odontogenic fibroma
• Granular cell odontogenic tumor
What type of tumors?
Ectomesenchymal Tumors
• Odontoma
• Ameloblastic fibroma
• Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
• Odontoameloblastoma
• Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma
What type of tumors?
Mixed tumors
what is a slow-growing, locally-invasive, benign tumor and is the second most common odontogenic tumor?
Ameloblastoma
what are the 3 patterns of ameloblastomas?
• 75-86% (Conventional) ameloblastoma
• 13-21% Unicystic ameloblastoma
• 1-4% Peripheral ameloblastoma
what is the average age of Ameloblastoma patients?
35 years
is there a gender predilection with Ameloblastoma?
no
Ameloblastomas occur >80% in the maxilla/mandible (which one?)
mandible (usually molar region)
how do Ameloblastomas present symptomatically?
Often asymptomatic
Usually presents as painless swelling
Rare pain or paresthesia
Ameloblastomas
how do ameloblastomas radiographically present?
well circumscribed, corticated
radiolucent
unilocular/multilocular (coarse/curved septae)
expansile
Tooth displacement/root resorption
ameloblastomas
well circumscribed, corticated
radiolucent
unilocular/multilocular (coarse/curved septae)
expansile
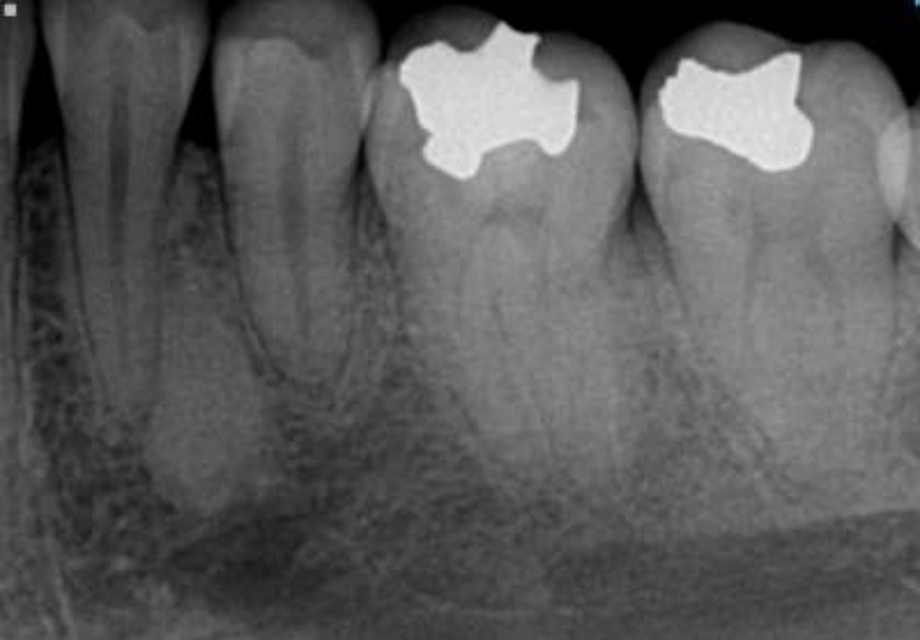
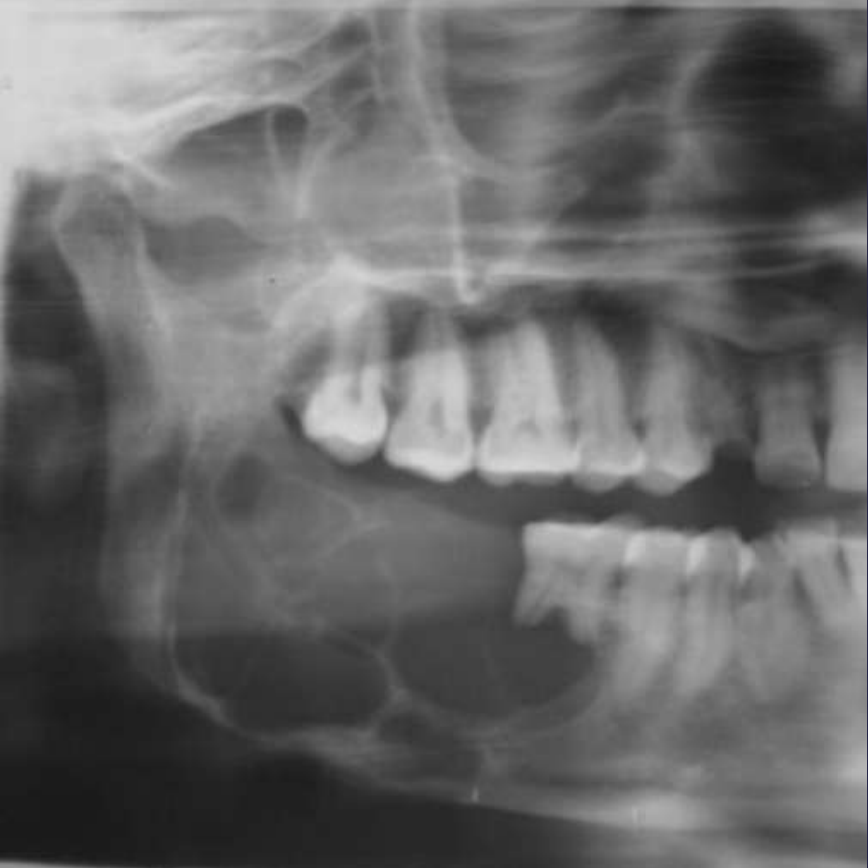
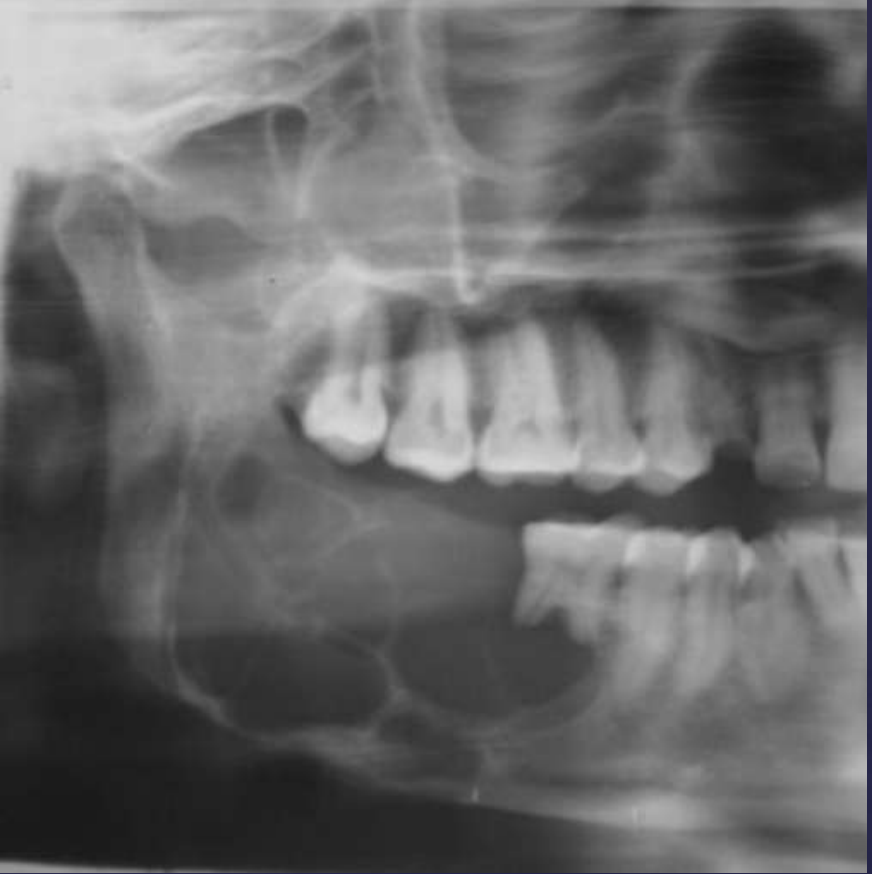
ameloblastoma
Pericoronal/mural; impacted tooth
Displacement of #32
Osseous expansion
Thinning of cortices
Displacement of inferior alveolar nerve canal
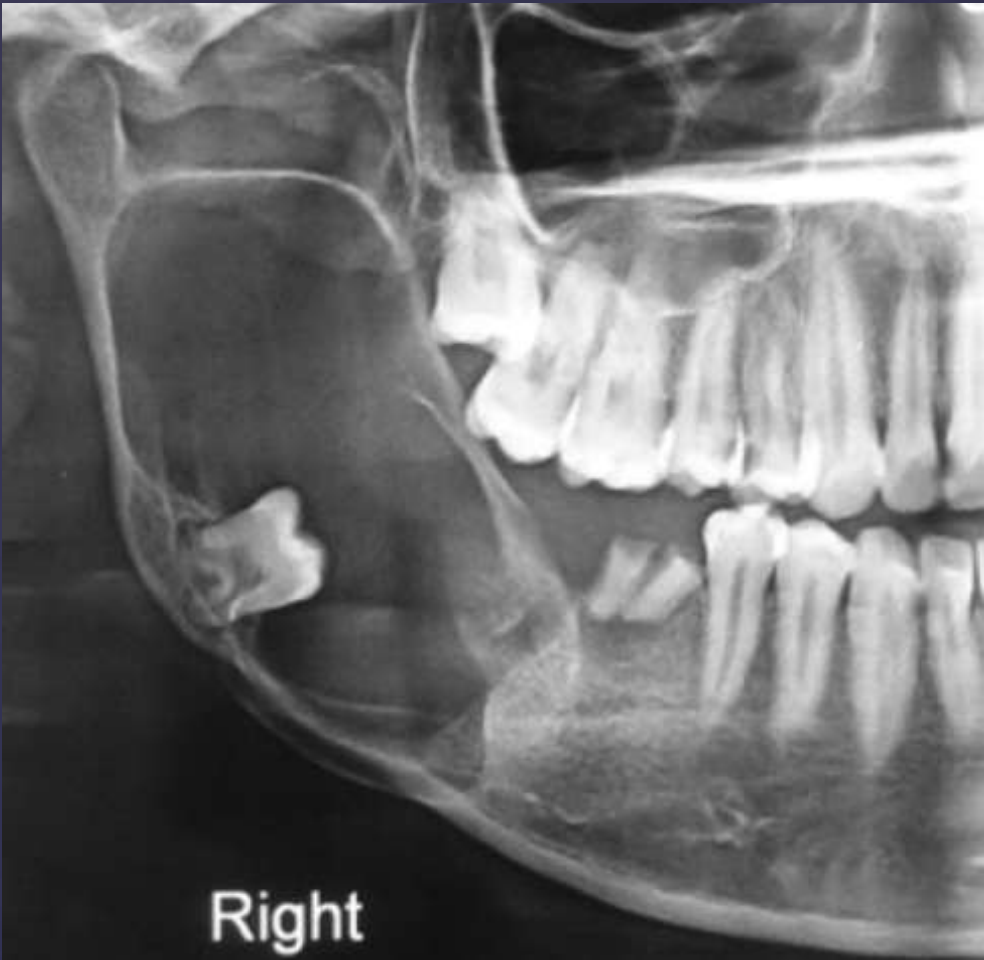
ameloblastoma
Multilocular
Root resorption
Thinning of inferior mandibular border
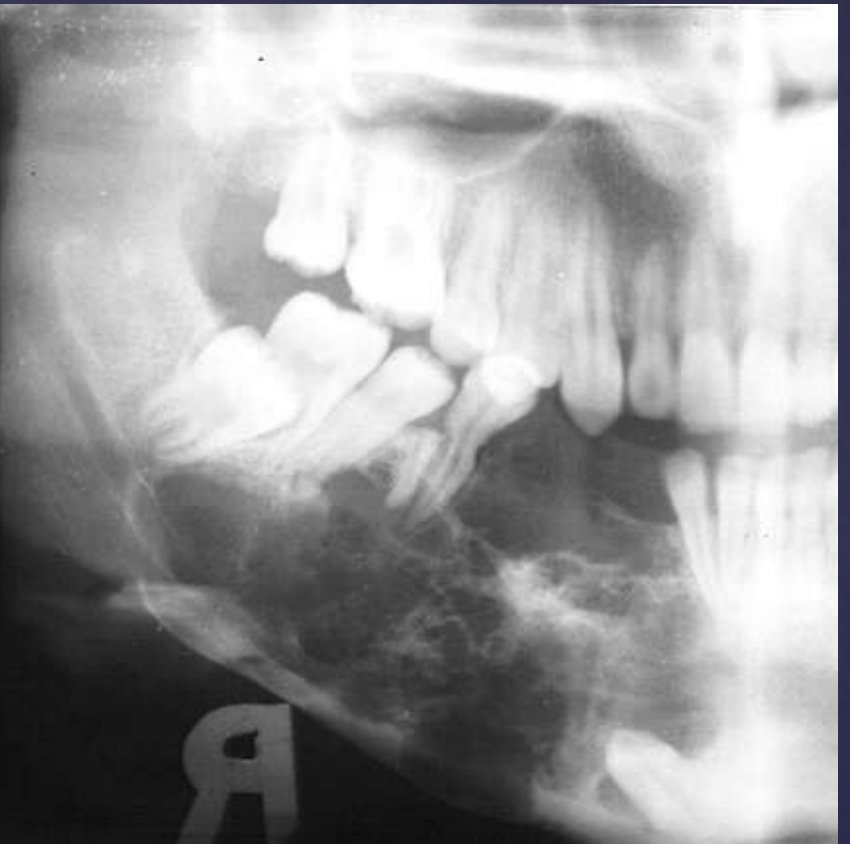
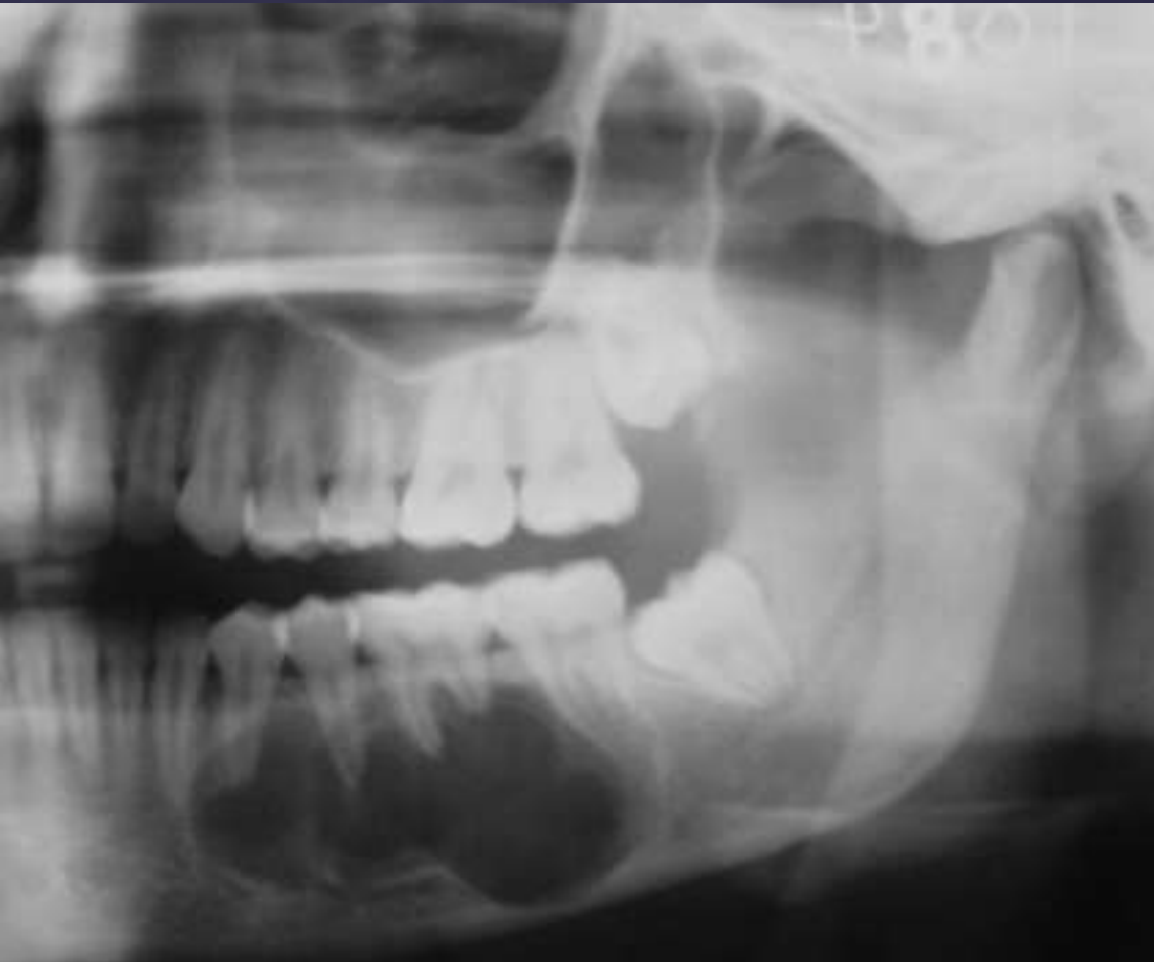
ameloblastoma
Multilocular
Septae appear coarse
Thinning of inferior mandibular border
Displacement of teeth
Displacement of inferior alveolar nerve canal
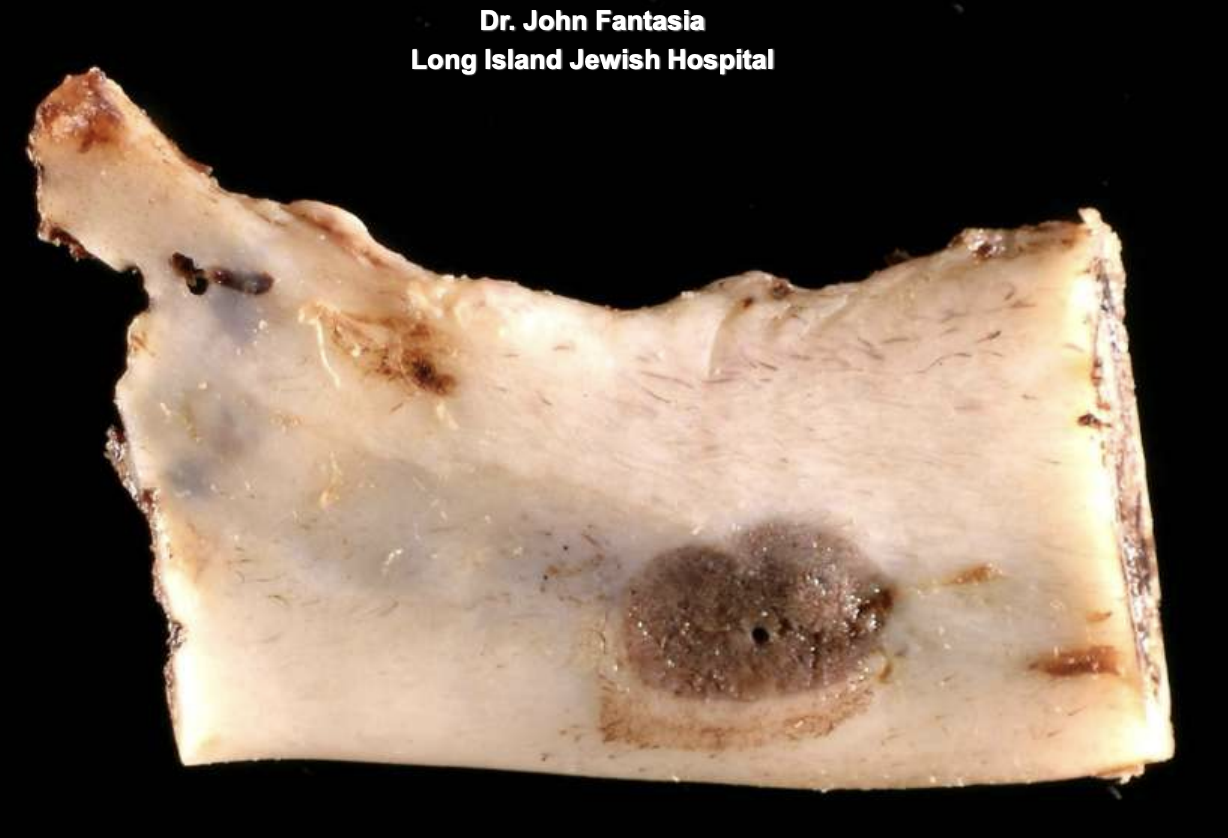
ameloblastomas may arise in the wall of a ____
cyst (mural ameloblastoma)
what are histopathologic patterns of ameloblastomas?
