[MOD2C - ANATOMY] Clinical Correlations_2028
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Femoral neck fracture
A common fracture in the elderly population because of osteoporosis.
Retinacular branches
Femoral neck fracture leads to avascular necrosis because of what specific blood vessels?
TRUE
True or False: If femur is fractured, especially in the elderly population, there is a higher chance of becoming immobilized.
Femoral neck fracture
Identify the type of fracture.
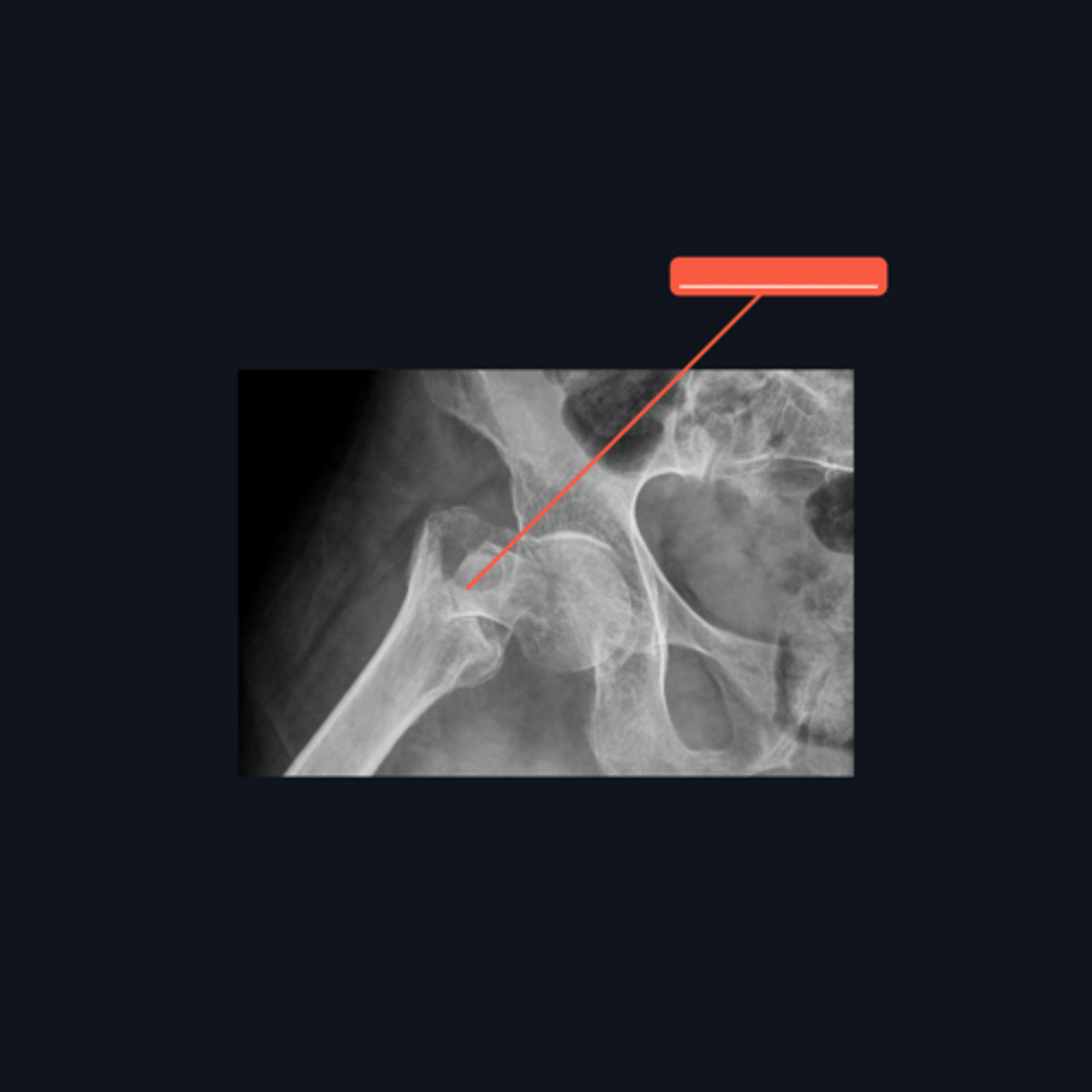
125°
What is the normal angle of the femoral neck and shaft?
