Histopathology colloqium
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
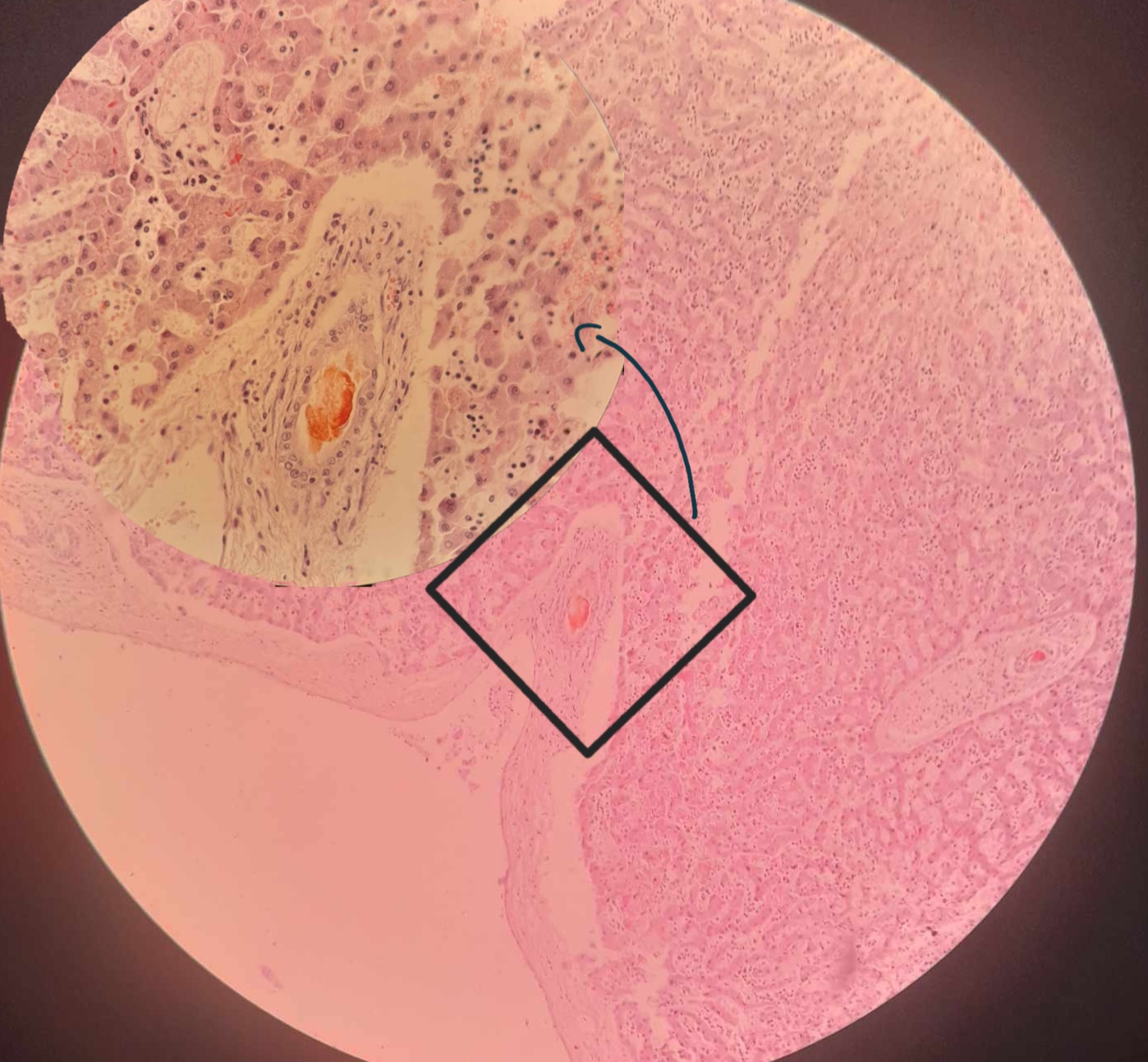
Icterus retention hepatis canis
Distended bile duct
Bile plug
Kupffer cells hyperplasia
Distended sinusoids
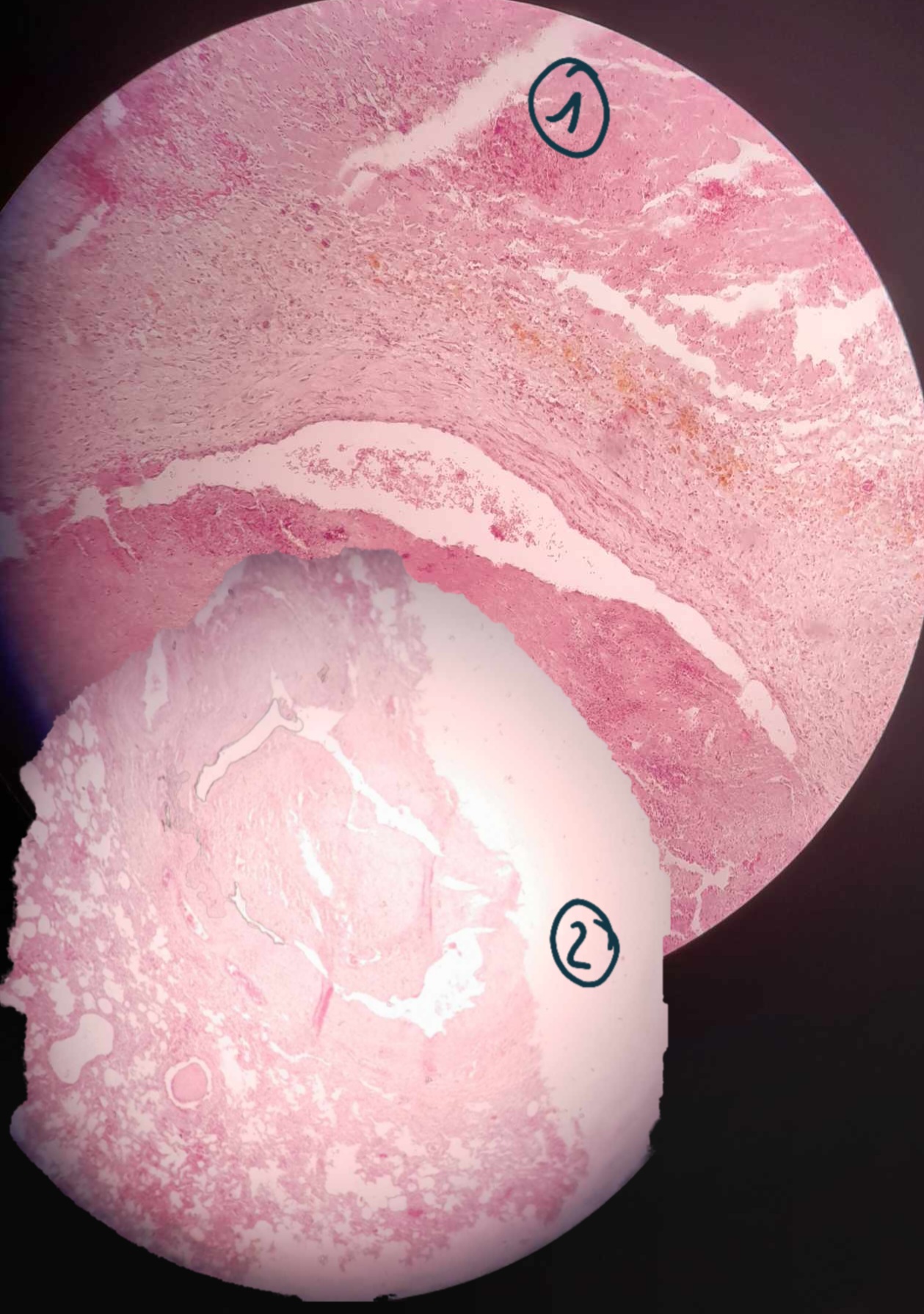
Thrombis of pulmonary artery branch
1- Fresh (Acute)Thrombus: fibrin mesh with embedded erythrocytes and leukocytes
2- old (chronic) Thrombus: Hyalinisation of the Thrombus + organization (fibrin)
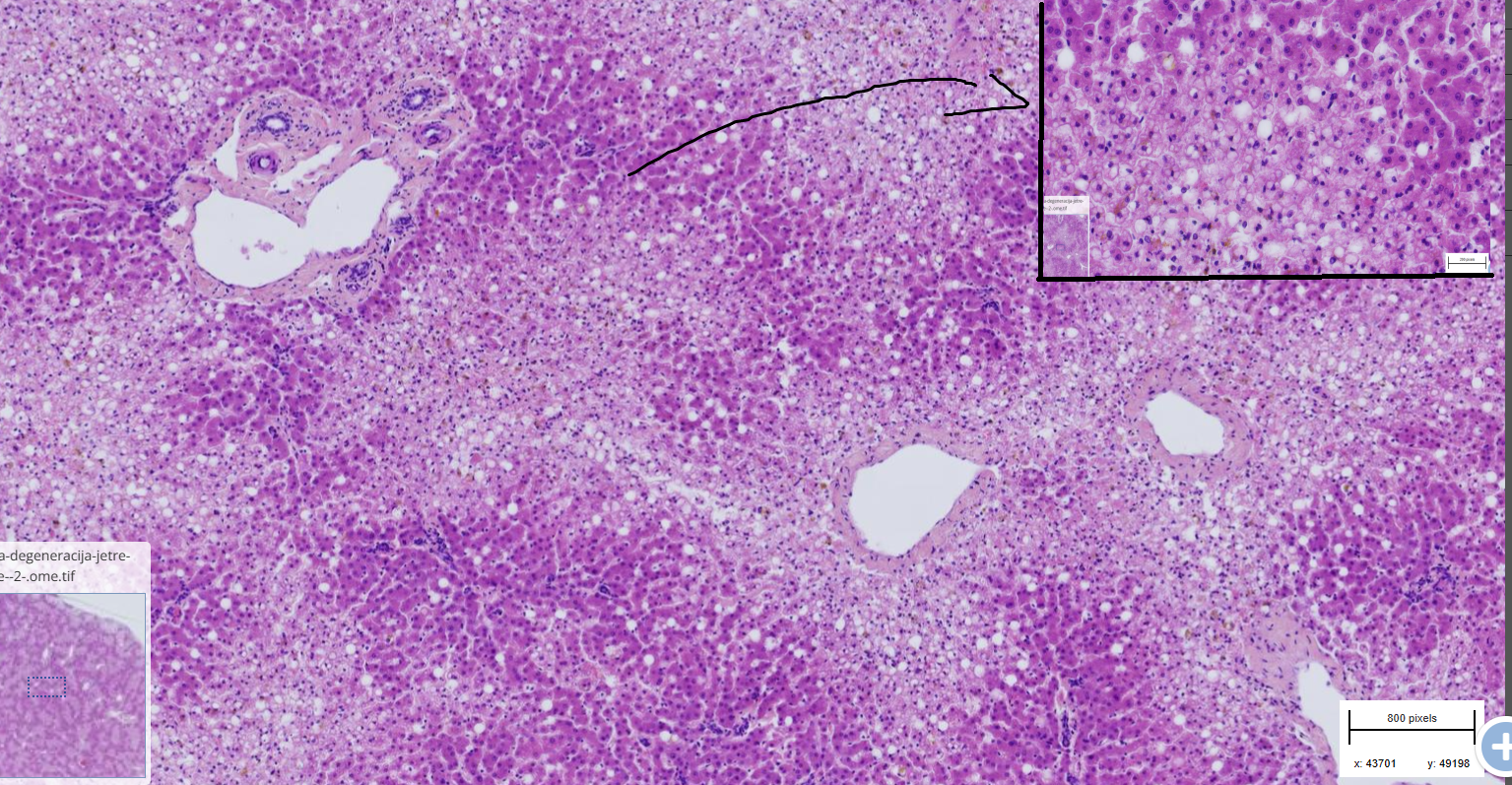
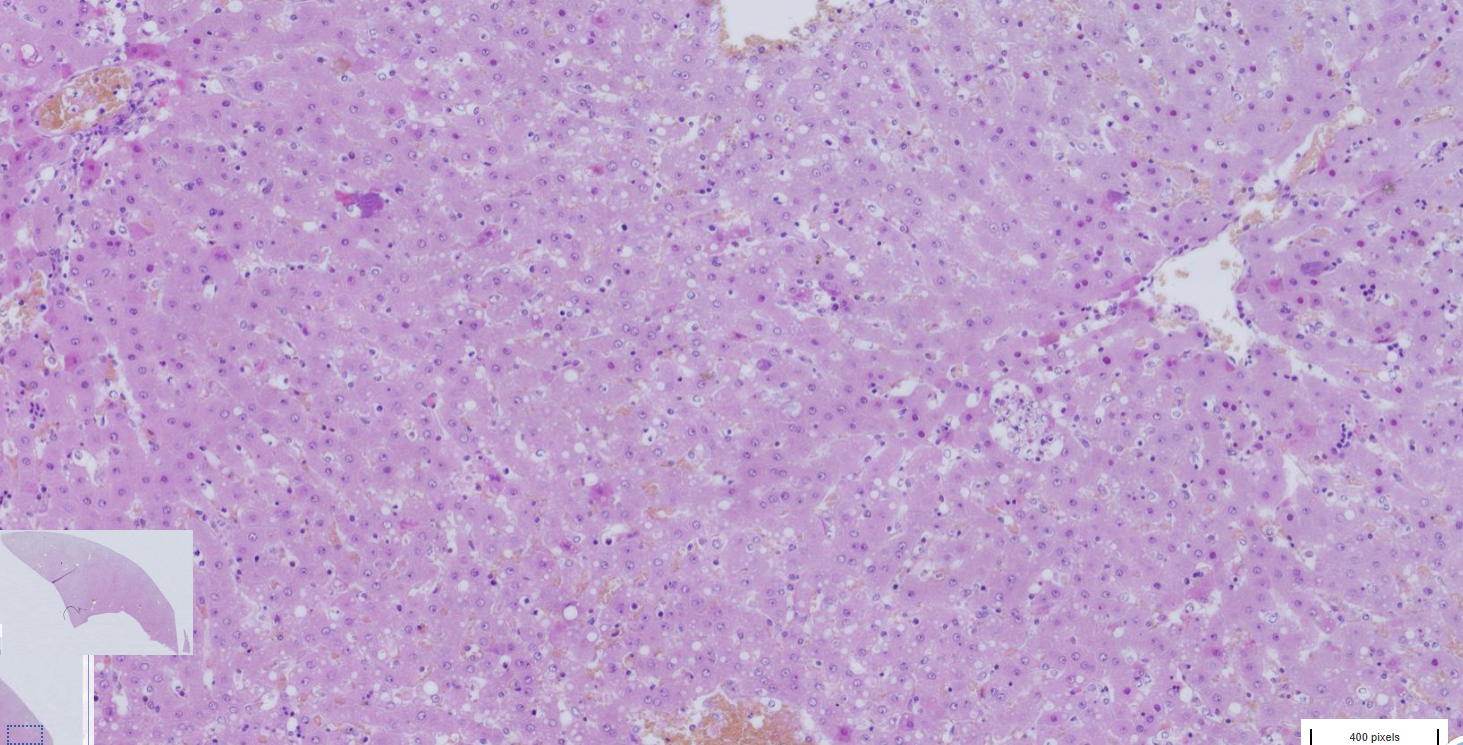
liver lipidosis
- peripherally displaced nuclei
- lipid droplets dissolved in ethanol in vacuoles
- hardly visible hepatocytes
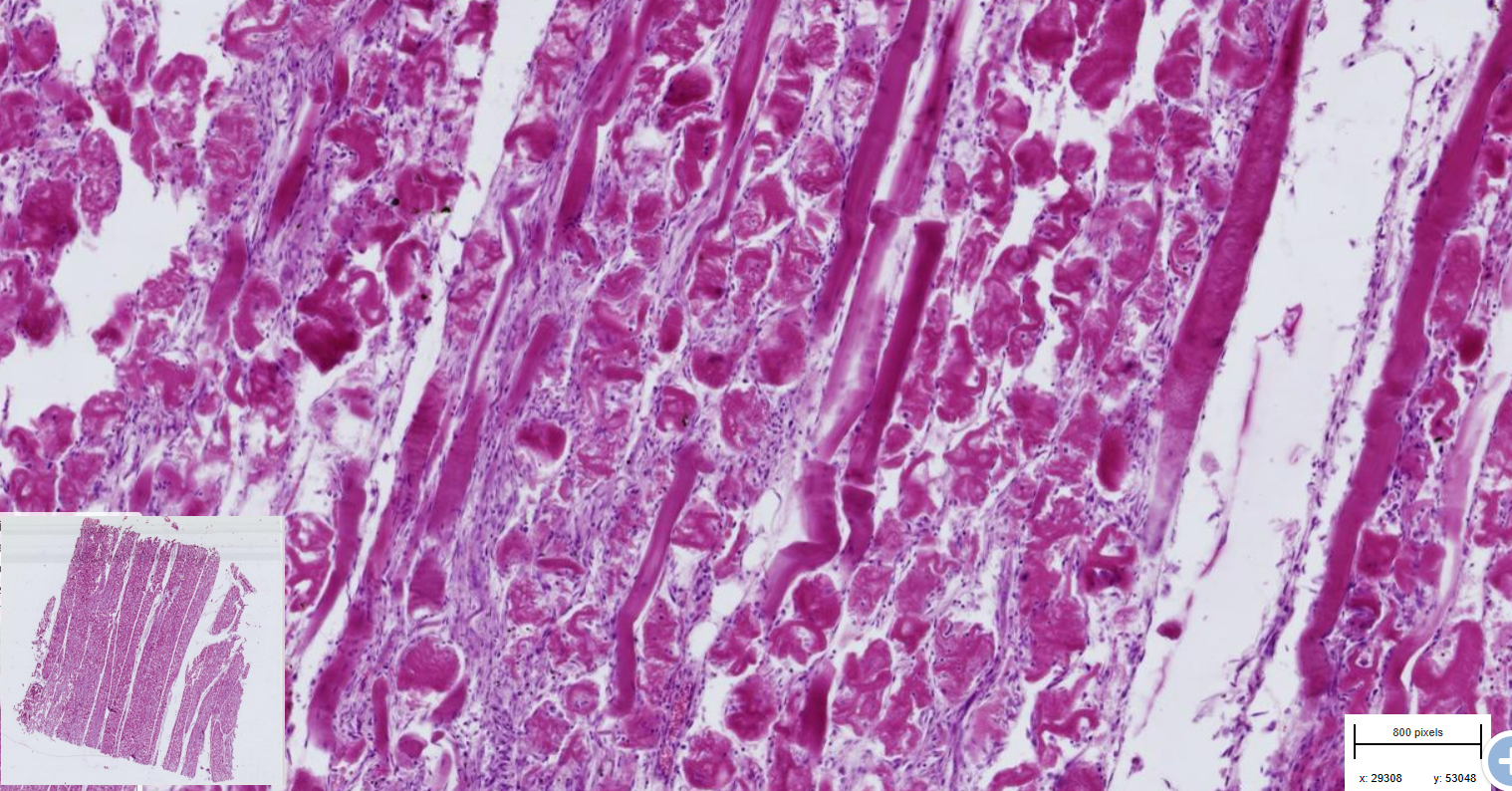
Myofirbril degeneration of skeletal muscle
- deep red color
- desintegrated myofibril surrounded by nuclei
-some myofibrils are still continuous
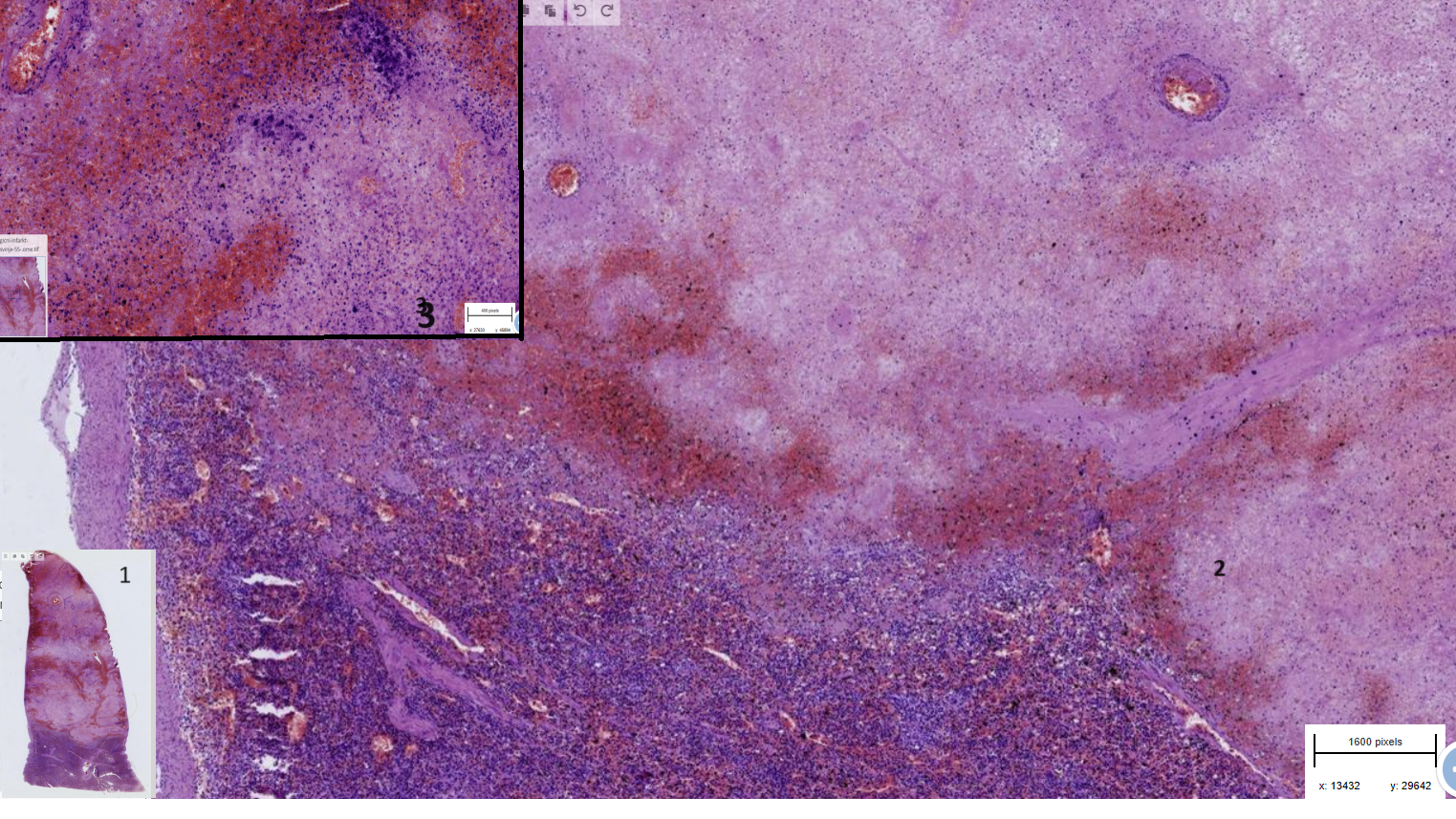
1,2,3= more and more zoomed in
Hemorraghic infarction of the spleen
- sharp transition between necrotic and normal area
- Necrotic area:
1- Haemmorraghe
2- Thrombosis of small vessels
3- hemosiderin pigments + calcium deposit
Liver hepatitis suppurative and necrotizing, multifocal, chinchilla
-disseminated small necrotic foci and bacterial colonies
-necrotic foci
- inflammatory cells within the foci