• Follicular
• Plexiform
• Acanthomatous
• Granular cell
• Basal cell
• Desmoplastic
what are the key microscopic histopathologic appearance of ameloblastomas?
Follicular pattern
Nests of epithelium
Island centers resembling stellate reticulum
Peripheral columnar cells with nuclei polarized opposite basement membrane (sub-nuclear vacuolization)
Mature fibrous background
Desmoplastic pattern
Compressed islands and cords of odontogenic epithelium in densely collagenized stroma
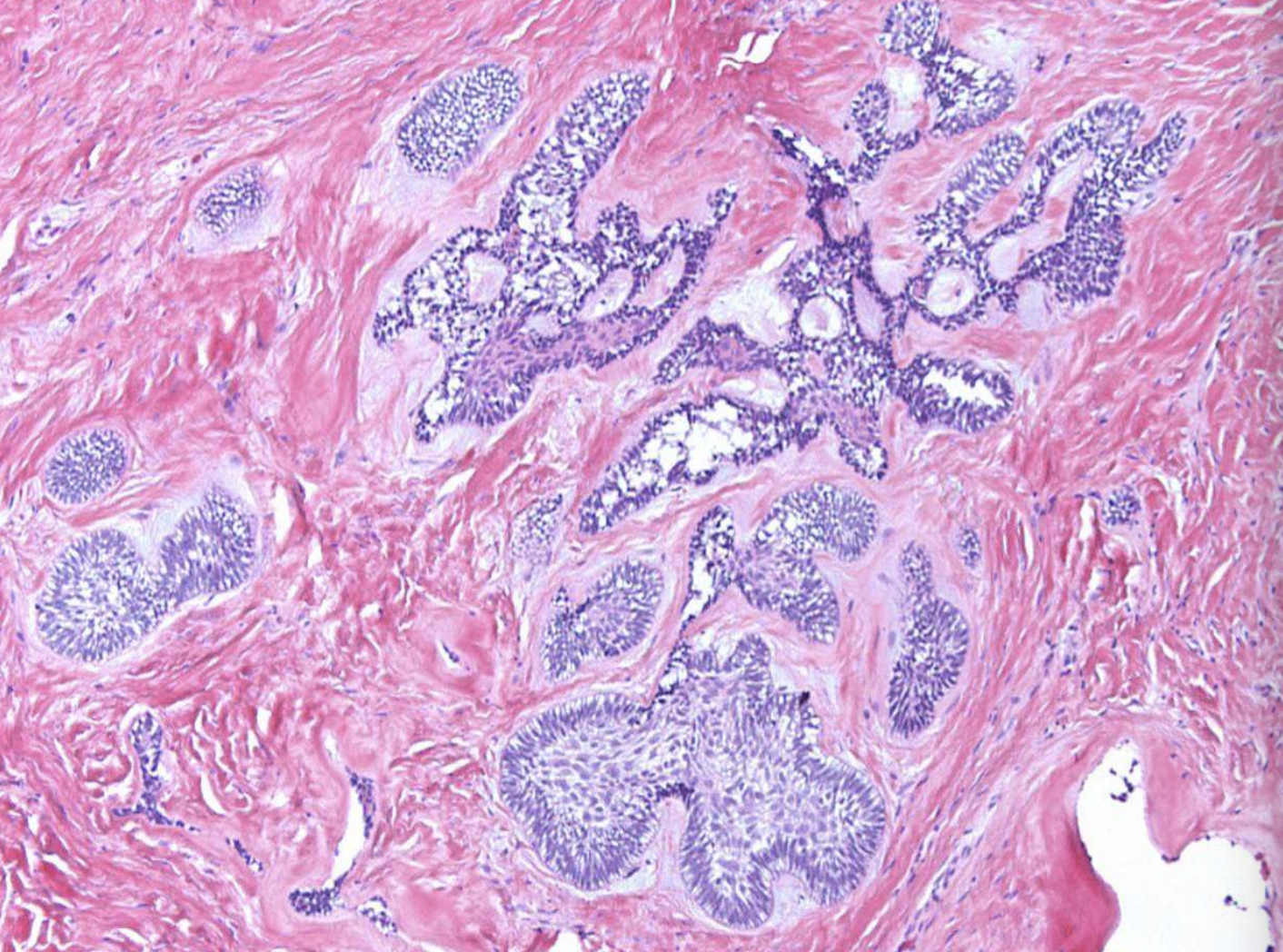
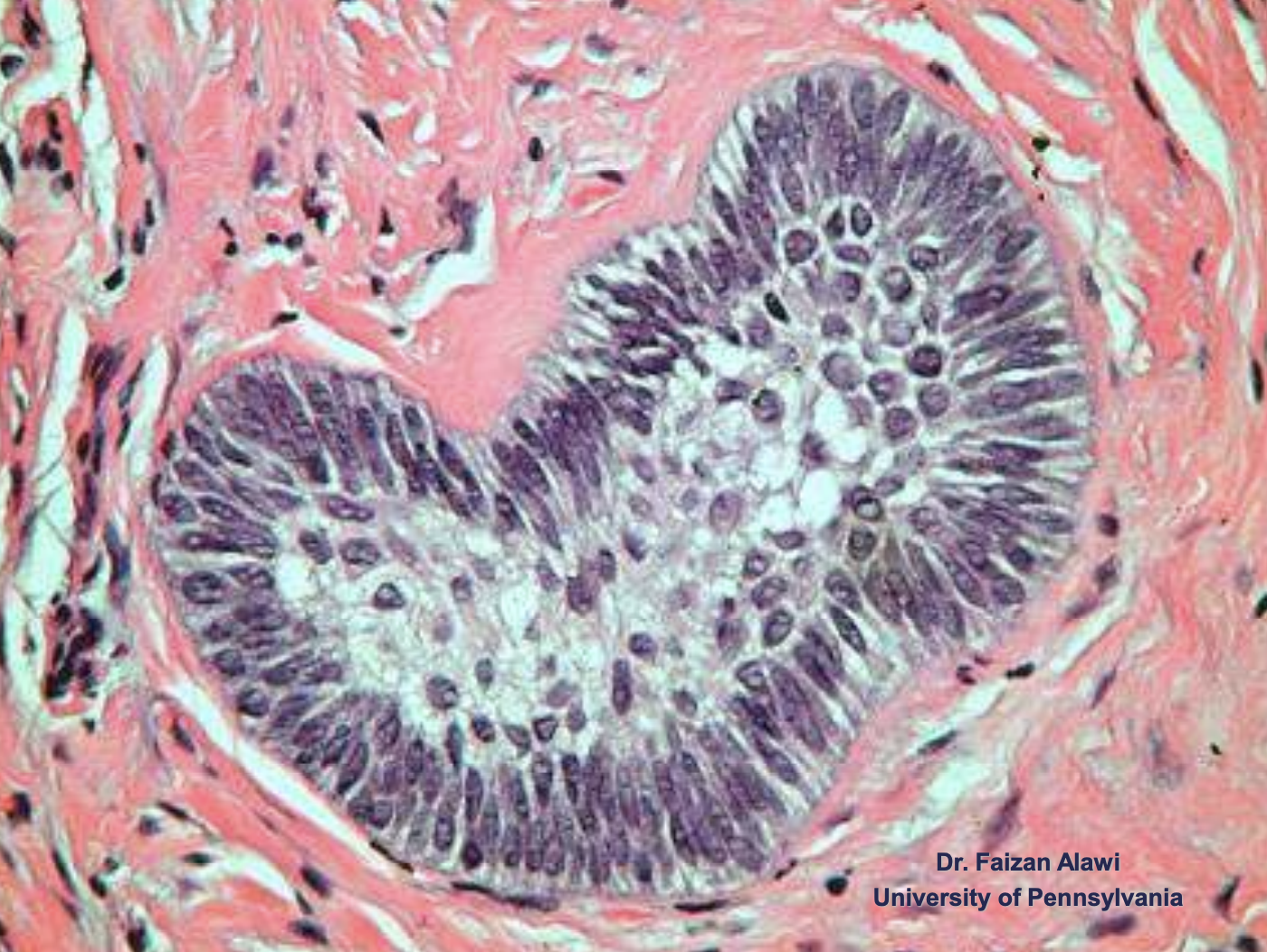
ameloblastoma (Island centers resembling stellate reticulum)
what treatment is indicated for ameloblastomas?
controversial
simple enucleation
curettage
marginal resection
long-term follow up required
what is the recurrence rate after curettage of ameloblastomas?
50-90%
what is the recurrence rate after marginal resection of ameloblastomas?
15%
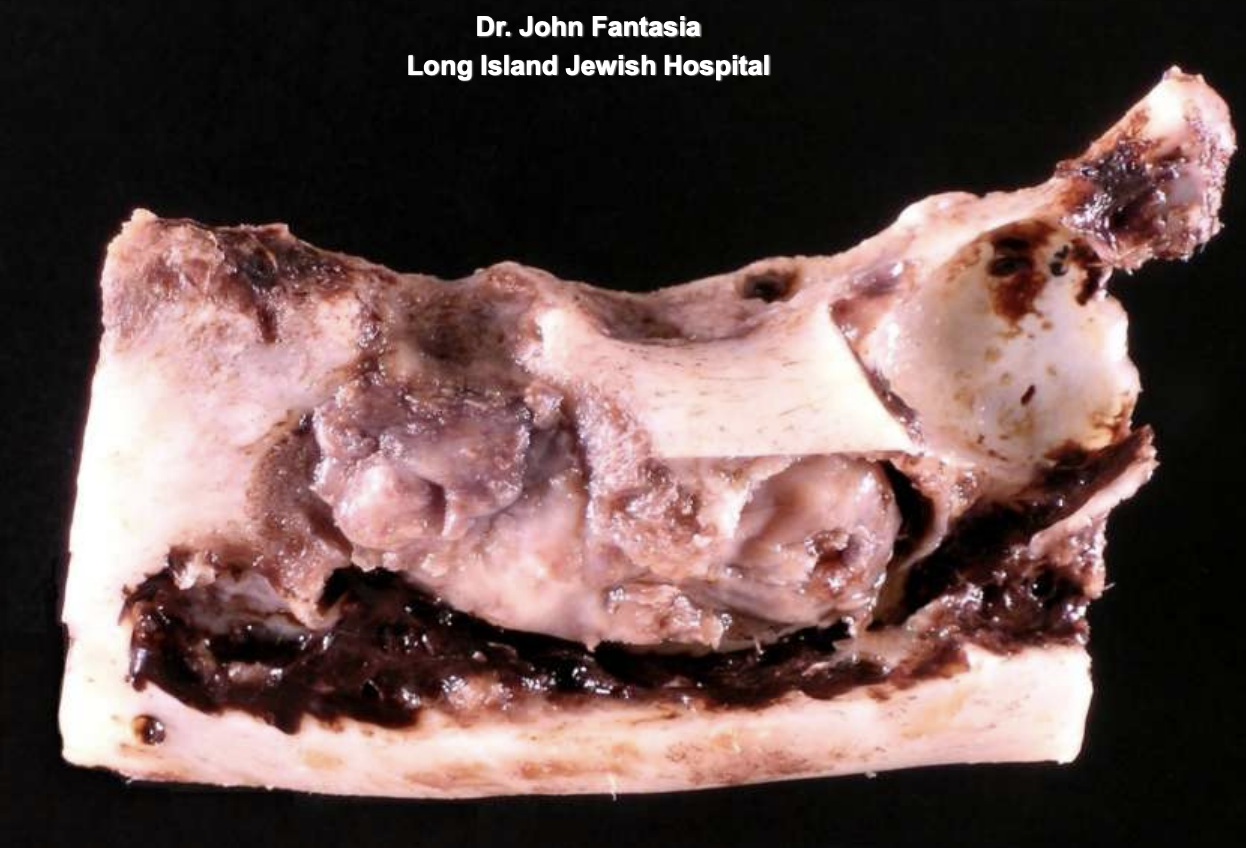
ameloblastoma
% of Unicystic Ameloblastomas are diagnosed between ages 10-20
50%
Unicystic Ameloblastomas have a predilection for what location?
posterior mandible
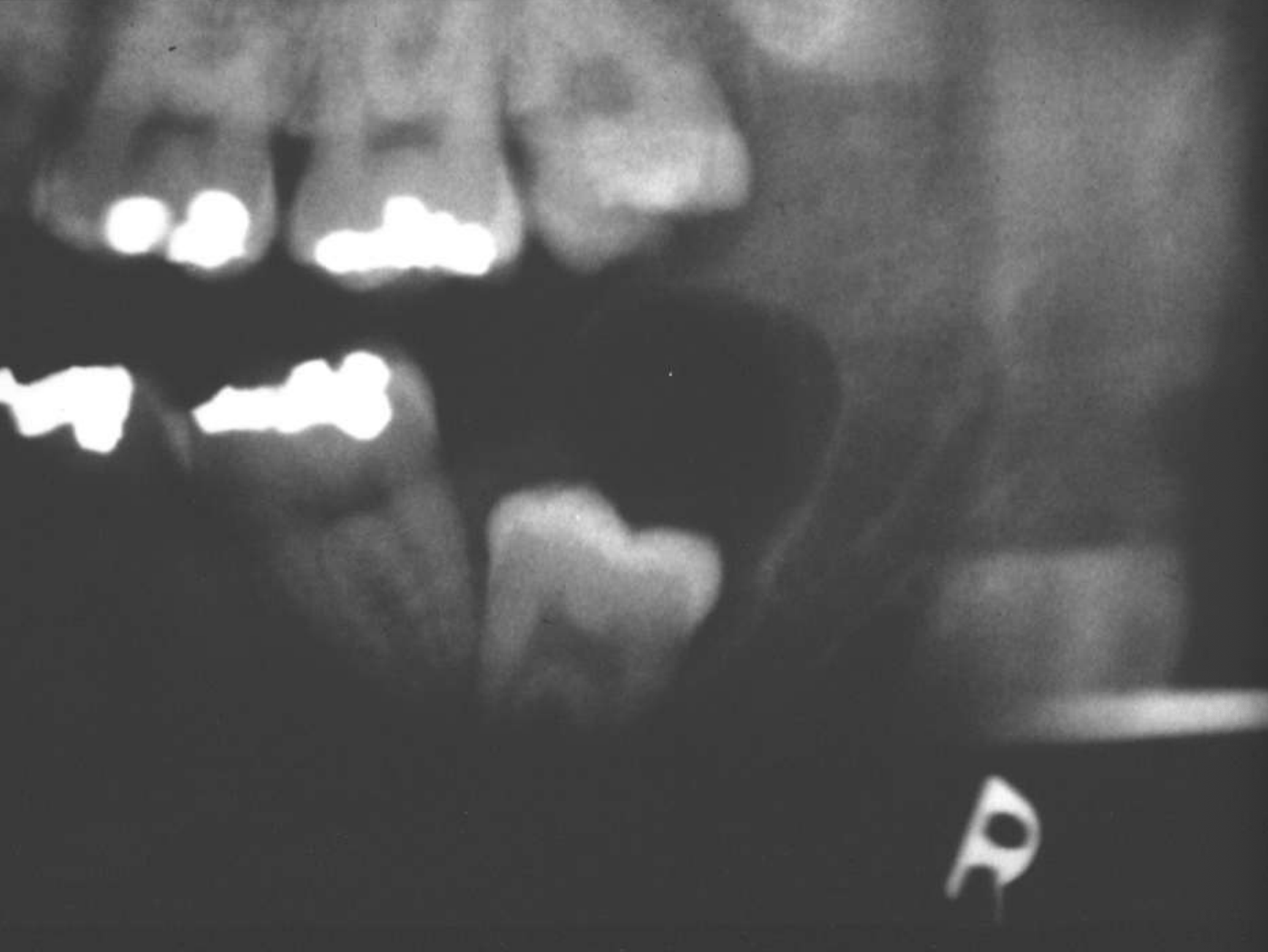
radiographically, Unicystic Ameloblastomas often mimic what?