Genu valgum under Coxa vara
Identify the knee condition pointed and what hip condition is it under?
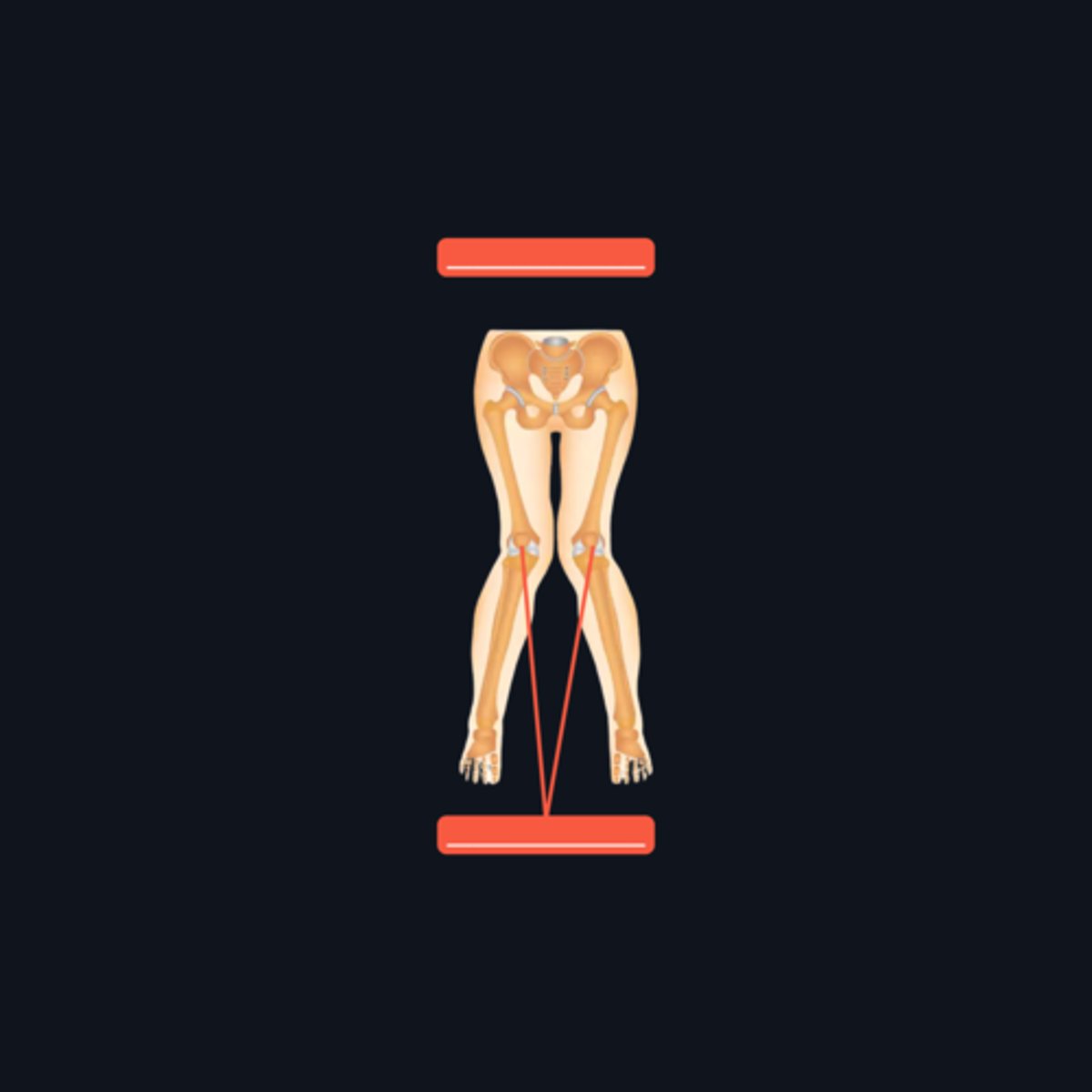
Coxa vara
A condition where there is a decrease in the angle formed by the femoral neck and shaft (<125°)
Pes valgus under Coxa valga
Identify the foot condition with the red line and what hip condition is it under?

F; It manifests Pes valgus and Genu varum
T of F: Coxa valga manifests Pes varum and Genu valgum
Between Iliac crest and ASIS
Which part of the "buttocks" is considered the safe area for injection?