- hypereosinophilic remains of hepatocytes
-congestion of blookd vessels
-vacuolization of liver parenchyma
-
Liver hepatitis fibrous, intersitial, chronic and eosinophilic
-pronounced lobular pattern
-interlobar septa thickened, distended and filled with thick fibrous tissue
-infiltration of eosinophil into the fibrous stroma
! difference with cirrhosis= decreased lobules due to pressure of fibrous tissue that doesnt enter the lobule !
Skin actinomycosis, swine
-multifocal to coalescing pyogranulomas — composed of degenerate neutrophils surrounded by macrophages
- with basophilic filamentous bacterial colonies in the center with eosiniphilic radiating material
-layers of dense connective tissue- fibrosis
-superficial epidermis is necrotic
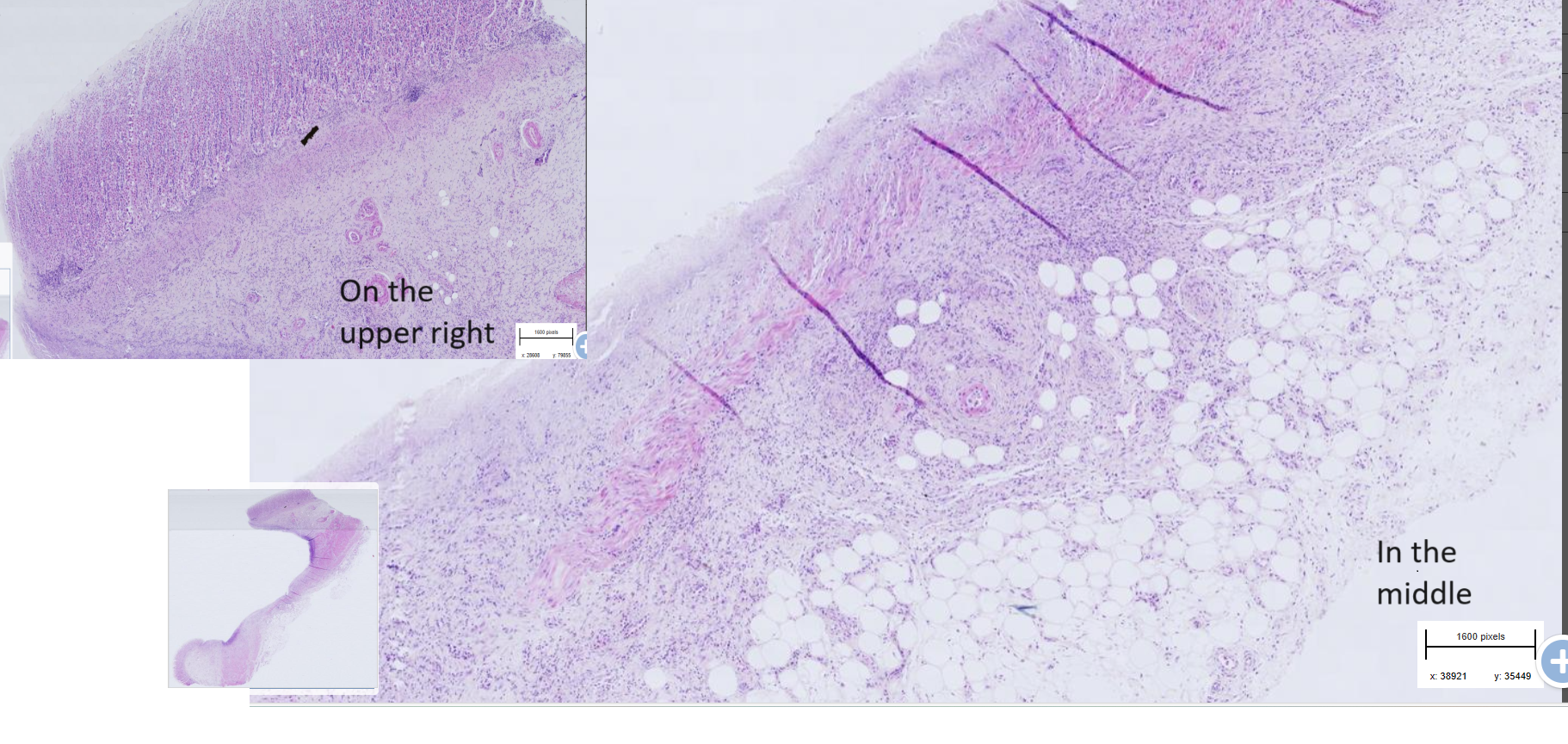
Stomach ulcer, dog
-necrotic mass in the lumen (not on this exemple slide)
- Thrombi within submucosal blood vessels
- Proliferation of fibrous connective tissue and inflammatory cells infiltration
- in ulcerative mucosa: loss of mucosal structure, disrupted normal architecture
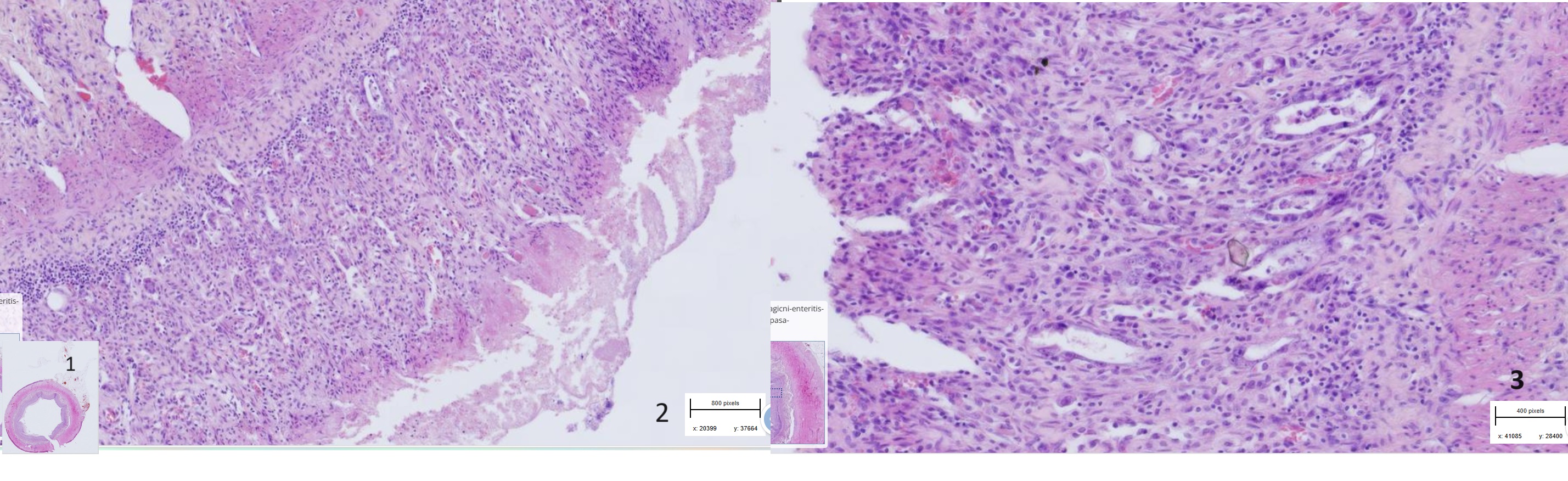
Small intestine : Necrohemorrhagic enteritis - parvovirosis
-Blunting and fusion of villi
-loss of apical enterocytes
-bacterial colonies in lumen
-crypts necrosis and regeneration