dentigerous cysts
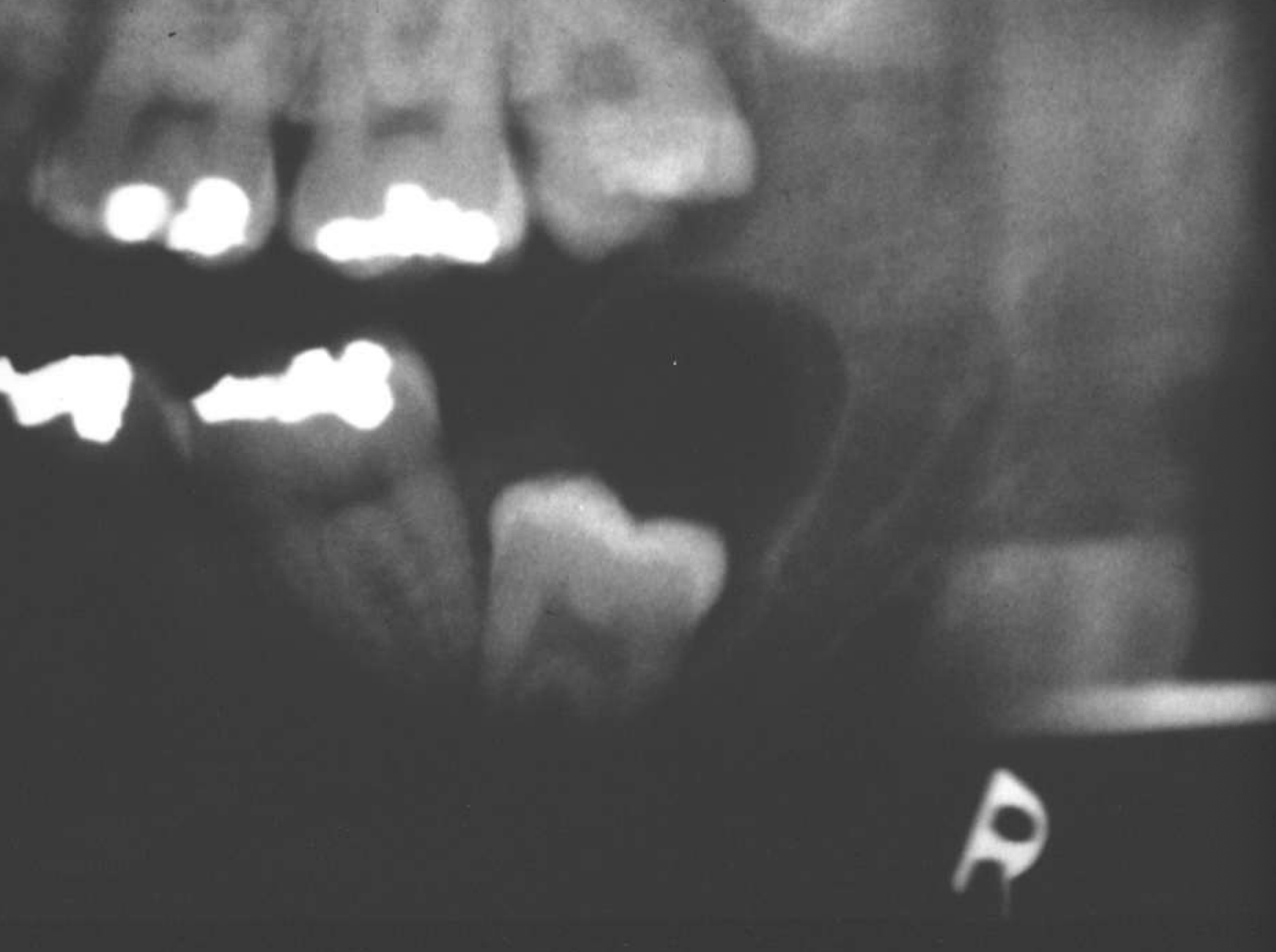

Unicystic Ameloblastomas
expansion/thinng ext. oblique ridge
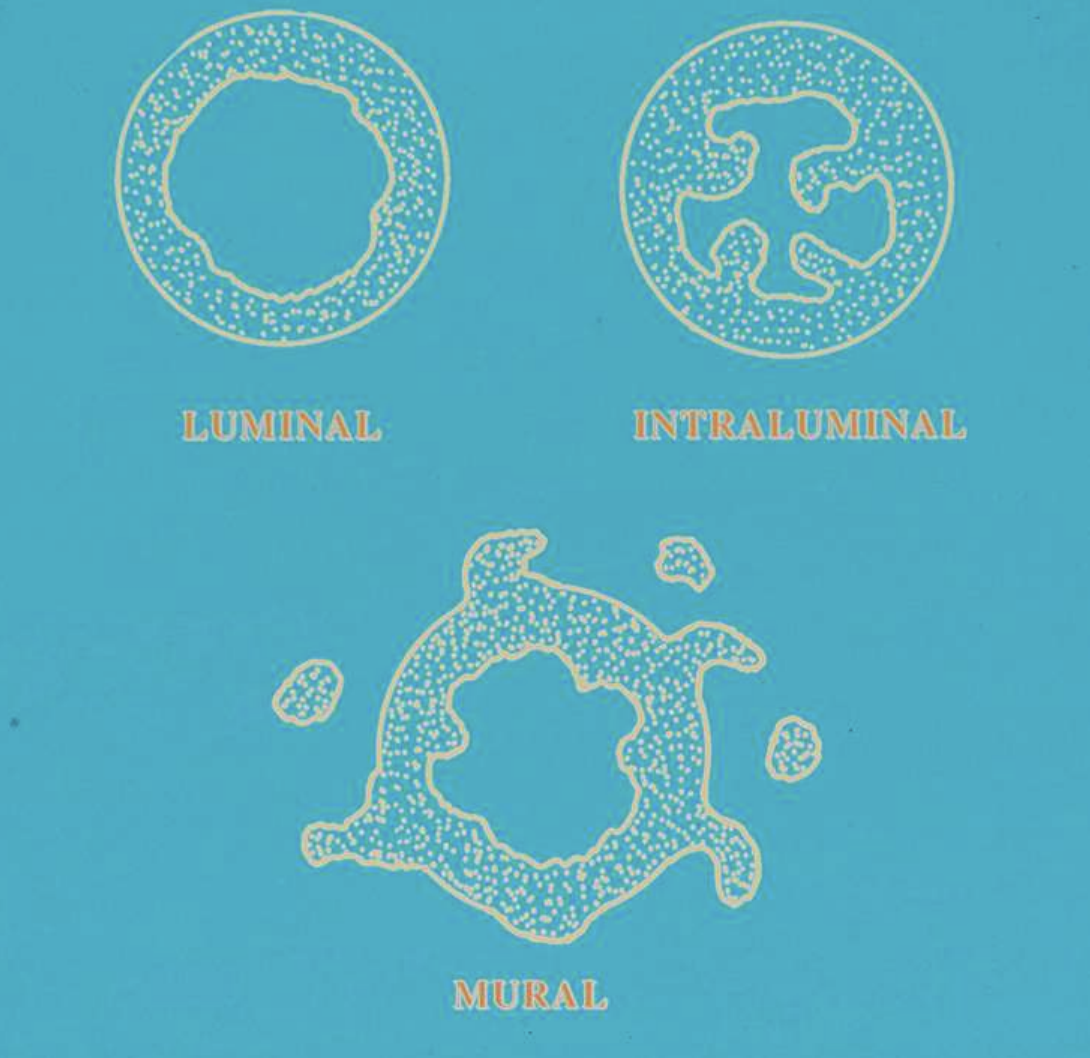
what are 3 types of Unicystic Ameloblastomas?
luminal type → tumor confined to luminal surface
intraluminal type → tumor nodules project from lining into lumen
mural type → tumor islands in wall of cyst
slide 44
what treatment is indicated for Unicystic and peripheral Ameloblastoma?
Luminal and intra-luminal types treated with enucleation and follow-up
Mural type treatment debatable
what is the recurrence rate for Unicystic Ameloblastoma?
10-20%
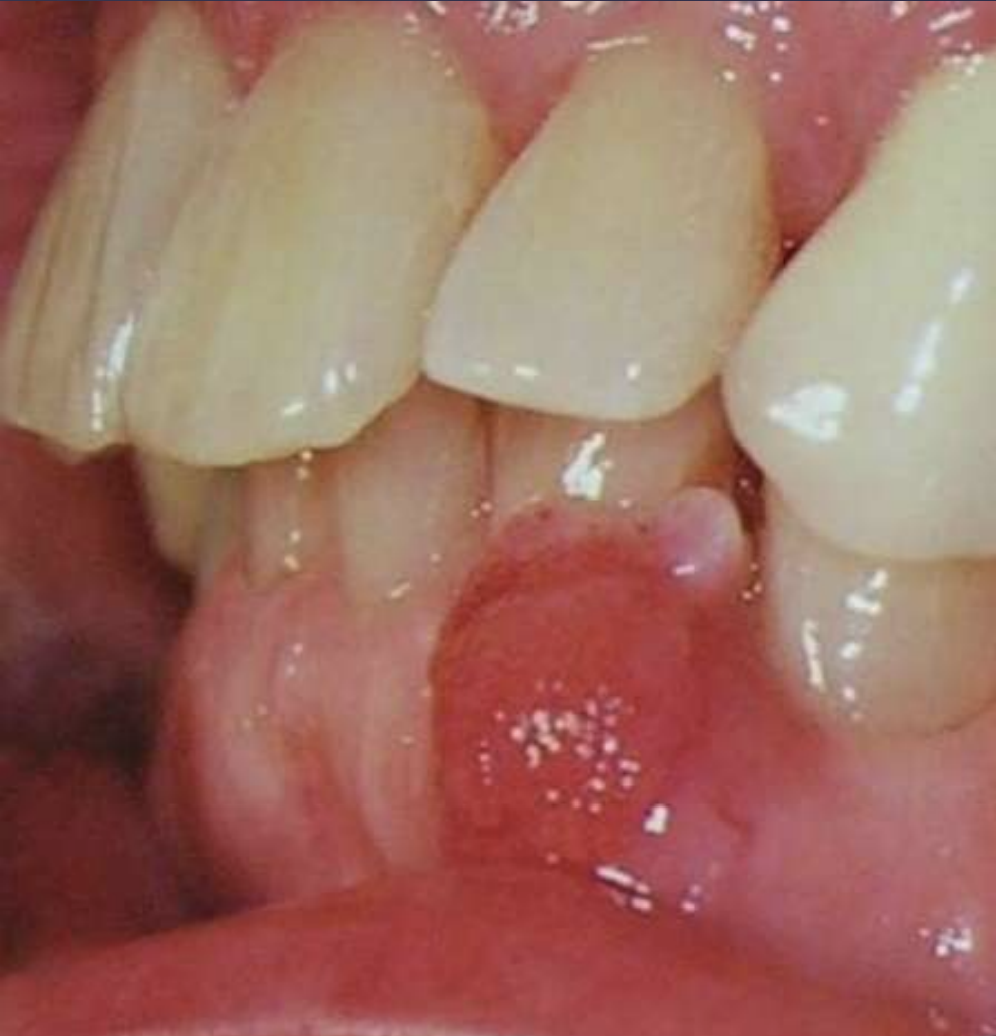
• Painless, non-ulcerated gingival nodule
• Resembles pyogenic granuloma or fibroma
• Usually < 1.5cm
• Superficial alveolar bone may be eroded
What benign tumor?
Peripheral Ameloblastoma
what is the average age of Peripheral Ameloblastoma?
52
which jaw do Peripheral Ameloblastoma have a predilection for?
manible
slide 49-54
what demographics are affected by Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor? and what location is there a predilection for?
Age: 70% 10-20 years
Location: 70% maxilla, 90% anterior
Sex: female>male
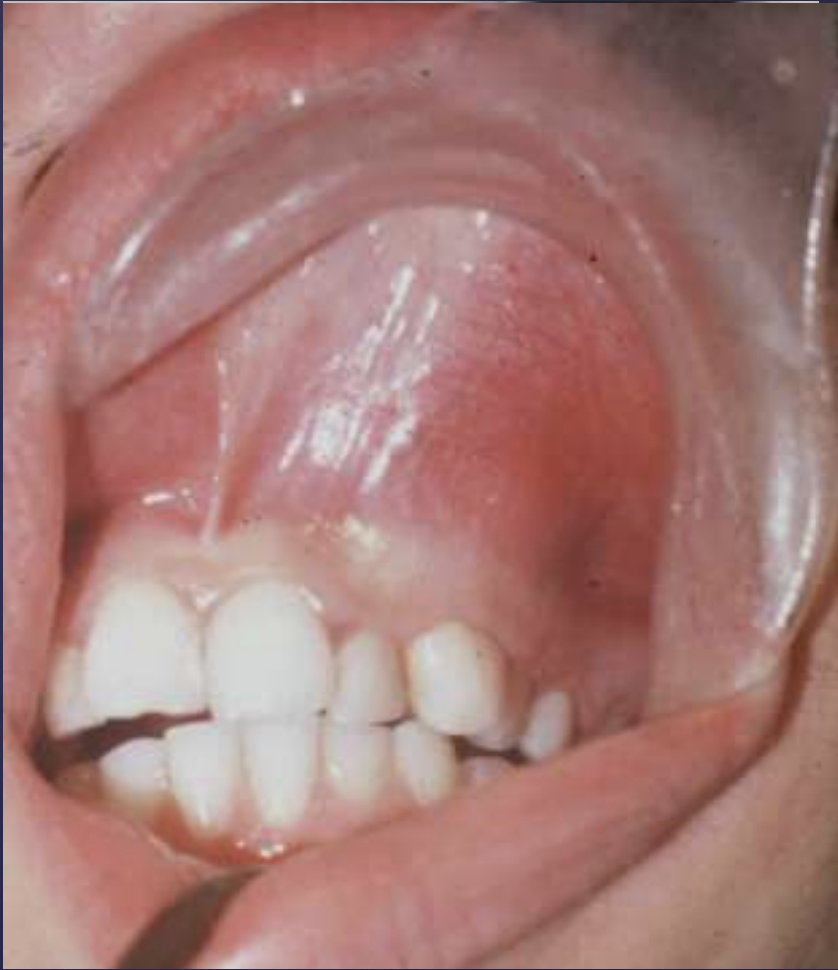
what are the radiographic findings of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor?
