IB Chemistry Option B
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
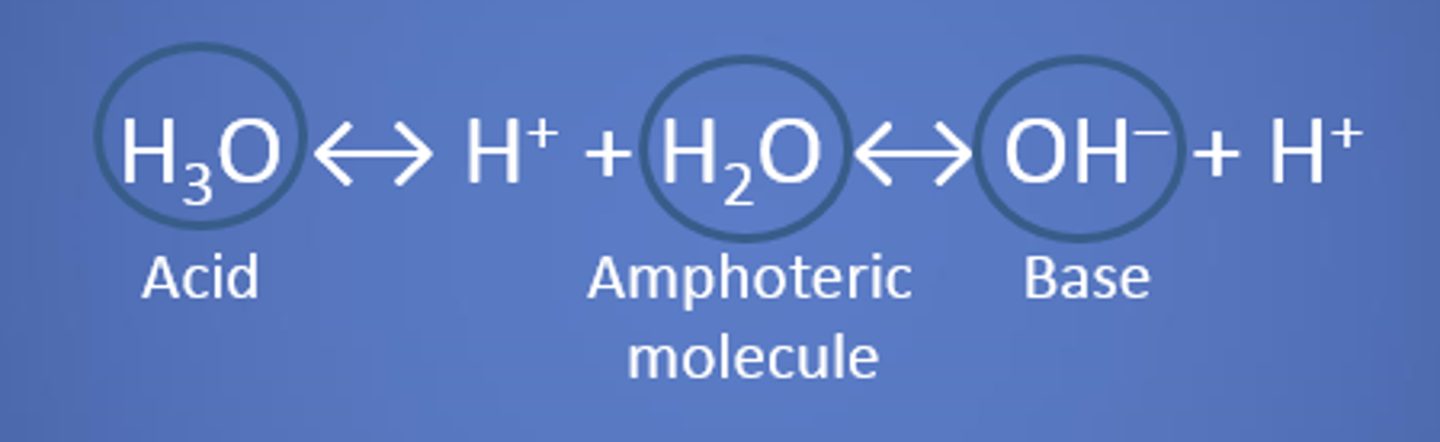
Amphoteric
a substance that can act as both an acid and a base
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
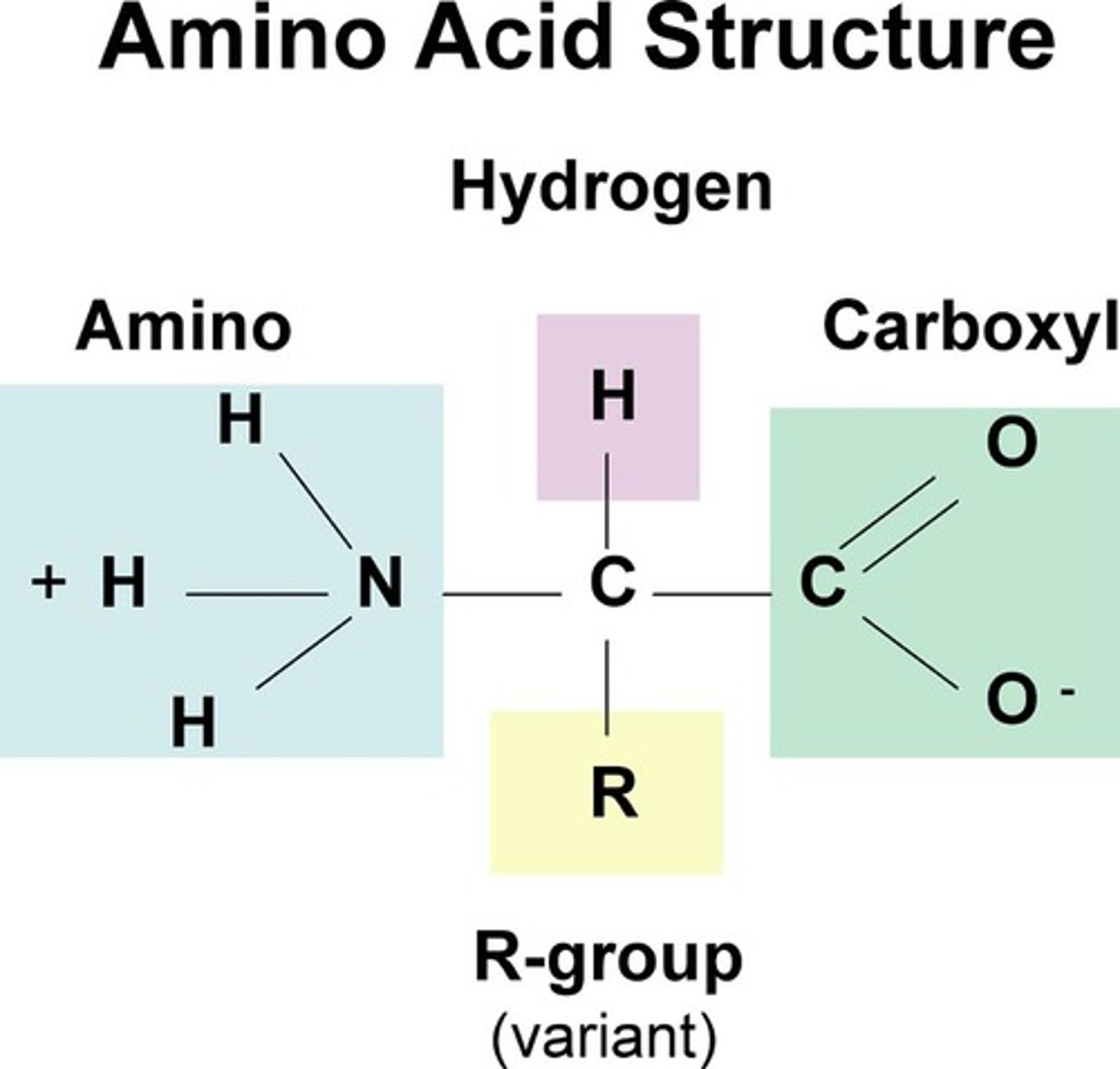
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller one with the release of energy.
condensation reaction
a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water or another simple molecule
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
isoelectric point
The pH at which an amino acid has no overall charge
Biomagnification
The increase in chemical concentration in animal tissues as the chemical moves up the food chain
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within a cell
Xenobiotics
compounds that are present in living organisms but should not normally be found there
zwitterions
the form of an amino acid that has no overall charge
allosteric effect
The binding of a ligand to one site on a protein molecule in such a way that the properties of another site on the same protein are affected
allosteric site
The place on an enzyme where a molecule that is not a substrate may bind, thus changing the shape of the enzyme and influencing its ability to be active.
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
conjugated system
Connected p-orbitals with the delocalized electrons in molecules with alternating single and multiple bonds.
Michaelis constant
A constant, Km, that is a measure of the kinetics of an enzyme reaction and that is equivalent to the concentration of substrate at which the reaction takes place at one half its maximum rate.
pH
hydrogen ion concentration
Enzyme
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Reactants
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
products
the substances that are formed by the chemical change
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
main energy source that cells use for most of their work
acidic