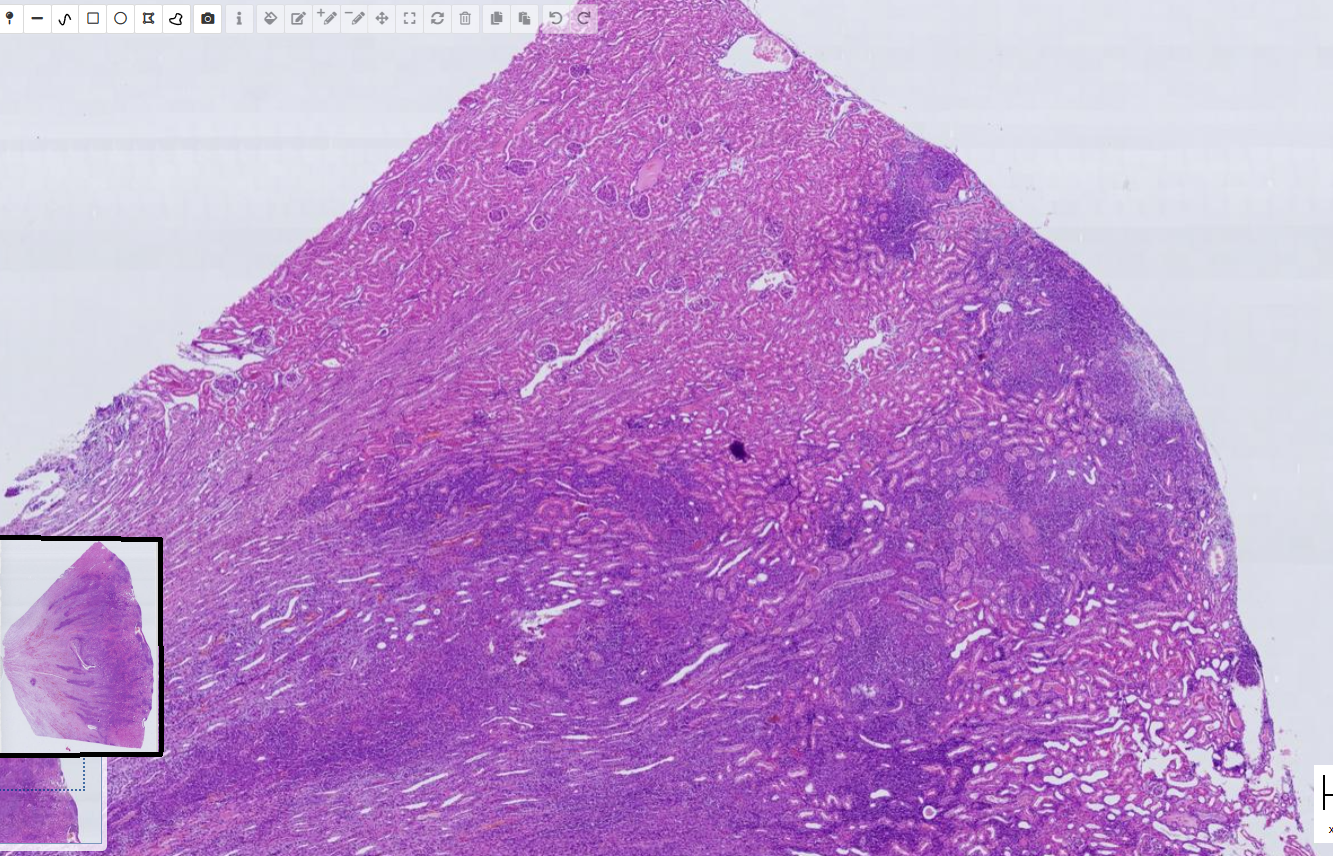
Pyogranulomatous interstitial nephritis plus phlebitis multifocal, severe, and thrombosis - FIP
-Pyogranuloma
-activated fibroblast
-thrombosis
- activation and necrosis of endothelial cells
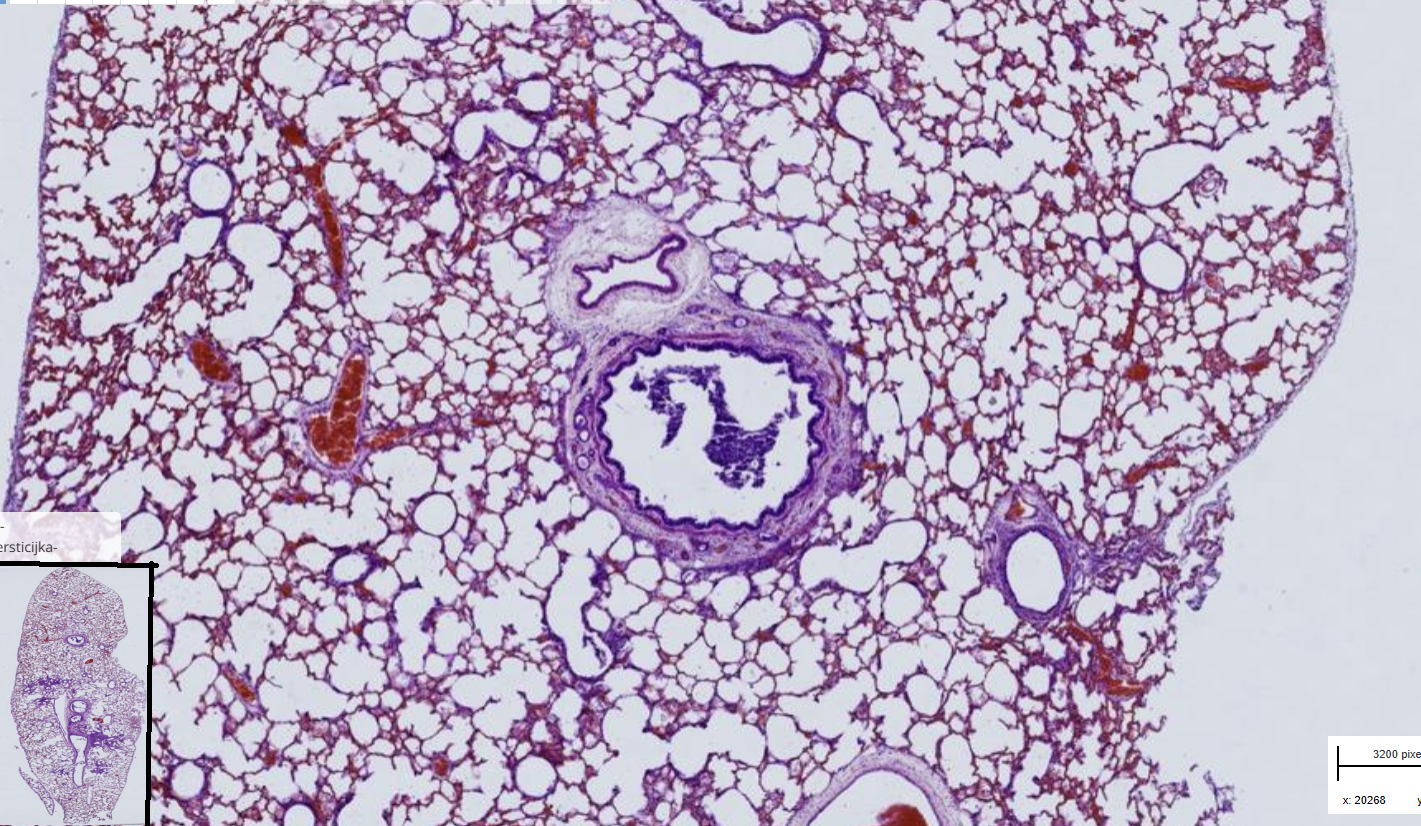
Lung : Multifocal, necrotic, partly purulent bronchointerstitial pneumonia, subacute
-supposed to have inflammatory foci but not visible on the picture
-purulent- necrotic bronchitis and bronchiolitis plus neutrophils and macrophages
- necrosis and exfoliation of pneumocytes
-eosinophilic inclusions ( not visible on picture)
-alveolar edema
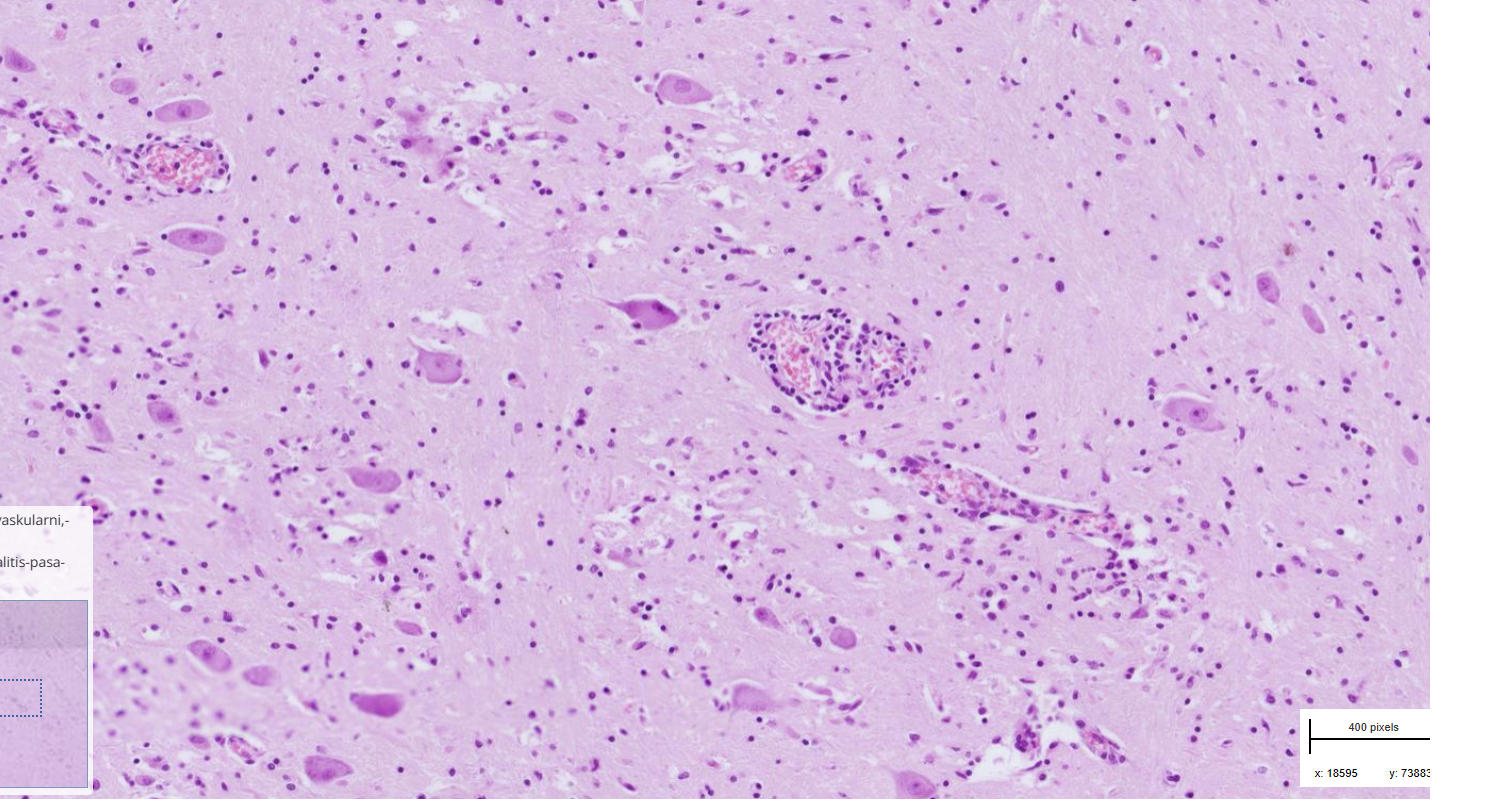
Brain : Multifocal, perivascular, nonsuppurative meningoencephalitis - rabies
-blood vessels surrounded by lymphocytes
-negri bodies
- degenerated neurons
-perivascular gliosis
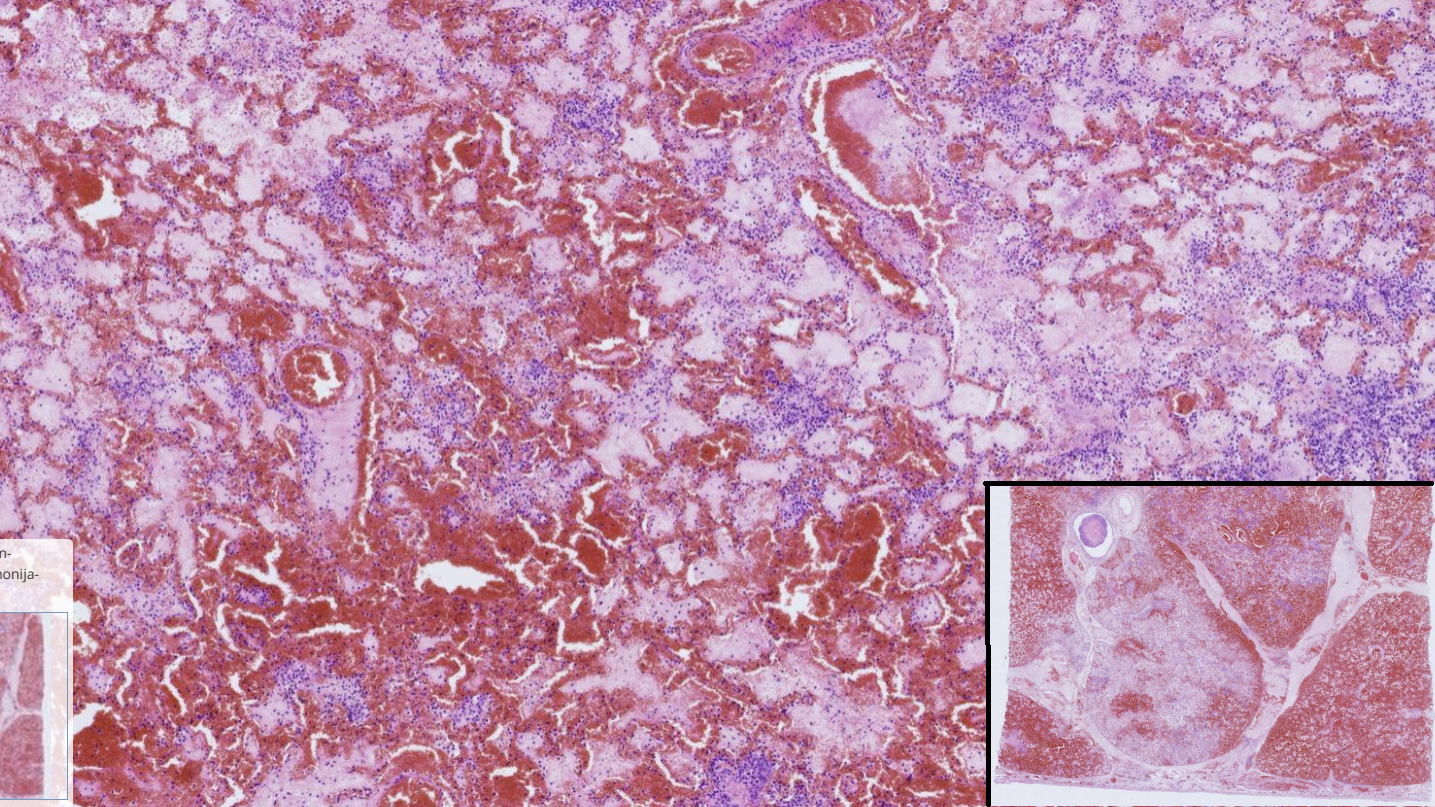
Fibrinous and necrotizing pneumonia
-Disrupted architecture
-Pleura : amorphous eosinophilic mass thickened by fluid (edema) and fibrin
-Bronchial walls are necrotic ( not on the picture)
-multifocal bacterial colonies
-Hemorrhages
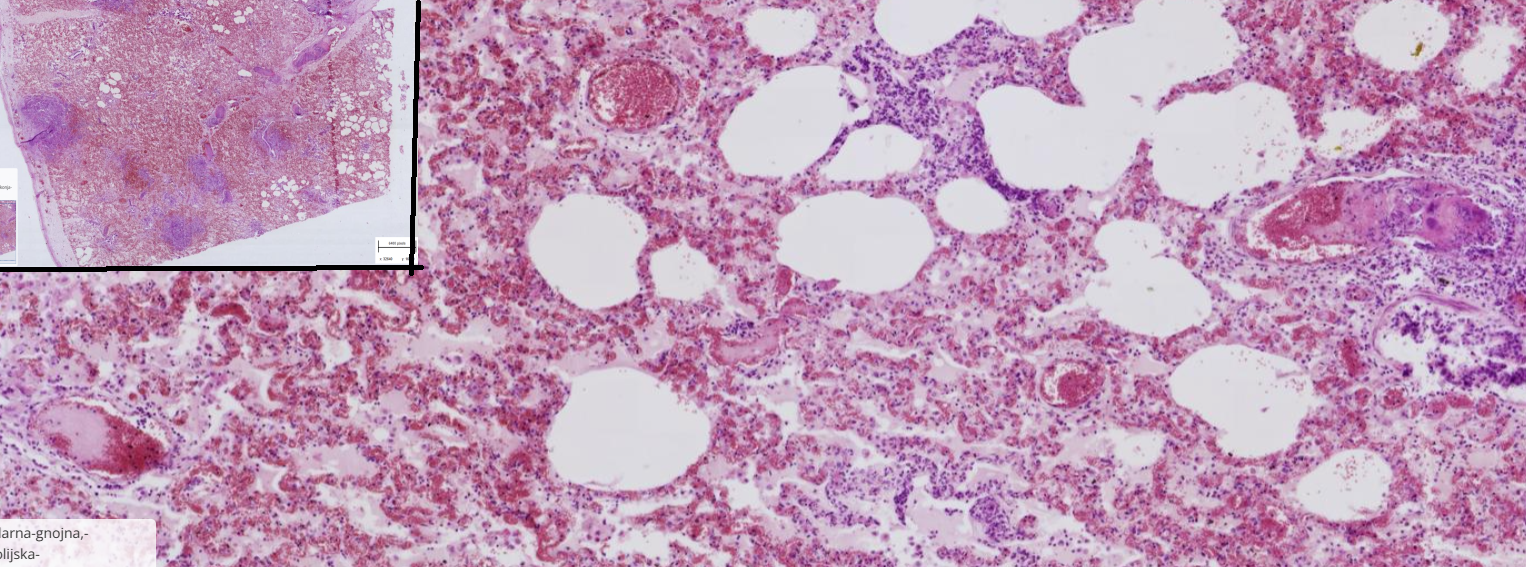
Bonchopneumonia , suppurative and embolic
-preserved architecture
-Thrombosis of blood vessel : 1-Fibrin + cell debris+ erythrocytes = fibrinous thrombus