• Well circumscribed, corticated
• Unilocular or multilocular
• Associated with unerupted tooth
• Mixed radiodensity
• Displacement of adjacent teeth
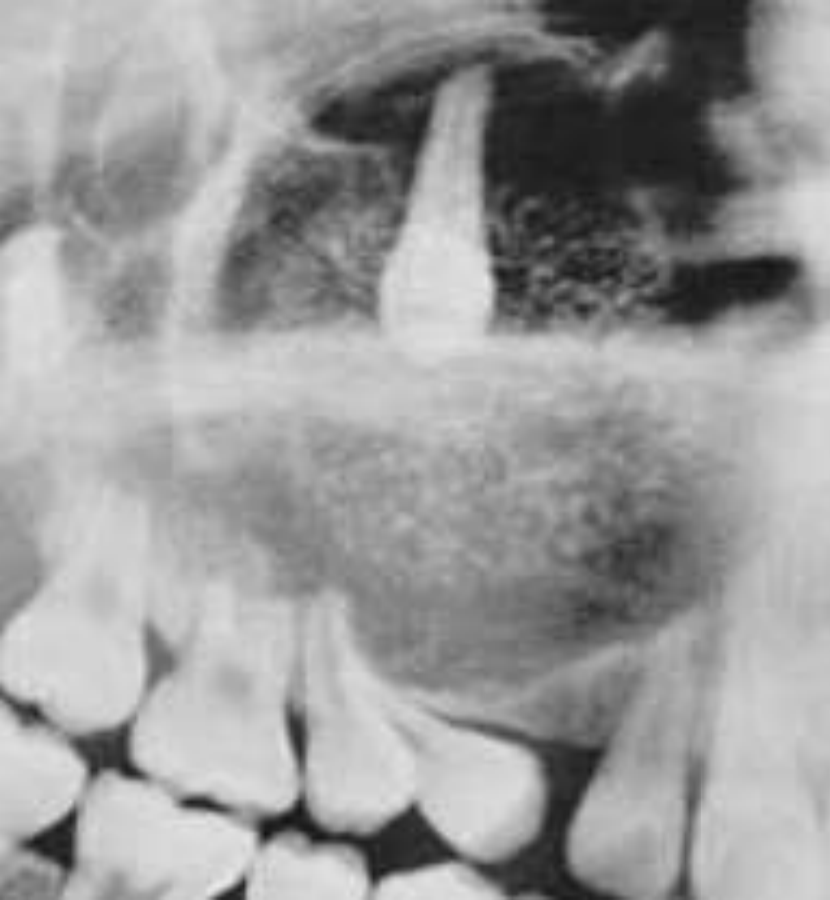
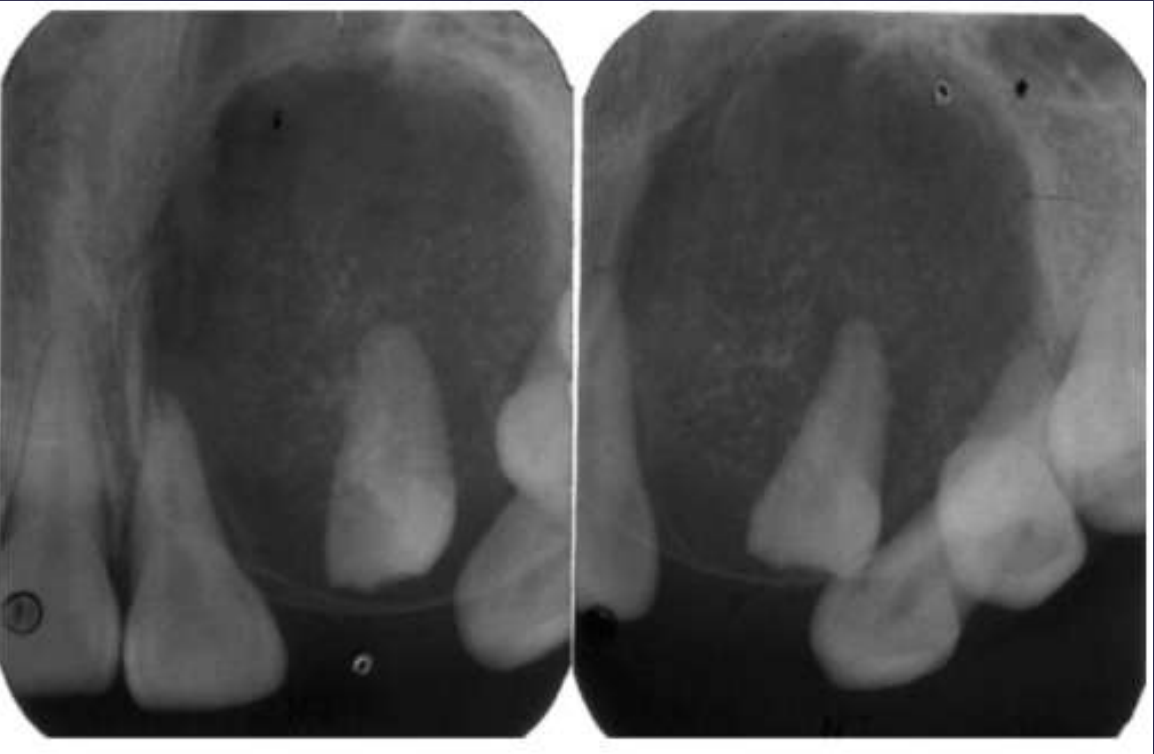
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor
Well defined, corticated
Mixed density (predominantly radiolucent with some radiopacity within)
Associated with impacted maxillary lateral incisor
Displacement of adjacent teeth
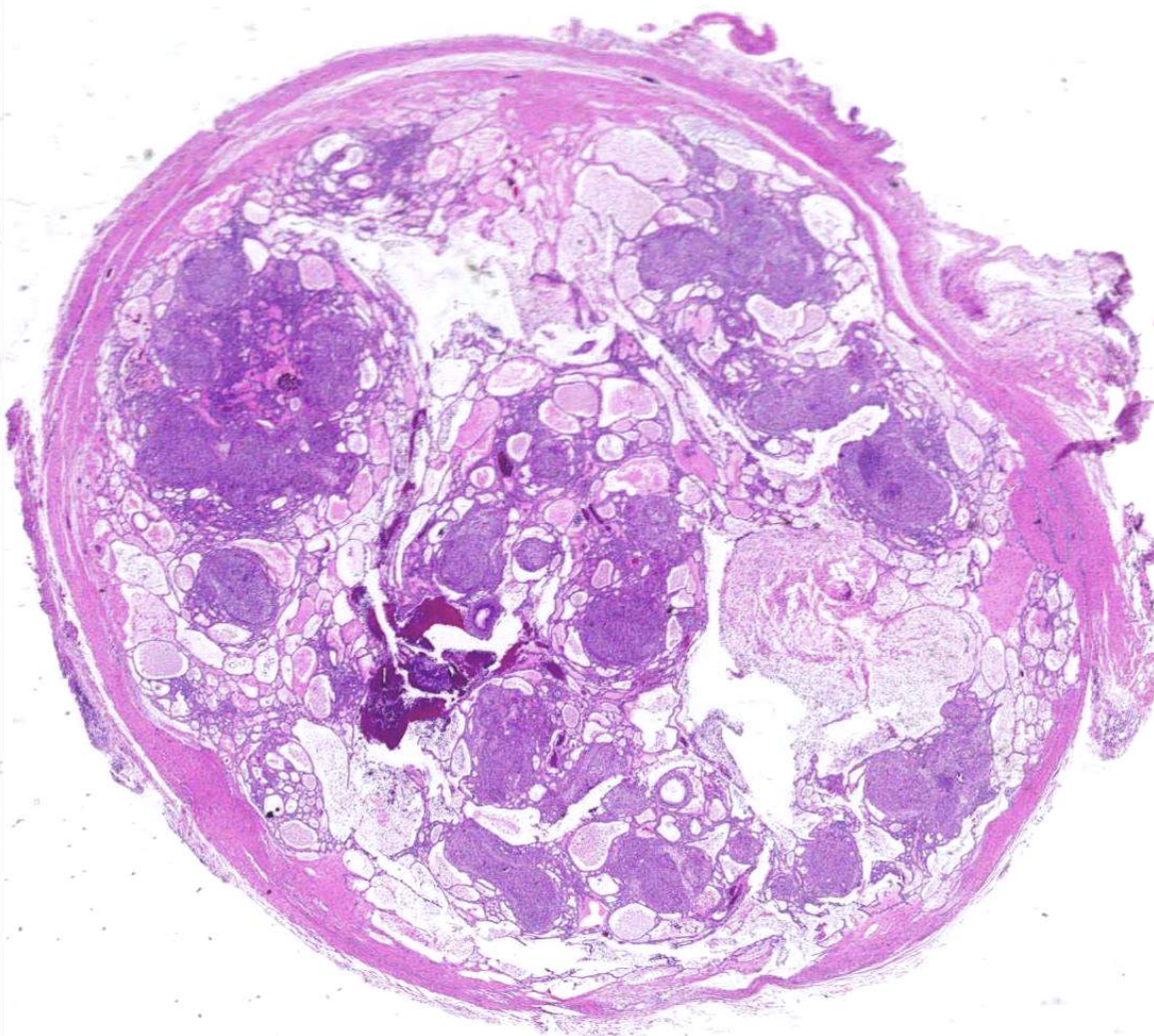
what are histopathologic features of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor?
• Well-defined lesion usually surrounded by thick fibrous capsule
• Spindle-shaped epithelial cells in sheets, strands, or whorled masses of cells in scant fibrous stroma
• Tubular or duct-like structures
• Scattered calcifications represent abortive enamel formation, dentinoid, or cementum
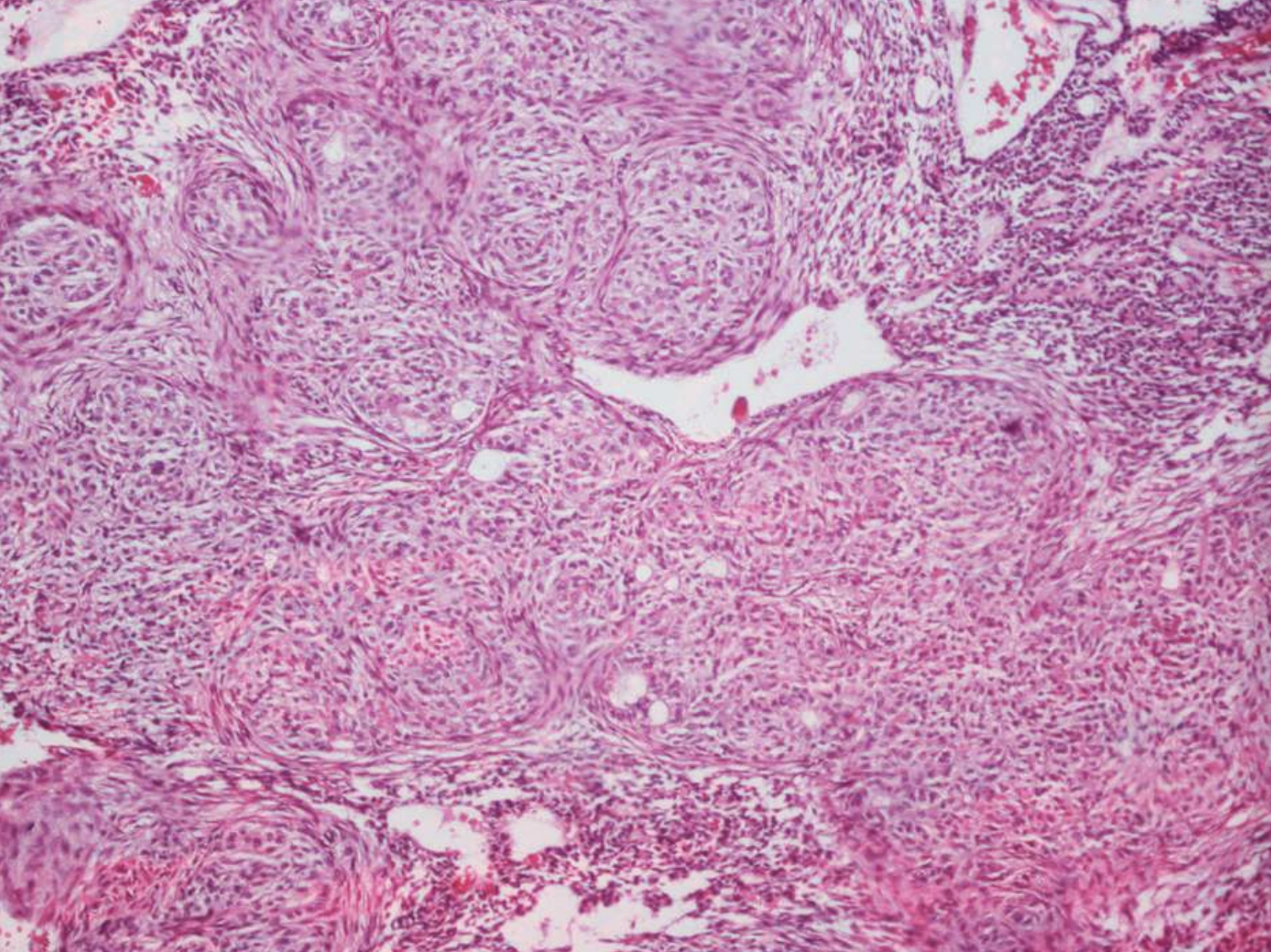
what treatment is inidicated for Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor? how common are recurrences?
• Completely benign
• Enucleates easily from bone
• Very rare recurrences
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor is also known as…?
Pindborg tumor
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor makes up % of odontogenic tumors
<1%
what demographics are affected by Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor? predilection for which jaw?
age range: 8-92 (mean age = 36)
mandible
rare peripheral tumor
slide 66-69
what are radiographic findings of Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor)?
• Well circumscribed, corticated
• Mixed density- central radiolucency with radiopaque foci
• Maybe associated with unerupted tooth
• Expansile- expands cortex
• Root resorption possible
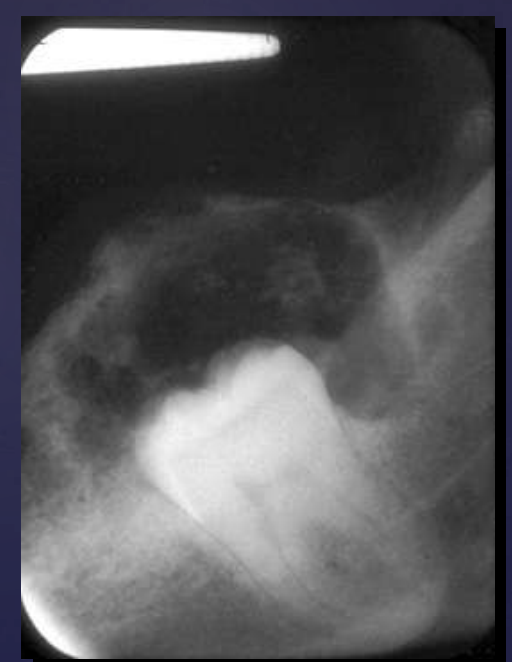
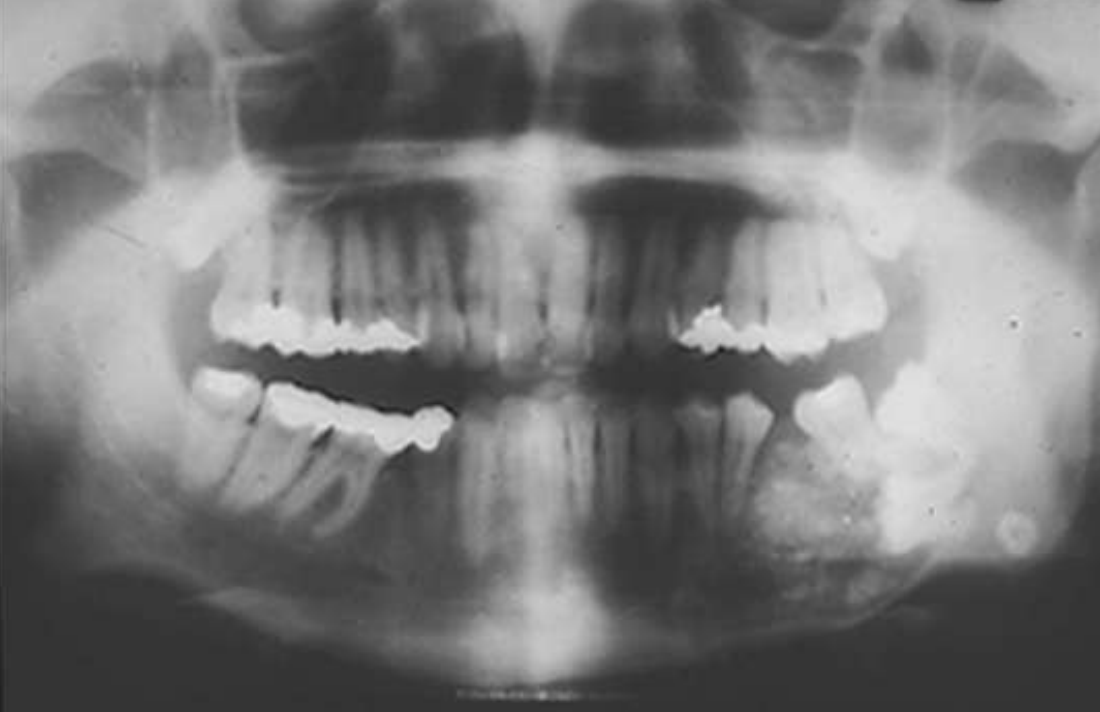
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor)
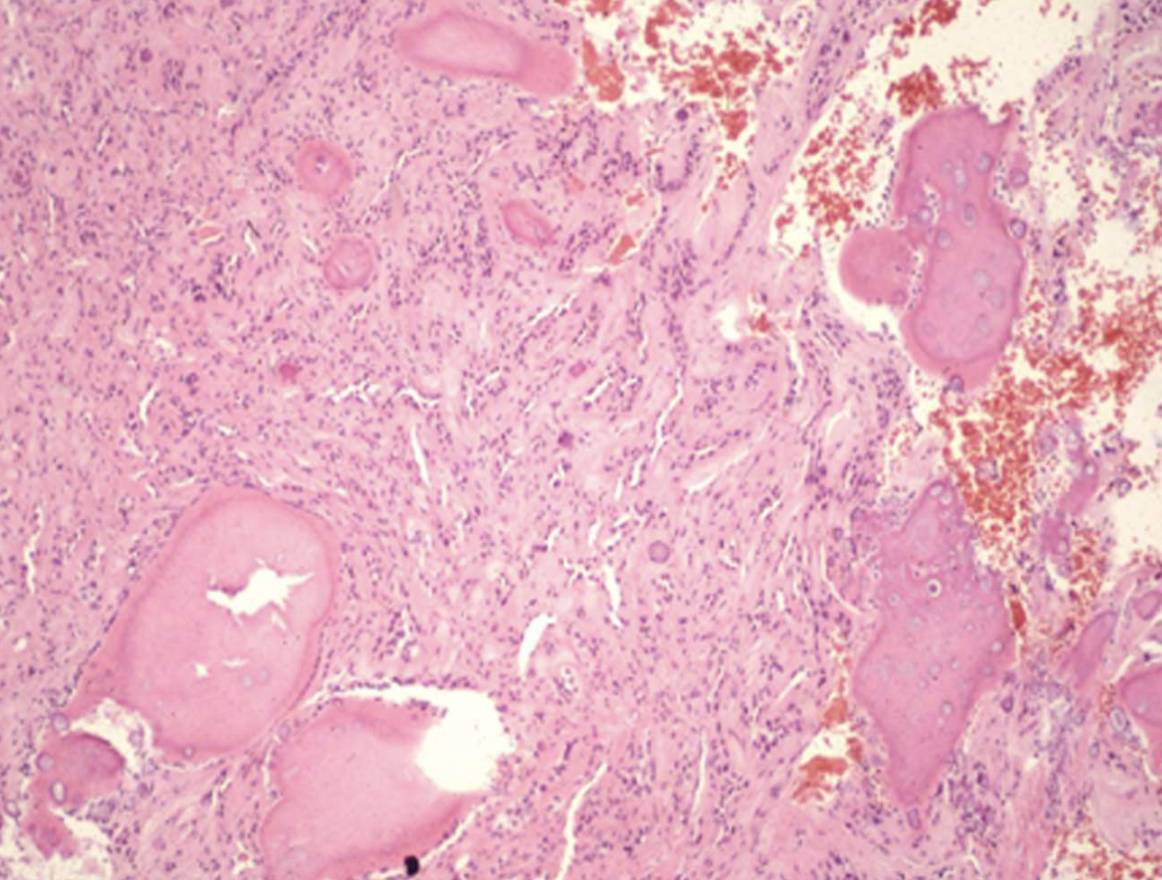
what are histopathologic features of Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor)?