pH less than 7; indicates a greater concentration of H+
Alkaline
a basic substance that absorbs hydrogen ions or releases hydroxyl ions and has a pH greater than 7
Photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
fibrous proteins
proteins shaped like long fibers or secondary structures
globular proteins
compact spherical molecules with dominant tertiary structures
polar
describes a molecule in which the positive and negative charges are separated and dissolves in water
nonpolar
a molecule in which all atoms have the same electronegativity and the electron distribution is equal and does not mix with water
Amide link
The amide link is CONH and is formed in a condensation reaction which joins together amino acids. It can also be known as a peptide link.
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
Bronsted-Lowry theorya
acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors
adipose tissue
Fat stores in animalslip
Lipid
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Carbohydrates
Broken down to glucose to provide energy.
Vitamins
Essential nutrients that do not yield energy, but that are required for growth and proper functioning of the body.
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Monomers
small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers
Cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids.
Steroids
A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings with various functional groups attached.
Triglycerides
an energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid.
Atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries
Iodine number of fat
the number of grams of iodine, which reacts with 100g of lipid.
rancidity
Spoilage caused by breakdown of fats
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
glycosidic bond/linkage
A covalent bond formed between 2 monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
Bioaccumulation
An increased concentration of a chemical within an organism over time