2- Fibrin+ bacteria = spectic thrombus
-Multifocal area of neutrophils, residues of necrotic alveolar septa, bacterial colonies
-parenchymal, interstitial and subpleural edema
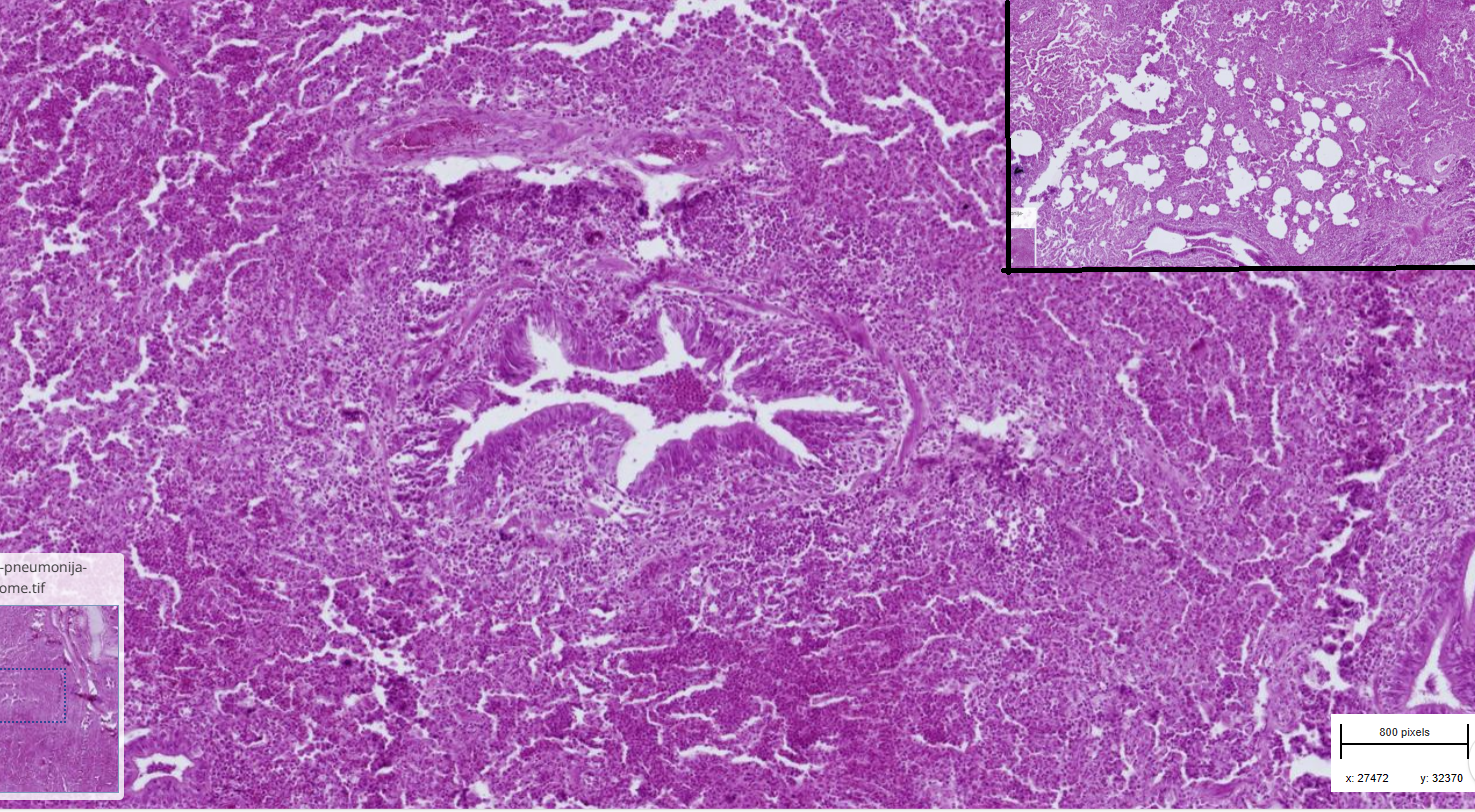
Bronchointerstitial pneumonia, lymphohistiocytic, lymphoid hyperplasia
-Lamina propria of bronchi and bronchioli are infiltrated by lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages
-hyperplasia of BALT
-in lumen of bronchi, extensive infiltration of neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes
-Focal emphysema
-Alveoli are filled with macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils
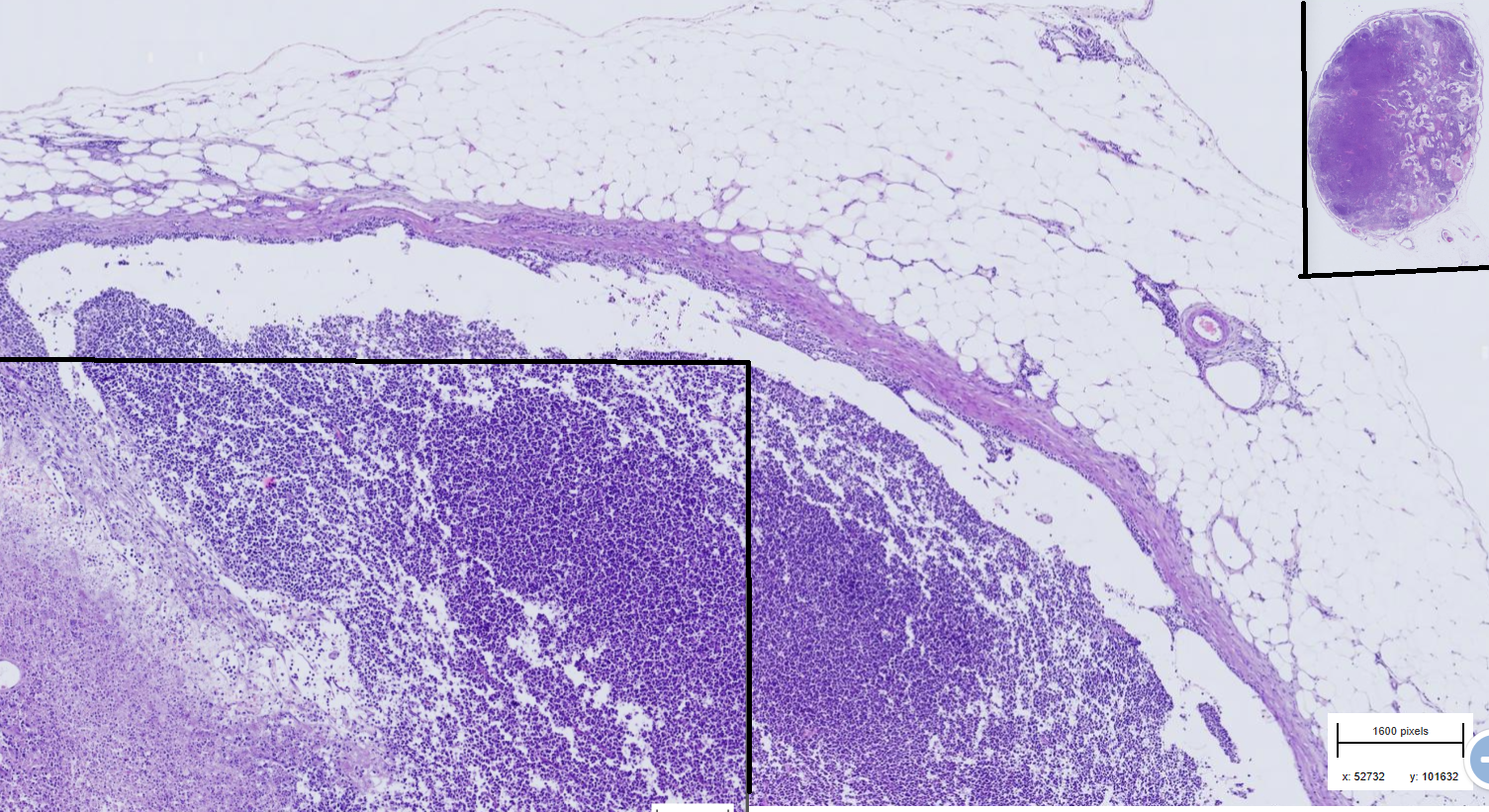
Lymphoma dog
-Disrupted architecture - difuse infiltration of dense round uniform neoplastic cells
-Tumor extends through capsule into perinodal tissue
-cytoplasm is eosinophilic
- tumor necrosis and hemorrhage
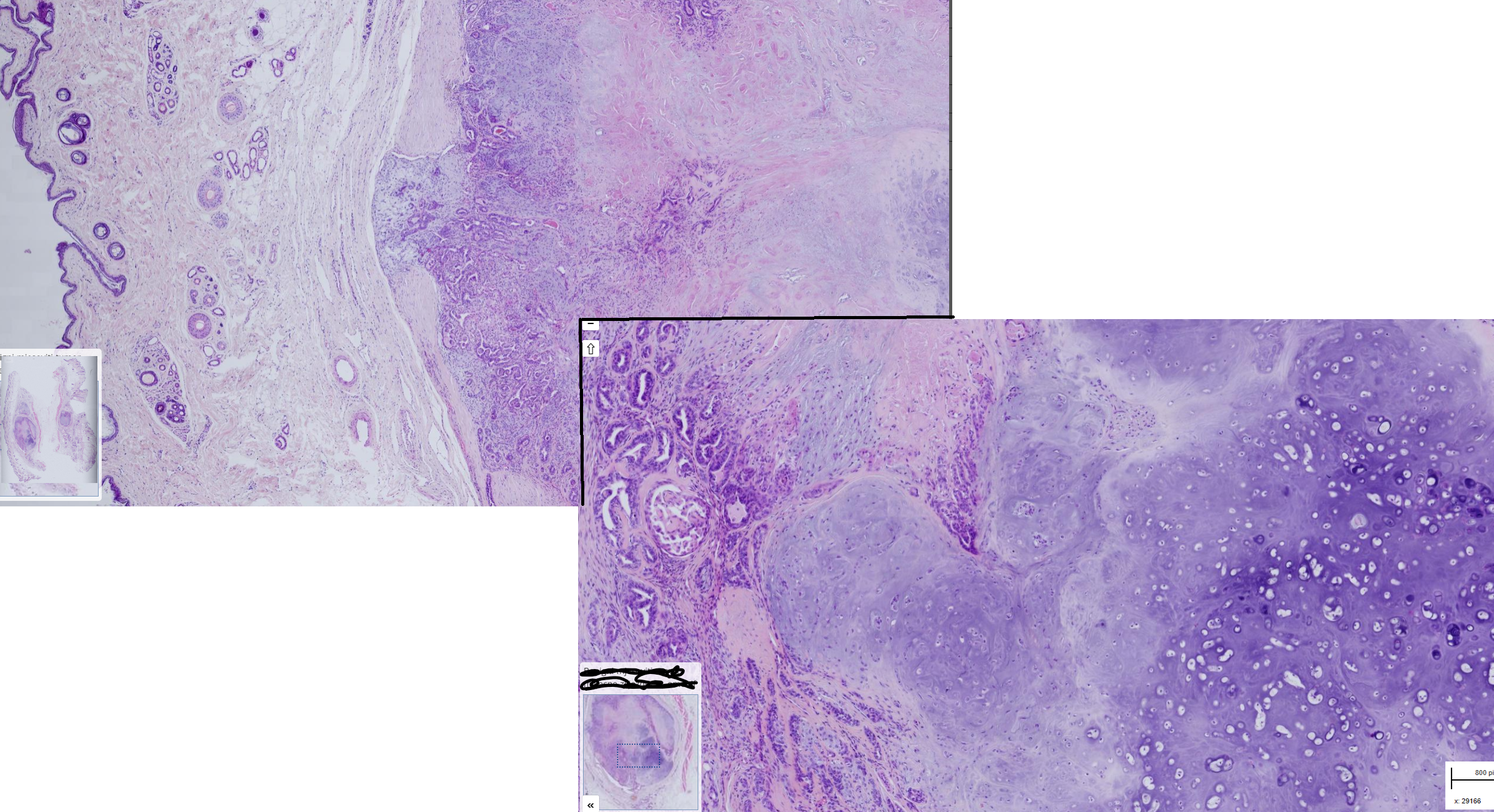
Mammary gland: Benign mixed mammary tumor, dog
-subcutis well demaracated, encapsulated neoplasm
-2 cell types : luminal epithelial ( form tubules, round nuclei with 1 nucleolus) and myoepithelial (spindle to stellate cells with oval nuclei)+ cartilage (hondrocytes in lacunae)
-moderate amount of fibrous stroma
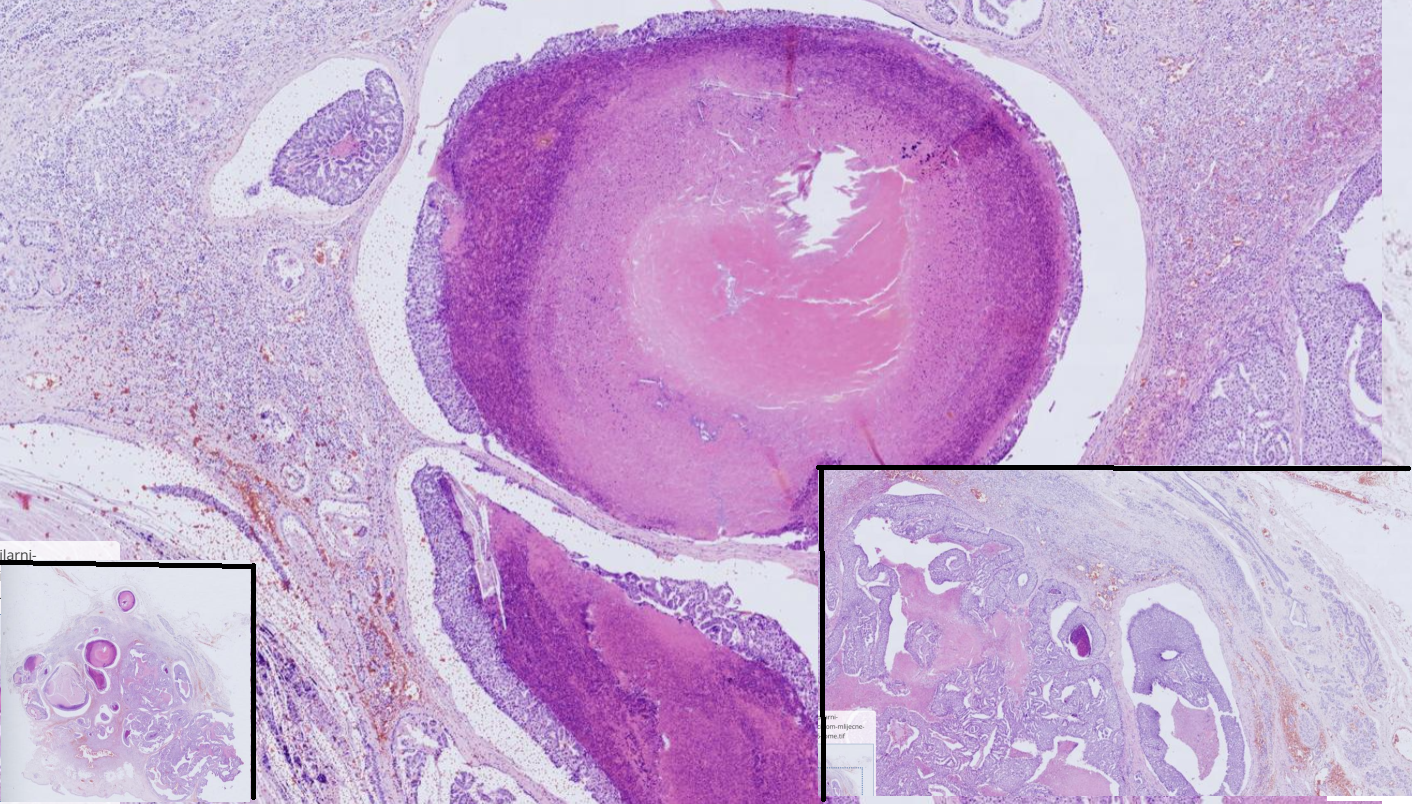
