Kinesiology Exam 1
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
We're at OTD Rutgers baby suffer. Received a 100 :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Kinetics
Study of motions AND the forces causing body motions
Kinematics
Study of JUST motions causing movement, not including forces
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
X and Y axes
Sagittal Plane
Y and Z axes
Transverse (Axial) Plane
X and Z axes
Rotary Motion (Angular Displacement)
Curved displacement around an axis (Center of Rotation)
Translatory Motion
Displacement along an axis in a straight line
Curvilinear Motion
Combined Rotary and Translatory Motion
Curvilinear Motion Axis
Axis is not fixed
Example of Rotary Motion
Shoulder flexion, fatty joint movement
Goniometer
Example of Translatory Motion
Elbow and knee gliding
Compression and Distraction
Example of Curvilinear
Walking and Cheer Motions
Joint Compression
Force on joint creates joint stability
Force push together joint surfaces
Joint Distraction
Force on joint creates joint mobility
Forces separate joint surfaces
Force
Uh force??
Vector
Representation of force
Gravity Force Type
External Force
Center of Mass (COM)
Hypothetical point where object’s mass is evenly distributed
Where gravity is applied DA
Gravity and Center of Mass (COM)
COM is Gravity’s Point of Application
Instability and Base of Support (BOS)
Line of Gravity outside BOS
Stability and Base of Support (BOS)
Line of Gravity inside BOS
How to Increase Stability
Increase BOS, equilibrium adjustments (adjusting COM)
Weight AKA:
Force of Gravity
Internal Force
Forces within body’s structure
External Force
Forces outside body’s structure
Point of Application
Where force is applied
Action Line
Direction of force
Length
Magnitude of force
Newton’s First Law Actual Definition
Object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon
Newton’s Second Law Actual Definition
The Force acting on a moving object is the product of the Mass and Acceleration
F = m * a
Newton’s Third Law Actual Definition
For every action there’s an equal and opposite reaction
Newton’s First Law Example
Lying down, resting against a wall
Newton’s Second Law Example
Pushing a shopping cart
Newton’s Third Law Example
Hammering a nail on the wall
Linear Force System Definition
Two or more forces acting on the same segment, plane and line
Concurrent Force System
Two or more forces acting on an object at different angles/axes & lines, but end up converging or intersecting
Concurrent Force System Example
Lateral and medial head of the gastrocnemius, they’re both on the Achilles tendon but in opposite X directions
Parallelogram Method
Create a parallelogram with given forces and split in half diagonally to create resultant force
Parallel Force System
Two or more forces acting on an object in the same axis, but not in the same line and do not end up converging
Parallel Force System Example
Turning a steering wheel, turning in a wheel chair, revolving door, see saw
Resultant Force (Vector Sum)
Direction and location of the Sum of unbalanced force(s) on an object in a Concurrent Force System
Force Couple
Forces are parallel and act in the same plane, but in opposite action lines
Type of Parallel Force System
Produces Rotary Motion
Axis
Point of Rotation, Fulcrum
Levers
Rigid segment that Rotates around a fulcrum/axis
Comprised of two forces applied to a lever and create opposing torques
Effort Force (Internal Force)
Force that produces Resultant Torque
Always the winner in torque battle
Resistance Force (External Force)
Force that produces Opposing Torque
Always the loser in torque battle
Point of Application
Where force is being applied
Moment Arm
Distance between Axis and Point of Application
Effort Arm
Distance between Axis and Effort Force’s Point of Application
Moment Arm of Effort Force
Resistance Arm
Distance between Axis and Resistance Force’s Point of Application
Moment Arm of Resistance Force
First Class Lever
EF - A - RF (Axis between)
Axis is between Point of Application of Effort Force and Point of Application of Resistance Force
First Class Lever Example (Axis Between)
Head and Neck:
RF- weight of head
Axis- neck joints
EF- neck muscles
Second Class Lever
A - RF - EF (Resistance Force Between)
Resistance Force is between Point of Application of Effort Force and Axis
Second Class Lever Example (RF Between)
Pushup:
Axis- toes
RF- weight of body
EF- arm muscles
Third Class Lever
A - EF - RF (Effort Force Between)
Effort Force is between Point of Application of Resistance Force and Axis
Third Class Lever Example (EF)
Biceps Brachii:
Axis- elbow
EF- biceps brachii
RF- weight
Torque
Strength of rotation produced by a force
T = F * MA (moment arm)
State of Equilibrium
Internal Torque = External Torque; Net Torque = 0
Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical efficiency of Effort Force compared to resistance force
Optimal Mechanical Advantage
M Ad > 1.0
Non-Optimal Mechanical Advantage
M Ad < 1.0
Concentric Contraction
Active Shortening