90 degree angle
Which angle is the safest to administer an intramuscular injection on the Gluteal area?
Infection, Vascular, Muscle and Nerve Damage, Paralysis,
What complications arise when the IM injection on gluteal region is wrongly administered?
-Centralized back pain due to nerve roots -Pain on the entire posterior leg to toe compartment"
What are common manifestations of sciatica?
Sciatica
What is the general term that affects the sciatic nerve?
Lumbar herniated disc
What is the general cause of sciatica?
Straight Leg Raise Test (SLR)
It is a test used to differentiate sciatic nerve damage from a tight hamstring.
It is considered positive when pain is elicited by lower limb flexion at an angle lower than 45°.
When is Straight Leg Raise Test positive?
piriformis syndrome
Happens when the piriformis muscle enlarges and compresses the sciatic nerve
sciatic nerve
what nerve is compressed/affected in piriformis syndrome
sciatica
piriformis syndrome is similar to the symptoms of that of the
Pain radiating by the foot, butt pain especially when walking
What are the symptoms of piriformis syndrome
Piriformis muscle
What muscle enlarges and compresses the sciatic nerve leading to piriformis syndrome
It keeps the pelvis level
What role does the gluteus medius play in maintaining pelvic alignment during gait?
Weakened gluteus medius
What is the consequence of an injury to the superior gluteal nerve?
The pelvis elevates on the stance leg
How does a weakened gluteus medius affect pelvic position during walking?
Trendelburg sign
What observable sign indicates a problem with the gluteus medius during stance phase of gait
The pelvis drops on the side opposite the stance leg
Explain the Trendelenburg sign in relation to pelvic movement
Complete, displaced, non-comminuted fracture.
What type of fracture is described in a complete, displaced femoral fracture?
No.
Can the laterality of a complete, displaced femoral fracture be determined from an X-ray?
It cannot determine whether the fracture is open (bone piercing through the skin).
What information cannot be determined about the femoral fracture from an X-ray radiograph?
Because of the pull of muscles attached to the femur, such as the gluteus medius.
Why are most femoral shaft fractures displaced?
The gluteus medius (attached to the greater trochanter, it pulls the fractured segment upward and adducts it).
Which muscle pulls a fractured femur segment upward and adducts it?
Traction (uses weights to counteract the muscle forces).
How were lower limb fractures treated before the invention of metal fixators?
Intramedullary implants (metal fixators)
What modern treatment is used to fix femoral fractures?
The adductor muscles, which are attached to the back of the femur (linea aspera), pull the distal segment towards the midline (adducted).
Which muscles are responsible for adducting the distal segment of the femur in a displaced femoral fracture?
quadriceps femoris.
What is the primary muscle responsible for the upward movement of the distal segment in a femoral fracture?
The gluteal muscles and iliopsoas.
Which muscles contribute to the abducted and superior displacement of the proximal segment in a femoral fracture?
The iliopsoas moves the proximal segment to the side and anteriorly.
What is the role of the iliopsoas in the displacement of the proximal segment?
condition: VARICOSITIES management: Elastic bandage, Elastic stockings, Elevating the leg while sleeping
Identify the medical condition and its three management strategies.