Mammary gld adenocarcinoma ( tubulopapillar), dog
-Poorly demarcated, partly encapsulated, partly infiltrative
-tumor cells- tubule and papillary proliferations are less pronounced
- scant to moderate fibrous stroma
-multifocal area of necrosis
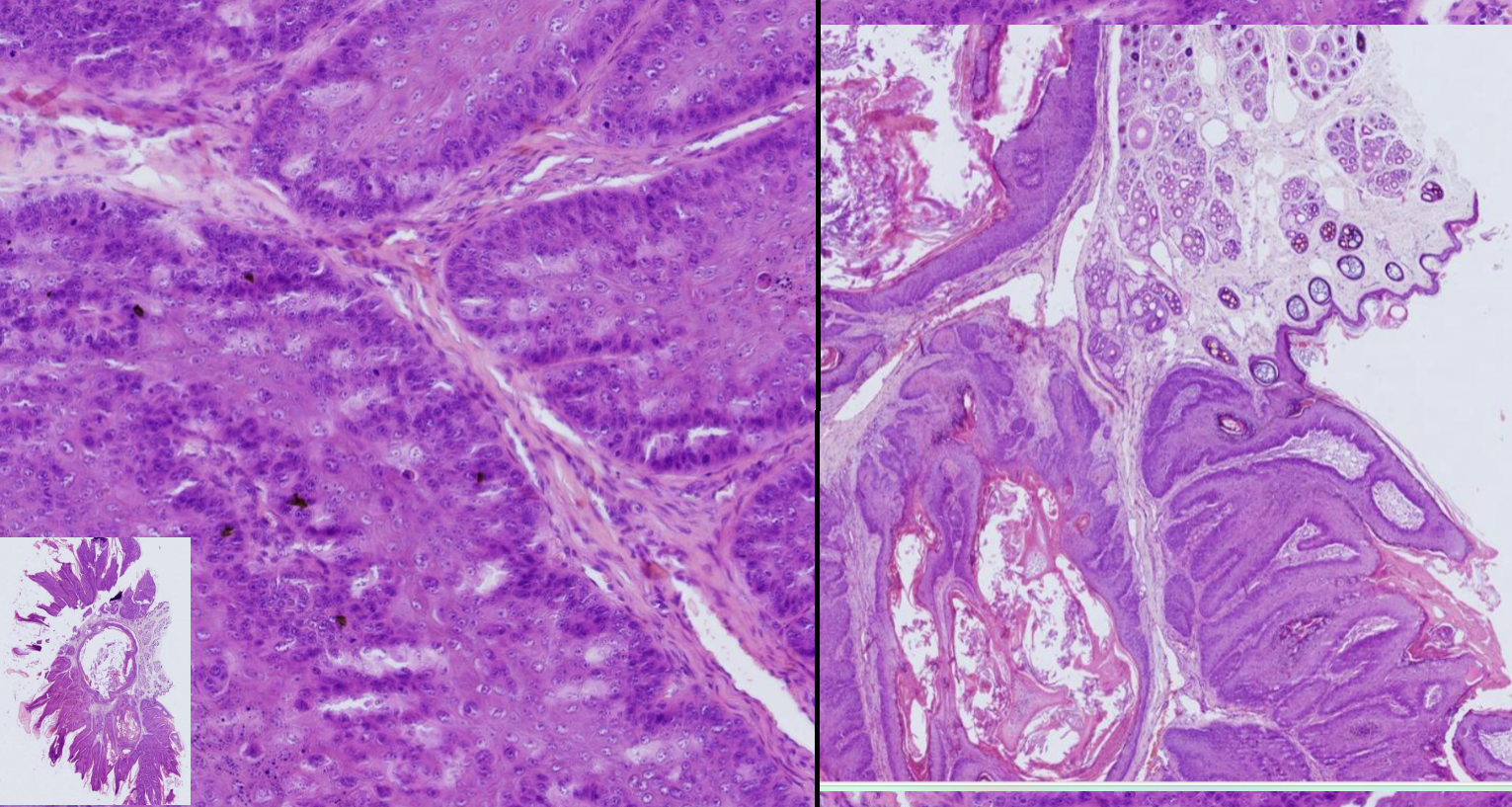
Papilloma- dog
- exophytic neoplasm from epidermis, form some papillary projections, supported by stroma
-neoplastic cells progress from a hypertrophied stratum basale to a thickened stratum spinosum
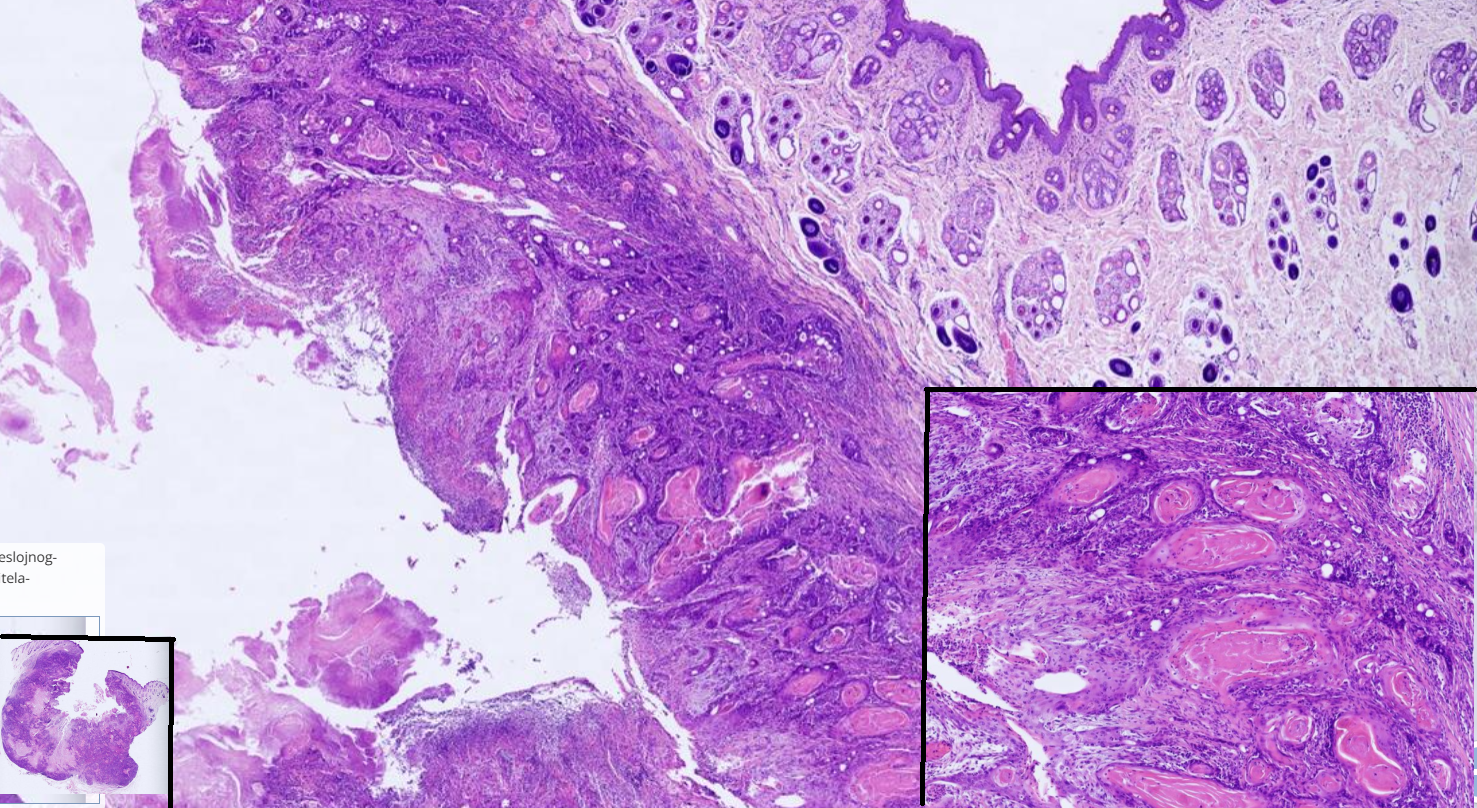
Squamous cell carcninoma
-poorly circumscribed unencapsulated, infiltrative neoplasm composed of polygonal cells, supported by stroma. Nuclei are irregularly round
-cord and island often contains compact eosinophilic lamellation of keratin ( keratin pearls)
-Multifocally stroma is infiltrated with abundant mixed inflammatory infiltrate
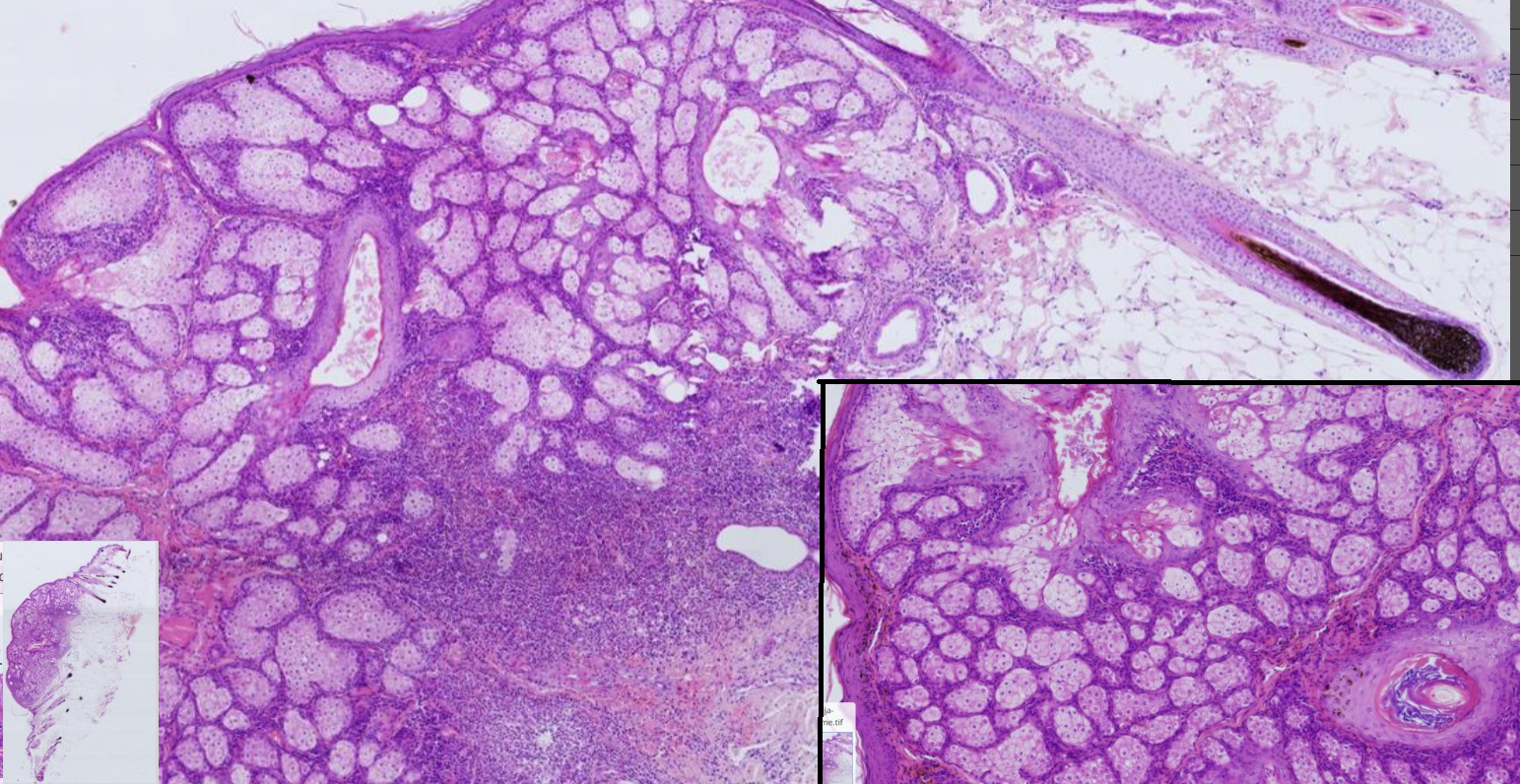
Nodular hyperplasia of sebaceous gland, dog
-unencaspulated, well circumscribed mass of multiple lobules which surround ectatic ducts, lined by keratinized stratified squamous ep. filled with keratin
-Lobules are divided into adenomeres
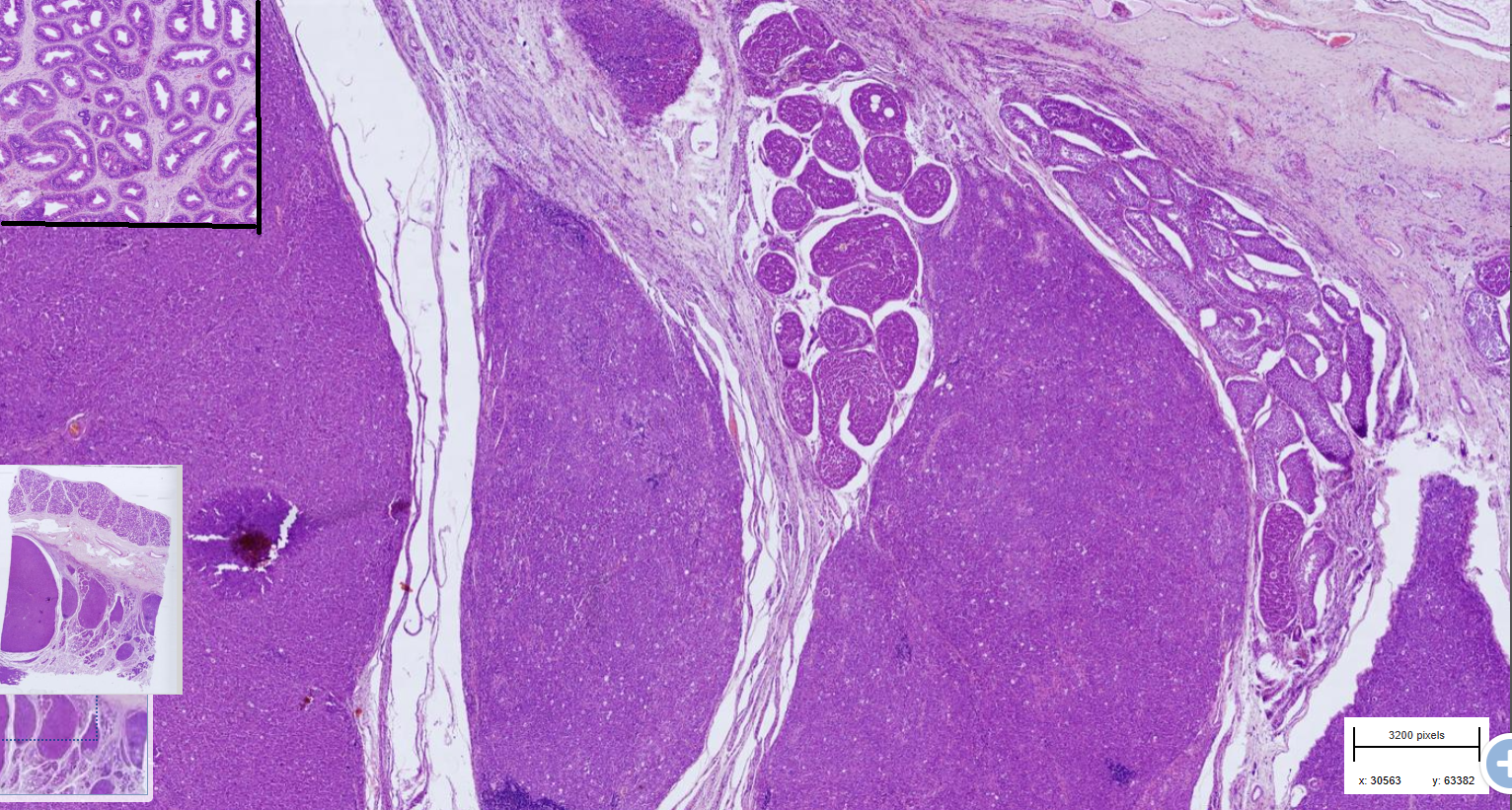
Testicular seminoma
-Multinodular neoplasm composed of round cells, large round, vesicular nuclei.