• Islands, strands, or sheets of epithelial cells in fibrous stroma
• Calcifications form concentric Liesegang rings
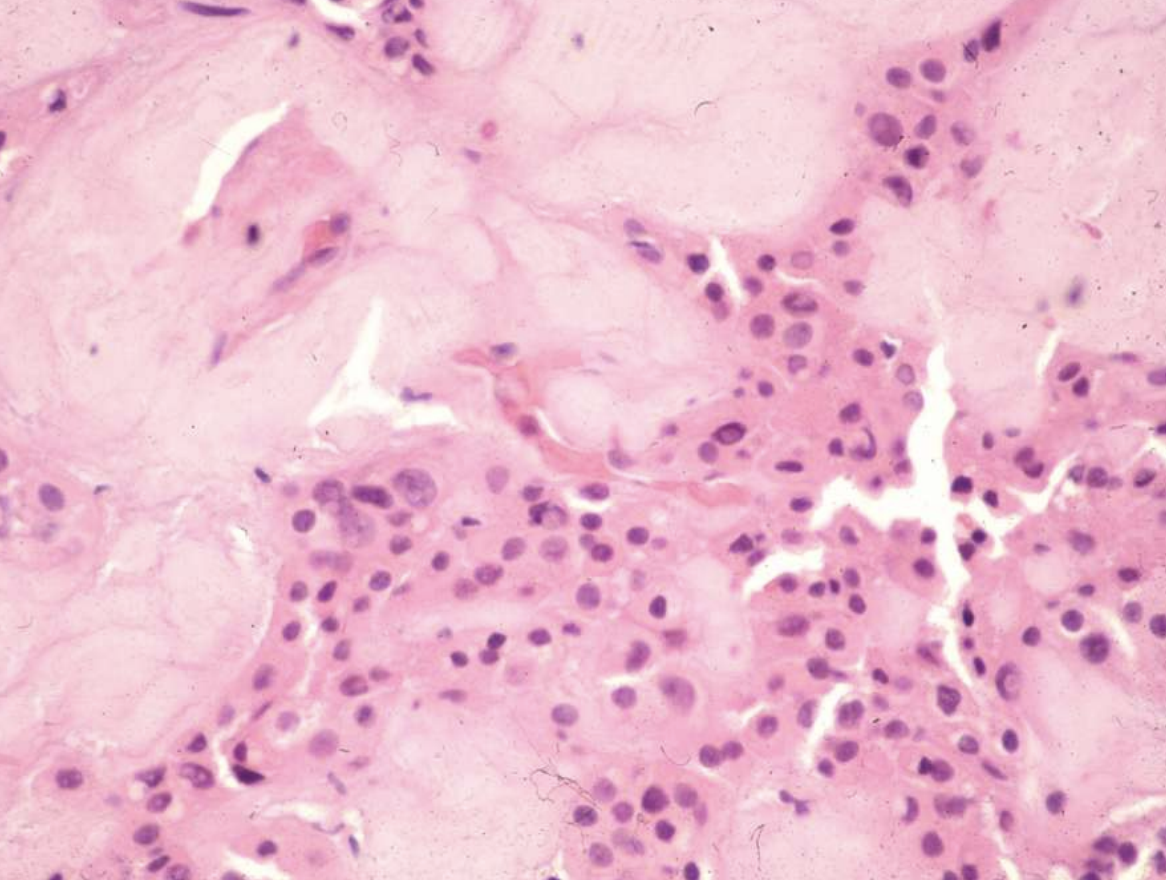
what treatment is indicated for Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor)?
• Less aggressive than ameloblastoma
• Conservative resection recommended
• Good prognosis
what is the recurrence rate of Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor)?
15%
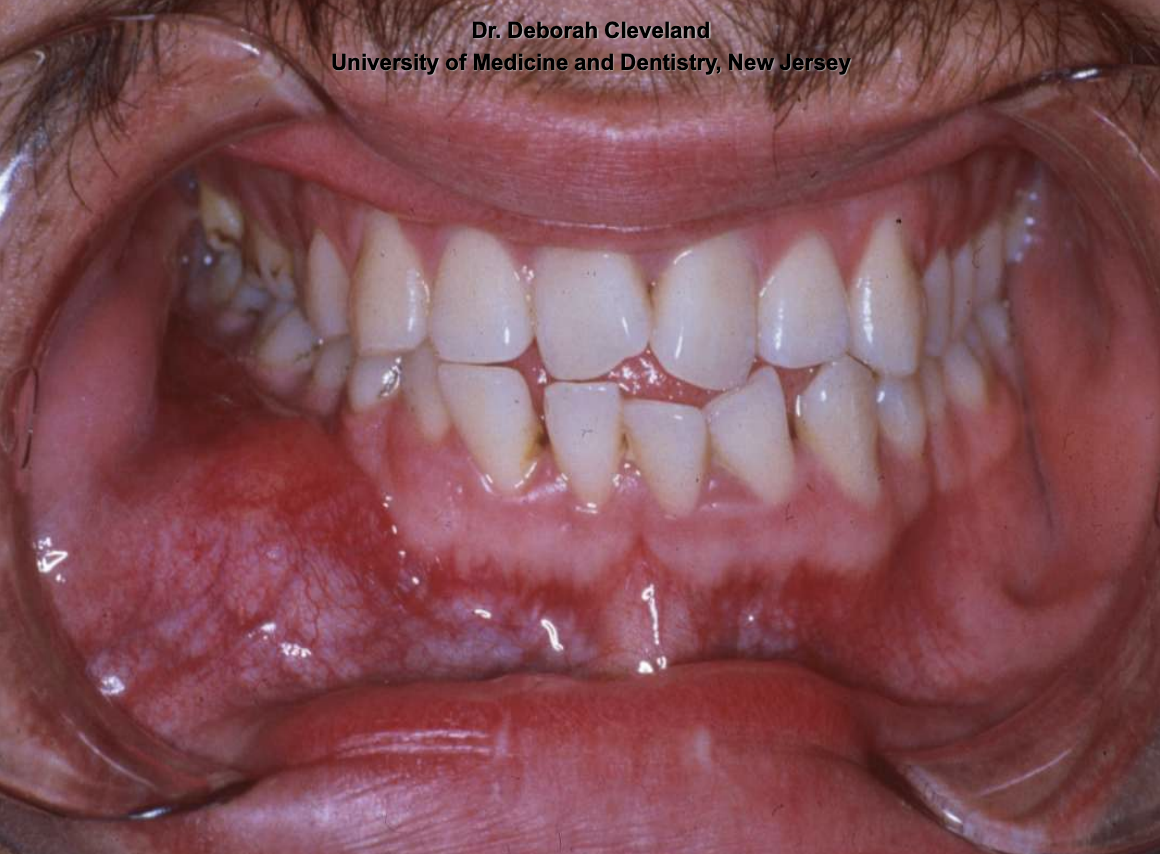
what demographics are affected by Odontogenic Myxoma? predilection for which jaw?
• Average age 25-30
• No significant gender predilection
• Posterior mandible most commonly affected
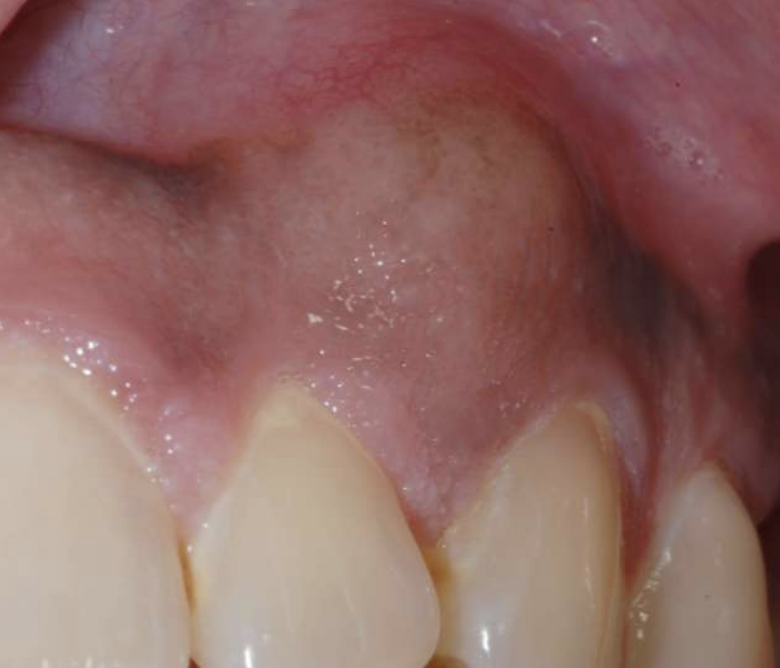
how do Odontogenic Myxoma present symptomatically?
• Small lesions asymptomatic
• Larger lesions associated with painless swelling
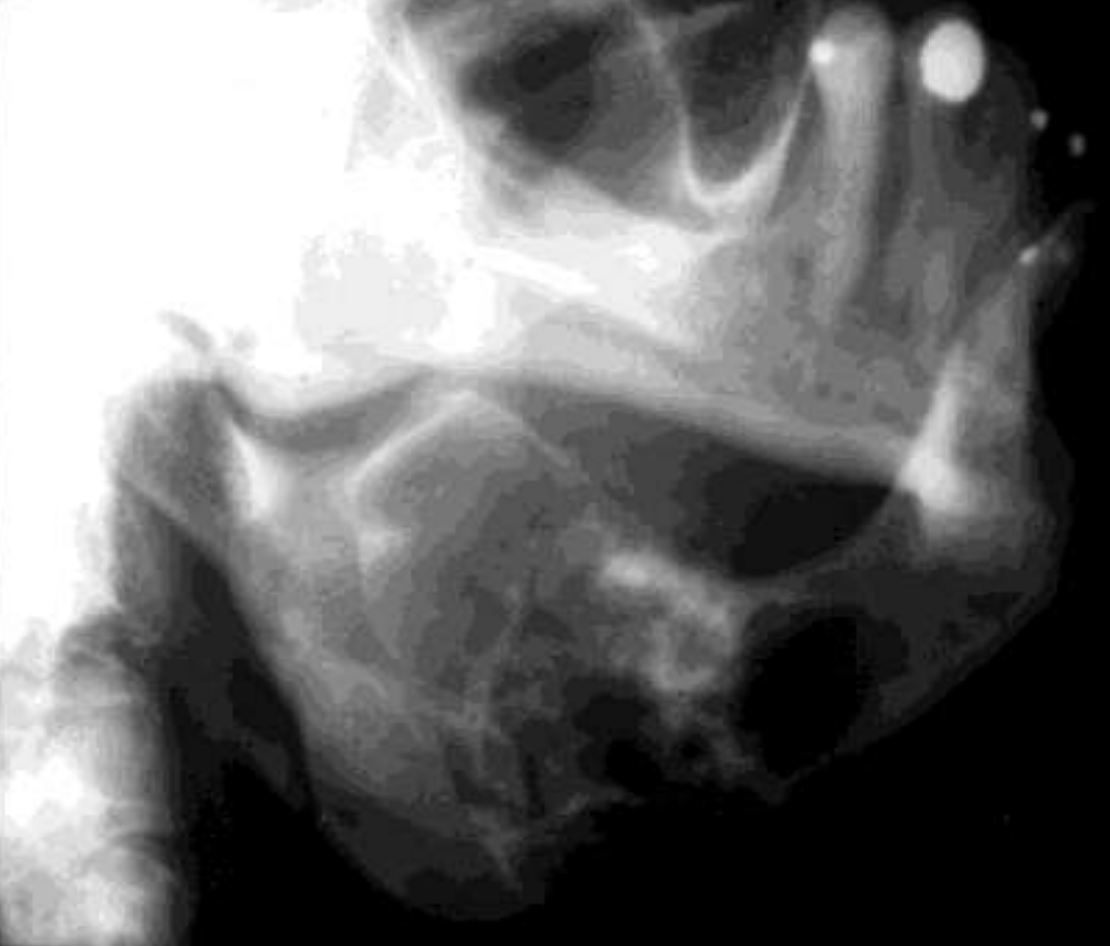
what are radiographic findings of Odontogenic Myxoma?
Variable margins
Well defined or poorly defined
Radiolucent
Multilocular
Few straight septae
Curved septae seen as well
Expansile- expands cortical margins
Tooth displacement
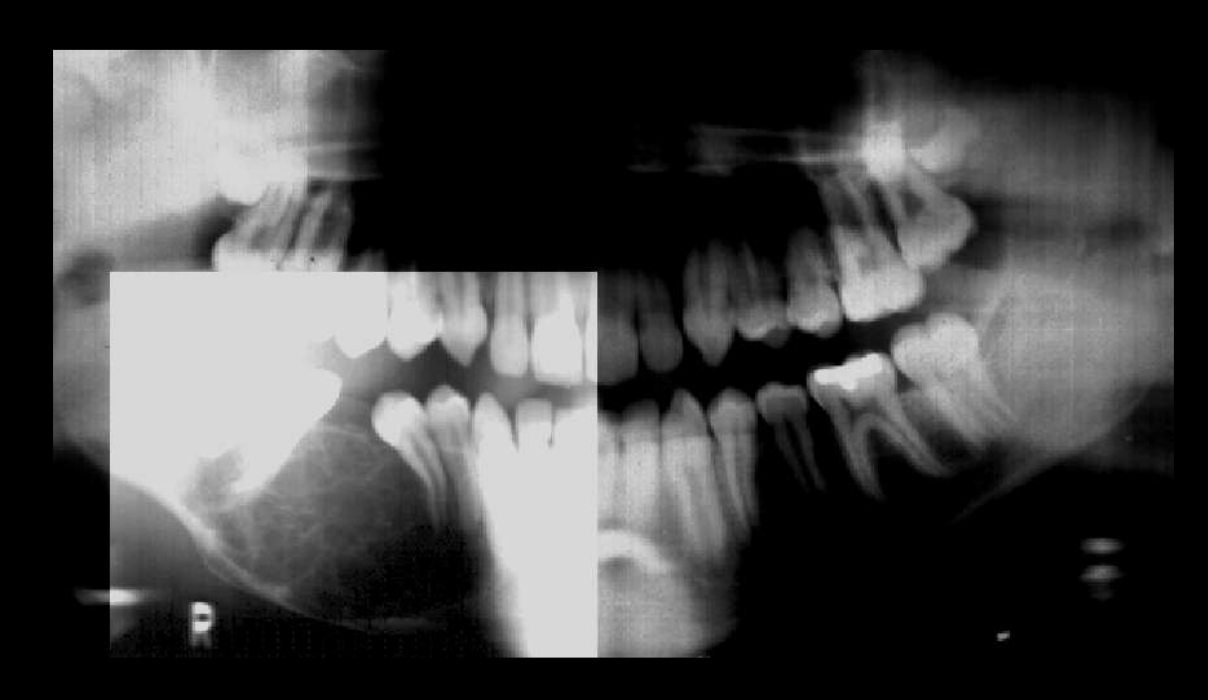
Odontogenic Myxoma
well-defined
multiple septum (thin, straight)
displacement of 29 root
expansion of inferior border of mandible
radiolucent
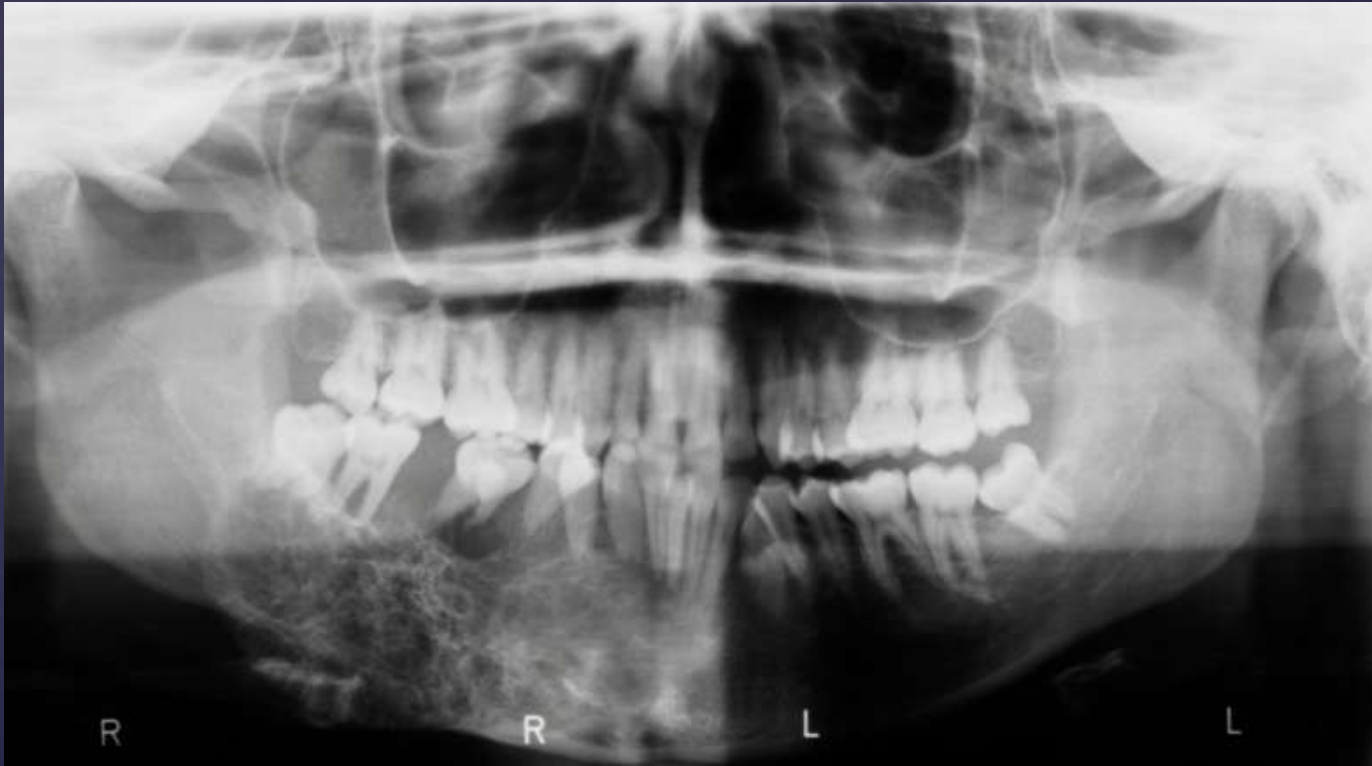
Odontogenic Myxoma
well defined corticated
displacement of 30, 29
external root resorption of 30
displacement of IAN canal
erosion of inferior border of mandible
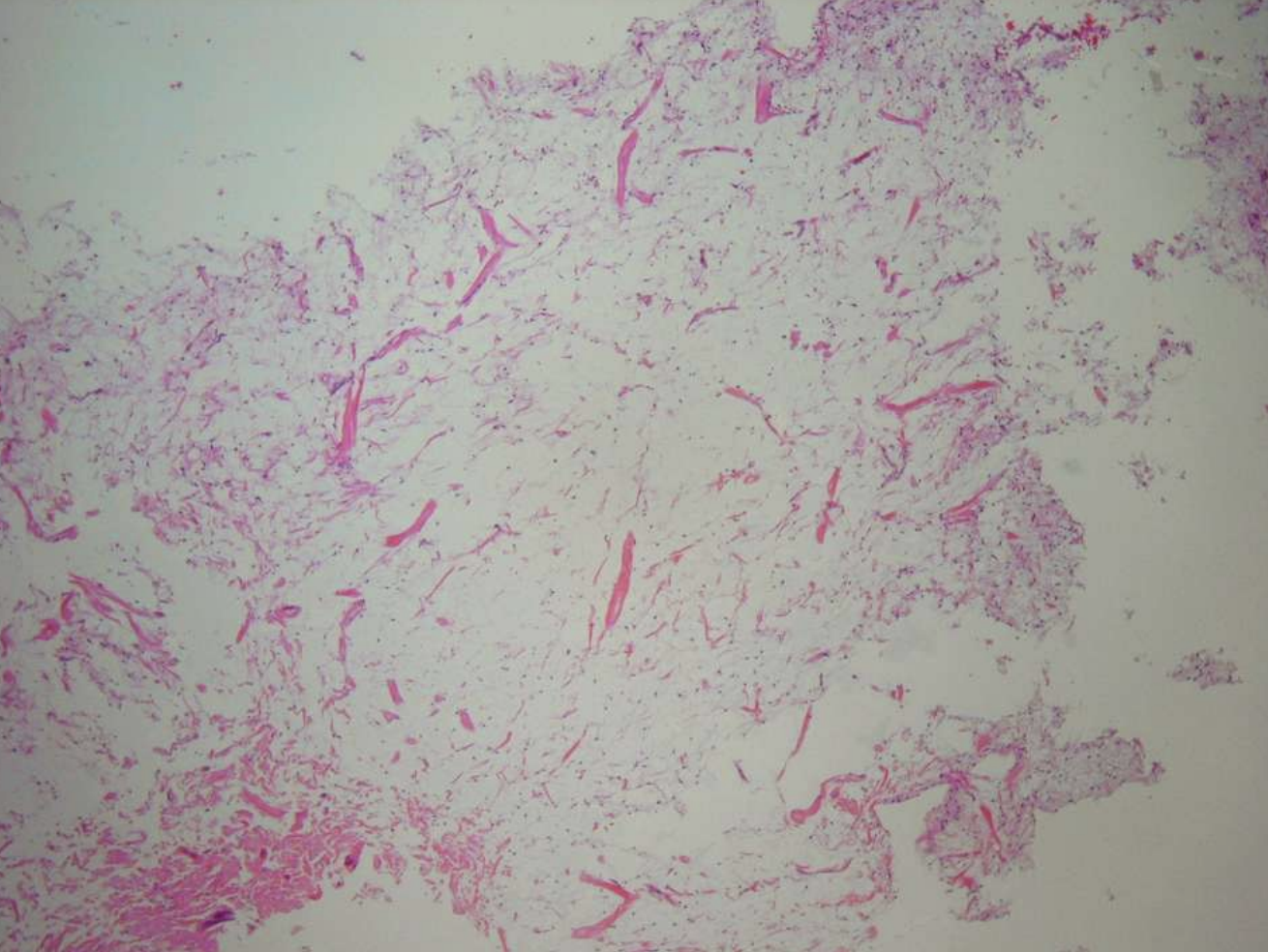
what are histopathologic features of Odontogenic Myxoma?