Muscle moves segment in direction of pull
Muscle is Effort Force
Muscle shortening creates Active Tension
Eccentric Contraction
Active Lengthening
Muscle moves opposite to segment to slow/control movement against gravity
Muscle is Resistance Force
Muscle lengthening creates active tension
Isometric Contraction
Muscle resists gravity/object, but system is not moving; in rotational equilibrium
Muscle can be either RF or EF
Muscle is not in motion but still creates active tension
Muscle Force & Angle of Application
Angle of Application is used to interact and oppose gravity so body maintains upright posture and produce movement
Gravity & Angle of Application
Angle of Application is used to provide body stability
Biceps @ 90 Degrees Flexion
Greatest Moment Arm for Biceps
Biceps @ Not 90 Degrees Flexion
Moment Arm SUCKS
Anatomic Pulley
Deflects Action Line of muscle force Farther from the joint axis, creating a Larger Moment Arm
Redirects force to make a task easier
Greater moment arm = Greater Torque
Anatomic Pulley Example
Patella in the knee
Gravity & Torque Relationship
The Farther the distance of the COM/Action Line from the Axis, the Greater the Moment Arm/Torque of Gravity
Greater distance COM vs. Axis = Greater Moment Arm = Torque of Gravity
Gravity & Torque Relationship Example
Biceps- gravity has greatest moment arm/torque at 90 degrees flexion
Sit Ups- gravity has lowest moment arm/torque when COM is closer to axis
Resolution of Forces
Breaking down original force into 2 or more forces, their sum is equivalent to the original force
Original Force → Perpendicular Forces & Parallel Forces
Resultant Force → Rotary Forces & Translatory Forces
Perpendicular Forces
Forces that are perpendicular to the long axis (bone)
Fy, Torque, Rotational Component
Rotary Component
Component of original/resulant force that produces Torque
Fy, Perpendicular Force
Parallel Forces
Forces that are parallel to the long axis (bone)
Fx, Compressive and Distractive Forces, Translatory Component
Translatory Component
Component of original/resultant force that creates Compressive/Distractive force
Fx, Parallel Force
Compressive Component - Stabilizing
Angle of Application < 90 degrees
Distractive Component - Tensile
Angle of Application > 90 degrees
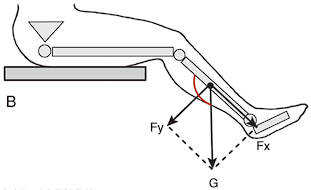
Compressive Component Example
Gravity on knee joint at 45 degrees, gravity’s parallel force pushes lower leg bones toward femur
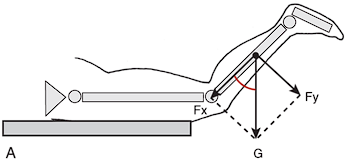
Distractive Component Example
Gravity on knee joint at 135 degrees, gravity’s parallel force pulls lower leg away from femur
Fascicles
Bundled muscle fiber groups
Parallel Forms
Muscles are parallel to long axis
Strap or fusiform
Oblique Forms
Muscles are oblique to long axis
Pennate, unipennate, bipennate, multipennate, triangular/convergent
Circular Forms
Muscles are concentric (surround an opening)
Concentric Contraction and Filaments
Active Shortening
Thin filaments are pulled Toward thick filaments
Cross-bridges between thin and thick filaments are formed
Eccentric Contraction and Filaments
Active Lengthening
Thin filaments are pulled Away from thick filaments
Cross-bridges between thin and thick filaments are broken then reformed in the process of lengthening
Isometric Contraction and Filaments
Muscle fiber does Not change in length
Thin filaments and thick filaments Remain connected
Cross-bridges between thin and thick filaments do not change
Alpha Motor Neuron (AMN)
Neuron that emerges from the anterior horn and extends to the muscle
Initiates muscle contraction
Motor Unit
One AMN and all the muscle fibers it innervates
Passive Tension
Tension created by lengthening the muscle beyond slack; noncontractile
Length increases past max, tension increases
Passive Insufficiency
When a muscle is elongated over 2+ joints simultaneously
Tension is too high for the length of muscle
Passive Insufficiency Examples
Wrist Flexion: wrist flexion creates tension in wrist extensors, pulling them and creating passive finger extension (tenodesis)
Wrist Extension: wrist extension creates tension in wrist flexors, pulling them and creating passive finger flexion
Active Tension
Tension created by contractions of muscle; contractile
Length decreases, tension increases
Active Insufficiency
Muscle crosses too many joints, when the entire muscle contracts the muscle shortens Decreasing Torque and Tension
Length is too short, can’t create enough tension
Optimal Grip in Hand
Slight wrist extension allows for full finger flexion
Synergist Muscle (Accessory Muscle)
Muscles that assist agonists in an action by initiating movement or by stabilizing the agonists
Synergist Example
Radial Deviation- Flexor Carpi Radialis can not perform radial deviation if Extensor Carpi Radialis is not active
Degrees of Freedom
Number of planes or axes which a movement can occur
Uniaxial Joints
1 action type
1 degree of freedom, 1 axis of rotation, 1 plane of motion
Ex: IP joint (flex/ext), elbow joint (flex/ext), radio-ulnar joint (sup/pro)