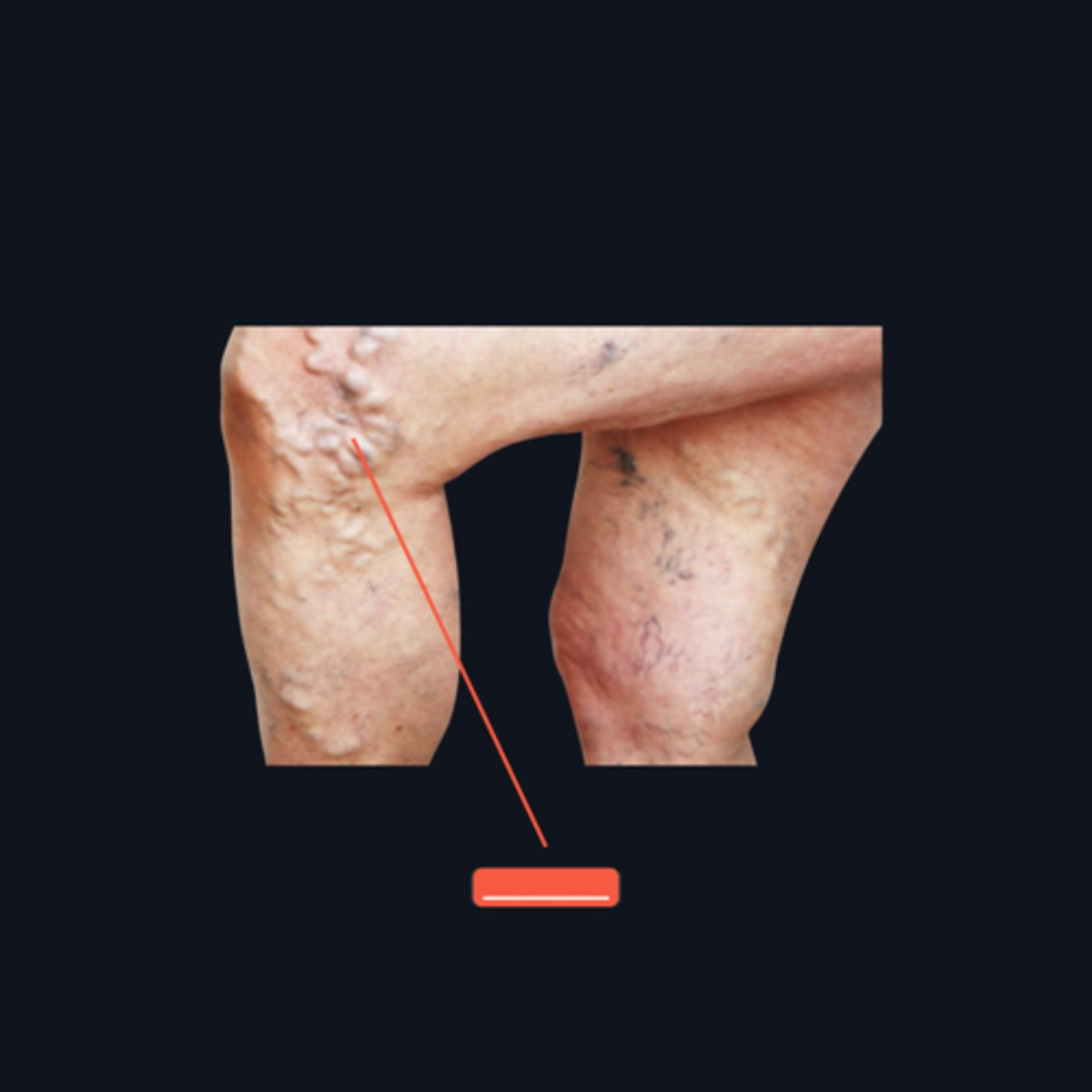
There is backflow of blood, causing engorged veins
What happens to blood flow in patients with varicosities?
Ankle pumping exercises
What can be done to contract the gastrocnemius during long flights?
Valves
What anatomical feature in the lower limb veins helps prevent backflow of blood?
The gastrocnemius muscle
Which muscle's contraction is important for pumping blood from lower limb vessels towards the heart?
A Filarial worm called Wuchereria bancrofti
What is the causative agent of elephantiasis?
The inguinal lymph nodes.
Which lymph nodes are commonly obstructed by Wuchereria bancrofti in elephantiasis that leads to enlargment of extremities?
Patellar Dislocation
A common dislocation along with patellar fracture usually caused by a sudden drop on the knees
Manual manipulation of the patella by an expert
How is patellar dislocation treated?
Sudden drop on the knees
What is the common cause of patellar dislocation?
Vastus medialis and lateral condyle of femur
What structures supposedly prevents the patella from being displaced during the action of the quadriceps?
Anterior Drawer's Test
What is the test for ACL injury?
Patient lying at supine position
In what anatomical position should you perform Anterior Drawer's Test?
ACL Tear
This is a common sports injury
Positive Anterior Drawer's Test
Tibia is pulled anteriorly, there is posterior displacement of femur, and excessive movement
Patient lying at supine position, flexing the hip joint and knee joint
How will you perform Anterior Drawer's Test?
Meniscus tear
This type of injury is caused by a valgus force, forcing the medial collateral ligament to be torn.