-moderate anisocytosis and anisokaryosis
-lymphocytic intratumoral infiltrates
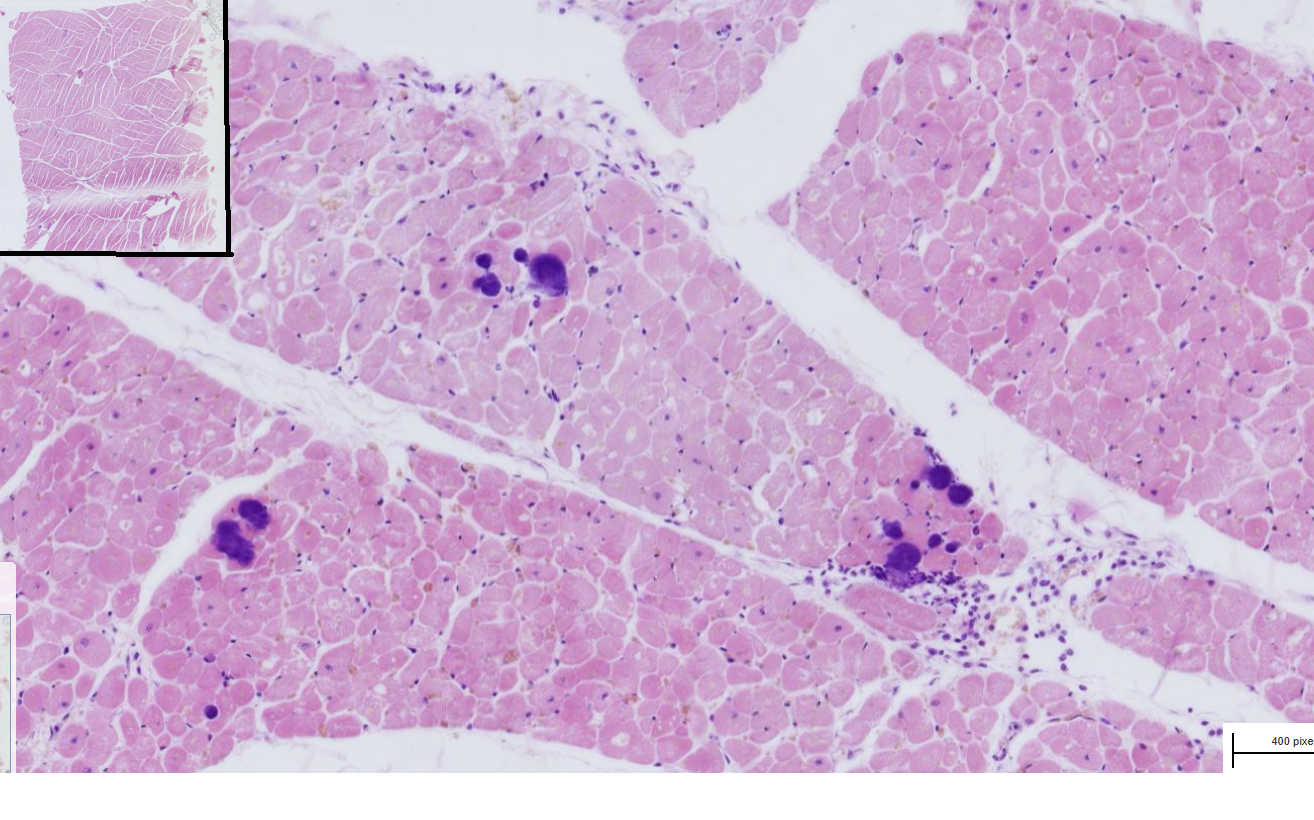
Embolic Myocarditis
-Multifocally, randomly distributed bacterial colonies within small blood vessels and myocytes
-Around bacterial colonies myocytes are swollen with hypereosinophilic sarcoplasm, loss of cross striation and pyknosis
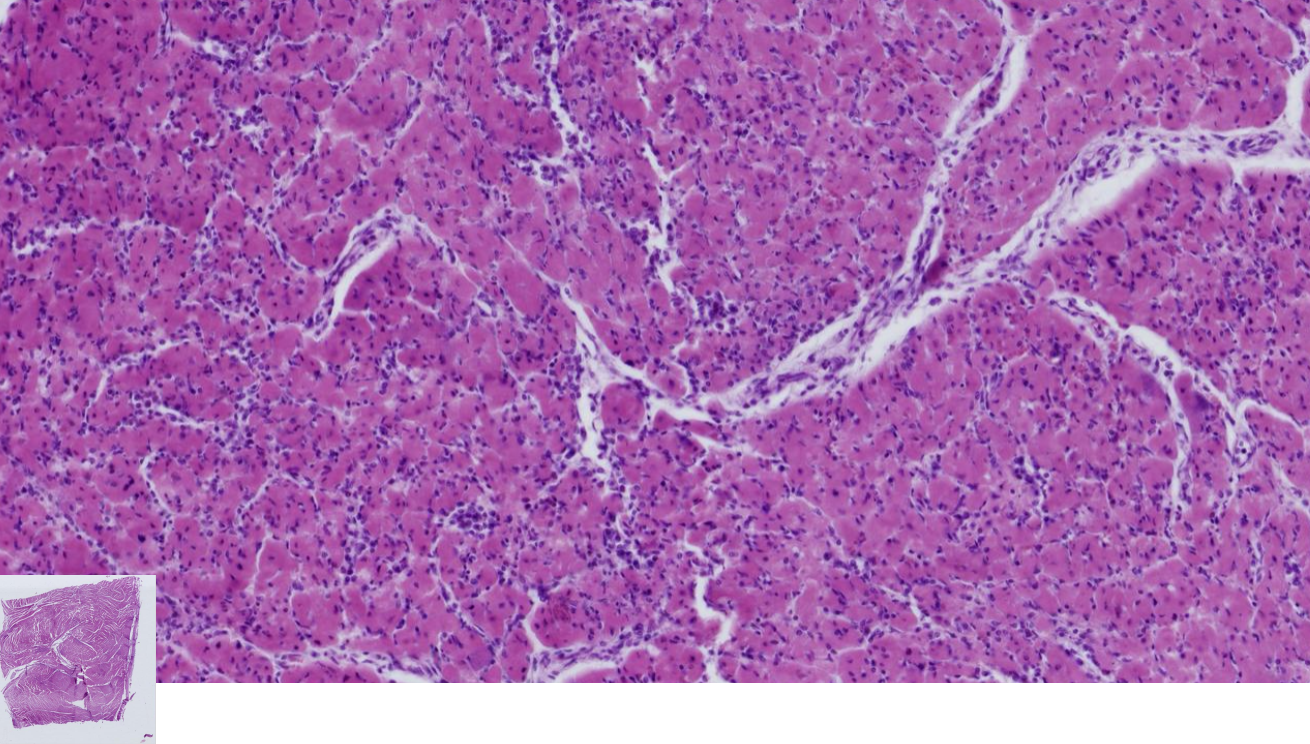
Lymphocytic myocarditis
-Multifocally disrupting the myocardium and endocardium, are lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages with some edema
-Cardiac myocytes are swollen with vacuolated or hypereosinophilic sarcoplasm, loss of cross striation and pyknosis
- Myocytes can be replaced by activated fibroblast that form fibrous tissue
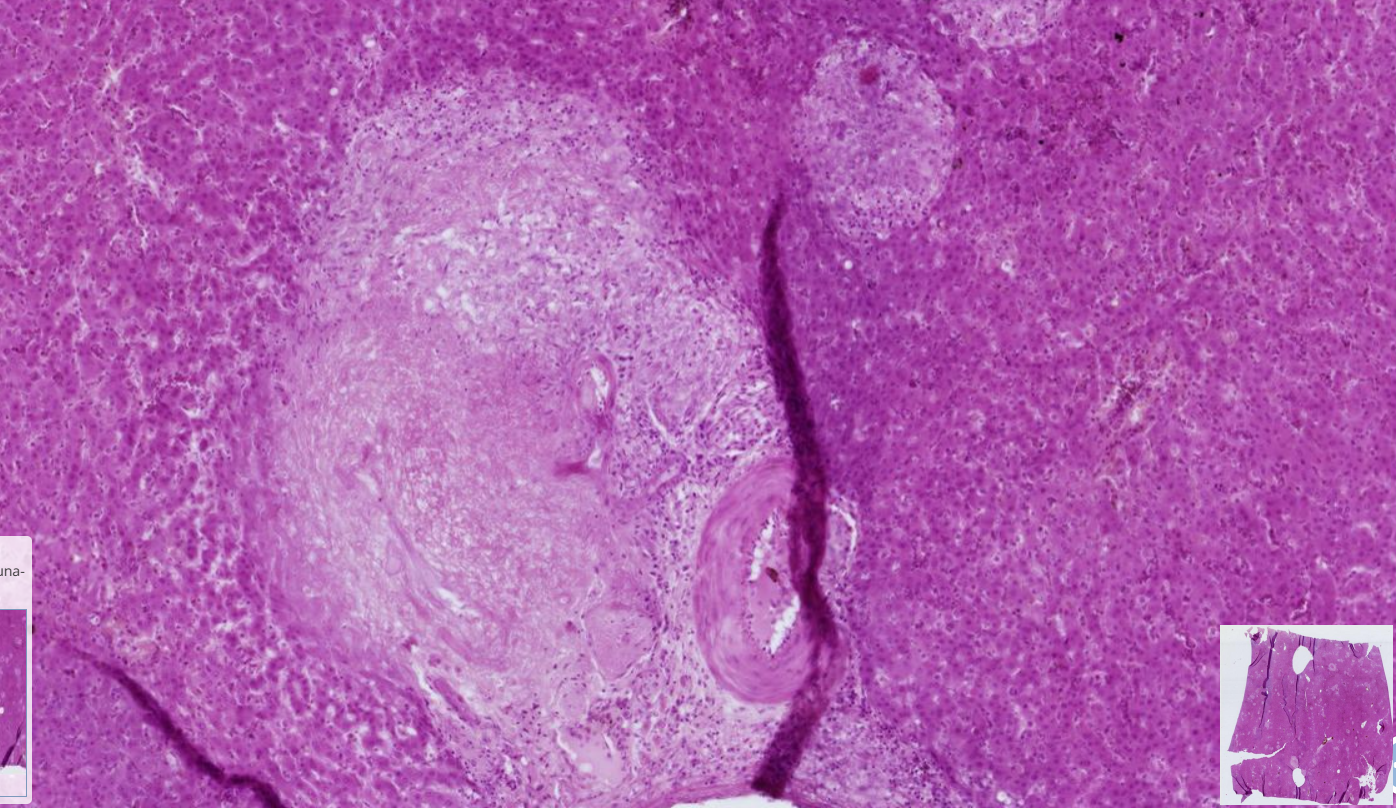
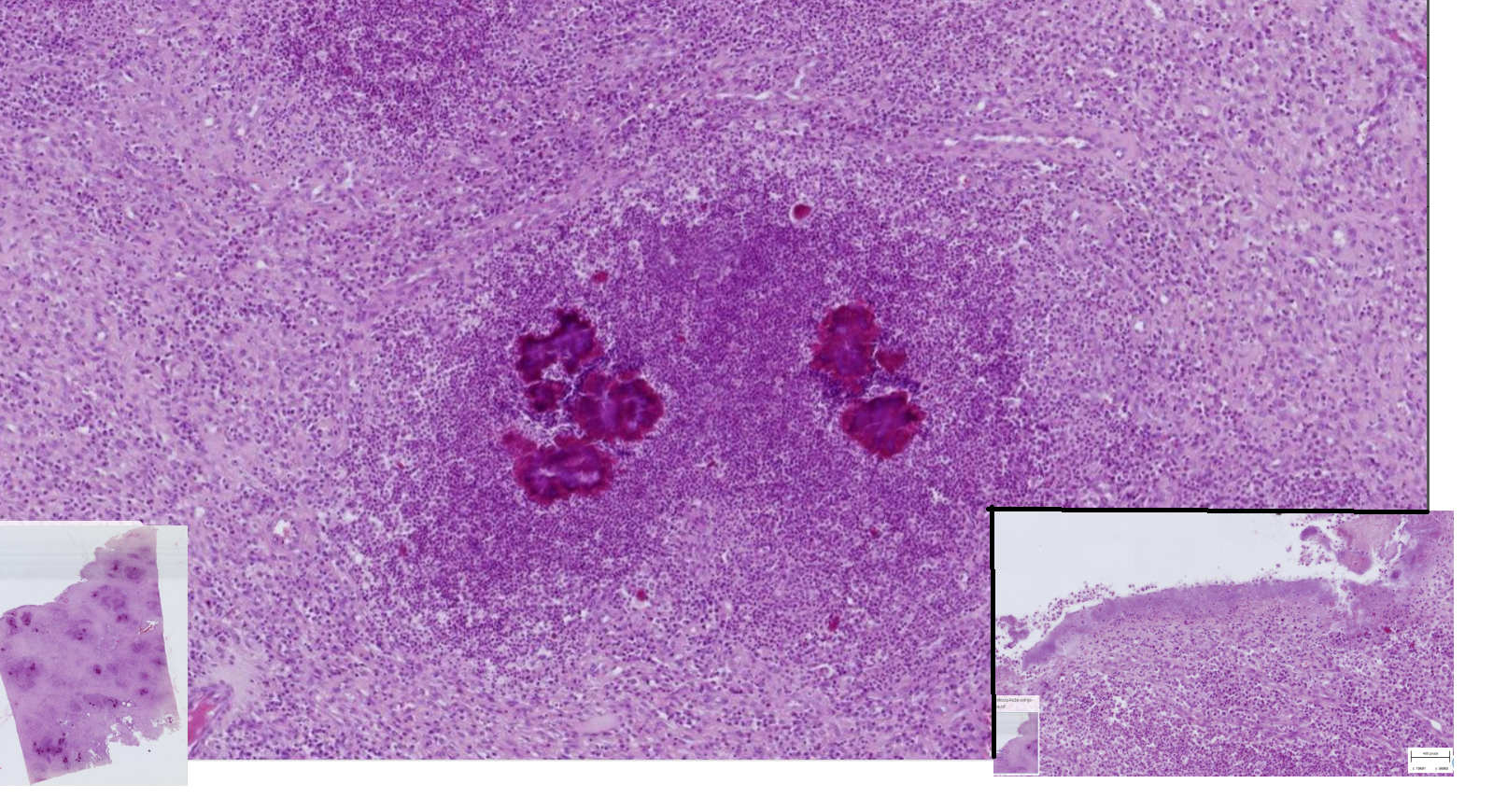
Milliary hepatic tuberculosis
-Multifocally, randomly distributed coalescing granulomas
-smaller granulomas : macrophages and epitheloid cells
-Larger granulomas : necrotic central core ( caseous necrosis) surrounding it are macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells and reactive fibroblast and concentric connective tissue
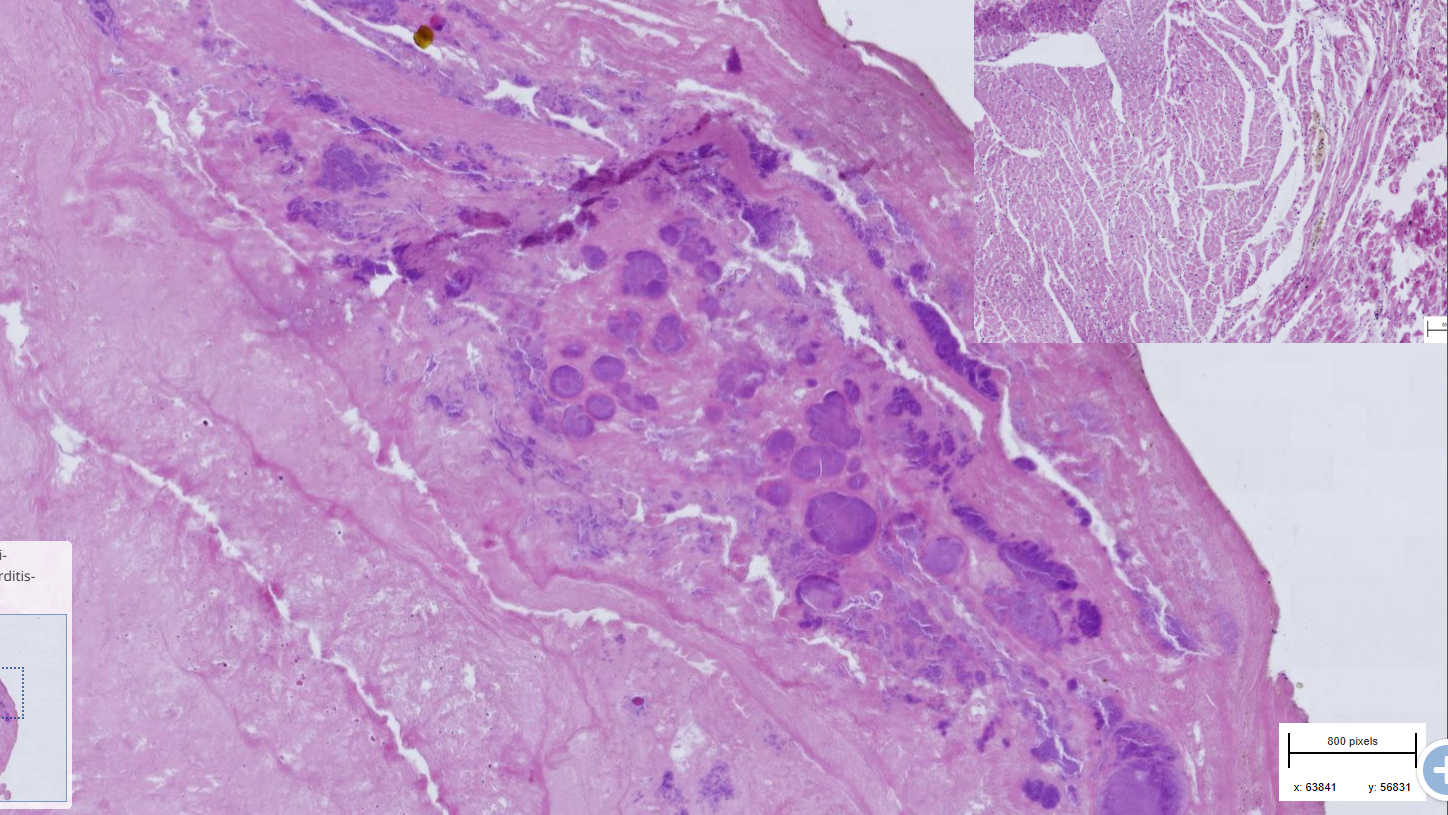
Valvular Endocarditis
-Accumulated layers of irregular deposit on the endothelium valves
Surface layer : fibrinous, homogenous, pink mass containing bacterial colonies and hemosiderin pigments
-middle layer : deposit of fibroblast, fibrocytes, collagenous fiber and mononuclear infl. cell
-last layer: reminder of mitral valves, fragments of undamaged endothelium, collagen and myocytes.