• Loose stroma with collagen fibrils
• Haphazardly arranged stellate, spindle-shaped, and round cells
• Inactive rests of odontogenic epithelium may be present
• May be misdiagnosed as hyperplastic dental follicle
what treatment is indicated for Odontogenic Myxoma?
• Small lesions treated with curettage and 5 yr follow-up
• Larger lesions resected
what is the recurrence rate of Odontogenic Myxoma?
25% (Egg-white consistency makes complete removal difficult)
what demographics are affected by Cementoblastoma?
• Equal gender incidence
• Most patients less than age 20
• 75% occur before age 3
how do cementoblastomas present symptomatically?
67% of patients report pain and swelling
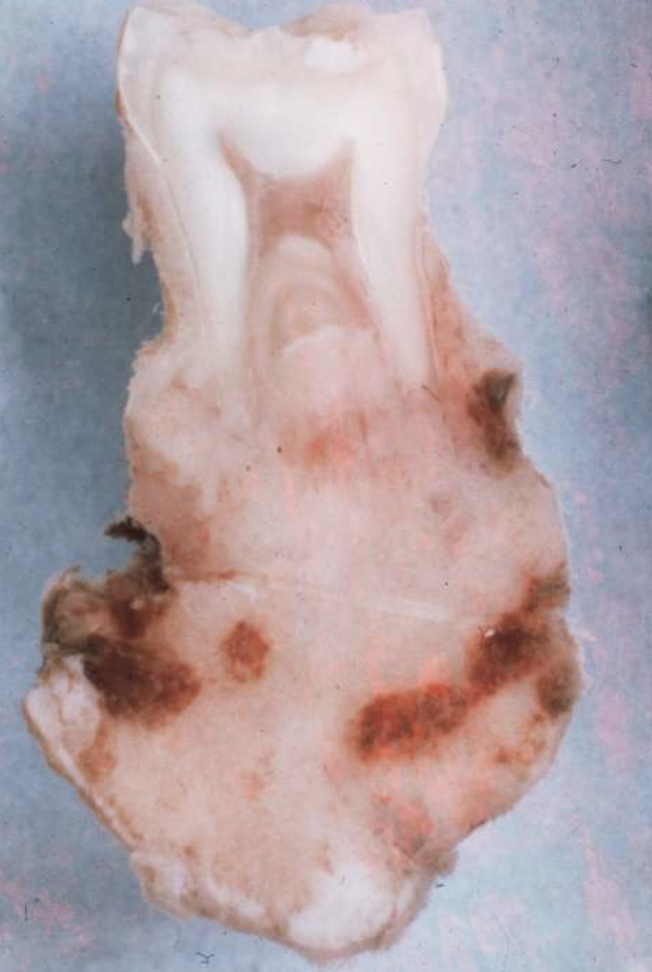
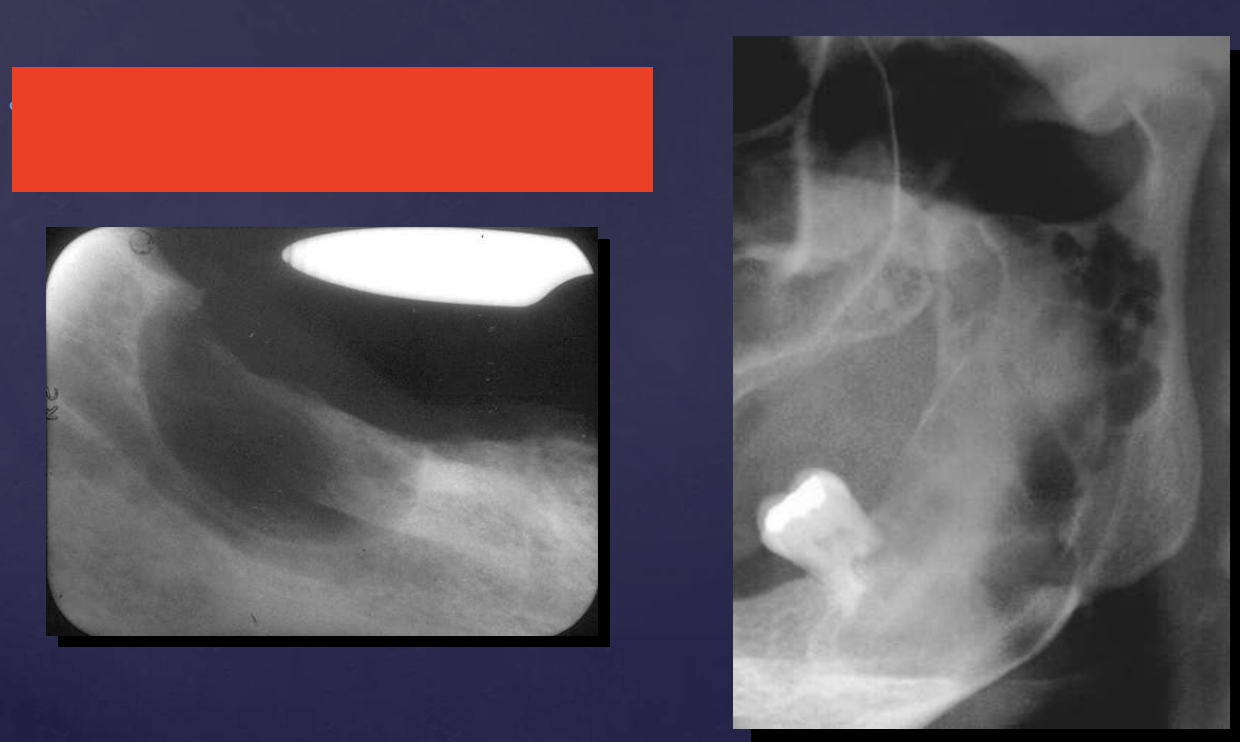
cementoblastoma
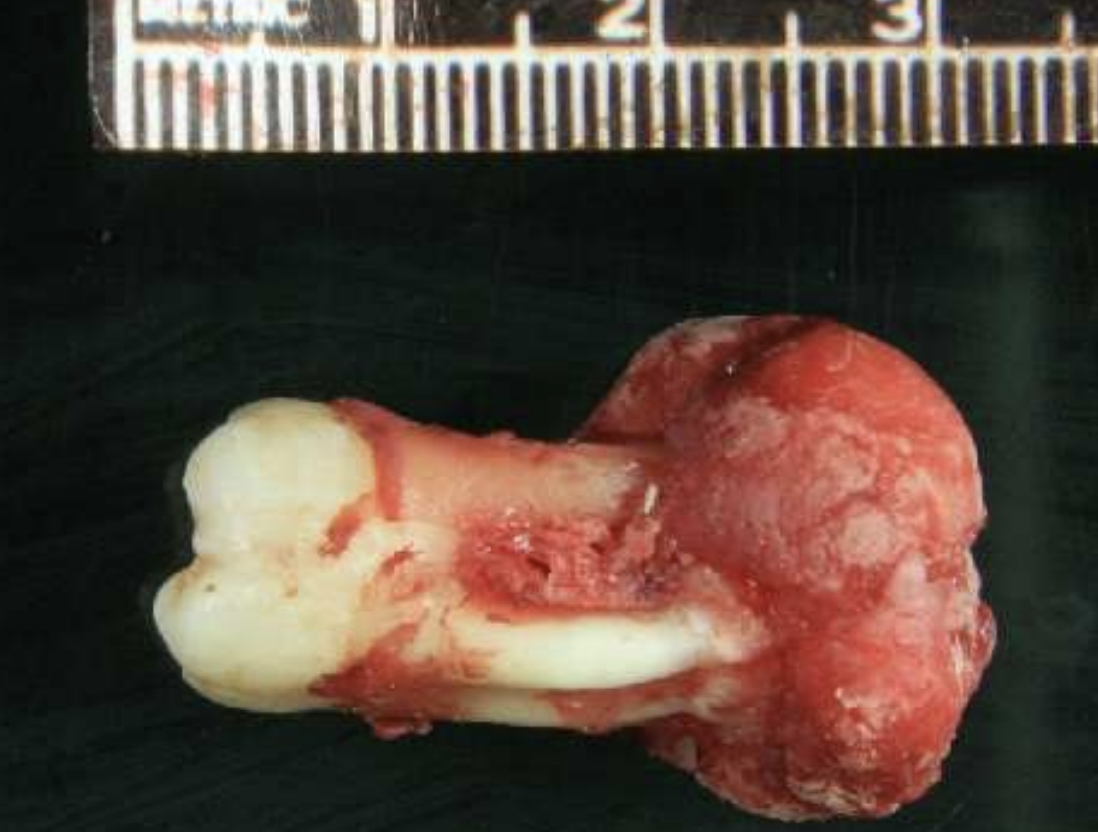
how do cementoblastomas present radiographically?
Multiple punctate radiopacities within a welldefined radiolucency
Homogeneous radiopaque mass
Mass attached to 1st mandibular molar roots
Obscured root outline, resorption
Radiolucent halo - continuity with PDL
Sclerotic border
cementoblastomas are in continuity with …?
root of a tooth (this feature differentiates it from osteoblastomas)
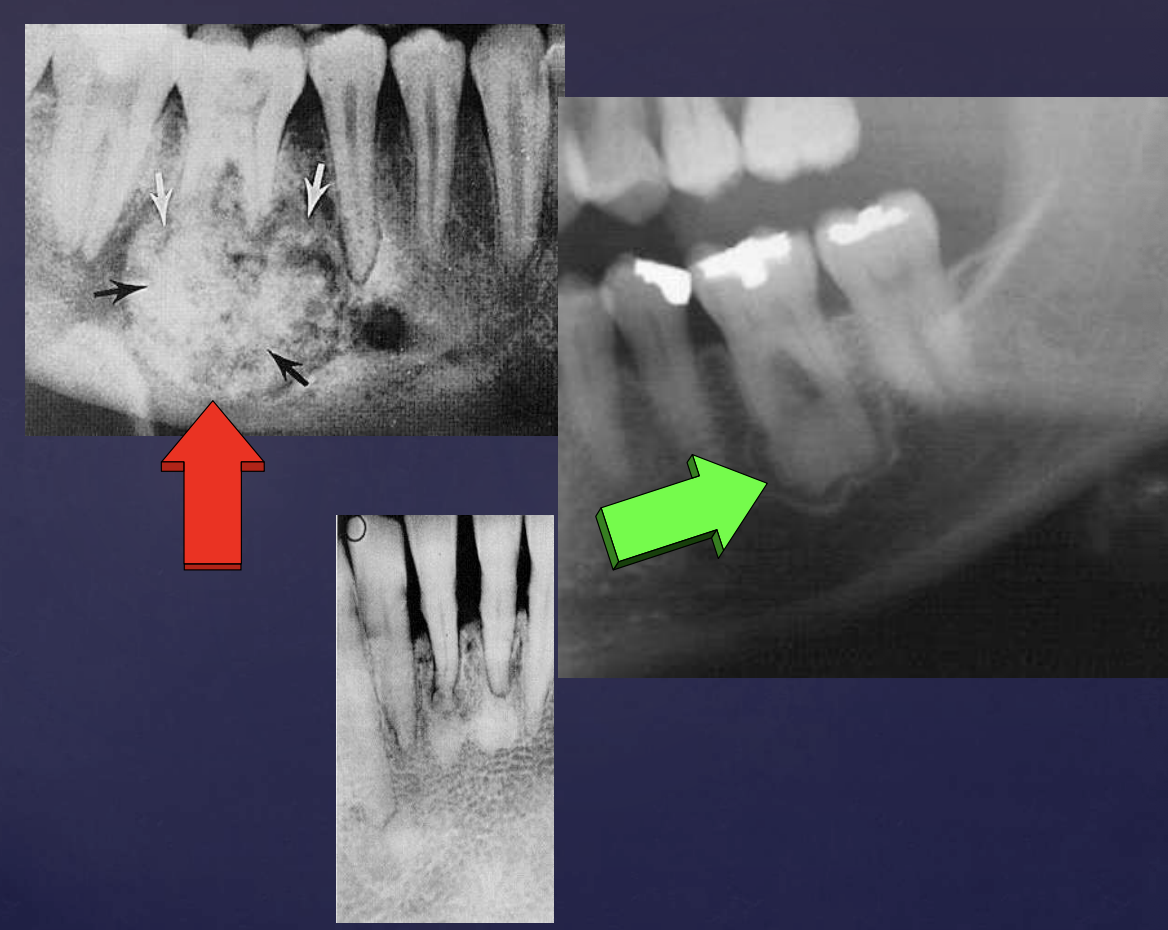
slide 92
cementoblastomas
external root resorption 30
displacement of IAN canal inferiorly
thinning/expansion of inferior border of mandible
slide 92
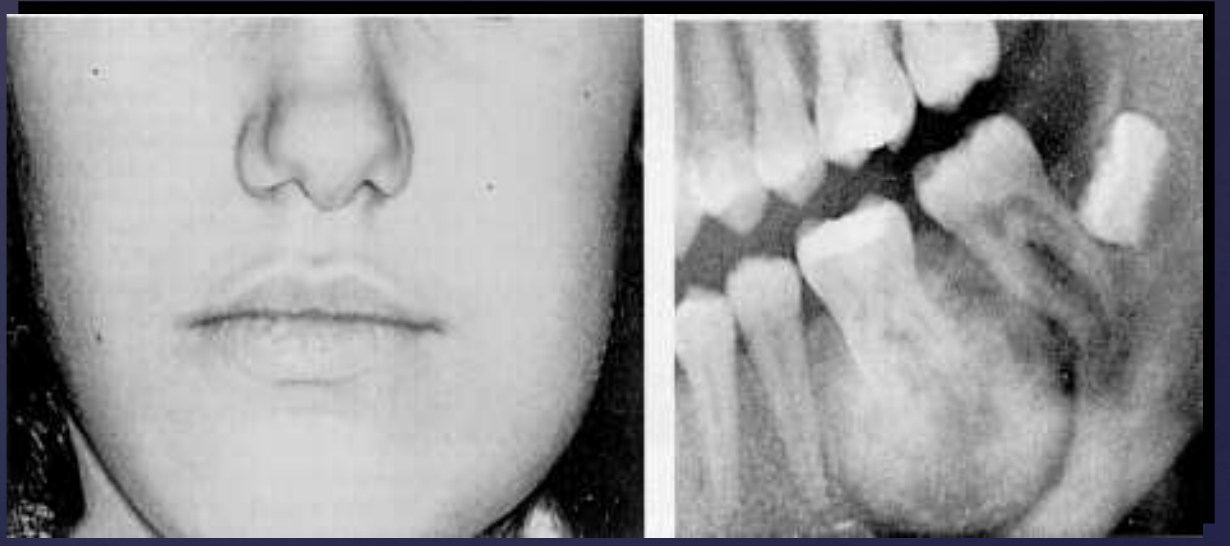
cementoblastoma
slide 94-98
what treatment is indicated for cementoblastomas?