Medial collateral ligament and anterior cruciate ligament
Meniscus tear is commonly associated with tearing of what ligaments?
TRUE; The medial meniscus is damaged more frequently due to its strong attachment to the medial collateral ligament which restricts Its mobility.
T or F: Medial meniscus tears occur more frequently than lateral meniscus tears in the knee joint.
Locking of the knee
What symptom is commonly associated with meniscus tears, characterised by inability to fully extend the knee?
Medial/Tibial collateral ligaments, Anterior cruciate ligaments, Medial meniscus
What are the ruptured structures in the Unhappy Triad of O'Donoghue?
Unhappy Triad of O'Donoghue
An injury that is usually the result of an external force applied to the lateral surface of the knee
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Which among the affected structures, when, if teared, in the Unhappy Triad of O'Donoghue is usually taut during extension
Osteoarthritis
It is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and changes in the underlying bone. It typically affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips and is often associated with aging.
Osteoarthritis
What is a common condition affecting the elderly in the knee?
It degenerates and bony spurs (osteophytes) develop, leading to pain.
What happens to the articular surface in osteoarthritis?
NSAIDS (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs)
What is the first-line management for osteoarthritis?
Gastric irritation
What is a common side effect of NSAIDs?
Celecoxib and Etoricoxib
Name two examples of selective COX-2 inhibitors
Knee joint replacement (femoral condyles and tibial plateau)
What severe treatment option may be required for advanced osteoarthritis?
Metal implants can distort MRI images and pose safety risks, as they may move or heat in the magnetic field. Ensuring no metal is present is essential for accurate imaging and patient safety.
Why is it important to ensure patients do not have metal implants before an MRI for knee evaluation?
The entire length of the medial surface of the tibia is covered only by skin and superificial fascia.
Why are fractures of the shaft of the tibia often open?
Distal third
Which part of the shaft of the tibia is prone to delayed union or nonunion (most frequent site of fracture)?
Proximal end, at the tibial condyles
In the middle-aged and elderly, which part of the tibia is commonly fractured?
Direct violence to the lateral side of the knee joint
What usually causes the fracture of the proximal end of the tibia?
Compartment Syndrome
What is the common outcome of a tibial fracture?
Fasciotomy
What is the treatment procedure for Compartment Syndrome that relieves the pressure in the leg muscles compartment by cutting of the leg's fascia?
Dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle joint and plantar flexion of the ankle
What movements can increase the severity of pain of Compartment Syndrome?
Dorsalis pedis arterial pulse
What pulse disappears when a patient has Compartment Syndrome?
Tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, and extensor hallucis longus
What muscles are paralyzed in Compartment Syndrome?
TRUE; Bones surrounded by muscles heal better due to the abundant blood vessels in muscles that support recovery. The tibia, being only covered by skin, struggles to heal properly after a fracture.
T or F: Fracture nonunion occurs when broken bones fail to unite or heal completely.
Muscles have abundant blood vessels that help in bone healing
Why do bones surrounded by muscles heal better?
Fracture Nonunion
What is a common complication of a tibial fracture called?
The tibia is only covered by skin and lacks the blood suppky provided by surrounding muscles
Why is the tibia prone to fracture nonunion?
FALSE; fractures of the DISTAL third of the shaft of the tibia are prone to delayed union or nonunion
T or F: Fractures of the proximal third of the shaft of the tibia are prone to delayed union or nonunion
Perforating peroneal artery, anterior tibial artery, posterior tibial artery
The main vascular structures affected by a talar fracture
Talar head and neck
The anterior tibial artery supplies blood to these parts of the talus
Talar head
The part of the talus where blood supply is still available during talar fracture cases
Avascular necrosis
A known condition that can be caused by a talar fracture
Violent dorsiflexion of the ankle joint
What is the common cause of talar neck fracture?
Jumping from a height
What usually causes the fracture of the body of the talus?
Don Juan's Fracture or Lover's Fracture
This is another term for calcaneal fracture, due to it being common in patients caught by their partners having an affair and jumping off the balcony, leading to the fracture of this bone.
Calcaneal fracture
This compression fracture of a particular tarsal bone commonly results from landing on one's feet after falling from great heights, causing the talus to drive downward upon this bone, crushing it.
Posterior portion of the calcaneum
What part of the calcaneus commonly fractures during a calcaneal fracture?