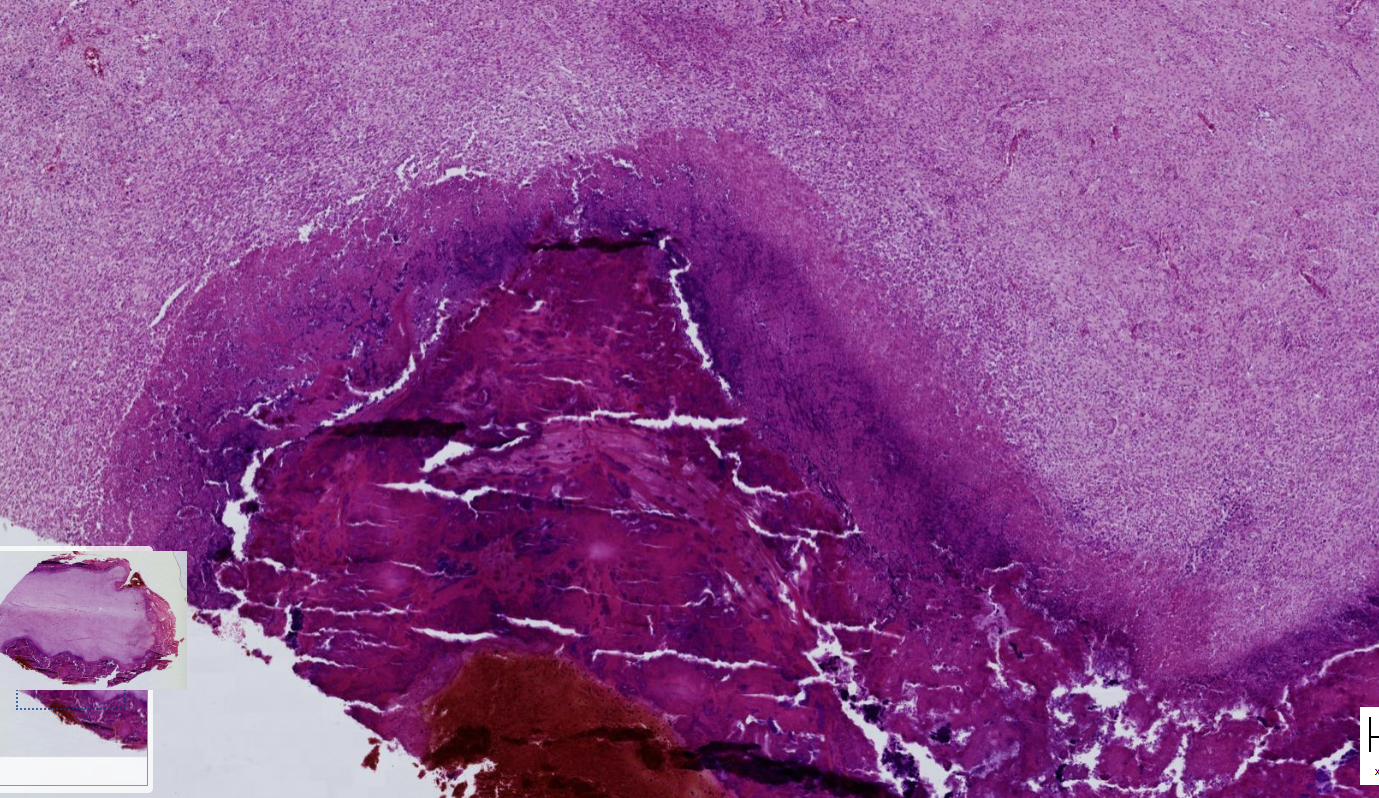
Endocarditis, thrombotic, septic, dog
-Acute : hemorrhage, fibrinous mesh, active fibroblast, neutrophils, macrophages and bacterial colonies
-Chronic : Hemosiderin, intracellular and extracellular accumulation of calcium, thick collagenous fibers, fibrocytes, macrophages, plasma cells
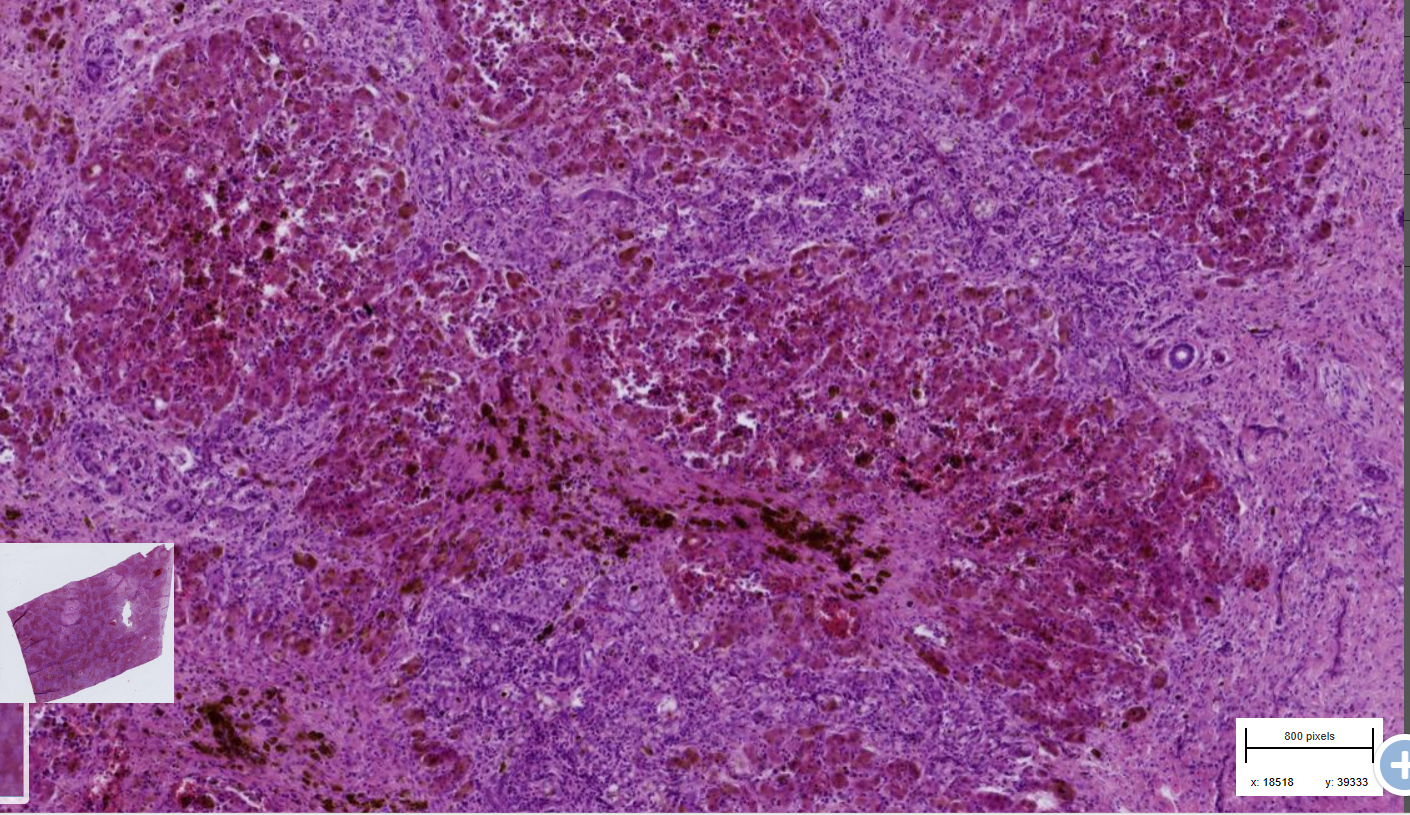
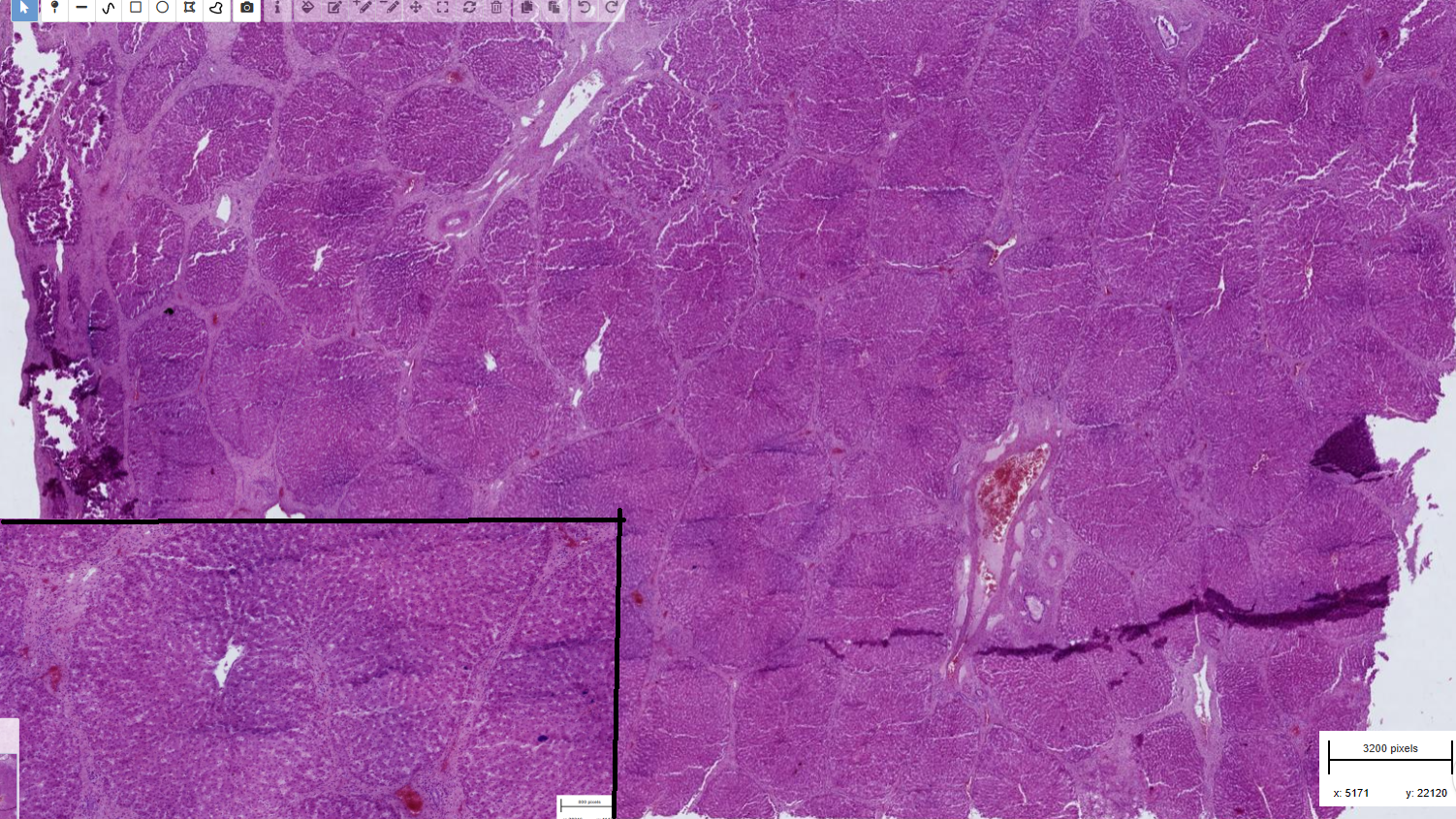
Post necrotic liver fibrosis with nodular regeneration - cirrhosis
-Parenchyma : hepatocytes islet which are various in size and shape - disrupted architecture
-irregular trabecular structures of lobules
-aggregation of necrotic cell+ rbc+ infl. cells
-Bile stasis
-hemosiderin- central area and within the fibrous tissues
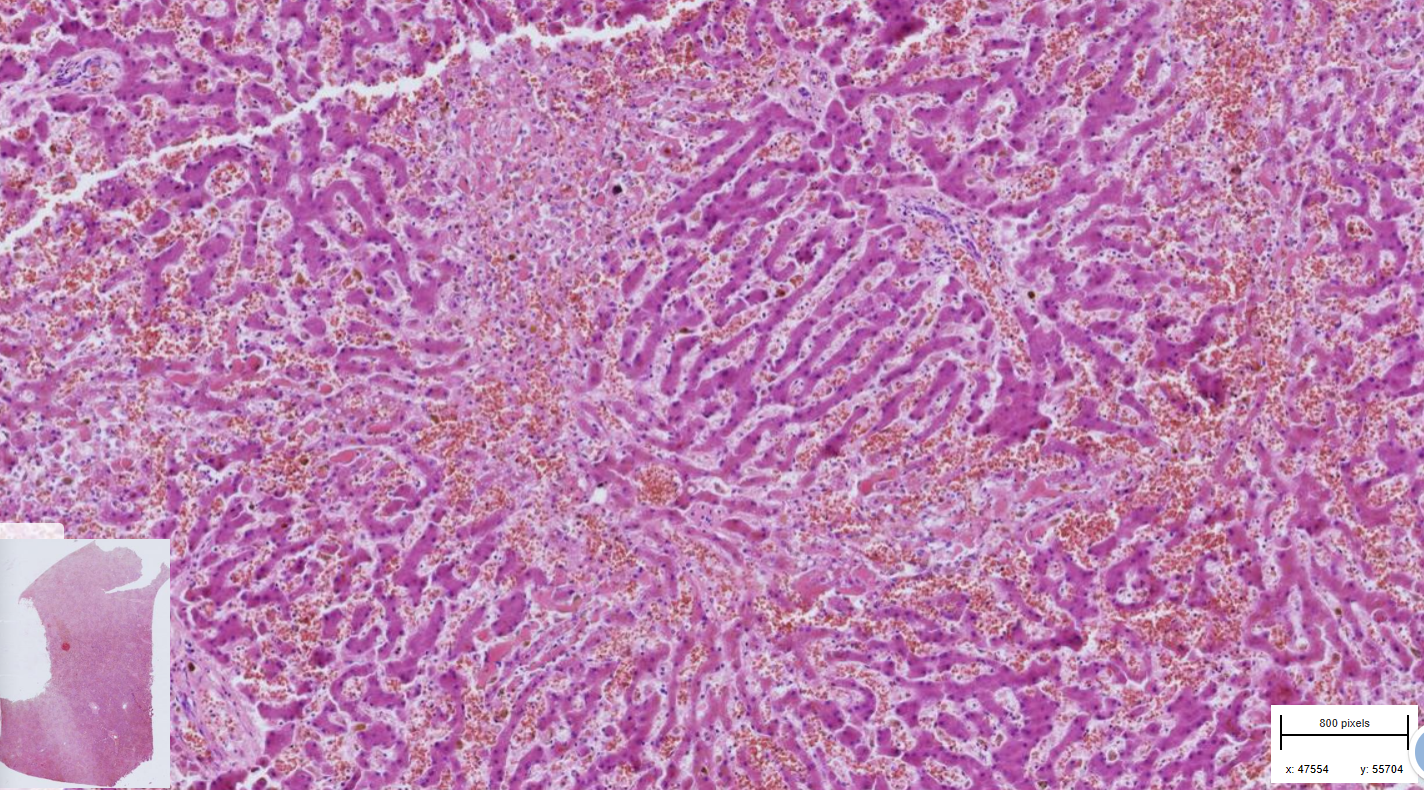
Liver : Centrilobullar necroses, multifocal to coalescing
-architectures of lobules are disrupted
- hepatocytes are swollen,, hypereosinophilic, with distinct cell border and pyknotic nuclei- necrosis
-surrounding of collapsed hepatocytes are individuals infl. cells - neutrophils and few macrophages + numerous rbc - hemorrhage
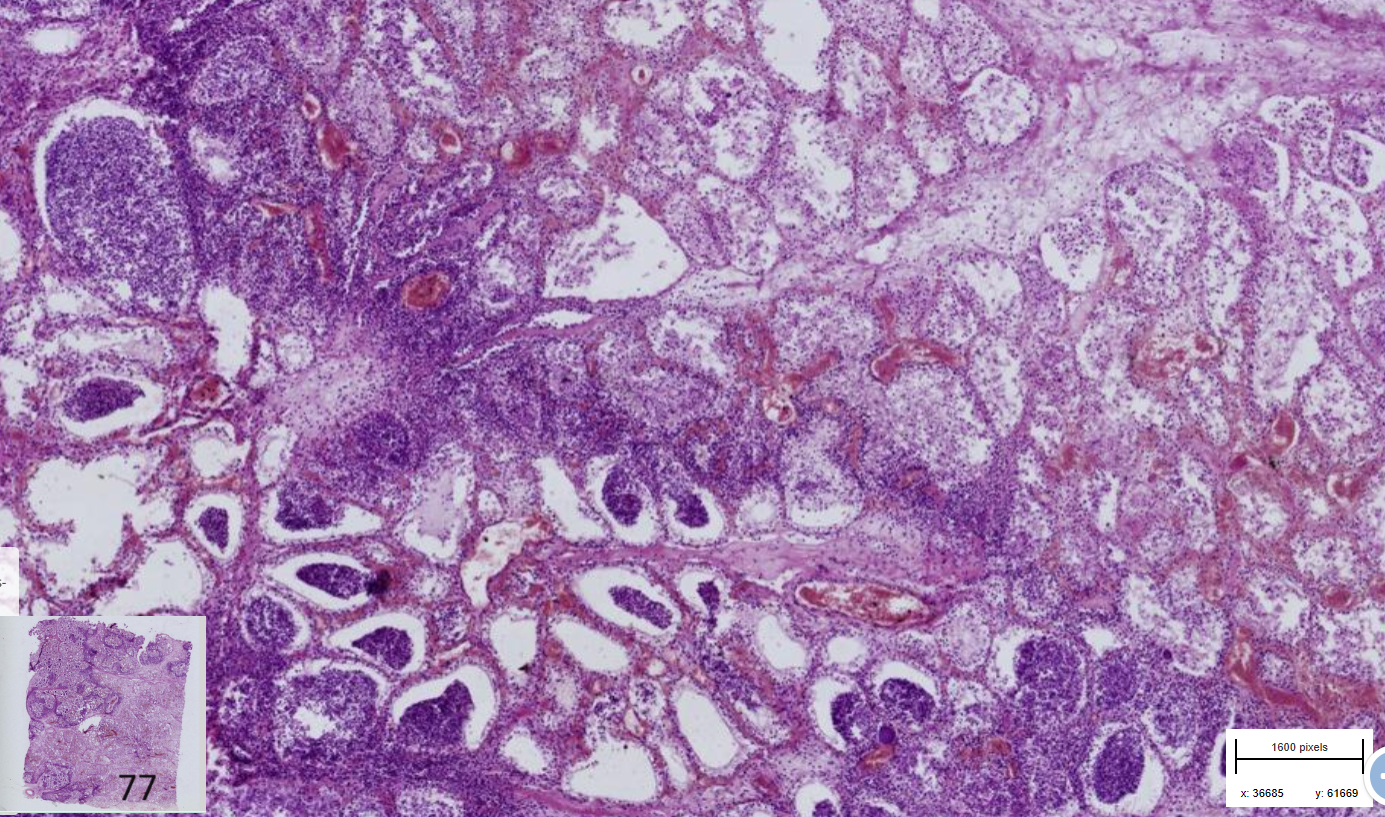
Mastitis : necrosuppurative , bovine
- Multifocal to coalescing foci
-Alveoli contains degenerated neutrophils and exfoliatred ep. cells
-Edema in alveoli and interstitium
-Tissue necrosis, melting of alveoli filled with pus = abceses
-Thrombosis of blood vessel, hemorrhage
-corpora amylacea
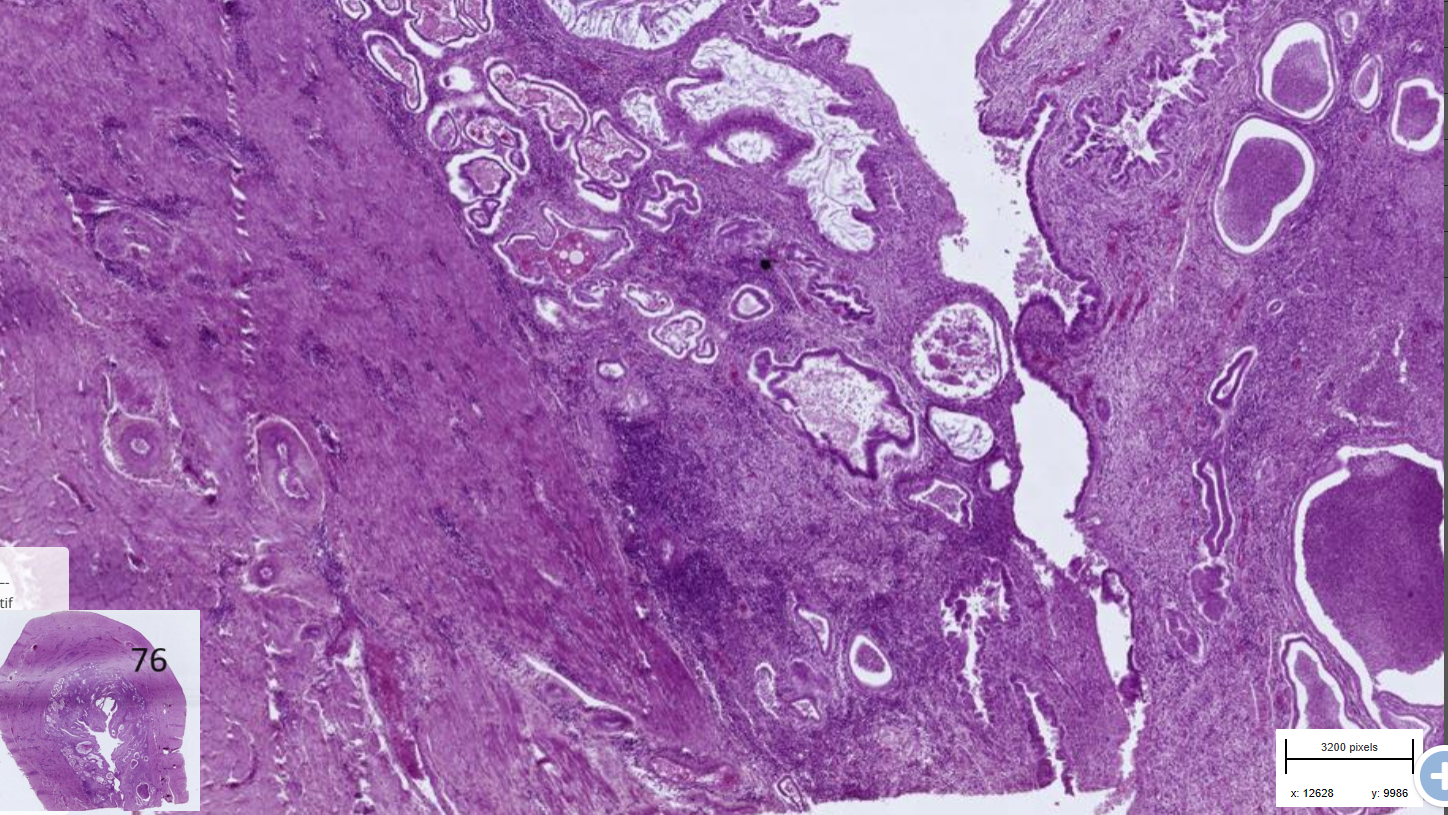