Extraction of tooth with calcified mass
Alternative therapy involves excision of mass, involved root amputation, and endodontic therapy
what is the recurrence rate of cementoblastomas?
tumor does not recur + excellent prognosis
what is the #1 most common odontogenic tumor/hamartoma?
odontoma
• 74% of odontogenic tumors in USA
• More common than all other odontogenic tumors combined
what are odontomas composed of?
enamel, detin, pulp, and/or cementum
what are 2 types of odontomas?
compound and complex
what are radiographic findings of odotomas?
• Well defined, corticated
• Radiolucent band/soft tissue capsule inside the cortical border
• Internal content is largely radiopaque
• Maybe associated with unerupted tooth
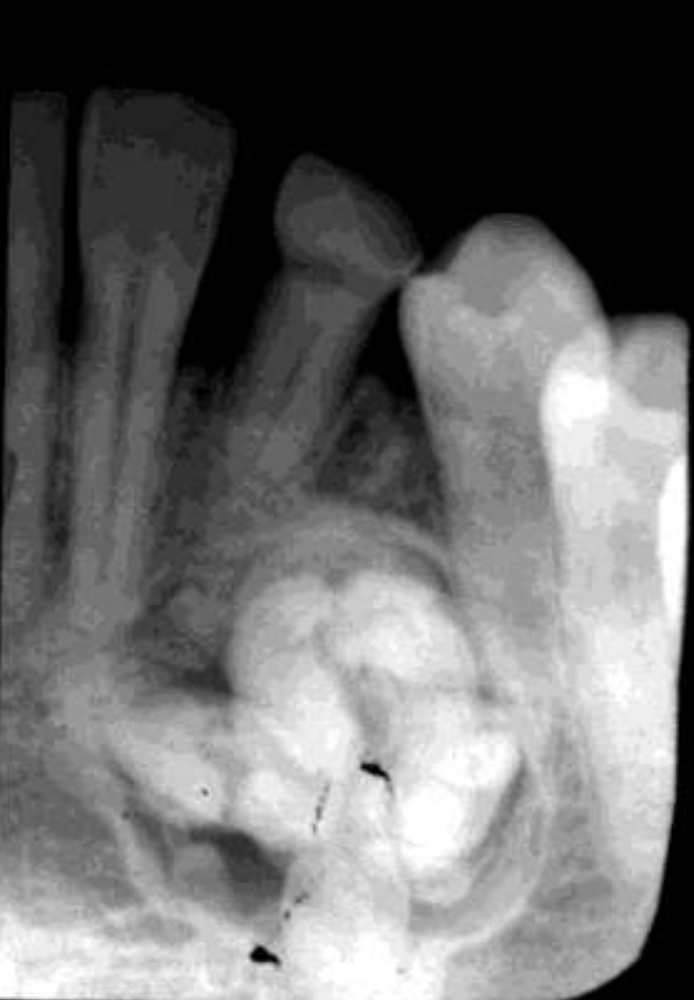
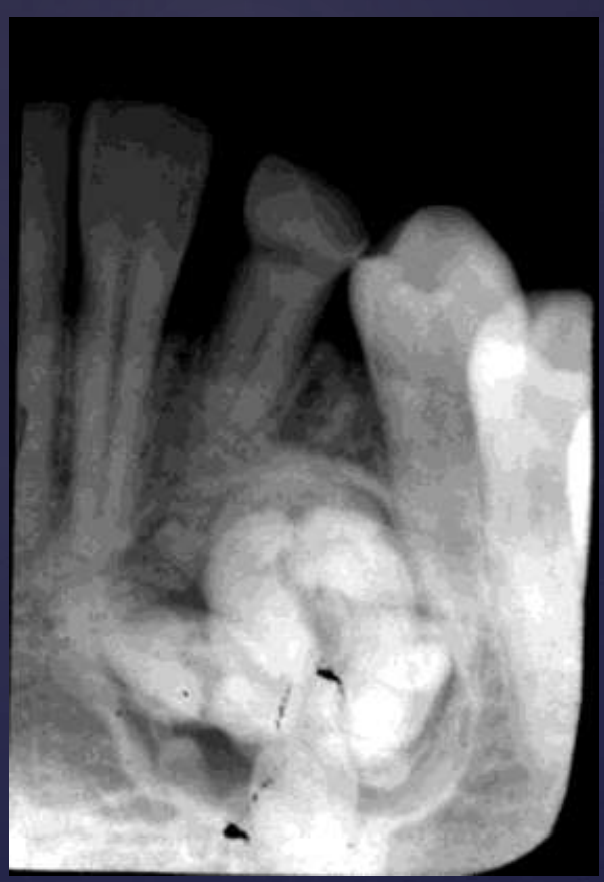
COMPOUND odontomas
• Well defined, corticated
• Radiolucent band/soft tissue capsule inside the cortical border
• Internal content is largely radiopaque- made of multiple tooth like structures called denticles
• Maybe be associated with unerupted tootH
COMPLEX odontomas
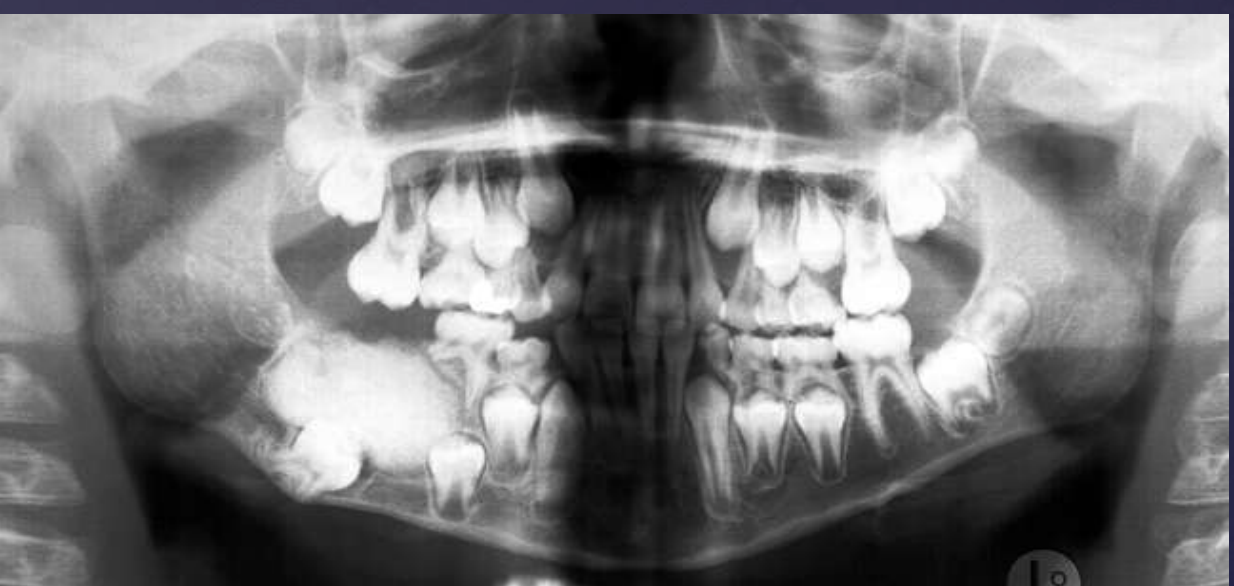
Well defined, corticated
Radiolucent band/soft tissue capsule inside the cortical border
Internal content is largely radiopaque- made of irregular mass of calcified tissue
Maybe be associated with unerupted tooth
Possible displacement of teeth (30, 29)
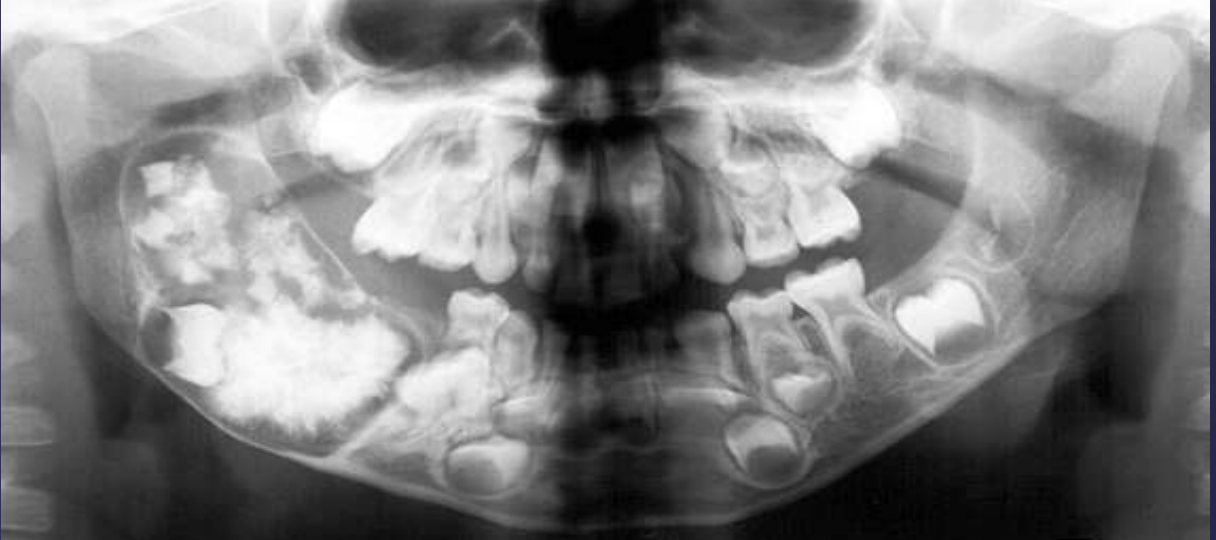
Compound –Complex Odontoma
Well defined
Mixed density, corticated
Combination of amorphous radiopaque mass and tooth like structures
Osseous expansion
Thinning of cortices
Displacement of teeth, unerupted tooth
what are histopathologic features of compound odontomas?
multiple structures resemble small teeth in loose fibrous matrix
what are histopathologic features of complex odontomas?
• mature tubular dentin with structures that contained enamel before decalcification
• 20% show ghost cells
• thin layer of cementum around mass
slide 107-110
what treatment is indicated for odontomas?
• Conservative enucleation
• Prognosis is excellent
what are radiographic findings of osteomas?
• Well defined radiopaque mass
• Internal structure- uniformly radiopaque or internal trabecular structure
• Maybe be exophytic, extending into adjacent soft tissue
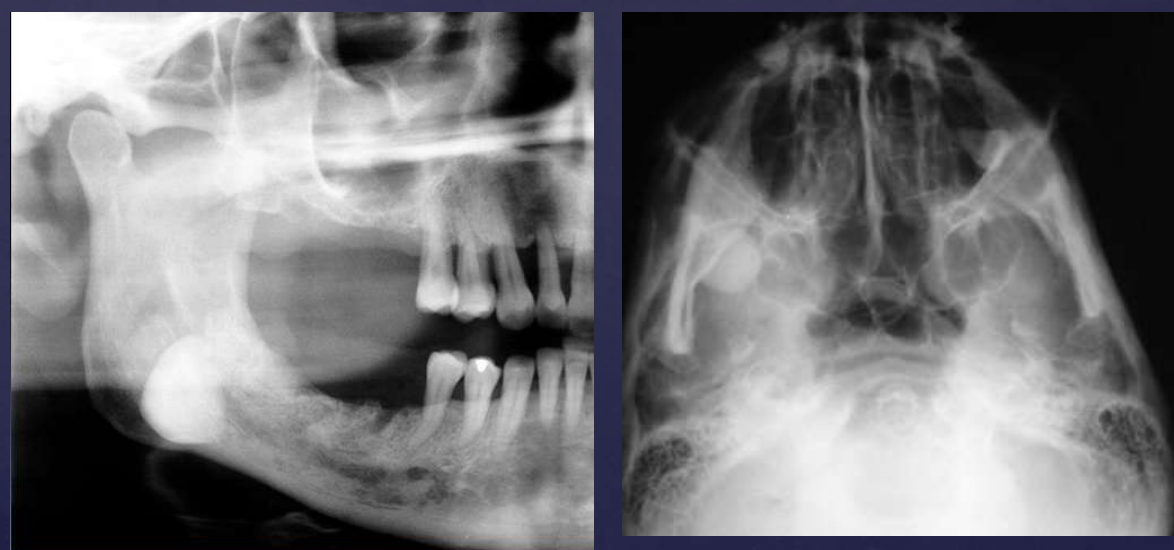
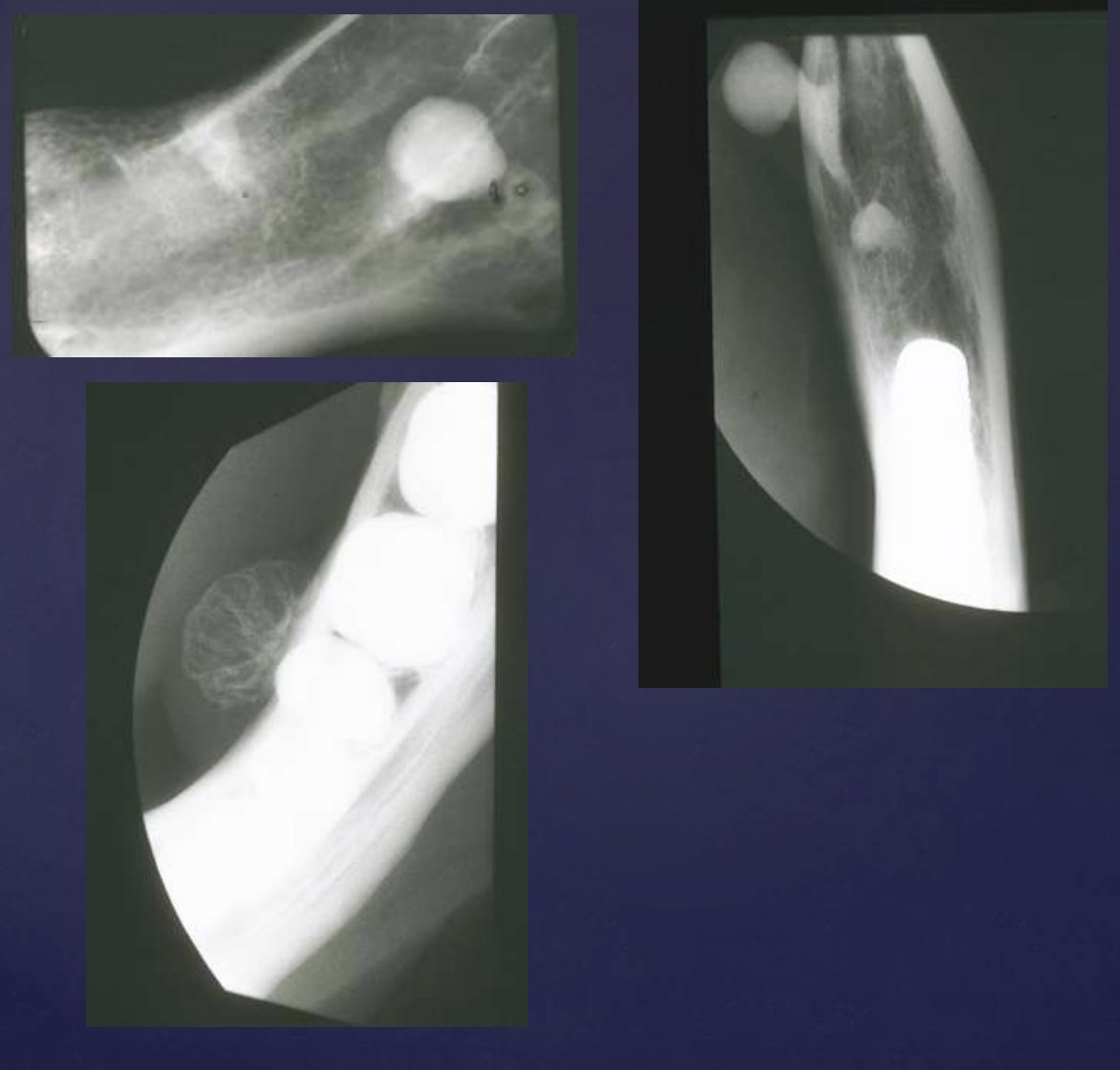
osteomas
bone and teeth are very radiopaque
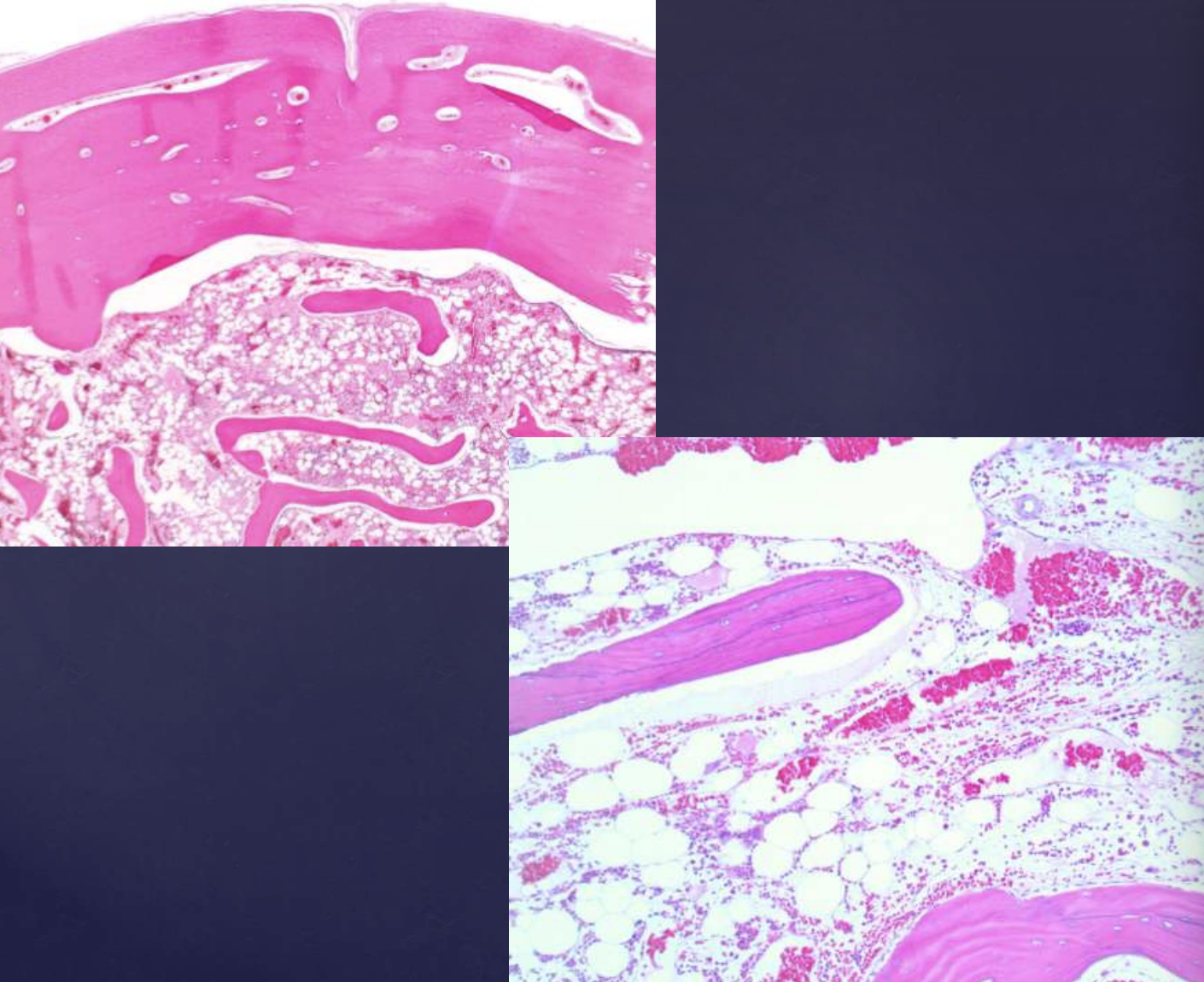
what are histopahtologic features of osteomas?
• Compact lamellar bone with fibrofatty marrow
• Identical to tori and exostoses
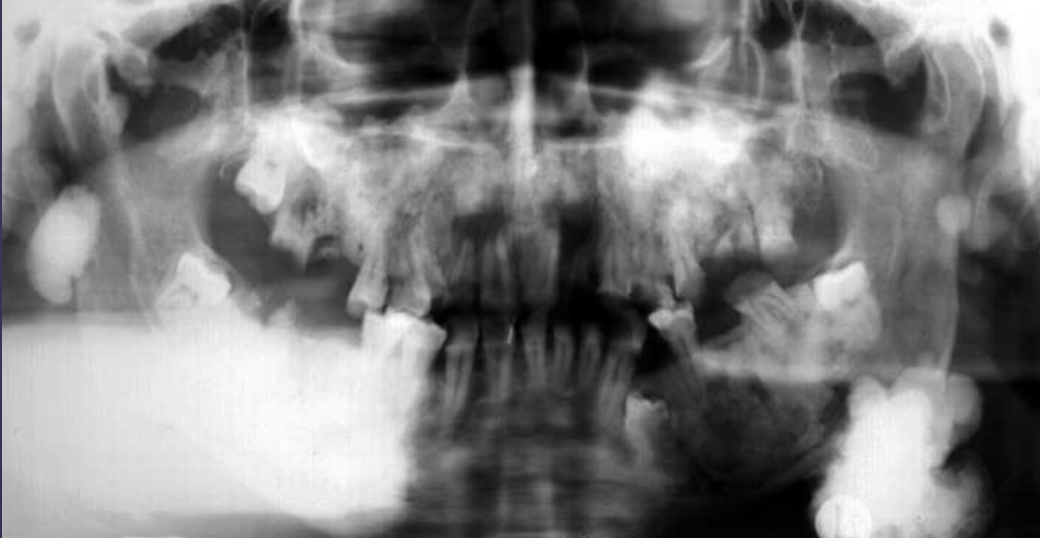
what condition?
• Multiple osteomas, multiple dense bone islands
• multiple unerupted supernumerary and permanent teeth
• epidermoid cysts, subcutaneous dermoid tumors,
• multiple polyps of small and large intestines. The polyps have a strong predilection for malignant transformation
Gardner’s Syndrome
slide 118-119
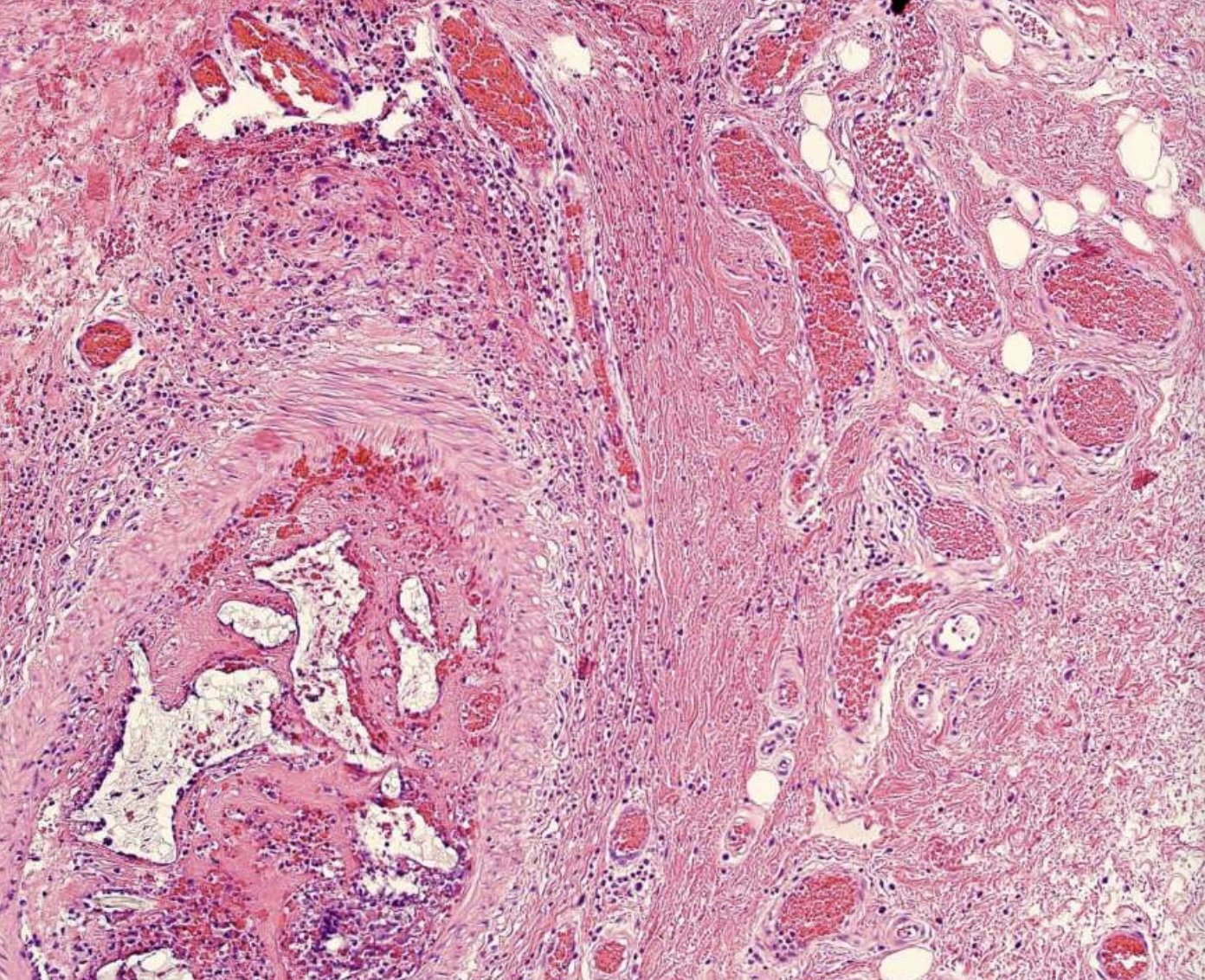
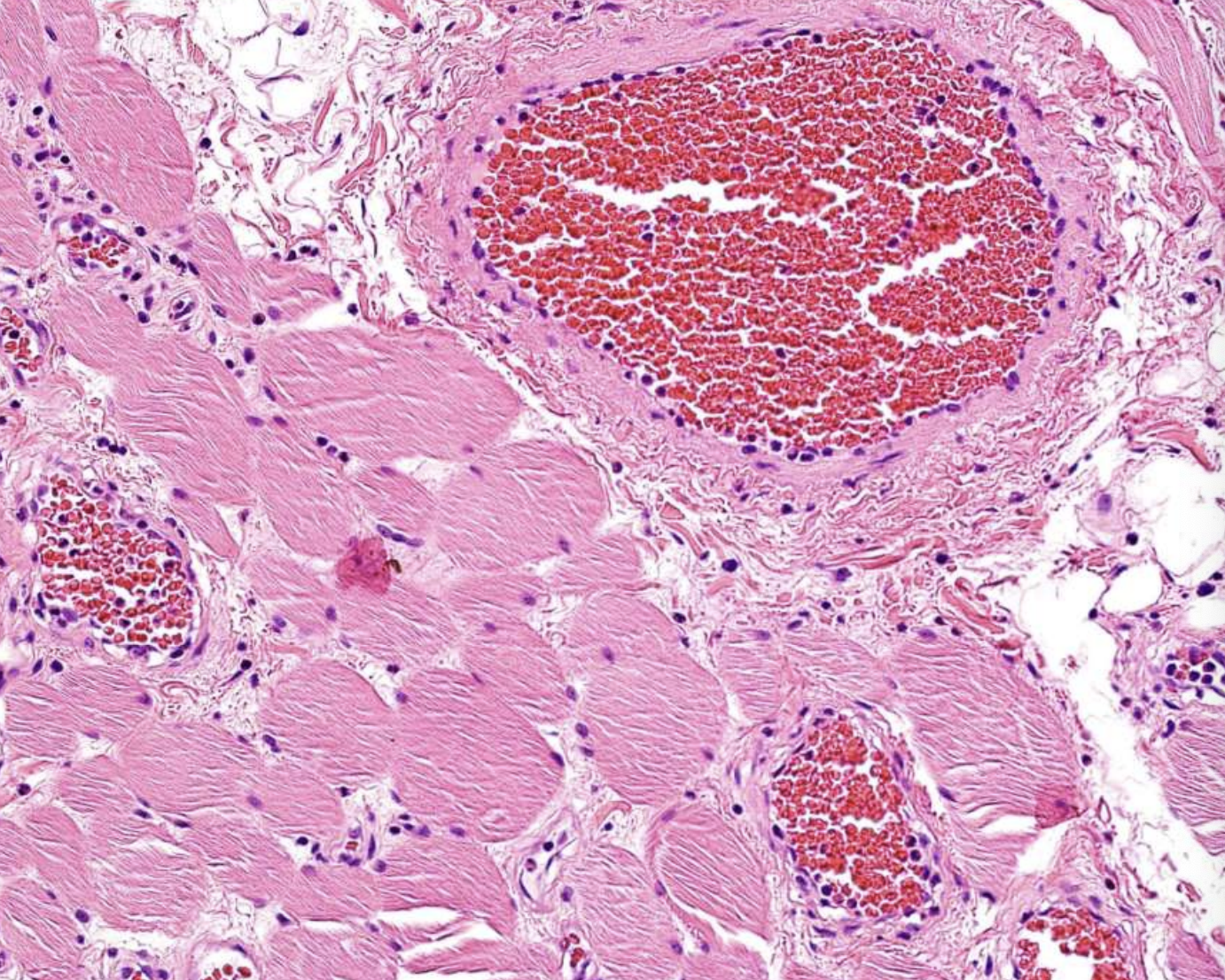
what are histopathologic features of Central Vascular Malformation?
Proliferation of capillaries and endothelial cells containing abundant blood
what are surface bony growths/bone hyperplasias called?
Exostosis/Torus
what are internal counterpart of exostoses called?
enostosis (dense bone island)
how do torus palatinus present radiographically?
• Dense radiopaque shadow attached to the hard palate
• Well defined periphery, may have convex or lobulated outline
• Maybe superimposed over roots of teeth
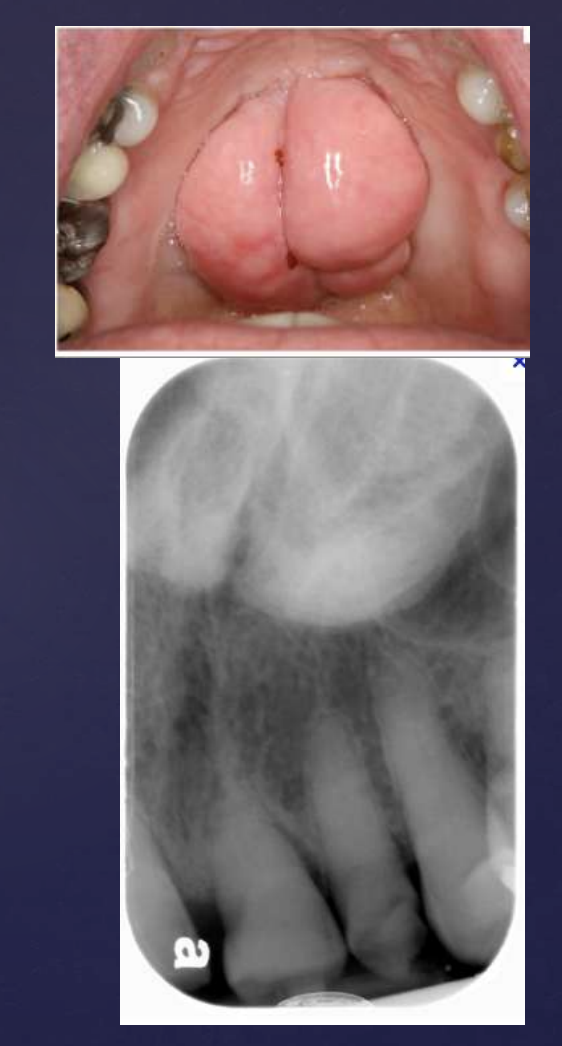
what is a hyperostosis that protrudes from lingual aspect of mandibular alveolar process?
Torus mandibularis
what area are Torus mandibularis located?
premolar area, bilaterally
how do Torus mandibularis appear radiographically?
Radiopaque shadow with defined borders superimposed over roots of teeth
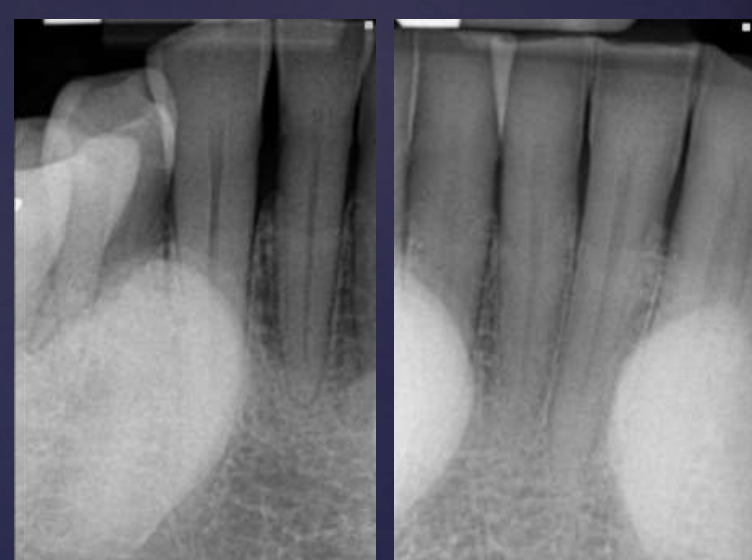
how do enostosis appear radiographically?
• Well defined periphery but may blend with trabeculae of surrounding bone
• No effect on teeth but rarely associated with root resorption