Endometritis, suppurative, cytsic, chronic -pyometra
-Mucosal epithelium : columnar epithelium, hyperplastic, partly exfiolated in the lumen with some suppurative exudate
-Lamina propria : dense infl. cell infiltrate, endometrial glands are ectatic, lined by flattened epithelium and filled with degenerated neutrophils (pus)
-Myometrium: contains perivascular predominantly plasmacytic infiltrate
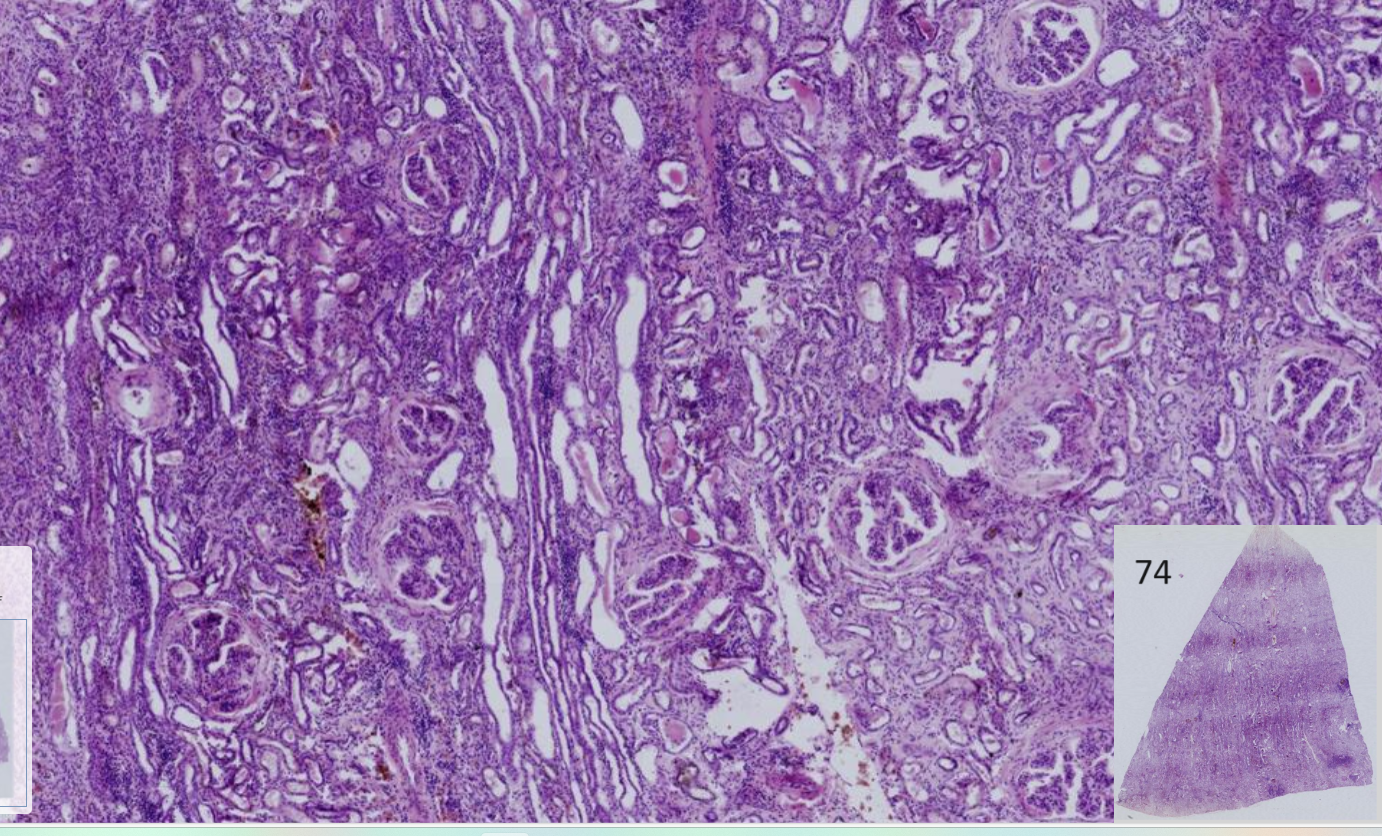
Nephritis: glomerular, interstitial, chronic
-Glomeruli : fibrin exudate in Bowman’s space, occasionally thickening of Bowman’s capsule, terminal phase= proliferation of fibrous connective tissue ( hyaline appearance)
-Tubules : Degeneration and necroses of tubular epithelial cells, occasionally flattened or ectatic with hyaline cylindres
-Interstitium : Multifocal neutrophils and fibrous tissues
Bacterial colonies
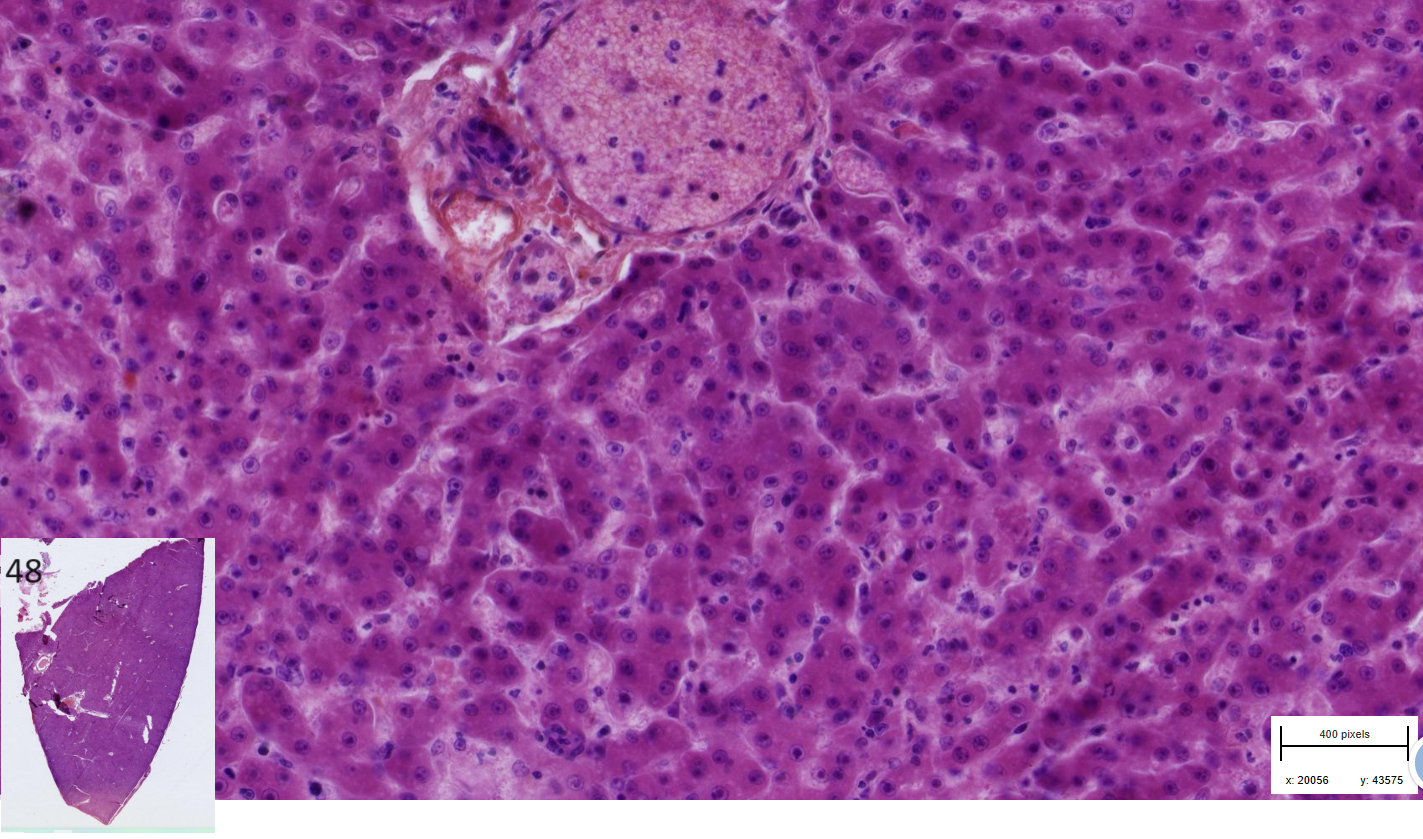
Hepatitis : necrotizing, acute, multifocal, with basophilic intranuclear viral inclusion bodies
-Hepatocytes are swollen
- Subscapular hemorrhage
-sinusoid dilated with exudate, rbc and mononuclear
- Interstitium contain occasionally mononuclear infiltrate
-Intranuclear basophilic inclusion bodies fill almost whole nucleus
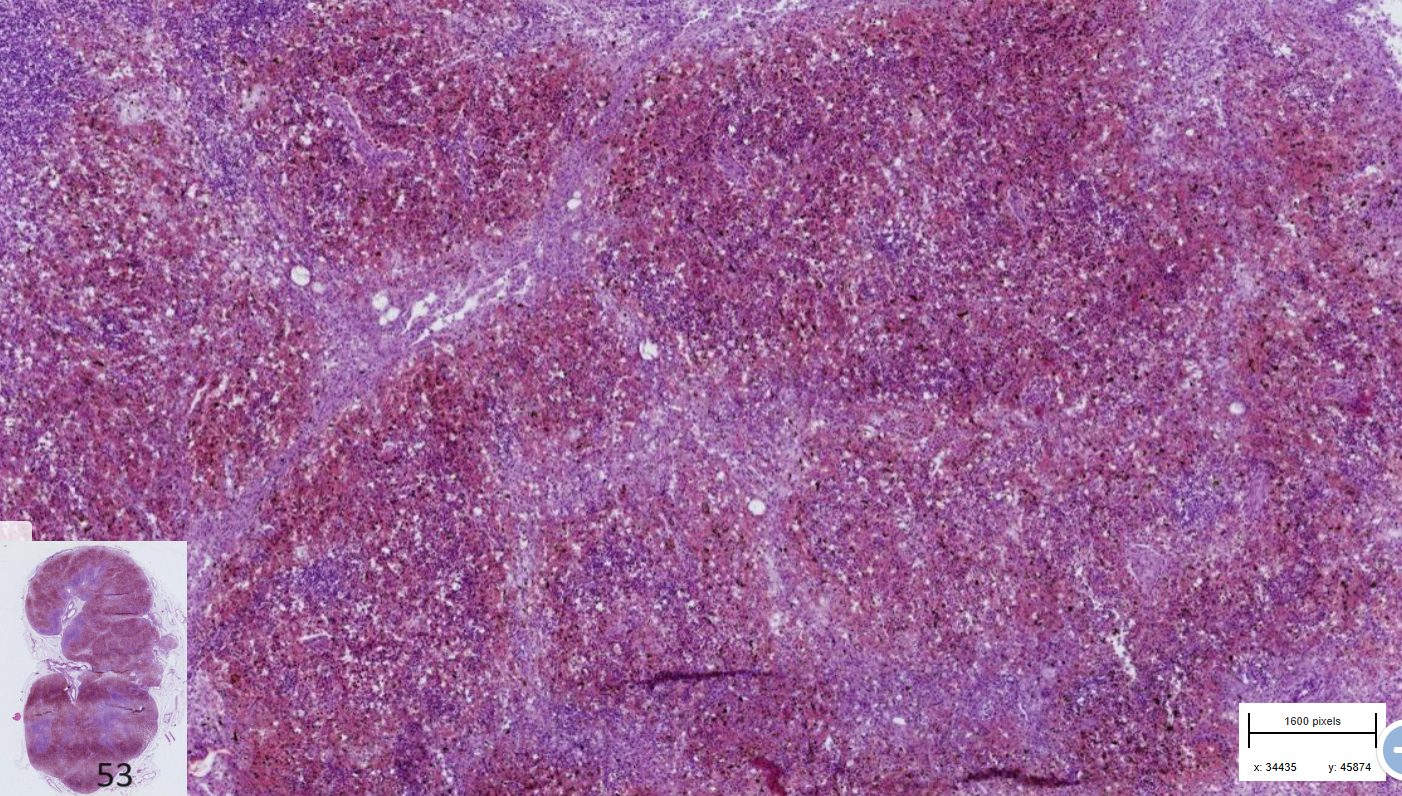
Lymphadenitis : Hemorrhagic, acute, pig
-Parenchyma : edematous, severe congestion and hemorrhage
-Peritrabecular sinuses and central area of lymph node without hemorrhages
-thrombosis of capillaries with around it most intense hemorrhages